- 1School of Management, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Central Laboratory, Shanghai Children's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 3School of Economics and Management, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
- 4Odette School of Business, University of Windsor, Windsor, ON, Canada
- 5School of Accounting, Nanjing Audit University, Nanjing, China
- 6Institute of Intelligent Management Accounting and Internal Control, Nanjing Audit University, Nanjing, China
Background: National fitness is a development plan formulated by China to promote people's participation in leisure and fitness, enhance people's physique, and realize the general goal of strengthening sports.
Methods: Based on combing the development process of China's national fitness after reform and opening up, using the improved “balanced scorecard” method, this article constructs an evaluation index system of the national fitness development index.
Results: The national fitness development index was established, including 4 first-level indicators, 14 second-level indicators, and 49 third-level indicators. It can calculate the national fitness development index with a total score of 100 points.
Conclusion: To verify the feasibility of the evaluation system, the goal current situation evaluation method is used to calculate the national fitness development index during the 14th Five Year Plan period based on the development of national fitness during the 13th Five Year Plan period to provide evaluation tools and theoretical reference for the development of national fitness in China.
Introduction
On October 20, 2014, The State Council of China issued several opinions on accelerating the development of the sports industry and promoting sports consumption, which clearly stated: “We must develop mass sports in an all-round way, constantly meet the growing demand of the people for sports, and make national fitness a national strategy (1).” The national fitness development of China is so far from the in-depth development stage into the optimization and upgrading stage (2). National fitness is a development plan formulated by China to promote leisure and fitness participation, enhance people's physique, improve people's health level, and realize the general goal of building a strong sports country (3). After years of efforts, the national fitness strategy has been deeply implemented, the level of public services has been significantly improved, and the proportion of people who often participate in physical exercise has reached 37.2%. At the same time, there are still some problems in the development of national fitness in China, such as the structural imbalance between supply and demand of public services, the insufficient distribution of the role of the market mechanism, and the insufficient construction of standardization (4).
Against the historical background of the new era, China is at a historical moment of moving from a great sports country to a great sports country (5, 6). With “Healthy China 2030” as the blueprint, the national fitness campaign is widely promoted to improve the health of the whole people (7). The Chinese government regards the national fitness strategy as a sports industrial revolution and adopts a series of effective measures to develop the sports environment and improve the participation rate of national fitness (8). Public service facilities are the physical space of national fitness and constructing public sports facilities is the key content of national fitness (9). The research shows that more than half of the residents are satisfied with the current national fitness public service, but problems such as low standardization, unequalization of service, and lack of professional talents still exist (10). Equalization of national fitness public services is to ensure that all citizens enjoy equal opportunities for fitness services (11). With the improvement of people's living standards, the contradiction between people's growing demand for sports service and the relatively backward sports service is becoming increasingly prominent (12). The goal of “national fitness and urban integration” can coordinate the layout of urban and rural public sports resources and services and achieve the equalization of basic public services of national fitness for residents (13). Community is the basic carrier of urban public services, so we should strengthen the construction of fitness facilities in urban communities, improve the fitness literacy of drama titles, and integrate sports activities into people's daily life (14). The construction of a policy system focusing on national fitness can rely on the driving force behind the policy to promote the progress of national fitness in organizational structure, laws and regulations, personnel training, and other aspects. The research shows that there is an asymmetric mutualistic symbiotic relationship between national fitness and the sports industry for a long time (15). In developing countries, sports have made a significant contribution to improving people's wellbeing (16).
The construction of the evaluation system of national fitness, scholars from different dimensions is studied in “sports power construction program” as the basic framework, build the mass sports, competitive sports, sports industry, sports culture, sports diplomacy, security system, and negative indicators of seven dimensions in a new era of comprehensive evaluation index system of sports development (17). The mass sports evaluation index system takes the goal realization, the main aspect, the development foundation, and the support system as the system-level evaluation index (18). The local government national fitness public service performance evaluation system is composed of four dimensions: efficiency, quality, democracy, and responsiveness. Ningbo national fitness basic public service quality evaluation system is composed of public sports facilities quality, public sports service quality, fitness environment quality, affiliated sports facilities quality, and mass fitness service personnel quality (19).
The development of national fitness is related to the effective implementation of “sports power strategy” and “healthy China strategy.” Existing studies lack a systematic and holistic development index evaluation system for national fitness, leading to the inability to quantify the development of national fitness, which is not conducive to scientific decision-making by government agencies. Therefore, by sorting out the development process of national fitness in China, this article understands the opportunities, problems, and requirements facing national fitness at present, and introduces the improved “balanced scorecard” based on policy documents, expert interviews, and relevant literature research. The establishment of the national fitness development index will evaluate the development of China's national fitness in a quantitative form for the first time. According to the index comparison, we can obtain the regional balanced development and growth of national fitness, to help government agencies, business entities, the public, and other stakeholders find the direction and ideas to improve and enhance national fitness.
