
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Plant Sci. , 16 July 2018
Sec. Crop and Product Physiology
Volume 9 - 2018 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00951
Interest in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as a crop for the biobased economy is growing worldwide because hemp produces a high and valuable biomass while requiring low inputs. To understand the physiological basis of hemp's resource-use efficiency, canopy gas exchange was assessed using a chamber technique on canopies exposed to a range of nitrogen (N) and water levels. Since canopy transpiration and carbon assimilation were very sensitive to variations in microclimate among canopy chambers, observations were adjusted for microclimatic differences using a physiological canopy model, with leaf-level parameters estimated for hemp from our previous study. Canopy photosynthetic water-use efficiency (PWUEc), defined as the ratio of gross canopy photosynthesis to canopy transpiration, ranged from 4.0 mmol CO2 (mol H2O)−1 to 7.5 mmol CO2 (mol H2O)−1. Canopy photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency (PNUEc), the ratio of the gross canopy photosynthesis to canopy leaf-N content, ranged from 0.3 mol CO2 d−1 (g N)−1 to 0.7 mol CO2 d−1 (g N)−1. The effect of N-input levels on PWUEc and PNUEc was largely determined by the N effect on canopy size or leaf area index (LAI), whereas the effect of water-input levels differed between short- and long-term stresses. The effect of short-term water stress was reflected by stomatal regulation. The long-term stress increased leaf senescence, decreased LAI but retained total canopy N content; however, the increased average leaf-N could not compensate for the lost LAI, leading to a decreased PNUEc. Although hemp is known as a resource-use efficient crop, its final biomass yield and nitrogen use efficiency may be restricted by water limitation during growth. Our results also suggest that crop models should take stress-induced senescence into account in addition to stomatal effects if crops experience a prolonged water stress during growth.
The pressures of climate change, natural resource scarcity and environmental pollution have fuelled interest in bio-economically sustainable agronomy that requires effective use of scarcely available resources. A range of focused studies have indicated that hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) may be a suitable crop for the bio-economy (Amaducci and Gusovius, 2010). Hemp is a high-yielding multi-purpose crop that requires low inputs (Struik et al., 2000; Tang et al., 2016, 2017a) and has a positive impact on the environment (Bouloc and van der Werf, 2013; Barth and Carus, 2015). Its stems contain high-quality cellulose (De Meijer and van der Werf, 1994); high added-value compounds can be recovered from the female inflorescence and from threshing residues (Bertoli et al., 2010; Calzolari et al., 2017) after harvesting the seeds, that contain healthy oil (Leizer et al., 2000). Although once an important crop to produce raw materials for textiles and ropes, hemp acreage declined in the last century and was displaced largely by cotton and synthetic fibers. Consequently, little attention has been paid to understanding the physiological basis of the high resource-use efficiency of hemp.
Water and nitrogen deficiencies are major constraints in hemp production (Cosentino et al., 2013; Tang et al., 2017a). Focused quantitative studies on hemp's water- and nitrogen-use efficiencies are therefore needed. Crop water- and nitrogen-use efficiencies can be defined in different ways depending on the temporal and spatial scales of the processes and system aggregation they are based upon. The most important physiological process determining crop resource use efficiency is photosynthesis, at both leaf and canopy levels. With the aim of understanding the physiological basis of hemp's resource use efficiency, photosynthesis physiology of hemp was assessed in our previous study (Tang et al., 2017b) on leaves exposed to a range of nitrogen and temperature levels. Correlations between leaf photosynthesis and canopy photosynthesis are not always significant (Linderson et al., 2012; Tomás et al., 2012), because the latter is also affected by canopy size and the profile of resource distribution. The present study focuses on the scaling up of hemp photosynthesis from leaf to canopy and on analysing canopy photosynthetic water-use efficiency (PWUEc) and canopy photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency (PNUEc).
One challenge in studying PWUEc and PNUEc is to properly assess canopy CO2 and H2O exchange rates under varying nitrogen and water regimes. To date, the canopy gas exchange rate is mainly assessed by micro-meteorological methods or by means of canopy-enclosure chamber systems. The micro-meteorological techniques such as the eddy covariance or Bowen ratio methods enable gas flux measurements without disturbing canopy micro-environment, and they are often applied to large homogeneous areas but are unsuitable in plot/pot-sized experiments (Jones, 2013). In contrast, the canopy chamber technique enables to determine precisely canopy gas exchange at a relatively small scale (Müller et al., 2005, 2009). However, enclosing a crop canopy with a chamber might result in significant changes in micro-environmental variables (e.g., CO2 concentration, air temperature and vapor pressure) as a consequence of photosynthetic CO2 uptake, the greenhouse effect and transpiration (Takahashi et al., 2008; Müller et al., 2009). The effect of micro-environmental changes within a canopy chamber on photosynthesis rates should be assessed when the chamber is used to analyse the responses of canopy photosynthesis to water shortage and nitrogen deficiency.
On the basis of a thorough understanding of the underlying mechanisms of leaf and canopy photosynthesis, models have been developed to quantify the response of canopy photosynthesis to varying micro-environments under different physiological conditions (Hikosaka et al., 2016). Such canopy models are capable of simulating instantaneous canopy gas exchange measurements by micro-meteorological techniques (Leuning et al., 1998; Wright et al., 2013) and in canopy chambers (Müller et al., 2005). In that context, a well-defined canopy model is a useful tool to normalize the changes in micro-environmental variables within a canopy chamber and to quantitatively assess the responses of canopy photosynthesis to nitrogen and water deficiencies.
The objective of this study was to experimentally assess hemp PWUEc and PNUEc in relation to nitrogen and water availabilities. To that end, we parameterized a canopy photosynthesis model (Yin and van Laar, 2005; Yin and Struik, 2017), with leaf-level parameters estimated from our previous study for hemp (Tang et al., 2017b). This model was used for a dual-purpose: (i) to correct gas exchange measurements within different canopy chambers, and (ii) to assess the main components of hemp PWUEc and PNUEc in order to provide supporting information for efficient use of water and nitrogen resources.
Field and container experiments were carried out at the research facilities of the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore (45.0° N, 9.8° E, 60 m asl; Piacenza, Italy). Field experiments were carried out in 2014 and 2015 to assess light and nitrogen distribution profiles of hemp canopies in response to nitrogen deficiency. A container experiment was carried out in 2014 to assess instantaneous and daily canopy gas exchange of hemp in response to nitrogen and water limitations. Between May and October (during the hemp season), the study site had monthly average temperatures ranging from 17.7 to 26.9°C; the monthly sum of precipitation ranged from 13.5 to 87.0 mm.
The experimental fields had silty clay loam soil (the clay:silt:sand ratio was 39:46:15) that contained 0.14% of total nitrogen and 2.2–2.6% of organic matter. Seeds of hemp cv. Futura 75 (obtained from Fédération National des Producteurs de Chanvre, Le Mans, France) were drilled, with a target density of 120 plants m−2, at 3–4 cm depth using an experimental plot machine on 7 April in 2014 and on 16 April in 2015. Single plot size was 60 m2. Nutrients other than nitrogen were assumed to be abundantly available in the experimental fields based on past experience and analysis (data not shown). During the growth season, plants were irrigated when leaf angle distribution of the canopy became more erectophile during mid-day. A total of 60 mm and 155 mm water was provided with a traveling sprinkler in 2014 and 2015, respectively.
Nitrogen fertilization effect was investigated in a randomized complete block design with four replicates. In both years, four levels of calcium nitrate were top-dressed after seedling emergence as: N0 (no fertilizer applied); N30 (30 kg N ha−1); N60 (60 kg N ha−1), and N120 (120 kg N ha−1). In the field experiment in 2014, the plants suffered from severe weed competition. Therefore, only the data collected in the plots of N60 that were not affected by weeds were reported in this paper.
Two destructive samplings were conducted in each plot at the onset of the linear growth phase and at full flowering. At each sampling, light interception by the canopy (the ratio of light intensity at depth i to that at the top of canopy: Ii/I0) was first assessed at 90, 75, 50, and 0% of canopy height using a ceptometer (AccuPAR LP-80, Decagon Devices, Inc., Pullman, Washington, USA). Subsequently, all plants in an area of 1 m2 were cut at ground surface to assess leaf area index (LAI) and specific leaf nitrogen (SLN) on four layers according to canopy height: 0–50, 50–75, 75–90, and 90–100%. The LAI was calculated as the product of leaf weight and specific leaf area (SLA) that was obtained by measuring the weight and area of all leaves of two representative plants. Leaf nitrogen concentration (Nleaf) was assessed using a CN analyser (Vario Max CN Analyzer; Elementar Americas Inc., Hanau, Germany). The SLN was calculated as Nleaf divided by SLA.
