
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 16 January 2025
Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1521758
This article is part of the Research Topic Integrative Multi-omics and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven Approaches for Superior Nutritional Quality and Stress Resilience in Crops View all 6 articles
 Priyanka Kumari1,2
Priyanka Kumari1,2 Sougata Bhattacharjee1,2
Sougata Bhattacharjee1,2 K. Venkat Raman1
K. Venkat Raman1 Jyotsana Tilgam1,2
Jyotsana Tilgam1,2 Krishnayan Paul1,2
Krishnayan Paul1,2 Kameshwaran Senthil1
Kameshwaran Senthil1 Mahi Baaniya1,2
Mahi Baaniya1,2 G. Rama Prashat3
G. Rama Prashat3 Rohini Sreevathsa1
Rohini Sreevathsa1 Debasis Pattanayak1*
Debasis Pattanayak1*The methylation- demethylation dynamics of RNA plays major roles in different biological functions, including stress responses, in plants. m6A methylation in RNA is orchestrated by a coordinated function of methyl transferases (writers) and demethylases (Erasers). Genome-wide analysis of genes involved in methylation and demethylation was performed in pigeon pea. Blast search, using Arabidopsis gene sequences, resulted in the identification of two methylation genes (CcMTA70, CcMTB70), two genes encoding adaptor proteins for methylation (CcFIPA and CcFIPB) and 10 demethylase (ALKBH) genes (CcALKBH1A, CcALKBH1B, CcALKBH1C, CcALKBH2, CcALKBH8, CcALKBH8A, CcALKBH8B, CcALKBH9, CcALKBH10A and CcALKBH10B) in the pigeon pea genome. The identified genes were analyzed through phylogenetic relationship, chromosomal position, gene structure, conserved motif, domain and subcellular location prediction etc. These structural analyses resulted in categorization of MTs and FIPs into one group, i.e., CcMTA/B and CcFIPA/B, respectively; and ALKBHs into four groups, viz. CcALKBH1/2, CcALKBH8, CcALKBH9 and CcALKBH10. Relative expression analysis of the identified genes in various tissues at different developmental stages revealed the highest level of expression in leaf and the least in root. CcMTs and CcFIPs had similar patterns of expression, and CcALKBH10B demonstrated the highest and CcALKBH2 the lowest level of expression in all the tissues analyzed. CcALKBH8 showed the highest induction in expression upon exposure to heat stress, and CcALKBH10B demonstrated the highest level of induction in expression during drought, salt and biotic (Helicoverpa armigera infestation) stresses. The present study would pave the way for detailed molecular characterization of m6A methylation in pigeon pea and its involvement in stress regulation.
Epigenetic modifications on both the DNA and RNAs, without any change of sequence, have emerged as an important player of gene regulation in living organisms (Meyer and Jaffrey, 2014). More than 160 RNA modifications have been identified in mRNA, tRNAs, rRNAs and long non-coding RNA until now (Cantara et al., 2010). Methylation is one of the dominant epigenetic modifications, and modification of adenine through methylation exists as an essential epigenetic mark in both DNAs and RNAs of eukaryotes (Liang et al., 2020). N6-methyladenosine (m6A), N1-methyladenosine (m1A), 5-methylcytidine (m5C) and 7-methylguanosine (m7G) are frequently identified in mRNA (Zhang et al., 2020). m6A is the most frequent and reversible modification of RNA (Yue et al., 2019; Duan et al., 2017). It plays a major role in the metabolism of RNA which includes mRNA splicing (Haussmann et al., 2016), control of translation (Luo et al., 2020), stability of RNA (Wang et al., 2014), processing of primary microRNA (Bhat et al., 2020) etc. m6A modification occurs mostly at the consensus sequence, RRACH (R = purine and H = A, C, or U), and this is conserved in animals and plants (Bhat et al., 2020). Also, a second consensus sequence, UGUAY (Y = pyrimidine), is found to be conserved only in plants for m6A modification. Modulation of RNA methylation takes place with the help of two enzymes, viz. RNA methyl transferases (“writers”) and demethylases (“erasers”). Writers help in installing and eraser in removing the methylation marks (Hu et al., 2019).
There are three broad groups for N6A-methyltranferases (Iyer et al., 2016). MT-A70 clade constitutes group 1, consisting of MTA and MTB genes. It is further divided into six different eukaryotic subclades (Iyer et al., 2016). Clades 1–3 are known as METTL3, METTL4 and METTL14, respectively and these three clades are conserved in higher eukaryotes. Clades 4–6 of group 1 occur in unicellular photosynthetic eukaryotes, basal fungi, and haptophyte algae (Iyer et al., 2016). The other two groups, group 2 and group 3, show independent transfer from bacteria and have restricted distribution (Iyer et al., 2016). Group 2 has been found in archaeal dsDNA viruses and mycobacterium, which are often seen, fused to RNA-binding PPR domains. Group 3 has been observed only in case of the heterolobosean Naegleria (Iyer et al., 2016). m6A modification is carried out by a core heterodimer formed by METTL3 and METTL14, whereas METTL4 is a DNA methylase (Greer et al., 2015). N6A methylation is facilitated by an adaptor protein, WTAP (Wilm’s tumor-associated protein), which stabilizes the heterodimer (formed by METTL3 and METTL14) in the nuclear speckle (Ping et al., 2014) and several co-factors like KIAA1429 and an RNA binding motif protein, RBM15/RBM15B. WTAP is found in the animal system, and its ortholog, FIP [FK506-binding protein 12 (FKBP12) interacting protein (FIP), FIP37 in case of Arabidopsis], is present in plants (Shen et al., 2016).
Demethylase (eraser) has been studied extensively in animals, but it is yet to be characterized in detail in plants. Nine demethylases have been reported in humans. Eight demethylases belong to ALKBH family (ALKBH 1-8) and the other one is FTO (Fat mass and obesity associated). Due to selectivity towards the substrate, functional diversity arises among the demethylases (Marcinkowski et al., 2020). Phylogenetic analysis could not detect presence of any FTO ortholog in plant system, but many orthologs of ALKBH5 are identified in Arabidopsis (Liang et al., 2020).
AlkB homologs (ALKBH) are specific demethylases, which are members of the dioxygenase superfamily and require Fe2+and α-ketoglutarate for demethylation catalysis of various substrates, viz. proteins, mRNA, tRNA, snRNA, ds/ss DNA, etc (Trewick et al., 2002). AlkB protein was initially found in Escherichia. coli (EcAlkB) (Kataoka et al., 1983). This protein has de-alkylation activity that repairs the damage caused by alkylating agents. Repairing of 3-methylcytosine (3-meC) and 1-methyladenine (1-meA) base modifications is more efficient compared to that of 1-methylguanine (1-meG) and 3-methylthymine (3-meT), which undergo less efficient repairing process. A single gene encoding ALKB is present in E. coli, but many ALKBH gene families are present in animals and plants (Marcinkowski et al., 2020). Also, ALKBH has repairing as well as regulatory roles in eukaryotes indicating a broader range of functions.
Fourteen ALKBH families have been identified in Arabidopsis using bioinformatic tools (Mielecki et al., 2012; Ougland et al., 2015; Marcinkowski et al., 2020). These Arabidopsis ALKBH proteins have functional diversity and act on different substrates. ALKBH1D is present in chloroplast. ALKBH2 does the repairing of 1-meA and 3-meC, ALKBH8 takes part in modification of tRNA by hydroxylating mcm5U to (S)-mchm5U, ALKBH9A and ALKBH10A are related to abiotic stresses and ALKBH9B and ALKBH10B have N6 demethylation activity (Eraser).
Methylase –demethylase system in Arabidopsis is involved in regulation of stem cell fate determination (Shen et al., 2016); embryo development (Zhong et al., 2008); and trichomes and leaf morphology (Wei et al., 2018). m6A modification is found to affect sporogenesis in rice (Zhang et al., 2019). However, the function of the methylase-demethylase system is yet to be studied in many agriculturally important crops.
Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) is a climate resilient orphan crop with rich source of proteins, essential amino acids and vital minerals. It is an important pulse crop grown in tropical and subtropical areas. India is the largest producer of pigeon pea in the world and presently it is grown on over 5.65 m ha in India (FAOSTAT, 2022). Despite the development of high yielding varieties through breeding efforts the productivity is stagnant at around 825kg/ha (FAOSTAT, 2022) which is not sufficient to meet the demand of ever increasing human population. The methylase-demethylase system has not been studied in pigeon pea. It has been reported that m6A modification has a role in abiotic and biotic stresses (Miao et al., 2020). Even though, pigeon pea considered as resilience to abiotic stresses, many factors like moisture and water logging stress affects the crop physiology and productivity. In North Western part of India, pigeon pea crop suffers from salinity stress (Choudhary et al., 2011). Extreme drought and heat conditions particularly at semi-arid areas, during the seedling and reproductive stages in pigeon pea plants often leads to yield loss (Bakala et al., 2024). Among Biotic stresses, infestation of pod borer (H armigera Hubner) poses major challenge to the pigeon pea productivity. With the availability of genomic sequence and annotations, there is a potential way to explore the genes to enhance the tolerance using advanced genomic, genome editing and speed breeding tools. So, considering the diverse role of methylase-demethylase system we made an attempt to identify the methyl transferase and demethylase in pigeon pea and a bioinformatics analysis was conducted for identification and analysis of methylase and demethylase genes in pigeon pea. The expression pattern of the identified genes was analyzed in different tissues and upon exposure to biotic and abiotic stress conditions.
Arabidopsis MT, FIP and ALKBH cDNA and protein sequences were downloaded from the ensemble (https://plants.ensembl.org/index.html) using the gene ID provided in the literature (Ougland et al., 2015). The protein sequence was then used for blast search in the Legume Information Database (https://www.legumeinfo.org/) to see the orthologous proteins in pigeon pea. E-value threshold was kept at zero for blast search with 98-100% coverage.
The different Expasy (https://www.expasy.org/) tools like ProtParam, compute pI/Mw etc was used to have a basic understanding of the identified genes in terms amino acid length, molecular weight, iso-electric point, GRAVY (Kyte and Doolittle, 1982), instability index and aliphatic index.
The chromosomal position was identified from the LIS database (https://www.legumeinfo.org/) and subsequently, the locus ID was also identified from the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Chromosome map was constructed using MapGene2Chrom web v2 (http://mg2c.iask.in/mg2c%5Fv2.1/).
A phylogenetic tree of the identified proteins was constructed to see their relative closeness. MEGA11 software was used for the phylogenetic tree construction (Tamura et al., 2021). First of all, after identification and retrieval of all the sequences Clustal omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/) was used to check for similarity among sequences. Further of full-length amino acid sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Glycine max and C. cajan were fed to MEGA and there again multiple sequence alignment was performed with ClustalW tool. The IDs for Oryza sativa and glycine max is provided in Table 1.While aligning the sequences of four species of crops in MEGA, alignments were made selecting “with gap option” and during construction of the phylogenetic tree, gap parameters were selected as ‘Use all site’. Phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Maximum Likelihood method and JTT matrix-based model taking bootstrap value 1000 (Tamura et al., 2021). For visualization of the phylogenetic tree an ‘Interactive Tree Of Life’ (iTOL) v6 (https://itol.embl.de/) was used.
For identification of gene structure GSDS 2.0 was used (http://gsds.gao-lab.org/). This gave the idea of exon-intron structure in MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs genes. The conserved motifs of the protein were examined using the MEME online software tool (https://meme-suite.org/meme/). The motif number was kept as 20. The motif width range was kept as minimum 6 and maximum of 50 (6-50) and in site distribution zero or one occurrence per sequence was selected.
The conserved domain of the genes was predicted using an online ‘CD Search tool’ (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi). The sub-cellular localization of pigeon pea MTs, FIPs, and ALKBHs was predicted using the WoLF PSORT web tool (https://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/).
Upstream genomic sequences of 2 kb from transcription start site (including 5’ UTR) were retrieved from the LIS database for MTs, FPIs and ALKBHs. Cis-regulatory elements were identified using the Plant Pan v3.0 (http://PlantPAN.itps.ncku.edu.tw/). Data obtained from the web tool was analyzed in MS Excel V.2013 and visualized in the TB tool (https://bio.tools/tbtools). Upstream sequences for MTs, FPIs and ALKBHs were analyzed to predict the m6A- methylation using the EpiSemble R-package v.0.1.1 (http://cabgrid.res.in:5799/). MethSemble 6mA tool was used in EpiSemble R-package to predict the methylation site. This package uses three models viz gradient boosting, random forest and Support vector machine.
