
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Psychiatry , 28 July 2022
Sec. Schizophrenia
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.922272
This article is part of the Research Topic Prognostic Imaging Biomarkers in Psychotic Disorders View all 7 articles
Background: Schizophrenia (SZ) is associated with the highest disability rate among serious mental disorders. Excited symptoms are the core symptoms of SZ, which appear in the early stage, followed by other stages of the disease subsequently. These symptoms are destructive and more prone to violent attacks, posing a serious economic burden to the society. Abnormal spontaneous activity in the orbitofrontal cortex had been reported to be associated with excited symptoms in patients with SZ. However, whether the abnormality appears in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ has still remained elusive.
Methods: A total of 56 first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ and 27 healthy controls underwent resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) and positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS). First, differences in fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (fALFF) between first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ and healthy controls were examined to identify cerebral regions exhibiting abnormal local spontaneous activity. Based on the fALFF results, the resting-state functional connectivity analysis was performed to determine changes in cerebral regions exhibiting abnormal local spontaneous activity. Finally, the correlation between abnormal functional connectivity and exciting symptoms was analyzed.
Results: Compared with the healthy controls, first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ showed a significant decrease in intrinsic activity in the bilateral precentral gyrus, bilateral postcentral gyrus, and the left orbitofrontal cortex. In addition, first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ had significantly reduced functional connectivity values between the left orbitofrontal cortex and several cerebral regions, which were mainly distributed in the bilateral postcentral gyrus, the right middle frontal gyrus, bilateral paracentral lobules, the left precentral gyrus, and the right median cingulate. Further analyses showed that the functional connectivity between the left orbitofrontal cortex and the left postcentral gyrus, as well as bilateral paracentral lobules, was negatively correlated with excited symptoms in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ.
Conclusion: Our results indicated the important role of the left orbitofrontal cortex in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ and suggested that the abnormal spontaneous activity of the orbitofrontal cortex may be valuable to predict the occurrence of excited symptoms. These results may provide a new direction to explore the excited symptoms of SZ.
Schizophrenia (SZ) is one of the most serious and disabling mental diseases (1). However, due to the complexity of brain structure and functional activities, the etiology of SZ has not been fully clarified yet. Researchers have put forward a series of hypotheses, demonstrating that abnormal cerebral blood flow and neurobiochemical activities may lead to clinical symptoms (2–6). A large number of studies have pointed out that compared with healthy individuals, SZ patients are at a significantly increased risk of excited symptoms (including excitement, hostility, uncooperativeness, and impulsivity) by 2.1–4.6 times (7, 8). The sudden events, such as destroyed items and violent assaults, are mainly associated with excited symptoms in patients with SZ, which have posed a great burden to society (9–13). Patients with excited symptoms may experience substance abuse, which may prolong the treatment cycle and deteriorate clinical treatment results (13–15). Nevertheless, few clinical studies have yet concentrated on excited symptoms in patients with SZ.
Hostility is the expression of anger or resentment toward others in terms of words or actions (13). Impulsivity is an obstacle to the regulation and control of internal impulse response when integrating internal and external stimuli (16–19), which may lead to reckless emotional catharsis and violence (20, 21). Patients with SZ lack the ability to timely deal with negative emotions. That is to say, they are highly sensitive to negative emotions and prone to negative urgency (10, 21). In SZ patients with delusions and hallucinations, sudden impulsive behavior in the face of stress or other extreme events is caused by uncontrolled internal regulation of emotional responses, as well as imbalance in external motor inhibition (16, 22). Such impulsive behaviors, which not accompany by poor prognostic outcomes, but also increase the burden of disease, are highly prevalent in patients with first-episode and chronic SZ (22–24). Hostility and impulsivity are the most problematic symptoms in patients with SZ (13). The study of impulsivity and hostility in patients with excited symptoms may provide new ideas for understanding the neuropathological mechanisms of SZ (25).
Hostility and impulsivity are closely associated with dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex, especially the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) (26). Studies have shown that impulsive, hostile, and antisocial behaviors are perpetrated by healthy individuals after OFC damage (27). OFC serves as a central region of emotional integration and inhibitory control (28). Alterations in this cerebral region have been demonstrated to be strongly associated with impulsive behaviors in patients with psychiatric disorders (18, 26). Structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies suggested that patients with SZ who were more impulsive showed larger gray and white matter volumes, as well as a smaller cortical thickness in the OFC area compared with those with no history of impulsivity (10, 29). Functional MRI studies revealed that patients with impulsivity showed anomalous functional connections between the OFC and anterior cingulate gyrus (19, 30). In addition, several MRI studies demonstrated that the reduced gray matter volume in OFC is negatively correlated with the severity of emotional instability, and an abnormal OFC function has also been shown to be associated with the expressions of negative emotions, such as anxiety and fear in patients with SZ (4, 6, 31, 32). OFC regulates negative emotions by receiving and transmitting relevant emotional information. After functional impairment, it shows emotional vulnerability and irritability (3, 5, 32, 33). Given that the OFC is a central element in the emotional and behavioral response network and plays a central role in both emotional regulation and motor inhibition (28), it is hypothesized that the dysfunction of the OFC is the basis of the manifestation of excited symptoms in patients with SZ.
OFC neurons are common targets for classic and glutamatergic antipsychotic drugs (34). After drug therapy for patients with chronic SZ, the functional activity of OFC increases significantly, and its association with excited symptoms may be affected (35). Previous studies could not well exclude the above-mentioned confounding factors (36). Therefore, after removing the effects of the course of the disease, the long-term use of antipsychotics, and progressive cerebral atrophy on OFC function, exploring the damage to OFC function in patients with first-episode SZ may assist clinicians in the early identification or remission of excited symptoms.
Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) is emerging as a valuable biomarker for measuring connectivity of the brain in patients with neural disorders. It can non-invasively measure internal neural activity with a great stability. The amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) is the most commonly used index to measure the intensity of regional spontaneous cerebral activities (37, 38). However, when capturing the relative amplitude of blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signal fluctuation in gray matter, a higher frequency range (> 0.08 Hz) of ALFF is sensitive to the interference of physiological factors, such as heartbeat, respiration, etc. (31, 37, 39). The fractional ALFF (fALFF) method provides a relative estimate of the BOLD signal intensity in the relevant frequency band (0.01–0.08 Hz) (37, 40). After significantly lessening non-specific signal components, the fALFF improved the sensitivity and specificity in detecting spontaneous cerebral activities (37, 41). As another frequently used index, resting-state functional connectivity (rs-FC) analysis describes the functional correlation among spatially unconnected cerebral regions (42, 43). Preliminary studies of SZ have reported abnormal fALFF in complex cerebral regions. The fALFF-based resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) analytical strategy has been scarcely utilized to examine the functional interactions of cerebral regions that showed an altered fALFF in drug-naïve patients with SZ.
The present cross-sectional study has mainly concentrated on OFC to explore abnormalities in the spontaneous cerebral activity of first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ. A great number of patients with the first onset of SZ who received few medical treatments, as well as age-, gender-, educational level-matched healthy controls (HCs) were recruited. All subjects underwent fMRI scan and positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS). Firstly, we attempted to determine the abnormal spontaneous cerebral activity in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ, which was measured by fALFF. It was supposed that the neural networks associated with OFC would be vulnerable. Secondly, we considered cerebral regions found in the previous fALFF analysis to compare the functional cerebral activities between first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ and HCs. Finally, to indicate whether the abnormalities found in the fALFF and fALFF-based rsFC analyses would be associated with excited symptoms in patients with SZ, we analyzed the correlation between abnormal indices and scores and sub-scores of excited symptoms.
The Ethics Committee of the Nanjing Brain Hospital (Nanjing, China; Approval No. 2013KY010) approved the study protocol. All participants signed the written informed consent form prior to enrollment.
We used the previously reported data (36, 44). First-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ (n = 63, 44 men) were recruited from Nanjing Brain Hospital. Patients were diagnosed via Structured Clinical Interview for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition (DSM-IV) (SCID-I/P), and met the criteria for SZ. In total, 30 HCs (17 men and 13 women) who were matched in age, educational level, and gender were recruited through advertisements in the local community of Nanjing city. An experienced psychiatrist assessed the current state of mind and personal or family history of any mental disorders. None of the HCs presented a personal or family history of psychiatric disorders.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients who aged 15–45 years old, (2) right-handed patients, and (3) an ability to understand the instructions and contents of the survey. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) a history of head injury, seizures, cerebrovascular disease, neurological diseases (excluding SZ), impaired thyroid function, (2) disability in learning, and (3) meeting DSM-IV criteria for alcohol or substance abuse or dependence in the past year.
Two trained specialists who had no idea of the content of the research assessed the mental state of patients using the PANSS on the day of the fMRI test. The PANSS originally designed by Kay et al. was used to better evaluate the heterogeneity of symptoms in patients with SZ (45–47). Positive factors, such as delusions, hallucinations, and unusual thought content are mainly considered by clinicians for inclusion of patients. Negative factors (e.g., motivation and social withdrawal, blunted affect, as well as motor retardation) were reported as prognostic factors (32). General psychopathology is composed of excited factors (mainly involving impulsive behaviors), disorganized/concrete factors (conceptual disorganization, difficulty in abstract thinking, stereotyped thinking, and poor attention), and depressed factors (anxiety, tension, guilt feelings, and depression) (46). The total score and five-factor scores of PANSS were assessed with SCID-I/P to measure the severity of psychotic symptoms.
