
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Robot. AI , 29 November 2022
Sec. Nano- and Microrobotics
Volume 9 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2022.1063987
This article is part of the Research Topic Intelligent Micro- and Nanorobotic Systems for Enhanced Medical Procedures View all 6 articles
While the potential of using helical microrobots for biomedical applications, such as cargo transport, drug delivery, and micromanipulation, had been demonstrated, the viability to use them for practical applications is hindered by the cost, speed, and repeatability of current fabrication techniques. Hence, this paper introduces a simple, low-cost, high-throughput manufacturing process for single nickel layer helical microrobots with consistent dimensions. Photolithography and electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation were used to fabricate 2D parallelogram patterns that were sequentially rolled up into helical microstructures through the swelling effect of a photoresist sacrificial layer. Helical parameters were controlled by adjusting the geometric parameters of parallelogram patterns. To validate the fabrication process and characterize the microrobots’ mobility, we characterized the structures and surface morphology of the microrobots using a scanning electron microscope and tested their steerability using feedback control, respectively. Finally, we conducted a benchmark comparison to demonstrate that the fabrication method can produce helical microrobots with swimming properties comparable to previously reported microrobots.
Micro/nanorobots can access hard-to-reach places and target specific locations in the body (Mhanna et al., 2014; Qiu et al., 2015; Felfoul et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2017). It is conceivable that these tiny machines will soon play important roles in the biological and medical fields, especially in tissue engineering and targeted therapy. There are many types of micro/nanorobots driven by different power sources, such as chemical fuel (Ma et al., 2015; Zhou et al., 2019), electric field (Loget and Kuhn, 2011; Kim et al., 2014), light (Palagi et al., 2016; Shahsavan et al., 2020), ultrasound (Li et al., 2015; Aghakhani et al., 2020), or magnetic field (Yu et al., 2018). Among these power sources, magnetic fields can safely penetrate biological barriers and other materials (Chen et al., 2018). Consequently, magnetic actuation seems to be a very promising avenue to actuate micro/nanorobots, especially when operating in vivo.
Inspired by Escherichia coli swim using rotating flagella (Berg and Anderson, 1973), magnetic helical micro/nanorobots had been proposed and manufactured using various methods, including self-scrolling (Zhang et al., 2009a), glancing angle deposition (GLAD) (Ghosh and Fischer, 2009), direct laser writing (DLW) (Tottori et al., 2012; Medina-Sánchez et al., 2016), template-assisted electrodeposition (TAE) (Zeeshan et al., 2014), and bio-templating synthesis (BTS) (Gao et al., 2014). In recent years, the focus is gradually shifting to the demonstration of their manipulation and functions, such as cargo transport (Tottori et al., 2012; Huang et al., 2014). However, there is a lack of development in trying to streamline the manufacturing process to massively produce helical microrobots with consistent structures, controllable helical parameters, and high repeatability. Most of the aforementioned methods can produce helical microrobots with excellent swimming properties, but their deployment and widespread usage in practical applications might be hindered by high cost, complicated fabrication processes, low throughput, or inconsistent geometries. To find manufacturing methods that can satisfy the requirements for large number deployment, parallel fabrication methods must be considered. Conventional parallel fabrication technologies at the microscale generally produce 2D patterns; this becomes an issue as the helices are 3D structures. Therefore, the stress-induced rolled-up technology based on photolithography has gradually gained importance for the fabrication of 3D microstructures (Zhang et al., 2009b; Mei et al., 2011; Smith et al., 2011; Sun et al., 2014; Tian et al., 2017; Tian et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2019).
To generate the stress within the 2D structures, the traditional rolled-up technology often involved complex fabrication procedures and expensive equipment. For instance, a molecular beam epitaxy machine was used and a dual-layer of semiconductor-metal materials was deposited when using the self-scrolling method to fabricate helical microrobots (Zhang et al., 2009a). In another example, expensive equipment for glancing angle deposition (GLAD) was used to produce anisotropic stress within 2D microstructures (Li et al., 2012a). In this paper, we propose a method to fabricate helical microrobots using a roll-up process achieved using conventional and commonly available microfabrication technologies: photolithography and electron beam evaporation. This method utilizes the roll-up of the photoresist to bend outer the metal layer, forming magnetic helical microrobots after the removal of the photoresist. The swimming properties of the helical microrobots in this work are comparable to the previously reported helical microrobots, which validates the feasibility to use the proposed fabrication method. Since the fabrication method only requires the use of conventional microfabrication technologies, this work has the potential to be useful for creating a variety of 3D complex microstructures with ease and may serve as a foundation for fabricating helical microrobots for large-number deployments in future applications. In short, the proposed fabrication method not only reduces the complicity of the current rolled-up technology but also reduces the cost of fabrication.
