- 1West China School of Nursing, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Innovation Center of Nursing Research, Nursing Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Background and aims: Along with an aging population, exploring the impact of oral health on holistic health and determining exact outcomes in elderly individuals are important in both scientific research and clinical practice. Significant increase in the number of systematic reviews shows that oral health can directly or indirectly affect the overall health of elderly people physically, mentally and socially. To systematically collate, appraise, and synthesize the current evidence, we carried out an umbrella review of the impacts of oral health on holistic health in elderly individuals.
Methods: A systematic reviews and meta-analyses search was performed in the major databases PubMed, MEDLINE, Web of Science and the Cochrane Library from inception to February 1, 2022, according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement. The JBI (Joanna Briggs Institute) Critical Appraisal Checklist for Systematic Reviews and Research Syntheses was referred to assess methodological quality, and the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, assessment, Development, and Evaluation working group classification) was used to assess the quality of evidence for each outcome included in the umbrella review.
Results: Out of 1,067 records, a total of 35 systematic reviews were included. Respiratory diseases, malnutrition, age-related oral changes, frailty, cognitive impairment, depression and poor quality of life were identified as seven key outcomes that affect the physical, mental and social health of elderly individuals. Meanwhile, three intervention measures of oral health were summarized as (i) more rigorous and universal scales, (ii) dental cleaning and denture installation, and (iii) improving self-awareness regarding oral care.
Conclusions: Evidence showed that oral health can significantly affect holistic health, and the diverse oral diseases directly lead to multiple health outcomes in elderly individuals. Clear high-quality evidence revealed that oral health is strongly associated with seven health outcomes covering physical, mental, and social levels, which directly corresponds to holistic health, and impacts the quality of life of elderly individuals. Such the results remind the importance of oral care in public health, and further studies need to be conducted to verity more specific association between oral health and other chronic diseases.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/#recordDetails, identifier: CRD42022315315.
Introduction
With the rapid aging of the population worldwide, the holistic health of elderly individuals has become a crucial issue in both developing and developed countries (1, 2). In general, holistic health is defined as a state of complete physical, mental and social functioning, not only the absence of disease and frailty (3), which has been increasingly studied, especially among older people. With increased life expectancy (4), the risks of multiple chronic communicable/non-communicable physical diseases, mental impairments and social disorders are increasing continuously (5, 6). In addition, people have become increasingly aware that the occurrence of such diseases tends to be a cross result; namely, there is always a strong correlation between one poor health outcome and multiple complications, which, however, is severely neglected (7). Typically, as one of the most crucial issues among elderly individuals, people realize that poor oral health is significantly associated with holistic health and can result in multiple health outcomes (8–11). Furthermore, instead of primarily addressing oral diseases or oral hygiene itself, an increasing number of studies in recent years have focused on revealing the correlation between oral health and different common diseases in elderly individuals (12–14).
For instance, evidence has shown that 15% of cases of community-acquired pneumonia or other respiratory diseases, which are considered some of the most common chronic diseases among elderly individuals, are significantly associated with oral bacteria (15). Correspondingly, it has been reported that once regular oral nursing care is lacking, the pathogenic microorganisms colonizing the oral microbiome are strongly correlated with the aggravation of respiratory diseases, including aspiration pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and even COVID-19, in elderly individuals in residential care (16–18). Simultaneously, older people with poor awareness of autonomous oral care not only take higher risks of periodontitis and/or dental caries related to oral diseases, but the higher load of microorganisms easily gives rise to frailty (11, 16), loss of function (19) and multiple chronic comorbidities (20, 21). Tooth loss and a decline in chewing ability are also considered to be accompanied by malnutrition and low quality of life (22, 23). In addition, poor oral health can directly and indirectly impact the mental health of elderly individuals and lead to cognitive impairment (24) and depression (25, 26). Moreover, it has also been reported that understanding the economic burden of oral diseases is essential to evaluate the societal relevance of preventing and addressing oral diseases (27).
Although there is an increasing amount of research and systematic reviews on the impacts of oral health on different health outcomes, and published articles on corresponding topics have covered a variety of general health outcomes among elderly individuals, such studies have mainly focused on the association between oral health and some specific diseases; a body of work describing the current landscape of intervention and nursing measures that links oral health and the diverse outcomes covering physical, mental, and social health is still missing (28, 29). Accordingly, it is still challenging for practitioners and decision-makers to find, interpret, and utilize related evidence in daily nursing and medical processes.
The aim of this umbrella review, therefore, is to provide an overall examination and synthesis of the available qualitative and quantitative evidence on the oral health of elderly individuals from a higher-level perspective and explain the impact of oral health on multiple outcomes of holistic health among elderly individuals. On this basis, the objectives of the review are to assess, identify, analyse, and synthesize the evidence on (1) an exact correlation between oral health and multiple outcomes of holistic health in older people and (2) solutions and suggestions, including effective interventions in clinical practice for nursing care.
Materials and methods
The protocol of this study was registered in PROSPERO registry (CRD42022315315), and the review is reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines (PRISMA).
Eligibility criteria
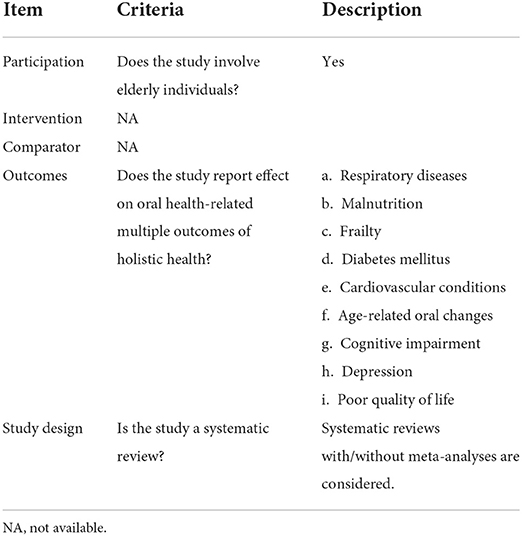
Studies were selected based on the following eligibility criteria: (a) included a systematic review with/without meta-analyses on oral health among older people; (b) investigated the association of different multiple outcomes of holistic health among older people; and (c) included older people as the study population, which exactly corresponds to populations, interventions, comparators, outcomes and study designs (PICOS) as presented in Table 1.