Overview of National Fitness in China
The Development of National Fitness
After China's reform and opening up, the development of national fitness has generally experienced three stages.
Full Start-Up Stage (1995–2008)
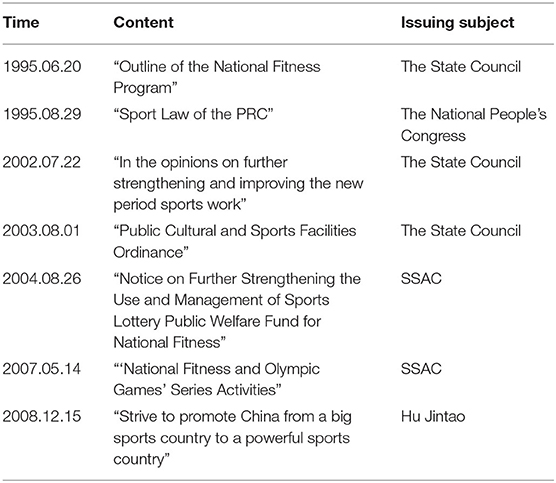
The relevant policy documents in the full start-up stage are shown in Table 1. In this stage, China's national fitness activities started in full swing, constantly improving the legal system and supporting facilities for national fitness, national fitness activities began to occupy an important position (20).
In-depth Development Stage (2009–2014)
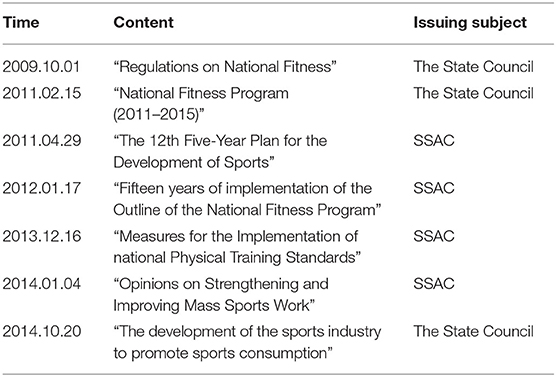
The relevant policy documents in the In-depth Development Stage are shown in Table 2. The success of the Beijing Olympic Games not only stimulated the enthusiasm of the people all over the country for sports but also promoted the rapid development of China's national fitness cause. According to statistics, in this stage, China has issued 118 policy documents related to national fitness (21).
In this stage, China gradually from a sports country to a sports power, by promoting the development of the sports industry to promote national fitness activities, national fitness has become a national strategy.
Optimization and Upgrading Stage (2015–Present)
The relevant policy documents in the Optimization and Upgrading Stage are shown in Table 3. Since 2015, the construction of China's national fitness system has entered a stage of continuous optimization and upgrading.
In this stage, the construction of China's national fitness system tends to be improved. The state attaches great importance to national fitness activities, and national fitness has risen to a new height.
Analysis on Opportunities and Bottlenecks of National Fitness
At present, the development of national fitness is facing major opportunities. First, the development of cross-domain integration has created new opportunities for the development of national fitness, and the development concepts of “integration of sports and health,” “integration of sports and education,” and “combination of sports and tourism” have been gradually deepened. Second, the vigorous development of the social economy has injected impetus into national fitness. The growing diversified fitness needs of the people and the market-oriented operation of non-basic public sports services will promote the prosperity and development of national fitness. Third, the development of modern information technology empowers national fitness. With the rapid development of modern information technologies such as the Internet of things, big data, cloud computing, 5G, and AI, the development of national fitness has been given more possibilities.
The development of national fitness still needs to break through the following problems. First, the overall effect of national fitness needs to be improved. The gap in the development level of mass sports between urban and rural areas and between regions still exists. Second, there is an urgent need to realize the core leading transformation from government satisfaction to people's satisfaction in the performance management of national fitness services. Third, the integrated development ability and effect of national fitness need to be improved.