The fabrication procedure is shown in Figure 1A. First, photoresist (MicroChemicals, AZ® nLof 2070) was spin-coated at 3000 rpm on a clean silicon wafer. The photoresist is then made into a sacrificial layer through photolithography (SUSS, MA6); parallelogram/rectangular shapes patterned on a mask were transferred to this photoresist layer. Then, a 100 nm nickel layer was deposited on the 2D photoresist patterns via electron beam evaporation (HVV, TF500); the nickel will make up the entire body of the microrobots. Next, the sample was immersed in N-Methyl Pyrrolidone (NMP) solution (Aladdin, 99.5%); subsequently, the photoresist was in contact with the NMP solution and swelled up causing the 2D patterns to spontaneously roll up into the coils. The final 3D helical-shaped nickel microstructures emerged when all the photoresists dissolved away in the NMP solution. Finally, the sample was washed three times using isopropanol (Aladdin, 99.5%) and then placed in deionized water for experiments later. The coils (before photoresist dissolution) and final helical microrobots (after photoresist removal) could be observed in Figures 1B,C, respectively.
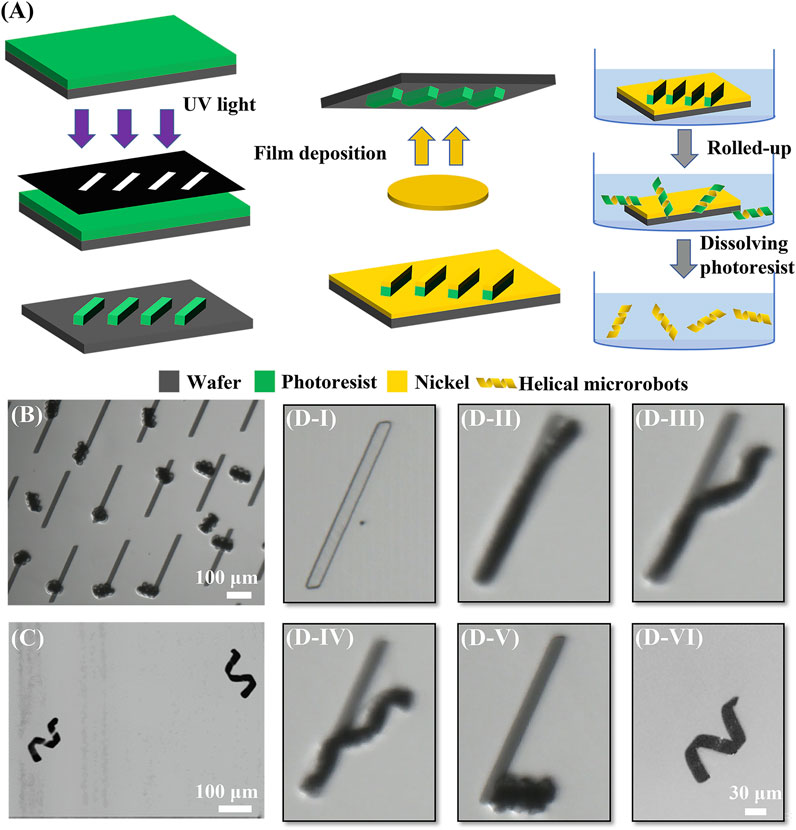
FIGURE 1. Fabrication procedure of helical microrobots. (A) Schematic diagram of the fabrication procedure. (B) Image of coils after rolling. (C) Image of helical microrobots via an optical microscope. (D) Microscope images of the rolled-up process. (D–I) 2D pattern after physical vapor deposition; (D-II) beginning of the rolled-up process when photoresist began to swell and one tip began to lift; (D-III) rolling up along the long edge and the other tip began to roll up; (D-IV) the two tips rolled up from opposing sides and met at the point of strongest interfacial adhesion; (D-V) rolled up into a coil as swelling completes; (D-VI) coil loosened into helical microrobot after the removal of photoresist sacrificial material.