Data sources and search strategy
The electronic databases PubMed, MEDLINE, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library were systematically searched for review articles to identify systematic reviews with meta-analyses of observational or interventional studies that researched the multiple oral health-related outcomes of holistic health among older people. The following research strategy was used to conduct the literature search: (oral health or oral diseases) AND (systematic review* OR meta-analysis*), using truncated terminology for all areas (see Supplementary Table 1). We limited search to reviews written in English or Chinese published before February 2022. Searches were restricted by the level of evidence (systematic review and meta-analysis, or other evidence syntheses). Literature reviews or other types of non-systematic reviews were excluded. In addition, we checked reference lists and performed lateral searches using the “related articles” option in PubMed and the “cite by” option in Web of Science. The reference lists of eligible papers and relevant clinical guidelines were also searched (see research strategy in Supplementary Table 1). All searches were carried out on 1 February 2022.
Selection of reviews
Two of the authors (FL and SS) worked together to remove duplicates with EndNote reference management software, reviewed titles and abstracts for relevance, and finally selected the papers, which required the agreement of both reviewers. Disagreements were resolved through consensus or discussion with the third researcher (XH).
Quality appraisal
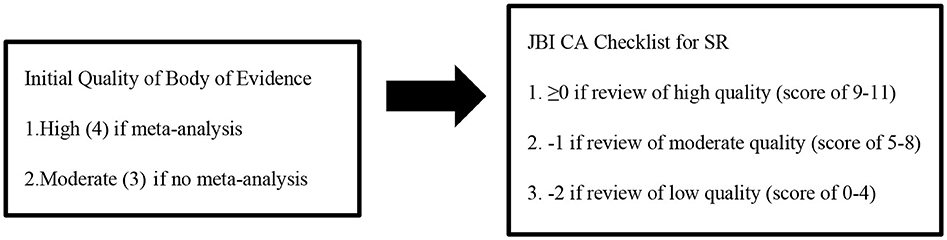
Review articles included in the final analysis were critically evaluated using the “JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Systematic Reviews and Research Syntheses” (JBI CAC for SRRS) by two reviewers (30), and no reviews were eliminated according to their results from this instrument. The JBI assessment tool consists of 11 questions (see the detailed checklist in the Supplementary material). Every question is assessed with four possible answers: Yes, No, Unclear or Not Applicable. Each “Yes” response gains one point, and all other answers receive zero points. Based on the sum of the points, the quality of papers was divided into three groups: low (0–4), moderate (5–8), and high (9–11) quality (31). The quality of the evidence (QoE) supporting each bottom-line statement was rated by using a method of the GRADE approach for primary evidence (1 = very low; 2 = low; 3 = moderate; 4 = high) (Box 1) (32, 33). This method takes into account the study design (meta-analysis; yes or no) and JBI CAC rating of the included systematic reviews.
Box 1. Method used to rate the quality of the evidence supporting each bottom-line statement.
CA, critical appraisal; SR, systematic reviews.
Data extraction and synthesis
The following data were extracted from each manuscript: (1) the name of the first author and publication year; (2) the study design, number of primary studies included in the meta-analysis, the study characteristics and the total number of participants; (3) the respective outcome according to the eligibility criteria; and (4) risk estimates and corresponding confidence intervals and the respective significance level. If relevant data were not available in the respective papers, we sent email inquiries to the corresponding authors. If the author did not reply or could not provide the missing data, we marked the missing information as “No”. Reviews and primary studies were classified as quantitative, qualitative or mixed methods studies. The primary studies in each review were tabulated to assess the overlap between reviews. Effectiveness was investigated by categorizing the different outcomes reported and tabulating the data, including an indication of whether the effects of the intervention were positive, negative or not statistically significant.
Results
Selection of relevant reviews
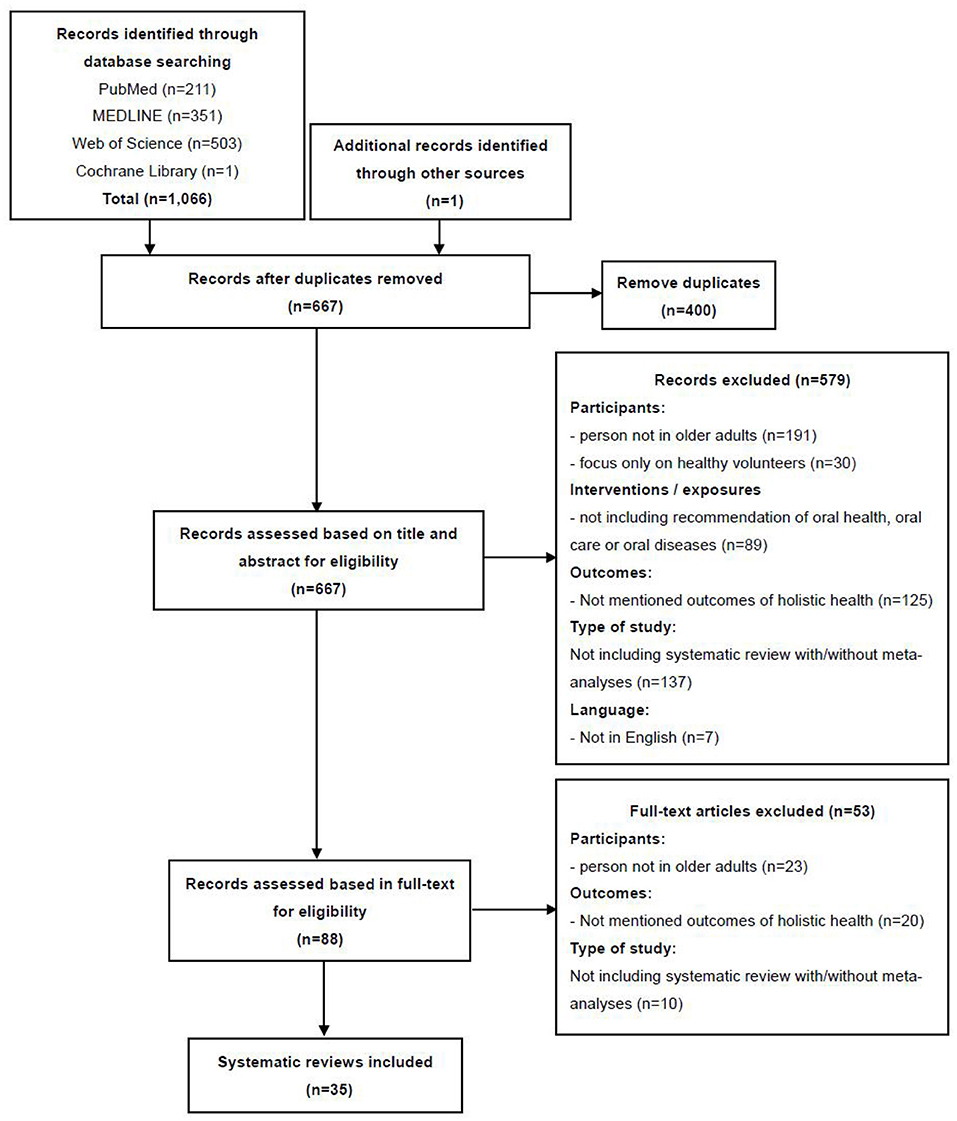
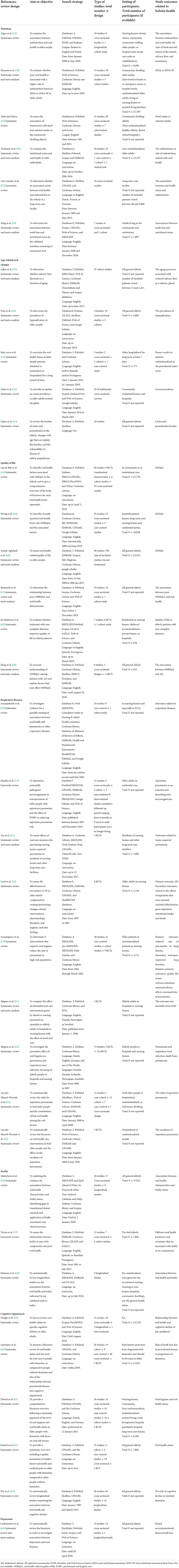
A total of 1,066 records identified through database searching and 1 additional record identified through other sources were imported into the reference management programme EndNote X9.3.1. After examining the records in this programme, 400 duplicates were removed, and 667 records remained. Next, two authors independently screened the titles and abstracts of the remaining records, and 579 papers were excluded because they did not meet the inclusion criteria. Furthermore, based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 53 of the 88 articles were excluded after full-text review because these studies did not focus on elderly individuals, did not mention outcomes of holistic health, or did not include systematic reviews with/without meta-analyses. Finally, 35 review papers met the inclusion criteria and were included in the analysis and synthesis of this study. Figure 1 illustrates the detailed selection of the review papers. The detailed information of the papers is shown in Table 2, which summarizes the elements of the selected reviews, indicating the diversity of research designs, participant groups and outcomes addressed by the authors.