Pigeon pea genotype, Pusa 992, was grown in the net house in a 4-inch pot (loamy soil) under natural day length (14hr light and 10 hr. dark) and temperature(30-32 °C) in July 2023 at ICAR-NIPB, New Delhi. Initially watering was done on every alternate day up to three leaved stage. After that when soil used to dry based on that watering was done. Plants were grown in triplicates. For heat stress, 20 days old seedlings are kept in a heat chamber at 42 °C and 60% relative humidity. Plants were kept for 6 hrs. (from 11:00 am to 5:00 pm) for two days (Supplementary Figure 1). After the second day leaf samples were taken. For drought stress, 20% PEG 6000 was prepared by adding 200gm of PEG 6000 in 1000ml of autoclaved water and 100ml of PEG was given per pot which contained a single plant. (Supplementary Figure 1). For salt stress 150 mM of NaCl was prepared by adding 8.766 gm in 1000 ml autoclaved water. and 100 ml of the solution was given to 20 days old seedlings (single plant in one pot) (Mi et al., 2024; Dokka et al., 2024) (Supplementary Figure 1). Helicoverpa armigera was used for biotic stress. Larvae were obtained from an in-house culture facility The larvae of H. armigera larvae were raised on an artificial diet with a 16 h light and 8 h dark photoperiod, at a temperature of 26± 1°C and 70-80% relative humidity was maintained. The second instar larvae of the polyphagous insect pest, Helicoverpa armigera, was reared on leaves of 20 days old seedlings of pigeon pea. Larvae were given 7 hrs. starvation and then two larvae were released per pot (1 Plant in each pot). Plants were covered with the perforated polythene which was secured with rubber band on the pots to prevent escape of larvae. After four days of infestation leaf samples were collected.
For tissue-specific expression studies different tissues were collected at different stages, but for stress related studies leaf tissues were collected from 20 days old seedlings. For abiotic stress-induced plants leaf samples were collected after 48 hours of treatment. Leaf samples were collected after 4 days of H. armigera infestation for gene expression study under biotic stress. Total RNA was isolated from different tissues (leaf, roots, internode, shoot apical meristem, flower apical meristem and immature pod) for tissue-specific qPCR and from leaf samples for stress-specific qPCR using RNA isolation kit (Genes2Me; India) according to the ‘manufacturer’s instruction. Isolated RNA was treated with DNaseI (RNase free) to remove any genomic DNA contamination. The quality of total RNA was checked using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific). Total RNA was then immediately stored at -80°C. cDNA was prepared using a PrimesScript cDNA synthesis kit (TaKaRa) and stored at -20 °C for further use. MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs-specific primers (Supplementary Table 2) were designed using the IDT web tool (https://www.idtdna.com/). qPCR assay was performed in Light Cycler 96 PCR detection system (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using TB green master mix (TaKaRa) using the following conditions: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, 40 cycles of amplification, each cycle of 95 °C for 30 sec, 60 °C for 30 sec and 72 °C for 20 sec. Also, three biological and three technical (cDNA replicates) replicates were taken for each sample. The CcIF4 was used as a reference gene (Bhattacharjee et al., 2023). The Sequence of the internal primer pair for the reference gene is included in the Supplementary File (Supplementary Table 2). The relative abundance of CcMTs, CcFIPs and CcALKBHs was calculated using the 2–ΔΔCt method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001).
For the gene expression study, three biological (separate plants grown in separate pots under different abiotic and biotic stress) and three technical replicates were taken. Wherein, an equal amount of each biological replicate was pooled for RNA isolation. Mean values were given with an error bar (standard error of means) for all the parameters. At 5%, the least significant difference (LSD) was calculated to see the significance of different treatment effects. After that, the significance level between and among the treatments in each experiment was checked by performing a range test.
The sequence information of methyl transferase and demethylase was retrieved from the LIS database and cross-checked through blast at NCBI database, which gave the Locus ID of respective genes. Arabidopsis has 2 MT, 1 FIP and 14 ALKBH genes, whereas in pigeon pea, 2 MT, 2 FIP and 10 ALKBH genes were identified (Table 2).
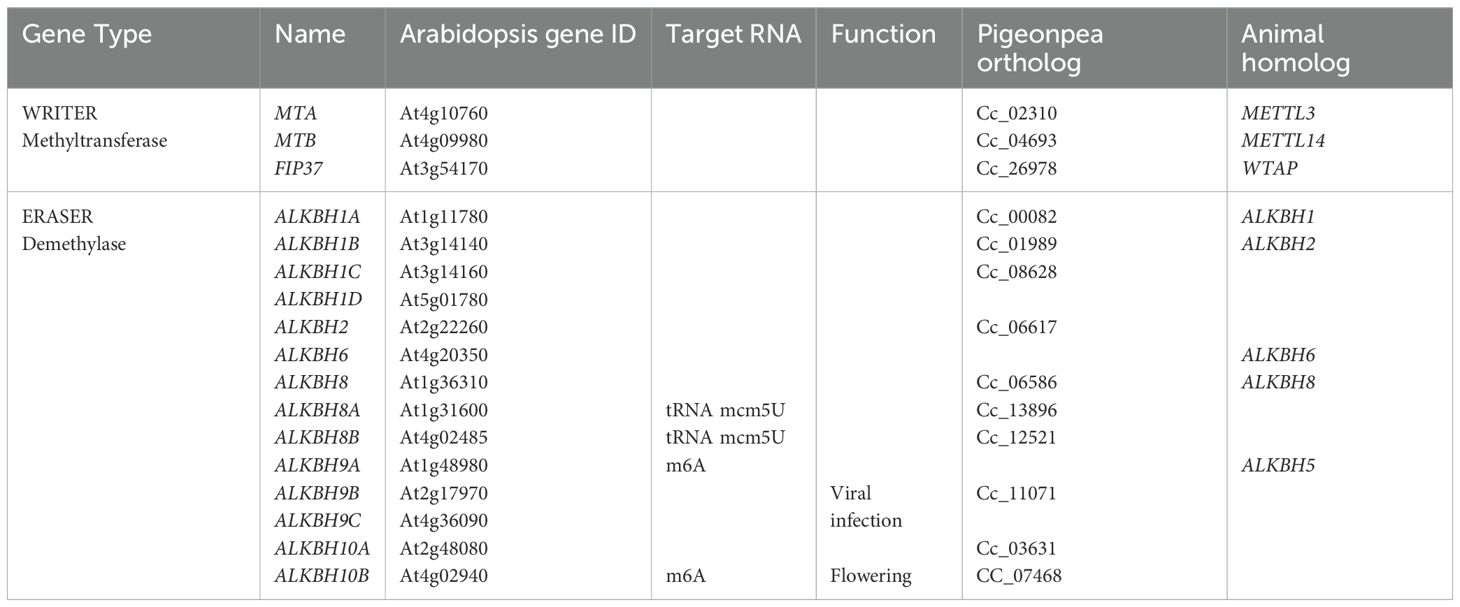
Table 2. List of methyl transferase and demethylase genes involved in RNA methylation in pigeon pea.
This exercise provided a complete framework of basic information on iso-electric point (pI), molecular weight (MW), instability index (II), aliphatic index (AI) and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) of the proteins identified in pigeon pea (Table 3). When the protein sequence of identified MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs of pigeon pea was analyzed it was found that there was variation in the genes. For instance, in case of predicted protein length, the amino acid sequence varies from 761 aa to 1089 aa for MTs, 337 aa to 338 for FIPs and 205 aa to 515 aa for ALKBHs family of pigeon pea. The iso-electric point for MTs ranged from 6 to 7, and for FIPs, it was between 5 and 6. The iso-electric point ranged from 5.57 to 8.7 for ALKBHs with CcALKBH1C having the highest PI and CcALKBH8B the lowest. All proteins of MTA, FIPs and ALKBH were hydrophilic as confirmed by GRAVY. Also, instability index analysis showed that MTA was more stable than MTB, and FIPA was more stable than FIPB. Among ALKBH proteins CcALKBH8 was the most stable, and CcALKBH8B was the least stable protein. Aliphatic index analysis indicated that MTA and FIPA had more aliphatic amino acids compared to MTB and FIPB, respectively. CcALKBH8 had the highest aliphatic index and CcALKBH9 had the lowest aliphatic index. The higher aliphatic index, the better the thermo-stability of protein.
From the analysis of the chromosomal position of the genes encoding pigeon pea MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs it was found that all the genes were localized within six chromosomes, viz. chr.01, chr.02, chr.03, chr.05, chr.06 and chr. 11. However, the majority of the genes were localized on the chr.03 (Table 4).
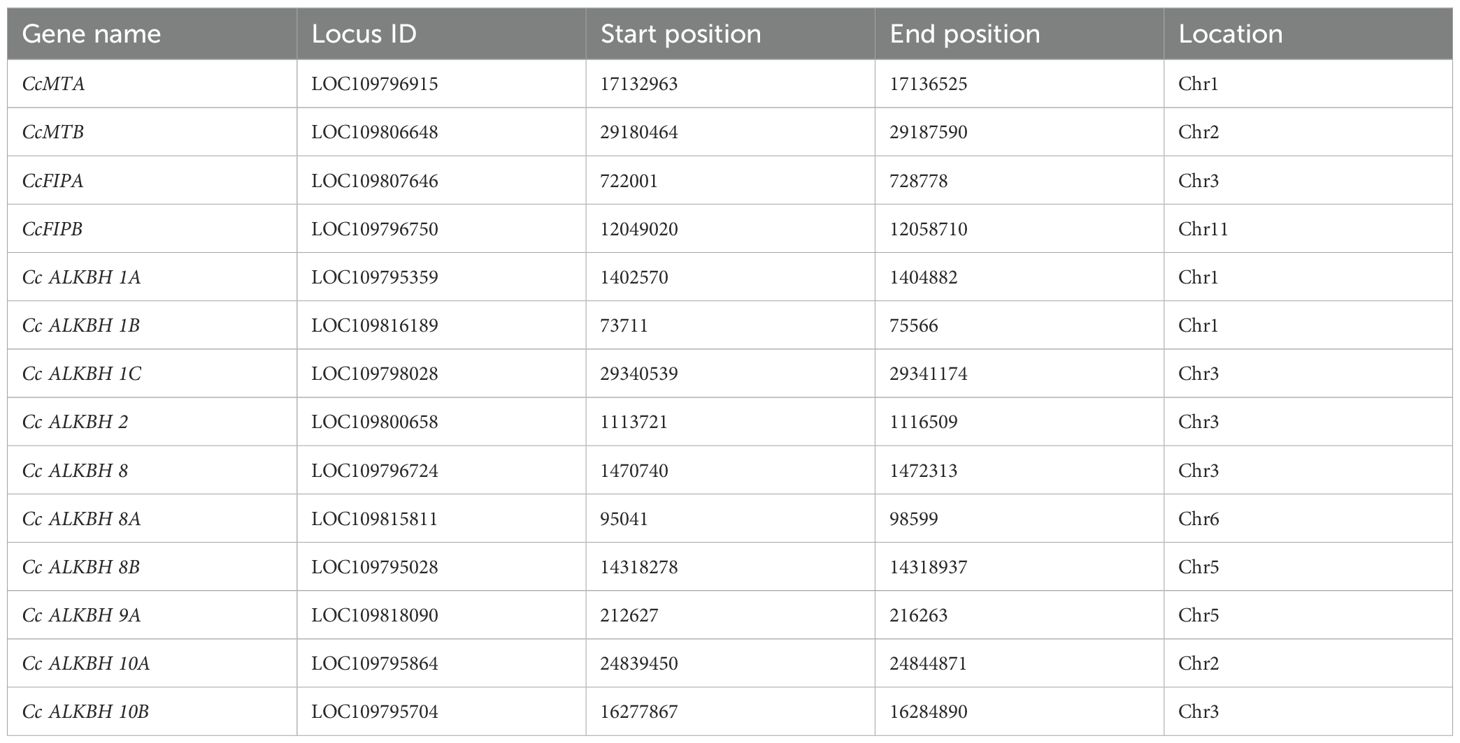
Table 4. Specific chromosomal location of the identified methylase and demethylase genes in pigeon pea.
