
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiomes , 08 January 2025
Sec. Nutrition, Metabolism and the Microbiome
Volume 3 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frmbi.2024.1510774
This article is part of the Research Topic Assessment and Application of Microbial Additives in Unconventional Feeds Fermentation View all 6 articles
Introduction: Increasing the research on the development and utilization of unconventional feed resources is one of the effective ways for the sustainable development of herbivorous animal husbandry. China is one of the countries most severely impacted by the invasion of the alien plant Solanum rostratum Dunal (S. rostratum), but this resource has not been used effectively.
Methods: The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and cellulase on the fermentation quality and microbial community in mixed silage of S. rostratum and alfalfa. Treatments were a control treatment with no additive (CK), Lactobacillus plantarum (LP), cellulase (CE), and Lactobacillus plantarum in combination with cellulase (L+C), all of which were stored at ambient temperature for 7, 15, 30, and 60 days.
Results: The results showed that the mixture could retain dry matter (DM), crude protein (CP), and water soluble carbohydrates (WSC) content, increase lactic acid (LA) content, decrease pH and alkaloid content, and improve fermentation quality during silage. The use of additives increased the abundance of Lactobacillus and Weissella, which was related to the improvement of the quality of mixed silage and the degradation of total alkaloids. Differential microbial functions were mainly carbohydrate metabolism, biosynthesis of secondary metabolites and carbon metabolism.
Conclusion: The application of additives and mixed silage provides a new idea for the feed utilization of S. rostratum.
Forage is a critical raw material in livestock production, and livestock products are a necessity in people’s daily lives, and a stable supply of forage is of great significance in guaranteeing national food security (Zhao et al., 2024). Against the backdrop of continuing global population growth and food shortages due to climate change, the shortage of feed resources and the irregular supply and high cost of concentrate feeds seriously threaten the sustainable development of the livestock sector (Moselhy et al., 2022). Therefore, scientifically and rationally developing and utilizing unconventional feed resources is one of the effective methods to alleviate the current shortage of conventional feed in China (Sun et al., 2024). This approach can not only effectively address the scarcity of fodder resources but also reduce feeding costs for herbivores, contributing to the advancement of modern livestock farming (Du et al., 2021).
Invasive plants have caused significant damage to the environment and socio-economic conditions in invaded areas, making them one of the five major global environmental issues of the 21st century (Rai and Singh, 2020). Invasive plants often have a stronger competitive ability for ecological resources compared to native plants. Once they invade, they can quickly reproduce and grow due to their inherent advantages, occupying dominant ecological niches and suppressing native plants (Wagg et al., 2014). S. rostratum is an annual herbaceous plant in the Solanaceae family and the Solanum genus, and it is recognized as an alien invasive malignant weed (Zhou et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2024). Its reproductive capacity is very high, a mature plant can produce 10,000 to 20,000 seeds in a year, which facilitates population growth and dispersal (Abu-Nassar et al., 2022), and poses significant challenges for management (Rai and Singh, 2020). S. rostratum is rich in nutritional value, with a protein content of 15.98% to 17.89%, it also contains various amino acids and vitamins, with vitamin C levels ranging from 0.92 g·kg-1~1.42 g·kg-1. In autumn and winter, when green forage is scarce, livestock may consume small amounts of S. rostratum. However, due to the presence of alkaloids and whole plant covered in sharp spines in S. rostratum, it has a very bitter taste and poor palatability, which often leads to livestock avoiding it during the green growth stage (Liu et al., 2021). This characteristic severely limits its utilization as fodder, resulting in significant resource waste and a decrease in its economic value.
At present, it is an effective way to eradicate invasive weeds by using reasonable processing and utilization methods (Raj and Syriac, 2016). Silage not only provides an opportunity to preserve pasture, but also produces lactic acid and other organic acids through the fermentation of microorganisms such as lactic acid bacteria, which can degrade toxic and hazardous substances in pasture, ensure the safety of pasture and improve the palatability of pasture (Huang et al., 2023). A study reported that after 35 days of ensiling Acacia sieberiana, the cyanide content in the raw material decreased from 130.6 mg·kg-1to 18.1 mg·kg-1. Additionally, ensiling improved the palatability of the forage, resulting in a pleasant aromatic and slightly acidic flavor, as well as a tender and juicy texture (Ngwa et al., 2004). Previous studies reported that the combination of Invasive plant water hyacinth with molasses and pig manure in the ratio of 85:10:5 is the best combination for silage production, after 28 days of silage, it can be used for livestock feeding (Polprasert et al., 1994). A recent experiment by Gottschalk et al. (2018) demonstrated that Silage and additive treatments can be can degrade some pyrrolizidine alkaloids in contaminated grass from eastern groundsel (Senecio vernalis). Klevenhusen et al. (2022) found that silage can reduce the content of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in mixed silage feed derived from common ragwort (Senecio jacobaea) and eastern groundsel (Senecio vernalis). Unconventional feed mulberry leaf silage reduces the anti-nutritional factors in mulberry leaves, improves the palatability of mulberry leaves, reduces nutrient loss and prolongs the storage time (Dong et al., 2020).
Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.), is a prominent legume forage known for its high crude protein content, making it a popular choice for animal feed (Bai et al., 2020). Numerous experiments have shown that to rationally develop and utilize unconventional feeds, mixing unconventional feeds with alfalfa for ensiling not only compensates for the deficiencies between the raw materials and reduces the difficulty of ensiling but also enhances the quality of the silage (Jiang et al., 2024). For example, the mixed silage of alfalfa and maize (Zea mays) (Liu et al., 2023), the mixed silage of alfalfa and sunflower straw, and the mixed silage of alfalfa and perennial ryegrass (Fan et al., 2022) have all produced high-quality mixed feed.
During the silage process, various additives have been proposed to ensure the quality of the produced silage feed. Lactobacillus plantarum is one of the most widely studied silage additives. It can rapidly initiate the process during the early stages of silage, converting water-soluble carbohydrates (WSC) into lactic acid, which promotes a rapid decrease in pH (Weinberg and Muck, 1996), and it can also inhibit the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria (Yan et al., 2019). Cellulase can degrade the cellulose in the cell walls of forage straw, thereby reducing the fiber content. It also hydrolyzes the polysaccharide materials abundant in the straw into monosaccharides, providing resources for the growth and reproduction of microorganisms and promoting the fermentation process (Khota et al., 2016). The study of Guo et al. (2023) showed that the addition of different starter cultures had significant effects on the fermentation quality and nutrient composition of silage, and might also lead to changes in alkaloid content.
Therefore, this study was performed with the purpose of probing the effect of the combination of Lactobacillus plantarum and cellulase on the nutritional quality, fermentation quality, total alkaloid content and microbial community of mixed silage of S. rostratum and alfalfa. We hypothesized that compound additives may improve the fermentation quality and nutritional value of silage, promote the degradation of total alkaloid content, and inhibit the growth of other harmful bacteria.
S. rostratum harvested during the flowering period at the at the experimental base of Institute of Grassland Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (40°40’ N, 111°22’ E), Hohhot, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, on August 14, 2023. Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L., Zhongmu No. 1) was planted on June 7, 2020 at the Grassland Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences in Hohhot (40°58′ N, 111°78′ E). Alfalfa was harvested at the early flowering stage at the third crop on August 15, 2023, with an average of three cuts per year. S. rostratum and Alfalfa were harvested with hand sickles. Two forages were harvested and subsequently chopped to a length of 2-3 cm using a hand hay cutter, and then dry them 24-hrs naturally, leading to its moisture content to be reduced to 55-65%. The two forages were thoroughly combined and blended in a 2:3 ratio (wet weight). The treatments were as follows: (1) no additive control (CK); (2) Lactobacillus plantarum (LP, Zhongke Jiayi Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., Shandong, China; LP was applied at a level of 106 colony-forming units (cfu) per gram of fresh material (FM)); (3) Cellulase (CE; Yidu Biological Technology Co., Ltd., Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China; CE activity as 5 × 105 U/g; addition amount: 1 × 105 U/kg fresh material (FM)); (4) Lactobacillus plantarum+Cellulase (L+C). All the additives were mixed homogenously with mixed forage. Each treated batch was divided into four replicates (one for backup), which were filled in 1L polythene silage tanks (11 cm diameter × 13.8 cm height) with a filling density of 750 kg/m3. Compact and cover with inner and outer lids and seal with tape. A total of 64 tanks (four treatments × four ensiling days × four repeats) were prepared and kept at room temperature (22~25°C). After 7, 15, 30, and 60 days of ensiling, the samples were analyzed.