Construction of National Fitness Development Index Evaluation System
Screening and Modification of Index Evaluation Indicators
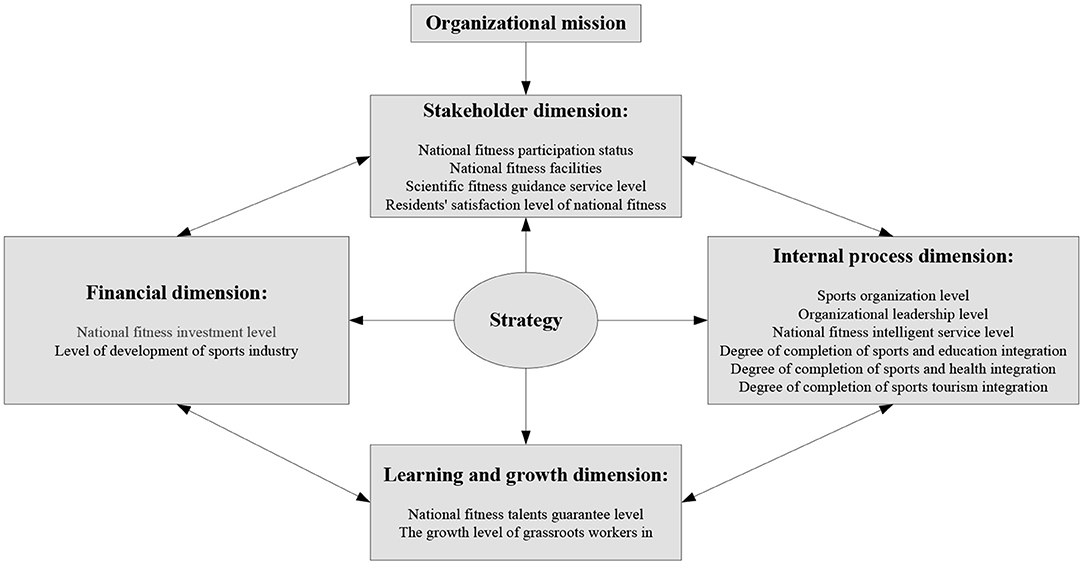
This article will introduce the idea of a “balanced scorecard” in the process of constructing the evaluation system of the national fitness development index. The improved “balanced scorecard” method is adopted to set up the index system from stakeholder dimension, financial dimension, learning and growth dimension, and internal process dimension, respectively, to comprehensively reflect the development of national fitness in China (22, 23). National fitness balanced scorecard model is shown in Figure 1.
This study focuses on the development of the four dimensions of national fitness during the 14th Five-year Plan period to ensure the comprehensiveness, consistency, and integrity of the index system. The improved Delphi method was adopted to screen the draft of the national fitness development index, and the final evaluation system was constructed by combining expert subjective judgment with objective data statistics (24). By designing the expert membership questionnaire of the national fitness development index evaluation system, the experts' opinions on the increase, deletion, and merger of indicators were obtained. The reliability and validity of the questionnaires were tested (25–27).
In the process of expert consultation, the questionnaire of “Expert membership degree of national fitness development index evaluation system construction” was distributed to the experts, and the experts were invited to judge the “rationality” of the specific measurement indicators in the evaluation system. “Rationality” refers to the importance of the indicator to the evaluation system. To facilitate quantitative analysis, 1–5 points are used, where 1 means “extremely unreasonable and should be removed,” while 5 means “completely reasonable and should be retained.” The corresponding evaluation results from 1 to 5 are positively increasing. In addition, experts were invited to put forward revised opinions and suggestions on the addition and deletion of measurement indicators. Stata 14 was used for data statistical processing, and the average, standard number, coefficient of variation, and coordination coefficient of each factor layer were calculated. The specific results are shown in Table 4 (28, 29).
According to the experts' questionnaire feedback results and the current development of national fitness, the index system is modified (30–32). Finally, combined with many in-depth interviews with experts in the industry, referring to the previous scholars' research on the evaluation system development and combing the related policy documents and leaders' relevant statements (33, 34). After sorting out, the final results of the national fitness development index evaluation system include 4 first-level indicators, 14 second-level indicators, and 49 third-level indicators, as shown in Table 5.
National Fitness Development Index Evaluation Index Meaning
Stakeholder Dimension
The stakeholder dimension includes four secondary indicators, namely, participation status of national fitness, facilities supply of national fitness venues, scientific fitness guidance service level, and residents' satisfaction level of national fitness conditions.
The proportion of people who regularly take part in physical exercise is used to reflect the state of national fitness participation. Regular physical activity was defined as more than three times per week of moderate-intensity exercise lasting more than 30 min.