MRI was performed within 3 days after confirmation of the diagnosis of SZ. The MRI data were collected using the 3.0-T Siemens Verio scanner (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). Besides, foam pads and soft earplugs were used to reduce head motion and scanning noise. Sagittal three-dimensional T1-weighted images were obtained using cerebral volume sequences with the following parameters: repetition time (TR) = 2,000 ms; echo time (TE) = 2.3 ms; reversal time = 900 ms; flip angle (FA) = 7°; field of view (FOV) = 256 mm × 256 mm; matrix size = 256 × 256; slice thickness = 1 mm, gap = 0.5 mm; sagittal section; and acquisition time = 353 s. The gradient echo single-shot echo-planar imaging sequence was used to collect functional BOLD images in the resting-state. The following parameters were considered: TR/TE = 2,000/30 ms; FOV = 240 mm × 240 mm; matrix size = 64 × 64; FA = 90°; slice thickness = 4 mm; no gap; 30 transverse cross-sections; 171 volumes; acquisition time = 346 s. All subjects were asked to lie quietly with their eyes closed, relax, and move as little as possible, without thinking about anything, especially avoiding fall asleep during data collection.
There were significant differences in the original data, which could not be analyzed directly, and the fMRI data were preprocessed using the MATLAB 2014a software and Data Processing Assistant for rs-fMRI (DPABI) software (48, 49). Due to abnormal anatomical scans or visible artifacts in the images caused by excessive head movement, the functional data were deleted. Discarding each participant’s first ten volumes made the machine signal stable and participants were adapted to scanning noise. The remaining volumes were processed for slice timing correction. Then, the computer automatically rearranged images and assessed movement parameters for each participant. The head motion amplitude of each subject was evaluated by the frame-wise displacement (FD). In the present study, FD was set to 0.5 (mean FD ± twice of standard deviation) (50). Due to the large differences in shape and size of different individuals’ brains, it was difficult to directly make a comparison. Registration and standardization were carried out via mapping of different subjects’ brains into a space with the same shape and size so that to make the cerebral anatomical structures of subjects corresponded to each other. The linear trend of covariates was removed and corrected with Friston-24 (51). We regressed out several nuisance covariates, such as the global brain signal, the white matter signal, and the cerebrospinal fluid signal (50). DARTEL was used to standardize different brains and to increase the comparability of cerebral functional data among subjects (52). Finally, 6 mm full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) was used for smoothing to improve the reliability of data.
However, 7 first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ and three HCs were excluded due to excessive head movement when MRI scans were performed.
Voxel-wise fALFF maps were scanned for each participant using the rs-fMRI machine. ALFF reflects the spontaneous activity of the local cerebral region. The time series of each voxel was first transformed into the frequency domain by the fast Fourier transform. The amplitudes were measured using fALFF within the slow-4 (range, 0.027–0.073 Hz) and slow-5 (range, 0.01–0.027 Hz) bands. FALFF was calculated by the ratio of the root mean square of the power spectrum of low-frequency (range, 0.01–0.08 Hz) to the root mean square of the power spectrum of the whole frequency (range, 0–0.25 Hz) (37, 40). The fALFF analysis was carried out to reduce the influences of low-frequency drift and high-frequency physiological noise by dividing the total value of full-band amplitude from 0.01 to 0.25 Hz (53).
The rsFC was calculated with the Fisher’s transformation of the correlation coefficient using seed-to-voxel analysis (50). The rsFC analysis was performed on the abnormal region (the left OFC) with global voxels. Connectivity maps were obtained for the left OFC by correlating its average time series with every voxel in the brain.
Group-level analyses were carried out to examine cerebral regions with detectable fALFF abnormalities in SZ. The two-sample t-test was used to compare fALFF between SZ and HC groups. The fALFF maps were calculated using permutation-based non-parametric inference with 5,000 permutations, with consideration of age, gender, and educational level as covariates of no interest. The statistical threshold was set at voxel level (p < 0.001) or cluster level (p < 0.05), and the correction was conducted for multiple comparisons by the threshold-free cluster enhancement (TFCE) (54). The rsFC between the region of interest (ROI) and global brain voxels was corrected by the TFCE (with 5,000 permutations; voxel level, p < 0.001; cluster level, p < 0.05; with consideration of age, gender, and educational level as covariates of no interest) to avoid multiple comparison corrections. The significant fALFF decreased areas in the patients were used as inclusion masks in the following voxel-wise correction analyses, which were carried out to explore the correction between the fALFF map and the severity of symptoms (five components of PANSS). The statistical threshold was also set at voxel level (p < 0.001 or cluster level (p < 0.05) in the TFCE. Age, gender, educational level, and illness duration were entered into the model as covariates of no interest. Pearson correlation analysis was then used to assess the possible clinical relevance between values of rsFC and the severity of clinical symptoms. PANSS items were converted into five factors. Associations between rsFC and PANSS scores were carried out by Pearson’s correlations, applying Bonferroni correction for the number of correlations (5 subscale scores at p = 0.05/5 subscales = 0.01) (55). When other clinical symptoms are also related to rsFC, it is necessary to controlled significant correlations for the impact of other symptoms. If there was a significant correlation among PANSS excited scores, post hoc analysis was employed to explore the correlation among the 2 excited sub-item scores. Although PANSS excited scale contains four groups of clinical symptoms, we only used two dimensions (hostility and impulsivity) for correlation analysis. Associations between rsFC and PANSS excited subscale score were carried out by Pearson’s correlations, also applying Bonferroni correction for 2 comparisons (2 subscale scores at p = 0.05/2 = 0.025).
Age, gender, educational level, and illness duration were entered into the models as covariates of no interest. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 21.00 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, United States). The two-sample t-test and the Chi-square test were used for comparing differences in continuous variables and categorical variables between the two groups, respectively. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Demographic characteristics of 83 subjects belonging to SZ and HC groups were compared. The detailed demographic characteristics of subjects in the SZ and HC groups are presented in Table 1. There was no significant difference in gender (Chi-square test, χ2 = 0.592, p = 0.441), age (two-sample t-test, t = −1.555, p = 0.08), and educational level (two-sample t-test, t = 1.569, p = 0.651) between the two groups.
In the current study, the fALFF values in several cerebral regions in the SZ group were lower than those in the HC group (TECE corrected, voxel-level, p < 0.001; cluster level, p < 0.05). Decreased fALFF values were found in the frontal and occipital lobes, including bilateral precentral gyrus, bilateral postcentral gyrus, right lingual gyrus, bilateral temporal superior gyrus, and left middle occipital gyrus, right calcarine, and left orbitofrontal cortex (LOFC) (Table 2 and Figure 1). There were no significant differences in fALFF values among the other cerebral regions.
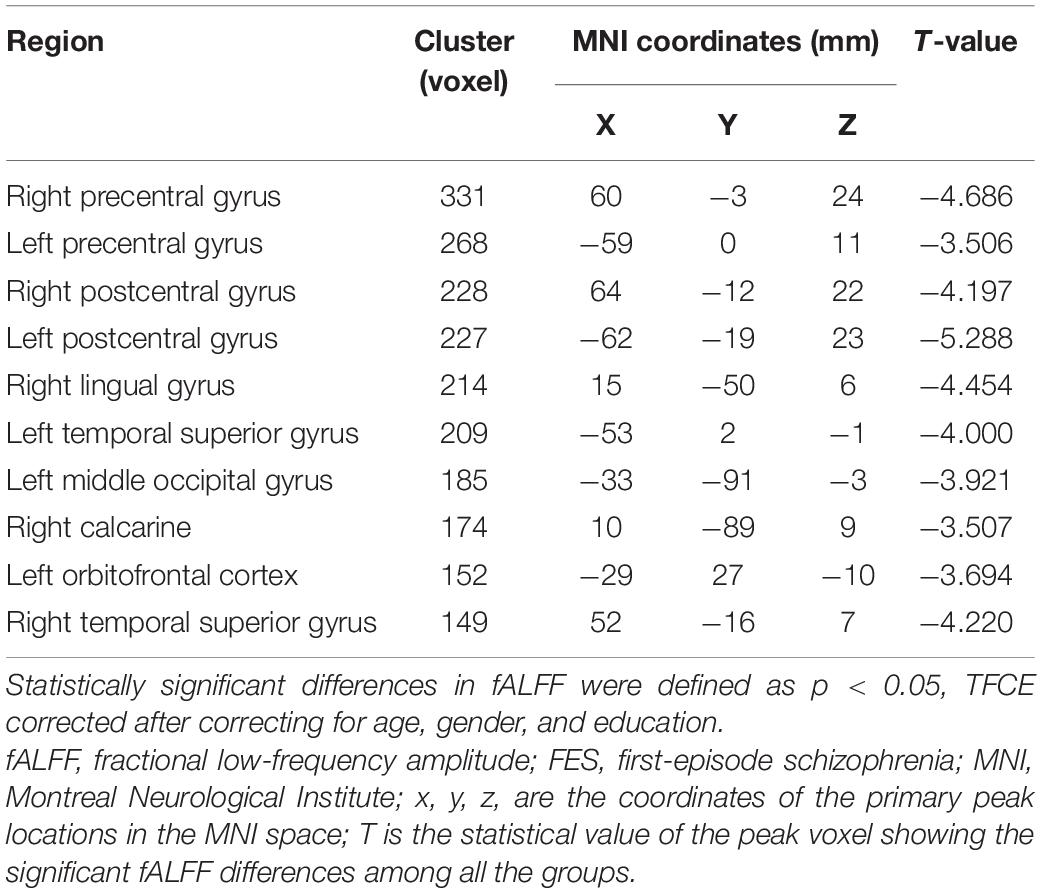
Table 2. Brain regions with decreased fALFF values in patients with FES compared with healthy controls (SCZ < HC).