Seeds of cv. Futura 75 were sown on 9 May 2014 in 18 containers (length × width × height: 40 × 40 × 30 cm). Each container was filled with 23 kg of soil (dry weight) that contained 0.22% total nitrogen and had a clay:silt:sand ratio of 30:43:27. Seeds were sown in excess in two rows and seedlings were hand-thinned to 18 uniform plants per container (ca. 113 plants m−2). Other nutrients than nitrogen were assumed to be abundantly available based on past experience in the field from which the soil was collected. During the growth period, water was supplied daily to field capacity for each container. The containers were placed outdoor and positioned tightly in a 1.2 × 2.4 m block. To avoid any border effect, the block perimeter was surrounded with a green shading net (transmitting 3% of the light); the height of the shading net was adjusted daily to account for the increment in plant height. The containers were rearranged weekly.
Three levels of dissolved urea fertilizer were applied to the soil after seedling emergence as: N1, no fertilizer applied; N2, 1.0 g N per container; N3, 2.0 g N per container, equivalent to ca. 0, 60, and 120 kg N (ha ground)−1, respectively. There were six containers per N level, subject to different levels of water supply during measurement (see later).
Whole canopy gas exchange was assessed twice during the course of the experiment by enclosing the canopy of each container in a flow-through gas exchange system. The first cycle of measurements (CAN1 hereafter) aimed to assess the response of diurnal canopy gas exchange to nitrogen and short-term water shortage. Canopy gas exchange in this cycle was assessed on 12 containers for 3 days, four containers per N treatment. Two of the containers per N treatment were supplied with sufficient water (measured as the amount of transpired water in the previous day) during the measurement while the water supply for the other two was halved. This cycle of measurements started 49 days after sowing when the 6th−8th pair of leaves appeared, the same leaf stages at which gas exchange at leaf level was assessed (Tang et al., 2017b). The second cycle of canopy gas exchange assessment (CAN2 hereafter) aimed to assess the response of canopy gas exchange to prolonged water shortage. In this cycle, canopy gas exchange was assessed on six containers during 13 subsequent days, two containers per N treatment. Measurement in this cycle started 79 days after sowing at the beginning of flowering. During the measurement, one container received the amount of water transpired during the previous day while the other one received half the amount, with the exception of the 8th day from the start of measurement when plants under stress showed signs of severe wilting. At the 8th day from the start of measurements, the same amount of water was supplied to all containers to avoid possible death of the plants under stress before the end of the experimental period.
Configuration of the flow-through gas exchange system was described by Poni et al. (2014) and refined by Fracasso et al. (2017). It consists of 12 cylindrical canopy chambers (diameter 50 cm) that are sealed with flexible plastic polyethylene on the side wall (transmitting 87% of the light) and a plastic polymethylmethacrylate disc on the top (transmitting 93% of the light). The air flowing through the canopy chamber (from the bottom to the top) was drawn from 3 m above ground using two centrifugal blowers (Vorticent C25/2M, Vortice, Milan, Italy). The system records instantaneous information for each chamber every 12 min using a CR1000 datalogger wired to an AM16/32B Multiplexer (Campbell Scientific, Logan, USA) as follows: CO2 concentration, vapor pressure and air temperature at the entrance of the chamber (CO2,in, VPin, and Tin, respectively) and the differences at the exit (CO2,dif, VPdif, and Tdif, respectively; calculated as the value at exit minus that at entrance), container weight (Wcontainer) and incident solar radiation intensity outside the chamber. The CO2,in, CO2,dif, VPin and VPdif were assessed using a CIRAS-DC dual-channel absolute CO2/H2O infrared gas analyser (PP-Systems, Amesbury, USA). The Tin and Tdif were assessed using PFA-Teflon insulated type-T thermocouples (Omega Engineering, Stamford, USA). The Wcontainer was monitored using a single cell platform scale placed under each container (ABC Bilance, Campogalliano, Italy).
In this study, the volume of each canopy chamber was 0.3 m3 (cross cutting area was 0.2 m2 and height was 1.5 m). Air flux entering each chamber was regulated at 4.3 × 10−3 m3 s−1. Thus, a complete volume air change required ca. 70 s. The flow rate was maintained constant during the whole measurement period. To prevent gas exchange between soil and plant chamber, the surface of each container was sealed with a plastic polyethylene film in which little slits were cut to allow hemp plants growing through. A small hole was made on the side wall of the container to supply water and allow gas exchange between soil and open air.
At the end of the canopy gas exchange assessment of each cycle, each container was assessed for the following parameters: the biomass weight of stems (Wstem), green leaves (Wleaf,g), senesced leaves (Wleaf,s; if present), inflorescences (Winflo; if present), and roots (Wroot), Ii/I0, LAI and SLN. For the containers receiving sufficient water in CAN1 the Ii/I0, LAI and SLN were assessed for four layers according to canopy height: 0–50, 50–75, 75–90, and 90–100%, while for the remaining containers the same parameters were assessed on the entire canopy. To estimate any system error introduced by gas leakage or soil respiration, gas exchange measurements were performed for 1–2 days on each container after the plants had been cut.
PAR was assumed to attenuate through the canopy following the Beer's law, based on LAI:
where LAIi is the LAI at depth i measured from the top; kL is the light extinction coefficient. kL was estimated by fitting the measured Ii/I0 and LAIi to Equation (1). To avoid any effect of measuring hour on the value of kL, all measured Ii/I0 were normalized to a value at zenith angle 0°, according to the manufacturer manual of AccuPAR LP-80.
The vertical gradient of SLN can be similarly described (Yin et al., 2003; Archontoulis et al., 2011):
where kn is the SLN extinction coefficient, SLN0 and SLNi are the SLN at the top of the canopy (i.e., at LAIi = 0) and at depth i, respectively. Thus, from canopy top to bottom, the cumulative nitrogen at depth i (Ni) can be solved from Equation (2) as:
By fitting the measured data for Ni-LAIi relationships to Equation (3), kn and SLN0 were estimated.
Data recorded from the multi-chamber gas exchange system was filtered to eliminate measurements impaired by short time fluctuations of air CO2 concentration and vapor pressure, and system mishaps. Subsequently, the values of CO2,dif and VPdif were corrected for potential system error due to gas leakage or soil respiration using data recorded in the chamber after the plants had been cut. Instantaneous canopy transpiration rate (Ec; mmol H2O m−2 s−1) and net photosynthesis rate (Ac,net; μmol CO2 m−2 s−1) were calculated using Equations (4, 5), respectively. These formulae were based on the study of Von Caemmerer and Farquhar (1981) for leaf gas exchange measurements. Different forms of these formulae were commonly used for calculating Ec and Ac,net in the studies of canopy gas exchange using the chamber system (Müller et al., 2005; Baker et al., 2009; Poni et al., 2014).
where ue (mol s−1) is air flux entering the plant chamber; a (m2) is the ground area of the canopy chamber; P (kPa) is the air pressure inside the plant chamber. The standard air pressure (101.3 kPa) was used as a proxy of P in the present study although a slight overpressure was maintained inside the plant chamber (less than 10 Pa) to avoid any flux of ambient air through possible leaks. The effect of overpressure on Ec and Ac,net was considered negligible (Burkart et al., 2007).
Canopy gross photosynthesis (Ac,gross) is the sum of Ac,net and canopy respiration (Rc). Rc during the night was estimated directly from Equation (5) as CO2,dif during the night was mainly a result of canopy respiration. During daytime, Rc was estimated considering the variation of temperature as:
where Rc,25 is the value of Rc at 25°C; ERc is the energy of activation; R is the universal gas constant (=8.314 J K−1 mol−1). The values of Rc25 and ERc were estimated from the measurements of Rc during night (Reichstein et al., 2005).