The samples underwent a drying process for 72 hours at 65°C to determine their dry matter (DM) content. Crude protein (CP) was analyzed using the Dumas nitrogen determination method with a Dumas-01 model by Gerhardt Analytical Instruments Co., Ltd., Germany. For quantification of acid detergent fiber (ADF), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), and acid detergent lignin (ADL), an ANKOM fiber analyzer (Model: A2000i) from Beijing ANKOM Technology Co., Ltd., China, was employed. Crude fat (EE) analysis utilized an ANKOM fat analyzer (Model: XT15i) from Beijing Anke Borui Technology Co., Ltd. Water-soluble carbohydrates (WSC) were assessed using anthrone colorimetry (Wu et al., 2023). pH levels were measured with a Shanghai Yida Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd. acidity meter (Model: LEICI pH S-3C) in China. Identification of lactic acid (LA), acetic acid (AA), propionic acid (PA), and butyric acid (BA) was conducted using high-performance liquid chromatography with a Waters e2695 model from Massachusetts, USA. Ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) content was determined using the phenol-hypochlorite colorimetric technique (Kozloski et al., 2006). The total alkaloid content in the sample was determined by a kit (Glace Biotechnology Co., LTD., Suzhou). Alkaloids reacted with bromocresol green to form yellow substance, which has a characteristic absorption peak at 415 nm.
Total DNA extraction, a DNeasy PowerSoil Kit (Qiagen, MD, USA) was used to process according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA gene were performed according to Yang et al. (2024) with primers 799F (AACMGGATTAGATACCCKG) and 1193R(ACGTCATCCCCACCTTCC) and PCR conditions were according to the study of (Wang et al., 2024). Purified amplicons were pooled in equimolar amounts and paired-end sequenced on an Illumina Nextseq2000 platform (Illumina, San Diego, USA) according to the standard protocols by Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The raw sequence data were uploaded to the NCBI archive of sequence reads under study record number PRJNA1170237. The sequencing data were analyzed according to Wang et al. (2019).
In this study, the Quantile-Quantile Plot was used to assess the normality of the data (Supplementary Figure S1), the data meet the normal requirements. SPSS 26 was used for two-factor analysis of variance, with 3 replicates per group, and P value less than 0.05 was considered significant. The reliability of sample means was evaluated using the standard error of the mean (SEM). Microsoft Excel 2010 was employed for table creation, while graph generation was conducted using Origin 2021 and R 4.1.2. Metabolite identification and annotation were carried out with the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) compound database, followed by mapping the annotated metabolites to the KEGG pathway database (Nwamba et al., 2021). The correlation between microorganism and quality was analyzed using Spearman correlation coefficient, where * means less than 0.05 and ** means less than 0.01.
The chemical composition and microbial quantity of fresh raw material is shown in Table 1. The DM content of S. rostratum was 26.97%FW, and the CP content was 16.12%DM, the NDF content was 54.32%DM, the ADF content was 31.54%DM, the WSC content was 6.34%DM, and the TA content was 7.97 g·kg-1. The DM content of alfalfa was 34.36%FW, and the CP content was 22.48%DM, the NDF content was 31.57%DM, the ADF content was 28.35%DM, the WSC content was 2.17%DM, and the TA content was 4.64 g·kg-1. The DM content of mixtures was 28.63%FW, and the CP content was 20.06%DM, the NDF content was 43.15%DM, the ADF content was 30.58%DM, the WSC content was 3.96%DM, and the TA content was 6.81 g·kg-1.
The chemical composition of mixed silage is shown in Table 2. The additives had significant effects on the contents of DM, CP, ADF, and WSC in mixed silage (p < 0.05). The silage time had significant effects on the contents of DM, CP, NDF, ADF, and WSC in mixed silage (p < 0.01). The interaction of additives and silage time had significant effects on DM content of mixed silage (p < 0.05). The contents of DM, CP, NDF, ADF, and WSC in each group gradually decreased with the extension of silage time, and were significantly lower at 60 days than at 7 days (p < 0.05). The contents of DM, CP, NDF, ADF, and WSC in each group gradually decreased with the extension of silage time, and were significantly lower at 60 days than at 7 days (p < 0.05). At 7 days of silage, CP content in L+C group was significantly higher than that in control group, WSC content in LP group was significantly higher than that in other groups (p < 0.05). At 15 days of silage, WSC content in LP group was significantly higher than that in other groups (p < 0.05). At 30 days of silage, the DM content in CE group was significantly higher than that in control group, the ADF content was significantly lower than that in control group (p < 0.05), and the WSC content in L+C group was significantly higher than that in control group (p < 0.05). At 60 days of silage, the contents of DM, CP and WSC in additive group were significantly higher than those in CK group (p < 0.05), while the contents of NDF and ADF were significantly lower than those in CK group (p < 0.05).
The fermentation composition of mixed silage is shown in Table 3. The contents of pH, LA, AA, PA, and NH3-N in mixed silage were significantly affected by additives and silage time (p < 0.05). The interaction of additives and silage time had significant effects on the contents of LA and PA in mixed silage (p < 0.05). The pH of each group decreased gradually with the extension of silage time, and was significantly lower at 60 days than at 7 days (p < 0.05). The contents of LA, AA, PA, and NH3-N increased gradually with the extension of silage time, and were significantly higher at 60 days than at 7 days (p < 0.05). At 7 days of silage, the pH of LP group was significantly lower than that of control group (p < 0.05). At 15 days of silage, the pH of additive group was significantly lower than that of control group (p < 0.05). At 30 and 60 days of silage, pH in the LP group was significantly lower than in the other groups (p < 0.05). During silage, the content of LA in L+C group was significantly higher than that in control group (p < 0.05), while the content of AA, PA, and NH3-N in additive group was significantly lower than that in control group (p < 0.05).
The difference of total alkaloid content in mixed silage is shown in Figure 1. With the delay of silage time, the TA content of silage decreased gradually. At 7 days of silage, TA content in LP group was significantly lower than that in other groups, and the content in CK group was the highest (p < 0.05). At 15 days of silage, the TA content in LP group was significantly lower than that in CK and CE groups was higher (p < 0.05). At 30 days of silage, TA content in LP group was significantly lower than that in other groups (p < 0.05), and there was no significant difference in other groups (p > 0.05). At 60 days of silage, the TA content in CK group was significantly higher than that in other groups, and the TA content in LP group was the lowest (p < 0.05).