A chromosomal map had been constructed showing the distribution of genes on chromosomes. CcMTA and CcMTB were located on chromosomes 01 and 02, respectively. CcFIPA and CcFIPB were located on chr.03 and 11, respectively. Two ALKBH genes, CcALKBH1A and CcALKBH1B, were located on chr.01, one ALKBH gene, CcALKBH10A, was on chr.02, and four genes, viz, CcALKBH1C, CcALKBH2, CcALKBH8 and CcALKBH10B, were onchr.03. CcALKBH8B, and CcALKBH9 were present on chr.05 and CcALKBH8A was found on chr. 06 (Figure 1).
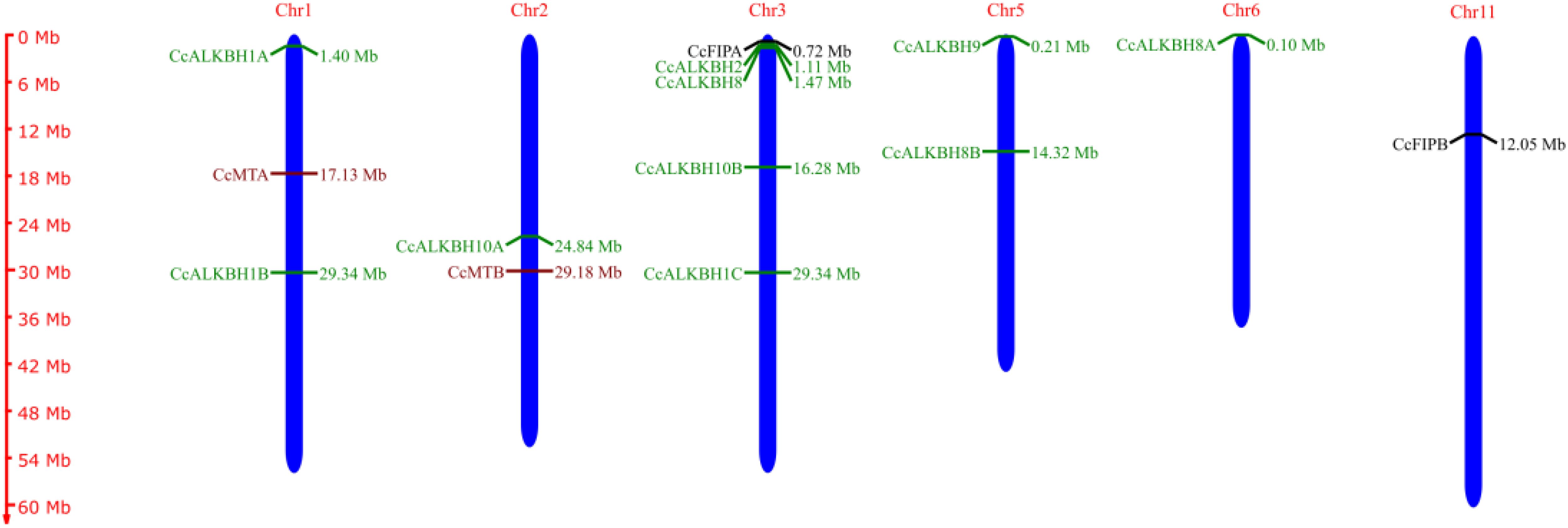
Figure 1. Chromosomal map (made using Map Gene 2 chromosome software) depicting chromosomal locations of the identified genes involved in methylation-demethylation in pigeon pea. The maroon colour indicates CcMTs, green indicates CcALKBHs and black indicates CcFIPs.
Deduced protein sequences of MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs from Arabidopsis (A. thaliana), rice (O. sativa), soybean (G. max) and pigeon pea (C. cajan) were taken and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA11 to find out the relationships between the identified genes and to see the evolutionary relics (Tamura et al., 2021) (Figure 2). The tree sub-clades were clubbed into groups to understand their evolutionary relations. One group for MTs and FIPs, viz. MTA/B and FIPA/B, respectively, and four groups for ALKBHs were made, viz, (ALKBH1/2, ALKBH8, ALKBH9, ALKBH10) following earlier nomenclature (Marcinkowski et al., 2020). The number of genes of MTs and FIPs was almost the same in above mentioned species. However, the number of ALKBH genes varied among species. The highest number of ALKBH genes (14) was found in Arabidopsis, while the least number of ALKBHs (10) was found in pigeon peas. The ALKBH6 group was found absent in pigeon pea. The ALKBH1 group had the highest number of genes (4), while ALKBH2 and AlKBH9 had the lowest number of genes (1). ALKBH10 was similar and related to m6A RNA demethylation in Arabidopsis.
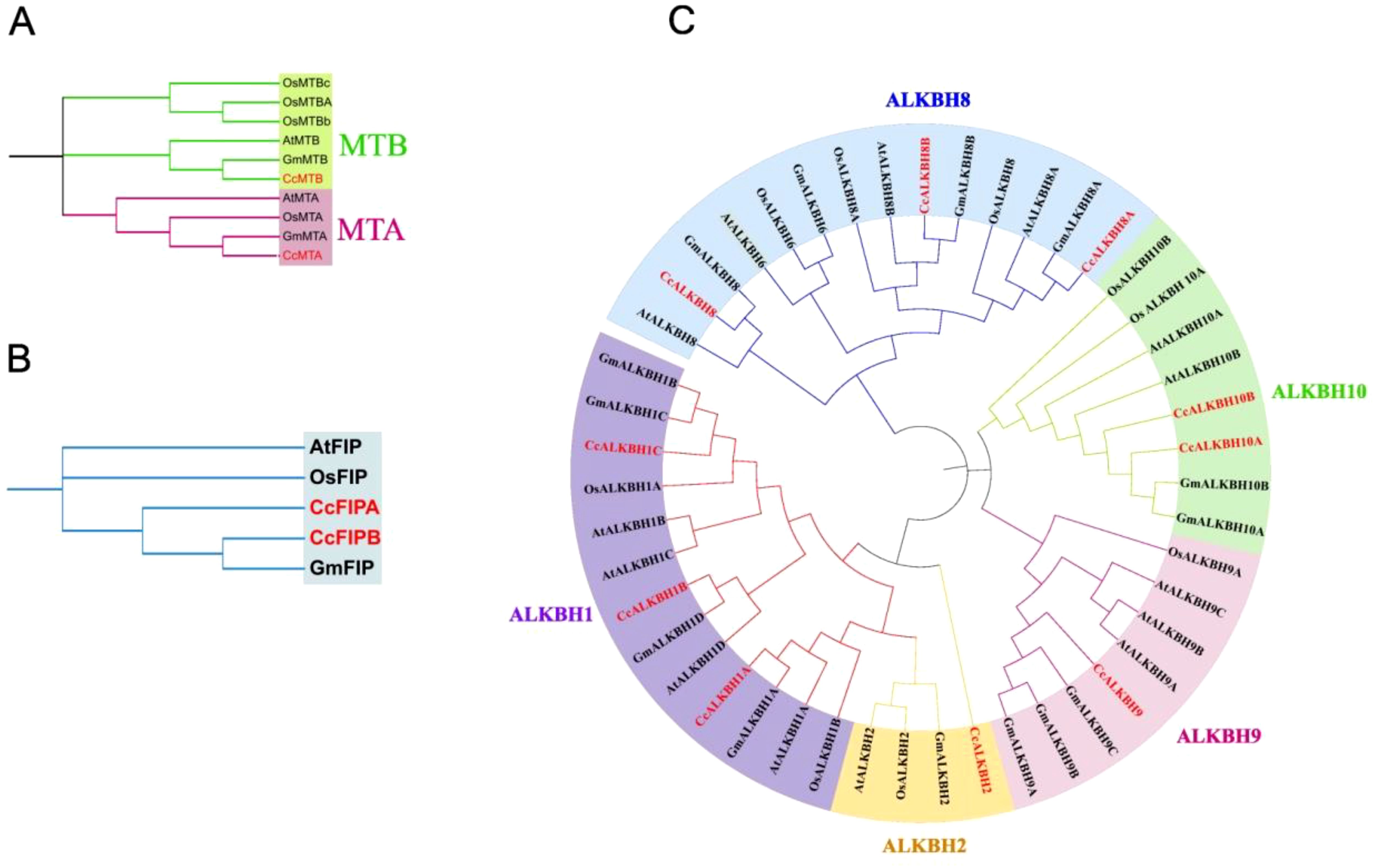
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship and closeness among the identified methylation-demethylation genes of Arabiopsis thaliana, rice (Oryza sativa), soybean (Glycine max) and pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan). (A) MTs, (B) FIPs, (C) ALKBHs. Phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA11.0 software by selecting the Maximum likelihood and keeping the bootstrap value at 1000.
Gene structure plays a major role in the evolution of gene families. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor joining method grouped CcALKBs into 4 paralogous clades. The members of CcALKBH1, CcALKBH2 and CcALKBH8 were 3 distinct clades whereas, the members of CcALKBH9 and CcALKBH10 together grouped as a separate clade (Figure 3A). Analysis of the exon-intron structure of MTs revealed that seven and six exons were present in MTA and MTB, respectively, but intronic portion was more in MTB (Figure 3B). In case of FIPA and FIPB there were eight and thirteen exons, respectively, and for FIPA, UTR was found only at the 3’ end (Figure 3B). Intronic portion was found to be more in FIPB. Further, for ten ALKBHs, it has been found that variations were present among the genes. Seven exons were present in five of the ALKBHs, viz. CcALKBH1A, CcALKBH8A, CcALKBH9, CcALKBH10A and CcALKBH10B; and the rest five ALKBHs, viz. CcALKBH2, CcALKBH1B, CcALKBH1C, CcALKBH8 and CcALKBH8B, had varying numbers of exons (five to one, respectively). CcALKBH10A and CcALKBH10B contained the largest intronic regions. It was noticed that the CcALKBH2 gene was devoid of any UTR region (Figure 3B).
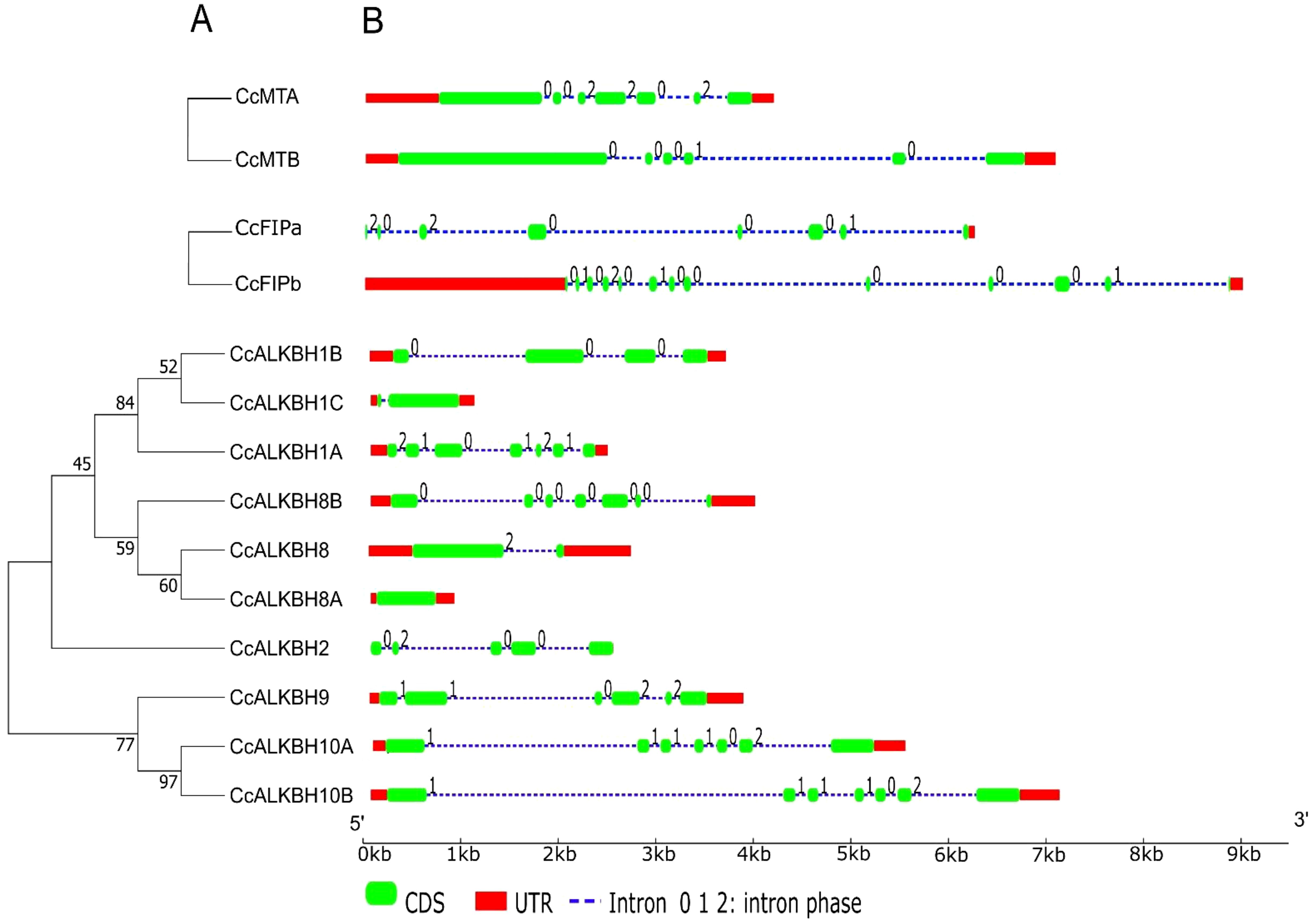
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree showing gene structure of the identified genes of pigeon pea involved in methylation-demethylation. (A) Phylogenetic tree of identified pigeon pea MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs proteins. (B) Gene structures of CcMTs, CcFIPs and CcALKBHs. The exons, introns and UTRs were represented by red rectangles, black lines and green rectangles respectively. 0, 1 and 2 represent the intron phase of the respective genes.
