- 1Shandong Key Laboratory of Eco-Environmental Science for the Yellow River Delta, Shandong University of Aeronautics, Binzhou, Shandong, China
- 2School of Geographical Sciences, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, Jilin, China
- 3Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, Jilin, China
Isotopic signatures offer new methods, approaches, and perspectives for exploring the ecological adaptability and functions of plants. We examined pattern differences in the isotopic signatures (δ13C, δ15N, δ34S) of Spartina alterniflora across varying plant life-death status along geographic clines. We extracted 539 sets of isotopic data from 57 publications covering 267 sites across a latitude range of over 23.8° along coastal wetlands. Responses of isotopic signatures to climate drivers (MAT and MAP) and the internal relationships between isotopic signatures were also detected. Results showed that the δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S of S. alterniflora were -13.52 ± 0.83‰, 6.16 ± 0.14‰, and 4.01 ± 6.96‰, with a range of -17.44‰ to -11.00‰, -2.40‰ to 15.30‰, and -9.60‰ to 15.80‰, respectively. The latitudinal patterns of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in S. alterniflora were shaped as a convex curve, a concave curve, and an increasing straight line, respectively. A decreasing straight line for δ13C within the ranges of MAT was identified under plant life status. Plant life-death status shaped two nearly parallel decreasing straight lines for δ34S in response to MAT, resulting in a concave curve of δ34S for live S. alterniflora in response to MAP. The δ15N of S. alterniflora significantly decreased with increasing δ13C of S. alterniflora, except for plant death status. The δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S of S. alterniflora are consistent with plant height, stem diameter, leaf traits, etc, showing general latitudinal patterns closely related to MAT. Plant life-death status altered the δ15N (live: 6.55 ± 2.23‰; dead: -2.76 ± 2.72‰), latitudinal patterns of S. alterniflora and their responses to MAT, demonstrating strong ecological plasticity and adaptability across the geographic clines. The findings help in understanding the responses of latitudinal patterns of the δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S isotope signatures of S. alterniflora in response plant life-death status, and provide evidence of robust ecological plasticity and adaptability across geographic clines.
1 Introduction
Biological invasion is a global problem that poses a threat to local plant communities, alters the patterns of macrobenthic animals, affects the habitat and food sources of migratory birds, and has negative effects on material circulation, energy flow, socio-economic activities, and other aspects of coastal wetland ecosystems (Sampaio et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021a; Li et al., 2022; He et al., 2023). Most invasive species can survive in large geographic areas where they germinate, colonize, grow, reproduce, expand, and develop corresponding adaptation strategies across latitudes (Liu et al., 2017 and 2022; Chen et al., 2023). Latitudinal gradients in abiotic factors, including temperature, precipitation, and soil physicochemical properties, increase environmental heterogeneity, shape the plant traits of invasive species, and form latitudinal patterns of plant communities coexisting with local and invasive species (Kirwan et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2020; Cheng et al., 2022). Altered plant traits (including plant height, stem diameter, leaf traits, specific leaf area, dry matter content, shoot density, productivity, reproductive traits, ecostoichiometry, etc.) through phenotypic plasticity promote the probability of successful invasion by invasive species, recognized as important mechanisms for invasion (Maron et al., 2004; Kirwan et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021a; Chen et al., 2022; Cheng et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Zheng et al., 2022). In recent decades, research on plant traits has made good progress, and the introduction of new technologies, represented by stable isotopes, has provided new methods and ideas for exploring the mechanisms of invasive species (Hill et al., 2018; Watson et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2023). Latitudinal patterns of isotope signatures in invasive plants across coastal wetlands have become a new topic.
Stable isotopes, a type of natural isotopes existing in organic organisms, are non-radioactive and stable (Lin and da SL Sternberg, 1993; Feng et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2023). They typically possess a relatively long half-life and are not limited by their duration. Stable isotopes offer numerous advantages, including easy operation, high sensitivity, safety, non-toxicity, rapid detection, accurate results, and relative stability (Spivak and Reeve, 2015). They primarily exploit the same physiological and biochemical properties of labeled compounds and their corresponding non-labeled compounds to trace the intricate and variable chemical reactions and biological processes in organic organisms. This facilitates the observation of metabolic patterns and bioavailability of the tracked substance in the organism by monitoring changes in isotopic ratios (Bai et al., 2012; Kou et al., 2020; Xia et al., 2023a). Carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and sulfur (S) are essential components in plant tissues, and their corresponding stable isotopes are closely associated with plant physiological metabolism, growth, and development processes (Hill et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2021; Wittyngham et al., 2023; Xiong et al., 2023). Plant photosynthesis plays a crucial role in the fractionation effect of δ13C. The δ13C can be utilized to study the chemical development process of biogeography, the allocation of photosynthetic carbon in plants, the identification of plant photosynthetic pathways, and the evaluation of water use efficiency and biomass changes in plants characterizing the litter decomposition process (Liu et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2021a; Xia et al., 2023b). The δ15N isotope is commonly employed to assess the utilization efficiency, loss, nutrient uptake, and transport process of nitrogen elements in plant organisms and even plant communities (Hill et al., 2018; Xia et al., 2023a). The δ34S isotope in plants can provide crucial information on the absorption of atmospheric sulfides by plants and the metabolism of sulfur in plants, offering a powerful tool for a deeper understanding of the interaction between organisms and their living environment (Guo et al., 2020; Jinks et al., 2020; Guiry et al., 2022). Stable isotopes, especially their local and global patterns, play a significant indicative role in monitoring short-term and long-term environmental changes in the biosphere. Applying stable isotopes in the study of invasive plant species in coastal wetlands and understanding the information reflected by isotopic changes contribute greatly to revealing the invasion mechanism.
Spartina alterniflora, recognized as a typical invasive plant, is a perennial monocotyledonous plant belonging to the Poaceae family (Cheng et al., 2022; Jia et al., 2022). It possesses extensive roots and robust reproductive capabilities, commonly growing in the intertidal zones of estuaries, bays, coastal mudflats, and tidal-influenced beaches worldwide (Humphreys et al., 2021; Mao et al., 2023). S. alterniflora plays a significant role in ecological and economic benefits, including carbon and nitrogen fixation, wind and wave prevention, embankment and beach protection, soil improvement, and the expansion of animal and plant habitats (Lu et al., 2020; Meng et al., 2020). However, the negative ecological impact of S. alterniflora invasion is becoming increasingly severe, affecting the structure and composition of biological communities. This invasion damages the composition and transmission of the food chain in coastal wetland ecosystems, leading to extreme instability in the ecological environment of coastal wetlands (Jinks et al., 2020; Li et al., 2022; Jia et al., 2022). Due to its high tolerance to salinity, rapid growth rate, and extensive range, S. alterniflora alters surrounding environmental factors by secreting a significant amount of salt into the environment during high-intensity transpiration. Simultaneously, it is an invasive species well-adapted to the coastal wetland environment, suppressing the growth of local plants in the surrounding environment by seizing living space and resources, thereby changing the structure and function of wetlands (Liu et al., 2017; Mao et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2020; Humphreys et al., 2021). Previous studies on S. alterniflora have focused on the invasion mechanism, physiological responses under different driving forces, competition mechanisms between native and invasive species, ecological prevention and control measures, and comprehensive analysis and utilization of biomass energy (Courtney et al., 2016; Ma et al., 2019; Hessini et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022). Some studies have explored S. alterniflora stable isotopes, systematically analyzing element dynamics during the decomposition process of S. alterniflora residues and changes in plant-soil element pools and nutrient transport processes. He et al. (2023) compared the trophic contribution of S. alterniflora to the macrozoobenthos between the dense S. alterniflora area and adjacent tidal bare mudflat in the Hepu coast by analyzing δ13C and δ15N. Wang et al. (2024) found that S. alterniflora invasion increased the values of δ13C and δ15N, as well as organic matter decomposition. Wu et al. (2024) used a 15N stable isotope dilution technique to investigate sediment gross N mineralization and NH4+ immobilization under aerobic and anaerobic conditions in S. alternifora communities. However, there has been little attention to the distribution pattern and influencing factors of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in S. alterniflora across latitudes (Kinney and Valiela, 2018; Chen et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021 and Zhang et al., 2021). Additionally, there is minimal research on the impact of the life-death status of S. alterniflora on isotopic distribution.