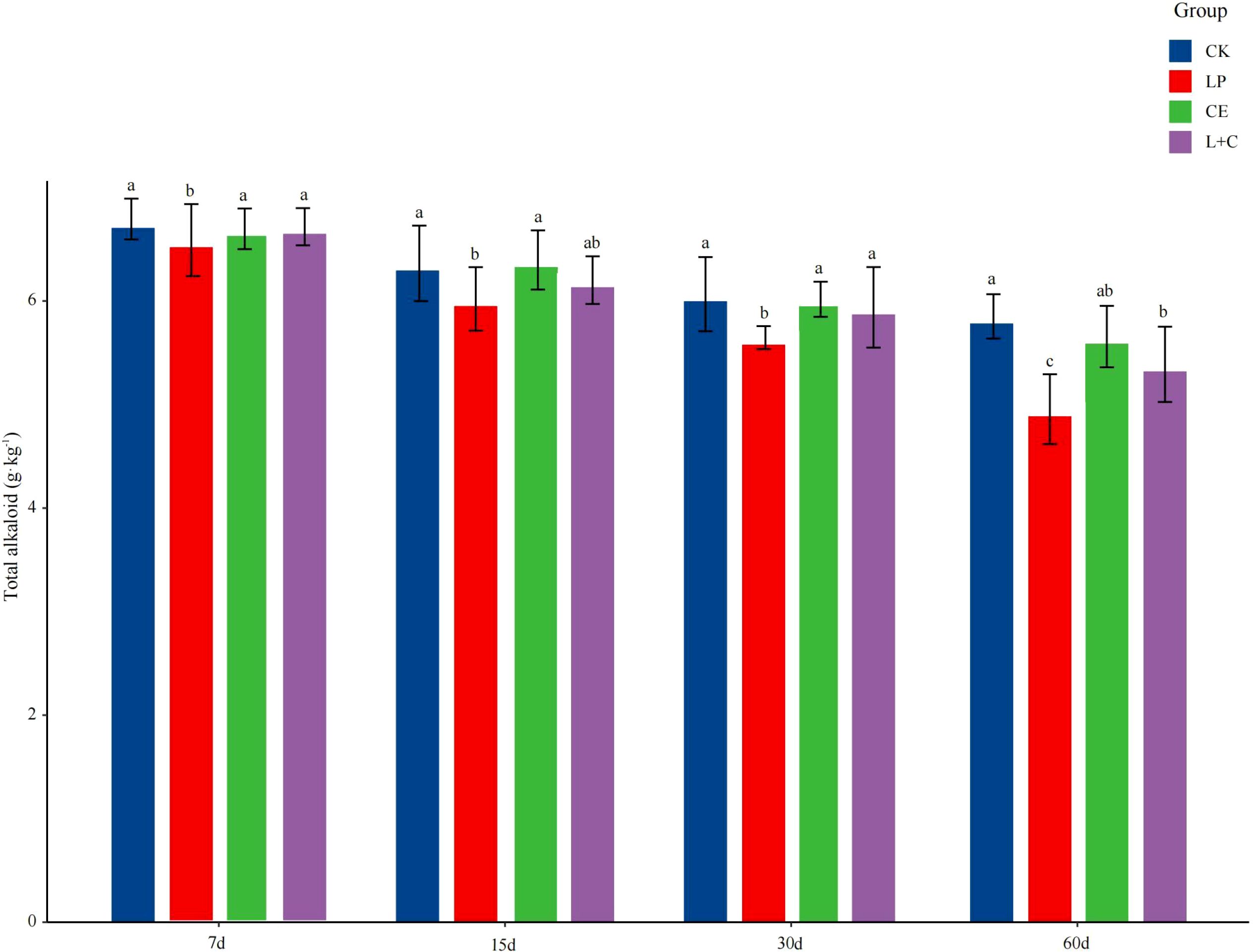
Figure 1. Total alkaloid content of mixed silage. CK, no additive control; LP, Lactobacillus plantarum; CE, cellulase; L+C, Lactobacillus plantarum + cellulase. Different letters indicated significant difference between groups (p< 0.05).
The difference of alpha diversity in mixed silage is shown in Table 4. The Sobs, Chao, Shannon, Simpson, and ACE in mixed silage were significantly affected by additives (p < 0.05). The interaction between additives and silage time had no significant effect on the alpha diversity of mixed silage (p > 0.05). During silage, Sobs, Chao, Shannon and ACE in LP group were significantly lower than those in other groups (p < 0.05), and Simpson was significantly higher than those in other groups (p < 0.05). Sobs, Chao, Shannon and ACE were significantly higher in the CE group than in the other groups (p < 0.05). Sobs, Chao, Shannon and ACE in group CK and group L+C were higher than those in LP group. There was no significant difference in Coverage among all groups (p > 0.05).
The composition of the bacterial phylum levels is shown in Figure 2A. The dominant phylum in all groups were Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, and the abundance of Firmicutes in additive group was higher than that in CK group, and Proteobacteria in additive group was lower than that in CK group. The abundance of Firmicutes in LP group was higher than that in other groups, and that in CE group was lower than that in LP group and L+C group. The abundance of Firmicutes increased and Proteobacteria decreased during silage. In the CK group, Firmicutes were more abundant at days 30 and 60 days than at 7 days and 15 days. In the LP group, Firmicutes abundance was lower at 15 days of silage than at 7 days, 30 days, and 60 days. In the CE group, Firmicutes were more abundant at 15 days of silage than at 7 days, 30 days, and 60 days. In the L+C group, Firmicutes abundance was lower at 7 days silage than at 15 days, 30 days and 60 days.
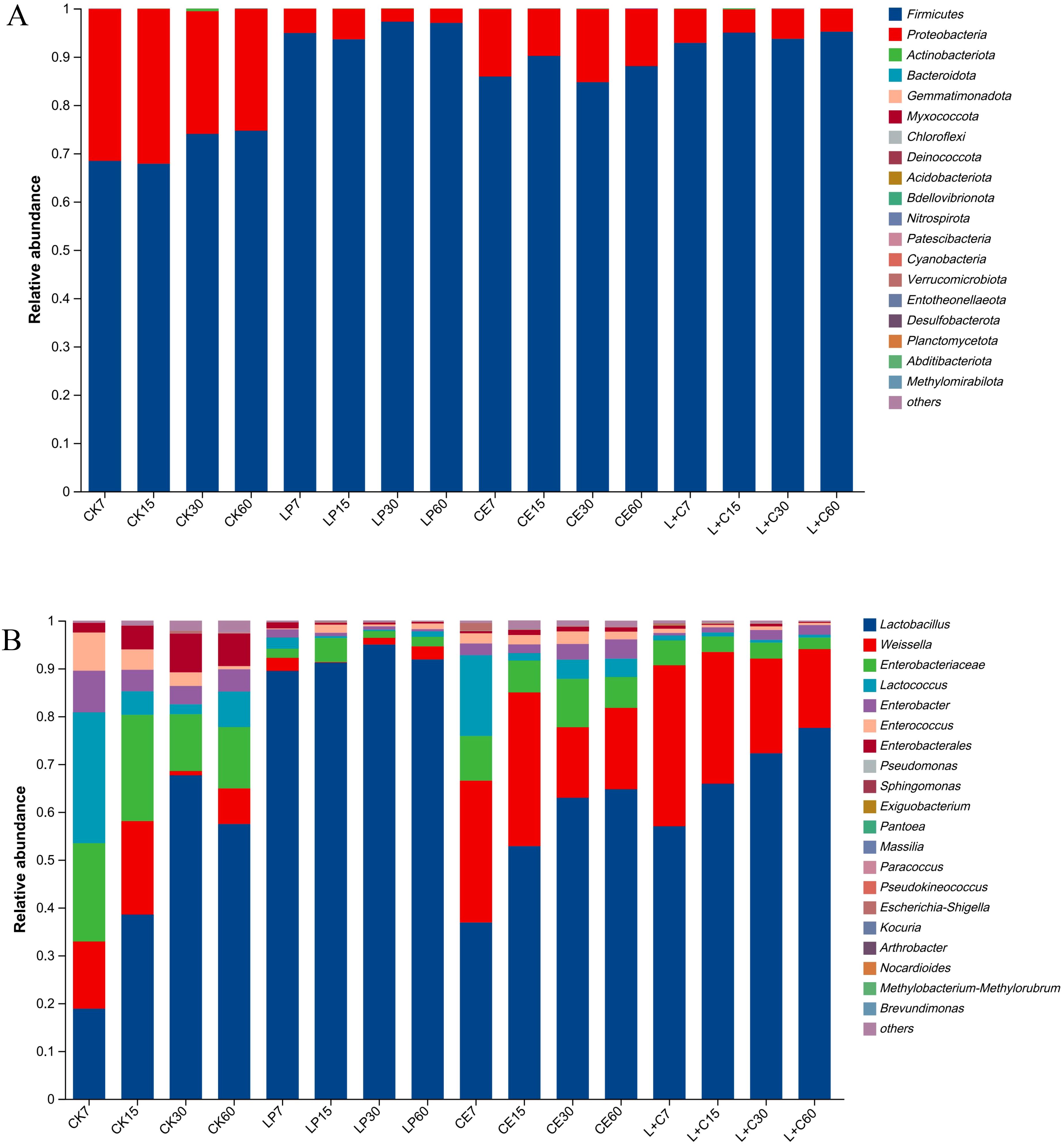
Figure 2. The bacterial abundance at phylum (A) and genus (B) composition of mixed silage. CK, no additive control; LP, Lactobacillus plantarum; CE, cellulase; L+C, Lactobacillus plantarum + cellulase.