The sun/shade model of De Pury and Farquhar (1997), as implemented in the crop model GECROS (Yin and van Laar, 2005; Yin and Struik, 2017), was validated against measured Ac,gross. In this model, canopy leaves are divided into sunlit and shaded fractions and each fraction is modeled separately using a leaf photosynthesis model. When there is no water stress, potential leaf photosynthesis rate (Ap) is calculated using an analytical solution of combined stomatal conductance, CO2 diffusion and biochemical leaf-photosynthesis models (Yin and Struik, 2009, 2017). In the presence of water limitation, actual available water for canopy transpiration (Ec in the present study) is considered as input to estimate actual stomatal resistance to water vapor (rsw,a) due to stomatal closure. The formula is expressed as (Yin and van Laar, 2005; Yin and Struik, 2017):
where Ea is actual available water for leaf transpiration while Ep is calculated from the Penman-Monteith equation representing potential leaf transpiration; s is the slope of the saturated vapor pressure curve; rbh, rbw, and rsw,p are boundary layer resistances to heat, boundary resistance to water, and stomatal resistance to water transfer in absence of water stress, respectively; γ is the psychrometric constant (=0.067 kPa °C−1). For calculation of s, rbh and rbw, see Yin and van Laar (2005) and Yin and Struik (2017). rsw,p is assumed equal to 1/(1.6gs), where gs is calculated according to Ap. The estimated rsw,a is then used to compute actual canopy photosynthesis in the presence of water limitation. Any non-stomatal effect of water stress on photosynthesis, which needs detailed biochemical modeling, is not considered in the present study. Relevant model algorithms are summarized in the Supplementary text.
The values of model input parameters required for leaf photosynthesis were presented in Tang et al. (2017b) for the same hemp cultivar and are summarized in Supplementary Table S1. The canopy related parameters LAI, SLN, kL (for diffuse light) and kn were derived in this study. The leaf angle that was used to calculate the direct light extinction coefficient was fixed at 15°, an average value assessed using a goniometer. Instantaneous environmental parameters, i.e., CO2, VP, Tair and irradiation intensity, were recorded by the canopy chamber system.
The micro-environment differed between canopy chamber and ambient open air, and among treatments (see Results). Thus, the measured Ec and Ac,gross in the canopy chamber were normalized to that in the open air using the validated canopy model. Firstly, a correction factor f Ec was obtained, based on simulated potential canopy transpiration Ecp as:
where Ecp,air(s) and Ecp,chamber(s) are simulated potential canopy transpiration using weather data in open air and in the canopy chamber, respectively. The value of Ec corresponding to the open-air condition was then obtained by multiplying the measured Ec in the chamber with the correction factor f Ec. Subsequently, the corrected value of Ec for the open air and the measured Ec in the canopy chamber were used as inputs to obtain simulated canopy photosynthesis, Ac,gross, air(s) and Ac,gross, chamber(s), using weather data in the open air and in the canopy chamber, respectively. This gave a correction factor for Ac,gross (f Ac) as:
Finally, the value of Ac,gross corresponding to the open-air condition was calculated by multiplying the measured Ac,gross in the chamber with the factor f Ac.
Nonlinear fitting was carried out using the GAUSS method in PROC NLIN of SAS (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Analysis of variance was conducted to assess the effects of nitrogen fertilization and water shortage on canopy structure and gas exchange related parameters using SPSS statistics 22.0 (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois, USA).
Nitrogen fertilization resulted in an increase in canopy size and leaf nitrogen content. In the N60 plots where weed competition was negligible in the field experiment in 2014, LAI (leaf area index) was on average 3.2 and 4.8 m2 m−2 at linear growth stage and full flowering, respectively; SLN (specific leaf nitrogen) was on average 0.97 and 0.67 g N (m2 leaf)−1, respectively. In the field experiment in 2015, LAI of the N120 plots was 4.0 and 6.4 m2 m−2 at the onset of the linear growth stage and at full flowering, respectively, while SLN was 1.27 and 1.17 g N (m2 leaf)−1, respectively (Figure S1). Providing less nitrogen fertilization than 120 kg N ha−1 resulted in reductions in LAI and SLN. The LAI and SLN of N120 plots were on average 2.8 times and 1.2 times higher than those of non-fertilized canopies. In CAN1, LAI ranged from 1.8 to 2.6 m2 m−2; SLN ranged from 0.84 to 1.02 g N (m2 leaf)−1. Nitrogen fertilization in CAN1 resulted in increases in LAI and SLN by 40 and 19%, respectively (Table 1). For the well-watered containers in CAN2, the average values of LAI and SLN were 2.0 m2 m−2 and 0.68 g N (m2 leaf)−1, respectively (Table 2). Withholding water for 13 days in CAN2 resulted in an increase in the weight of senesced leaves while the weight of green leaves was reduced (Table 3). Consequently, water-stressed canopies had a 36% lower LAI than well-watered canopies (Table 2). While water stress resulted in a reduction in canopy size, the SLN of water-stressed canopies was 51% higher than that of well-watered canopies.
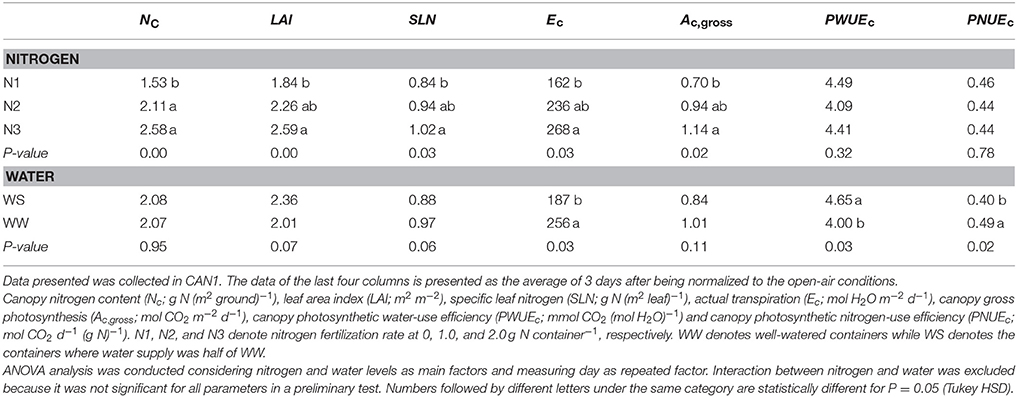
Table 1. The effects of nitrogen deficiency and short-term water shortage on canopy transpiration and carbon assimilation.
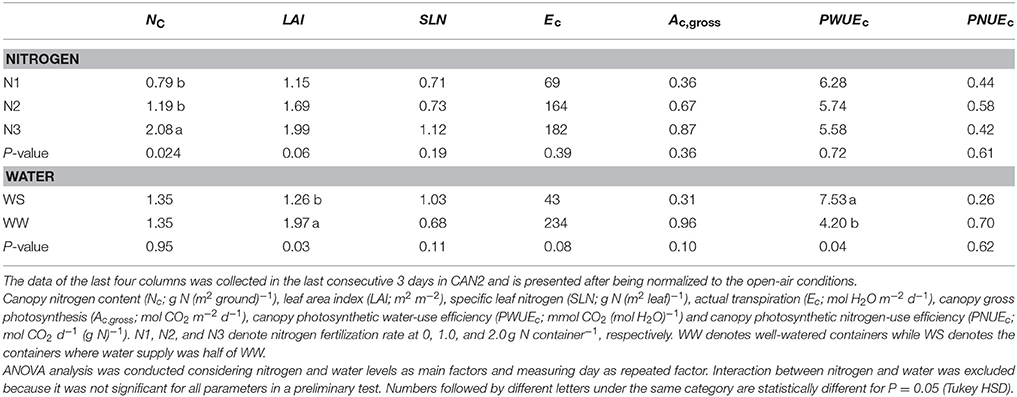
Table 2. The effects of nitrogen deficiency and long-term water shortage on canopy transpiration and carbon assimilation.
Light intensity and SLN decreased progressively with increasing depth from top to bottom (Figure S2). The value of kL (the light extinction coefficient) was 0.96 ± 0.04 m2 m−2 and was similar for nitrogen fertilization levels and growth environments (Figure S3A). The SLN0 (SLN at the top of the canopy) ranged from 1.43 to 2.72 g N (m2 leaf)−1 and the kn (nitrogen extinction coefficient) ranged from 0.09 to 0.89 m2 m−2. The values of kn decreased exponentially with an increase in LAI (Figure S3B). This relationship between kn and LAI was consistent among nitrogen fertilization levels and growth environments. Thus, this relationship was applied to calculate kn in subsequent model analyses.