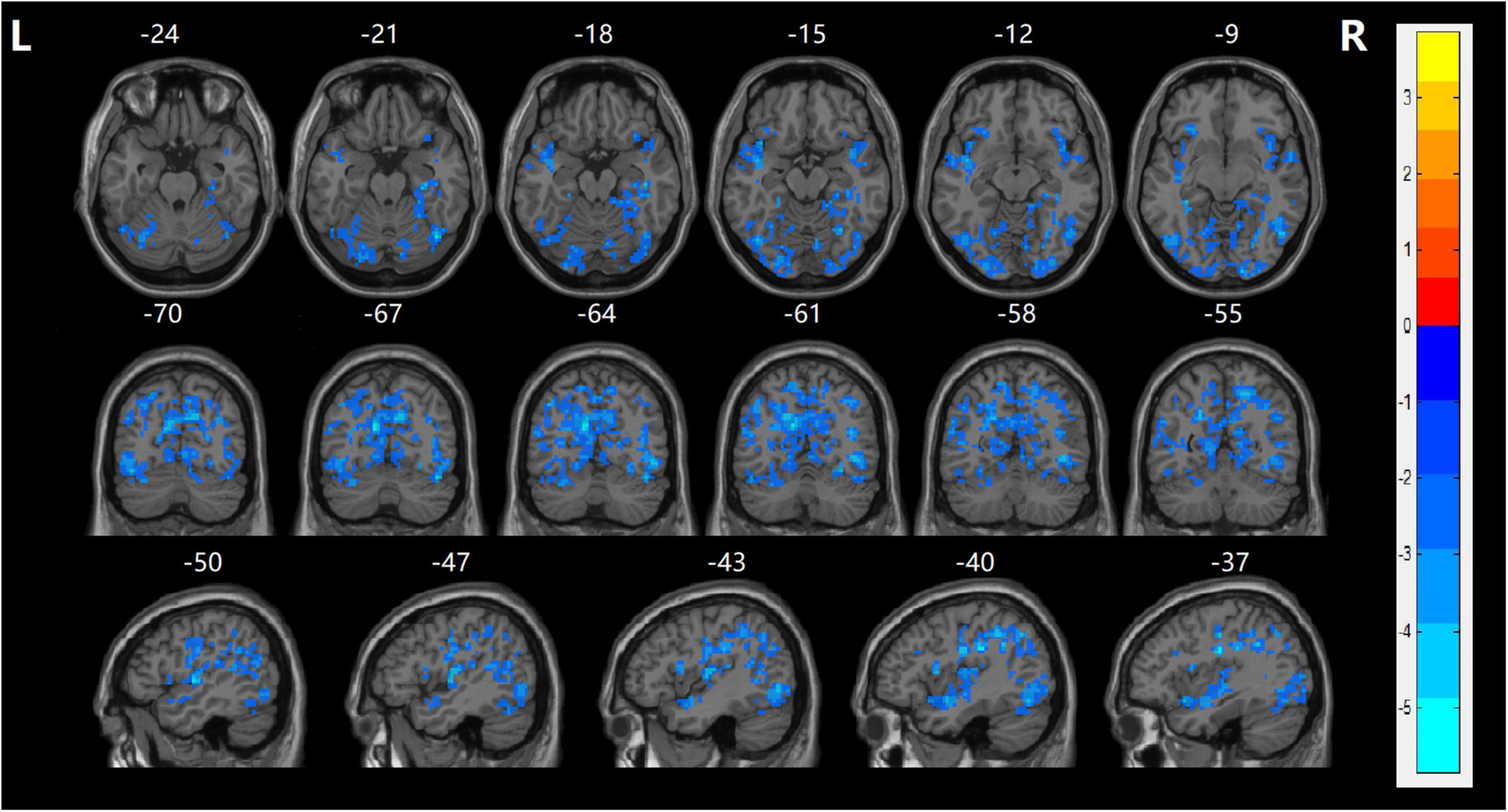
Figure 1. fALFF maps show differences between the naïve patients with FES and HCs (p < 0.05). The patients with FES showed significantly lower values in the bilateral precentral gyrus, bilateral postcentral gyrus, right lingual gyrus, bilateral temporal superior gyrus, left middle occipital gyrus, right calcarine, and left orbitofrontal cortex (LOFC) relative to both the HC group. Statistically significant differences in fALFF were defined as voxel-level, p < 0.001; cluster level, p < 0.05, TFCE corrected after correcting for age, gender, and education. T, statistical value of peak voxel showing fALFF values differences between the two groups. The cool color indicated that it decreased in the naïve patients with FES. Reversely, warm color indicated increased values in the naïve patients with FES.
Functional connectivity between the LOFC and each voxel of the global brain was performed to examine network abnormalities in the SZ group. After making correction for multiple comparisons, patients in the SZ group demonstrated significantly reduced rsFC values between the LOFC and several cerebral regions, which were mainly distributed in the bilateral postcentral gyrus, right middle frontal gyrus, left precentral gyrus, bilateral paracentral lobule, and right median cingulate compared with HC group (TECE corrected, voxel-level, p < 0.001; cluster level, p < 0.05) (Table 3 and Figure 2).
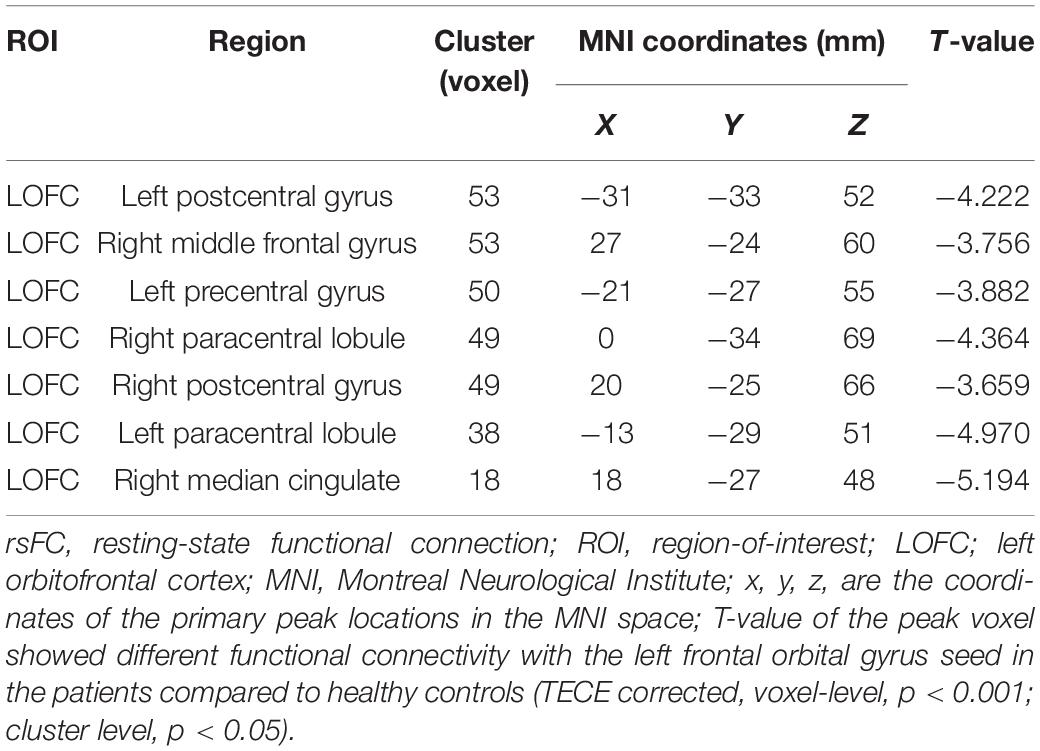
Table 3. Coordinates the peaks of the brain regions with decreased rsFC in naïve schizophrenic patients.
