Association between meeting 24-h movement guidelines and health in children and adolescents aged 5–17 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1Department of Sports Science, College of Education, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
- 2Shanghai Innovation Center of Traditional Chinese Medicine Health Service, School of Public Health, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 3Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences, University of Jyväskylä, Jyväskylä, Finland
- 4Institute of Biomedicine, School of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland
A corrigendum on
Association between meeting 24-h movement guidelines and health in children and adolescents aged 5–17 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis
by Zhao, H., Wu, N., Haapala, E. A., and Gao, Y. (2024). Front. Public Health. 12:1351972. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1351972
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2 as published. The numbers were in the wrong place. The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
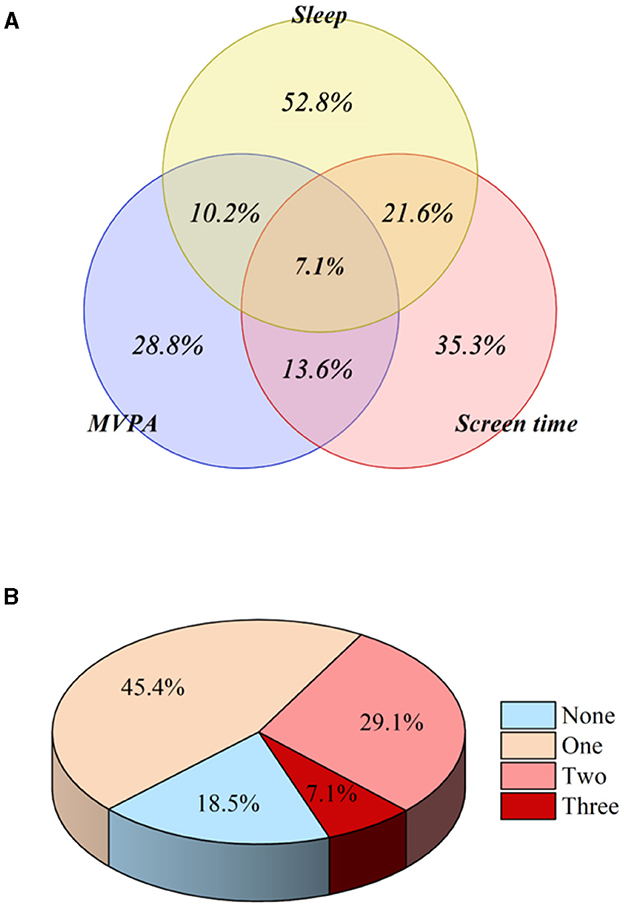
Figure 2. Proportion of children and adolescents meeting the specific combination (A) and general combination (B) of 24-h movement guidelines.
In the published article, there was an error. [Adherence to all three 24-h movement guidelines was updated with 7.6%].
A correction has been made to Abstract, Paragraph one. This sentence previously stated:
“In a total of 61 studies that discussed compliance with 24-h movement guidelines, the overall adherence rate was very low (7.1%).”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“In a total of 61 studies that discussed compliance with 24-h movement guidelines, the overall adherence rate was very low (7.6%).”
A correction has been made to Discussion, Paragraph one. This sentence previously stated:
“We found that only 7.1% of children and adolescents met all three guidelines of the 24-h movement guidelines.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“We found that only 7.6% of children and adolescents met all three guidelines of the 24-h movement guidelines.”
A correction has been made to Conclusion, Paragraph one. This sentence previously stated:
“Overall, the overall adherence rate is alarmingly low (7.1%).”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“The overall adherence rate is alarmingly low (7.6%).”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: physical activity, screen time, sleep, 24-h movement guidelines, health indicators, children and adolescents
Citation: Zhao HH, Wu N, Haapala EA and Gao Y (2024) Corrigendum: Association between meeting 24-h movement guidelines and health in children and adolescents aged 5–17 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 12:1435964. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1435964
Received: 21 May 2024; Accepted: 10 July 2024;
Published: 19 July 2024.
Edited and reviewed by: Gianpaolo De Filippo, Hôpital Robert Debré, France
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Wu, Haapala and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Gao, eWlnYW9Aemp1LmVkdS5jbg==
†ORCID: Ying Gao orcid.org/0000-0003-1440-0681
 HanHua Zhao
HanHua Zhao Na Wu
Na Wu Eero A. Haapala
Eero A. Haapala Ying Gao
Ying Gao