Participants and settings
Six of the included papers were from the Netherlands, five were from the United States, five were from Brazil, four were from China, three were from Canada, two were from Australia, Iran and Sweden, and one was from the United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, Spain, Denmark and Belgium, respectively. The average number of authors was 5.3 ± 1.9. The publishing year of the papers ranged from 2003 to 2021. The average number of databases referred was 4.5 ± 1.6.
The most common groups of participants investigated were elderly individuals living in hospitals or nursing homes. Meanwhile, community-dwelling or institutionalized/non-institutionalized older adults were also the main participant groups investigated in the primary studies. In addition, three studies considered all elderly individuals in general. Among the included reviews, total participants ranged from 618 to 121,547, while 13 of the included papers did not report the total number but presented the ranges of the ages of the elderly participants instead.
Designs and characteristics of the reviewed articles
Most of the included systematic reviews consisted of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies, and 12 reviews consisted of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The summarized findings of the included reviews came from between 4 and 68 primary studies. Eleven reviews also conducted meta-analyses with/without RCT results that were relevant to the present umbrella review.
Critical assessment and risk of bias in the included review papers
The corresponding detailed critical assessment and risk of bias of the reviews are shown in Supplementary Table 2. Eight papers were evaluated as medium quality, and the others were graded as high quality.
Key data synthesis results
The included papers showed a varied range of the impacts of oral health on holistic health among older people. According to the definition of holistic health, three secondary level subthemes can be conceptualized to meaningfully generalize the comprehensive outcomes.
In terms of the research topics, the subthemes based on the main theme can be identified as (i) physical outcomes (N = 23); (ii) mental outcomes (N = 6); and (iii) social outcomes (N = 6), as shown in Supplementary Table 3.
Physical outcomes
Twenty-three systematic reviews provided data on physical outcomes, of which 7 included a meta-analysis. Nine systematic reviews (2 with a meta-analysis) (29, 30) focused on respiratory diseases (13, 15, 50–56), 5 (2 with a meta-analysis) (39, 40) on age-related oral changes (39–43), 6 (3 with a meta-analysis) (28, 36, 38) mainly on malnutrition and 3 (none with a meta-analysis) on frailty (29, 57, 58).
Respiratory diseases
All the corresponding reviews, in general, showed that oral health is crucially related to the incidence of aspiration pneumonia, and various poor oral hygiene factors are considered significant risk factors for different respiratory diseases. Five systematic reviews with low to high quality scores showed that the prevalence of cariogenic and periodontal pathogens in saliva and dental plaque as well as dental decay due to poor oral hygiene are potential risk factors for pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (13, 15, 50, 55, 56). One systematic review of moderate quality pointed out that higher plaque scores were strongly associated with a previous history of respiratory tract infection (50). In particular, one moderate-quality review mentioned that the detection and isolation rates of Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant S. aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and even Escherichia, which are strongly related to mortality due to aspiration pneumonia, are much higher among older people with poor oral health (13).
On the other hand, 6 systematic reviews (2 with meta-analyses) of moderate to high quality showed that regular oral care intervention and cleaning are significant factors for preventing aspiration pneumonia in older people (13, 15, 51–54). Mechanical and/or topical chemical disinfection or antibiotics such as povidone iodine can greatly reduce the incidence of nosocomial pneumonia (15, 52). Both the meta-analyses of high quality examined the impacts of oral hygiene on the incidence rate of hospital aspiration pneumonia (HAP) and showed that while there was no evidence verifying whether professional oral care was better or worse than routine oral care, it demonstrated that professional oral care can truly reduce mortality from HAP (51, 53). One review of low quality pointed out that tooth brushing, denture cleaning and regular professional oral health care are the best interventions to reduce the incidence of aspiration pneumonia (56). Combined with the quality and results of the included reviews, respiratory diseases should be considered to be closely associated with poor oral health.