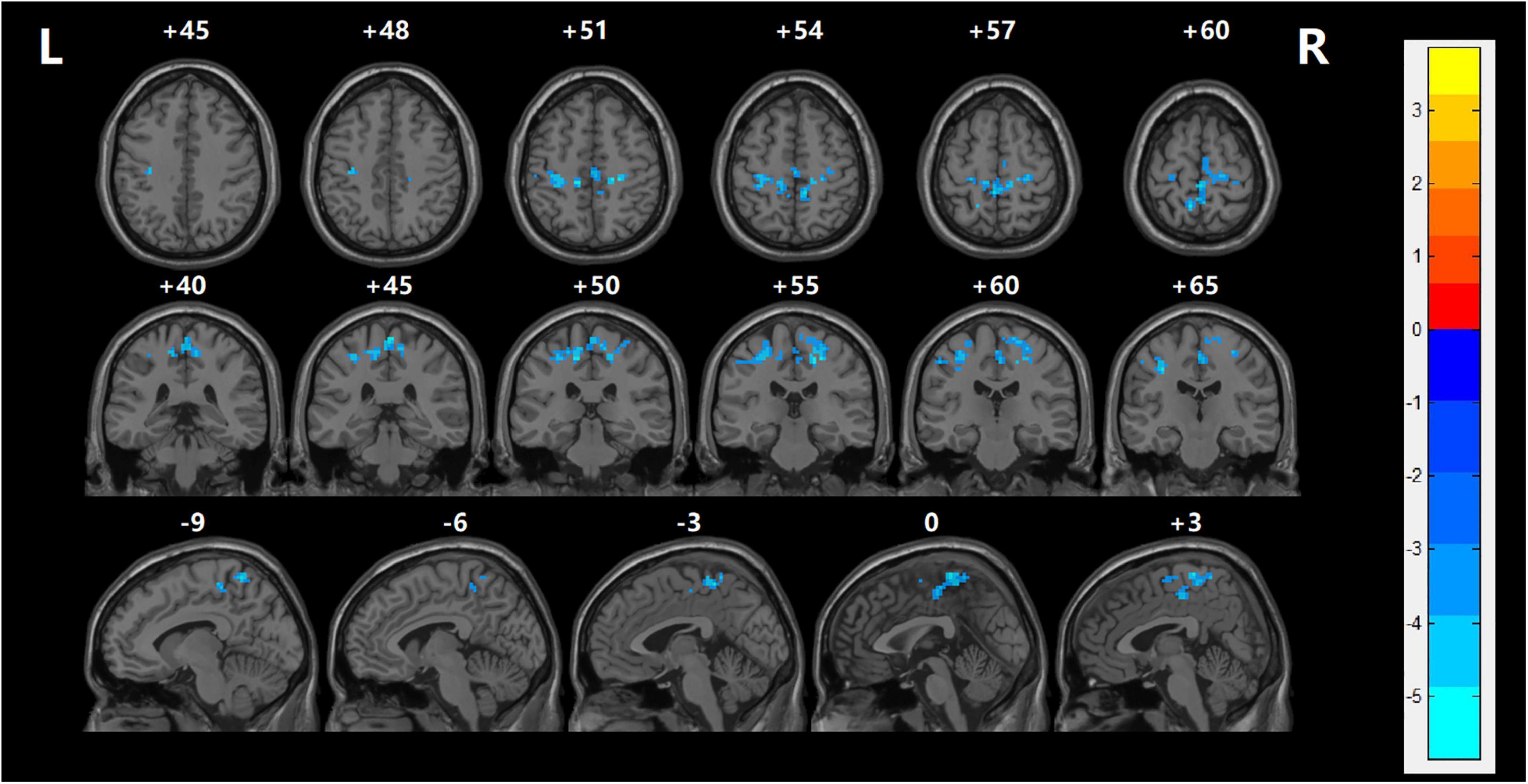
Figure 2. The resting-state functional connection was analyzed between the left orbitofrontal cortex and the global brain. With regards to the HC group, left OFC had lower rsFC values in several regions including the left postcentral gyrus, left precuneus, left superior temporal gyrus, and left precentral gyrus with FES (TECE corrected, voxel-level, p < 0.001; cluster level, p < 0.05). The cool color indicates that rsFC is decreased in the naïve patients with FES. Reversely, warm color indicates rsFC is higher than in the healthy control group.
To detect possible associations of spontaneous cerebral activity with psychiatric symptoms, the PANSS was used for the assessment of symptoms, which included symptoms in 5 dimensions (55). These symptoms were correlated with cerebral activation and behavioral activities in patients in the SZ group. It was attempted to elucidate the relationship between the fALFF values and PANSS scores (five dimensions of symptoms) using age, gender, educational level, and illness duration as covariates. However, no voxel has existed after TFCE correction (voxel-level, p < 0.001; cluster level, p < 0.05).
The relationship between the rsFC values and PANSS scores in patients in the SZ group was assessed (Tables 4, 5). There were several significantly negative correlations between the rsFC values and PANSS excited scores (five dimensions of symptoms) after Bonferroni correction (significant after Bonferroni correction for 5 correlations, all p < 0.05/5). After consideration of age, gender, educational level, and illness duration as covariates, these significantly negative correlations could be summarized as follows (Table 5): (i) the LOFC and the left paracentral lobule (r = −0.396, p = 0.004, Figure 3), (ii) the LOFC and the right paracentral lobule (r = −0.400, p = 0.003, Figure 4), (iii) the LOFC and the left postcentral gyrus (r = −0.417, p = 0.002, Figure 5), (iv) LOFC and the right postcentral gyrus (r = −0.354, p = 0.01). However, PNASS excited scores did not similarly exhibit a significantly negative correlation with the rsFC values between the LOFC and the right postcentral gyrus, when age, gender, educational level, and illness duration were not included as covariates (r = −0.326, p = 0.014, Table 4).
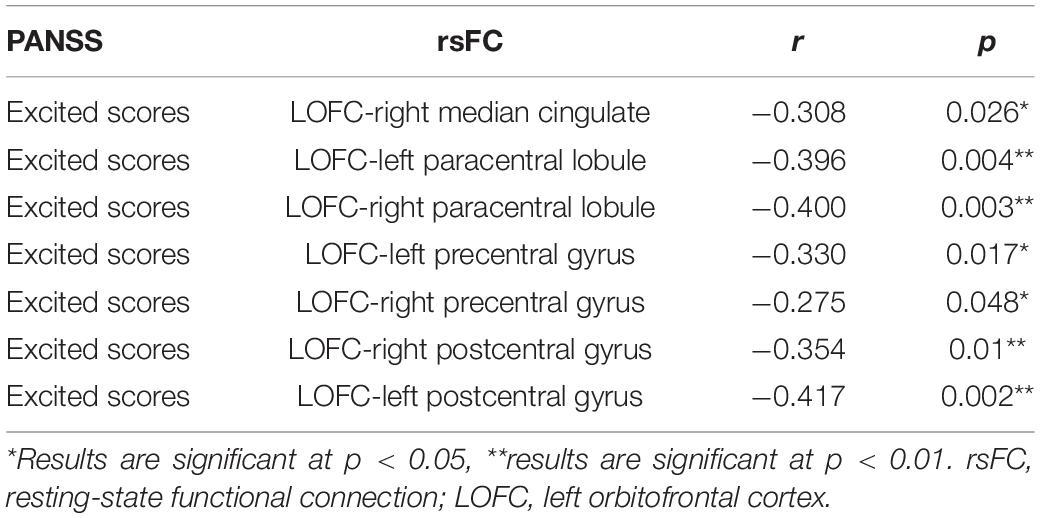
Table 5. Correlations between the rsFC values and PANSS excited scores in patients with FES (taking age, gender, education, and illness duration into covariates).
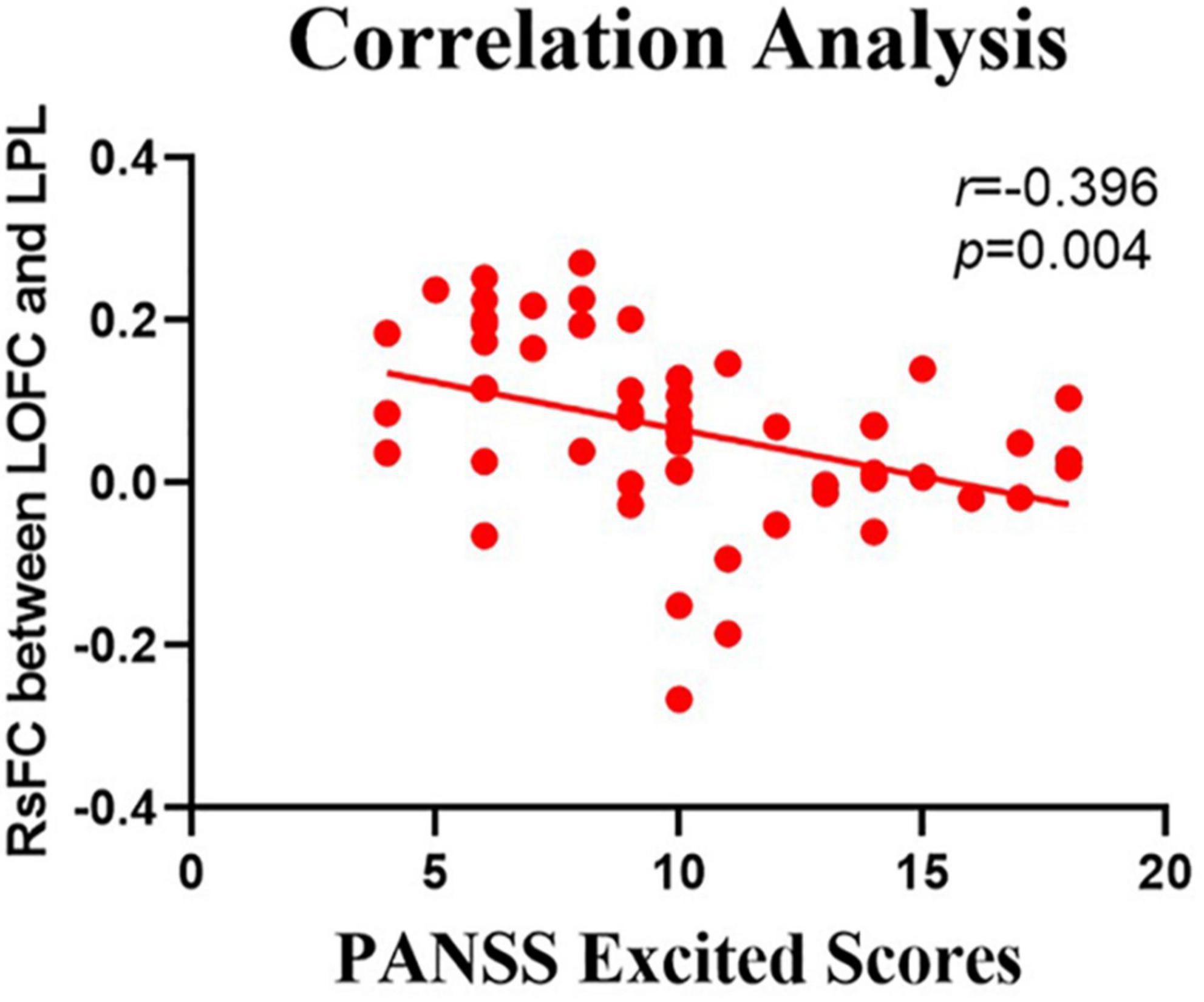
Figure 3. Negative correlation between the resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) values and the severity of excited symptoms in the FES. The X-axis is the score of the excited factors of the PANSS scale, and the Y-axis shows the functional connectivity of the left orbitofrontal cortex (LOFC) and left paracentral lobule (LPL) (after correcting for positive symptoms, age, gender, education, and illness duration).
