
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol. , 10 February 2025
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1532246
This article is part of the Research Topic Naturally Occurring Compounds and Their Applications in Endocrinology: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Potential and Clinical Applications View all 3 articles
Diabetes mellitus (DM) and its various complications, including diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, cardiovascular disease, and ulcers, pose significant challenges to global health. This review investigates the potential of procyanidins (PCs), a natural polyphenolic compound, in preventing and managing diabetes and its complications. PCs, recognized for their strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-hyperglycemic properties, play a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress and enhancing endothelial function, which are essential for managing diabetic complications. This review elucidates the molecular mechanisms by which PCs improve insulin sensitivity and endothelial health, thereby providing protection against the various complications of diabetes. The comprehensive analysis underscores the promising therapeutic role of PCs in diabetes care, indicating the need for further clinical studies to confirm and leverage their potential in comprehensive diabetes management strategies.
DM is a major global health issue characterized by persistent hyperglycemia due to insufficient insulin secretion or action (Ill-Min et al., 2020; Constanze et al., 2017; Zhimei et al., 2019). The main symptoms include increased appetite, thirst, urination, and weight loss (Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus, 2013). In 2021, approximately 536.6 million people aged 20–79 were diagnosed with diabetes globally, and this number is projected to reach 783.2 million by 2045 (Hong et al., 2022). Diabetes is triggered by genetic and environmental factors, leading to the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic-β-cells, impairing insulin production, and disrupting metabolic processes, resulting in hyperglycemia (Décio et al., 2020; Aleksey and Peter, 2008; Kathryn et al., 2013). Prolonged hyperglycemia can lead to severe complications such as diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiomyopathy (Janika et al., 2022; David et al., 2023) (Figure 1). Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death among diabetic patients, particularly cardiac complications (Justin et al., 2016; Anoop et al., 2015).
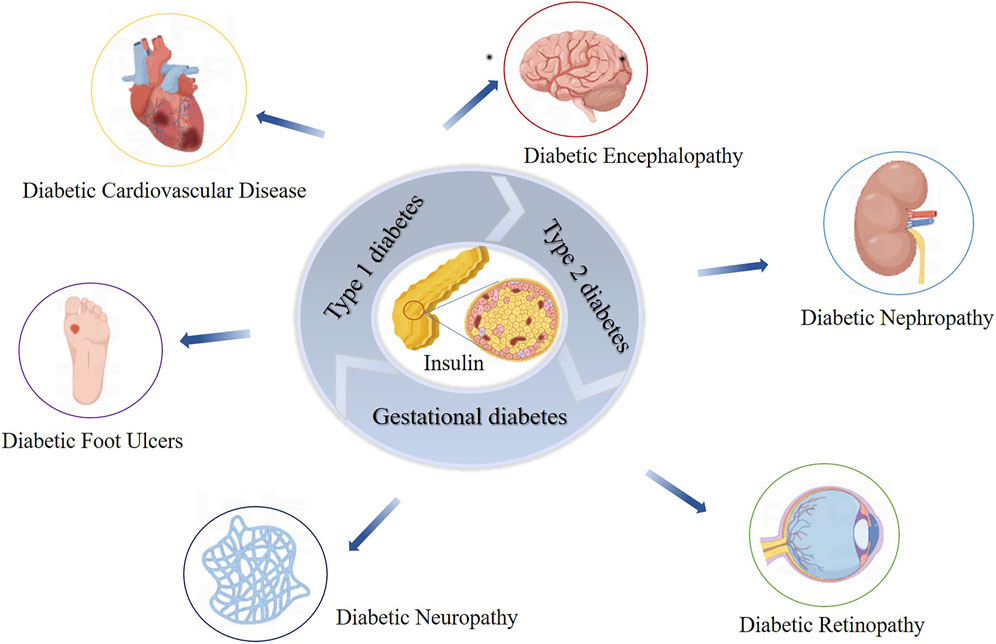
Figure 1. Impact of Insulin Dysfunction on Diabetes Mellitus and Related Complications. This figure illustrates the impact of insulin dysfunction on the development of diabetes mellitus and its associated complications. It shows how impaired insulin action leads to widespread metabolic disturbances, culminating in serious health issues such as nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, cardiovascular disease, and diabetic ulcers.