The night-time chamber air temperature Tair ranged from 14.7 to 25.7°C and from 17.1 to 27.0°C during the measurements in CAN1 and CAN2, respectively. There was little difference in micro-environmental variables [i.e., Tair, CO2 (CO2 concentration) and VP (vapor pressure)] during the night-time between chamber and ambient open air, and among treatments within chambers (Figure 1). During daytime, incident PAR reached up to 2,100 μmol m−2 s−1 while Tair, CO2 and VP in the open air ranged from 17.6°C to 35.9°C, from 359.7 μmol mol−1 to 439.4 μmol mol−1, and from 1.7 kPa to 2.5 kPa, respectively. The daytime Tair and VP within chambers were higher than those in the open air while the CO2 was lower (Figure 1). Increasing nitrogen fertilization rate increased the differences in Tair, VP and CO2 between chamber and ambient open air while reducing water supply increased the difference in Tair but decreased the differences in VP and CO2.
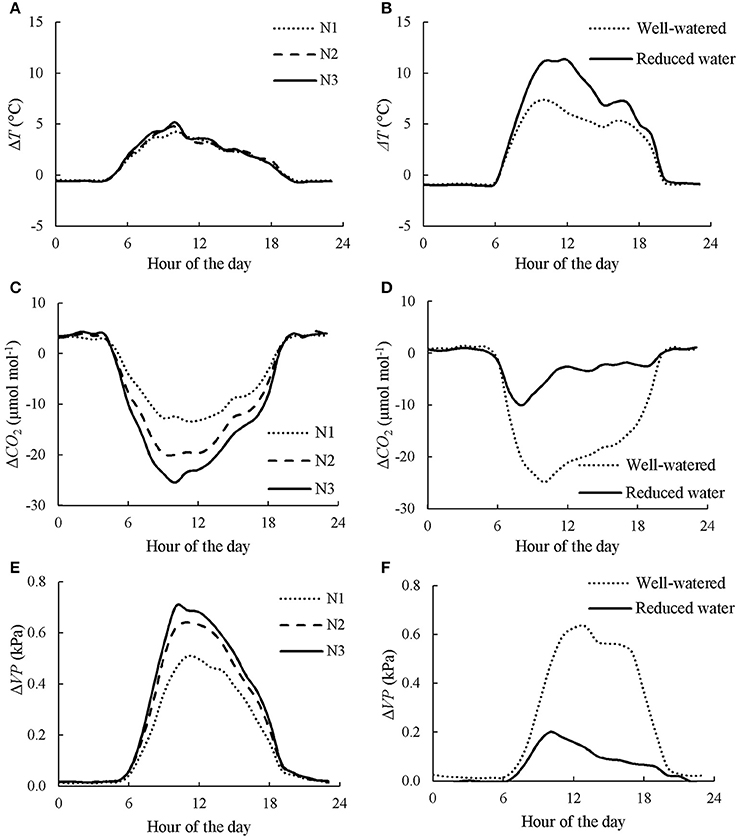
Figure 1. Diurnal courses of canopy chamber effects on air temperature (ΔT), CO2 concentration (ΔCO2), and vapor pressure (ΔVP) under different nitrogen (A,C,E) and water (B,D,F) regimes. Data presented in A,C,E is the average of 3 days in CAN1. N1, N2, and N3 denote the level of received nitrogen, see text for details. Data presented in B,D,F is the average of the last consecutive 3 days in CAN2.
The night-time canopy respiration Rc varied largely from minute to minute, presumably due to a relatively low Rc and high flow rate. Nevertheless, Rc increased slightly with increasing chamber Tair (Figure S4). By fitting these data to Equation (6), ERc (activation energy for Rc) was estimated as 9,559 ± 2,779 J mol−1. The estimate of Rc25 (Rc at 25°C) ranged from 3.9 to 4.9 μmol CO2 m−2 s−1 in CAN1, and from 0.50 to 2.09 μmol CO2 m−2 s−1 in CAN2 (Figure 2A). The difference in respiration rate between experiments was probably due to differences in growth stage. With the estimated ERc and Rc25, instantaneous gross canopy photosynthesis rate Ac,gross in CAN1 and CAN2 was estimated. The daily Rc (canopy respiration) increased with increasing Ac,gross in both CAN1 and CAN2 but with different relationships (Figure 2B), and accounted for on average 40 and 15% of Ac,gross in CAN1 and CAN2, respectively.
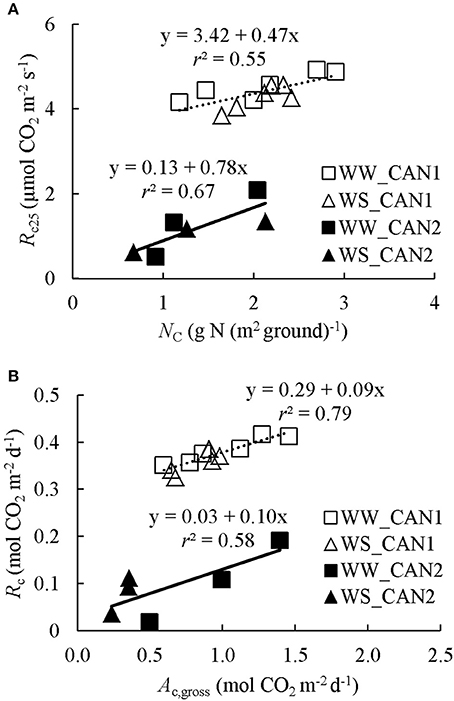
Figure 2. (A) Responses of canopy respiration at 25°C (Rc25) to canopy leaf nitrogen content (NC). (B) Relationship between daily integrated canopy respiration (Rc) and gross photosynthesis (Ac,gross). WW and WS denote well-watered and water-limited conditions, respectively. CAN1 and CAN2 are experimental codes, see text for details.
Examples of diurnal courses of measured canopy transpiration Ec and Ac,gross within canopy chambers are presented in Figure 3. The Ec and Ac,gross were close to nil during night-time while during the daytime their values rose up to 11.1 mmol H2O m−2 s−1 and 38.1 μmol CO2 m−2 s−1, respectively. For the well-watered containers, the values of Ec and Ac,gross throughout the day followed closely their simulated potential transpiration Ecp and simulated potential photosynthesis Acp,gross (Figure 3). As expected, the values of Ec and Ac,gross of the containers that received half amount of water were lower than their Ecp and Acp,gross from the late morning to the end of daytime. Integration of the instantaneous Ec to daily values matched well with the amount of supplied water per day (Figure 4). Thus, the Ac,gross was simulated considering Ec as available water for transpiration at canopy level. The Ec was partitioned between sunlit and shaded leaves according to the relative share of their Ecp to obtain their actual transpiration (Ea) at leaf level in Equation (7). There was a good agreement between the measured and simulated Ac,gross under different nitrogen and water regimes (Figure 3). The values of r2 and rRMSE for the comparison between measured and simulated values of all data points in CAN1 were 0.80 and 32%, respectively (part of the data points can be seen in Figure S5). For the measurements in CAN2, they were 0.78 and 66%, respectively.
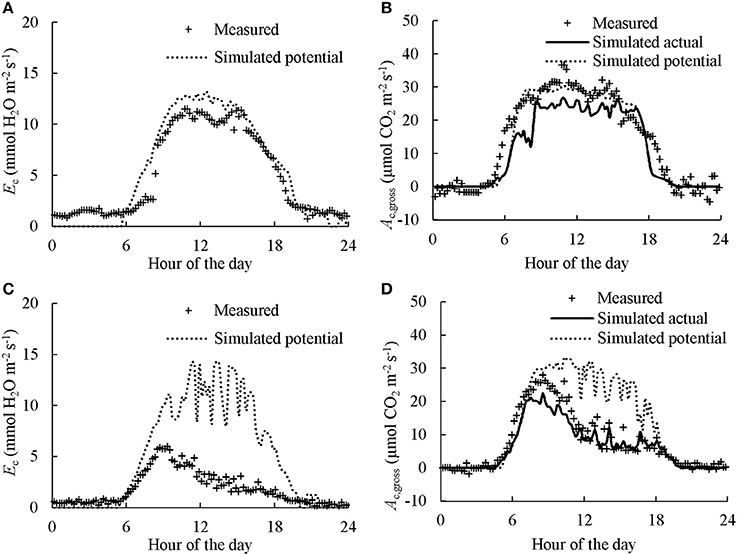
Figure 3. Diurnal courses of measured and simulated canopy transpiration (Ec; A,C) and gross photosynthesis rates (Ac,gross; B,D). The “Measured” dots present the values calculated from gas exchange measurement. The “Simulated potential” line presents the outcome of model simulation without considering water stress. The “Simulated actual” line in B,D presents the outcome of model simulation considering the estimated Ec as actual available water for transpiration while the effect of water deficiency on stomatal resistance was estimated using Equation (7). Data presented was collected in the first day of N2 in CAN1.The canopy in A,B received sufficient water while water supply in C,D was halved.