The MEME suite was used for conserved motif analysis, and 20 motifs were identified. According to the phylogenetic analysis (Figure 4A), motif distribution was found conserved for closely related genes as shown in Figure 4B. All 20 motifs were found to be present in both the MTs, but their distance varied. FIPs had all the motifs conserved and at the same distance. For ALKBHs, CcALKBH10A and CcALKBH10B had the greatest number of genes conserved at the same distance (Figure 4B). Motif 1 was found to be conserved in all the genes except for CcALKBH2 and CcALKBH8. Motif 20 was specific to CcALKBH8A and CcALKBH8B. Similarly, motif 18 was specific to CcALKBH1B and CcALKBH1C, and motif 19 was specific to CcALKBH2 and CcALKBH8 (Figure 4B). CcALKBH2 and CcALKBH8 had shown the least conservation of motifs which might be an indication of performing different functions.
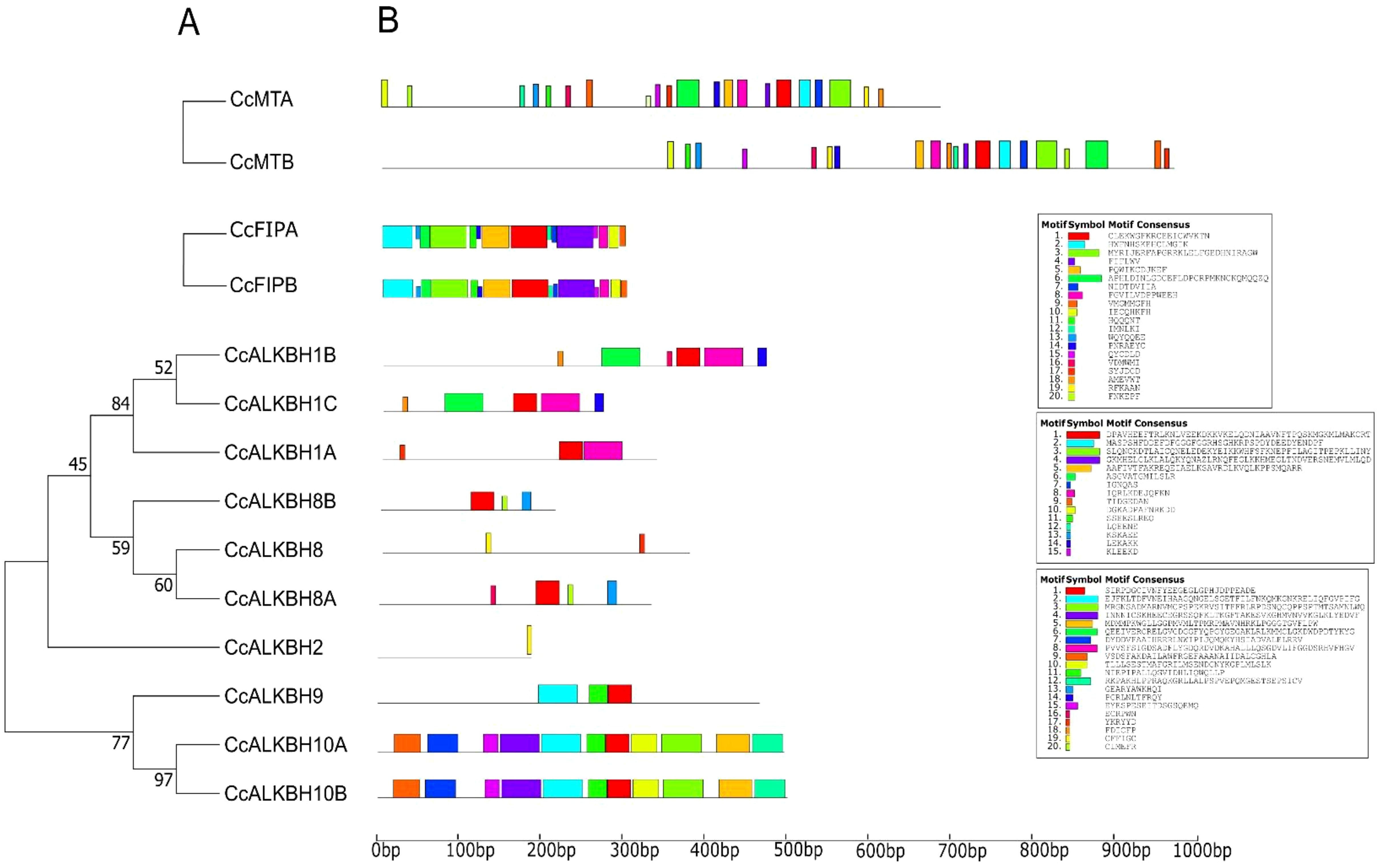
Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree showing conserved motifs. (A) Conserved motifs are present in the identified MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs proteins of pigeon pea. (B) Distribution of identified conserved motifs of CcMTs, CcFIPs, and CcALKBHs genes of pigeon pea. Different motifs are shown in different colors.
Domains are the self-stabilizing polypeptide chain that works independently. It was observed that MTs (CcMTA and CcMTB) contained domain MTA-70 which is a major domain involved in methylation (Figure 5). Microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules domain was found in FIPs, viz. CcFIPA and CcFIPB (Figure 5). Most of the ALKBHs contained 2OG-FeII_Oxy_2 domain which is a characteristic feature of the ALKBH gene family. Although the 2OG-FeII_Oxy_2 domain was absent in CcALKBH2, it had a completely different domain of DUF4057 superfamily, which is yet to be characterized (Figure 5). Apart from this, CcALKBH8A was found to have an RRM (RNA recognition motif) domain, which is an essential domain involved in tRNA modification. In addition, CcALKBH8 also had a methyl transferase domain. So, it might have a role in both demethylation and methylation.
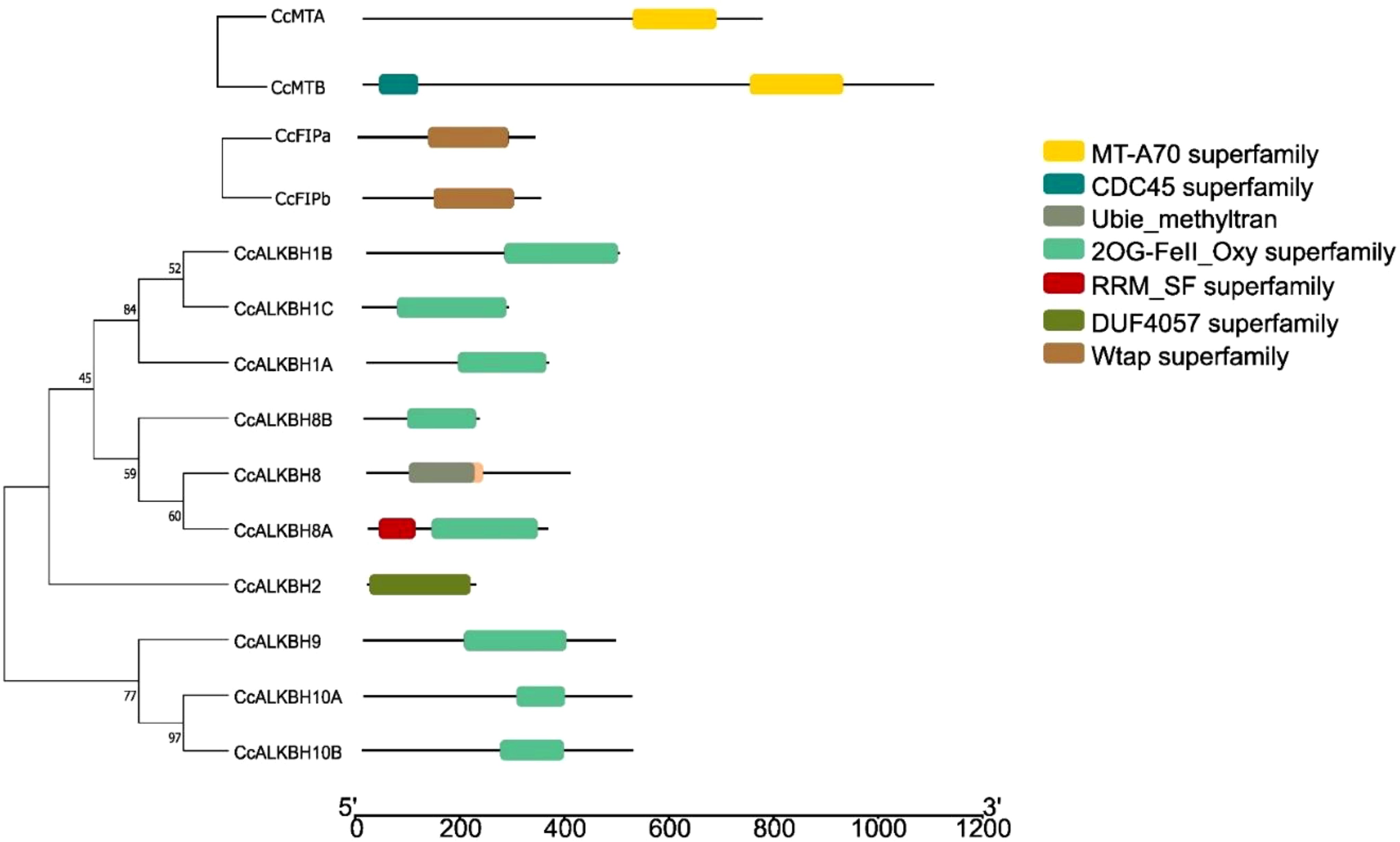
Figure 5. Phylogenetic tree constructed based on conserved domains of identified CcMTs, CcFIPs and CcALKBHs genes of pigeon pea. Different domains are shown in different colors.
Regarding subcellular location, it was found that MTs, FIPs and a majority of ALKBHs had nuclear localization signal. However, a few ALKBHs, viz. CcALKBH1B, and CcALKBH10B, had chloroplast targeting signals, CcALKBH8 had signal peptide sequence targeting the plasma membrane (Supplementary Table 1), and CcALKBH9 had both nuclear and cytoplasm localization signals.