Over the past few decades, several pharmacological agents have been developed to regulate blood glucose. Metformin primarily reduces hepatic gluconeogenesis through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), while sulfonylureas (e.g., glimepiride) enhance insulin secretion by closing pancreatic β-cell ATP-sensitive potassium channels (Reuben et al., 2005; Gaochao et al., 2001; Mary, 2004). Thiazolidinediones (e.g., pioglitazone) improve insulin sensitivity via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) modulation (Aya et al., 2020; Zhiwei et al., 2021). More recent approaches include dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which prolong the half-life of incretin hormones, and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, which stimulate insulin secretion and reduce glucagon levels (Daniel and Michael, 2006). Additionally, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors lower blood glucose by promoting urinary glucose excretion (André, 2019). Current antidiabetic drugs mainly control blood glucose levels but cannot prevent or reverse complications (Dandan et al., 2020). Therefore, effective therapeutic strategies are urgently needed to halt or mitigate the progression of diabetes and its complications.
PCs, composed of flavan-3-ol and flavan-3, 4-diol units, include catechins, apocynin, and gallocatechins (Chunhui, 2014; Liwei et al., 2002; Linards et al., 2022; Liang et al., 2016). Their main sources encompass grains, legumes, fruits, chocolate, and drinks like tea and wine (Abdur et al., 2019; Feng et al., 2016) (Figure 2). PCs exhibit diverse bioactivities such as anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and cardiovascular protective effects (Eskandar et al., 2023; Antoni et al., 2012; Qian et al., 2023; Chuntang et al., 2022; Van Long et al., 2014; Liang et al., 2012). Studies suggest that PCs can lower blood glucose, improve insulin resistance, regulate insulin secretion, protect pancreatic β-cells in diabetic patients, and effectively alleviate diabetes complications (Javier et al., 2018; Suzanne et al., 2017; Anna et al., 2012). This review summarizes the molecular mechanisms and protective effects of PCs in diabetes treatment, which are shown in Table 1.
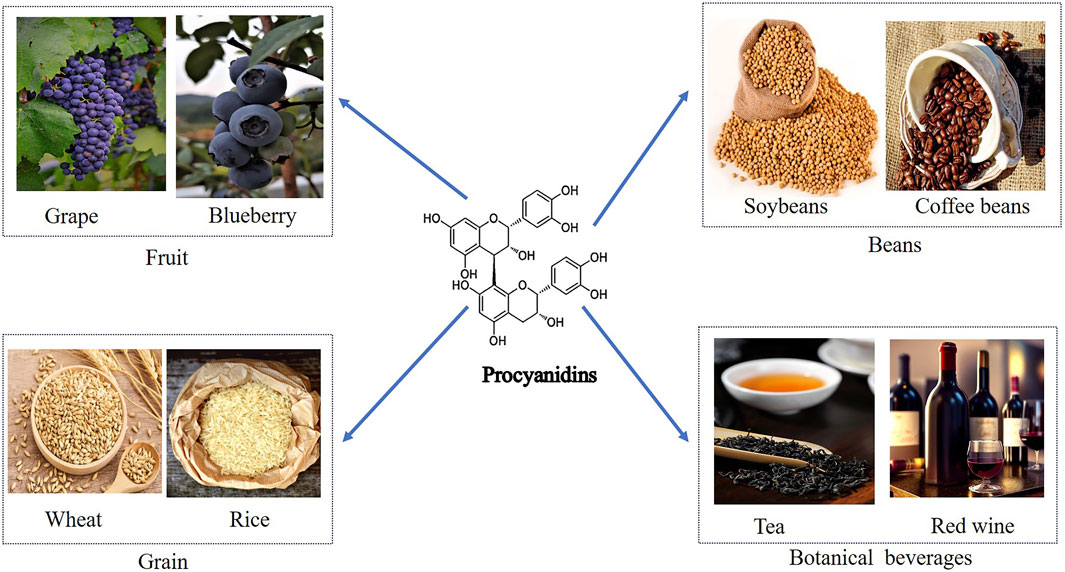
Figure 2. Dietary Sources of Procyanidins and Its Chemical Structure. This figure displays the major dietary sources of PCs and its chemical structure. The sources are grouped into categories including fruits like grapes and blueberries, beans such as soybeans and coffee beans, grains like wheat and rice, and botanical beverages including tea and red wine. The centralfigure illustrates the molecular structure of PCs, emphasizing its presence across diverse food groups.