National fitness facilities include sports venues, fitness centers, school sports facilities, etc. The area of public sports venues per 10,000 people can reflect the scale of sports venues and facilities. The standard rate of school stadium facilities and equipment is the necessary condition and material guarantee to carry out normal physical education. The coverage rate of public fitness facilities and 15-min fitness circles in counties (cities, districts), towns (streets), and administrative villages (communities) can reflect the regional distribution of national fitness venues and ensure the demand of residents for fitness activities.
To improve the service level of scientific fitness guidance, it is related to the number of social sports instructors, sports volunteers, and national physical monitoring centers. Social sports instructors are those who provide voluntary service for national fitness to the public and obtain technical ratings. The National Fitness Monitoring Center is a non-profit organization engaged in various kinds of national fitness testing and provides the scientific basis for promoting the implementation of the national fitness plan. And “national student physical health standard” is specially used to evaluate the health status of students in school standards. Young people's sports activities are an important way to promote the healthy growth of young people. The participation of youth in national fitness was measured by the daily physical activity hours of primary and secondary school students in and out of school.
In addition, citizens' satisfaction with national fitness is mainly reflected in three aspects: venue facilities, fitness guidance, and activity organization.
Financial Dimension
The financial dimension of national fitness is reflected in the input level and output level of national fitness (the development level of national fitness).
The total scale of residents' sports consumption includes the service and life consumption of residents' national fitness, which can reflect whether the current national fitness service can meet the demand. To a certain extent, the per capita investment in fitness activities reflects the government's emphasis on national fitness. The public welfare fund of sports lottery is the main source of funds for fitness activities, which can support the construction of a large number of public service venues for national fitness and the holding of mass sports activities.
The output dimension of national fitness is mainly reflected by the current development level of national fitness. The industrial scale is an important index to measure the development of national fitness. The reasonable industrial structure is of great significance to promote the high-quality development of the national fitness industry. The added value of the sports industry includes the added value of sports goods and related products manufacturing, the added value of sports facilities construction, and added value of sports services. Among them, fitness, leisure, and competition performance are the core of the sports service industry and the main direction of national fitness industry development in the future.
Dimension of Learning and Growth
The dimensions of learning and growth of national fitness include the level of talent guarantee and the level of growth of grass-roots staff.
The number of employees and the number of industrial legal entities, respectively, reflect the capacity of the industry to absorb the employment population and the power of market subjects. The future development of national fitness is closely related to the participation of grassroots staff.
The level of grassroots staff's participation in decision-making, job satisfaction, and degree of autonomy can largely determine the promotion and implementation of national fitness among the masses.
Internal Process Dimension
The internal process dimension of national fitness represents the development capability of the national fitness industry, including the level of a sports organization, organization leadership, intelligent service, and integration with education, health, and tourism.
Social sports organizations refer to non-profit social organizations that carry out nationwide fitness and sports competition activities and improve the fitness level of the masses. Grassroots social sports organizations include government sports organizations and social sports organizations, and their participation ratio can show the current marketization level of national fitness. The national sports industry demonstration base is the starting point of the top-level design of national sports industry development and the benchmark of regional sports development.
The level of organization and leadership is reflected in the number of joint meetings of the national fitness work of people's governments at all levels and the proportion of the government absorbing social forces to participate in the national fitness construction work. The National Fitness Plan (2021–2025) points out that the national fitness service level should be promoted by establishing provincial and municipal information service platforms and carrying out online and intelligent sports events.
The integrated development of the national fitness industry includes the integration of physical education, physical health, and sports travel. The number of traditional sports characteristic schools and the number of national youth sports clubs can directly reflect the current development of sports and education integration. The transformation from sports medical integration to sports health integration, through the establishment of sports rehabilitation centers and the training of sports rehabilitation teachers to provide sports rehabilitation plans for patients with chronic diseases and improve the sports rehabilitation level of the whole society. Sports is an important resource to develop the tourism industry, and tourism is an important driving force to promote the sports industry. The number of national sports tourism demonstration bases and the market size of the sports tourism industry are adopted to represent the level of sports tourism integration.
Empirical Study
This article calculates the weight of each index through the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) by aiming at the index system of national fitness development. The corresponding data of the last 5 years were collected as the base data of the index system, and the target value of each index needed to be achieved in the end, and the interval reference standard of the national fitness evaluation system was established, to form a complete national fitness development index evaluation system. The evaluation system can be used to calculate the development index in the next 5 years, which can be used as a tool to measure the development of national fitness in China in the future.
Weight Calculation of National Fitness Development Index
The reasonable degree of weight setting will affect the objectivity and fairness of the results. In this study, experts were invited to score the weights, AHP was used to distinguish the weights of evaluation indexes, a hierarchical model was established according to the evaluation index system, and a judgment matrix was constructed. Finally, the corresponding weight coefficients of evaluation indexes at each level were obtained (Figure 2).