Here, we compared the latitudinal patterns of the isotope signatures (δ13C, δ15N, δ34S) of S. alterniflora and their responses to climate drivers under different plant life-death status by collecting isotopic data from literature records at 267 sites across coastal wetlands. Building upon previous findings on plant traits of S. alterniflora, we tried to address the following questions: (1) Do the latitudinal patterns of the isotope signatures of S. alterniflora vary with life-death status? (2) How is the geographical variation in S. alterniflora isotope signature influenced by mean annual temperature (MAT) and mean annual precipitation (MAP)? (3) Have strong coupling relationships formed between the isotope signatures of S. alterniflora? We hypothesized that: (1) The latitudinal patterns of the S. alterniflora isotope signature under the life status would outperform the dead status; (2) Geographical variation in S. alterniflora isotope signature would be driven by MAT and MAP; (3) The δ15N and δ34S of S. alterniflora would respond to the corresponding δ13C in a linear or nonlinear form.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Literature sources and screening
We conducted a systematic literature search for peer-reviewed publications using the China National Knowledge Infrastructure and Web of Science databases. The search term “Spartina alterniflora” was employed on both websites to compile a database of the δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S values of S. alterniflora. We gathered 13540 published papers and dissertations from January 1970 to September 2023. Additionally, we identified relevant literature in Chinese or English related to the δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S of S. alterniflora through manual screening methods. During the screening process, publications without latitude and longitude (or map, or location name), those with blurry images, or experiments conducted in greenhouses or involving isotope labeling processing about δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S of S. alterniflora were excluded. After removing duplicates, the literature was refined to 57 publications, comprising 48 publications for δ13C (1976–2023), 31 publications for δ15N (1985–2022), and 8 publications for δ34S (1982–2019) of S. alterniflora (Figure 1). The number of corresponding publications increased over time (Supplementary Figure S1).
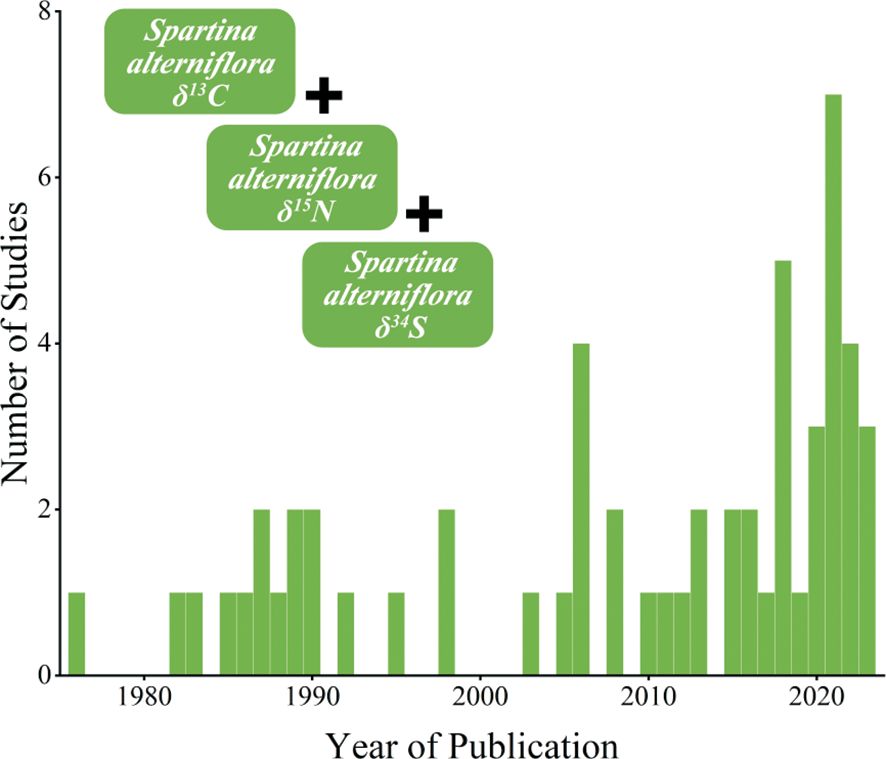
Figure 1 Number of relevant studies included in this study (N=57) published per year (1978–2023). The figure style reference Mason et al, 2023.
2.2 Data extraction and proceeding
We extracted data from 57 publications using three methods: firstly, by recording the values of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S of S. alterniflora from tables; secondly, by measuring values from figures using Digitizer in Origin software; and thirdly, by collecting data from Supplementary Materials accompanying the publications. The criteria for data extraction included values for δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in various plant parts such as root (fine root, rhizome, coarse roots), stem (aboveground stem, belowground stem), leaf, litter (fresh litter, litter, leaf litter, plant detritus), standing dead, and dead biomass of S. alterniflora. Additionally, the criteria specified that the data should pertain to natural plants or samples collected in the field, be unlabeled with isotopes, or represent the initial values before isotope labeling. Furthermore, the values of isotope signatures were required to be expressed in parts per thousand (‰) and calculated following a specified equation (Equation 1).
Where X is 13C, 15N, or 34S, and R is 13C/12C, 15N/14N, 34S/32S, respectively (Wooller et al., 2003a; Gao et al., 2018; Nelson et al., 2019).
To make the information contained in the database more comprehensive, we recorded the following variables for each value: the first author, year of publication, study site, month or season in the year of sampling, latitude, longitude, treatment, plant tissue (root, stem, leaf), live or dead state, reference.
If the latitude and longitude information for the study sites was not available in the publication, we opted to identify them on the Ovital map, primarily using the map of sampling points and secondarily relying on the name of the study site. In specific cases, we distinguished between live S. alterniflora by examining green leaves and categorized plant senescent tissue as dead S. alterniflora.
We collected climate data for each sample site from the Worldclim online repository (https://www.worldclim.org/data/index.html; Fick & Hijmans, 2017). The mean annual temperature (MAT) and mean annual precipitation (MAP) were calculated based on the extracted data from Worldclim 2.1 referencing the latitude and longitude of sample sites (Figure 2).
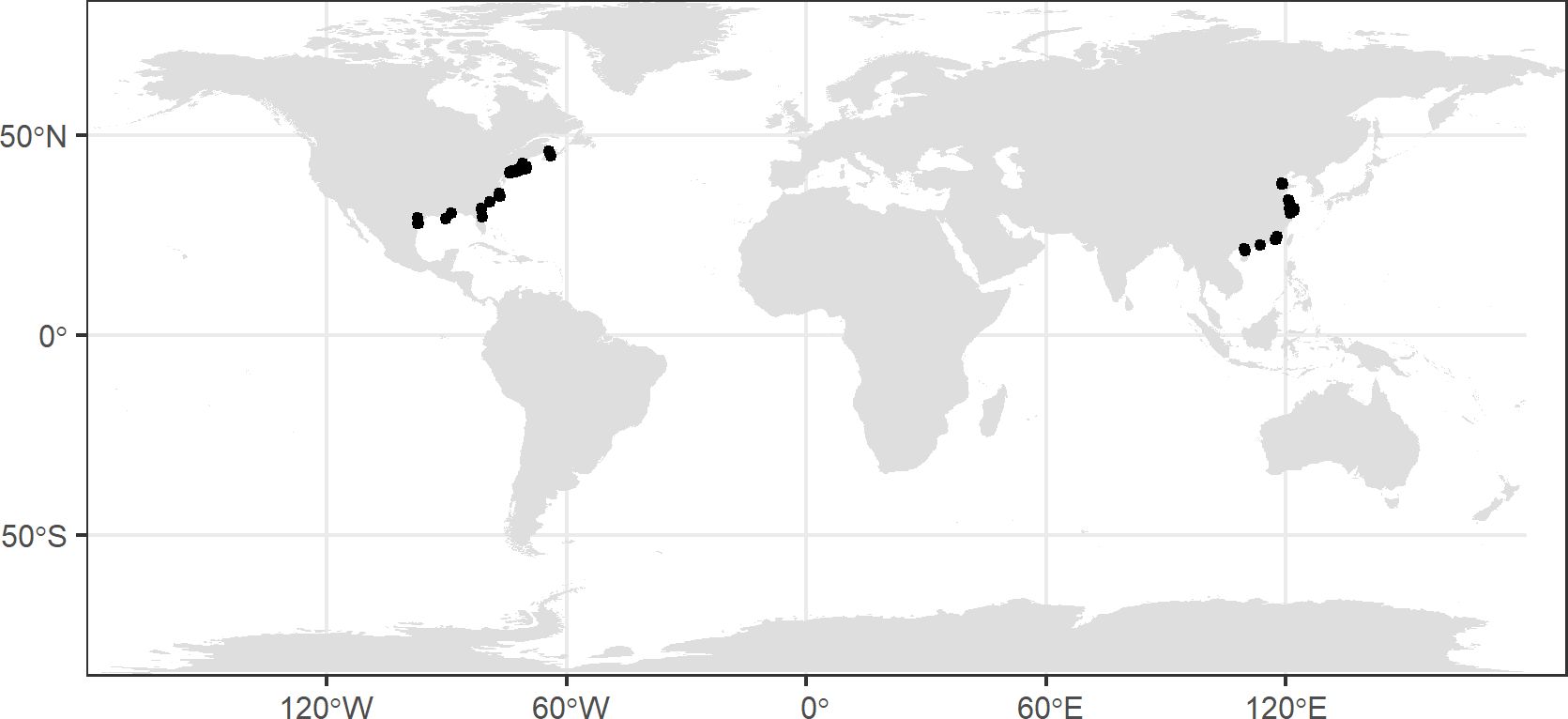
Figure 2 Global distribution of the sample sites of the isotope signature of Spartina alterniflora..