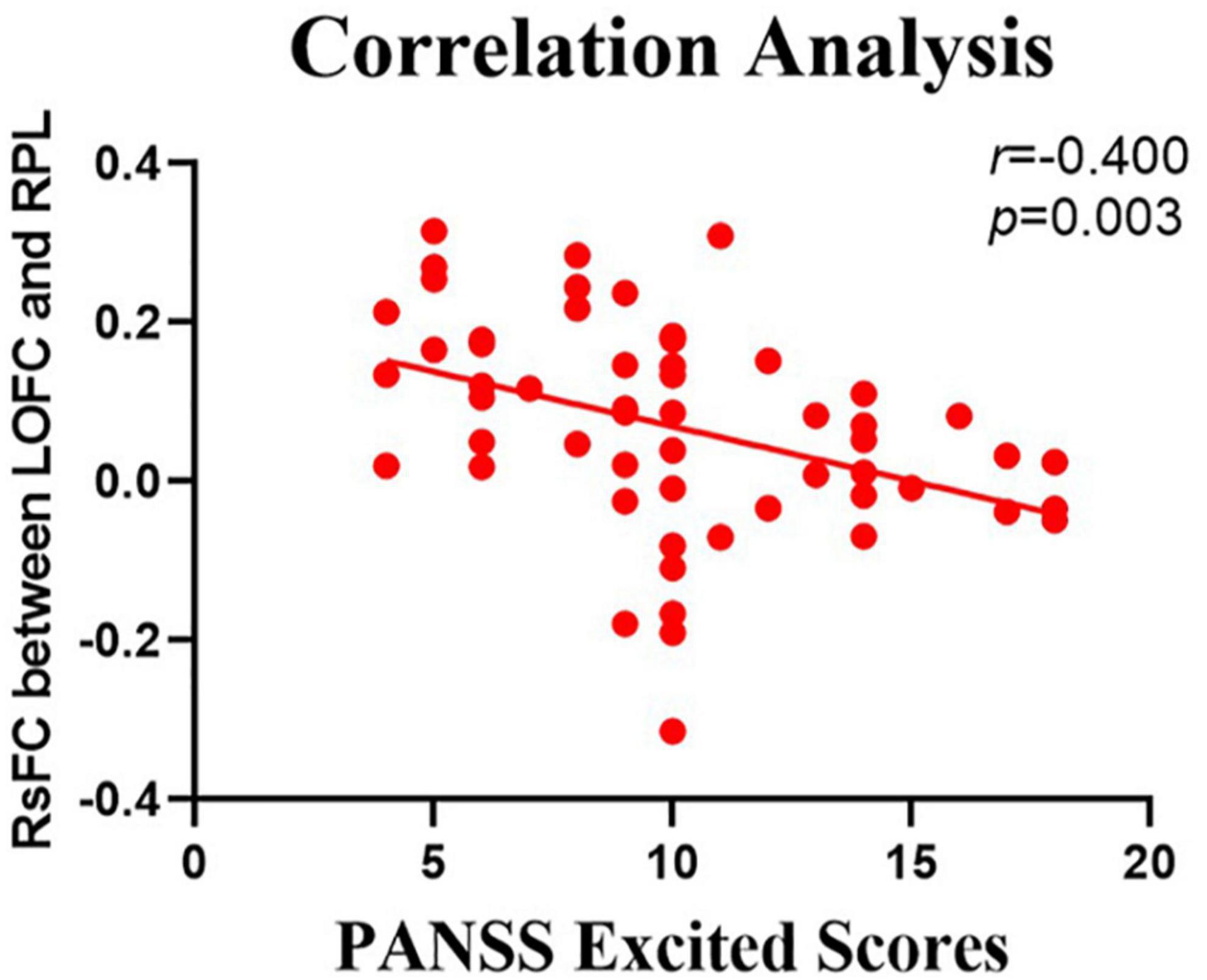
Figure 4. Negative correlation between the resting-state functional connection (rsFC) values and the severity of excited symptoms in the FES. The X-axis is the score of the excited factors of the PANSS scale, and the Y-axis shows the functional connectivity of the left orbitofrontal cortex (LOFC) and right paracentral lobule (RPL) (after correcting for positive symptoms, age, gender, education, and illness duration).
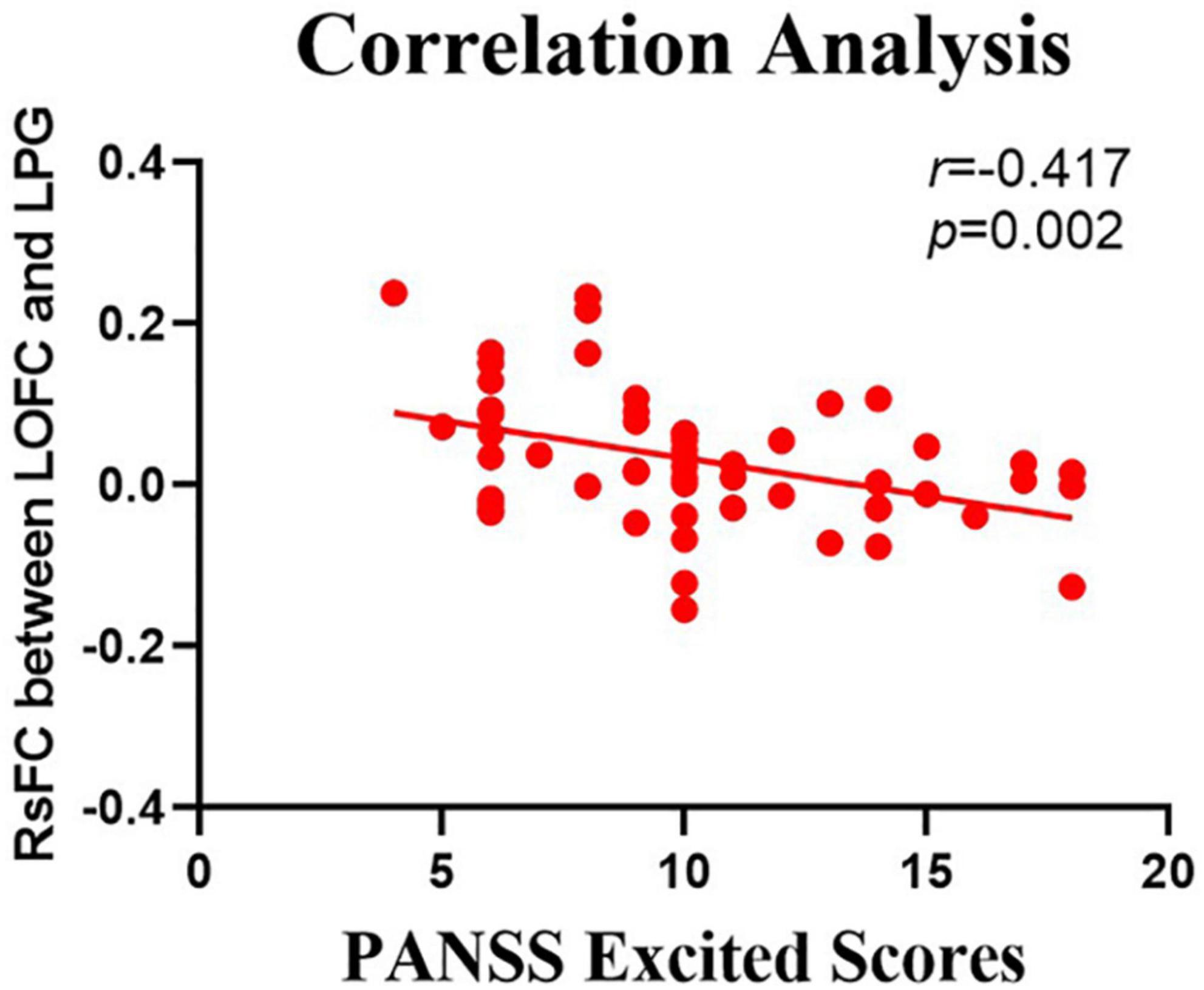
Figure 5. Negative correlation between the resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) values and the severity of exited scores in the FES. The X-axis is the score of the excited factors of the PANSS scale, and the Y-axis shows the functional connectivity of the left orbitofrontal cortex (LOFC) and left postcentral gyrus (after correcting for positive symptoms, age, gender, education, and illness duration).