Age-related oral changes
Poor oral health adds to the burden of the change in the microenvironment for older people (43), which directly aggravates dental/root caries and periodontitis in both developing and developed countries among institutionalized elderly individuals (42). Two high-quality meta-analyses that assessed the salivary flow rate of elderly people showed that the prevalence of hyposalivation in older people is higher than that in other populations, but there was no clear evidence to verify the relevance between the level of salivary production and function in elderly people (39, 40). Simultaneously, as a counterpart of the outcome, 1 systematic review of moderate quality showed that one of the reasons for oral changes in older people over 65 is long hospital stays or being institutionalized in a residential home (41), which therefore demonstrated the importance of developing protocols for elderly individuals' oral health care and providing more professional training to caregivers. Combined with the quality and results of the included reviews, malnutrition should be considered to be closely associated with poor oral health.
Malnutrition
Five reviews of low to high quality showed that the condition of the dentition is strongly associated with the prevalence of malnutrition in elderly individuals (28, 35–38), of which 2 quantitative meta-analyses of high quality pointed out that the nutritional status of elderly individuals with good dentition or dentures is significantly better than those with fewer functional tooth units or anodontia (28, 36). Meanwhile, 3 reviews of low to high quality demonstrated that masticatory problems, which have been identified as independent predictors for low BMI and serum albumin level, weight loss and protein-energy malnutrition (37), are also key for malnutrition (28, 35, 37). Elderly people with chewing problems had nearly twice the risk of malnutrition, and importantly, a lack of tooth/denture cleaning lack of autonomy for oral care, no access to the dentist and being edentulous placed elderly individuals at higher risk of malnutrition (28). On the other hand, two systematic reviews of moderate quality also showed that soft tissue problems, including tongue with blisters, dry or cracked lips and other functional loss, may hinder the intake of nutrients, which can also lead to malnutrition among older people (34, 37). Combined with the quality and results of the included reviews, malnutrition should be considered to be closely associated with poor oral health.
Frailty
The evidence for frailty in elderly individuals is complex. Two systematic reviews of moderate quality analyzed the factors including the number of teeth, chewing ability, oral function and the accumulation of oral health problems and showed that the prevalence of frailty, which is expected to increase rapidly in the aging population, is significantly related to oral health (29, 58), while 1 review of low quality that also included dental service use and Geriatric Oral Health Assessment Index scores claimed that poor oral health has not been evaluated longitudinally to show an association (57). This is because the assessment of frailty remains easily ignored in translational dental research and clinical practice (29). Therefore, combined with the quality and results of the included reviews, although evidence showed a positive association between oral health and frailty, the diversity of the included samples resulted in the outcome variable, and frailty should not be considered a clear outcome of poor oral health.
Mental outcomes
Six systematic reviews provided data on mental outcomes (59–64), of which 1 included a meta-analysis (64). Five systematic reviews (none with a meta-analysis) focused on cognitive impairment (59–63), and 1 (with a meta-analysis) focused mainly on depression (64).
Cognitive impairment
One qualitative systematic review of low quality provided evidence of an association between learning and memory and complex attention and executive function and oral health in elderly individuals, of which most of the primary studies independently identified one or more significant unadjusted associations or adjusted covariates correlated with oral health (59). Correspondingly, the remaining 4 review articles of low to moderate quality focused on verifying the relation between oral health and dementia based on various oral assessment criteria (60–63). While one review of low quality showed that a few studies claimed that there was ambiguous evidence to demonstrate the association between oral health and dementia (63), most of the included studies reported that the risk of prevalence of orofacial pain, gingival bleeding or inflammation and dental caries is much higher in people with senile dementia (60–62). Together, these data suggest a positive effect of improving dental care and designing corresponding oral scales for earlier identification and effective interventions for preventing cognitive impairment in older people (59). Combined with the quality and results of the included reviews, cognitive impairment should be considered a possible outcome of poor oral health.
Depression
One systematic review with a meta-analysis of high quality studied the correlation between oral health and depression, which is the main cognitive disability in elderly individuals worldwide (64). The review quantitatively analyzed the outcome of oral diseases, where depression was considered the main potential result. Generally, although more longitudinal research to test causal and temporal relationships between depression and oral health status needs to be conducted, the existing results showed a positive association between depression and oral diseases in older people. Combined with the quality and results of the included reviews, depression should be considered a possible outcome of poor oral health.
Social outcomes
Six systematic reviews provided data on social outcomes (44–49), of which 3 included a meta-analysis (46, 47, 49). The included reviews focused on analyzing the association between oral health and quality of life, which can be reflected by oral health-related quality of life (OHQoL) or the Geriatric Oral Health Assessment Index (GOHAI).
Quality of life
Four systematic reviews of moderate to high quality showed that a higher number of teeth, occluding pairs, implant-retained overdentures, and shortened dental arches were positively associated with OHQoL (45, 46, 48, 49), while xerostomia and orofacial pain were negatively related (44). Meanwhile, chewing is considered significantly relevant to talking, comfort, retention and aesthetics, which are crucial factors for improving quality of life (44, 48). Importantly, one review of moderate quality determined that there also exists a bidirectional relationship between oral health and diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, and cerebral vascular accidents (45). One meta-analysis of high quality reported a similar association in elderly individuals with Alzheimer's disease (49). Once the 2 meta-analyses of high quality quantitively analyzing the assessment of oral-related quality of life were included (46, 47), the data together showed that regular oral health care and utilizing dentures can greatly increase quality of life for older people. Combined with the quality and results of the included reviews, quality of life should be considered to be closely associated with poor oral health.
Discussion
The aim of this umbrella review was to provide a systematic overview of the impacts of oral health on holistic health among elderly people, and summarize effective approaches for enhancing public oral health. According to the review and systematic synthesis of the included review papers (N = 35), the majority focused on multiple physical outcomes (N = 23); six papers mainly discussed mental outcomes, and 6 papers explored social outcomes. Correspondingly, clear evidence is available to support diverse outcomes covering physical, mental and social health in elderly individuals and included respiratory diseases, malnutrition, age-related oral changes, frailty, cognitive impairment, depression and poor quality of life. It is worth noting that although there were many commonalities among the reviews included, the perspectives of the papers varied, and none of the current articles provided a systematic summary of the diverse results, which is crucial for providing better health care for elderly individuals as well as reducing the cost of medical resources (28, 42, 50).