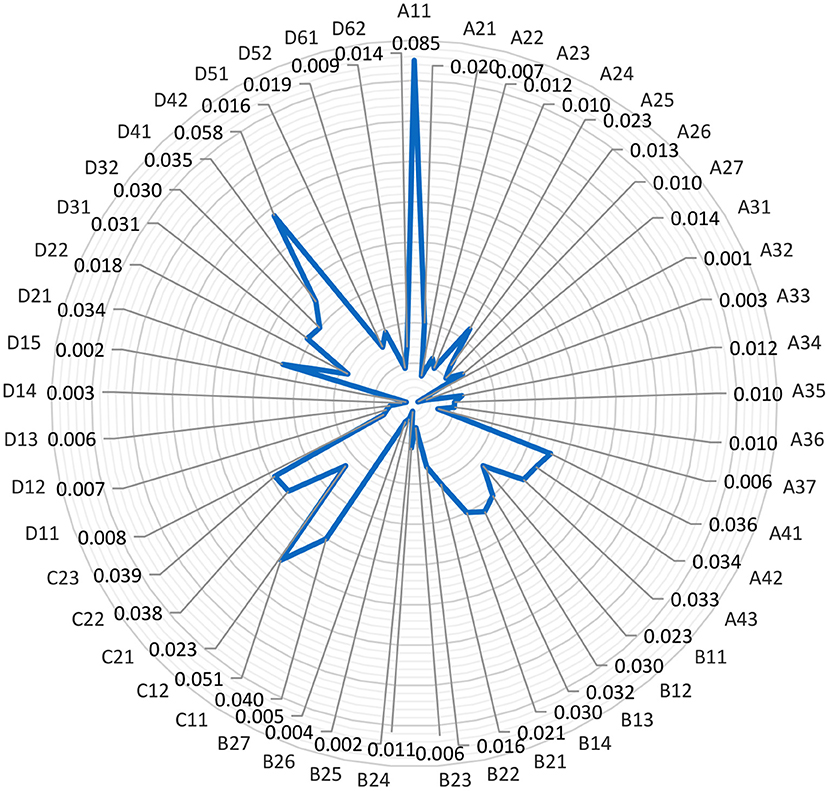
Figure 2. The evaluation system of the national fitness development index and the weight value of each evaluation index.
Interval Reference Standard of National Fitness Development Index Evaluation System
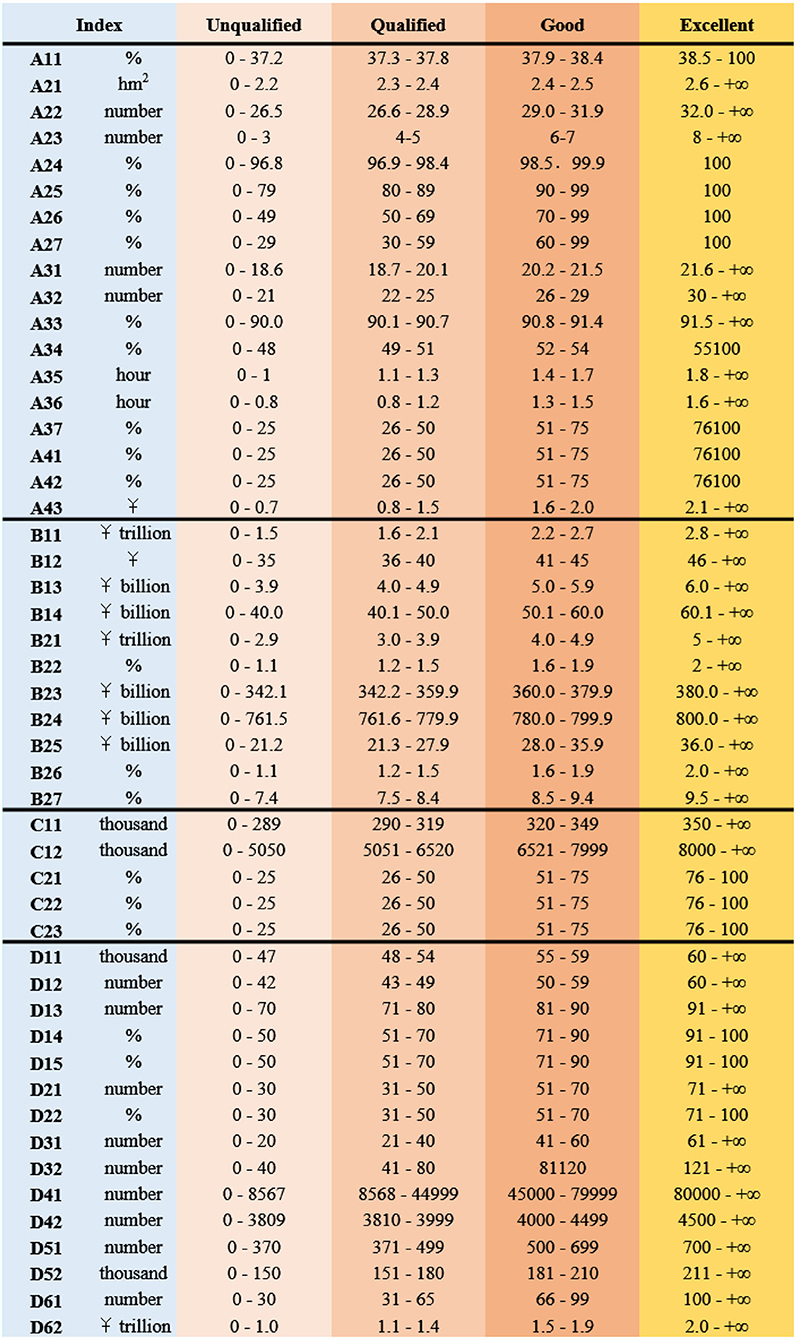
Taking the relevant data of the last 5 years as the base period data, the target value method is adopted to set the target data. In the evaluation of the national fitness development index, the index less than the base period is unqualified, the index greater than the target data is excellent, and the index between the two is qualified and good, respectively. Points 25, 50, 75, and 100 are awarded to unsatisfactory, acceptable, good, and excellent, respectively. The development of national fitness is a relative and dynamic stage process, so the development index is evaluated by selecting the goal-status evaluation method. National Fitness assessment index interval reference standard is shown in Figure 3. The symbol in Figure 3 represents the evaluation index, which has been explained in Table 5.
For quantitative indicators, benchmarking method and local fitting method are, respectively, used to set standards. The benchmarking method is based directly on the target values of relevant national plans, programs, and opinions. Among them, the “14th Five-year Plan for Sports Development” and “National Fitness Plan (2021–2025)” are programmatic documents for national fitness and the most important basis for establishing a comprehensive evaluation system. Partial fitting method: for some indicators with no clear target value, collect official statistical data, functional department work reports, consult relevant personnel, count relevant data in the past, and calculate the target value of the required variable according to the growth rate.
The achievement evaluation of qualitative indicators is mainly based on the objectives and tasks in relevant documents and plans, and the rationality of the achievement standard of each evaluation indicator is scored by experts.