To elucidate the mechanism of the rolled-up process caused by the swelling of the photoresist layer, the entire process was recorded at 100 frames per second for observation (see Supplementary Video S1). The entire rolled-up process using a parallelogram pattern with a length of 300 μm and a tilt angle of 60° is shown in the zoomed-in snapshots of Supplementary Video S1 in Figure 1(D-I)–1 (D-V). First, the NMP solution was added to the 2D parallelogram patterns. After the photoresist absorbed solvent molecules from the NMP solution, the macromolecular polymers would begin to swell and roll up. Due to the edge effect (Alben et al., 2011) and the internal stress generated by the swelling at the interface between the photoresist and the nickel layer, one tip of the 2D pattern was lifted off; subsequently, the 2D pattern rolled up along the direction parallel to the short edge, as shown in Figure 1(D-II). Next, the other tip lifted off in the direction perpendicular to the respective short edge, and the pattern began to roll up from the other tip, as shown in Figure 1(D-III). The different etch rates would produce an anisotropic driving force; thus, the two tips would have different lifting directions and rollup from opposite directions; this caused the two opposing tips to form two independent microhelices. Then, the two sides met at the point of strongest interfacial adhesion causing the two microhelices to combine into one single microhelix, as shown in Figure 1(D-IV). When the roll-up process was finished, the pattern became a coil, as shown in Figure 1(D-V). The cross-linked photoresist, which was immersed in the 80°C NMP solution, continued to swell until it reached maximum volume, at which point the polymer network structure broke down and slowly dissolved in the NMP solution. The photoresist sacrificial material took about two days to be completely removed, leaving only the nickel layer. Without the constraint from the photoresist sacrificial material, the coil was loosened into a helix with a single layer of nickel, as shown in Figure 1(D-VI); this final structure is representative of the magnetic helical microrobots.
According to Bell et al, (2006), if the orientation of a nanomembrane strip deviates from the rolling direction, a helical structure can be formed. In our experiments, we observed that the photoresist rolled perpendicular to the short side, which is in agreement with the experimental observation and theoretical results of Chun et al, (2010). The orientation of the photoresist in a parallelogram pattern deviated from the rolling direction; thus, the parallelogram patterns are prone to roll up into helical structures after swelling.
During wet etching, the photoresist absorbed the NMP molecules and swelled. The swelling of the photoresist induced strain in the metal layer, which caused the structures to roll up into coils. The outer layer photoresist of the coils would dissolve eventually, and the metal layer was left to constitute the helical microrobots. Therefore, the microrobots are comprised of a single layer of nickel. A mathematical model (Li et al., 2012b) is included to relate the radius of the rolled-up structures with the swelling of the photoresist. The radius R of the rolled-up structure is given by the following equation:
where
The geometry and dimension of the 2D patterns used in experiments were varied to examine the effects of the 2D geometrical parameters on the shape of the helical microrobots. Two kinds of patterns were examined - rectangular and parallelogram patterns. Each of these patterns rolled up into different types of structures according to the way the photoresist swelled. As shown in the scanning electron microscope (SEM) images in Figures 2A,B, helical microrobots were obtained through rectangular templates with lengths of 50 μm and 100 μm. However, the helical angles of the helical microrobots created with these lengths were random. This could be attributed to the change in the folding direction, which is determined by the lowest bending energy state (Chun et al., 2010). To further improve the controllability of the helical parameters of the microrobots during the manufacturing process, parallelogram patterns with tilt angles of 15° and 60° were used. Each tilt angle was observed to have a different folding direction causing the parallelogram patterns to roll up into microhelices with different helical angles. For instance, a 2D parallelogram with a tilt angle of 60° will produce a helical structure with a helical angle of 58 ± 4° (n = 20, the detailed dimensions of 20 helical microrobots are summarized in Supplementary Table S1; these helical microrobots are obtained from 4 batches). A 2D parallelogram with a tilt angle of 15° will produce a helical structure with a helical angle of 36 ± 4° (n = 20, the detailed dimensions of 20 helical microrobots are summarized in Supplementary Table S2; these helical microrobots are obtained from 4 batches). Representative helical microrobots with helical angles of 36°, and 57° were fabricated using the aforementioned respective tilt angles, and their corresponding SEM images are shown in Figures 2C,D.