The composition of the bacterial genus levels is shown in Figure 2B. The dominant genera in each group were Lactobacillus, Weissella, Enterobacteriaceae, Lactococcus, and Enterobacter. The Lactobacillus abundance in the additive group was higher than that in the CK group and the Lactobacillus abundance in the LP group was higher than that in the other groups. The abundance of Enterobacteriaceae and Lactococcus in group CK was high, and the abundance of Weissella in group CE and group L+C was high. In group CK, the Lactobacillus abundance at 7 days was low and reached the highest at 30 days, while the abundance of Weissella, Enterobacteriaceae, Lactococcus, and Enterobacter was high. In the LP group, the Lactobacillus abundance was consistently higher than that of other genera during silage. In CE group and L+C group, the abundance of Lactobacillus continued to rise during silage, while the abundance of Weissella and Lactococcus decreased.
The results based on KEGG database at level 2 are shown in Figure 3A. At 60 days of silage, the main functions of each group were: carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid metabolism, membrane transport, energy metabolism, and metabolism of cofactors and vitamins. The carbohydrate metabolism of additive group was significantly higher than CK group, while membrane transport, energy metabolism, and metabolism of cofactors and vitamins was significantly lower than CK group. The carbohydrate metabolism of LP group and L+C group was higher, while membrane transport, energy metabolism, and metabolism of cofactors and vitamins were low. The results based on KEGG database at level 3 are shown in Figure 3B. At 60 days of silage, the main functions of each group were: biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, microbial metabolism in diverse environments, biosynthesis of amino acids, abc transporters and carbon metabolism. The biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, biosynthesis of amino acids, and carbon metabolism of additive group were significantly higher than CK group, while microbial metabolism in diverse environments and abc transporters were significantly lower than CK group. The biosynthesis of secondary metabolites and carbon metabolism of LP group and L+C group were higher, while microbial metabolism in diverse environments and abc transporters of cofactors and vitamins were low.
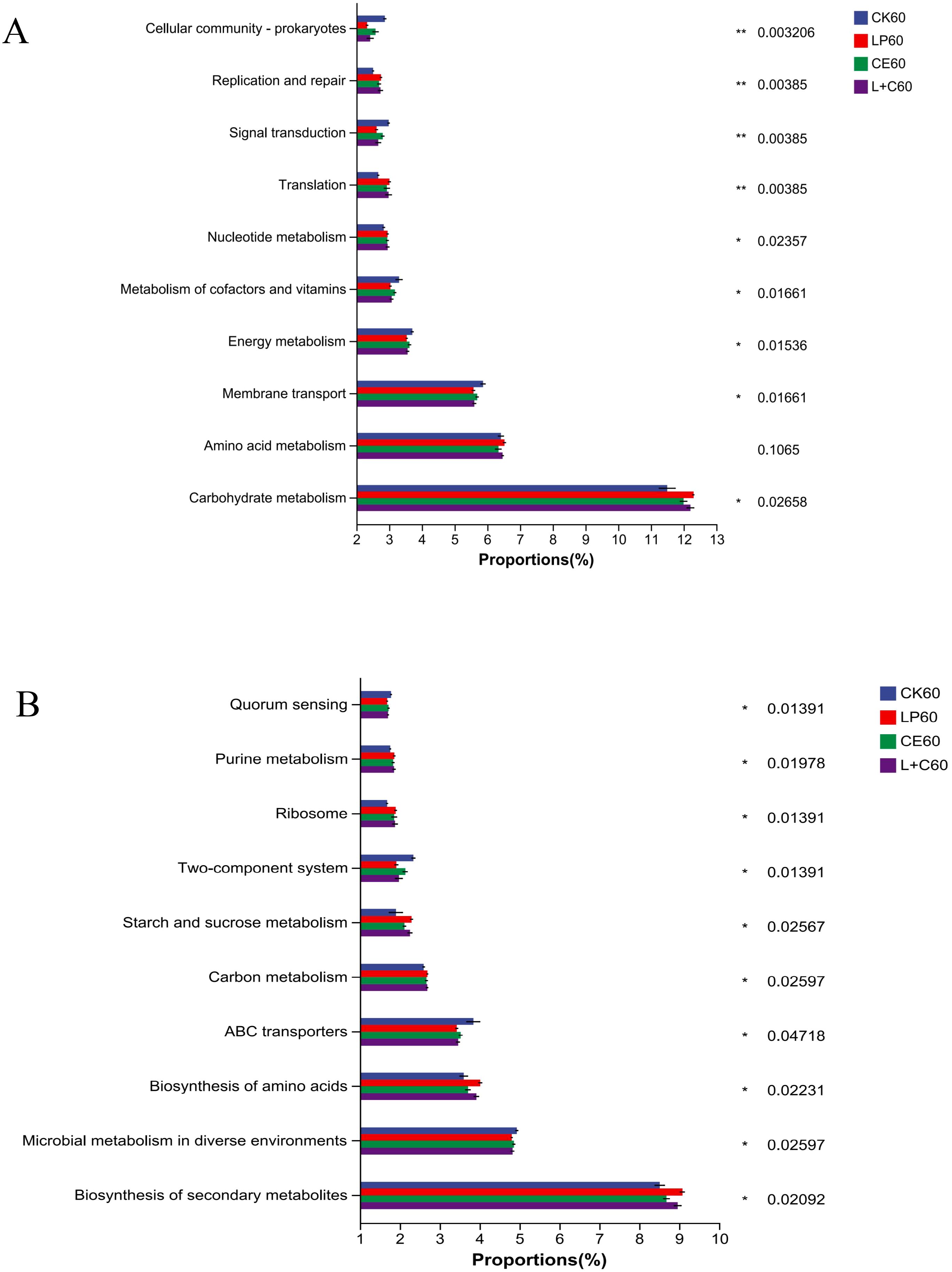
Figure 3. Functional prediction of bacteria at level 2 (A) and at level 3 (B). CK, no additive control; LP, Lactobacillus plantarum; CE, cellulase; L+C, Lactobacillus plantarum + cellulase. *, significant at 0.05; **, significant at 0.01.
The correlations between silage quality and bacterial genus are shown in Figure 4. Lactobacillus was positively correlated with LA (p < 0.05), while negatively correlated with DM (p < 0.05) and extremely negatively correlated with pH, ADF, and TA (p < 0.01). Pseudomonas was positively correlated with LA and PA (p < 0.05), and extremely significant negative correlation with pH, ADF, TA, and NDF (p < 0.01). Weissella was extremely positively correlated with DM (p < 0.01) and negatively correlated with NH3-N (p < 0.05). Enterobacterales and Enterobacter were significantly positively correlated with pH and AA (p < 0.05). Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus, and Lactococcus were significantly positively correlated with pH and TA (p < 0.05). Sphingomonas had a significant negative correlation with WSC (p < 0.05).