Finally, the national fitness development index was established, including 4 first-level indicators, 14 second-level indicators, and 49 third-level indicators. It can calculate the national fitness development index with a total score of 100 points. Through index calculation, it can help government agencies, enterprises, the public, and other stakeholders to know the current development status and improvement direction of national fitness.
Result Analysis
Through the calculation of the weight of national fitness development indicators and the formulation of interval reference standards, it can be seen that the current development of national fitness should focus on the following areas:
Based on system construction, the legal environment for the implementation of the national strategy of national fitness is improved. The legislation and revision of laws and regulations in key areas of national fitness are strengthened, and a policy guarantee for the construction of a national fitness development index evaluation system is provided.
With resource integration as the core, the construction of a new pattern of coordinated governance of national fitness is deepened. The integrated development of national fitness is the general trend of the development of the times. The integration of national fitness with health, education, culture, science and technology, tourism, pension, and other fields is strengthened.
The main contradiction is taken as the starting point to make up for the shortboard of public service supply of national fitness. We should pay special attention to making up the shortcomings from the three aspects of the supply of national fitness venues and facilities, the supply of events and activities, and the supply of guidance services, to promote the equal development of public services for national fitness.
With the goal of enabling science and technology, the construction level of intelligent fitness services for the whole people is improved. The construction of an intelligent information platform for national fitness service supply is promoted, and the research on key technologies and products in the intelligent field of national fitness is strengthened.