Oral factors and global outcomes
Oral health is inseparable from holistic health and wellbeing, and the oral diseases are prevalent worldwide, which considerably placing a huge global burden and reducing the quality of life (65). Crucially, it is necessary to emphasize that this umbrella review showed that the oral health and holistic health of elderly individuals are strongly related. With aging, a decline in the physiology of elderly individuals is accompanied by the weakening of oral function and an increase in oral problems. Specifically, age-related oral changes can be summarized in three main aspects: (i) oral diseases such as dental caries and periodontitis resulting from bacterial colonization, which greatly increase the difficulty of oral cleaning (42, 43); (ii) tooth loss and chewing problems, which are closely associated with the diet of older people (29, 57, 58); and (iii) a decrease in salivary flow rate and oral soft issue function, which, however, have not been verified to affect the lives of the participants (39, 40, 61). Correspondingly, the changes were considered to physically lead to a range of impacts. As a consensus, microorganisms such as dental caries and periodontal pathogens colonized in saliva and dental plaque are the main potential risk factors for hospitalization and respiratory diseases, which significantly increase the incidence of aspiration pneumonia (13, 50, 55).
On the other hand, a complete lack of functional dentition and decreased masticatory ability can notably affect the selection and intake of food (35), e.g., fruits and vegetables containing various dietary fibers and vitamins, naturally resulting in malnutrition, including low BMI and serum albumin levels, weight loss and protein-energy malnutrition (28, 34–38). Additionally, the number of oral problems is positively related to the severity of malnutrition (37). In the meantime, poor oral health and oral-related physical diseases can directly or indirectly result in a multifaceted and complex condition of general health, i.e., frailty (29, 57, 58). Clearly, oral health is still considered to have a cumulative effect on frailty throughout life, which slowly contributes to the development of additional chronic conditions and leads to the deterioration of general health quickly in old age (57).
Similarly, in addition to physical outcomes, poor oral health can directly or indirectly affect the mental health of elderly individuals. Nangle's review clearly reported that oral health is significantly associated with cognitive conditions, including study, memory, complex attention, and executive function (59). Meanwhile, they also pointed out that there is still a lack of evidence to verify the relationship between poor oral health and the decrease in language and perceptual motor function in elderly individuals. Interestingly, the rest of the included reviews focusing on cognitive impairment mainly analyzed the impacts of oral health on older people with dementia (60–63). On the one hand, the prevalence of diseases of oral hard tissue (including dental caries, periodontitis and orofacial pain) and oral soft tissue (including gingival bleeding, periodontal pockets, stomatitis, mucosal lesions and reduced salivary flow) is significantly higher in elderly individuals with dementia than in people without dementia (60–62). One review also mentioned that some primary studies have found that oral health measures such as number of teeth and periodontal disease were associated with risk of cognitive decline or incident dementia, whereas others did not find an association (63); this needs further research. Importantly, one review of high quality showed a positive correlation between oral diseases and depression among elderly individuals over 65 years of age, probably because missing teeth hinder smiling, laughing or showing teeth without embarrassment (64). In addition, pain and difficulty speaking also leads to embarrassment and a loss of self-esteem contributing to loneliness and social isolation (66).
Finally, as a comprehensive and complex outcome, quality of life is also considered to be associated with oral health. Although there were different assessment criteria used in the included reviews, such as OHQoL, GOHAI, and OHIP (44–49), all the results supported the fact that some specific oral problems significantly impact quality of life. In particular, the number of teeth and chewing function were considered the main issues positively associated with quality of life (44, 45, 48). Moreover, oral problems can also lead to a host of socioeconomic problems; for example, receiving regular dental care or treatment of complications adds to the financial burden of older people, which is reflected by the generally lower OHQoL of socially deprived residents (45). However, a clearer map between diverse oral issues and quality of life requires more relevant research.
To summarize, the present results showed that oral health is significantly associated with holistic health in older people. Intuitively, poor oral condition can directly impact the physical health of elderly individuals and add to their mental burden or aggravate cognitive impairments; moreover, such physical and mental obstruction not only impacts quality of life socioeconomically but also worsens oral health. On the other hand, oral health has always been a neglected topic given low priority in contrast with many other competing health problems worldwide (67). As with most non-communicable diseases, oral conditions are chronic and strongly socially patterned, with elderly individuals being one of the groups affected (68). Therefore, to achieve significant improvements in oral health, effective strategies including oral health policy and guidelines are required to improve oral health of people with special health care needs. Good oral health can be established by early exposure to dental services, risk assessment and check-ups, as well as a meticulous oral health prevention regimen (7, 69).
Solutions and suggestions
To establish a better relationship between oral health and holistic health, improvements can be summarized in the following three main aspects in public oral health.
(i) More rigorous and universal scales are needed. Although multiple outcomes of holistic health have been presented in a range of reviews and primary studies of high quality, it remains difficult to explain the relationship precisely. Moreover, popular scales are not always appropriate and may not fully represent actual oral health problems (49).
(ii) Providing oral hygiene and professional oral health care are important factors. Although evidence has demonstrated that routine oral care can achieve the same positive results (51, 53), professional methods are still considered effective measures to decrease the load of potentially pathogenic microorganisms and reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia related to poor oral health (13, 15, 56). Especially for elderly individuals with limited mobility living in the community, nursing homes, and ICUs, professional oral health or routine oral hygiene care can not only reduce incidence of aspiration pneumonia and mortality rates due to oral-related diseases but can also result in significant cost savings in light of the economic burden of hospitalization to improve quality of life (50). Nurses should play a key role in referring elderly individuals to general practitioners or dental care providers (37). Attitudes and knowledge related to the screening, prevention and treatment of oral health problems need to be improved through the training and education of professional caregivers, which are important to eliminate the anxiety-related responses of dental fear among the elderly patients (70).
(iii) Improving self-awareness regarding oral care for elderly individuals is important. Oral problems are considered a cumulative process along with aging (57), and the older adults are generally at higher risk for dental infections and associated complex complications. Therefore, it is important for older people to clean their teeth regularly and use dentures once it becomes difficult to maintain their original dental habits (28, 29, 35, 36, 38, 57, 58). Simultaneously, the neatness and integrity of teeth is considered aesthetically attractive and is related to confidence in elderly individuals, which directly affects their mental and social wellbeing (64). Therefore, the importance of oral care should be emphasized more for elderly individuals during the nursing process.