The impact of symptoms other than excited ones on these correlation results was considered. There was a weak negative correlation (r = −0.282, p = 0.043, Supplementary Table 1) between positive symptoms and rsFC (left OFC—left postcentral gyrus). There was no significant correlation between rsFC and negative, cognitive as well as depressed symptoms (all p > 0.05). In order to control the impact of positive symptoms on correlation analysis, positive symptoms, age, gender, course of the disease, and years of education were taken as covariates, excited symptoms were still negatively correlated with rsFC. These negative correlations could be summarized as follows (Supplementary Table 2): (i) the LOFC and the left paracentral lobule (r = −0.327, p = 0.019), (ii) the LOFC and the right paracentral lobule (r = −0.343, p = 0.014), (iii) the LOFC and the left postcentral gyrus (r = −0.347, p = 0.013).
The relationship between the rsFC values and PANSS excited subscale scores in patients in the SZ group was assessed (Tables 6, 7). There were several significantly negative correlations between the rsFC values and hostility (two dimensions of symptoms) after Bonferroni correction (significant after Bonferroni correction for 2 correlations, all p < 0.05/2). Significantly negative correlations were found between the LOFC and the bilateral paracentral lobule, as well as between the rsFC value of the right median cingulate and hostility symptoms (r = −0.369, p = 0.007, r = −0.328, p = 0.018, r = −0.459, p = 0.001, gender, age, and illness duration were taken as covariates into account, Table 7). Impulsivity symptoms showed negative correlations with the rsFC value of the right paracentral lobule and left postcentral gyrus (r = −0.327, p = 0.018, r = −0.315, p = 0.023, gender, age, and illness duration were taken as covariates into account, Table 7).
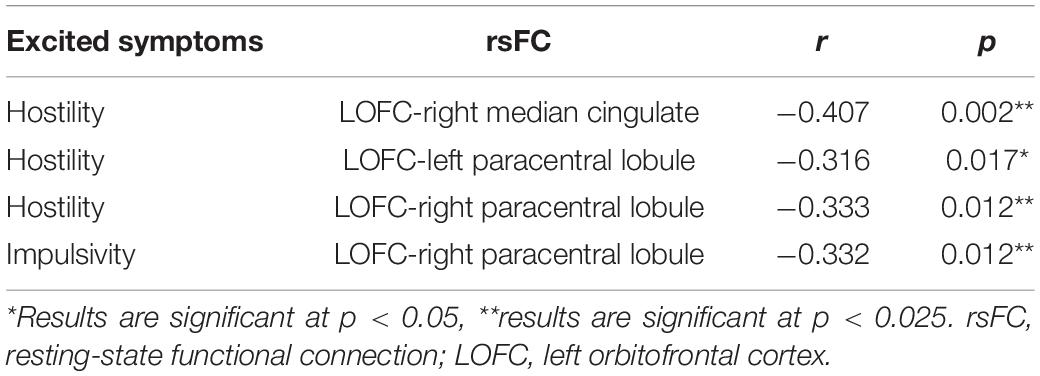
Table 6. Correlations between the rsFC values and PANSS excited subscale scores in patients with FES.
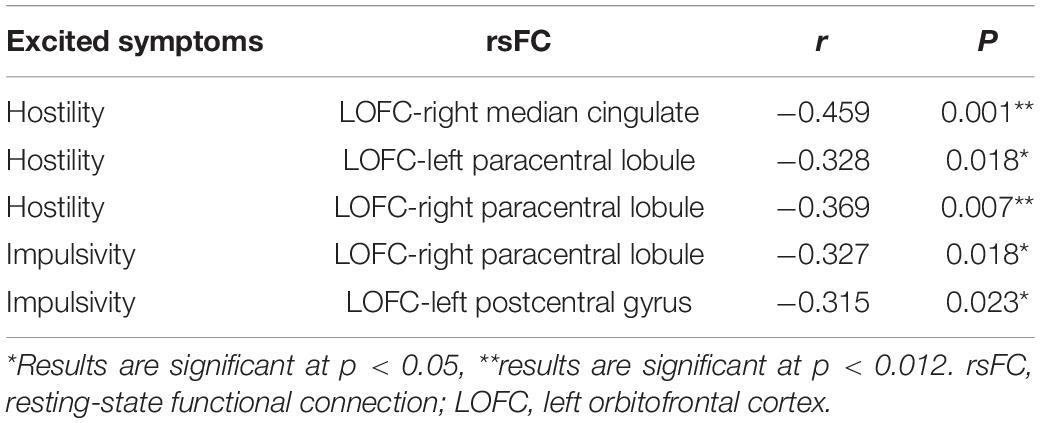
Table 7. Correlations between the rsFC values and PANSS excited subscale scores in patients with FES (after correcting for age, gender, education, and illness duration).
There were several significantly negative correlations between the rsFC values and PANSS excited subscale scores (hostility and impulsivity) after consideration of positive symptoms, age, gender, educational level, and illness duration as covariates. These significantly negative correlations of hostility could be summarized as follows (Supplementary Table 3): (i) the LOFC and the right paracentral lobule (r = −0.332, p = 0.017), (ii) the LOFC and the right postcentral gyrus (r = −0.321, p = 0.022), (iii) the LOFC and the right median cingulate (r = −0.428, p = 0.002), (iv) the LOFC and the left precentral gyrus (r = −0.328, p = 0.019), (v) the LOFC and the right precentral gyrus (r = −0.318, p = 0.023). Impulsivity symptoms showed negative correlations with the rsFC value of the right paracentral lobule and left precentral gyrus (r = −0.335, p = 0.016, r = −0.337, p = 0.015, p < 0.025, Supplementary Table 3). However, hostility did not similarly exhibit a significantly negative correlation with the rsFC values, when positive symptoms, age, gender, educational level, and illness duration were not included as covariate. These not significant negative correlations were summarized as follows (Table 6): (i) the LOFC and the right postcentral gyrus, (ii) the LOFC and the right precentral gyrus, (iii) the LOFC and the left precentral gyrus. Impulsivity symptoms showed negative correlations with the rsFC value of the right paracentral lobule and left precentral gyrus (r = −0.335, p = 0.016, r = −0.337, p = 0.015, p < 0.025, Table 7).
We, in the present study, utilized rs-fMRI data, including fALFF and fALFF-based rsFC values to measure the resting-state of spontaneous cerebral functions in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ who did not experience antipsychotic medication. The results initially confirmed that compared with HCs, first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ exhibited decreased fALFF values in the LOFC, bilateral precentral gyrus, and bilateral postcentral gyrus. In the second step, the LOFC was taken as a seed into account to explore rsFC values in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ. We found decreased rsFC values between the LOFC and frontal cortex, including bilateral postcentral gyrus, right middle frontal gyrus, bilateral paracentral lobules, the left precentral gyrus, and the right median cingulate. Finally, several correlation analyses were conducted to indicate whether the functional connectivity in the LOFC could be negatively correlated with excited symptoms, especially impulsive behaviors, and hostility. Considering the influences of potential confounding factors of the course of the disease and drugs, our results may provide a possible direction for exploring the pathogenesis of excited symptoms in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ.
FALFF or ALFF is an index that always measures the spontaneous activity of the cerebral regions, reflecting the levels of cerebral blood flow (CBF) and glucose metabolism. The decreased fALFF value in the LOFC in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ was previously reported repeatedly (23, 35). To our knowledge, OFC is important for the assessment of thoughts and intentions on social communication by information flow integration and feedback (3, 5, 56). The fALFF value reflects the speed or amount of information flow in OFC. Neuroimaging studies indicated that the density of the LOFC gray matter also decreased in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ (4, 26, 57). The loss of gray matter volume was reported to be associated with N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) dysfunction and dopamine hyperfunction, which activated neurotoxic signal transduction pathways and induced neuronal, and synaptic necrosis (5). This triggered off the compressing or blocking of the transmitted information in varying degrees, explaining the functional deactivation state of OFC. The same decreased fALFF value in the LOFC was also found in patients with impulsive SZ (30). The impaired OFC decreased the inhibitory control mechanism through GABAergic neurons, and the change of OFC might lead to the delay of impulse inhibition (18). Hoptman et al. found the increased fALFF values of OFC in patients with chronic SZ (58), which was contrary to our results. Further study suggested that antipsychotics could be effective by partially restoring the function of the frontal cortex through synaptic plasticity (35, 59). The reason for the increase in fALFF value may be that the chronic patients received medication, and the function of OFC was partially recovered and played a super-compensatory role (58). These findings suggested that the anomalous OFC function in SZ patients may be related to the time of onset.
Numerous studies demonstrated that SZ is a functional connectivity disorder, and our research provided new evidence for this statement (59, 60). Anatomically, the paracentral lobule is the medial extension of the precentral and postcentral gyri (61). Precentral gyrus and postcentral gyrus, as well as paracentral lobule possess a consistency in segregating and conveying sensorimotor information, and they are the main components of the sensorimotor network (SMN) (56, 62). Recently, it was suggested that a sufficient information flow in SMN is essential to ensure unbiased emotional and behavioral responses (63). Several studies have reported the associations of impulsive violence to motor errors and the reduced speed of perceptual information processing in daily life (21).
The cingulate cortex is a structure implicated in behavioral adaptation and control. The median cingulate cortex is highly connected to areas involved in action control and decision making, such as OFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, sensorimotor, and motor cortices. The median cingulate cortex has been emphasized to play a role in different facets of cognitive control, including response selection, attentional processing, conflict monitoring, and detecting errors (64). Our results also confirmed that the functional association between the LOFC and the right median cingulate is sparse in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ. It was demonstrated that the median cingulate cortex harbors a large number of short cortical contact fibers connected to the frontal cortex (65). The decreased connectivity indicated impaired sensorimotor integration and motor control in the early onset (66, 67).