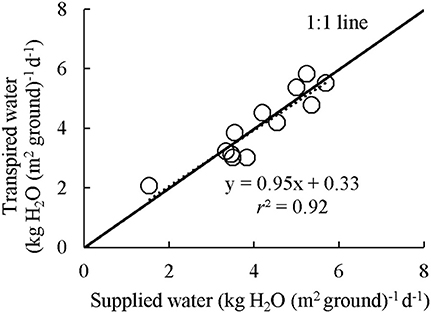
Figure 4. Integrated water loss through transpiration as measured by canopy gas exchange in comparison with the amount of supplied water. Each point represents the daily average of water loss versus water gain over the measuring period for each container in CAN1. The amount of supplied water was calculated as the difference of container weight at before and after watering.
The effects of micro-environmental differences between chamber and open air, and among treatments within chambers on canopy gas exchange were assessed using the validated model (Table 4). The presence of the plant chamber increased Ecp by 6.9–11.2% in CAN1 and by 19.6–34.2% in CAN2 while it decreased Acp,gross by 0.3–1.4% in CAN1 and by 3.5–4.2% in CAN2. The chamber effect on Ecp varied little among nitrogen treatments while the effect on Acp,gross increased with an increase in nitrogen rate. Water shortage increased the effects of the chamber on both Ecp and Acp,gross. Therefore, to account for any effect of varying micro-environmental variables due to the presence of the canopy chamber, the measured Ec and Ac,gross within each chamber were normalized to the conditions in the open air.
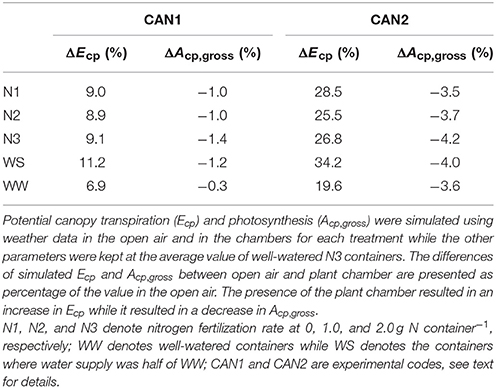
Table 4. The effects of plant chamber on canopy transpiration and photosynthesis under different nitrogen and water regimes.
Examples of the diurnal courses of normalized Ec and Ac,gross in CAN1 are presented in Figure 5. Despite minute-to-minute fluctuations due to environmental variability, the Ec and Ac,gross were consistently higher in the fertilized canopies than in the non-fertilized canopies and water shortage resulted in reductions in Ec and Ac,gross occurring from the late morning to the end of the day. Consequently, daily integrated Ec and Ac,gross increased with an increase in nitrogen fertilization rate while they decreased under water limiting conditions (Table 1). The daily integrated Ec and Ac,gross ranged from 162 to 268 mol H2O m−2 d−1 and from 0.70 to 1.14 mol CO2 m−2 d−1, respectively. The canopy photosynthetic water-use efficiency (PWUEc), defined as the ratio of Ac,gross to Ec, ranged from 4.00 to 4.65 mmol CO2 (mol H2O)−1. The PWUEc did not differ significantly among nitrogen treatments while it increased by 16% under water limiting conditions compared to the control. The canopy photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency (PNUEc), the ratio of Ac,gross to Nc, ranged from 0.40 to 0.49 mol CO2 d−1 (g N)−1. No significant effect of nitrogen fertilization on PNUEc was observed (P > 0.05), while PNUEc decreased significantly (by 18%; P < 0.05) under water limiting conditions (Table 1).
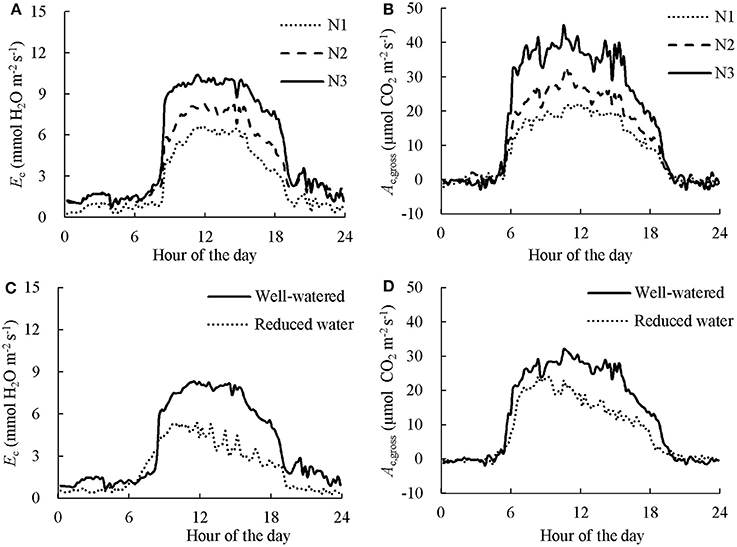
Figure 5. The effect of nitrogen (A,B) and short-term water stress (C,D) on instantaneous canopy transpiration (A,C) and photosynthesis rate (B,D). Data presented was collected in the first day in CAN1. The data has been normalized to the open-air conditions. N1, N2, and N3 denote the level of received nitrogen, see text for details.
As water shortage was prolonged in CAN2, the progressive responses of Ec, Ac,gross, and PWUEc are presented in Figure 6. Despite day to day fluctuations due to variable weather, reductions of Ec and Ac,gross emerged 4 days after withholding water and lasted until the end of the gas exchange measurements when all plants were cut for analysis. A short recovery was observed during the 8th day due to a brief re-watering of wilting plants in the water-stressed canopies (see Materials and Methods section). During the last 3 days, the average daily Ec, Ac,gross, PWUEc, and PNUEc in the well-watered canopies were 234 mol H2O m−2 d−1, 0.96 mol CO2 m−2 d−1, 4.20 mmol CO2 (mol H2O)−1, and 0.70 mol CO2 d−1 (g N)−1, respectively (Table 2). The values of Ec, Ac,gross and PNUEc were higher than those of water-stressed canopies by 82, 68, and 63%, respectively, while the PWUEc was lower than that of water-stressed canopies by 79%.
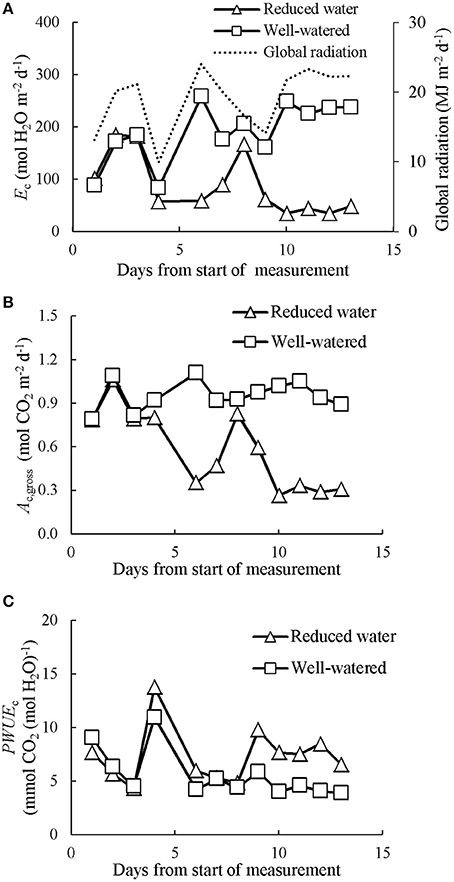
Figure 6. The evolution of prolonged water limitation effects on daily canopy transpiration (Ec; A), gross photosynthesis (Ac,gross; B) and canopy photosynthetic water-use efficiency (PWUEc; C). Data presented was collected in CAN2. The data has been normalized to the open-air conditions.