2.3 Statistical analysis
The distribution and homogeneity of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S isotope signature (δX) in S. alterniflora were assessed in R before conducting further analyses (Supplementary Figure S2). A t-test was employed to determine differences in the values of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S between live and dead S. alterniflora at a 0.05 significance level. Linear regression and binomial regression were utilized to explore the responses in the values of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S for the whole plant, live S. alterniflora, and dead S. alterniflora to latitude, MAT, and MAP using paired data (δX-latitude, δX-MAT, δX-MAP). In cases where neither of the two regressions mentioned above matched, loess regression was applied to illustrate the changes in δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S with increasing latitude, MAT, and MAP. Additionally, the relationship between any two indicators (paired data) of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S was examined using the previously mentioned regression techniques.
3 Results
3.1 Latitudinal patterns of the δ13C, δ15N, δ34S in S. alterniflora
The value of δ13C of S. alterniflora ranged from -17.44‰ to -11.00‰ (M=-13.52 ± 0.83‰, N=195; Figure 3A) and firstly increased and then decreased with increasing latitudes (p=0.000, Figure 4A).
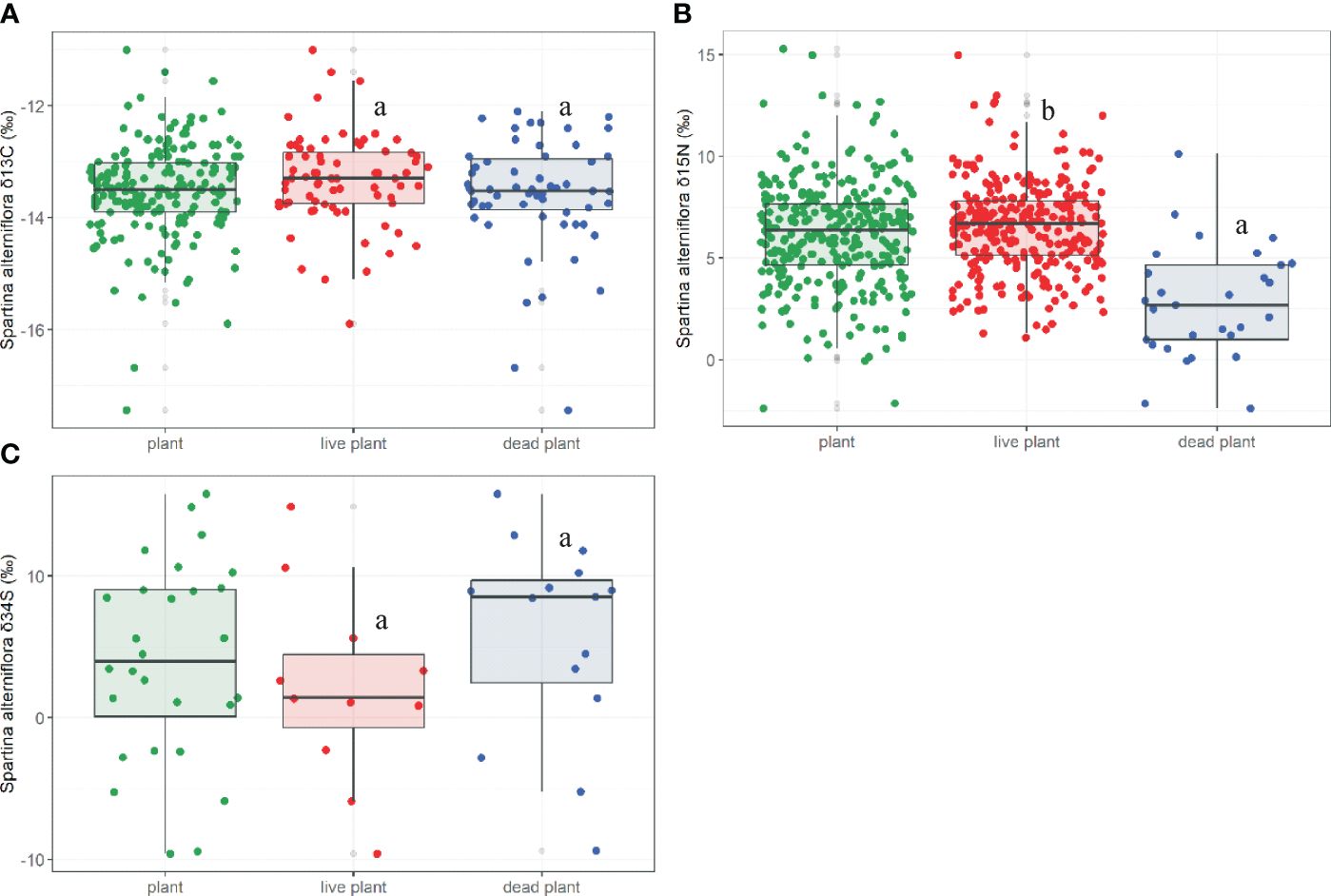
Figure 3 The δ13C (A), δ15N (B), δ34S (C) in live and dead S. alterniflora. Different letters stand for significant differences at the 0.05 significance level in live and dead S. alterniflora.
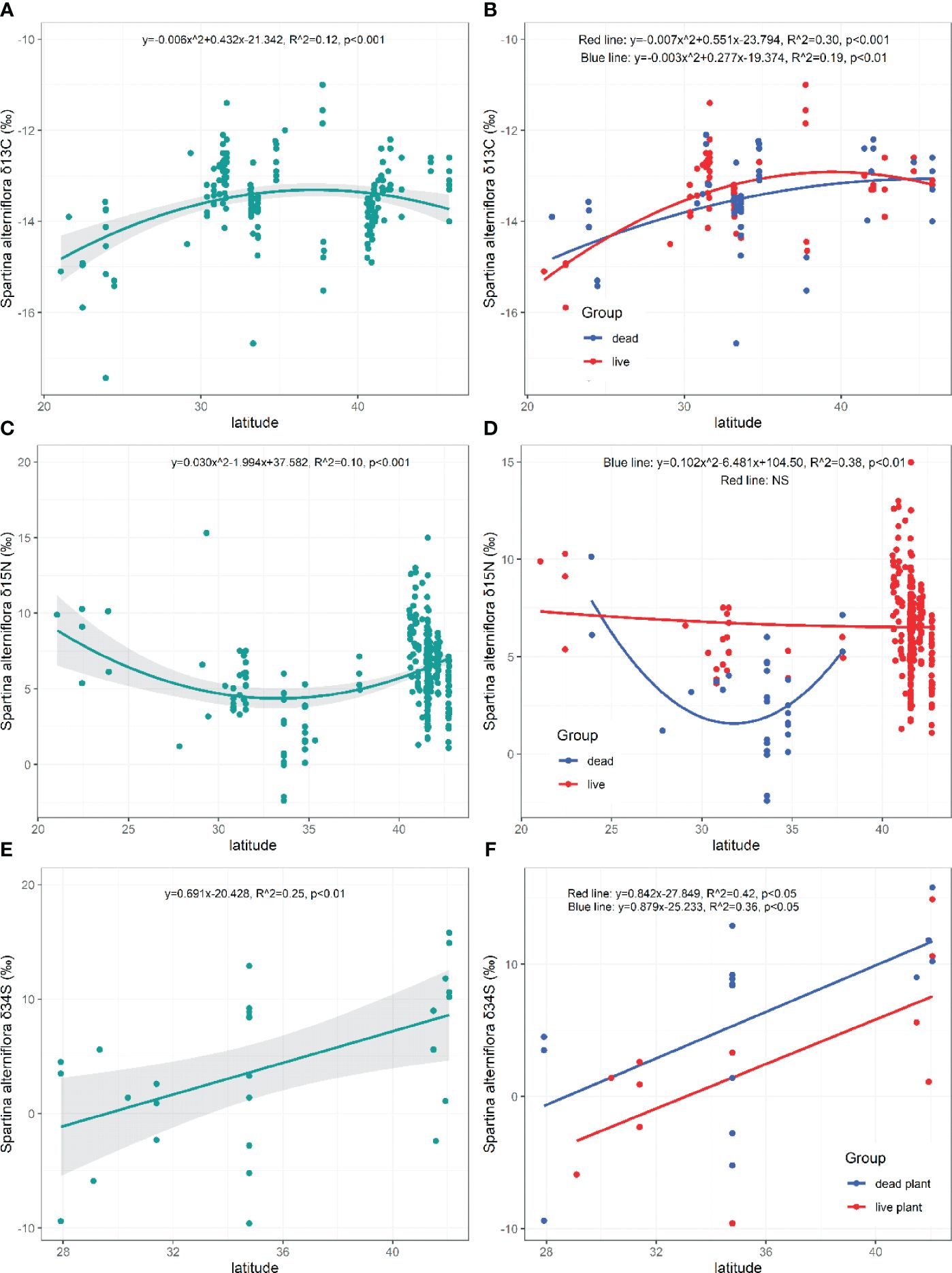
Figure 4 Latitudinal patterns of the of δ13C, δ15N, δ34S in live and dead S. alterniflora. NS, the fitting is not statistically significant.