The cis-regulatory elements in the promoter region of Pigeonpea MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs genes were predicted using the 2kb upstream sequence retrieved from the available database for pigeon pea (LIS database). The identified cis-elements were then selected based on their role in growth and development, hormone response and stress. Growth and development regulatory elements like ARID, AT-Hook, Dof, NAC, LOB, SBP, HD-ZIP, PLATZ and FAR1 were selected. AT-Hook, B3, BBR-BPC, BES1 were selected for hormone response and AP2, bHLH, MADS Box, GATA, WOX, WRKY, C3H-Zinc finger, Dehydrin and VOZ were selected for stress response. Cis-elements varied between genes based on the presence and absence and also on the frequency by which they appear. For instance, both the MTs, viz. MTA and MTB, had almost equal number of cis-elements (Figure 6). MTs had the highest number of AP2 binding sequences followed by Dof (Figure 7). Between the two FIPs, FIPA had a greater number of elements as compared to FIPB. CG, FAR1 and HD-ZIP binding sequences were absent in FIPB but present in FIPA (Figure 6). In case of ALKBHs, CcALKBH9 had the highest number of cis-regulatory elements followed by CcALKBH8 and CcALKBH1B (Figure 6). MYB cis-regulatory binding elements were found to be the highest among ALKBHs followed by cis-regulatory binding elements for GATA, bZIP and Dof. (Figure 7). A table of cis-elements with their numbers for all three genes, viz, MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs, were provided in the Supplementary Files (Supplementary Table 3).
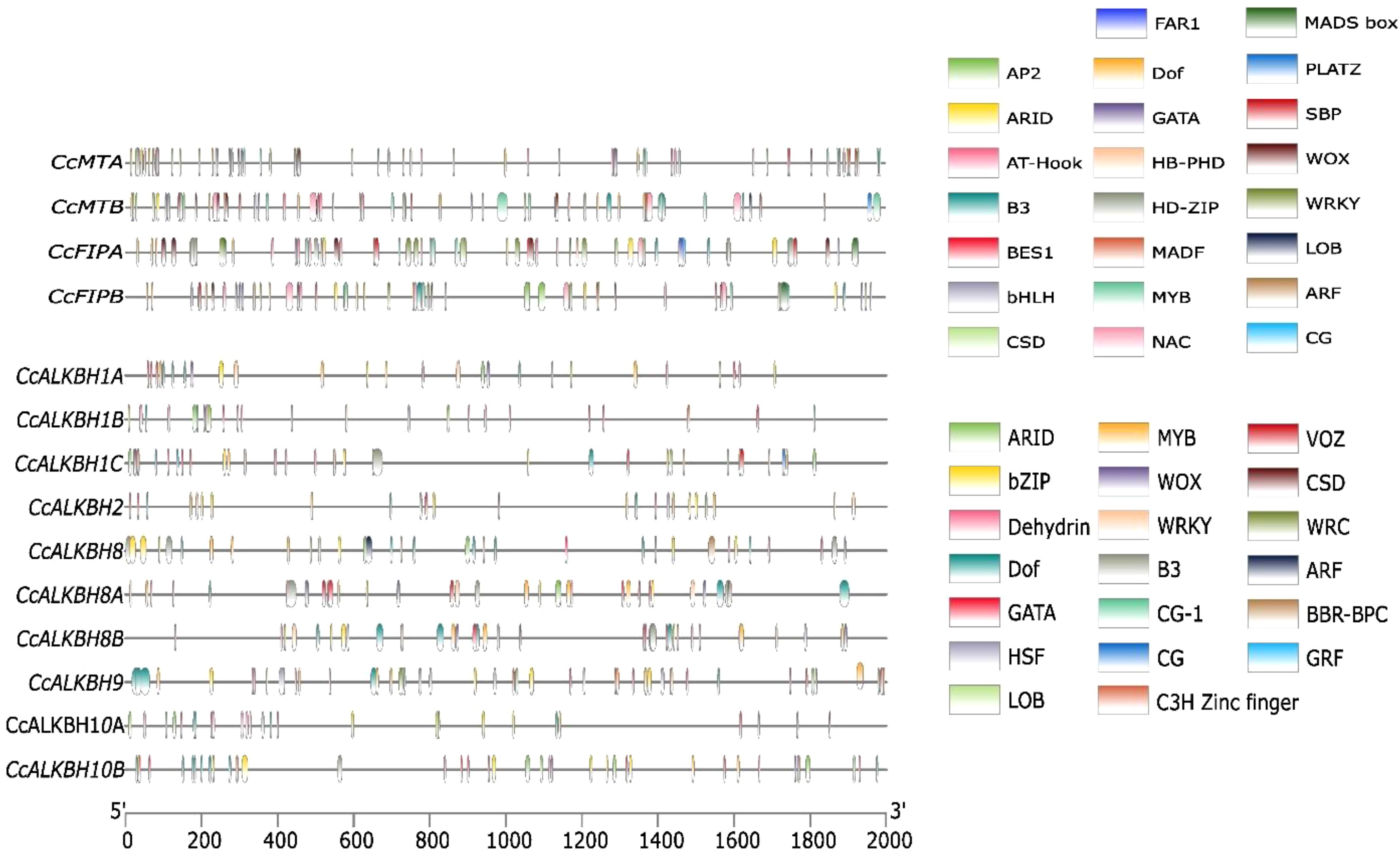
Figure 6. Cis-regulatory elements present in the promoter region of CcMTs, CcFIPs and CcALKBHs genes. Different colour lines represent different cis-regulatory elements.
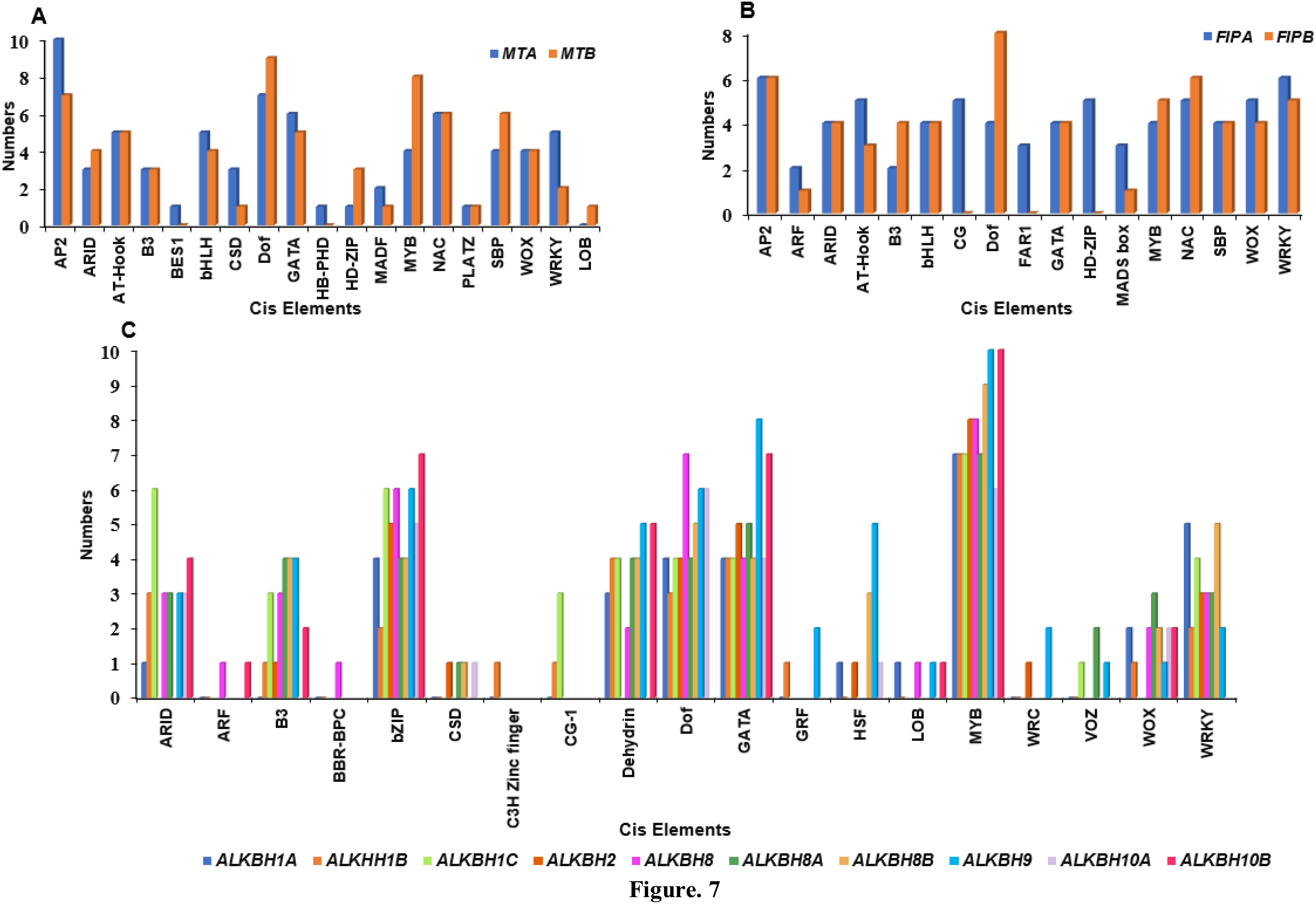
Figure 7. Graph showing enrichment of cis-regulatory elements in identified MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs. (A) Enrichment graph for MTA (blue bar) and MTB (Maroon bar). (B) enrichment bar for FIPA (blue bar) and FIPB (Maroon bar). (C) Graph representing ALKBHs identifies cis elements analysis. Ten different colour bars represent the ten ALKBHs genes in pigeon pea.
EpiSemble R-package was used to predict the m6A methylation pattern in MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs. This exercise was carried out to understand the epigenetic regulation of the genes. In case of MTs five and four methylation sites were found in the upstream 2 kb region (Figure 8). For FIPs, three and two sites were found for FIPA and FIPB, respectively (Figure 8). Further in case of ALKBHs, CcALKBH9 and CcALKBH10A had the highest number of methylation site (six), but the lowest methylation site was found for CcALKBH1B and CcALKBH10B (two) (Figure 8).
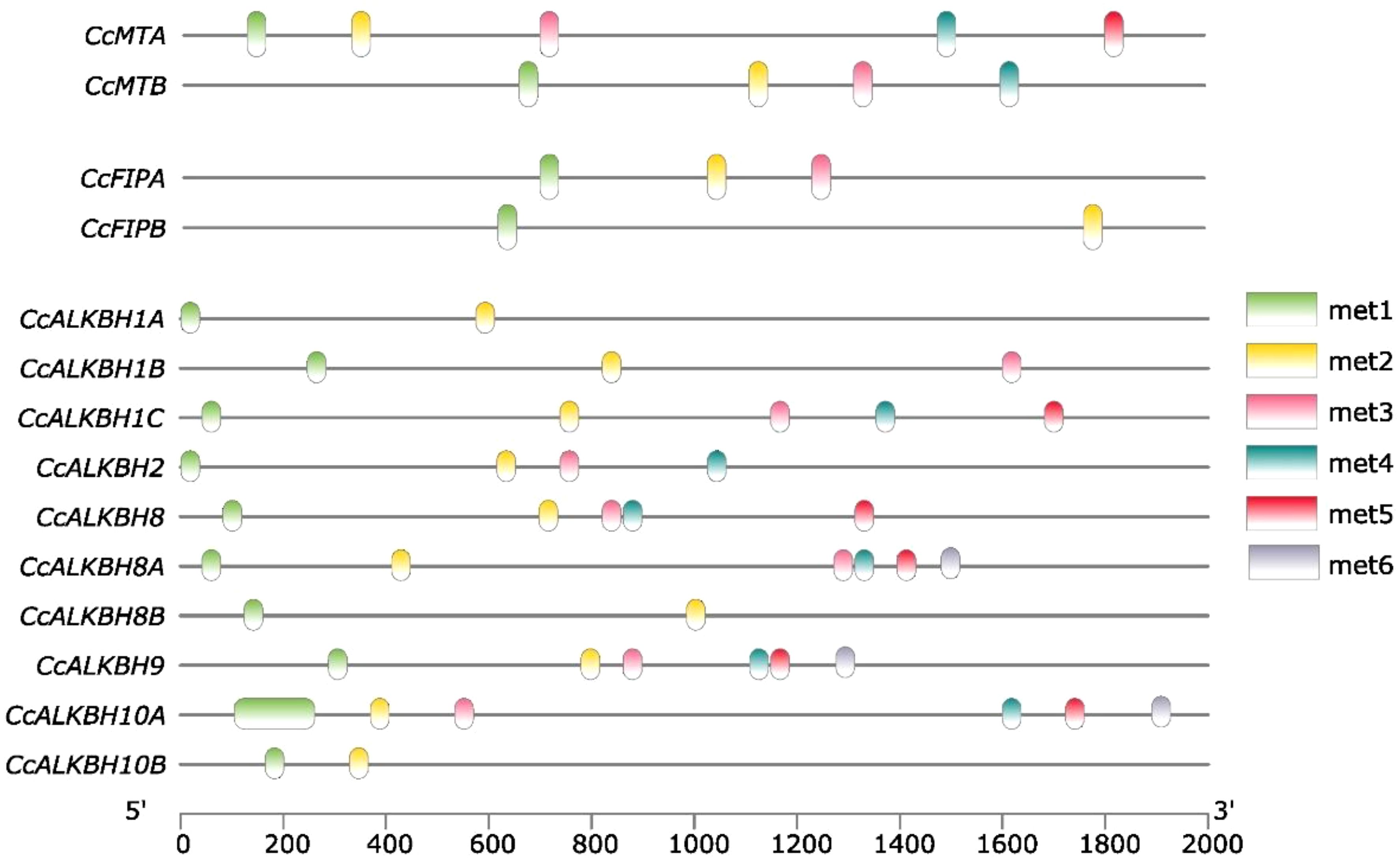
Figure 8. Predicted m6A-methylation position at identified cis-regulatory elements in the promoter region of CcMTs, CcFIPs and CcALKBHs genes. Different colour lines indicate the position of methylation.