Model analyses were performed to assess the relative importance of LAI and SLN, the two important canopy physiological parameters, in determining potential PWUEc (PWUEcp) and PNUEc (PNUEcp) in both the field experiment and the chamber experiment. This was done by first using the measured SLN and LAI of each nitrogen level as the default simulation and then forcing LAI or SLN of all treatments to their respective values at the non-fertilized or water stressed treatment (Figure 7). For both linear-growth and flowering stages of the field experiment, when forcing SLN to the value at non-fertilized treatment the values of Ecp, Acp,gross, PWUEcp, and PNUEcp changed little in comparison with those of the default simulation, whereas when forcing LAI to the value at non-fertilized treatment their values deviated significantly from the default simulation. In the chamber experiment in CAN1, the variations of Ecp, Acp,gross, and PWUEcp with increasing nitrogen rate were mainly due to a change in LAI whereas the variation of PNUEcp was due to combined changes in LAI and SLN. In the chamber experiment in CAN2, the decrease in Ecp under long-term stress was mainly due to a change in LAI while the variations of Ac,gross, PWUEcp, and PNUEcp were due to combined changes in LAI and SLN.
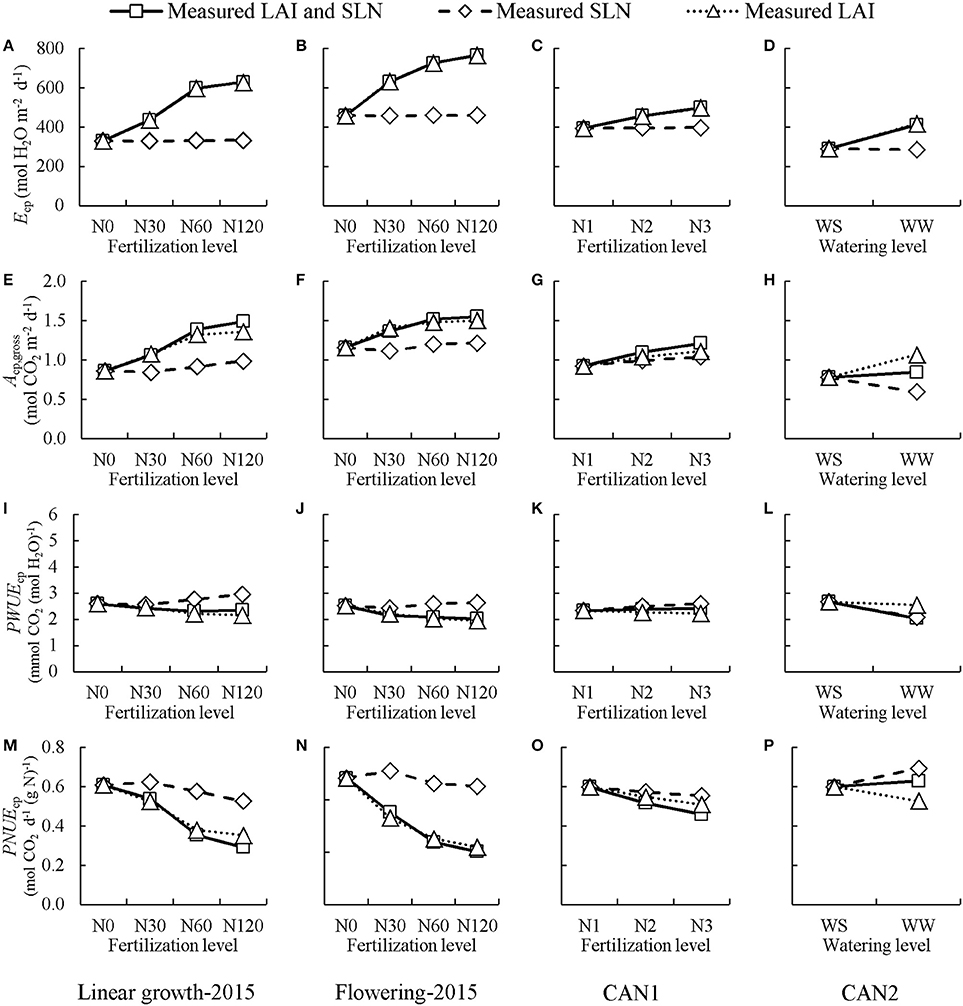
Figure 7. The simulated effects of nitrogen fertilization and water shortage on daily potential canopy transpiration (Ecp; A–D), gross photosynthesis (Acp,gross; E–H), and canopy photosynthetic water-use efficiency (PWUEcp; I–L). and canopy photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency (PNUEcp; M–P). “Measured LAI and SLN” line: the default simulations performed using the measured leaf area index (LAI) and specific leaf nitrogen (SLN) at each nitrogen level or each water level. “Measured SLN” line: simulations performed with measured SLN at each nitrogen level (or each water level) while keeping LAI fixed at the values of non-fertilization (or water-stressed) treatment. “Measured LAI” line: simulations performed with measured LAI at each nitrogen level (or each water level) while keeping SLN fixed at the values of non-fertilization (or water-stressed) treatment. Linear growth-2015 (A,E,I,M) denotes the case where the values of LAI and SLN were collected at the linear growth stage in the field experiment in 2015; Flowering-2015 (B,F,J,N) denotes the case where the values of LAI and SLN were collected at full flowering in the field experiment in 2015; CAN1 (C,G,K,O) denotes the case where the values of LAI and SLN were collected in the CAN1; CAN2 (D,H,L,P) denotes the case where values of LAI and SLN were collected in the CAN2. N0, N30, N60, N120 denote nitrogen fertilization rate in 2015 at 0, 30, 60, and 120 kg N ha−1, respectively; N1, N2, and N3 denote nitrogen fertilization rate in CAN1 at 0, 1.0, and 2.0 g N container−1, respectively. Note the x-axes of the N treatment are not on scale. WW denotes well-watered containers in CAN2 while WS denotes the containers where water supply was half of WW.
Bio-economically sustainable agronomy requires effective use of scarce nitrogen and water resources. While hemp is considered as a bio-economically sustainable crop (Finnan and Styles, 2013; Amaducci et al., 2015; Tang et al., 2017b), its water- and nitrogen-use efficiencies have not been well addressed so far. As photosynthesis is the most important physiological process determining crop water- and nitrogen-use efficiencies, this study combined experimental and modeling analyses to assess the balance between canopy photosynthetic carbon gain and its water and nitrogen costs under different nitrogen and water regimes.
The canopy chamber technique is a useful tool to assess crop responses to nitrogen deficiency and water shortage at canopy scale. However, the presence of the chamber wall had a significant effect on the micro-environment within the chambers (Figure 1), confirming the results of previous studies (Poni et al., 1997; Takahashi et al., 2008; Müller et al., 2009). In the present study, a large difference of the micro-environment was also observed among nitrogen and water treatments that is probably due to their different rates of canopy transpiration and photosynthesis. The micro-environment conditions within the chamber resulted in a lower Acp,gross and a higher Ecp than those in the open air, and this effect was larger in the chambers with higher fertilization rate and lower water supply (Table 4). As responses of Ec and Ac,gross to environmental variables are probably not linear (Hikosaka et al., 2016), it is necessary to normalize measurements within different chambers to avoid any confounding effect due to the differences in chamber micro-environmental factors.
In line with previous studies (Leuning et al., 1998; Müller et al., 2005), the variation of Ec and Ac,gross in response to fluctuating environmental conditions under different nitrogen and water regimes can be precisely described using a process-based physiological model (Figure 3). Thus, discrepancies in Ec and Ac,gross among chambers due to differences in micro-environment at measuring time could be properly accounted for through correction factors f Ec and f Ac, respectively (see Equations 8, 9), in our study.
The reason for the lack of significant responses of PWUEc and PNUEc to the decrease in nitrogen rate in the container experiments is not clear (Table 1). It is probably due to small variations in LAI and SLN among nitrogen treatments. This is confirmed in the model analysis for the field experiment in 2015, where the variation in LAI among N treatments was much more significant than that in our container experiment. This model analysis suggested that both PWUEc and PNUEc increased with decreasing nitrogen fertilization rate, and that the increases in PWUEc and PNUEc were mainly a result of a reduction in LAI (Figure 7). The reduced LAI resulted in increases in PWUEc and PNUEc, i.e., the reduction in Ac,gross with a decrease in LAI is less than the reductions in Ec and in NC. This could be explained by an optimum SLN gradient relative to the light gradient in the canopy. It has been reported that the profile of SLN in a canopy is a whole-plant process that depends on canopy size (Moreau et al., 2012). Our data showed that the value of kn increased with decreasing LAI (Figure S3B), up to a value of ca. 0.9 close to the LAI-independent value of kL (0.96 m2 m−2, Figure S3A). So, the value of kn in a large hemp canopy was generally lower than its theoretical value for a maximized canopy photosynthesis, which could be achieved only when kn = kL (Hirose and Werger, 1987; Hikosaka et al., 2016). When LAI is low, canopy photosynthesis is close to a maximum value as a result of kn being close to kL; in such a case, the average leaf photosynthesis rate could be increased for a given amount of Nc, while Ec stayed largely unchanged.