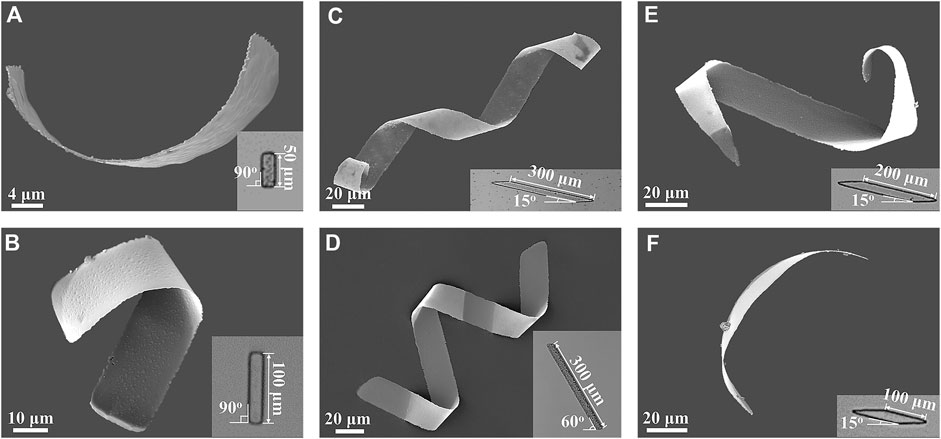
FIGURE 2. SEM images of helical microrobots fabricated using rectangular and parallelogram templates; the insets are the microscopy images of the corresponding 2D patterns. Rectangular templates with lengths of (A) 50 μm and (B) 100 μm. Parallelogram templates with the length of 300 μm and tilt angles of (C) 15° and (D) 60°. Parallelogram templates with the length of (E) 200 μm and (F) 100 μm and tilt angles of 15°.
The number of turns of the helical microrobots, which also determines their length, can be controlled by tuning the length of the 2D patterns. For rectangular patterns that exceed the length of 100 μm, helical microstructures would not be formed, and delamination between the nickel and sacrificial layer will occur. The delamination is due to a larger folding curvature when the rectangular patterns with a high aspect ratio roll up from the short edge. Microrobots created using parallelogram patterns, on the other hand, do not have this problem. To determine the relationship between the number of turns of the helical microrobots and the length of 2D parallelogram patterns, parallelogram templates with lengths of 100 µm, 200 µm, and 300 µm and a tilt angle of 15° were tested. Using parallelogram templates with lengths of 300, 200, and 100 um, representative helical microrobots with 2, 1, and 0.5 turns, respectively, were created, as shown in Figures 2C,E, and Figure 2F; this indicates that the number of helical turns can be affected by the length of the parallelogram patterns. Note that the number of turns obtained from 300 μm patterns is very consistent; it is only when we decreased the length to 100 and 200 μm did we see inconsistency in the number of turns. This is because the strain
The swimming properties of helical microrobots with different helical parameters were tested in deionized water under the actuation of a rotating magnetic field (RMF). The detailed swimming test procedures and the mechanism of the magnetic coil system can be found in the Supplementary Material S1. Figure 3A shows the time-sequence swimming of the helical microrobot fabricated through the parallelogram templates with the length of 300 μm and tilt angles of 60° under the rotational frequency of 4 Hz. The forward swimming speed of the helical microrobots is plotted against rotational frequency, as shown in Figures 3B,C. Each data point represents the average speed of five microrobots and the respective error bars represent the standard deviation. The results indicate a linear relationship between forward swimming speed and rotational frequency.
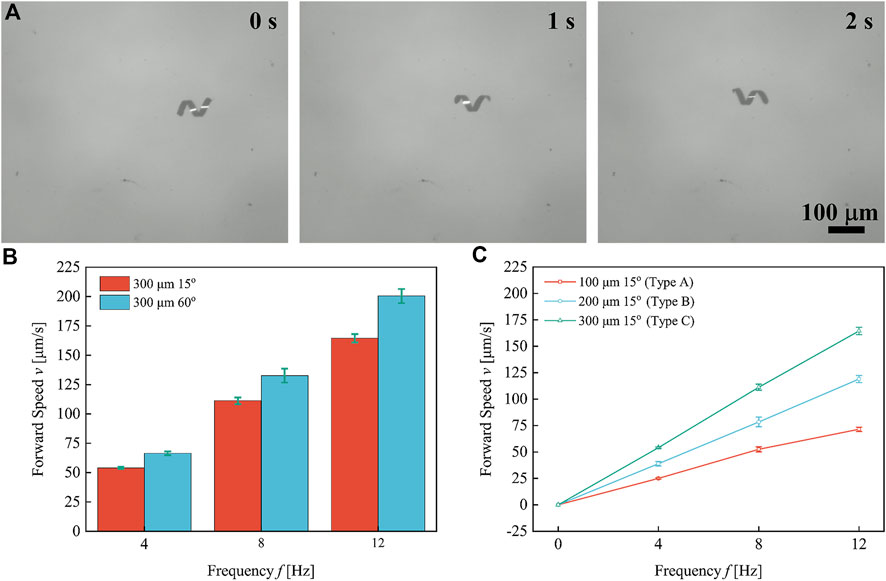
FIGURE 3. Forward swimming speed of helical microrobots under different rotational frequencies. (A) The time-sequence swimming of the helical microrobot fabricated through the parallelogram templates with the length of 300 μm and tilt angles of 60° under the rotational frequency of 4 Hz. (B) The forward swimming speed of helical microrobots with different helical angles versus frequency. (C) The forward swimming speed of helical microrobots with different body lengths versus frequency.