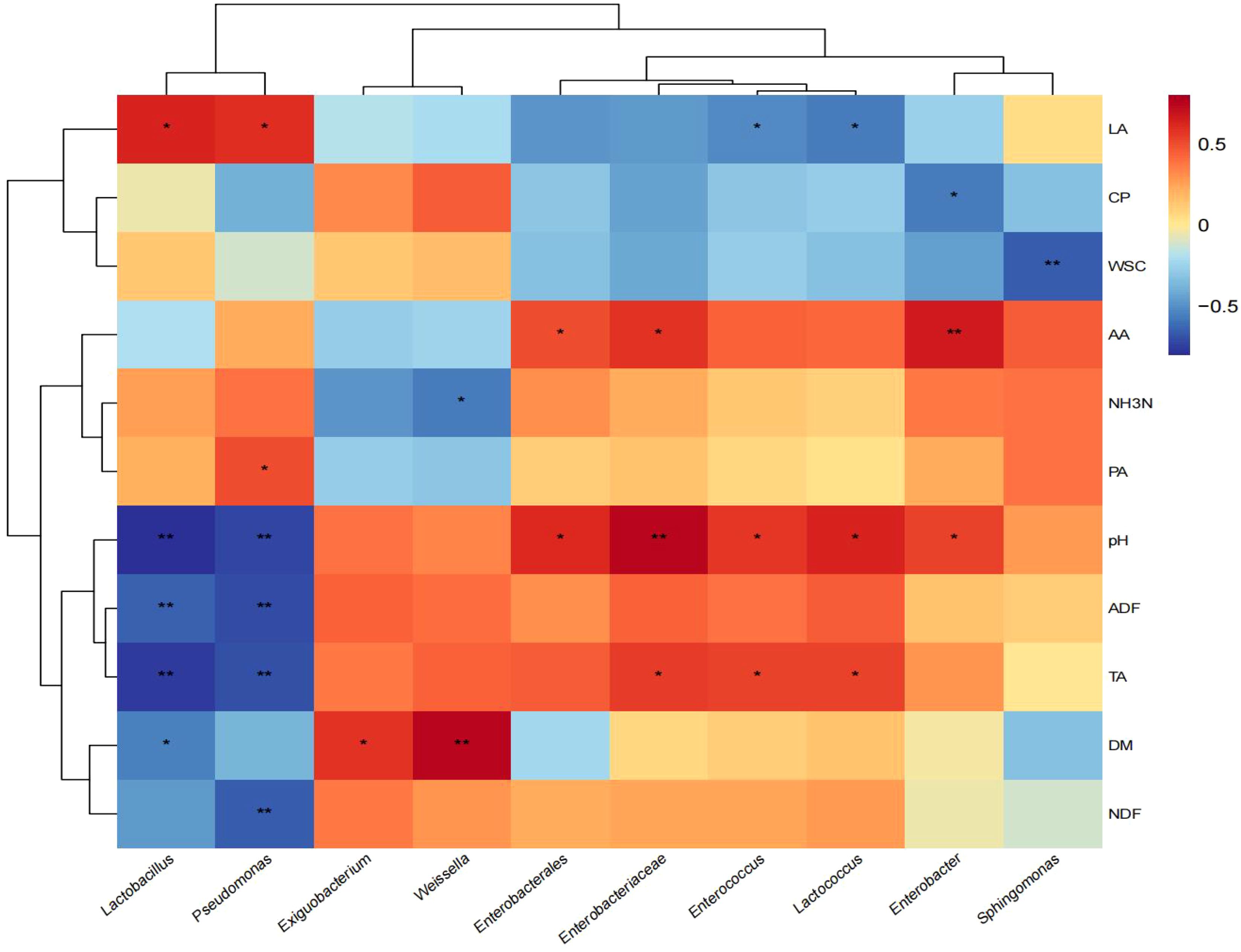
Figure 4. Correlation between silage quality and bacteria at genus level. DM, dry matter; CP, crude protein; NDF, neutral detergent fiber; ADF, acid detergent fiber; WSC, water-soluble carbohydrates; TA, total alkaloids; LA, lactic acid; AA, acetic acid; PA, propionic acid; BA, butyric acid; NH3-N, ammonia nitrogen. *, significant at 0.05; **, significant at 0.01.
The examination of raw materials indicated that S. rostratum had elevated levels of soluble carbohydrates, neutral detergent fiber, acid detergent fiber, and total alkaloids, whereas alfalfa demonstrated larger concentrations of dry matter and crude protein. Soluble carbohydrates serve as the primary energy source for lactic acid bacteria during silage fermentation; inadequate levels may result in incomplete fermentation and insufficient acidity, thereby heightening the risk of spoilage and mold (Mahanna and Chase, 2003). Neutral detergent fibers and acid detergent fibers mostly comprise cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Silage with elevated fiber content is less appealing, adversely impacting animal consumption and digestibility (Grant and Ferraretto, 2018). Numerous alkaloids possess bitter or otherwise unpalatable flavors, potentially diminishing the acceptability of silage. Moreover, specific alkaloids are poisonous and can induce animal poisoning, manifest central nervous system symptoms, and perhaps result in fatality in extreme instances (Cheeke, 1995). At the same time, the microbial count showed that the number of lactic acid bacteria was higher in S. rostratum and lower in alfalfa. More lactic acid bacteria in raw materials can help to accelerate the fermentation process, rapidly reduce pH value, and improve the storage quality and palatability of silage (You et al., 2022). The mixture of alfalfa and S. rostratum as silage raw materials can effectively reduce the content of fiber and alkaloid, increase the content of dry matter, crude protein and soluble sugar, improve the quality of raw materials, and promote the fermentation process of lactic acid bacteria.
The chemical composition analysis of silage indicated a declining trend in the levels of dry matter, crude protein, fiber, and soluble sugar throughout the silage process. From the commencement of the 15-day silage period, the chemical quality of the additive group consistently surpassed that of the control group, demonstrating superior nutrient retention. The inclusion of lactic acid bacteria as an additive accelerates the silage fermentation process, suppresses the growth and metabolism of detrimental microorganisms, hence enhancing the preservation quality of feed, corroborating the findings of Wang et al. (2022b) in whole corn silage. The addition of cellulase can break down complex polysaccharides into simple sugars by breaking down cellulose in plant cell walls, increasing the substrate available for fermentation (Li et al., 2018). In the additive group, the concurrent application of both agents enhances nutrient quality retention, as cellulase liberates additional sugars accessible to lactic acid bacteria by degrading fiber structures. This process accelerates the proliferation of lactic acid bacteria and the production of lactic acid, thereby more effectively preserving feed nutrition and mitigating material loss and spoilage risks during fermentation, corroborating the findings Xu et al. (2022) ‘s study on oat silage.
The analysis of fermentation components of silage showed that the pH of silage decreased, while lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid and ammonium nitrogen increased. The fermentation quality of additive group was always better than that of control group, and the fermentation effect was better. This is due to the fact that lactic acid bacteria produce a large amount of lactic acid through lactic acid fermentation, reducing the acidity of the silage environment (Okoye et al., 2023). The addition of cellulase can degrade a variety of sugars produced by fiber, and by participating in the synthesis of organic acids such as acetic acid and propionic acid, it can effectively inhibit the growth and metabolism of harmful microorganisms and avoid the occurrence of bad fermentation, which is consistent with the research results of Bai et al. (2023) in Caragana korshinskii silage. In the additive group, the fermentation effect of both is better, because cellulase can quickly form an anaerobic acidic environment by decomposing plant cell wall and promoting lactic acid fermentation, and the proliferation of lactic acid bacteria can inhibit the activities of harmful bacteria.
Alkaloids are secondary metabolites produced by plants, and high concentration of alkaloids may cause harm to the nervous system, digestive system and cardiovascular system of livestock (Poutaraud et al., 2017). The examination of alkaloid levels in silage revealed that as the duration of silage increased, the alkaloid content exhibited a declining pattern, with the additive group consistently demonstrating lower alkaloid levels than the control group. This occurs because certain alkaloids can be destroyed or altered by microorganisms, such as lactic acid bacteria, during fermentation, resulting in the formation of non-toxic or less toxic metabolites (Tao et al., 2020). Han et al. (2024) found similar results in the fermentation process of tea. At the same time, many alkaloids are unstable under acidic conditions and may undergo chemical decomposition or structural changes, resulting in reduced activity and toxicity (Basiliere and Kerrigan, 2020). The addition enhances the metabolic activity of lactic acid bacteria during silage fermentation and expedites the biodegradation and acidolysis of alkaloids. The alkaloid concentration in the Lactobacillus plantarum group was consistently lower than in the other groups, attributable to the rapid establishment of an acidic environment from the efficient fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum, which facilitated alkaloid degradation. The sustained low pH and anaerobic conditions further inhibited the accumulation and regeneration of alkaloids, corroborating the findings of Klevenhusen et al. (2022) in the mixed silage of common ragwort (Senecio jacobaea) and eastern groundsel (Senecio vernalis), inoculum lactobacillus in silage promotes the degradation of alkaloids.