Conclusion
At present, China is in the key stage of transforming into a “sports power,” with both opportunities and challenges. How to grasp this key journey, build a higher level and higher quality national fitness, and form a national fitness work pattern of “government led, social coordination, public participation, and legal guarantee” is an important topic. Based on a deep understanding of the important connotation of “national fitness under social change,” this article uses the improved “balanced scorecard” method to construct an evaluation index system of national fitness development, including 4 primary indicators, 14 secondary indicators, and 49 tertiary indicators. Through the combination of qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis, the interval reference standard of the national fitness evaluation system is evaluated, and finally, the national fitness development index evaluation system is formed, to provide evaluation tools and theoretical reference for the development and improvement direction of national fitness.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author Contributions
ZL and LL: conceptualization and methodology. ZL and YZ: resources. ZL and BH: supervision. ZL, BH, and SZ: writing—original draft. SZ: validation, software, and formal analysis. LL, YZ, RL, BH, and SZ: investigation. RL: visualization. ZZ and BH: data curation. YZ, RL, SZ, and ZZ: writing—review and editing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 71901141), the Soft Science Research Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (Grant No. 22692104000), Municipal Key Curriculum Construction Project of University in Shanghai (Grant No. S202003002), and Shanghai Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project (Grant No. 2020BGL007).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participants who participated in the study.
References
1. Li XR. On national development status of national fitness strategy. J Nanjing Sport Inst. (2016) 30:7–12. doi: 10.15877/j.cnki.nsic.2016.05.002
2. Liu F. Strategy, rights and industry: the Institutional guarantee of the realization of fitness of all. Canadian Social Science. (2019) 15:74–82. doi: 10.3968/11333
3. Fu AG, Fang XD. The development ideas of sports for all national strategy. China Sport. (2016) 36:3–9. doi: 10.16469/j.css.201603001
4. Chen W. To study the development status of China's National Fitness Campaign. Adv Mat Res. (2011) 347:3103–6. doi: 10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/AMR.347-353.3103
5. Gao HL, Li FX. Research on the development of school sports from the perspective of the strategy of healthy China and sports power. Adv Phys Sci. (2020) 08:214–8. doi: 10.12677/APS.2020.84034
6. Wu Y. Reconsideration of exercise prescription in the context of healthy China 2030 blueprint. J Sports Sci. (2019) 7:96–8. doi: 10.17265/2332-7839/2019.03.004
7. Dai JH, Menhas R. Sustainable development goals, sports and physical activity: the localization of health-related sustainable development goals through sports in China: a narrative review. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. (2020) 13:1419–30. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S257844
8. Wang K, Wang XH. Providing sports venues on mainland China: implications for promoting leisure-time physical activity and national fitness policies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:5136. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17145136
9. Qiu D. Analysis of the satisfaction status and influence factors of the standardized construction of public service for national fitness. Adv Phys Educ. (2020) 10:354–63. doi: 10.4236/ape.2020.104029
10. Cui RX, Su LN. Research status on equalization of public sports service for nationwide fitness in Hebei. Phys Proc. (2012) 25:2298–303. doi: 10.1016/j.phpro.2012.03.387
11. Zhang Z, Guo JQ. Research on the causes of hindering the performance of campus sports resources in public sports service. J Sports Sci. (2017) 12:231–4. doi: 10.17265/2332-7839/2017.04.008
12. Zhang JH. Research on the status quo and the character of the development of the national fitness program. Adv Mat Res. (2014) 3349:1769–72. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.998-999.1769
13. Guo CY, Xu SJ, Luo G. Research on the integration development of sports intangible cultural heritage and national fitness. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. (2020) 510:032002. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/510/3/032002
14. Tan TC. The transformation of China's National Fitness Policy: from a major sports country to a world sports power. Int J Hist Sport. (2015) 32:1071–84. doi: 10.1080/09523367.2015.1036240
15. Lan Q, Liu CX, Ling S. Research on measurement of symbiosis degree between national fitness and the sports industry from the perspective of collaborative development. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:2191. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16122191