The speed of the helical microrobots as a function of geometric parameters and rotational frequency is expressed as (Tottori et al., 2012)
where
The comparison of swimming ability between our helical microrobots and the previously reported helical microrobots can be made using dimensionless speed
where
To verify the steerability of a helical microrobot, a microrobot was steered to swim along pre-programmed tracks to write out the word HELIX (see Figure 4 and Supplementary Video S2). While the microrobots are swimming close to the substrate, the hydrodynamic interaction with the surface causes drifting motion that leads to a deviation from the intended swimming direction (Peyer et al., 2010). To account for this, a feedback control strategy was applied to the microrobot’s motion control to compensate for the deviation from the intended path (Cheang et al., 2017). The implementation method is described in the Supplementary Material.
The helical microrobots were created from rolled-up parallelogram structures triggered through the swelling of the photoresist sacrificial layer. When the polymer structure of the photoresist broke down, the dissolution of the photoresist would happen in the NMP solution. Ultimately, helical microrobots with a layer of nickel were acquired. The results show the helical angle of the helical microrobots can be tuned by adjusting the angle of the parallelogram patterns and the number of turns will increase proportionately with the length of the parallelogram templates. These findings will provide insights into the fabrication of helical microrobots with a variety of geometry parameters and offer experimental validations for previous theoretical results on the effects of different helical parameters to swimming performance.
Compared with the self-scrolling method, our fabrication method does not require multiple-layer deposition, and it can be realized in four steps using commonly available equipment. For GLAD, DLW, and TAE, a specialized deposition machine or a high-performance laser lithography system is required, which may hinder basic research on helical microrobots due to the availability of equipment. Using two-photon polymerization (TPP) methods (including DLW and TAE), each robot must be created one by one. Thus, research work using TTP to create helical microrobots might be hindered by time and cost. While TTP has obvious advantages in terms of material and precision control over geometrical features, the fabrication method in this work can present an alternative means to obtain helical microrobots using a parallel fabrication process with the advantages of low cost, high throughput, and equipment availability. For BTS, natural helical biotemplates can be acquired from various sources such as spiral xylem vessel plant fibers, helical microorganisms (such as Spirulina), and lotus-root fibers. Biotemplates need to be carefully prepared to avoid damage and have geometrical variations among structures. Although the researchers did not represent quantitative data to verify the consistency of the helical microrobots fabricated via this method, control over the helical parameters of the biotemplates can be challenging due to the mechanical isolation processes and ductile properties of the biological materials. In the case of the flagellar biotemplated microrobots, for instance, flagella obtained from live bacteria vary in length and are easily deformable during the biotemplating process, leading to variations in the helical structures (Ali et al., 2017). Thus, the popularity of this method is limited by either inconsistent structures or low geometry controllability. On the contrary, our helical microrobots consist of a nickel layer, and they can keep the intact helical shape during the fabrication process. Therefore, our proposed method may bring about two positive contributions: (1) the low resource investment may promote basic research on helical microrobots, and (2) the low cost and high throughput technique may be useful in the future for applications that requires a large number microrobots.
Under a RMF, the swimming speed of the helical microrobots increased linearly with the rotating frequency was proportional to its body length and diameter; this is consistent with the theoretical formula. Our proposed method can fabricate helical microrobots with low cost and high throughput while maintaining comparable swimming performance with previously reported helical microrobots. Furthermore, the steerability of the helical microrobots was demonstrated by swimming along a pre-programmed trajectory through feedback control; this also serves as a demonstration that these helical microrobots are feasible for applications that require precise control.