Both the δ13C in live and dead S. alterniflora displayed similar patterns toward higher latitudes (Live: p=0.000; Dead: p=0.003, Figure 4B). There were no significant differences in the δ13C of live (M=-13.32 ± 0.82‰, N=72) and dead S. alterniflora (M=-13.59 ± 1.01‰, N=59; p=0.097; Figure 3A). The δ15N values of S. alterniflora ranged from -2.40‰ to 15.30‰ (M=6.16 ± 0.14‰, N=316; Figure 3B) and initially decreased and then increased with increasing latitudes (p=0.000, Figure 4C). The δ15N of dead S. alterniflora displayed similar patterns toward higher latitudes, unlike the live S. alterniflora (Live: p=0.756, Dead: p=0.002; Figure 4D). The δ15N of live S. alterniflora (M=6.55 ± 2.23‰, N=272) was significantly higher than that of dead S. alterniflora (M=-2.76 ± 2.72‰, N=29; p=0.000; Figure 3B). The δ34S values of S. alterniflora ranged from -9.60‰ to 15.80‰ (M=4.01 ± 6.96‰, N=28; Figure 3C) and showed a significant increase toward higher latitudes (p=0.006, Figure 4E). Both the δ34S in live and dead S. alterniflora displayed similar patterns toward higher latitudes (Live: p=0.030; Dead: p=0.016, Figure 4F), but live S. alterniflora had a higher fitting value of δ34S at the same latitude. There were no significant differences in the δ34S of live (M=2.05 ± 6.88‰, N=11) and dead S. alterniflora (M=5.78 ± 7.09‰, N=15; p=0.193; Figure 3C).
3.2 Responses of the δ13C, δ15N, δ34S in S. alterniflora to MAT and MAP
The δ13C value of S. alterniflora significantly decreased with higher MAT (p=0.050, Figure 5A). Both the δ13C values of live and dead S. alterniflora showed significant decreasing trends at elevated MAT levels (Live: p=0.029, Dead: p=0.026, Figure 5B). The δ15N value of S. alterniflora initially declined and then increased with rising MAT (p=0.002, Figure 5C). However, the δ15N value of live S. alterniflora first increased and then decreased in response to MAT (Live: p=0.043, Figure 5D). The δ34S value of S. alterniflora (both live and dead) exhibited a significant decrease with increasing MAT (Plant: p=0.007, Live: p=0.025, Dead: p=0.016, Figures 5E, F).
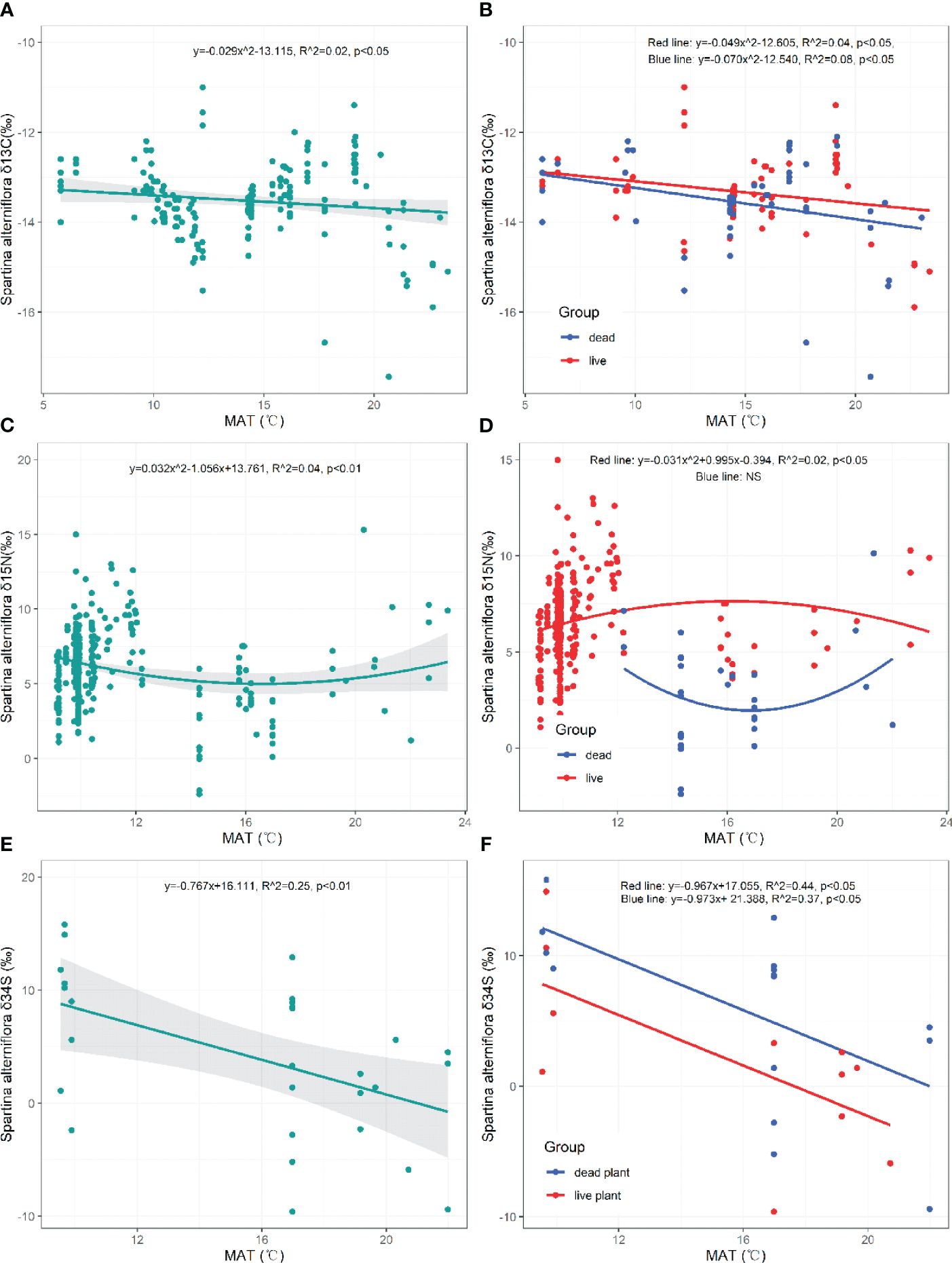
Figure 5 Responses of δ13C, δ15N, δ34S in live and dead S. alterniflora to mean annual temperature (MAT). NS, the fitting is not statistically significant.
There are no significant trends in the δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S values of S. alterniflora with increasing MAP (p>0.05, Figures 6A, C–E). The δ13C of live S. alterniflora exhibited a significant decreasing trend when the MAP is >869 mm (p=0.017, Figure 6B). The δ34S value of live S. alterniflora initially decreased and then increased with increasing MAP (Live: p=0.048, Figure 6F), whereas the δ34S of dead S. alterniflora initially increased and then decreased with increasing MAP (Dead: p=0.063, Figure 6F).