The results of silage α diversity showed that the community diversity of LP group was lower than that of other groups, and the community uniformity was higher than that of other groups. This is because Lactobacillus plantarum usually has strong competitiveness in the fermentation environment and can quickly dominate, thus inhibiting the growth of other microorganisms. This dominance can lead to a decrease in microbial diversity, as other types of microbes struggle to compete with Lactobacillus plantarum for resources (Xu et al., 2019). Lactobacillus plantarum concurrently generates metabolites, including lactic acid, via fermentation metabolism, thereby lowering the environmental pH and suppressing the proliferation of other acid-sensitive microorganisms, resulting in diminished diversity, corroborating the findings of Wu et al. (2022) in whole mulberry silage. Because the remaining microorganisms adapt to this acidic environment, the internal population structure of the dominant species is more stable and the uniformity is relatively high. The community diversity of the CE group was higher than that of the other groups, because the basal cellulase is an enzyme capable of breaking down cellulose, which is a complex carbon source that is difficult for many microorganisms to use directly. By adding cellulase, complex cellulose is broken down into simpler sugars, thus providing a more abundant and available nutrient source for a variety of microorganisms (Zhang et al., 2023). As cellulose decomposes, the variety of nutrient sources in the environment expands, allowing various microorganisms to inhabit distinct ecological niches. Certain microorganisms utilize the intermediate products of cellulose degradation, whereas others are better suited to the end products, this diversification of ecological niches enhances community diversity (Kukkar et al., 2022).
The analysis results of phylum level showed that abundance of Firmicutes in additive group was higher than that in control group and Proteobacteria was lower than that in control group. Additives can change the nutrient environment in silage, especially the effects on carbon and nitrogen sources. Many members of Firmicutes, especially lactic acid bacteria and other anaerobic fermenters, grow well in anaerobic environments and at lower pH levels, excelling at utilizing easily fermentable sugars and other simple carbon sources, which allows them to exhibit higher abundance in the additive group (Peng et al., 2024). Numerous bacteria within the Proteobacteria phylum necessitate intricate or particular nutritional requirements, and several species exhibit heightened sensitivity to oxygen or favor neutral over acidic environments (Li et al., 2021). Therefore, when additives alter the environment of silage, such as by promoting lactic acid fermentation and lowering pH, it may be detrimental to the growth of Proteobacteria, resulting in a lower abundance than the control group, which is the same pattern found in maize silage by Guo et al. (2022). The examination of genus-level composition indicated that the abundance of Lactobacillus in the LP group surpassed that of the other groups. The prevalence of Enterobacteriaceae and Lactococcus was greater in the CK group, while Weissella was more abundant in the CE and L+C groups. Lactobacillus plantarum can adapt to anaerobic growth conditions during silage, potentially providing it with a competitive edge over other strains, enabling rapid proliferation and increased abundance during silage (Keshri et al., 2018). At the beginning of silage, Enterobacteriaceae and Lactococcus gained a certain initial advantage, possibly due to a slower decline in acidity in the control group, resulting in a higher abundance, which is consistent with the changes of microbial community after adding Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus buchneri to silage by Drouin et al. (2019). Weissella may have a better ability to utilize cellulose degradation products as a source of nutrients for growth, thereby increasing its abundance in this group (Liao et al., 2022). The use of Lactobacillus plantarum and cellulase can effectively improve the composition of silage microbial community, inhibit the growth and metabolism of hybrid bacteria, and thus improve the effect of silage fermentation.
The microbial function study results indicated that glucose metabolism was elevated, but membrane transport, energy metabolism, and cofactor and vitamin metabolism were diminished in the additive group compared to the control group. Cellulase may enhance the availability of carbohydrates, including glucose and fructose, by degrading cellulose, thereby serving as energy and carbon sources for microorganisms like Lactobacillus plantarum, which promotes carbohydrate metabolism activity within the microbial community (Du et al., 2023). The low membrane transport may be due to the fact that the additives affect the absorption and excretion process of nutrients and metabolites by microorganisms, leading to the reduction of membrane transport function (Lei et al., 2024). The lower energy metabolism may be due to additives that change the way microorganisms use energy, such as reducing the activity of certain metabolic pathways, or inhibiting the activity of key enzymes related to energy metabolism, resulting in reduced energy metabolism of the microbial community (Wang et al., 2022a). The diminished metabolism of cofactors and vitamins may stem from additions that decrease microbial demand for specific cofactors and vitamins, consequently lowering metabolic activity towards these compounds (Labuschagne and Divol, 2021). Compared with the control group, the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, amino acid biosynthesis and carbon metabolism were higher in the additive group, while the microbial metabolism and abc transporters in different environments were lower. This is because secondary metabolites are compounds synthesized by microorganisms under special environmental conditions and have a variety of biological activities and functions. Lactobacillus plantarum may promote the activity of microbial synthesis of secondary metabolites, thereby increasing the metabolic activity of this functional class (Raman et al., 2022). Amino acids serve as the fundamental components of proteins, and additives may have supplied the necessary ingredients and circumstances for their synthesis, hence facilitating the manufacture of amino acids within microbial communities, aligning with the findings of Zhao et al. (2022) ‘s study in amaranth silage. Carbon metabolism is one of the basic metabolic processes in the microbial community, and the degradation of cellulase may provide organic substances required for carbon metabolism in the microbial community, thus increasing the activity of carbon metabolism (Si et al., 2023). Microbial metabolism regulation in different environments is to adapt to specific environmental conditions and achieve optimal growth and survival. Additives change the adaptability and metabolic activity of microorganisms to different environmental factors, resulting in reduced microbial metabolism in a specific environment (Wu et al., 2020). ABC transporters are a category of membrane proteins prevalent in microorganisms, responsible for the transport of protons and ions. The additions may have modified the microbial community’s requirement for and transport of protons and ions, leading to diminished activity of ABC transporters (Keshri et al., 2019).
The results of correlation between silage quality and bacteria genus showed that Lactobacillus was positively correlated with LA and negatively correlated with DM, pH, ADF and TA. Lactobacillus is an important microorganism in silage fermentation, which produces lactic acid by fermentation of sugars during silage. The production of lactic acid can reduce the pH in the silage, inhibit the growth of other bacteria and molds, and help to maintain the quality and shelf life of the silage raw material (Muck et al., 2018). Lactobacillus may produce various degrading enzymes, promote the decomposition of cellulose and alkaloids in silage raw materials, and improve feeding value, which is consistent with the results obtained by Tao et al. (2020) in mixed silage of Oxytropis glabra and corn. Pseudomonas was positively correlated with LA and PA, but negatively correlated with pH, ADF, TA, and NDF. Pseudomonas had a positive correlation with LA and PA, while demonstrating a negative correlation with pH, ADF, TA, and NDF. Pseudomonas possesses a significant metabolic capacity, enabling it to breakdown complex organic compounds in silage raw materials, such as cellulose and other polysaccharides, hence enhancing the nutritional content of silage materials (Du et al., 2021). Weissella was positively correlated with DM and negatively correlated with NH3N. Weissella is abundant in the early stage of fermentation and can produce lactic acid and acetic acid through the fermentation process, and helps to reduce the pH value in the silage raw material, and gradually decreases with the extension of silage time, which is consistent with the results found by Mu et al. (2022) in mixed alfalfa and straw silage. Enterobacter and Enterococcus exhibited a positive association with pH, AA, and TA, and their competitive interactions with other bacteria during silage may influence the acidity and alkaloid content, indicating a favorable correlation. Sphingomonas exhibits a negative correlation with WSC, as it decomposes proteins and carbohydrates in silage by the secretion of exogenous enzymes and proteases, resulting in silage spoiling. Certain Sphingomonas bacteria can digest sugars in silage, generating gases like carbon dioxide and methane, which leads to a reduction in the soluble carbohydrate content of silage (Liu et al., 2022). The analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and mixed silage components can provide a new idea for reducing alkaloid content and improving feed quality.