While the helical microrobots presented in this work were not made from fully biocompatible materials, our work successfully created a low-cost helical microrobotic platform that can be fabricated easily using widely available materials and equipment. We envision that future work by our group or others will be able to use this platform to create biocompatible microrobots by replacing/covering the nickel with biocompatible materials. For instance, it has been demonstrated that the biocompatibility of helical microrobots can be improved by coating with Titanium (Tottori et al., 2012; Gao et al., 2014) or co-depositing iron and platinum followed by one single annealing step (Kadiri et al., 2020). Thus, we believe that replacing nickel with iron or covering the nickel with platinum or titanium can make the roll-up helical microrobots biocompatible.
In summary, this work proposes a novel microfabrication method based on rolled-up technology that is more convenient and feasible for the parallel fabrication of helical microrobots for large number deployment. The helical microrobots were created from rolled-up parallelogram structures triggered through the swelling of the photoresist sacrificial layer. Our approach can allow for the manufacture of helical microrobots with different helical angles and numbers of turns. These findings will enhance the understanding of how to fabricate helical microrobots with a variety of geometry parameters using a roll-up mechanism and provide further experimental validation of the existing theoretical model for helical microrobots with different geometrical parameters. Under a RMF, the swimming speed of the helical microrobots will increase linearly with rotating frequency and was proportional to their body length and diameter. Our proposed method can fabricate helical microrobots with low cost and high throughput while maintaining swimming performance. Furthermore, the steerability of the helical microrobots was demonstrated by swimming along a pre-programmed trajectory through feedback control, demonstrating that the helical microrobots created in this work can potentially be used as a microrobotic platform for applications that require high-precision motion control, such as targeted therapy.
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
ZW conducted experiments, prepared images, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. XM contributed to SEM characterization, discussed the results, and wrote the manuscript. LT performed the swimming test experiments. YZ draw the schematics. UKC supervised the whole project and revised the manuscript. All authors approved it for publication.
The work described in this article received funding from the Department of Education of Guangdong (2021ZDZX2037), Science and Technology Innovation Committee Foundation of Shenzhen (20200925155648005, RCYX20210609103644015, and ZDSYS20200811143601004), Shenzhen municipal government (Peacock Plan, 20181119590C).
The authors would like to acknowledge the technical support from the SUSTech Core Research Facilities (SCRF).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frobt.2022.1063987/full#supplementary-material
Aghakhani, A., Yasa, O., Wrede, P., and Sitti, M. (2020). Acoustically powered surface-slipping mobile microrobots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117, 3469–3477. doi:10.1073/pnas.1920099117
Alben, S., Balakrisnan, B., and Smela, E. (2011). Edge effects determine the direction of bilayer bending. Nano Lett. 11, 2280–2285. doi:10.1021/nl200473p
Ali, J., Cheang, U. K., Darvish, A., Kim, H., and Kim, M. J. (2017). Biotemplated flagellar nanoswimmers. Apl. Mater. 5, 116106. doi:10.1063/1.5001777
Bell, D. J., Dong, L., Nelson, B. J., Golling, M., Zhang, L., and Grutzmacher, D. (2006). Fabrication and characterization of three-dimensional InGaAs/GaAs nanosprings. Nano Lett. 6, 725–729. doi:10.1021/nl0525148
Berg, H. C., and Anderson, R. A. (1973). Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature 245, 380–382. doi:10.1038/245380a0
Cheang, U. K., Kim, H., Milutinović, D., Choi, J., and Kim, M. J. (2017). Feedback control of an achiral robotic microswimmer. J. Bionic Eng. 14, 245–259. doi:10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60395-5