PCs are characterized by their double and single bonds, with catechols or epicatechols as fundamental components (Kaul, 1996). The health benefits of PCs are constrained by their low oral bioavailability due to incomplete intestinal absorption and extensive metabolism and excretion (Brigitte et al., 1989; Yue et al., 2021; Claudine et al., 2005; Ying Yng et al., 2014). It is estimated that over 90% of dietary polyphenols remain in the colon, with only a small fraction being indirectly absorbed in the small intestine through interactions with carbohydrates, fibers, and proteins (Michael, 2004; Gary and Claudine, 2005). Multiple factors influence the hydrolytic absorption of PCs, including gastrointestinal pH, dietary composition, and solubility in gastric and intestinal fluids. The acidic environment of the stomach may facilitate initial PCs release from food matrices but can also degrade certain oligomers, reducing their structural integrity and bioavailability. In the small intestine, dietary fibers and proteins can form complexes with PCs, limiting absorption, whereas lipids may enhance PCs solubility through micelle or emulsion formation. Tannins can further decrease bioavailability by competing for binding sites or forming insoluble complexes. Once in the colon, unabsorbed PCs oligomers and polymers interact with enterocyte membrane proteins, potentially modulating metabolic pathways (Liang et al., 2016). Meanwhile, gut microbiota convert these higher-order PCs into smaller phenolic acids (e.g., hydroxybenzoic, hydroxyphenylacetic, and hydroxycinnamic acids) with better solubility and increased absorption (Maaike et al., 2009). Ultimately, these metabolites are excreted in the urine (Figure 3).
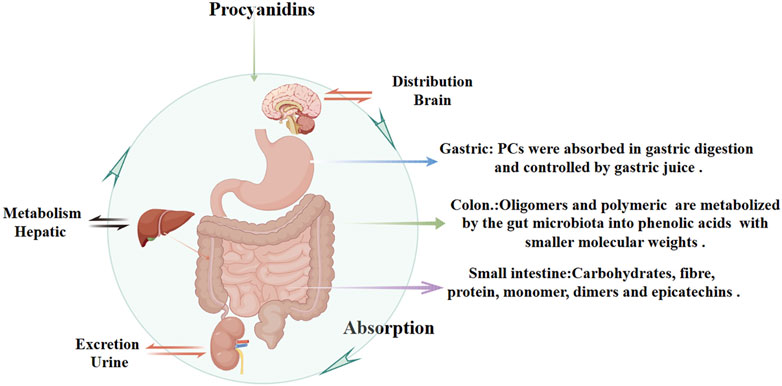
Figure 3. Pharmacokinetics of Procyanidins. This figure illustrates the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of PCs. PCs are partially absorbed in the stomach and small intestine, with interactions involving dietary components like carbohydrates, fibers, and proteins. In the colon, unabsorbed PCs are metabolized by gut microbiota into phenolic acids with smaller molecular weights, improving solubility and systemic absorption. Hepatic metabolism further processes PCs, and their metabolites are eventually excreted through urine.
Low bioavailability remains a major hurdle for harnessing the therapeutic benefits of PCs, necessitating innovative delivery approaches such as nano-encapsulation, phospholipid complexation, and co-administration with permeability enhancers. These strategies aim to stabilize PCs structure against pH-induced degradation, improve solubility, and promote systemic circulation. Further studies are required to elucidate the optimal conditions, formulations, and dietary adjuncts that maximize PCs efficacy in diabetes management. By advancing our understanding of PCs pharmacokinetics, including absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, and refining targeted formulations, we can better leverage their therapeutic potential in preventing and managing diabetes and its complications.
We conducted a comprehensive search on the PubMed (www.pubmed.com) and Web of Science (www.webofscience.com) databases for articles on procyanidins and diabetes published from 1 January 2000, to 30 December 2024. The research methodology is illustrated in Figure 4.
Procyanidins OR Procyanidin B2 OR GSPE OR Procyanidin B3 OR Catechin OR flavan-3-ol) AND (Diabetes mellitus OR diabetic nephropathy OR diabetic retinopathy OR diabetic neuropathy OR diabetic foot ulcer OR diabetic encephalopathy OR diabetic cardiovascular disease OR diabetic cardiomyopathy.
(1): The document type is limited to original research articles or reviews; (2) Relevant to the topic of “procyanidins” and “diabetes”.
(1) Irrelevant to the objective of this review; (2) Duplicated or outdated literature.
Insulin, an essential hormone secreted by pancreatic β-cells, regulates glucose metabolism and exerts a profound influence on blood glucose levels (Gary and Patricia, 2021). Typically, insulin binds to receptors on the surfaces of target cells, thereby reducing hepatic glucose output and promoting glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue (Benedetta et al., 2019). When various internal and external factors drive target cells toward insulin resistance, greater amounts of insulin are required to trigger glucose transport and utilization. This phenomenon, referred to as insulin resistance, features elevated glucose and insulin levels in the bloodstream (Rosalyn and Solomon, 1960; Christian et al., 2013).