The variation in PWUEc and PNUEc with decreasing nitrogen fertilization rate may also be attributed to the variation in the absolute amount of SLN. It has been widely reported that SLN positively correlates with water-use efficiency while it negatively correlates with nitrogen-use efficiency at leaf level (Van den Boogaard et al., 1995; Shangguan et al., 2000; Cabrera-Bosquet et al., 2007). However, in response to nitrogen stress, hemp tends to maintain SLN at the expense of LAI (Figure S1). This response is in line with that of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.), canola (Brassica napus L.) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) whereas it contrasts with that of maize (Zea mays L.), which tends to maintain LAI under nitrogen stress at the expense of SLN (Lemaire et al., 2008). As a result of the relative small variation in SLN among nitrogen treatments, little effect of SLN was detected on the hemp PWUEc and PNUEc (Figure 7).
The effects of nitrogen fertilization on crop water-use efficiency and nitrogen-use efficiency are whole plant processes that depend on leaf photosynthetic capacity and canopy size, and our analysis showed that relative to leaf photosynthetic capacity (determined by SLN), canopy size (LAI) plays a predominant role in this.
Field observations generally show that water stress results in an increase in hemp water-use efficiency (Cosentino et al., 2013). This is confirmed by our results showing both short-term and long-term water shortages that resulted in an increase in PWUEc (Tables 1, 2). However, our study further showed that the effect differed between short- and long-term stresses.
In response to short-term water stress, the increase in PWUEc is mainly a consequence of stomatal closure as the variations in Ec and Ac,gross with decreasing water supply were precisely captured by considering the response of stomatal conductance (Figure 3). In fact, stomatal closure is one of the earliest responses to water deficit, protecting the plants from extensive water loss (Chaves et al., 2003). Stomatal closure restricts both H2O and CO2 exchange between leaf intercellular and ambient air that leads to great decreases in Ec and Ac,gross (Table 1; Figure 3). However, the reductions in Ec and Ac,gross are not parallel and the PWUEc increased under water stress, probably because of the non-linear relationship between carbon assimilation rate and CO2 concentration in the intercellular space (Tang et al., 2017b). The higher value of PWUEc under water stress indicates that the estimation of canopy photosynthesis under water limiting condition by assuming a consistent PWUEc in the crop models, such as SUCROS (van Laar et al., 1997), is only an approximation. Instead, the present study considered the response of stomatal conductance using Equation (7) that results in higher value of PWUEc under water stress. This approach is therefore preferable in the simulation of canopy photosynthesis under short-term water stress conditions. Nevertheless, we could not exclude the possibility that non-stomatal limitations were involved in our experiment. Further researches are needed to understand the effect of non-stomatal change under water-stress conditions on canopy photosynthesis, such as change of leaf angle (Archontoulis et al., 2011).
As water stress continued, hemp responded through reducing LAI and increasing SLN, while NC stayed unchanged (Table 2). The reduced LAI was largely caused by increased senescence (Table 3). Because of this additional response, model analysis for the sensitivity in response to changing LAI or SLN was contrasting between CAN1 and CAN2 (Figure 7). This type of response to a long-term water stress was also observed in studies on other species such as kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) and sunflower (Danalatos and Archontoulis, 2010; Archontoulis et al., 2011). The response could result in more significant increases in PWUEc as a result of both the stomatal response discussed above and the reduced evaporative surfaces. However, an increase in SLN could not compensate for the loss in LAI; so, the long-term stress resulted in large reductions in the Acp,gross, Ecp, and PNUEc (Table 2). This result indicates that crop models for predicting the effect of long-term water stress should introduce mechanisms on the responses of canopy-level traits (like LAI) in addition to stomatal regulation. It also suggests that although hemp is tolerant to long-term water stress through improving water-use efficiency (Cosentino et al., 2013), its final biomass yield and nitrogen-use efficiency may be restricted largely by water limitation during growth.
KT, XY, and SA conceived and planned the experiment. KT and AF set up and monitored the canopy gas exchange system. KT performed the experimental work and data analysis. KT and AF drafted the manuscript. SA, PS, and XY revised the manuscript. SA and XY supervised the research. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development and demonstration under grant agreement n° 311849. Drs Steven Driever and Tjeerd-Jan Stomph are thanked for their early discussions.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2018.00951/full#supplementary-material
Amaducci, S., and Gusovius, H. J. (2010). “Hemp-cultivation, extraction and processing,” in Industrial Applications of Natural Fibres: Structure, Properties and Technical Applications, ed J. Müssig (West Sussex: John Wiley Sons Ltd.), 109–134.
Amaducci, S., Scordia, D., Liu, F. H., Zhang, Q., and Guo, H. (2015). Key cultivation techniques for hemp in Europe and China. Ind. Crops Prod. 68, 2–16. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.06.041
Archontoulis, S. V., Vos, J., Yin, X., Bastiaans, L., Danalatos, N. G., and Struik, P. C. (2011). Temporal dynamics of light and nitrogen vertical distributions in canopies of sunflower, kenaf and cynara. Field Crops Res. 122, 186–198. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.03.008
Baker, J. T., Van Pelt, S., Gitz, D. C., Payton, P., Lascano, R. J., and McMichael, B. (2009). Canopy gas exchange measurements of cotton in an open system. Agronomy J. 101, 52–59. doi: 10.2134/agronj2008.0007x
Barth, M., and Carus, M. (2015). Carbon Footprint and Sustainability of Different Natural Fibres for Biocomposites and Insulation Material. Hürth: Nova-Institute. Available online at: http://eiha.org/media/2017/01/15-04-Carbon-Footprint-of-Natural-Fibres-nova1.pdf (Accessed Sept 5, 2017).
Bertoli, A., Tozzi, S., Pistelli, L., and Angelini, L. G. (2010). Fibre hemp inflorescences: from crop-residues to essential oil production. Ind. Crops Prod. 32, 329–337. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.05.012
Bouloc, P., and van der Werf, H. M. G. (2013). “The role of hemp in sustainable development,” in Hemp: Industrial Production and Uses. eds P. Bouloc, S. Allegret and L. Arnaud (Croydon: CPi Group (UK) Ltd.), 278–289
Burkart, S., Manderscheid, R., and Weigel, H. J. (2007). Design and performance of a portable gas exchange chamber system for CO2-and H2O-flux measurements in crop canopies. Environ. Exp. Bot. 61, 25–34. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.02.007
Cabrera-Bosquet, L., Molero, G., Bort, J., Nogués, S., and Araus, J. (2007). The combined effect of constant water deficit and nitrogen supply on WUE, NUE and Δ13C in durum wheat potted plants. Ann App Biol. 151, 277–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.2007.00195.x
Calzolari, D., Magagnini, G., Lucini, L., Grassi, G., Appendino, G. B., and Amaducci, S. (2017). High added-value compounds from Cannabis threshing residues. Ind. Crops Prod. 108, 558–563. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.06.063
Chaves, M. M., Maroco, J. P., and Pereira, J. S. (2003). Understanding plant responses to drought—from genes to the whole plant. Funct. Plant Biol. 30, 239–264. doi: 10.1071/FP02076
Cosentino, S. L., Riggi, E., Testa, G., Scordia, D., and Copani, V. (2013). Evaluation of European developed fibre hemp genotypes (Cannabis sativa L.) in semi-arid Mediterranean environment. Ind. Crops Prod. 50, 312–324. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.07.059
Danalatos, N. G., and Archontoulis, S. V. (2010). Growth and biomass productivity of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus, L.) under different agricultural inputs and management practices in central Greece. Ind. Crops Prod. 32, 231–240. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.04.013
De Meijer, E. P. M., and van der Werf, H. M. G. (1994). Evaluation of current methods to estimate pulp yield of hemp. Ind. Crops Prod. 2, 111–120. doi: 10.1016/0926-6690(94)90092-2
De Pury, D., and Farquhar, G. (1997). Simple scaling of photosynthesis from leaves to canopies without the errors of big-leaf models. Plant Cell Environ. 20, 537–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.1997.00094.x
Finnan, J., and Styles, D. (2013). Hemp: a more sustainable annual energy crop for climate and energy policy. Energy Policy 58, 152–162. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2013.02.046
Fracasso, A., Magnanini, E., Marocco, A., and Amaducci, S. (2017). Real-time determination of photosynthesis, transpiration, water-use efficiency and gene expression of two sorghum bicolor (Moench) genotypes subjected to dry-down. Front. Plant Sci. 8:932. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00932
Hikosaka, K., Kumagai, T., and Ito, O. A. (2016). “Modeling canopy photosynthesis,” in Canopy Photosynthesis: From Basics to Applications, eds K. Hikosaka, Ü. Niinemets, and N. P. R. Anten (Dordrecht: Springer), 239–268.