16. Menhas R, Dai J, Ashraf MA, Noman SM, Khurshid S, Mahmood S, et al. Physical inactivity, non-communicable diseases and national fitness plan of China for physical activity. Risk Manag Healthcare Policy. (2021) 14:2319–331. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S258660
17. Li Y, Hu JS, Huang HY. Evaluation system construction of sports development in the new era and empirical research. China Sport Sci. (2020) 40:14–24+39. doi: 10.16469/j.css.202007002
18. Xia MN, Li Y, Hu JS. Research on Chinese sports evaluation index system of building a well-off society in an all-round way. J Capital Univ Phys Educ Sports. (2020) 32:392–401. doi: 10.14036/j.cnki.cn11-4513.2020.05.003
19. Zhang SL. Construction of evaluation system of Ningbo National Fitness Basic Public Service quality based on service quality. J Guangzhou Sport Univ. (2021) 41:32–6. doi: 10.13830/j.cnki.cn44-1129/g8.2021.02.010
20. Wang F, Ding WS. The development track and future prospect of national fitness in China since twenty-first century. Bull Sport Sci Technol. (2020) 28:61–4. doi: 10.19379/j.cnki.issn.1005-0256.2020.12.025
21. Ye HH. The historical logic and practical path of general secretary Xi Jinping's discourse on national fitness. J Anhui Normal Univ. (2021) 44:83–7. doi: 10.14182/J.cnki.1001-2443.2021.01.013
22. Zhang RL, Wang XF, Wang XL. Performance management of public service of national fitness program based on balanced scorecard. J Chengdu Sport Univ. (2013) 39:8–13+21. doi: 10.15942/j.jcsu.2013.01.005
23. Wang XF, Liu JH, Pang Y. Balanced scorecard-based performance management of nonprofit sports organizations. J Nanjing Sport Institute. (2015) 29:70–5. doi: 10.15877/j.cnki.nsic.2015.02.012
24. Geng BQ. Research on the application of balanced score card in performance evaluation of large-scale sports venues. J Beijing Sport Univ. (2012) 35:1–6. doi: 10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2012.12.001
25. Liu Z, Lang LL, Li LL, Zhao YJ, Shi LH. Evolutionary game analysis on the recycling strategy of household medical device enterprises under government dynamic rewards and punishments. Math Biosci Eng. (2021) 18:6434–51. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021320
26. Liu Z, Lang LL, Hu B, Shi LH, Huang BT, Zhao YJ. Emission reduction decision of agricultural supply chain considering carbon tax and investment cooperation. J Clean Prod. (2021) 294:8. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126305
27. Liu Z, Guo H, Zhao Y, Hu B, Ji X, Lang L, et al. Optimal pricing decision of composite service offered by network providers in E-commerce environment. Electron Commer Res. (2021) 22:193. doi: 10.1007/s10660-021-09487-8
28. Cao J, Wen Y. Research on the performance evaluation index system of sports industry guiding funds in China——based on BSC. J Nanjing Sports Inst. (2020) 19:47–54. doi: 10.15877/j.cnki.nsin.2020.12.008
29. Zhang S, Wang JH. The performance measurement of corporate social responsibility in Chinese professional sport clubs. J Chengdu Sport Univ. (2019) 45:76–82. doi: 10.15942/j.jcsu.2019.02.012
30. Hu T, Wang S, She B, Zhang M, Huang X, Cui Y, et al. Human mobility data in the COVID-19 pandemic: characteristics, applications, and challenges. Int J Digital Earth. (2021) 14:1126–47. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2021.1952324
31. Ul Ain Q, Rehman G, Zaheer M. An analysis of water flow in subsurface environment by using a domain decomposition method. Water Conserv Manag. (2019) 3:27–9. doi: 10.26480/wcm.01.2019.27.29
32. D Agata C, Diolaiuti G, Maragno D, Smiraglia C, Pelfini M. Climate change effects on landscape and environment in glacierized Alpine areas: retreating glaciers and enlarging forelands in the Bernina group (Italy) in the period 1954–2007. Geol Ecol Landsc. (2020) 4:71–86. doi: 10.1080/24749508.2019.1585658
33. Babu L, Mohan SV, Mohan M, Pradeepkumar AP. Highly mature sediments in the tropical monsoonal environment of southwestern India: an appraisal based on weathering indices. Ecofem Clim Change. (2021) 2:69–82. doi: 10.1108/EFCC-05-2020-0017
Keywords: national fitness, evaluation index system, balanced scorecard, social reform, prediction
Citation: Liu Z, Zhang S, Li L, Hu B, Liu R, Zhao Z and Zhao Y (2022) Research on the Construction and Prediction of China's National Fitness Development Index System Under Social Reform. Front. Public Health 10:878515. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.878515
Received: 18 February 2022; Accepted: 14 March 2022;
Published: 16 May 2022.
Edited by:
Fu-Sheng Tsai, Cheng Shiu University, TaiwanReviewed by:
Chunming Ye, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, ChinaRuqia Shaikh, Henan University, China
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhang, Li, Hu, Liu, Zhao and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shijia Zhang, TTAzMDEyMDIyN0BzdWVzLmVkdS5jbg==; Yuanjun Zhao, enlqMjA5MDgzNEAxNjMuY29t
 Zheng Liu1
Zheng Liu1 Shijia Zhang
Shijia Zhang Bin Hu
Bin Hu Ran Liu
Ran Liu Zhao Zhao
Zhao Zhao Yuanjun Zhao
Yuanjun Zhao