Located in the cell membrane, the insulin receptor exhibits a tetrameric structure with two α-chains and two β-chains, serving as the primary hub for insulin action and orchestrating the insulin signaling cascade. Upon binding to the α-chain, insulin governs glucose transport and adiposity and modulates cell proliferation and differentiation. This interaction enhances gluconeogenesis while suppressing adipose tissue catabolism (Marinko et al., 2021). When insulin engages the β-chain, it triggers the insulin receptor substrate (IRS1/2), thereby boosting glucose metabolism (via the PI3K/PKB/AKT pathway), protein synthesis (via the TSC1/2-mTOR pathway), and cell proliferation and differentiation (via the RAS-MAPK-ERK1/2 pathway) (Rebecca et al., 2017; Barbara Di et al., 2016; Teri et al., 1991). Interruptions throughout the insulin signaling pathway can ultimately lead to insulin resistance. Often, diverse kinases and phosphatases—for instance, phosphorylated tyrosine—amplify serine/threonine phosphorylation, inactivating IRS proteins and worsening insulin resistance (Kyle and Morris, 2012). Additionally, processes involving kappa kinase β (IKK-β), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK-1), protein kinase C (PKC), and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-driven serine modification of IRS1 also contribute to insulin resistance, further intensified by free fatty acids, lipotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammation (Stergios et al., 2009). PCs are frequently cited for their ability to improve insulin sensitivity in experimentally induced diabetic rats (Antoni et al., 2017; Anna et al., 2013). Previous studies underscore the marked antihyperglycemic effects of PCs in rats maintained on a high-fructose diet (Najim et al., 2004; Takako et al., 2008; Hsiang-Jung et al., 2008). Ramesh CK and colleagues found that PCs extracts from cranberries and blueberries, administered prophylactically, significantly mitigated insulin resistance, boosted glucose sensitivity, and lowered blood glucose in diabetic rats fed a high-fructose diet, reinforcing the therapeutic value of PCs (Ramesh et al., 2010; Ramesh et al., 2012). M Liu et al. provided PCs to T2D mice (75, 150, and 300 mg/kg) via continuous gavage for 4 weeks, documenting improvements in intestinal barrier integrity by restoring morphology and raising the expression of tight junction proteins, including Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), Claudin-1, and occludin. This approach substantially reduced insulin resistance, promoted glucose uptake, and lowered blood glucose levels by activating the IRS1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (Min et al., 2022). Further in vitro research corroborated these results. I Cordero-Herrera et al. cultured insulin-sensitive human HepG2 cells under high-glucose conditions and administered cocoa-derived polyphenols and epicatechin, which blocked tyrosine phosphorylation and lowered total IR, IRS-1, and IRS-2 levels through PI3K/AKT and AMPK pathway inhibition, thereby mitigating high-glucose-induced insulin signaling impairment that alters gluconeogenesis (Isabel et al., 2014). The activation and subsequent engagement of the insulin receptor (IR) and its downstream mediators, IRS-1 and IRS-2, remain critical for regulating insulin signaling (Mary et al., 2002). In hepatic insulin resistance, normal tyrosine phosphorylation of IR and IRS is compromised, diminishing PI3K activity associated with IRS. Conversely, the oligomeric form of grape seed procyanidin (GSPE) extract induces tyrosine phosphorylation, thereby activating the IR and decreasing AKT and GSK-3β phosphorylation via PI3K/AKT pathway stimulation. This process augments GS phosphorylation, thereby improving hepatic insulin sensitivity (Aurèle et al., 2019; Rui et al., 2020; Gemma et al., 2010a) (Figure 5). Meanwhile, a glucose-lowering formulation containing hawthorn polyphenols, D-chiro-inositol, and epigallocatechin gallate exhibited synergistic hypoglycemic activity, markedly improving insulin resistance in mice, decreasing fasting blood glucose and hepatic gluconeogenesis, and enhancing hepatic glycogen synthesis and storage (Chao et al., 2021). Additionally, a randomized controlled trial revealed that a combination of flavan-3-ols and isoflavones enhanced insulin sensitivity and lipoprotein profiles compared to placebo, further lowering the estimated 10-year CVD risk in women with type 2 diabetes (Peter et al., 2012).
