
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Plant Sci. , 29 November 2023
Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1329188
This article is a correction to:
Integrated GWAS and transcriptomic analysis reveal the candidate salt-responding genes regulating Na+/K+ balance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)
A Corrigendum on
Integrated GWAS and transcriptomic analysis reveal the candidate salt-responding genes regulating Na+/K+ balance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)
by Xu T, Meng S, Zhu X, Di J, Zhu Y, Yang X and Yan W (2023) Front. Plant Sci. 13:1004477. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1004477
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 4. The image in Figure 6 was used as the image in Figure 4. The corrected Figure 4 appears below.
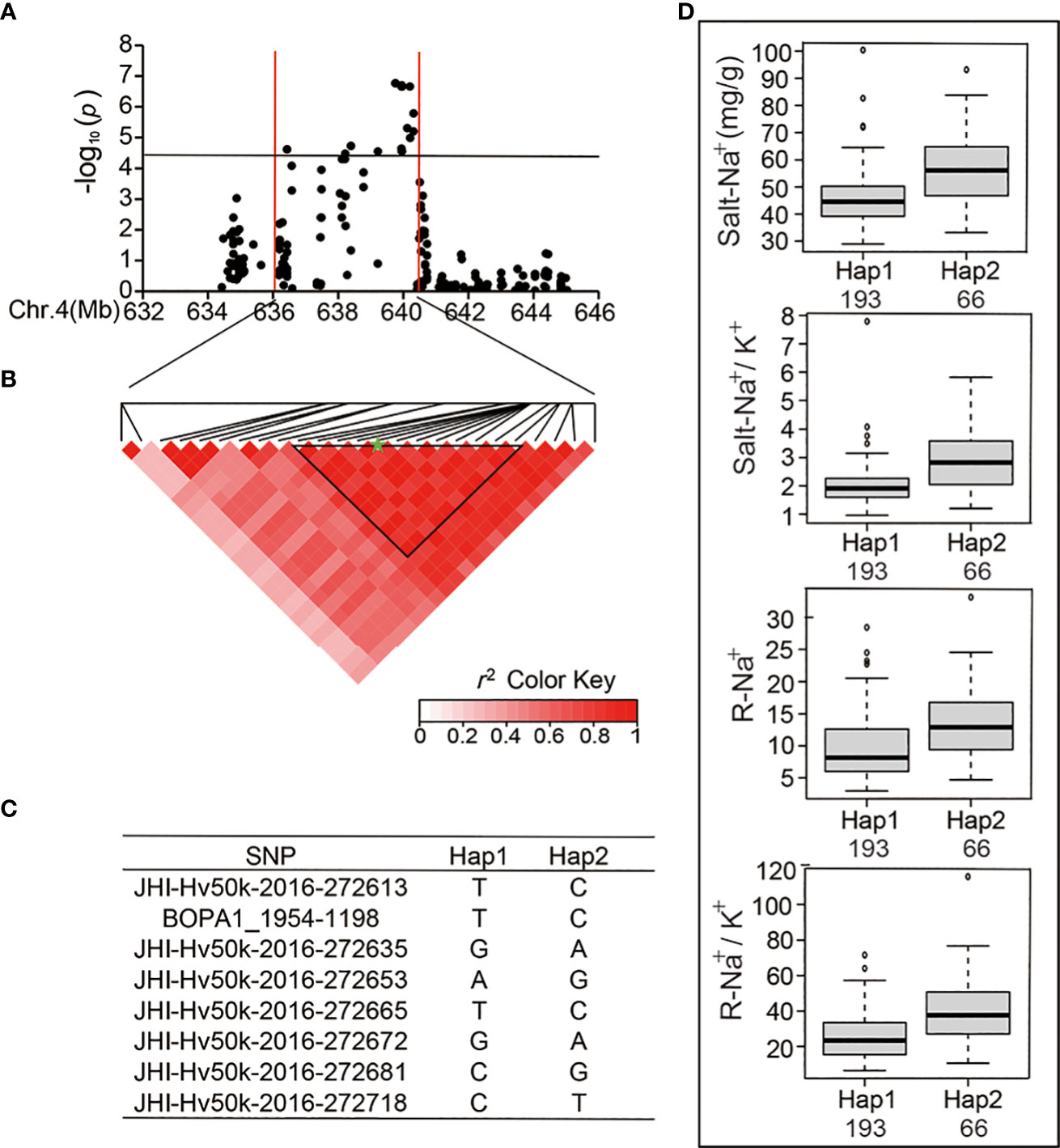
Figure 4 Analysis of the SNP peak and the candidate genes on chromosome 4. (A) Manhattan plots for Chr 4. The black line represents the significance threshold (P < 10-4.40) and a red line indicates the position of the strong SNP peak. (B) LD based on pairwise r2 values between the SNPs estimated on Chr 4. The black inverted triangles indicate 8 significantly associated SNPs that were repeatedly detected. The green five-pointed star indicates the strongest SNP with the highest threshold. (C) Haplotypes were found among the barley accessions using the 8 SNPs. (D) Phenotypic differences of Salt-Na+, Salt-Na+/K+, R-Na+, and R-Na+/K+ between the two haplotypes.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: barley, GWAS, RNA-Seq, salt tolerance, Na +/K + balance, candidate genes
Citation: Xu T, Meng S, Zhu X, Di J, Zhu Y, Yang X and Yan W (2023) Corrigendum: Integrated GWAS and transcriptomic analysis reveal the candidate salt-responding genes regulating Na+/K+ balance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Front. Plant Sci. 14:1329188. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1329188
Received: 28 October 2023; Accepted: 17 November 2023;
Published: 29 November 2023.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Zulfiqar Ali, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, PakistanCopyright © 2023 Xu, Meng, Zhu, Di, Zhu, Yang and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Yan, eWFud2VpQGphYXMuYWMuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.