During the fermentation process of the mixed silage of alfalfa and S. rostratum, Lactobacillus plantarum and cellulase can better preserve the contents of DM, CP and WSC, increase the content of LA, lower pH and the content of alkaloids, and enhance the fermentation quality. The application of additives augmented the abundance of Lactobacillus and Weissella, which are associated with the improvement of quality and the degradation of alkaloids. The differential microbial functions were mainly carbohydrate metabolism, biosynthesis of secondary metabolites and carbon metabolism. By combining nutritional quality, fermentation quality, total alkaloid content and microbial community analyses, it was determined that the addition of Lactobacillus plantarum alone or mixed addition of Lactobacillus plantarum and cellulase could obtain high-quality in mixed silage of alfalfa and S. rostratum.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. HW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. LG: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. LH: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. KL: Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1400301), Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2024MD753998), Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation Project (2024QN03021), and National Forage Industry Technology System CARS-34-20.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frmbi.2024.1510774/full#supplementary-material
Abu-Nassar J., Gal S., Shtein I., Distelfeld A., Matzrafi M. (2022). Functional leaf anatomy of the invasive weed Solanum rostratum Dunal. Weed. Res. 62, 172–180. doi: 10.1111/wre.12527
Bai B., Qiu R., Wang Z., Liu Y., Bao J., Sun L., et al. (2023). Effects of cellulase and lactic acid bacteria on ensiling performance and bacterial community of Caragana korshinskii silage. Microorganisms 11, 337. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020337
Bai J., Xu D., Xie D., Wang M., Li Z., Guo X. (2020). Effects of antibacterial peptide-producing Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus buchneri on fermentation, aerobic stability, and microbial community of alfalfa silage. Bioresour. Technol. 315, 123881. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123881
Basiliere S., Kerrigan S. (2020). Temperature and pH-dependent stability of mitragyna alkaloids. J. Anal. Toxicol. 44, 314–324. doi: 10.1093/jat/bkz103
Cheeke P. (1995). Endogenous toxins and mycotoxins in forage grasses and their effects on livestock. J. Anim. Sci. 73, 909–918. doi: 10.1080/00071669508417765
Dong Z., Wang S., Zhao J., Li J., Shao T. (2020). Effects of additives on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility and aerobic stability of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves silage. Asian Austral J. Anim. 33, 1292. doi: 10.5713/ajas.19.0420
Drouin P., Tremblay J., Chaucheyras-Durand F. (2019). Dynamic succession of microbiota during ensiling of whole plant corn following inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii alone or in combination. Microorganisms 7, 595. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120595
Du Z., Sun L., Chen C., Lin J., Yang F., Cai Y. (2021). Exploring microbial community structure and metabolic gene clusters during silage fermentation of paper mulberry, a high-protein woody plant. Anim. Feed. Sci. Tech. 275, 114766. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114766
Du Z., Yamasaki S., Oya T., Cai Y. (2023). Cellulase–lactic acid bacteria synergy action regulates silage fermentation of woody plant. Biotechnol. Biof. Biop. 16, 125. doi: 10.1186/s13068-023-02368-2
Fan X., Xie Z., Cheng Q., Li M., Long J., Lei Y., et al. (2022). Fermentation quality, bacterial community, and predicted functional profiles in silage prepared with alfalfa, perennial ryegrass and their mixture in the karst region. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1062515
Gottschalk C., Ostertag J., Meyer C., Gehring K., Thyssen S., Gareis M. (2018). Influence of grass pellet production on pyrrolizidine alkaloids occurring in Senecio aquaticus -infested grassland. Food Add. Contam. A. 35, 750–759. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2018.1430901
Grant R., Ferraretto L. (2018). Silage review: Silage feeding management: Silage characteristics and dairy cow feeding behavior. J. Dairy. Sci. 101, 4111–4121. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13729
Guo X., Guo W., Yang M., Sun Y., Wang Y., Yan Y., et al. (2022). Effect of Bacillus additives on fermentation quality and bacterial community during the ensiling process of whole-plant corn silage. Processes 10, 978. doi: 10.3390/pr10050978
Guo L., Wang X., Chen H., Li X., Xiong Y., Zhou H., et al. (2023). Exploring the fermentation quality, bacterial community and metabolites of alfalfa ensiled with mugwort residues and Lactiplantibacillus pentosus. Chem. Biol. Technol. Ag. 10, 107. doi: 10.1186/s40538-023-00472-x
Han Y., Wang X., Gao Z. (2024). Microbial species, metabolites, and natural safety control strategies for harmful factors during the fermentation process of Fu Brick Tea. Food Biosci. 61, 104753. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104753
Huang R., Chen Y., Ma C., Chai Y., Jia S., Zhang F. (2023). Potential factors causing failure of whole plant nettle (Urtica cannabina) silages. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1113050
Huang T. C., Yang T., Wang K., Huang W. ,. J. (2024). Assessing the current and future potential distribution of solanum rostratum dunal in China using multisource remote sensing data and principal component analysis. Remote Sens. 16, 271. doi: 10.3390/rs16020271
Jiang H., Wang S. Y., Wang H. R., Jing Y. Y., Qu H., Sun L., et al. (2024). Influence on the fermentation quality, microbial diversity, and metabolomics in the ensiling of sunflower stalks and alfalfa. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1333207
Keshri J., Chen Y., Pinto R., Kroupitski Y., Weinberg Z. G., Sela S. (2018). Microbiome dynamics during ensiling of corn with and without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 102, 4025–4037. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8903-y
Keshri J., Chen Y., Pinto R., Kroupitski Y., Weinberg Z. G., Sela Saldinger S. (2019). Bacterial dynamics of wheat silage. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01532
Khota W., Pholsen S., Higgs D., Cai Y. (2016). Natural lactic acid bacteria population of tropical grasses and their fermentation factor analysis of silage prepared with cellulase and inoculant. J. Dairy. Sci. 99, 9768–9781. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11180
Klevenhusen F., These A., Taenzer J., Weiß K., Pieper R. (2022). Effects of ensiling conditions on pyrrolizidine alkaloid degradation in silages mixed with two different Senecio spp. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 76, 93–111. doi: 10.1080/1745039X.2022.2084321
Kozloski G., Senger C., Perottoni J., Sanchez L. B. (2006). Evaluation of two methods for ammonia extraction and analysis in silage samples. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 127, 336–342. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2005.08.014
Kukkar D., Sharma P. K., Kim K. H. (2022). Recent advances in metagenomic analysis of different ecological niches for enhanced biodegradation of recalcitrant lignocellulosic biomass. Environ. Res. 215, 114369. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114369
Labuschagne P., Divol B. (2021). Thiamine: a key nutrient for yeasts during wine alcoholic fermentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 105, 953–973. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-11080-2
Lei Y., Li M., Liu Y., Wang J., He X., Zhao Y., et al. (2024). Lactic acid bacteria and formic acid improve fermentation quality and beneficial predicted functional characteristics in mixed silage consisting of alfalfa and perennial ryegrass. Fermentation 10, 43. doi: 10.3390/fermentation10010043
Li J., Wang W., Chen S., Shao T., Tao X., Yuan X. (2021). Effect of lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality and mycotoxins concentrations of corn silage infested with mycotoxigenic fungi. Toxins 13, 699. doi: 10.3390/toxins13100699
Li J., Yuan X., Dong Z., Mugabe W., Shao T. (2018). The effects of fibrolytic enzymes, cellulolytic fungi and bacteria on the fermentation characteristics, structural carbohydrates degradation, and enzymatic conversion yields of Pennisetum sinese silage. Bioresour. Technol. 264, 123–130. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.059
Liao C., Tang X., Li M., Lu G., Huang X., Li L., et al. (2022). Effect of lactic acid bacteria, yeast, and their mixture on the chemical composition, fermentation quality, and bacterial community of cellulase-treated Pennisetum sinese silage. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1047072
Liu X., Li D., Ge Q., Yang B., Li S. (2023). Effects of harvest period and mixed ratio on the characteristic and quality of mixed silage of alfalfa and maize. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 306, 115796. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2023.115796
Liu Y., Li Y., Lu Q., Sun L., Du S., Liu T., et al. (2022). Effects of lactic acid bacteria additives on the quality, volatile chemicals and microbial community of leymus chinensis silage during aerobic exposure. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.938153
Liu Z., Wang M., Tian M., Yuan L., Yu B., Qu B., et al. (2021). Pyrrole alkaloids from Solanum rostratum and their chemical defense function against Henosepilachna vigintioctomaculata. Fitoterapia 155, 105031. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2021.105031