To better evaluate the relationship between excited symptoms and cerebral functional conditions, we further proved that the functional connection between OFC and SMN including bilateral paracentral lobules, as well as median cingulate was negatively correlated with the scores of excited symptoms. The thickness of the gray matter cortex of OFC and paracentral lobule was smaller, which was related to its perceived function in SZ (68). Anatomical studies demonstrated defects in the cingulate cortex and OFC that were bound up with impulsive behaviors and hostility in psychiatric patients and HCs (27, 52, 69–71). Due to the role of the paracentral lobule in transmitting sensory and motor information to the SMN, an abnormal connectivity could lead to misperceptions and inappropriate behaviors. People could be fully mobilized flexibility through the OFC to adapt emotions to environmental changes, and functional connectivity might lead to disease-related painful experience and expressions of abnormal emotions or behaviors. We analyzed this correlation and clarified the changes in the brain network in the early stage of SZ, and clinical excited symptoms of SZ could be attributed to abnormal OFC-SMN circuits (56). Reduced functional connectivity between OFC and MCC could lead to an attenuated ability to monitor conflicts and detect errors (64). Functional deactivation of relevant cerebral regions, reduced information flow, difficulty in synchronizing activity between cerebral regions, decreased connectivity, and other dysfunctions could occur continuously in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ. All these constitute the neuropathological basis of excited symptoms. Psychotic symptoms including excited symptoms could be effectively relieved by adherence to antipsychotic medication during the acute phase of the disease. As the target of 5-OH and DA, OFC had been shown to partially restore its function (34, 35). However, long-term antipsychotic treatment had not achieved sustained results. The future research will concentrate on performing effective and accurate treatments.
In the subsequent analysis, we also observed a significantly negative correlation between connectivity strength in OFC and hostility symptoms in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ (P < 0.025). Similarly, the correlation between impulsivity and functional connection decreased, while the significance was not comparable to hostility. The possible reason is that abnormal connectivity of the OFC circuit enhanced the reactivity of negative stimuli (72), and was further considered to increase the tendency of personal hostility and impulsivity (73). Patients in our study had the first onset of SZ. The spontaneous activity and functional connection of OFC decreased, resulting in mild agitation symptoms, such as hostility. When the course of the disease continued to progress, they further showed impulsive behaviors. Based on the negative correlation, the level of functional connection between OFC and SMN deviated from the normal, representing the severity of excited symptoms. We could make full use of this result to further predict the risk of impulsive behaviors in patients with SZ. Such accurate prediction and control measures may enable us to reduce social and public hazards.
There are several limitations in the present study. First, the study used a cross-sectional design and could not forecast how cerebral spontaneous activity may change during the clinical course of SZ. Further studies are therefore needed to fully understand the implications of our findings. Second, the sample size of our research was small, although it was comparable to most fMRI studies on first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ, and it is essential to enrich the theoretical basis. Third, we clarified the correlation between LOFC-SMN connection and excitatory symptoms. However, it remained elusive whether the pathophysiology of excitatory symptoms originates from LOFC, SMN, or LOFC-SMN. Last but not least, our research concentrated on excited symptoms, while the severity of the symptoms varied among subjects, and the monotonic function of the measurement tool was noteworthy.
In summary, first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ were found to be associated with the decreased spontaneous cerebral activity in the LOFC. The rsFC values, in association with the LOFC, were significantly correlated with excited symptoms. More importantly, we determined that these coupling strengths could early predict the violent behaviors exhibited by these patients. Our findings might provide some perspectives for the study of hostility and impulsivity in first-episode drug-naïve patients with SZ.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Medical Research Ethics Committee of Nanjing Brain Hospital. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
YS and JY designed the study. JY and YLv conducted the literature searches and analysis. CC and JL performed the statistical analysis. XXZ and XYZ managed the assessment of the risk of bias. CC wrote the manuscript. JL contributed to the final review of the manuscript. YLi provided a lot of useful feedback and helped modify the wording and syntax of the article during the revision of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This study was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant no. BK20151076), and the Key Points of Nanjing Health and Family Planning Commission (grant no. ZKX17030).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
We are deeply grateful to the participants for their generous dedication. Equally important were the contributions of the psychiatrists involved with recruiting and diagnosing patients.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.922272/full#supplementary-material
2. Rapoport JL, Giedd JN, Gogtay N. Neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia: update 2012. Mol Psychiatry. (2012) 17:1228–38.
3. Liu C, Xue Z, Palaniyappan L, Zhou L, Liu H, Qi C, et al. Abnormally increased and incoherent resting-state activity is shared between patients with schizophrenia and their unaffected siblings. Schizophr Res. (2016) 171:158–65. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2016.01.022
4. Zhao C, Zhu J, Liu X, Pu C, Lai Y, Chen L, et al. Structural and functional brain abnormalities in schizophrenia: a cross-sectional study at different stages of the disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2018) 83:27–32. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.12.017
5. Velásquez E, Martins-De-Souza D, Velásquez I, Carneiro GRA, Schmitt A, Falkai P, et al. Quantitative subcellular proteomics of the orbitofrontal cortex of schizophrenia patients. J Proteome Res. (2019) 18:4240–53. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00398
6. McCutcheon RA, Reis Marques T, Howes OD. Schizophrenia-An overview. JAMA Psychiatry. (2020) 77:201–10.
10. Hoptman MJ, Antonius D, Mauro CJ, Parker EM, Javitt DC. Cortical thinning, functional connectivity, and mood-related impulsivity in schizophrenia: relationship to aggressive attitudes and behavior. Am J Psychiatry. (2014) 171:939–48. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.13111553
11. Millier A, Schmidt U, Angermeyer MC, Chauhan D, Murthy V, Toumi M, et al. Humanistic burden in schizophrenia: a literature review. J Psychiatr Res. (2014) 54:85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.03.021
12. Fleischhacker W, Galderisi S, Laszlovszky I, Szatmari B, Barabassy A, Acsai K, et al. The efficacy of cariprazine in negative symptoms of schizophrenia: post hoc analyses of PANSS individual items and PANSS-derived factors. Eur Psychiatry. (2019) 58:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2019.01.015
13. An I, Choi TK, Bang M, Lee SH. White matter correlates of hostility and aggression in the visuospatial function network in patients with schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:734488. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.734488
14. Volavka J, Citrome L. Pathways to aggression in schizophrenia affect results of treatment. Schizophr Bull. (2011) 37:921–9. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbr041
15. Cho W, Shin WS, An I, Bang M, Cho DY, Lee SH. Biological aspects of aggression and violence in schizophrenia. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. (2019) 17:475–86. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2019.17.4.475
16. Reagu S, Jones R, Kumari V, Taylor PJ. Angry affect and violence in the context of a psychotic illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Schizophr Res. (2013) 146:46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.01.024
17. Mackey S, Chaarani B, Kan KJ, Spechler PA, Orr C, Banaschewski T, et al. Brain regions related to impulsivity mediate the effects of early adversity on antisocial behavior. Biol Psychiatry. (2017) 82:275–82. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.12.027
18. Ucha M, Roura-Martinez D, Contreras A, Pinto-Rivero S, Orihuel J, Ambrosio E, et al. Impulsive action and impulsive choice are differentially associated with gene expression variations of the GABAA receptor Alfa 1 subunit and the CB1 receptor in the lateral and medial orbitofrontal cortices. Front Behav Neurosci. (2019) 13:22. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00022
19. Han YL, Dai ZP, Ridwan MC, Lin PH, Zhou HL, Wang HF, et al. Connectivity of the frontal cortical oscillatory dynamics underlying inhibitory control during a go/no-go task as a predictive biomarker in major depression. Front Psychiatry. (2020) 11:707. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00707
20. Velotti P, Garofalo C, Petrocchi C, Cavallo F, Popolo R, Dimaggio G. Alexithymia, emotion dysregulation, impulsivity and aggression: a multiple mediation model. Psychiatry Res. (2016) 237:296–303. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.01.025
21. Hsu MC, Ouyang WC. Effects of integrated violence intervention on alexithymia, cognitive, and neurocognitive features of violence in schizophrenia: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Sci. (2021) 11:837. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11070837
22. Bari A, Robbins TW. Inhibition and impulsivity: behavioral and neural basis of response control. Prog Neurobiol. (2013) 108:44–79. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.005
23. He Z, Deng W, Li M, Chen Z, Jiang L, Wang Q, et al. Aberrant intrinsic brain activity and cognitive deficit in first-episode treatment-naive patients with schizophrenia. Psychol Med. (2013) 43:769–80. doi: 10.1017/S0033291712001638
24. Zhou Y, Rosenheck R, Mohamed S, Zhang J, Chang Q, Ou Y, et al. Insight in inpatients with schizophrenia: relationship to symptoms and neuropsychological functioning. Schizophr Res. (2015) 161:376–81. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.12.009
25. Li CS, Huang C, Constable RT, Sinha R. Imaging response inhibition in a stop-signal task: neural correlates independent of signal monitoring and post-response processing. J Neurosci. (2006) 26:186–92.