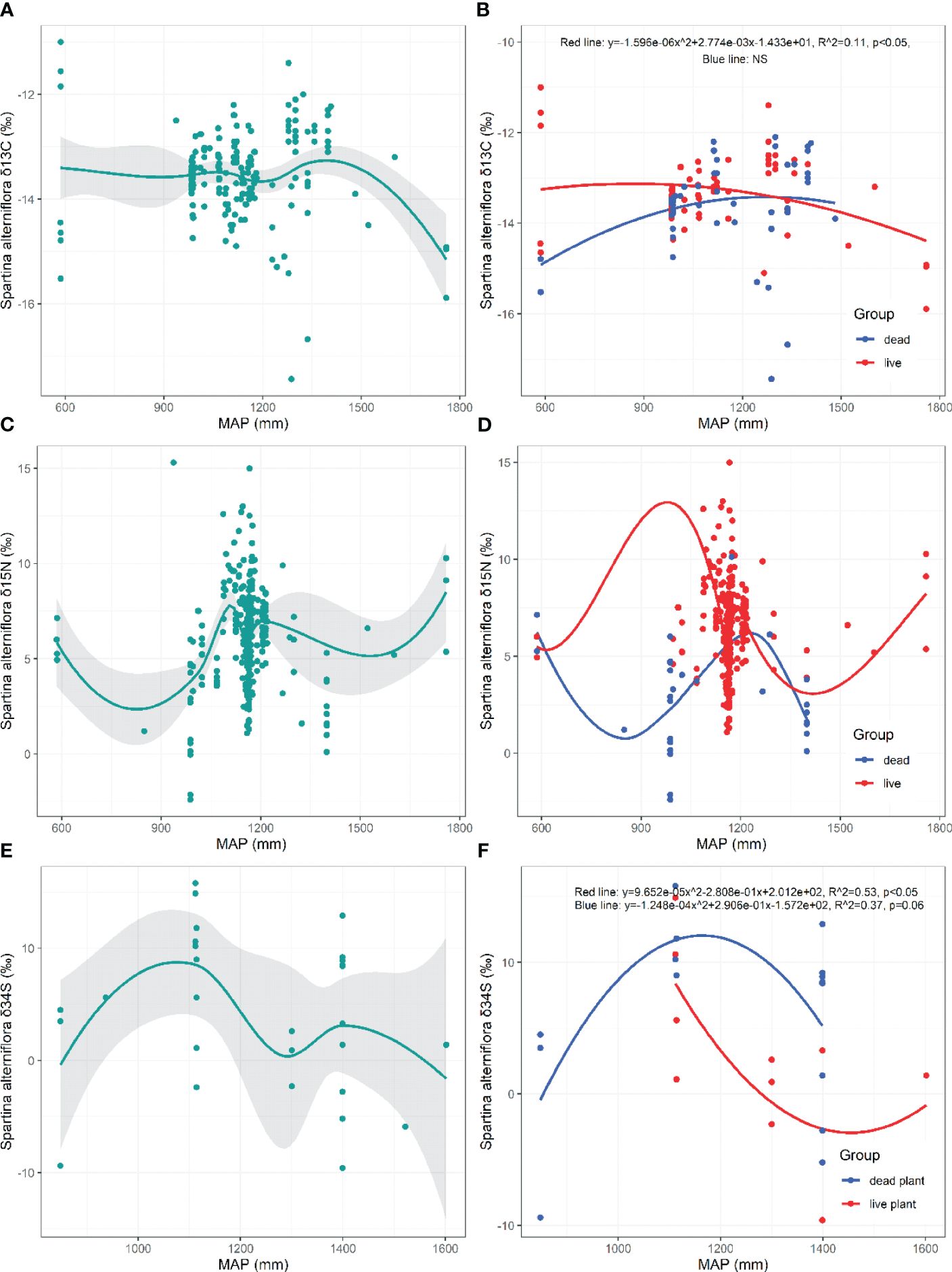
Figure 6 Responses of δ13C, δ15N, δ34S in live and dead S. alterniflora to mean annual precipitation (MAP). NS, the fitting is not statistically significant.
3.3 Relationships of the δ13C, δ15N, δ34S in S. alterniflora
The δ15N of S. alterniflora showed a significant negative relationship with the δ13C of S. alterniflora (p=0.001, N=102; Figure 7A). Plant life status shaped a decreasing curve for the δ15N in response to increasing δ13C of S. alterniflora (Live: p=0.013, N=18, Figure 7B). However, the relationships between the δ34S and δ13C of S. alterniflora (p=0.110, N=14; Supplementary Figure S3), the δ34S and δ15N (p=0.667, N=14; Supplementary Figure S3) of S. alterniflora (or dead or live) were fuzzy.
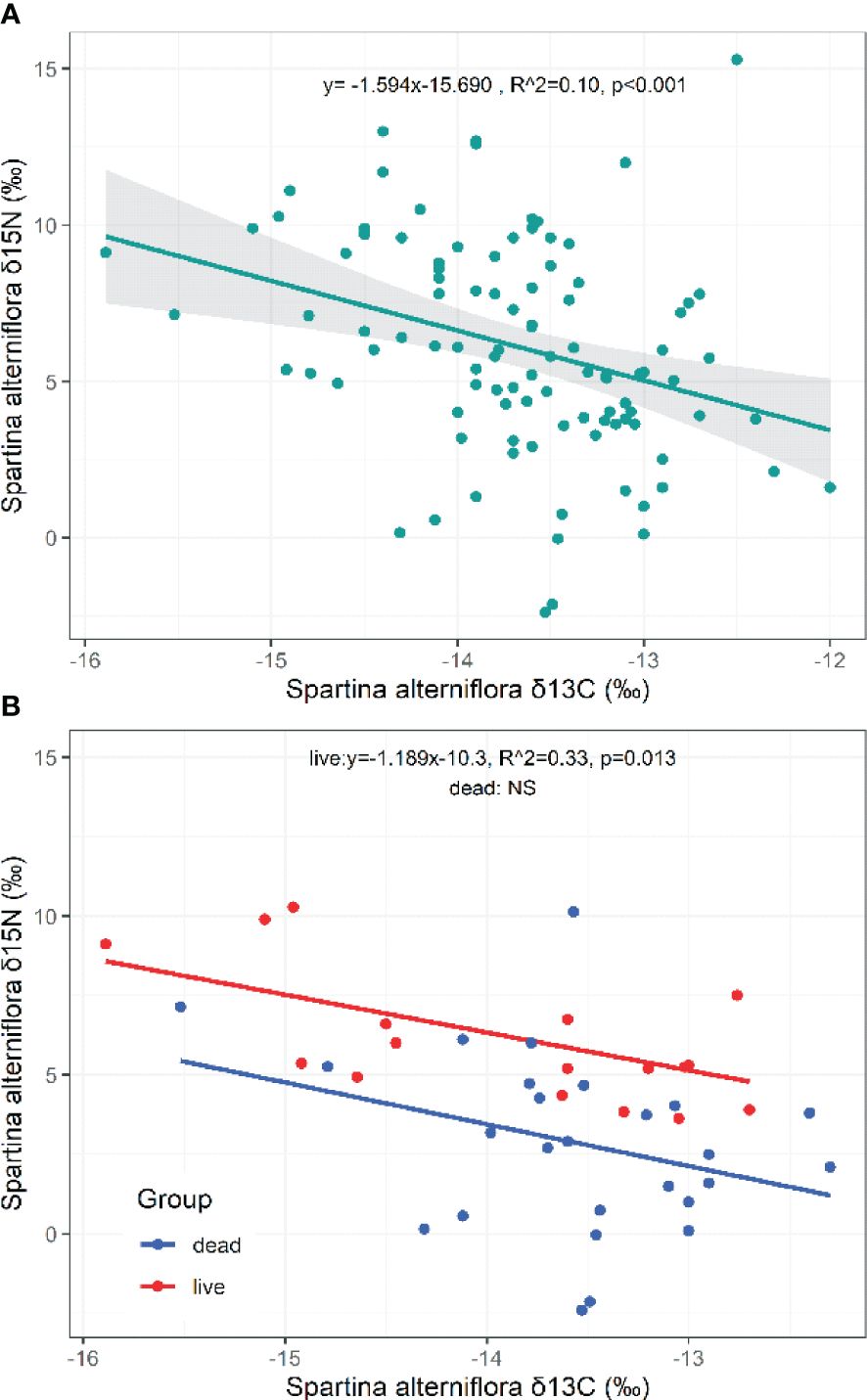
Figure 7 Relationships of the δ13C and δ15N in S. alterniflora. NS, the fitting is not statistically significant.