Chen, X-Z., Hoop, M., Shamsudhin, N., Huang, T., Ozkale, B., Li, Q., et al. (2017). Hybrid magnetoelectric nanowires for nanorobotic applications: Fabrication, magnetoelectric coupling, and magnetically assisted in vitro targeted drug delivery. Adv. Mat. 29, 1605458. doi:10.1002/adma.201605458
Chen, X-Z., Jang, B., Ahmed, D., Hu, C., De Marco, C., Hoop, M., et al. (2018). Small-scale machines driven by external power sources. Adv. Mat. 30, 1705061. doi:10.1002/adma.201705061
Chun, I. S., Challa, A., Derickson, B., Hsia, K. J., and Li, X. (2010). Geometry effect on the strain-induced self-rolling of semiconductor membranes. Nano Lett. 10, 3927–3932. doi:10.1021/nl101669u
Felfoul, O., Mohammadi, M., Taherkhani, S., de Lanauze, D., Zhong Xu, Y., Loghin, D., et al. (2016). Magneto-aerotactic bacteria deliver drug-containing nanoliposomes to tumour hypoxic regions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 941–947. doi:10.1038/nnano.2016.137
Gao, W., Feng, X., Pei, A., Kane, C. R., Tam, R., Hennessy, C., et al. (2014). Bioinspired helical microswimmers based on vascular plants. Nano Lett. 14, 305–310. doi:10.1021/nl404044d
Ghosh, A., and Fischer, P. (2009). Controlled propulsion of artificial magnetic nanostructured propellers. Nano Lett. 9, 2243–2245. doi:10.1021/nl900186w
Huang, T-Y., Qiu, F., Tung, H-W., Peyer, K. E., Shamsudhin, N., Pokki, J., et al. (2014). Cooperative manipulation and transport of microobjects using multiple helical microcarriers. RSC Adv. 4, 26771–26776. doi:10.1039/C4RA02260B
Kadiri, V. M., Bussi, C., Holle, A. W., Son, K., Kwon, H., Schutz, G., et al. (2020). Biocompatible magnetic micro- and nanodevices: Fabrication of FePt nanopropellers and cell transfection. Adv. Mat. 32, 2001114. doi:10.1002/adma.202001114
Kim, K., Xu, X., Guo, J., and Fan, D. L. (2014). Ultrahigh-speed rotating nanoelectromechanical system devices assembled from nanoscale building blocks. Nat. Commun. 5, 3632. doi:10.1038/ncomms4632
Li, J., Li, T., Xu, T., Kiristi, M., Liu, W., Wu, Z., et al. (2015). Magneto–acoustic hybrid nanomotor. Nano Lett. 15, 4814–4821. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b01945
Li, W., Huang, G., Wang, J., Yu, Y., Wu, X., Cui, X., et al. (2012a). Superelastic metal microsprings as fluidic sensors and actuators. Lab. Chip 12, 2322–2328. doi:10.1039/C2LC40151G
Li, W., Huang, G., Yan, H., Wang, J., Yu, Y., Hu, X., et al. (2012b). Fabrication and stimuli-responsive behavior of flexible micro-scrolls. Soft Matter 8, 7103–7107. doi:10.1039/C2SM25366F
Loget, G., and Kuhn, A. (2011). Electric field-induced chemical locomotion of conducting objects. Nat. Commun. 2, 535. doi:10.1038/ncomms1550
Ma, X., Jannasch, A., Albrecht, U-R., Hahn, K., Miguel-Lopez, A., Schaffer, E., et al. (2015). Enzyme-Powered hollow mesoporous janus nanomotors. Nano Lett. 15, 7043–7050. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b03100
Medina-Sánchez, M., Schwarz, L., Meyer, A. K., Hebenstreit, F., and Schmidt, O. G. (2016). Cellular cargo delivery: Toward assisted fertilization by sperm-carrying micromotors. Nano Lett. 16, 555–561. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04221
Mei, Y., Solovev, A. A., Sanchez, S., and Schmidt, O. G. (2011). Rolled-up nanotech on polymers: From basic perception to self-propelled catalytic microengines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 2109–2119. doi:10.1039/C0CS00078G
Mhanna, R., Qiu, F., Zhang, L., Ding, Y., Sugihara, K., Zenobi-Wong, M., et al. (2014). Artificial bacterial flagella for remote-controlled targeted single-cell drug delivery. Small 10, 1953–1957. doi:10.1002/smll.201303538
Morozov, K. I., and Leshansky, A. M. (2014). The chiral magnetic nanomotors. Nanoscale 6, 1580–1588. doi:10.1039/C3NR04853E
Pak, O. S., Gao, W., Wang, J., and Lauga, E. (2011). High-speed propulsion of flexible nanowire motors: Theory and experiments. Soft Matter 7, 8169–8181. doi:10.1039/C1SM05503H
Palagi, S., Mark, A. G., Reigh, S. Y., Melde, K., Qiu, T., Zeng, H., et al. (2016). Structured light enables biomimetic swimming and versatile locomotion of photoresponsive soft microrobots. Nat. Mat. 15, 647–653. doi:10.1038/nmat4569
Peyer, L., Kratochvil, B. E., and Nelson, B. J. (2010). Non-ideal swimming of artificial bacterial flagella near a surface. Alaska, USA: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Anchorage.