26. Merz EC, He X, Noble KG, Pediatric Imaging N, Genetics S. Anxiety, depression, impulsivity, and brain structure in children and adolescents. Neuroimage Clin. (2018) 20:243–51. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.07.020
28. Deng W, Rolls ET, Ji X, Robbins TW, Banaschewski T, Bokde ALW, et al. Separate neural systems for behavioral change and for emotional responses to failure during behavioral inhibition. Hum Brain Mapp. (2017) 38:3527–37. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23607
29. Hoptman MJ, Volavka J, Weiss EM, Czobor P, Szeszko PR, Gerig G, et al. Quantitative MRI measures of orbitofrontal cortex in patients with chronic schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Psychiatry Res. (2005) 140:133–45. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2005.07.004
30. Athanassiou M, Dumais A, Tikasz A, Lipp O, Dubreucq JL, Potvin S. Increased cingulo-orbital connectivity is associated with violent behaviours in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. (2022) 147:183–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.01.001
31. Duff EP, Johnston LA, Xiong J, Fox PT, Mareels I, Egan GF. The power of spectral density analysis for mapping endogenous BOLD signal fluctuations. Hum Brain Mapp. (2008) 29:778–90. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20601
32. Shukla DK, Chiappelli JJ, Sampath H, Kochunov P, Hare SM, Wisner K, et al. Aberrant frontostriatal connectivity in negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bull. (2019) 45:1051–9. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sby165
33. Duffau H, Gatignol P, Mandonnet E, Peruzzi P, Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Capelle L. New insights into the anatomo-functional connectivity of the semantic system: a study using cortico-subcortical electrostimulations. Brain. (2005) 128:797–810. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh423
34. Homayoun H, Moghaddam B. Orbitofrontal cortex neurons as a common target for classic and glutamatergic antipsychotic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2008) 105:18041–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806669105
35. Li F, Lui S, Yao L, Hu J, Lv P, Huang X, et al. Longitudinal changes in resting-state cerebral activity in patients with first-episode schizophrenia: a 1-Year Follow-up functional MR imaging study. Radiology. (2016) 279:867–75. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151334
36. Zhao X, Yao J, Lv Y, Zhang X, Han C, Chen L, et al. Abnormalities of regional homogeneity and its correlation with clinical symptoms in Naive patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Brain Imaging Behav. (2019) 13:503–13. doi: 10.1007/s11682-018-9882-4
37. Zou QH, Zhu CZ, Yang Y, Zuo XN, Long XY, Cao QJ, et al. An improved approach to detection of amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) for resting-state fMRI: fractional ALFF. J Neurosci Methods. (2008) 172:137–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.04.012
38. Turner JA, Damaraju E, Van Erp TG, Mathalon DH, Ford JM, Voyvodic J, et al. A multi-site resting state fMRI study on the amplitude of low frequency fluctuations in schizophrenia. Front Neurosci. (2013) 7:137. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00137
39. Fox MD, Raichle ME. Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2007) 8:700–11. doi: 10.1038/nrn2201
40. Yan CG, Craddock RC, Zuo XN, Zang YF, Milham MP. Standardizing the intrinsic brain: towards robust measurement of inter-individual variation in 1000 functional connectomes. Neuroimage. (2013) 80:246–62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.081
41. Kublbock M, Woletz M, Hoflich A, Sladky R, Kranz GS, Hoffmann A, et al. Stability of low-frequency fluctuation amplitudes in prolonged resting-state fMRI. Neuroimage. (2014) 103:249–57. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.09.038
42. Margulies DS, Vincent JL, Kelly C, Lohmann G, Uddin LQ, Biswal BB, et al. Precuneus shares intrinsic functional architecture in humans and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2009) 106:20069–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905314106
43. Uddin LQ, Kelly AM, Biswal BB, Castellanos FX, Milham MP. Functional connectivity of default mode network components: correlation, anticorrelation, and causality. Hum Brain Mapp. (2009) 30:625–37. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20531
44. Zhang X, Yao J, Lv Y, Zhao X, Li Y, Sui Y, et al. An association study on the cognitive function and the cerebral grey matter volume of patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. (2018) 30:154–67. doi: 10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.217138
45. Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. (1987) 13:261–76.
46. Wallwork RS, Fortgang R, Hashimoto R, Weinberger DR, Dickinson D. Searching for a consensus five-factor model of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. (2012) 137:246–50. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2012.01.031
47. Jerrell JM, Hrisko S. A comparison of the PANSS pentagonal and Van Der Gaag 5-factor models for assessing change over time. Psychiatry Res. (2013) 207:134–9. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.12.010
48. Yan C, Zhang Y. DPARSF: a MATLAB toolbox for “pipeline” data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Front Syst Neurosci. (2010) 4:13. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2010.00013
49. Yan CG, Wang XD, Zuo XN, Zang YF. DPABI: data processing & analysis for (Resting-State) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics. (2016) 14:339–51.
50. Power JD, Barnes KA, Snyder AZ, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE. Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage. (2012) 59:2142–54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.018
51. Friston KJ, Williams S, Howard R, Frackowiak RS, Turner R. Movement-related effects in fMRI time-series. Magn Reson Med. (1996) 35:346–55. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910350312
53. Song XW, Dong ZY, Long XY, Li SF, Zuo XN, Zhu CZ, et al. REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e25031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025031
54. Smith SM, Nichols TE. Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage. (2009) 44:83–98. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.061
55. Krug A, Cabanis M, Pyka M, Pauly K, Kellermann T, Walter H, et al. Attenuated prefrontal activation during decision-making under uncertainty in schizophrenia: a multi-center fMRI study. Schizophr Res. (2014) 152:176–83. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.11.007
56. Wei Y, Chang M, Womer FY, Zhou Q, Yin Z, Wei S, et al. Local functional connectivity alterations in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. (2018) 236:266–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.04.069
57. Jackowski AP, De Araújo Filho GM, De Almeida AG, De Araújo CM, Reis M, Nery F, et al. The involvement of the orbitofrontal cortex in psychiatric disorders: an update of neuroimaging findings. Rev Brasileira Psiquiatria. (2012) 34:207–12. doi: 10.1590/s1516-44462012000200014
58. Hoptman MJ, Zuo XN, Butler PD, Javitt DC, D’angelo D, Mauro CJ, et al. Amplitude of low-frequency oscillations in schizophrenia: a resting state fMRI study. Schizophr Res. (2010) 117:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2009.09.030
59. Friston K, Brown HR, Siemerkus J, Stephan KE. The dysconnection hypothesis (2016). Schizophr Res. (2016) 176:83–94. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2016.07.014
60. McNabb CB, Sundram F, Soosay I, Kydd RR, Russell BR. Increased sensorimotor network connectivity associated with clozapine eligibility in people with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. (2018) 275:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2018.02.008
61. Patra A, Kaur H, Chaudhary P, Asghar A, Singal A. Morphology and morphometry of human paracentral lobule: an anatomical study with its application in neurosurgery. Asian J Neurosurg. (2021) 16:349–54. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_505_20
62. Kaufmann T, Skatun KC, Alnaes D, Doan NT, Duff EP, Tonnesen S, et al. Disintegration of sensorimotor brain networks in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. (2015) 41:1326–35. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbv060
64. van Heukelum S, Mars RB, Guthrie M, Buitelaar JK, Beckmann CF, Tiesinga PHE, et al. Where is cingulate cortex? A cross-species view. Trends Neurosci. (2020) 43:285–99. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.03.007
65. Huang XQ, Lui S, Deng W, Chan RC, Wu QZ, Jiang LJ, et al. Localization of cerebral functional deficits in treatment-naive, first-episode schizophrenia using resting-state fMRI. Neuroimage. (2010) 49:2901–6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.072
66. Xu Y, Qin W, Zhuo C, Xu L, Zhu J, Liu X, et al. Selective functional disconnection of the orbitofrontal subregions in schizophrenia. Psychol Med. (2017) 47:1637–46. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717000101
67. Lottman KK, Gawne TJ, Kraguljac NV, Killen JF, Reid MA, Lahti AC. Examining resting-state functional connectivity in first-episode schizophrenia with 7T fMRI and MEG. Neuroimage Clin. (2019) 24:101959. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101959
68. Butler PD, Abeles IY, Weiskopf NG, Tambini A, Jalbrzikowski M, Legatt ME, et al. Sensory contributions to impaired emotion processing in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. (2009) 35:1095–107. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbp109
69. Kumari V, Aasen I, Taylor P, Ffytche DH, Das M, Barkataki I, et al. Neural dysfunction and violence in schizophrenia: an fMRI investigation. Schizophr Res. (2006) 84:144–64. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2006.02.017
70. Gansler DA, Mclaughlin NC, Iguchi L, Jerram M, Moore DW, Bhadelia R, et al. A multivariate approach to aggression and the orbital frontal cortex in psychiatric patients. Psychiatry Res. (2009) 171:145–54. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2008.03.007
71. Fjellvang M, Grøning L, Haukvik UK. Imaging violence in schizophrenia: a systematic review and critical discussion of the MRI literature. Front Psychiatry. (2018) 9:333. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00333
Keywords: schizophrenia, orbitofrontal cortex, fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations, functional connectivity, hostility, impulsivity
Citation: Chen C, Yao J, Lv Y, Zhao X, Zhang X, Lei J, Li Y and Sui Y (2022) Aberrant Functional Connectivity of the Orbitofrontal Cortex Is Associated With Excited Symptoms in First-Episode Drug-Naïve Patients With Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 13:922272. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.922272
Received: 17 April 2022; Accepted: 06 June 2022;
Published: 28 July 2022.
Edited by:
Daiki Sasabayashi, University of Toyama, JapanReviewed by:
Junya Fujino, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, JapanCopyright © 2022 Chen, Yao, Lv, Zhao, Zhang, Lei, Li and Sui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuan Li, liyuan97y35@163.com; Yuxiu Sui, suiyuxiu@aliyun.com
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.