4 Discussion
We observed a consistent pattern in the δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S values of S. alterniflora across latitudes, providing evidence for the latitudinal variation in vegetative growth traits. These traits are likely associated with the plant’s invasive mechanisms. Previous studies have documented general patterns, such as linear or binomial, in plant height, stem diameter, leaf characteristics (leaf area, thickness, toughness, specific leaf area, dry matter content), shoot density, plant productivity, reproductive traits (seed set, seed production, seeding density, seed germination, first flower day, flowering culm, number of spikelets), ecostoichiometry (C, N, P, and their ratios), and leaf litter decomposition rate in response to increasing latitudes within the specified range (Kirwan et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2022; Cheng et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2021a; Zheng et al., 2022). The latitudinal patterns of vegetative traits collectively regulate the growth, reproduction, and expansion of S. alterniflora through plastic deformation strategies. The plastic deformation strategies altered plant form and function so as to match environmental changes in a new environment, these enhancing plants competitiveness for space and resources, allowing it to occupy vacant ecological niches (Liu et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2023; Xiong et al., 2023). Previous research has shown that the plant height of S. alterniflora forms a convex curve with increasing latitudes (20°N~40°N), aligning with the latitudinal pattern of δ13C but contrasting with that of δ15N in S. alterniflora (Liu et al., 2017). In general, larger S. alterniflora plants with greater height exhibit strong photosynthesis, altering carbon isotope fractionation and increasing the potential accumulation of 13C (Lin and da SL Sternberg, 1993; Essemine et al., 2020; Mao et al., 2023). When nutrient resources are limited, larger plants typically require a significant amount of nutrients to sustain rapid growth, resulting in a dilution of 15N and a decrease in its accumulation within the plant (Hill et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2022). Moreover, an increase in dry matter content induces plant senescence, leading to a reduction in 15N-related enzymes and influencing plant 15N levels (Hessini, 2022; Xia et al., 2023a). Hence, the varied latitudinal patterns of S. alterniflora’s plant traits facilitate its adaptive response to environmental changes associated with different latitudes.
Plant life-death status have complex effects on isotopes, and then affecting their latitudinal patterns. In this study, the plant life status did not alter the δ13C and δ34S values or their corresponding latitudinal patterns in S. alterniflora. These findings are consistent with prior research; Schwamborn et al. (2002) and Kieckbusch et al. (2004) discovered that live leaves and senescent leaves exhibited similar δ13C values. Similar evidence was observed in the δ13C of Kandelia candel and Rhiziophora mangle during the senescence process (Wooller et al., 2003b). However, Rao et al. (1994) reported no difference in δ13C between fresh and senescent tissues of five mangrove species in Kenya, while the other four mangrove species displayed differentiation. Robin et al. (2024) found that fresh leaves are more enriched in 13C than senescent leaves for Avicennia marina and Rhizophora stylosa, but for R. stylosa they are less enriched in 15N. Furthermore, we observed that the death of plants led to a reduction in δ15N in S. alterniflora compared to their living status. This phenomenon may be attributed to the inactivation of N-related enzymes in S. alterniflora (Hessini, 2022; Xia et al., 2023a). The status of plant death resulted in a δ15N response in the form of a concave curve with increasing latitude but exhibited a less distinct response under the plant life status. These findings suggest that live S. alterniflora demonstrates a broad range of δ15N responses to latitude, particularly at higher latitudes. There is no consensus on whether there are differences in plant isotopes and their latitudinal patterns across species under different life states. This inconsistency with our hypothesis (1) leads us to speculate that variations in plant isotopes and their latitudinal patterns under different life status may depend on the species, its strength, the type of isotopes (Wooller et al., 2003b; Rao et al., 1994), and specific evidence that needs further exploration.
MAT and MAP play crucial roles in shaping latitude and influencing plant growth and reproduction (Yuan and Chen, 2009; Zhang et al., 2019; Xia et al., 2023a). Prior studies have demonstrated that temperature and precipitation contribute to the formation of linear or quadratic polynomial patterns in plant growth and reproductive traits (Kirwan et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2017, Liu et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2022; Cheng et al., 2022; Zheng et al., 2022). Latitude changes increase environmental heterogeneity, especially in hydrothermal environments; Simultaneously, it shapes different plant traits to adapt to environmental changes. Therefore, we hypothesize that the isotopes of S. alterniflora, closely linked to these traits, are affected by MAT and MAP. While general patterns of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in response to MAT along latitudinal gradients were identified, this was not observed for MAP, which is not entirely consistent with our hypothesis (2). A consensus emerges, indicating that MAT is the controlling factor for the latitudinal patterns of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in S. alterniflora. The marginal influence of precipitation in this study warrants thorough consideration, deviating from previous research conclusions (Yuan and Chen, 2009; Xia et al., 2023a). In Supplementary Figure S2, MAP exhibits a trend of decreasing and then increasing with latitude. Additionally, MAP is influenced by various factors, including the relative position of land and sea, terrain, pressure bands, wind belts, monsoons, cyclones, fronts, underlying surfaces, ocean currents, and human activities (Fick & Hijmans, 2017). The complexity of these factors reduces the interpretability of latitude’s impact on MAP and disrupts the response patterns of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in S. alterniflora to MAP. Interestingly, the δ15N of S. alterniflora under live plant conditions shows a significant response to MAT, unlike its death status. This observation aligns with the notion that temperature influences enzyme activity in live plant bodies (Hessini, 2022). The δ13C and δ34S of live S. alterniflora exhibit a significant response to MAP due to their stability and the importance of precipitation for plant survival (Yuan and Chen, 2009; Xia et al., 2023a). Phenotypic plasticity, by altering plant isotopes and their other traits, fully ensures their survival in changing environments, and enables invasive plants to successfully customize and spread in the invasive ranges.
The relationships among plant elements or isotopes are crucial for studying plant adaptation mechanisms at the single-species scale and element flux in food webs at the whole ecosystem scale (Gao et al., 2018; Jinks et al., 2020; Li et al., 2022). However, the paired relationships between any two indicators of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in S. alterniflora have been overlooked. In this study, we hypothesize that the δ15N and δ34S of S. alterniflora exhibit stable relationships with the corresponding δ13C. The δ15N of S. alterniflora decreases with increasing δ13C, supporting parts of hypothesis (3). When having similar δ13C values, the decrease in δ15N of deceased S. alterniflora disrupts the general relationship between δ13C and δ15N. Additionally, the indistinct relationships between δ34S and δ13C (or δ15N) of S. alterniflora may be associated with the δ34S in the environment. Excessive δ34S in the soil (found in salt marshes with sulfate-type soil) or atmosphere (in areas with acid rain) leads to an increase in δ34S in plant bodies, resulting in a mismatch in the relationship between δ34S and δ13C (or δ15N) of S. alterniflora (Guo et al., 2020; Jinks et al., 2020; Guiry et al., 2022). These findings highlight the isotopic flexibility within S. alterniflora.
Although our results provide strong evidence for the latitudinal patterns and their climate drivers of the δ13C, δ15N, δ34S isotope signatures of S. alterniflora across plant life-death status based on a global analysis, there were several limitations in this study, such as how soil isotope signatures affected plant isotope signatures. Soil is recognized as a key factor influencing available nutrient for plant, and their large-scale patterns of isotope signatures have an imprint on plant isotope signatures (Amundson et al., 2003; Craine et al., 2015). Plant δ13C (δ15N) was significantly positively related to soil δ13C (δ15N) across varied plant species and functional types (Peri et al., 2012; Xia et al., 2023b). Although soil δ13C and δ15N was shaped by MAT and MAP, future research should pay attentions to the imprint of soil isotope signatures on corresponding isotope signatures.