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (q-PCR) was performed to understand the expression pattern of the identified MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs in pigeon pea. Different tissues (leaf, root, internode, shoot apical meristem, flower apical meristem and immature pod) were checked for the relative abundance of the transcripts (Figure 9). In case of MTs, it was found that overall expression of CcMTA was higher in the six selected tissues compared to that of CcMTB. The highest expression for MTA was observed in leaf tissues (~4.3 fold), while the highest expression for MTB was detected in FAM tissues (~3.7 fold). A similar kind of expression pattern was observed for these two genes in other tissues (root, internode, SAM and immature pod), but with varied expression levels i.e., CcMTA (~2.5 fold) had significantly higher expression compared to that of CcMTB (~1.0 fold) in root tissues. But, CcMTB (~3.7 fold) had more expression in SAM tissues compared to that of CcMTA (~3.1 fold) (Figure 9). In case of FIPs, both the genes, viz. CcFIPA and CcFIPB, showed the highest expression in leaf and internode. However, higher expression of CcFIPB was detected in the leaf (~6.0 fold) and root (~4.0 fold), and relatively more expression of CcFIPA was detected in FAM (~4.4 fold) tissues (Figure 9).
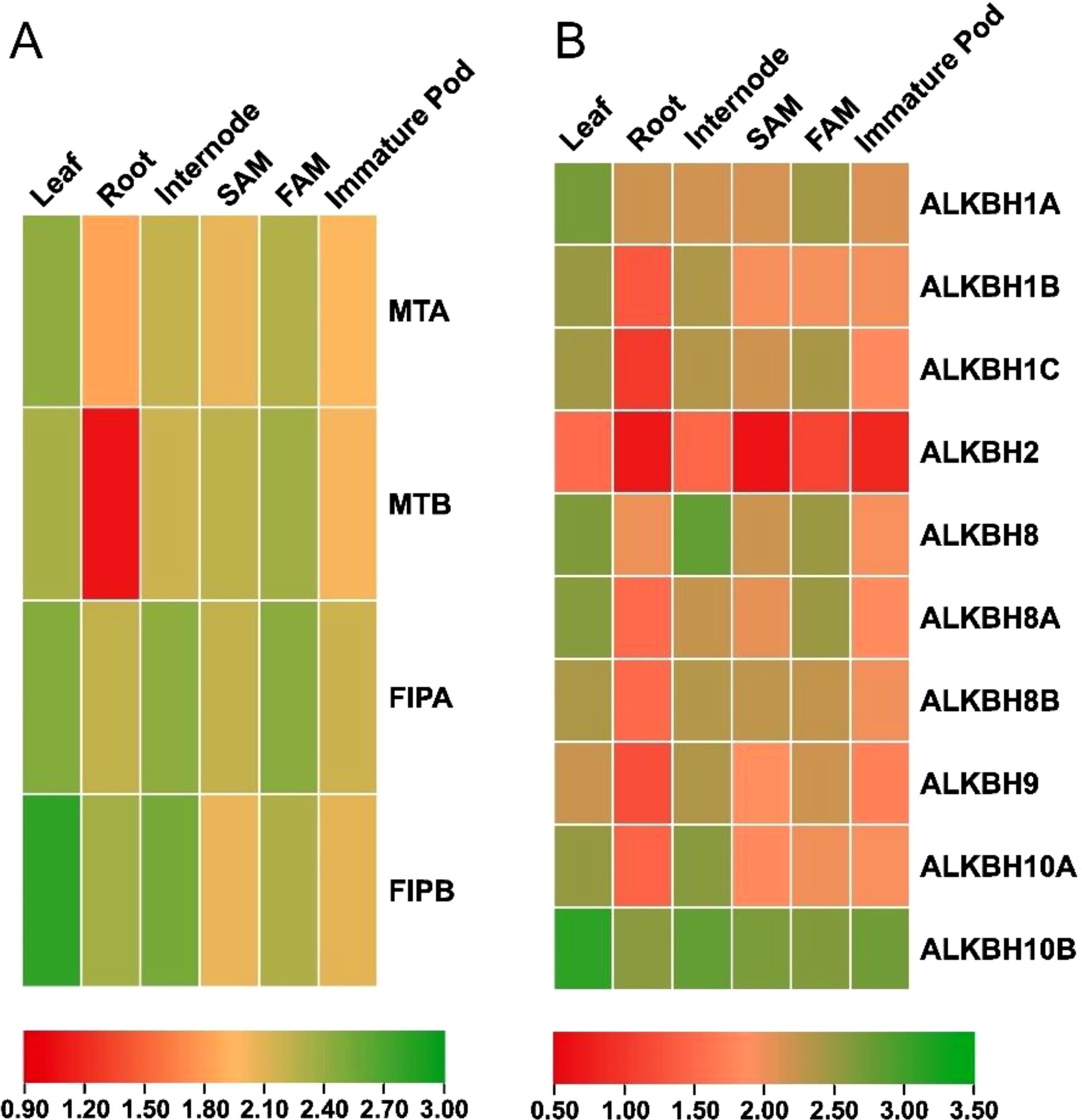
Figure 9. Expression analysis of the identified pigeon pea genes involved in methylation-demethylation. (A) Heat map analysis of pigeon pea MTs and FIPs genes. (B) Heat map analysis of pigeon pea ALKBHs genes. Column represents different plant tissues and rows represent the identified genes. Significant up-regulationin expression is shown in green, while significant down regulation in expression is shown in red.
Majority of the genes encoding ALKBHs displayed similar kind of expression patterns with the highest level of expression in leaf tissues, except for CcALKBH8 (~5.9 fold), CcALKBH9 (~4.1 fold) and CcALKBH10A (~4.9 fold), which showed the highest expression in internode tissue. The second highest expression of seven ALKBH genes was also detected in internode tissue, but three genes, viz. CcALKBH1A (~4.5 fold), CcALKBH1C (~4.3 fold) and CcALKBH8A (~4.5 fold) showed the second highest expression in FAM tissue. Among the ten ALKBH genes, CcALKBH10B had the highest expression in all the six tissues analyzed and CcALKBH2 had the lowest expression (Figure 9). Overall, the highest level of expression of genes encoding MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs was detected in leaf and the lowest expression in root tissues (Figure 9).
We wanted to see the expression level changes in the identified genes under various abiotic and biotic stresses. So, we subjected pigeon pea seedlings under various stresses and the morphological changes which was found is provided in Supplementary Figure 1 Further relative expression of MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs genes of pigeon pea during biotic and abiotic stresses was studied by qPCR analysis. During heat stress the highest induction in expression was observed in CcALKBH8 (~9.5 fold) followed by CcALKBH10B (~8.0 fold), but no induction in expression was found in CcALKBH2 (~1 fold) compared to that of control (Figure 10). Among the methyl transferase genes induction in expression was not so prominent, and about two-fold induction in expression was detected for CcMTA (~2.1fold) and CcMTB (~1.9 fold), whereas very low induction was observed for CcFIPB (~1.2 fold) and CcFIPA (~1.0 fold) during heat stress (Figure 10). Under drought stress, CcALKBH10B showed nine-fold more expression, followed by CcALKBH9 (~7.5 fold) and CcALKBH10A (~7.3 fold). CcALKBH2 (~1.0 fold) showed negligible induction (Figure 10). In case of methyl transferase genes, about four-fold induction in expression was observed in CcMTA (~4.3 fold) and CcMTB (~4.0 fold), but induction was not so prominent in CcFIPB (~1.1 fold) and CcFIPA (~1.0 fold) (Figure 10). The highest level of induction in gene expression of 13-fold was detected in CcALKBH10B (~13.3 fold) during salt stress. Two other genes, CcALKBH10A (~7.6 fold) and CcALKBH9 (~5.7 fold) showed 8- and 6-fold induction, respectively, during salt stress. Whereas, CcALKBH2 (~1) showed negligible induction (Figure 10). Two methyl transferase genes, CcMTB (~5.5 fold) and CcMTA (~5.3 fold), showed about five-fold more expression during salt stress. Again, CcFIPB (~1.6 fold) and CcFIPA (~1.0 fold) showed very little induction in expression during salt stress (Figure 10).
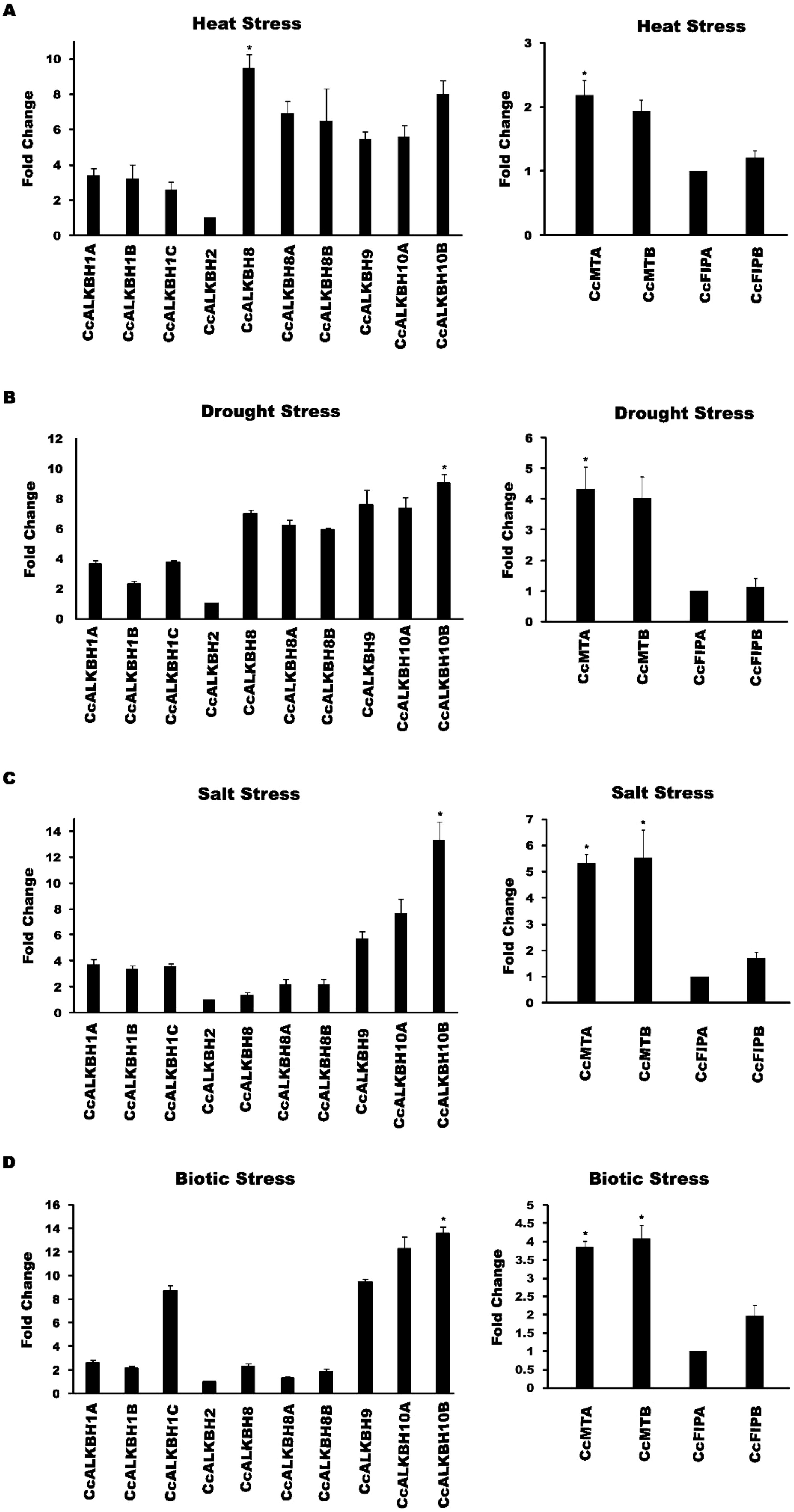
Figure 10. Graphical representations of fold change in expression of CcMTs, CcFIPs, CcALKBHs genes of pigeon pea under different stress conditions as revealed by qPCR analysis. (A) Heat stress induced change in expression of CcALKBHs (demethylase) and CcMTs & CcFIPs (methyl transferase). (B) Expression induction of CcALKBHs (demethylases) and CcMTs & CcFIPs (methyl transferases) during drought stress. (C) Salt stress-induced change in expression of CcALKBHs (demethylases) and CcMTs & CcFIPs (methyl transferases). (D) Fold change in expression of CcALKBHs (demethylases) and CcMTs & CcFIPs (methyl transferases) upon H. armigera infestation. Three biological and three technical replicates were taken for expression studies. Star mark indicates the significant difference between the different treatment. For the study of gene expression in abiotic and biotic stress condition three biological and three technical replicates were taken. And mean values were calculated and given error bar (standard error of means). So, Values are the mean ± SE obtained from three independent replicates. At 5% Least significant difference (LSD) was calculated to see the significance of different treatment effect and after that level of significance between and among the treatments in each experiment was checked by performing range test WASP package (AKMU ICAR-CCRI, GOA.).