In the process of screening the literature, we noticed some interesting primary studies verifying the relationship between oral health and other chronic diseases, such as diabetes (71), hypertension and metabolic syndrome; however, there was no corresponding systematic review, or the reviews did not focus on older people and therefore did not meet the screening criteria. In such cases, more cross-sectional and longitudinal research and corresponding systematic reviews should be conducted to help in the evaluation, prevention, intervention, and clinical practice of oral-related holistic health.
Implications and limitations
There has been a rapid increase in research and corresponding systematic reviews on the impact of oral health on diverse chronic or non-chronic diseases in elderly individuals, which indicates the promotion of health awareness among elderly people in society. Accordingly, an umbrella review that qualitatively and quantitatively synthesizes studies by mixed methods provides an effective platform to efficiently extract relevant information for clinical practice and future research. Because the literature search was also systematic, according to the PRISMA guidelines, it gives a more comprehensive overview and a higher-level perspective than a narrative review with a narrow topic. Meanwhile, a convincing result of the umbrella review depends on the quality of the included systematic reviews with or without meta-analyses. Eleven of the 35 included reviews were of high quality.
In terms of the limitations, a more complete map of the final result in this research requires the inclusion of more studies written in languages other than English. Regarding the results of this study, although almost all of the included studies were associated with oral health, only one systematic review with 15 studies focused on depression and mental outcomes, which weakens the integrity of the conclusions. More importantly, it is worth noting that holistic health is a relatively broad concept, which indicates a wider result beyond the 7 exact outcomes in the present study. As a result, we are aware that the whole picture of the relationship between oral health and holistic health still has not been displayed through our analysis of the included papers, and that other symptoms or diseases remain to be further researched.
Conclusion
This umbrella review provided a macro perspective to determine the multiple outcomes of holistic health associated with oral health and summarized intervention measures to improve public oral hygiene. On the basis of the consistent findings, clear evidence is available to show the multidimensional results of holistic health. Evidence indicates that oral health can be mainly divided into two issues: (i) poor oral hygiene, where the multiple pathogenic microorganisms colonizing the oral microbiome are significantly associated with respiratory disease, dental caries and periodontitis, and (ii) tooth loss and chewing problems, with which elderly individuals have a higher risk of malnutrition and frailty. The combination of the two issues can also result in poor mental health, such as cognitive impairment and depression, in older people. Correspondingly, to acquire a higher quality of life, elderly people are encouraged to clean their teeth regularly, to have dentures fitted and to receive timely oral care.
Among the included reviews, the majority provided a precise point of view to illustrate the results, while a few papers, especially those regarding mental and social outcomes, were more conservative in their discussions and argued that more research is needed, although evidence has shown significant correlations. In addition, it is necessary to emphasize that due to the lack of relevant systematic reviews, some other popular chronic oral-related diseases were not included in the present umbrella review. Although there are still some limitations and other different oral-related diseases remain to be studied, this umbrella review is expected to provide a global and effective reference for clinical practice in public health.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
FL and XH led the current study. FL and SS initiated the study design and drafted the manuscript. FL, SS, and XH searched databases and screened the articles and extracted the data. XY and SH conducted the quality of the studies. XH, JH, and GW reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Science & Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2020JDKP0016).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge AJE for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1021104/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Word Health Organization. Aging and Health 2021. (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed 3 March 2022).
2. Meurman JH, McKenna G, Murtomaa H, Nakao M, Ogawa H, Walls A, et al. Managing our older population: the challenges ahead. J Dent Res. (2018) 97:1077–8. doi: 10.1177/0022034518784916
3. Niebroj LT. Defining health/illness: societal and/or clinical medicine? J Physiol Pharmacol. (2006) 57:251–62.
4. Rong C, Shen SH, Xiao LW, Huang Q, Lu HT, Wang HX, et al. A comparative study on the health status and behavioral lifestyle of centenarians and non-centenarians in Zhejiang Province, China-a cross-sectional study. Front Public Health. (2019) 7:344. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2019.00344
5. Kassebaum NJ, Smith AGC, Bernabé E, Fleming TD, Reynolds AE, Vos T, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence, incidence, and disability-adjusted life years for oral conditions for 195 countries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. J Dent Res. (2017) 96:380–7. doi: 10.1177/0022034517693566
6. Afshar S, Roderick PJ, Kowal P, Dimitrov BD, Hill AG. Multimorbidity and the inequalities of global ageing: a cross-sectional study of 28 countries using the World Health Surveys. BMC Public Health. (2015) 15:776. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-2008-7
7. Watt RG, Daly B, Allison P, Macpherson LMD, Venturelli R, Listl S, et al. Ending the neglect of global oral health: time for radical action. Lancet. (2019) 394:261–72. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31133-X
8. Thomson WM. Epidemiology of oral health conditions in older people. Gerodontology. (2014) 31:9–16. doi: 10.1111/ger.12085
9. Lockhart PB, Bolger AF, Papapanou PN, Osinbowale O, Trevisan M, Levison ME, et al. Periodontal disease and atherosclerotic vascular disease: does the evidence support an independent association? A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2012) 125:2520–44. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31825719f3