Qiu, F., Fujita, S., Mhanna, R., Zhang, L., Simona, B. R., and Nelson, B. J. (2015). Magnetic helical microswimmers functionalized with lipoplexes for targeted gene delivery. Adv. Funct. Mat. 25, 1666–1671. doi:10.1002/adfm.201403891
Shahsavan, H., Aghakhani, A., Zeng, H., Guo, Y., Davidson, Z. S., Priimagi, A., et al. (2020). Bioinspired underwater locomotion of light-driven liquid crystal gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117, 5125–5133. doi:10.1073/pnas.1917952117
Smith, E. J., Makarov, D., Sanchez, S., Fomin, V. M., and Schmidt, O. G. (2011). Magnetic microhelix coil structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 097204. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.097204
Sun, X., Yan, C., Chen, Y., Si, W., Deng, J., Oswald, S., et al. (2014). Three-dimensionally “curved” NiO nanomembranes as ultrahigh rate capability anodes for Li-ion batteries with long cycle lifetimes. Adv. Energy Mat. 4, 1300912. doi:10.1002/aenm.201300912
Tian, Z., Huang, W., Xu, B., Li, X., and Mei, Y. (2018). Anisotropic rolling and controlled chirality of nanocrystalline diamond nanomembranes toward biomimetic helical frameworks. Nano Lett. 18, 3688–3694. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b00828
Tian, Z., Zhang, L., Fang, Y., Xu, B., Tang, S., Hu, N., et al. (2017). Deterministic self-rolling of ultrathin nanocrystalline diamond nanomembranes for 3D tubular/helical architecture. Adv. Mat. 29, 1604572. doi:10.1002/adma.201604572
Tottori, S., Zhang, L., Qiu, F., Krawczyk, K. K., Franco-Obregon, A., and Nelson, B. J. (2012). Magnetic helical micromachines: Fabrication, controlled swimming, and cargo transport. Adv. Mat. 24, 811–816. doi:10.1002/adma.201103818
Xu, B., Tian, Z., Wang, J., Han, H., Lee, T., and Mei, Y. (2018). Stimuli-responsive and on-chip nanomembrane micro-rolls for enhanced macroscopic visual hydrogen detection. Sci. Adv. 4, eaap8203. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aap8203
Xu, C., Wu, X., Huang, G., and Mei, Y. (2019). Rolled-up nanotechnology: Materials issue and geometry capability. Adv. Mat. Technol. 4, 1800486. doi:10.1002/admt.201800486
Yu, J., Wang, B., Du, X., Wang, Q., and Zhang, L. (2018). Ultra-extensible ribbon-like magnetic microswarm. Nat. Commun. 9, 3260. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-05749-6
Zeeshan, M. A., Grisch, R., Pellicer, E., Sivaraman, K. M., Peyer, K. E., Sort, J., et al. (2014). Hybrid helical magnetic microrobots obtained by 3D template-assisted electrodeposition. Small 10, 1284–1288. doi:10.1002/smll.201302856
Zhang, L., Abbott, J. J., Dong, L., Kratochvil, B. E., Bell, D., and Nelson, B. J. (2009a). Artificial bacterial flagella: Fabrication and magnetic control. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 064107. doi:10.1063/1.3079655
Zhang, L., Abbott, J. J., Dong, L., Peyer, K. E., Kratochvil, B. E., Zhang, H., et al. (2009b). Characterizing the swimming properties of artificial bacterial flagella. Nano Lett. 9, 3663–3667. doi:10.1021/nl901869j
Keywords: rolled-up technology, swelling effect, helical microrobots, controllable, feedback control strategy
Citation: Wang Z, Mu X, Tan L, Zhong Y and Cheang UK (2022) A rolled-up-based fabrication method of 3D helical microrobots. Front. Robot. AI 9:1063987. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2022.1063987
Received: 07 October 2022; Accepted: 15 November 2022;
Published: 29 November 2022.
Edited by:
Kaiyan Yu, Binghamton University, United StatesReviewed by:
Veronika Magdanz, University of Waterloo, CanadaCopyright © 2022 Wang, Mu, Tan, Zhong and Cheang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: U. Kei Cheang, Y2hlYW5ndWtAc3VzdGVjaC5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.