A higher level of induction in gene expression, ranging from 13 to 9-fold, was detected in ALKBH genes in pigeon pea upon H. armigera infestation. The highest induction was observed in CcALKBH10B (~13.5 fold), followed by CcALKBH10A (~12.2 fold), CcALKBH9 (~9.4 fold) and CcALKBH1C (~8.6 fold). Again, CcALKBH2 (~1.0 fold) showed negligible induction during biotic stress (Figure 10). Less pronounced induction was observed for MTs genes with about four-fold induction in CcMTB (~4.0 fold) and CcMTA (~3.8 fold) followed by 2-fold induction in CcFIPB (~1.9 fold). However, induction in CcFIPA (~1.0 fold) was not significant (Figure 10).
Methylation and demethylation dynamics have a major role in epigenetic regulation of plants growth and development (Huong et al., 2020; Liang et al., 2020) and stress responses (Shoaib et al., 2021). The methylation of adenine (6-methyladenosine, m6A) in plants was initially seen in maize, oats, and wheat (Nichols, 1980). mRNAs move to various body parts where they act as potential signaling molecules. The translational state in maize is correlated with m6A methylation (Luo et al., 2020). Global m6A RNA methylation in seagrass has a significant role in circadian regulation and may have an impact on their photo-biological behavior (Ruocco et al., 2020). Furthermore, m6A methylation is required to maintain levels of mature miRNAs and their precursors, as evidenced by a report on its effects on microRNA (miRNA) production in Arabidopsis (Bhat et al., 2020). RNA methylation has a role in the mobility and transport of RNA in plants (Yang et al., 2018). Further m6A demethylation plays an important role in abiotic stress (heat, drought and salt stress) response (Huong et al., 2020). The methyl transferase (MT gene family) and demethylase genes (ALKBH gene family) have been identified in the model plant Arabidopsis (Wan et al., 2015) and a major crop plant, rice (Liang et al., 2020). However, the MTs and ALKBHs gene families are yet to be studied in pigeon pea, an important legume crop. In the present study, we have carried out a genome-wide analysis by comparing the alignments of homologous ALKBH protein sequences from Arabidopsis and pigeon pea to find out methylation and demethylation-related genes. A total of four methylation-related (two methyl transferases, MTs and two adaptors proteins for methylation; FIPA and FIPB) and 10 ALKBH (CcALKBH1A, CcALKBH1B, CcALKBH1C, CcALKBH2, CcALKBH18, CcALKBH8A, CcALKBH8B, CcALKBH9, CcALKBH10, and CcALKBH10B) family genes had been identified. The identified MTs and ALKBHs were similar in number as that of tomato and sugar beet genomes, but gene numbers were less than that of Arabidopsis, rice, wheat and Populus. This could be possible because of the evolutionary time gap.
Phylogenetic analysis is used for the identification of orthologous proteins (Bauwens et al., 2018). In the present study, MT and FIP genes were divided into two groups each (CcMTA, CcMTB and FIPA, FIPB) and the ALKBH genes were divided into four groups, viz. CcALKBH1A/1B/1C/2 like, CcALKBH8/8A/8B like, CcALKBH9 like and CcALKBH10A/10B like. Whereas in Arabidopsis, one more group was found, i.e., AtALKBH6 (Mielecki et al., 2012), which was absent in pigeon pea. Among the identified groups, CcALKBH9 and CcALKBH10A/10B are homologs of AtALKBH9A/9B/9C and AtALKBH10A/10B/10C, respectively, which were reported to carry out m6A demethylation (Duan et al., 2017; Martínez-Pérez et al., 2017). Therefore, it is perceived that CcALKBH9 and CcALKBH10A/10B could be putative m6A demethylases. However, this needs further validation. The gene structures of CcMTs, CcFIP and CcALKBHs were analyzed (Figure 3B). It has been found that gene structure for methyl transferase genes is more or less conserved. This conservation of gene architecture for MTs could be to ensure gene stability and integrity and to limit random changes. However, genes encoding FIPs (adaptor protein for methylase transferase) and ALKBHs have shown variation in gene structure. These changes might have occurred during evolution, and this could be the basis for different functions of the identified demethylase genes.
CcMTs had methyl transferase domain, which might be responsible for methylation. For the demethylation activity of ALKBH, one important factor is the presence of the Fe2+ binding domain required for its catalytic activity (Fedeles et al., 2015), and all the identified CcALKBHs contain the Fe2+ binding domain (Figure 4). This Fe2+ binding domain might mediate the oxidative demethylation of nucleic acids. Additionally, CcALKBH8 contains a methyl transferase domain, which might be responsible for both methylation and demethylation activity.
Further, CcALKBH8A contains an RRM (RNA recognition motif), which is required for tRNA binding and its modification (Pastore et al., 2012). ALKBH of the same sub-group has been found to exhibit a similar pattern in gene structure and conserved motifs, but variation was present among the sub-groups. The conserved motifs analysis of the identified MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs of pigeon pea revealed that a few motifs were conserved across genes but some motifs were unique to some particular genes. The variation in sequence structure and motifs might be responsible for changes in function over a period of time.
Upstream promoter sequences analysis of MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs revealed presence of many regulatory elements related to abiotic stress, hormones and light responses. The promoter sequence of MTs harbors more recognition elements for AP2 which has an important role in transcription stimulation in low temperature and water deficit (Sharoni et al., 2011). MTA and MTB promoter sequences also have presence of GATA and Dof recognition sequence. These elements have role in development and growth of plant (Cai et al., 2020). FIP promoter has a high number of recognition elements for Dof which has a role in phytohormone production, seed development and cold stress. Further, ALKBH upstream sequence has elements for MYB, which has recently been reported to have a role in m6A methylation modification (Xing et al., 2023).
The role of various MTs and ALKBHs has been characterized in a few plant species. MTA and MTB are reported to function in embryo development in Arabidopsis (Zhong et al., 2008). MTA has also been reported to impart drought tolerance in poplar by regulating the development of trichomes and roots through m6A methylation (Lu et al., 2020). FIP37 has been reported to play a role in endosperm and embryo development (Zhong et al., 2008). It was first identified in Arabidopsis as an interacting partner of MTA. Similarly, ALKBHs of Arabidopsis act on different substrates, i.e., ALKBH2 does repairing of 1-meA and 3-meC, ALKBH8 takes part in modification of tRNA by hydroxylating mcm5U to (S)-mchm5U. AtALKBH6 has been reported to have a role in abiotic stress response where it acts as negative regulator in cold and salt stress but a positive regulator in dehydration stress, viz, heat and drought (Huong et al., 2020). AtALKBH9B has been reported to modulate systemic viral infection by demethylating the alfalfa mosaic virus genome (Martínez-Pérez et al., 2017). AtALKBH10B has a role in floral transition by affecting the stability of key floral regulators, including FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE 3 (SPL3) and SPL9 which results in early flowering (Duan et al., 2017). AtALKBH10B is also involved in drought tolerance, where it affects m-RNA stability through demethylation of m6A (Han et al., 2023). It also modulates ABA response during seed germination (Tang et al., 2021) and was found to impart tolerance to salt stress in Arabidopsis (Shoaib et al., 2021). A recent study showed that in case of cotton, GhALKBH10B affects the mRNA stability of genes linked to photosynthesis and GhSnRK2;3, which leads to a negative response to drought stress (Zhang et al., 2024). In case of tomato, SlALKBH2 has been reported to have RNA demethylase activity, which delays fruit ripening (Zhou et al., 2019).
The qPCR analysis of the identified MTs, FIPs and ALKBHs revealed the changes in the expression level of genes in six different tissues (Leaf, Root, Internode, SAM, FAM and Immature pod). In case of MTs, CcMTA has a slightly higher expression as compared to CcMTB. Similarly, CcFIPB showed comparatively higher expression than that of CcFIPA. So, CcMTA and CcMTB could be the probable methyl transferase genes in pigeon pea, and CcFIPB might be the adaptor protein that stabilizes the methyl transferase components during methylation process. However, further validation is needed to confirm their function.
AtALKBH9B and AtALKBH10B have been reported as the major demethylases in Arabidopsis (Duan et al., 2017; Martínez-Pérez et al., 2017). The highest expression of CcALKBH10B was detected in different tissues of pigeon pea compared to that of CcALKBH8, CcALKBH10A and CcALKBHB9. Hence, it could be possible that CcALKBH10B could be primarily involved in demethylation in pigeon pea as perceived from the expression analysis.
Expression profiling of the CcMTs, CcFIPs and CcALKBHs under abiotic (Heat, Drought and salt) and biotic stress (H. armigera) revealed a similar trend of induction in expression. CcMTA and CcMTB showed similar patterns of induction under both the biotic and abiotic stresses. Similarly, a high level of induction in expression was observed in CcALKBH8, CcALKBH10A and CcALKBH10B under both the biotic and abiotic stress conditions. This indicated that both CcMTA and CcMTB could be the major methyl transferase genes, and CcALKBH8, CcALKBH10A and CcALKBH10B could be the major demethylase genes in pigeon pea. Arabidopsis demethylase gene, AtALKBH10B, was reported to be involved in drought and salt stress tolerance by affecting mRNA stability through demethylation of m6A (Shoaib et al., 2021; Han et al., 2023).
Methylation demethylation dynamics plays an important role in imparting abiotic (like heat, drought and salt stress) and biotic (like against viral infection) tolerance. However, these genes and their function yet to be explored in pigeon pea. Hence, we conducted initial study to find out the different methyltrasferase and demethylase genes present in the pigeon pea genome and their expression pattern in different tissues and stress conditions. Now, from this study the genes which are expressing in response to stress will be selected for functional analysis. Hence this study has its importance by providing the basic knowledge of different methyltransferase and demethylase gene present in pigeon pea and their expression level which will finally help in selection and manipulation of genes for imparting abiotic and biotic stress tolerance.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
PK: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SB: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. KV: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Project administration. JT: Writing – review & editing. KP: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. KS: Writing – review & editing, Visualization. MB: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. GR: Writing – review & editing, Resources. RS: Resources, Writing – review & editing. DP: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Supervision.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The work was supported by in-house funding by ICAR-NIPB, New Delhi.