10. Petersen PE, Yamamoto T. Improving the oral health of older people: the approach of the WHO Global Oral Health Programme. Commun Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2005) 33:81–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2004.00219.x
11. Tanaka T, Takahashi K, Hirano H, Kikutani T, Watanabe Y, Ohara Y, et al. Oral frailty as a risk factor for physical frailty and mortality in community-dwelling elderly. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2018) 73:1661–7. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx225
12. Nangle MR, Manchery N. Can chronic oral inflammation and masticatory dysfunction contribute to cognitive impairment? Curr Opin Psychiatry. (2020) 33:156–62. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000581
13. Khadka S, Khan S, King A, Goldberg LR, Crocombe L, Bettiol S. Poor oral hygiene, oral microorganisms and aspiration pneumonia risk in older people in residential aged care: a systematic review. Age Ageing. (2021) 50:81–7. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afaa102
14. Ioannidou E. The Sex and Gender Intersection in Chronic Periodontitis. Front Public Health. (2017) 5:189. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00189
15. Scannapieco FA, Bush RB, Paju S. Associations between periodontal disease and risk for nosocomial bacterial pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol. (2003) 8:54–69. doi: 10.1902/annals.2003.8.1.54
16. Takahashi Y, Watanabe N, Kamio N, Kobayashi R, Iinuma T, Imai K. Aspiration of periodontopathic bacteria due to poor oral hygiene potentially contributes to the aggravation of COVID-19. J Oral Sci. (2020) 63:1–3. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.20-0388
17. Naidu RS, Nunn JH, Pahel B, Niederman R. Editorial: promoting oral health in early childhood: the role of the family, community and health system in developing strategies for prevention and management of ECC. Front Public Health. (2021) 9:716695. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.716695
18. Wu B, Liang J, Luo H, Furter R. Racial and ethnic variations in preventive dental care utilization among middle-aged and older Americans, 1999-2008. Front Public Health. (2013) 1:65. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2013.00065
19. Zenthöfer A, Navratil SD, Rammelsberg P, Cabrera T, Gorenc L, Urbanowitsch N, et al. Oral health and apraxia among institutionalized elderly people–a pilot study. Acta Odontol Scand. (2015) 73:150–5. doi: 10.3109/00016357.2014.961956
20. Saarela RK, Soini H, Hiltunen K, Muurinen S, Suominen M, Pitkälä K. Dentition status, malnutrition and mortality among older service housing residents. J Nutr Health Aging. (2014) 18:34–8. doi: 10.1007/s12603-013-0358-3
21. Takeuchi K, Izumi M, Furuta M, Takeshita T, Shibata Y, Kageyama S, et al. Posterior teeth occlusion associated with cognitive function in nursing home older residents: a cross-sectional observational study. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0141737. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141737
22. Klotz AL, Hassel AJ, Schröder J, Rammelsberg P, Zenthöfer A. Oral health-related quality of life and prosthetic status of nursing home residents with or without dementia. Clin Interv Aging. (2017) 12:659–65. doi: 10.2147/cia.S125128
23. Porter J, Ntouva A, Read A, Murdoch M, Ola D, Tsakos G. The impact of oral health on the quality of life of nursing home residents. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2015) 13:102. doi: 10.1186/s12955-015-0300-y
24. Brennan LJ, Strauss J. Cognitive impairment in older adults and oral health considerations: treatment and management. Dent Clin North Am. (2014) 58:815–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2014.07.001
25. Anttila SS, Knuuttila ML, Sakki TK. Relationship of depressive symptoms to edentulousness, dental health, and dental health behavior. Acta Odontol Scand. (2001) 59:406–12. doi: 10.1080/000163501317153275
26. Okoro CA, Strine TW, Eke PI, Dhingra SS, Balluz LS. The association between depression and anxiety and use of oral health services and tooth loss. Commun Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2012) 40:134–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2011.00637.x
27. Listl S, Galloway J, Mossey PA, Marcenes W. Global economic impact of dental diseases. J Dent Res. (2015) 94:1355–61. doi: 10.1177/0022034515602879
28. Hussein S, Kantawalla RF, Dickie S, Suarez-Durall P, Enciso R, Mulligan R. Association of oral health and mini nutritional assessment in older adults: a systematic review with meta-analyses. J Prosthodont Res. (2021) 66:208–20. doi: 10.2186/jpr.JPR_D_20_00207
29. Slashcheva LD, Karjalahti E, Hassett LC, Smith B, Chamberlain AM, A. systematic review and gap analysis of frailty and oral health characteristics in older adults: a call for clinical translation. Gerodontology. (2021) 38:338–50. doi: 10.1111/ger.12577
30. Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey CM, Holly C, Khalil H, Tungpunkom P. Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. Int J Evid Based Healthc. (2015) 13:132–40. doi: 10.1097/xeb.0000000000000055
31. Teixeira SMA, Coelho JCF, Sequeira C, Lluch ICMT, Ferré-Grau C. The effectiveness of positive mental health programs in adults: a systematic review. Health Soc Care Commun. (2019) 27:1126–34. doi: 10.1111/hsc.12776
32. Austin TM, Richter RR, Sebelski CA. Introduction to the GRADE approach for guideline development: considerations for physical therapist practice. Phys Ther. (2014) 94:1652–9. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20130627
33. Gielen E, Beckwée D, Delaere A, De Breucker S, Vandewoude M, Bautmans I. Nutritional interventions to improve muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical performance in older people: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Nutr Rev. (2021) 79:121–47. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuaa011
34. Algra Y, Haverkort E, Kok W, Etten-Jamaludin FV, Schoot LV, Hollaar V, et al. The association between malnutrition and oral health in older people: a systematic review. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3584. doi: 10.3390/nu13103584
35. Tada A, Miura H. Systematic review of the association of mastication with food and nutrient intake in the independent elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2014) 59:497–505. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2014.08.005
36. Toniazzo MP, Amorim PS, Muniz F, Weidlich P. Relationship of nutritional status and oral health in elderly: systematic review with meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. (2018) 37:824–30.