5 Conclusions
The latitudinal patterns of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in S. alterniflora are depicted as a convex curve, a concave curve, and an increasing straight line, respectively. The responses of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in S. alterniflora to MAT manifest as a decreasing line, a concave curve, and a decreasing line, respectively, but exhibit indistinct responses to MAP. The life-death status of plants alters the δ15N-latitudinal patterns and their responses of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S in S. alterniflora to MAT. The δ13C and δ34S of living S. alterniflora demonstrate robust responses to MAP. Plant death status results in a significant decrease in δ15N, but not in δ13C and δ34S. Paired δ15N and δ13C of S. alterniflora exhibit a noteworthy negative relationship across the entire dataset and plant life status. All these findings provide evidence of robust ecological plasticity and adaptability across geographic clines.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
DZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HW: Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. KA: Data curation, Writing – original draft. WH: Writing – review & editing. TW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. MZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ST: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42101111); the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2021QD101; ZR2020MD007); the PhD research startup foundation of Binzhou University (No. 2021Y14); the Youth Innovation Support Program of Shandong Universities (No. 2023KJ273); Binzhou Youth Science and Technology Rising Star Program Project (QMX2023001) and College Student Innovation Training Program Plan (S202210449026).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer XW declared a past co-authorship with the author(s) DZ, MZ, and ST to the handling editor.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1384914/full#supplementary-material
References
Amundson, R., Austin, A. T., Schuur, E. A., Yoo, K., Matzek, V., Kendall, C., et al. (2003). Global patterns of the isotopic composition of soil and plant nitrogen. Global biogeochemical cycles 17, 1–10. doi: 10.1029/2002GB001903
Bai, E., Houlton, B. Z., Wang, Y. P. (2012). Isotopic identification of nitrogen hotspots across natural terrestrial ecosystems. Biogeosciences 9, 3287–3304. doi: 10.5194/bg-9-3287-2012
Chen, C. J., Liu, X. Y., Wang, X. W., Hu, C. C., Xu, S. Q., Mao, R., et al. (2021). Different leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry and carbon and nitrogen isotopes among peatland plants in northeastern China. Plant Soil 467, 345–357. doi: 10.1007/s11104-021-05085-7
Chen, S., Gao, D., Zhang, J., Müller, C., Li, X., Zheng, Y., et al. (2022). Invasive Spartina alterniflora accelerates soil gross nitrogen transformations to optimize its nitrogen acquisition in an estuarine and coastal wetland of China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 174, 108835. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108835
Chen, X., Liu, W., Zhang, Y. Y., Zhang, Y. (2023). Altered trait covariances between invasive and native ranges of a global plant invader. Funct. Ecol. 37, 1280–1290. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.14298
Cheng, J., Huang, H., Liu, W., Zhou, Y., Han, W., Wang, X., et al. (2022). Unraveling the effects of cold stratification and temperature on the seed germination of invasive Spartina alterniflora across latitude. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 911804. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.911804
Courtney, A. J., Xu, J., Xu, Y. (2016). Responses of growth, antioxidants and gene expression in smooth cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora) to various levels of salinity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 99, 162–170. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.12.016
Craine, J. M., Brookshire, E. N. J., Cramer, M. D., Hasselquist, N. J., Koba, K., Marin-Spiotta, E., et al. (2015). Ecological interpretations of nitrogen isotope ratios of terrestrial plants and soils. Plant Soil 396, 1–26. doi: 10.1007/s11104-015-2542-1
Essemine, J., Qu, M., Lyu, M. J. A., Song, Q., Khan, N., Chen, G., et al. (2020). Photosynthetic and transcriptomic responses of two C4 grass species with different NaCl tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 253, 153244. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2020.153244
Feng, H., Qian, Y., Cochran, J., Zhu, Q., Heilbrun, C., Li, L., et al. (2018). Seasonal differences in trace element concentrations and distribution in Spartina alterniflora root tissue. Chemosphere 204, 359–370. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.058
Fick, S. E., Hijmans, R. J. (2017). WorldClim 2: new 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. climatol. 37, 4302–4315. doi: 10.1002/joc.5086
Gao, X., Wang, M., Wu, H., Wang, W., Tu, Z. (2018). Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on the diet of mangrove crabs (Parasesarma plicata) in the Zhangjiang Estuary, China. J. Coast. Res. 34, 106–113. doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-17-00002.1
Guiry, E. J., Orchard, T. J., Needs-Howarth, S., Szpak, P. (2022). Freshwater wetland–driven variation in sulfur isotope compositions: Implications for human paleodiet and ecological research. Front. Ecol. Evol. 10, 953042. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.953042
Guo, W., Cecchetti, A. R., Wen, Y., Zhou, Q., Sedlak, D. L. (2020). Sulfur cycle in a wetland microcosm: extended 34S-stable isotope analysis and mass balance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 5498–5508. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b05740
He, S., Lin, J., Liu, X., Jia, S., Chen, S. (2023). Cordgrass Spartina alterniflora acts as a key carbon source to support macrozoobenthos in the salt marsh and nearby mudflat communities. Ecol. Indic. 148, 110052. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110052
Hessini, K. (2022). Nitrogen form differently modulates growth, metabolite profile, and antioxidant and nitrogen metabolism activities in roots of Spartina alterniflora in response to increasing salinity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 174, 35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.01.031
Hill, T. D., Sommer, N. R., Kanaskie, C. R., Santos, E. A., Oczkowski, A. J. (2018). Nitrogen uptake and allocation estimates for Spartina alterniflora and Distichlis spicata. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 507, 53–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2018.07.006
Humphreys, A., Gorsky, A. L., Bilkovic, D. M., Chambers, R. M. (2021). Changes in plant communities of low-salinity tidal marshes in response to sea-level rise. Ecosphere 12, e03630. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.3630
Jia, P., Qu, G., Jia, J., Li, D., Sun, Y., Liu, L. (2022). Long term Spartina alterniflora invasion simplified soil seed bank and regenerated community in a coastal marsh wetland. Ecol. Appl. 34, e2754. doi: 10.1002/eap.2754
Jinks, K. I., Rasheed, M. A., Brown, C. J., Olds, A. D., Schlacher, T. A., Sheaves, M., et al. (2020). Saltmarsh grass supports fishery food webs in subtropical Australian estuaries. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 238, 106719. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106719
Kieckbusch, D. K., Koch, M. S., Serafy, J. E., Anderson, W. T. (2004). Trophic linkages among primary producers and consumers in fringing mangroves of subtropical lagoons. Bull. Mar. Sci. 74, 271–285.
Kinney, E. L., Valiela, I. (2018). Spartina alterniflora δ15N as an indicator of estuarine nitrogen load and sources in Cape Cod estuaries. Mar. pollut. Bull. 131, 205–211. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.04.006
Kirwan, M. L., Guntenspergen, G. R., Morris, J. T. (2009). Latitudinal trends in Spartina alterniflora productivity and the response of coastal marshes to global change. Global Change Biol. 15, 1982–1989. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01834.x
Kou, D., Yang, G., Li, F., Feng, X., Zhang, D., Mao, C., et al. (2020). Progressive nitrogen limitation across the Tibetan alpine permafrost region. Nat. Commun. 11, 3331. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17169-6
Li, H., Mao, D., Wang, Z., Huang, X., Li, L., Jia, M. (2022). Invasion of Spartina alterniflora in the coastal zone of mainland China: Control achievements from 2015 to 2020 towards the Sustainable Development Goals. J. Environ. Manage. 323, 116242. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116242
Li, S., Xie, T., Bai, J., Cui, B. (2022). Degradation and ecological restoration of estuarine wetlands in China. Wetlands 42, 90. doi: 10.1007/s13157-022-01589-9
Li, X., Yang, W., Sun, T., Yang, Z. (2022). Trophic diversity and food web structure of vegetated habitats along a coastal topographic gradient. Front. Mar. Sci. 9, 920745. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.920745
Lin, G., da SL Sternberg, L. (1993). “Hydrogen isotopic fractionation by plant roots during water uptake in coastal wetland plants,” in Stable isotopes and plant carbon-water relations (San Diego, United States: Academic Press). doi: 10.1016/B978-0-08-091801-3.50041-6
Liu, C., Li, P., Xie, W., Sha, M., Ding, W. (2021). Changes of sulfur fractions in sediment following Spartina alterniflora invasion in a seaward direction in a temperate salt marsh, China. Ecol. Indic. 131, 108217. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108217
