
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 19 February 2025
Sec. Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Pharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1554390
This article is a correction to:
Alcohol Abstinence Rescues Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury via Improving Metabolic Reprogramming in Chronic Alcohol-Fed Mice
 Aiwen Pi1,2,3†
Aiwen Pi1,2,3† Kai Jiang2,4†
Kai Jiang2,4† Qinchao Ding1,3
Qinchao Ding1,3 Shanglei Lai1,2
Shanglei Lai1,2 Wenwen Yang1,2
Wenwen Yang1,2 Jinyan Zhu1,3
Jinyan Zhu1,3 Rui Guo1,3
Rui Guo1,3 Yibin Fan5
Yibin Fan5 Linfeng Chi6*
Linfeng Chi6* Songtao Li1,4,3*
Songtao Li1,4,3*A Corrigendum on
Alcohol Abstinence rescues hepatic steatosis and liver injury via improving metabolic reprogramming in chronic alcohol-fed mice
by Pi A, Jiang K, Ding Q, Lai S, Yang W, Zhu J, Guo R, Fan Y, Chi L and Li S (2021). Front. Pharmacol. 12:752148. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.752148
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 4 as published. The statistical analysis column chart in Figure 4B was based on the ratio of phosphorylation target proteins to non-phosphorylation of target proteins, but not to internal reference protein GAPDH. To avoid any potential misunderstanding, the band of GAPDH was removed from Figure 4B, as it is unrelated to the quantification of detected proteins.
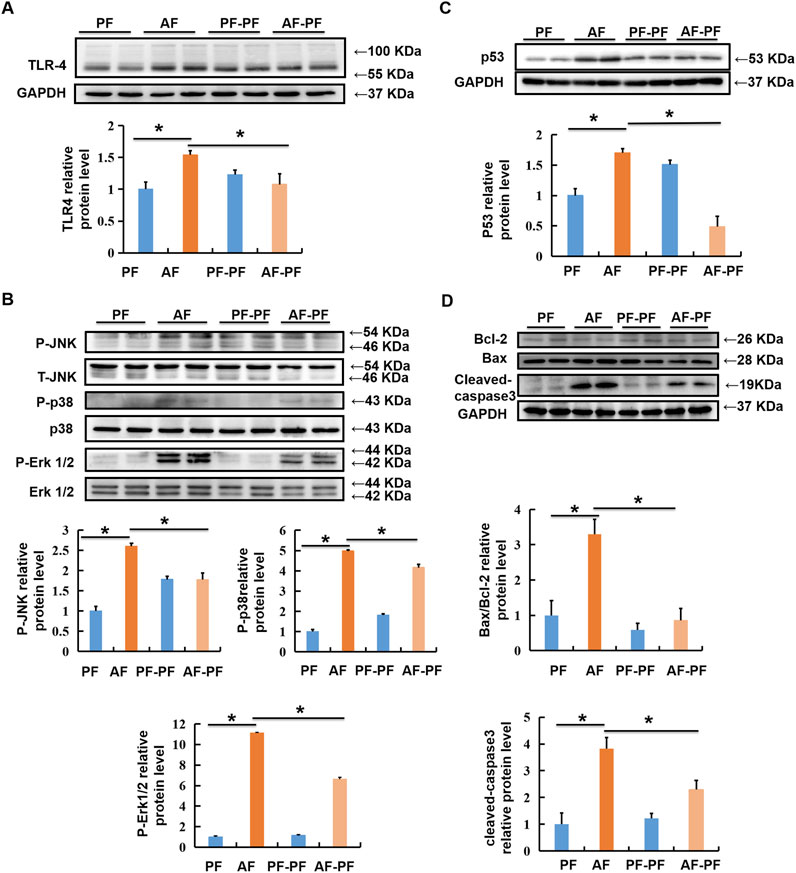
Figure 4. Alcohol withdrawal rescues alcohol-stimulated TLR4/MAPKs and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways. Total cellular lysates were extracted from mice liver tissues. (A, B) Immunoblotting assay was performed for TLR-4, p-JNK, p-P38, and p-ERK1/2. (C, D) Immunoblotting assay was performed for P53 and Bax/Bcl-2. *p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences (n = 8).
Additionally, the same band of GAPDH was used both in Figures 4C, D, since the bands and data in those panels were based on the same samples with the same loading amount. In order to avoid confusion, we have replaced the band in Figure 4C with other representative images selected from our research records. In the original version, the statistical analysis of data was performed based on all the bands, including previously and currently displayed, therefore, this replacement does not affect the results and conclusions. The corrected Figure 4 and its caption appear below.
‘Alcohol withdrawal rescues alcohol-stimulated TLR4/MAPKs and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways. Total cellular lysates were extracted from mice liver tissues. (A, B) Immunoblotting assay was performed for TLR-4, p-JNK, p-P38, and p-ERK1/2. (C, D) Immunoblotting assay was performed for P53 and Bax/Bcl-2. *p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences (n = 8).’
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: alcoholic liver disease, alcohol abstinence, hepatic steatosis, liver injury, hepatic inflammation
Citation: Pi A, Jiang K, Ding Q, Lai S, Yang W, Zhu J, Guo R, Fan Y, Chi L and Li S (2025) Corrigendum: Alcohol abstinence rescues hepatic steatosis and liver injury via improving metabolic reprogramming in chronic alcohol-fed mice. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1554390. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1554390
Received: 02 January 2025; Accepted: 31 January 2025;
Published: 19 February 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Zhenyuan Song, University of Illinois Chicago, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Pi, Jiang, Ding, Lai, Yang, Zhu, Guo, Fan, Chi and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Songtao Li, bGlzb25ndGFvQHpjbXUuZWR1LmNu; Linfeng Chi, bGluZmVuZ2NoaUB6Y211LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.