37. Van Lancker A, Verhaeghe S, Van Hecke A, Vanderwee K, Goossens J, Beeckman D. The association between malnutrition and oral health status in elderly in long-term care facilities: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. (2012) 49:1568–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2012.04.001
38. Zelig R, Goldstein S, Touger-Decker R, Firestone E, Golden A, Johnson Z, et al. Tooth loss and nutritional status in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JDR Clin Trans Res. (2022) 7:4–15. doi: 10.1177/2380084420981016
39. Affoo RH, Foley N, Garrick R, Siqueira WL, Martin RE. Meta-analysis of salivary flow rates in young and older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2015) 63:2142–51. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13652
40. Pina GMS, Mota Carvalho R, Silva BSF, Almeida FT. Prevalence of hyposalivation in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gerodontology. (2020) 37:317–31. doi: 10.1111/ger.12497
41. Ruiz-Roca JA, Fuentes DM, Gómez García FJ, Martínez-Beneyto Y. Oral status of older people in medium to long-stay health and social care setting: a systematic review. BMC Geriatr. (2021) 21:363. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02302-x
42. Chan AKY, Tamrakar M, Jiang CM, Lo ECM, Leung KCM, Chu CH. A systematic review on caries status of older adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:1–15. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182010662
43. López R, Smith PC, Göstemeyer G, Schwendicke F. Ageing, dental caries and periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. (2017) 44(Suppl 18):S145–52. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12683
44. van de Rijt LJM, Stoop CC, Weijenberg RAF, de Vries R, Feast AR, Sampson EL, et al. The influence of oral health factors on the quality of life in older people: a systematic review. Gerontologist. (2020) 60:e378–94. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnz105
45. Wong FMF, Ng YTY, Leung WK. Oral health and its associated factors among older institutionalized residents-a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:1–29. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16214132
46. Azami-Aghdash S, Pournaghi-Azar F, Moosavi A, Mohseni M, Derakhshani N, Kalajahi RA. Oral health and related quality of life in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Public Health. (2021) 50:689–700. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v50i4.5993
47. Baniasadi K, Armoon B, Higgs P, Bayat AH, Mohammadi Gharehghani MA, Hemmat M, et al. The association of oral health status and socio-economic determinants with oral health-related quality of life among the elderly: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dent Hyg. (2021) 19:153–65. doi: 10.1111/idh.12489
48. de Medeiros AKB, Campos M, da Silva Costa RSG, de Melo LA, Barbosa GAS, Carreiro A. Improvement in quality of life of elderly edentulous patients with new complete dentures: a systematic review. Int J Prosthodont. (2019) 32:272–7. doi: 10.11607/ijp.6075
49. Ming Y, Hsu SW, Yen YY, Lan SJ. Association of oral health-related quality of life and Alzheimer disease: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. (2020) 124:168–75. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.08.015
50. Azarpazhooh A, Leake JL. Systematic review of the association between respiratory diseases and oral health. J Periodontol. (2006) 77:1465–82. doi: 10.1902/jop.2006.060010
51. Liu C, Cao Y, Lin J, Ng L, Needleman I, Walsh T, et al. Oral care measures for preventing nursing home-acquired pneumonia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2018) 9:CD012416. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012416.pub2
52. Loeb MB, Becker M, Eady A, Walker-Dilks C. Interventions to prevent aspiration pneumonia in older adults: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2003) 51:1018–22. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.51318.x
53. Sjögren P, Wårdh I, Zimmerman M, Almståhl A, Wikström M. Oral care and mortality in older adults with pneumonia in hospitals or nursing homes: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2016) 64:2109–15. doi: 10.1111/jgs.14260
54. Sjögren P, Nilsson E, Forsell M, Johansson O, Hoogstraate J, A. systematic review of the preventive effect of oral hygiene on pneumonia and respiratory tract infection in elderly people in hospitals and nursing homes: effect estimates and methodological quality of randomized controlled trials. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2008) 56:2124–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.01926.x
55. van der Maarel-Wierink CD, Vanobbergen JN, Bronkhorst EM, Schols JM, de Baat C. Risk factors for aspiration pneumonia in frail older people: a systematic literature review. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2011) 12:344–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2010.12.099
56. van der Maarel-Wierink CD, Vanobbergen JN, Bronkhorst EM, Schols JM, de Baat C. Oral health care and aspiration pneumonia in frail older people: a systematic literature review. Gerodontology. (2013) 30:3–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-2358.2012.00637.x
57. Tôrres LH, Tellez M, Hilgert JB, Hugo FN, de Sousa MD, Ismail AI. Frailty, frailty components, and oral health: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2015) 63:2555–62. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13826
58. Hakeem FF, Bernabé E, Sabbah W. Association between oral health and frailty: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. Gerodontology. (2019) 36:205–15. doi: 10.1111/ger.12406
59. Nangle MR, Riches J, Grainger SA, Manchery N, Sachdev PS, Henry JD. Oral health and cognitive function in older adults: a systematic review. Gerontology. (2019) 65:659–72. doi: 10.1097/yco.0000000000000581
60. Lauritano D, Moreo G, Della Vella F, Di Stasio D, Carinci F, Lucchese A, et al. Oral health status and need for oral care in an aging population: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:1–23. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16224558
61. Delwel S, Binnekade TT, Perez R, Hertogh C, Scherder EJA, Lobbezoo F. Oral hygiene and oral health in older people with dementia: a comprehensive review with focus on oral soft tissues. Clin Oral Investig. (2018) 22:93–108. doi: 10.1007/s00784-017-2264-2
62. Delwel S, Binnekade TT, Perez RS, Hertogh CM, Scherder EJ, Lobbezoo F. Oral health and orofacial pain in older people with dementia: a systematic review with focus on dental hard tissues. Clin Oral Investig. (2017) 21:17–32. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1934-9
63. Wu B, Fillenbaum GG, Plassman BL, Guo L. Association between oral health and cognitive status: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2016) 64:739–51. doi: 10.1111/jgs.14036
64. Cademartori MG, Gastal MT, Nascimento GG, Demarco FF, Corrêa MB. Is depression associated with oral health outcomes in adults and elders? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. (2018) 22:2685–702. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2611-y
65. Duangthip D, Chu CH. Challenges in oral hygiene and oral health policy. Front Oral Health. (2020) 1:575428. doi: 10.3389/froh.2020.575428
66. Raphael C. Oral health and aging. Am J Public Health. (2017) 107:S44–s5. doi: 10.2105/ajph.2017.303835
67. The Lancet. Oral health at a tipping point. Lancet. (2019) 394:188. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31639-3
68. Peres MA, Macpherson LMD, Weyant RJ, Daly B, Venturelli R, Mathur MR, et al. Oral diseases: a global public health challenge. Lancet. (2019) 394:249–60. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31146-8
69. Duangthip D, Crystal YO, Chu CH. Editorial: oral health and policy for patients with special health care needs. Front Oral Health. (2021) 2:802255. doi: 10.3389/froh.2021.802255
70. Crego A, Carrillo-Díaz M, Armfield JM, Romero M. From public mental health to community oral health: the impact of dental anxiety and fear on dental status. Front Public Health. (2014) 2:16. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2014.00016
Keywords: oral health, holistic health, elderly individuals, multiple outcomes, umbrella review
Citation: Liu F, Song S, Ye X, Huang S, He J, Wang G and Hu X (2022) Oral health-related multiple outcomes of holistic health in elderly individuals: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Front. Public Health 10:1021104. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1021104
Received: 17 August 2022; Accepted: 29 September 2022;
Published: 27 October 2022.
Edited by:
Roy Rillera Marzo, Management and Science University, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Marija Jevtic, University of Novi Sad, SerbiaBing Yang, Stomatological Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, China
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Song, Ye, Huang, He, Wang and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiuying Hu, aHV4aXV5aW5nQHNjdS5lZHUuY24=
 Fan Liu1,2
Fan Liu1,2 Guan Wang
Guan Wang Xiuying Hu
Xiuying Hu