Liu, W., Strong, D. R., Pennings, S. C., Zhang, Y. (2017). Provenance-by-environment interaction of reproductive traits in the invasion of Spartina alterniflora in China. Ecology 98, 1591–1599. doi: 10.1002/ecy.1815
Liu, W., Wang, W., Zhang, Y. (2022). Differences in leaf traits of Spartina alterniflora between native and invaded habitats: Implication for evolution of alien species competitive ability increase. Ecol. Indic. 138, 108799. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108799
Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Maung-Douglass, K., Strong, D. R., Pennings, S. C. (2020). Contrasting plant adaptation strategies to latitude in the native and invasive range of Spartina alterniflora. New Phytol. 226, 623–634. doi: 10.1111/nph.16371
Liu, Y., Ding, Z., Bachofen, C., Lou, Y., Jiang, M., Tang, X., et al. (2018). The effect of saline-alkaline and water stresses on water use efficiency and standing biomass of Phragmites australis and Bolboschoenus planiculmis. Sci. total Environ. 644, 207–216. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.321
Liu, Y., Xu, X., Liu, H. (2020). Latitude gradient variations of leaf functional traits of Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis along the coastal saltmarshes of China. J. Fudan Univ. (Natural Science) 59, 381–389. doi: 10.15943/j.cnki.fdxb-jns.2020.04.001
Lu, H. F., Zhang, H. S., Qin, P., Li, X. Z., Campbell, D. (2020). Integrated energy and economic evaluation of an ecological engineering system for the utilization of Spartina alterniflora. J. Cleaner Production 247, 119592. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119592
Ma, X., Yan, J., Wang, F., Qiu, D., Jiang, X., Liu, Z., et al. (2019). Trait and density responses of Spartina alterniflora to inundation in the Yellow River Delta, China. Mar. pollut. Bull. 146, 857–864. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.022
Mao, D., Liu, M., Wang, Z., Li, L., Man, W., Jia, M., et al. (2019). Rapid invasion of Spartina alterniflora in the coastal zone of mainland China: Spatiotemporal patterns and human prevention. Sensors 19, 2308. doi: 10.3390/s19102308
Mao, L., Mishra, D. R., Hawman, P. A., Narron, C. R., O’Connell, J. L., Cotten, D. L. (2023). Photosynthetic performance of tidally flooded Spartina alterniflora salt marshes. J. Geophysical Res.: Biogeosciences 128, e2022JG007161. doi: 10.1029/2022JG007161
Maron, J. L., Vilà, M., Bommarco, R., Elmendorf, S., Beardsley, P. (2004). Rapid evolution of an invasive plant. Ecol. Monogr. 74, 261–280. doi: 10.1890/03-4027
Mason, V., Burden, A., Epstein, G., Jupe, L., Wood, K., Skov, M. (2023). Blue carbon benefits from global saltmarsh restoration. Global Change Biology 29 (23), 6517–6545. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16943
Meng, W., Feagin, R. A., Innocenti, R. A., Hu, B., He, M., Li, H. (2020). Invasion and ecological effects of exotic smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora in China. Ecol. Eng. 143, 105670. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105670
Nelson, J. A., Lesser, J., James, W. R., Behringer, D. P., Furka, V., Doerr, J. C. (2019). Food web response to foundation species change in a coastal ecosystem. Food Webs 21, e00125. doi: 10.1016/j.fooweb.2019.e00125
Peri, P. L., Ladd, B., Pepper, D. A., Bonser, S. P., Laffan, S. W., Amelung, W. (2012). Carbon (δ13C) and nitrogen (δ15N) stable isotope composition in plant and soil in Southern P atagonia’s native forests. Global Change Biol. 18, 311–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02494.x
Rao, R. G., Woitchik, A. F., Goeyens, L., Van Riet, A., Kazungu, J., Dehairs, F. (1994). Carbon, nitrogen contents and stable carbon isotope abundance in mangrove leaves from an east African coastal lagoon (Kenya). Aquat. Bot. 47, 175–183. doi: 10.1016/0304-3770(94)90012-4
Robin, S. L., Le Milbeau, C., Gututauava, K., Marchand, C. (2024). Influence of species and stand position on isotopic and molecular composition of leaf litter during degradation in an urban mangrove forest. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 372, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2024.03.008
Sampaio, J. A. G., Reis, C. R. G., Cunha-Lignon, M., Nardoto, G. B., Salemi, L. F. (2021). Plant invasion affects vegetation structure and sediment nitrogen stocks in subtropical mangroves. Mar. Environ. Res. 172, 105506. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2021.105506
Schwamborn, R., Ekau, W., Voss, M., Saint-Paul, U. (2002). How important are mangroves as a carbon source for decapod crustacean larvae in a tropical estuary? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 229, 195–205. doi: 10.3354/meps229195
Spivak, A. C., Reeve, J. (2015). Rapid cycling of recently fixed carbon in a Spartina alterniflora system: a stable isotope tracer experiment. Biogeochemistry 125, 97–114. doi: 10.1007/s10533-015-0115-2
Wang, F., Sun, X., Zhao, Y., Wang, H., Song, X., Wei, S., et al. (2023). Does Spartina invasion affect the carbohydrate assimilation of polychaetes in mangroves? A case study in the Zhangjiang Estuary Mangrove National Nature Reserve. J. Sea Res. 195, 102435. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2023.102435
Wang, F., Zhang, N., Yang, S., Li, Y., Yang, L., Cao, W. (2024). Source and stability of soil organic carbon jointly regulate soil carbon pool, but source alteration is more effective in mangrove ecosystem following Spartina alterniflora invasion. Catena 235, 107681. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2023.107681
Watson, E. B., Powell, E., Maher, N. P., Oczkowski, A. J., Paudel, B., Starke, A., et al. (2018). Indicators of nutrient pollution in Long Island, New York, estuarine environments. Mar. Environ. Res. 134, 109–120. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2018.01.003
Wittyngham, S. S., Carey, J., Johnson, D. S. (2023). Resource availability and plant age drive defense against herbivory in salt marshes. Oikos 2023, e09672. doi: 10.1111/oik.09672
Wooller, M., Smallwood, B., Jacobson, M., Fogel, M. (2003a). Carbon and nitrogen stable isotopic variation in Laguncularia racemosa (L.)(white mangrove) from Florida and Belize: implications for trophic level studies. Hydrobiologia 499, 13–23. doi: 10.1023/A:1026339517242
Wooller, M. J., Swain, D. L., Ficken, K. J., Agnew, A. D. Q., Street-Perrott, F. A., Eglinton, G. (2003b). Late Quaternary vegetation changes around Lake Rutundu, Mount Kenya, East Africa: evidence from grass cuticles, pollen and stable carbon isotopes. J. Quaternary Sci.: Published Quaternary Res. Assoc. 18, 3–15. doi: 10.1002/jqs.725
Wu, Z., Wang, X., Chen, M., Lai, Y., Lin, X. (2024). Changes in sediment N mineralization and immobilization in association with Spartina alterniflora invasion in mangrove wetland. Plant Soil, 1–20. doi: 10.1007/s11104-024-06532-x
Xia, N., Du, E., Tang, Y., Guo, H. (2023b). A distinctive latitudinal trend of nitrogen isotope signature across urban forests in eastern China. Global Change Biol. 29, 5666–5676. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16899
Xia, S., Song, Z., Singh, B. P., Guo, L., Bolan, N., Wang, W., et al. (2023a). Contrasting patterns and controls of soil carbon and nitrogen isotope compositions in coastal wetlands of China. Plant Soil 489, 483–505. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-06034-2
Xiong, J., Shao, X., Yuan, H., Liu, E., Xu, H., Wu, M. (2023). Effect of human reclamation and Spartina alterniflora invasion on C-N-P stoichiometry in plant organs across coastal wetlands over China. Plant Soil 494, 167–183. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-06264-4
Yuan, Z. Y., Chen, H. Y. (2009). Global-scale patterns of nutrient resorption associated with latitude, temperature and precipitation. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 18, 11–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1466-8238.2008.00425.x
Zhang, G., Bai, J., Zhao, Q., Jia, J., Wang, X., Wang, W., et al. (2021). Soil carbon storage and carbon sources under different Spartina alterniflora invasion periods in a salt marsh ecosystem. Catena 196, 104831. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104831
Zhang, X., He, X., Gao, J., Wang, L. (2019). Latitudinal and climate effects on key plant traits in Chinese forest ecosystems. Global Ecol. Conserv. 17, e00527. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00527
Zhang, Y., Pennings, S. C., Liu, Z., Li, B., Wu, J. (2021a). Consistent pattern of higher lability of leaves from high latitudes for both native Phragmites australis and exotic Spartina alterniflora. Funct. Ecol. 35, 2084–2093. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.13826
Keywords: latitudinal pattern, biological invasion, isotope signature, coupling relationship, climate drivers
Citation: Zhang D, Wang H, Liu X, Ao K, He W, Wang T, Zhang M and Tong S (2024) Latitudinal patterns and their climate drivers of the δ13C, δ15N, δ34S isotope signatures of Spartina alterniflora across plant life-death status: a global analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1384914. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1384914
Received: 15 February 2024; Accepted: 17 May 2024;
Published: 31 May 2024.
Edited by:
Xin-Sheng Chen, Anhui University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Zhang, Wang, Liu, Ao, He, Wang, Zhang and Tong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dongjie Zhang, emhhbmdkb25namllMTRAbWFpbHMudWNhcy5hYy5jbg==; Mingye Zhang, emhhbmdtaW5neWVAaWdhLmFjLmNu
 Dongjie Zhang
Dongjie Zhang Hui Wang1
Hui Wang1 Mingye Zhang
Mingye Zhang Shouzheng Tong
Shouzheng Tong