PK acknowledges the IARI Post Graduate School for providing fellowship for her Ph. D. study. We would like to acknowledge ICAR- National Institute for Plant Biotechnology, New Delhi, and ICAR- Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi for providing Research facilities and funds and other supports for this work.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1521758/full#supplementary-material
Bakala, H. S., Devi, J., Singh, G., Singh, I. (2024). Drought and heat stress: insights into tolerance mechanisms and breeding strategies for pigeon pea improvement. Planta. 259, 123. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04401-6
22Bauwens, E., Joosten, M., Taganna, J., Rossi, M., Debraekeleer, A., Tay, A., et al. (2018). In silico proteomic and phylogenetic analysis of the outer membrane protein repertoire of gastric Helicobacter species. Scientific Reports 8(1), 15453.
Bhat, S. S., Bielewicz, D., Gulanicz, T., Bodi, Z., Yu, X., Anderson, S. J. (2020). mRNA adenosine methylase (MTA) deposits m6A on pri-miRNAs to modulate miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 21785–21795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2003733117
Bhattacharjee, S., Bhowmick, R., Paul, K., Venkat Raman, K., Jaiswal, S., Tilgam, J., et al. (2023). Identification, characterization, and comprehensive expression profiling of floral master regulators in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan [L.] Millspaugh). Funct. Integr. Genomics 23, 311. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01236-4
Cai, M., Lin, J., Li, Z., Lin, Z., Ma, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2020). Allele specific expression of Dof genes responding to hormones and abiotic stresses in sugarcane. PloS One 15, e0227716. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq196
Cantara, W. A., Crain, P. F., Rozenski, J., McCloskey, J. A., Harris, K. A., Zhang, X., et al. (2010). The RNA modification database, RNAMDB. Nucleic Acids Res. 10, D195–D201. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1028
Choudhary, A. K., Sultana, R., Pratap, A., Nadarajan, N., Jha, U. C. (2011). Breeding for abiotic stresses in pigeon pea. J. Food Legumes. 24, 165–174.
Dokka, N., Tyagi, S., Ramkumar, M. K., Rathinam, M., Senthil, K., Sreevathsa, R. (2024). Genome-wide identification and characterization of DIRIGENT gene family (CcDIR) in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan L.) provide insights on their spatial expression pattern and relevance to stress response. Gene 914, 148417. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148417
Duan, H. C., Wei, L. H., Zhang, C., Wang, Y., Chen, L., Lu, Z., et al. (2017). ALKBH10B is an RNA N 6-methyladenosine demethylase affecting Arabidopsis floral transition. Plant Cell 29, 2995–3011. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00912
FAOSTAT. (2022). https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home.
Fedeles, B. I., Singh, V., Delaney, J. C., Li, D., Essigmann, J. M. (2015). The AlkB family of Fe (II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases: repairing nucleic acid alkylation damage and beyond. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 20734–20742. doi: 10.1074/jbcR115.656462
Greer, E. L., Blanco, M. A., Gu, L., Sendinc, E., Liu, J., Aristizábal-Corrales, D., et al. (2015). DNA methylation on N6-adenine in C. elegans. Cell 161, 868–878. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.005
Han, R., Shoaib, Y., Cai, J., Kang, H. (2023). ALKBH10B-mediated m6A demethylation is crucial for drought tolerance by affecting mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 209, 105–306. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2023.105306
Haussmann, I. U., Bodi, Z., Sanchez-Moran, E., Mongan, N. P., Archer, N., Fray, R. G. (2016). m6A potentiates Sxl alternative pre-mRNA splicing for robust Drosophila sex determination. Nature 540, 301–304. doi: 10.1038/nature20577
Hu, J., Manduzio, S., Kang, H. (2019). Epitranscriptomic RNA methylation in plant development and abiotic stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00500
Huong, T. T., Ngoc, L. N., Kang, H. (2020). Functional characterization of a putative RNA demethylase ALKBH6 in Arabidopsis growth and abiotic stress responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 6707. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186707
Iyer, L. M., Zhang, D., Aravind, L. (2016). Adenine methylation in eukaryotes: Apprehending the complex evolutionary history and functional potential of an epigenetic modification. Bioessays 38, 27–40. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500104
Kataoka, H. I., Yamamoto, Y. O., Sekiguchi, M. U. (1983). A new gene (alkB) of Escherichia coli that controls sensitivity to methyl methane sulfonate. J. Bacteriol 153, 1301–1307. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1301-1307.1983
Kyte, J., Doolittle, R. F. (1982). A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 157, 105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0
Liang, Z., Riaz, A., Chachar, S., Ding, Y., Du, H., Gu, X. (2020). Epigenetic modifications of mRNA and DNA in plants. Mol. Plant 3, 14–30. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.12.007
Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2– ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.126
Lu, L., Zhang, Y., He, Q., Qi, Z., Zhang, G., Xu, W., et al. (2020). MTA, an RNA m6A methyltransferase, enhances drought tolerance by regulating the development of trichomes and roots in poplar. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 2462. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072462
Luo, J. H., Wang, Y., Wang, M., Zhang, L. Y., Peng, H. R., Zhou, Y. Y. (2020). Natural variation in RNA m6A methylation and its relationship with translational status. Plant Physiol. 182, 332–344. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00987
Marcinkowski, M., Pilžys, T., Garbicz, D., Steciuk, J., Zugaj, D., Mielecki, D., et al. (2020). Human and Arabidopsis alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase homolog proteins—New players in important regulatory processes. IUBMB Life 72, 1126–1144. doi: 10.1002/iub.2276
Martínez-Pérez, M., Aparicio, F., López-Gresa, M. P., Bellés, J. M., Sánchez-Navarro, J. A., Pallás, V. (2017). Arabidopsis m6A demethylase activity modulates viral infection of a plant virus and the m6A abundance in its genomic RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 10755–10760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1703139114
Meyer, K. D., Jaffrey, S. R. (2014). The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cel Bio 15, 313–326. doi: 10.1038/nrm3785
Mi, J., Ren, X., Shi, J., Wang, F., Wang, Q., Pang, H., et al. (2024). An insight into the different responses to salt stress in growth characteristics of two legume species during seedling growth. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1342219
Miao, Z., Zhang, T., Qi, Y., Song, J., Han, Z., Ma, C. (2020). Evolution of the RNA N 6-methyladenosine methylome mediated by genomic duplication. Plant Physiol. 182, 345–360. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00323
Mielecki, D., Zugaj, DŁ., Muszewska, A., Piwowarski, J., Chojnacka, A., Mielecki, M., et al. (2012). Novel AlkB dioxygenases—alternative models for in silico and in vivo studies. PloS One 7, e30588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030588
Nichols, J. L. (1980). N6-methyladenosine in maize poly(A)-containing RNA. Plant Sci. Lett. 15, 357–361. doi: 10.1016/0304-4211(79)90141
Ougland, R., Rognes, T., Klungland, A., Larsen, E. (2015). Non-homologous functions of the AlkB homologs. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 494–504. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjv029
Pastore, C., Topalidou, I., Forouhar, F., Yan, A. C., Levy, M., Hunt, J. F. (2012). Crystal structure and RNA binding properties of the RNA recognition motif (RRM) and AlkB domains in human AlkB homolog 8 (ABH8), an enzyme catalyzing tRNA hyper modification. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 2130–2143. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.286187
Ping, X. L., Sun, B. F., Wang, L. U., Xiao, W., Yang, X., Wang, W. J., et al. (2014). Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 24, 177–189. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.3
Ruocco, M., Ambrosino, L., Jahnke, M., Chiusano, M. L., Barrote, I., Procaccini, G. (2020). m6A RNA methylation in marine plants: First insights and relevance for biological rhythms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1–21. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207508
Sharoni, A. M., Nuruzzaman, M., Satoh, K., Shimizu, T., Kondoh, H., Sasaya, T., et al. (2011). Gene structures, classification and expression models of the AP2/EREBP transcription factor family in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 52, 344–360. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq196
Shen, L., Liang, Z., Gu, X., Chen, Y., Teo, Z. W., Hou, X., et al. (2016). N6-methyladenosine RNA modification regulates shoot stem cell fate in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 38, 186–200. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.06.008
Shoaib, Y., Hu, J., Manduzio, S., Kang, H. (2021). Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase homolog 10B, an N6-methyladenosine mRNA demethylase, plays a role in salt stress and abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant 173, 1078–1089. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13505
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Kumar, S. (2021). MEGA 11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38 (7), 3022–3027. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
Tang, J., Yang, J., Duan, H., Jia, G. (2021). ALKBH10B, an mRNA m6A demethylase, modulates ABA response during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.712713
Trewick, S. C., Henshaw, T. F., Hausinger, R. P., Lindahl, T., Sedgwick, B. (2002). Oxidative demethylation by Escherichia coli AlkB directly reverts DNA base damage. Nature 419, 174–178. doi: 10.1038/nature00908
Wan, Y., Tang, K., Zhang, D., Xie, S., Zhu, X., Wang, Z., et al. (2015). Transcriptome-wide high-throughput deep m6A-seq reveals unique differential m6A methylation patterns between three organs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Biol. 16, 1–26. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0839-2
Wang, X., Lu, Z., Gomez, A., Hon, G. C., Yue, Y., Han, D. (2014). N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 505, 117–120. doi: 10.1038/nature12730
Wei, L. H., Song, P., Wang, Y., Lu, Z., Tang, Q., Yu, Q., et al. (2018). The m6A reader ECT2 controls trichome morphology by affecting mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 30, 968–985. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00934
Xing, K., Liu, Z., Liu, L., Zhang, J., Qanmber, G., Wang, Y., et al. (2023). N6-methyladenosine mRNA modification regulates transcripts stability associated with cotton fiber elongation. Plant J. 115 (4), 967–985. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16274
Yang, Y., Hsu, P. J., Chen, Y. S., Yang, Y. G. (2018). Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: Writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 28, 616–624. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0040-8
Yue, H., Nie, X., Yan, Z., Weining, S. (2019). N6-methyladenosine regulatory machinery in plants: composition, function and evolution. Plant Biotechnol. J. 17, 1194–1208. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13149
Zhang, D., Li, M., Chen, C., Wang, Y., Cheng, Z., Li, W., et al. (2024). Downregulation of GhALKBH10B improves drought tolerance through increasing the stability of photosynthesis related-and ABA signalling pathway genes in cotton. Environ. Exp. Bot. 7, 105687. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2024.105687
Zhang, M., Yang, S., Nelakanti, R., Zhao, W., Liu, G., Li, Z., et al. (2020). Mammalian ALKBH1 serves as an N6-mA demethylase of unpairing DNA. Cell Res. 30, 197–210. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0237-5
Zhang, F., Zhang, Y. C., Liao, J. Y., Yu, Y., Zhou, Y. F., Feng, Y. Z., et al. (2019). The subunit of RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase OsFIP regulates early degeneration of microspores in rice. PloS Genet. 15, e1008120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008120
Zhong, S., Li, H., Bodi, Z., Button, J., Vespa, L., Herzog, M., et al. (2008). MTA is an Arabidopsis messenger RNA adenosine methylase and interacts with a homolog of a sex-specific splicing factor. Plant Cell 20, 1278–1288. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.058883
Keywords: methylation, demethylation, pigeon pea, m6A modification, ALKBHs
Citation: Kumari P, Bhattacharjee S, Venkat Raman K, Tilgam J, Paul K, Senthil K, Baaniya M, Rama Prashat G, Sreevathsa R and Pattanayak D (2025) Identification of methyltransferase and demethylase genes and their expression profiling under biotic and abiotic stress in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan [L.] Millspaugh). Front. Plant Sci. 15:1521758. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1521758
Received: 05 November 2024; Accepted: 18 December 2024;
Published: 16 January 2025.
Edited by:
Gurjeet Singh, Texas A and M University, United StatesReviewed by:
Viswanathan Satheesh, Iowa State University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Kumari, Bhattacharjee, Venkat Raman, Tilgam, Paul, Senthil, Baaniya, Rama Prashat, Sreevathsa and Pattanayak. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Debasis Pattanayak, ZGViYXNpc3BhdHRhbmF5YWtAeWFob28uY28uaW4=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.