Mahanna B., Chase L. E. (2003). Practical applications and solutions to silage problems. Silage. Sci. Technol. 42, 855–895. doi: 10.3168/jds.2009-2352
Moselhy M. A., Borba J. P., Borba A. E. (2022). Production of high-quality silage from invasive plants plus agro-industrial by-products with or without bacterial inoculation. Biocatal. Agr. Biotech. 39, 102251. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102251
Mu L., Wang Q., Cao X., Zhang Z. (2022). Effects of fatty acid salts on fermentation characteristics, bacterial diversity and aerobic stability of mixed silage prepared with alfalfa, rice straw and wheat bran. J. Sci. Food Agric. 102, 1475–1487. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11482
Muck R., Nadeau E., McAllister T., Contreras-Govea F., Santos M., Kung J. L. (2018). Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy. Sci. 101, 3980–4000. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13839
Ngwa T. A., Nsahlai I. V., Iji P. A. (2004). Ensilage as a means of reducing the concentration of cyanogenic glycosides in the pods of Acacia sieberiana and the effect of additives on silage quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 84, 521–529. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.1650
Nwamba M. C., Sun F., Mukasekuru M. R., Song G., Harindintwali J. D., Boyi S. A., et al. (2021). Trends and hassles in the microbial production of lactic acid from lignocellulosic biomass. Environ. Technol. Inno. 21, 101337. doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2020.101337
Okoye C. O., Wang Y., Gao L., Wu Y., Li X., Sun J., et al. (2023). The performance of lactic acid bacteria in silage production: A review of modern biotechnology for silage improvement. Microbiol. Res. 266, 127212. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127212
Peng W., Zhang L., Wei M., Wu B., Xiao M., Zhang R., et al. (2024). Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum (L) and molasses (M) on nutrient composition, aerobic stability, and microflora of alfalfa silage in sandy grasslands. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1358085
Polprasert C., Kongsricharoern N., Kanjanaprapin W. (1994). Production of feed and fertilizer from water hyacinth plants in the tropics. Waste. Manage. Res. 12, 3–11. doi: 10.1177/0734242X9401200102
Poutaraud A., Michelot-Antalik A., Plantureux S. (2017). Grasslands: a source of secondary metabolites for livestock health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 65, 6535–6553. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00425
Rai P. K., Singh J. (2020). Invasive alien plant species: Their impact on environment, ecosystem services and human health. Ecol. Indic. 111, 106020. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.106020
Raj S. K., Syriac E. K. (2016). Invasive alien weeds as bio-resource: a review. Agric. Rev. 37, 196–204. doi: 10.18805/ag.v37i3.3535
Raman J., Kim J. S., Choi K. R., Eun H., Yang D., Ko Y. J., et al. (2022). Application of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in sustainable agriculture: advantages and limitations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7784. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147784
Si Q., Wang Z., Liu W., Liu M., Ge G., Jia Y., et al. (2023). Influence of cellulase or Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the ensiling performance and bacterial community in mixed silage of alfalfa and leymus chinensis. Microorganisms 11, 426. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020426
Sun H., X., Jiang Z., P., Chen Z., M., Liu G., H., Liu Z., X. (2024). Effects of fermented unconventional protein feed on pig production in China. Front. Vet. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/FVETS.2024.1446233
Tao Y., Niu D., Li F., Zuo S., Sun Q., Xu C. (2020). Effects of ensiling oxytropis glabra with whole-plant corn at different proportions on fermentation quality, alkaloid swainsonine content, and lactic acid bacteria populations. Animals 10, 1733. doi: 10.3390/ani10101733
Wagg C., Bender S. F., Widmer F., van der Heijden M. G. (2014). Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 5266–5270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320054111
Wang C., He L., Xing Y., Zhou W., Yang F., Chen X., et al. (2019). Fermentation quality and microbial community of alfalfa and stylo silage mixed with Moringa oleifera leaves. Bioresour. Technol. 284, 240–247. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.129
Wang W., Portal-Gonzalez N., Wang X., Li J., Li H., Portieles R., et al. (2024). Insights into the microbial assembly and metabolites associated with ginger (Zingiber officinale L. Roscoe) microbial niches and agricultural environments. Sci. Total. Environ. 947, 174395. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174395
Wang S., Shao T., Li J., Zhao J., Dong Z. (2022a). A survey of fermentation parameters, bacterial community compositions and their metabolic pathways during the ensiling of sorghum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 132, 3563–3577. doi: 10.1111/jam.15484
Wang Y. L., Wang W. K., Wu Q. C., Zhang F., Li W. J., Yang Z. M., et al. (2022b). The effect of different lactic acid bacteria inoculants on silage quality, phenolic acid profiles, bacterial community and in vitro rumen fermentation characteristic of whole corn silage. Fermentation 8, 285. doi: 10.3390/fermentation8060285
Weinberg Z. G., Muck R. (1996). New trends and opportunities in the development and use of inoculants for silage. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 19, 53–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1996.tb00253.x
Wu Z., Luo Y., Bao J., Luo Y., Yu Z. (2020). Additives affect the distribution of metabolic profile, microbial communities and antibiotic resistance genes in high-moisture sweet corn kernel silage. Bioresour. Technol. 315, 123821. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123821
Wu C., Sun W., Huang Y., Dai S., Peng C., Zheng Y., et al. (2022). Effects of different additives on the bacterial community and fermentation mode of whole-plant paper mulberry silage. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.904193
Wu Q., Xiao Y., Shao T., Zong C., Li M., Liu Q. (2023). Effects of additives containing a novel strain on the fermentation characteristics, structural carbohydrates, and α-tocopherol content of rice straw and corn stover silages. Chem. Biol. Technol. Ag. 10, 21. doi: 10.1186/s40538-023-00382-y
Xu D., Ding W., Ke W., Li F., Zhang P., Guo X. (2019). Modulation of metabolome and bacterial community in whole crop corn silage by inoculating homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum and heterofermentative Lactobacillus buchneri. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03299
Xu J., Zhang K., Lin Y., Li M., Wang X., Yu Q., et al. (2022). Effect of cellulase and lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality, carbohydrate conversion, and microbial community of ensiling oat with different moisture contents. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1013258
Yan Y., Li X., Guan H., Huang L., Ma X., Peng Y., et al. (2019). Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 279, 166–173. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.107
Yang M., Wang F., Xu W., Li X., Yin H., Tuluhong M., et al. (2024). Effects of the fermentation quality and microbial community of waxy maize mixed with fodder soybean silage. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1405018
You J., Zhang H., Zhu H., Xue Y., Cai Y., Zhang G. (2022). Microbial community, fermentation quality, and in vitro degradability of ensiling caragana with lactic acid bacteria and rice bran. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.804429
Zhang Y., Wang M., Usman S., Li F., Bai J., Zhang J., et al. (2023). Lignocellulose conversion of ensiled Caragana korshinskii Kom. facilitated by Pediococcus acidilactici and cellulases. Microb. Biotechnol. 16, 432–447. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14130
Zhao M., Bao J., Wang Z., Sun P., Liu J., Yan Y., et al. (2024). Utilisation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and propionic acid to improve silage quality of amaranth before and after wilting: fermentation quality, microbial communities, and their metabolic pathway. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1415290
Zhao M., Wang Z., Du S., Sun L., Bao J., Hao J., et al. (2022). Lactobacillus plantarum and propionic acid improve the fermentation quality of high-moisture amaranth silage by altering the microbial community composition. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1066641
Keywords: Solanum rostratum, alfalfa, mixed silage, additives, bacterial community
Citation: Li Y, Wang H, Zhang Y, Ji Y, Guo L, Hao L and Lin K (2025) Influence of Lactobacillus plantarum and cellulase on fermentation quality and microbial community in mixed silage of Solanum rostratum and alfalfa. Front. Microbiomes 3:1510774. doi: 10.3389/frmbi.2024.1510774
Received: 13 October 2024; Accepted: 16 December 2024;
Published: 08 January 2025.
Edited by:
Smerjai Bureenok, Rajamangala University of Technology Isan, ThailandReviewed by:
Jean Debédat, University of California, Davis, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Li, Wang, Zhang, Ji, Guo, Hao and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lifen Hao, aGFvbGlmZW5AY2Fhcy5jbg==; Kejian Lin, bGlua2VqaWFuQGNhYXMuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.