Hirose, T., and Werger, M. J. A. (1987). Maximizing daily canopy photosynthesis with respect to the leaf nitrogen allocation pattern in the canopy. Oecologia 72, 520–526. doi: 10.1007/BF00378977
Jones, H. G. (2013). “Heat, mass and momentum transfer,” in Plants and Microclimate: A Quantitative Approach to Environmental Plant Physiology, ed H. G. Jones (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press), 47–67.
Leizer, C., Ribnicky, D., Poulev, A., Dushenkov, S., and Raskin, I. (2000). The composition of hemp seed oil and its potential as an important source of nutrition. J Nutrac. Funct. Med. Foods 2, 35–53. doi: 10.1300/J133v02n04_04
Lemaire, G., Van Oosterom, E., Jeuffroy, M.-H., Gastal, F., and Massignam, A. (2008). Crop species present different qualitative types of response to N deficiency during their vegetative growth. Field Crops Res. 105, 253–265. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2007.10.009
Leuning, R., Dunin, F., and Wang, Y.-P. (1998). A two-leaf model for canopy conductance, photosynthesis and partitioning of available energy. II. Comparison with measurements. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 91, 113–125. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(98)00074-4
Linderson, M.-L., Mikkelsen, T. N., Ibrom, A., Lindroth, A., Ro-Poulsen, H., and Pilegaard, K. (2012). Up-scaling of water use efficiency from leaf to canopy as based on leaf gas exchange relationships and the modeled in-canopy light distribution. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 152, 201–211. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2011.09.019
Moreau, D., Allard, V., Gaju, O., Le Gouis, J., Foulkes, M. J., and Martre, P. (2012). Acclimation of leaf nitrogen to vertical light gradient at anthesis in wheat is a whole-plant process that scales with the size of the canopy. Plant Physiol. 160, 1479–1490. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.199935
Müller, J., Behrens, T., and Diepenbrock, W. (2005). Measurement and modelling of canopy gas exchange of oilseed rape. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 132, 181–200. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.07.006
Müller, J., Eschenröder, A., and Diepenbrock, W. (2009). Through-flow chamber CO2/H2O canopy gas exchange system—Construction, microclimate, errors, and measurements in a barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) field. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 149, 214–229. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2008.08.007
Poni, S., Magnanini, E., and Rebucci, B. (1997). An automated chamber system for measurements of whole-vine gas exchange. Hort Sci. 32, 64–67.
Poni, S., Merli, M. C., Magnanini, E., Galbignani, M., Bernizzoni, F., Vercesi, A., et al. (2014). An improved multichamber gas exchange system for determining whole canopy water use efficiency in the grapevine. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 65, 268–276. doi: 10.5344/ajev.2014.13117
Reichstein, M., Falge, E., Baldocchi, D., Papale, D., Aubinet, M., Berbigier, P., et al. (2005). On the separation of net ecosystem exchange into assimilation and ecosystem respiration: review and improved algorithm. Global Change Biol. 11, 1424–1439. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2005.001002.x
Shangguan, Z., Shao, M., and Dyckmans, J. (2000). Nitrogen nutrition and water stress effects on leaf photosynthetic gas exchange and water use efficiency in winter wheat. Environ. Exp. Bot. 44, 141–149. doi: 10.1016/S0098-8472(00)00064-2
Struik, P. C., Amaducci, S., Bullard, M. J., Stutterheim, N. C., Venturi, G., and Cromack, H. T. H. (2000). Agronomy of fibre hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) in Europe. Ind. Crops Prod. 11, 107–118. doi: 10.1016/S0926-6690(99)00048-5
Takahashi, N., Ling, P. P., and Frantz, J. M. (2008). Considerations for accurate whole plant photosynthesis measurement. Environ. Control Bio. 46, 91–101. doi: 10.2525/ecb.46.91
Tang, K., Struik, P. C., Amaducci, S., Stomph, T., and Yin, X. (2017b). Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) leaf photosynthesis in relation to nitrogen content and temperature: implications for hemp as a bio-economically sustainable crop. GCB Bioenergy 9, 1573–1587. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12451
Tang, K., Struik, P. C., Yin, X., Calzolari, D., Musio, S., Thouminot, C., et al. (2017a). A comprehensive study of planting density and nitrogen fertilization effect on dual-purpose hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivation. Ind. Crops Prod. 107, 427–438. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.06.033
Tang, K., Struik, P. C., Yin, X., Thouminot, C., Bjelková, M., Stramkale, V., et al. (2016). Comparing hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivars for dual-purpose production under contrasting environments. Ind. Crops Prod. 87, 33–44. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.026
Tomás, M., Medrano, H., Pou, A., Escalona, J., Martorell, S., Ribas-Carbó, M., et al. (2012). Water-use efficiency in grapevine cultivars grown under controlled conditions: effects of water stress at the leaf and whole-plant level. Aust. J. Grape Wine R. 18, 164–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0238.2012.00184.x
Van den Boogaard, R., Kostadinova, S., Veneklaas, E., and Lambers, H. (1995). Association of water use efficiency and nitrogen use efficiency with photosynthetic characteristics of two wheat cultivars. J. Exp. Bot. 46, 1429–1438. doi: 10.1093/jxb/46.special_issue.1429
van Laar, H. H., Goudriaan, J., and van Keulen, H. (1997). SUCROS97: Simulation of Crop Growth for Potential and Water-Limited Production Situations, as Applied to Spring Wheat. Report series No. 14, Quantitative Approaches in Systems Analysis, Wageningen.
Von Caemmerer, S., and Farquhar, G. D. (1981). Some relationships between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and the gas exchange of leaves. Planta 153, 376–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00384257
Wright, J., Williams, M., Starr, G., McGee, J., and Mitchell, R. (2013). Measured and modelled leaf and stand-scale productivity across a soil moisture gradient and a severe drought. Plant Cell Environ. 36, 467–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02590.x
Yin, X. Y., Lantinga, E. A., Schapendonk, A. H. C. M., and Zhong, X. H. (2003). Some quantitative relationships between leaf area index and canopy nitrogen content and distribution. Ann. Bot. 91, 893–903. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcg096
Yin, X. Y., and Struik, P. C. (2009). C3 and C4 photosynthesis models: an overview from the perspective of crop modelling. NJAS Wageningen J. Life Sci. 57, 27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.njas.2009.07.001
Yin, X. Y., and Struik, P. C. (2017). Can increased leaf photosynthesis be converted into higher crop mass production? A simulation study for rice using the crop model GECROS. J. Exp. Bot. 68, 2345–2360. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx085
Keywords: canopy gas exchange, hemp, Cannabis sativa L., nitrogen use efficiency, water use efficiency
Citation: Tang K, Fracasso A, Struik PC, Yin X and Amaducci S (2018) Water- and Nitrogen-Use Efficiencies of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Based on Whole-Canopy Measurements and Modeling. Front. Plant Sci. 9:951. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00951
Received: 14 March 2018; Accepted: 13 June 2018;
Published: 16 July 2018.
Edited by:
Luis A. N. Aguirrezabal, National University of Mar del Plata, ArgentinaReviewed by:
Xinguang Zhu, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS), ChinaCopyright © 2018 Tang, Fracasso, Struik, Yin and Amaducci. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xinyou Yin, eGlueW91LnlpbkB3dXIubmw=
Stefano Amaducci, c3RlZmFuby5hbWFkdWNjaUB1bmljYXR0Lml0
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.