
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 27 March 2025
Sec. Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Pharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1591086
This article is a correction to:
Cynaroside ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway
 Ju Huang1,2†
Ju Huang1,2† Jing Li1,2†
Jing Li1,2† Zhijun Geng2,3†
Zhijun Geng2,3† Lixia Yin1,2
Lixia Yin1,2 Minzhu Niu2
Minzhu Niu2 Qingqing Li1,4
Qingqing Li1,4 Xinyue Liu2
Xinyue Liu2 Xinke Cheng2
Xinke Cheng2 Xiaofeng Zhang2
Xiaofeng Zhang2 Xue Song2,3
Xue Song2,3 Yueyue Wang1,2
Yueyue Wang1,2 Lian Wang2
Lian Wang2 Lugen Zuo2
Lugen Zuo2 Jianguo Hu1,2*
Jianguo Hu1,2*A Corrigendum on
Cynaroside ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway
by Huang J, Li J, Geng Z, Yin L, Niu M, Li Q, Liu X, Cheng X, Zhang X, Song X, Wang Y, Wang L, Zuo L and Hu J (2025). Front. Pharmacol. 15:1496068. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1496068
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 7 as published. Two Western blot (WB) strips were misused in Figure 7L (markers: Cas3 and GAPDH). The incorrect strips in Figure 7L were mistakenly used from two strips in Figure 8G (markers: Cas3 and GAPDH). The corrected Figure 7 and its caption appear below.
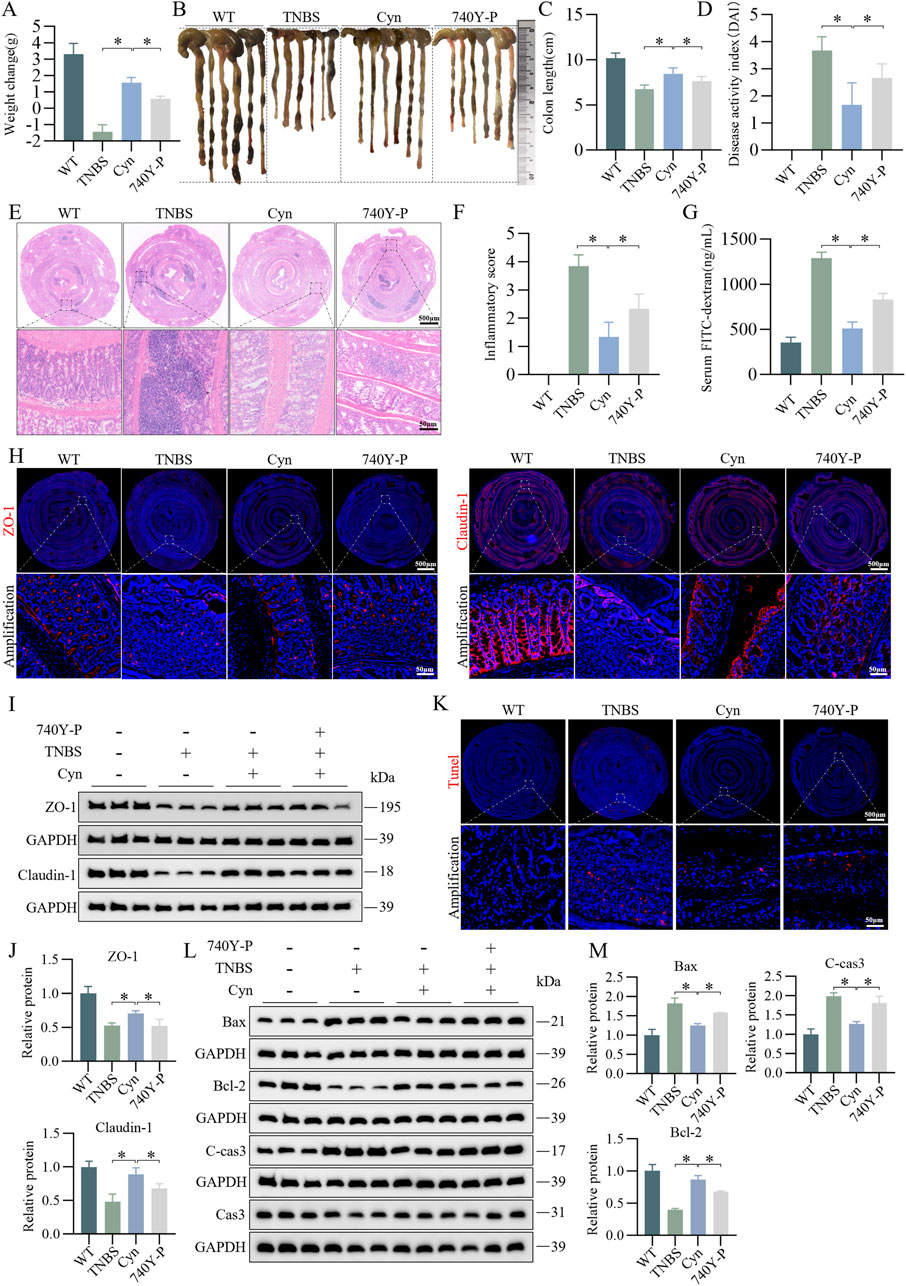
Figure 7. Cyn suppresses IEC apoptosis through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in TNBS mice. (A) Changes in mouse weight. (B, C) Appearance of mouse colon and colon length. (D) DAI scores. (E, F) Colon inflammation scores and H&E staining for each mouse group. (G) FITC-dextran (FD4) levels in mouse blood. (H) Immunofluorescence analysis of ZO-1 and Claudin-1 in mouse colon tissues. (I, J) Western blot analysis of ZO-1 and Claudin-1 in mouse colon mucosa tissues, with relative quantification of protein levels. (K) TUNEL staining of colon tissues from mice. (L, M) Western blot analysis of apoptosis-related proteins in mouse colon mucosa tissues, with relative quantification of protein levels. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations, n = 6, *p < 0.05.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease, cynaroside, IECs apoptosis, colonic organoids, PI3K/AKT
Citation: Huang J, Li J, Geng Z, Yin L, Niu M, Li Q, Liu X, Cheng X, Zhang X, Song X, Wang Y, Wang L, Zuo L and Hu J (2025) Corrigendum: Cynaroside ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1591086. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1591086
Received: 10 March 2025; Accepted: 21 March 2025;
Published: 27 March 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Zhenhua Li, Jinan University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Huang, Li, Geng, Yin, Niu, Li, Liu, Cheng, Zhang, Song, Wang, Wang, Zuo and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianguo Hu, amdodTkyMDBAYmJtYy5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.