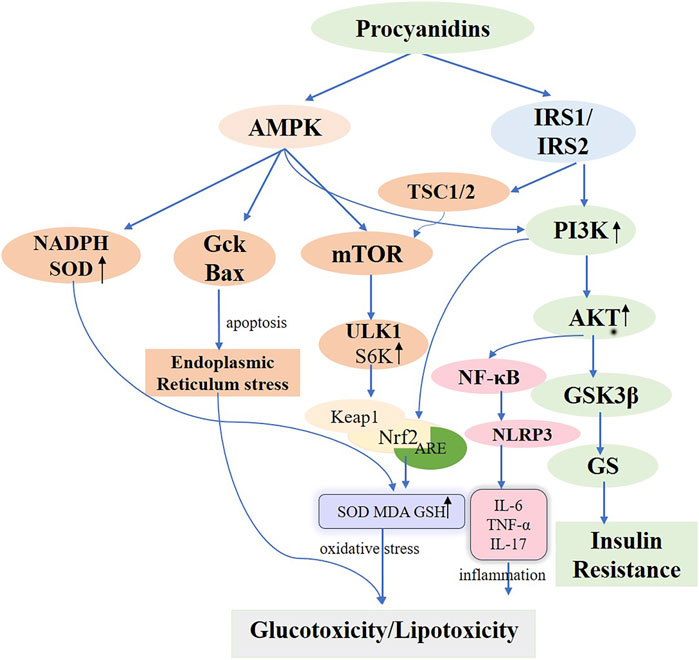
Figure 5. Molecular Mechanisms of Procyanidins in Modulating Diabetes Mellitus. This figure delineates the comprehensive molecular pathways impacted by PCs in the management of DM. PCs enhance insulin sensitivity by activating PI3K/AKT signaling via IRS1/IRS2 and reduce insulin resistance through GSK3β inhibition. PCs also alleviate oxidative stress by activating AMPK and Nrf2 pathways, increasing antioxidants like SOD and GSH, while reducing inflammatory responses mediated by NF-κB and NLRP3. Additionally, PCs modulate cellular stress and autophagy, mitigating endoplasmic reticulum stress and promoting metabolic homeostasis. These mechanisms collectively address glucotoxicity, lipotoxicity, and insulin resistance in diabetes.
In summary, under insulin-resistant conditions, polyphenolic PCs can effectively bolster cellular insulin sensitivity. However, prior investigations have yet to establish the ideal PCs concentration and dose for mitigating insulin resistance or to clarify the therapeutic distinctions among active metabolites from diverse sources. Future studies should center on identifying effective concentrations and characterizing botanical metabolites derived from multiple sources.
Glucotoxicity is characterized by irreversible tissue and cell damage resulting from insulin resistance and persistently elevated glucose levels stemming from excessive carbohydrate intake (Mota et al., 2016). The primary cause of glucotoxicity is insulin resistance, which arises from defective islet cell function and damage caused by reduced insulin mRNA expression, associated with diminished transcription or activity of transcription factors involved in insulin production (Daniël and Michaëla, 2011). Insulin resistance significantly contributes to hyperglycemia-induced glucotoxicity. Excess carbohydrates are metabolized into free fatty acids and triglycerides, promoting adipogenesis and lipoatrophy through the activation of enzymes like acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FAS), and SCD-1 (Mota et al., 2016). These processes are influenced by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and islet inflammation (Maria et al., 2020; Wenqian et al., 2018; Jiwon and Kun-Ho, 2011).
Prolonged exposure to elevated fatty acid levels triggers lipotoxicity, compromising pancreatic β-cell functionality and viability. This condition activates multiple stress pathways, resulting in β-cell impairment and mortality. ER stress and oxidative stress are especially well-documented contributors to this effect (Kerry et al., 2005; Eloisa Aparecida et al., 2021; Andrei et al., 2007). Cellular lipotoxicity, also known as glycolipotoxicity, is exacerbated by elevated glucose levels (Yiqi et al., 2022). Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX), a producer of reactive oxygen species (ROS), acts as a key generator of oxidative stress within pancreatic islet β-cells, significantly affecting glucose-induced insulin release and β-cell viability in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes (Eloisa Aparecida et al., 2021). Animal studies demonstrate that palmitate impairs insulin secretion by upregulating the p47phox NOX subunit protein within rat pancreatic islets (Marta et al., 2010). Shuang et al. (2017) demonstrated that PCs from lychee pericarp decrease mRNA levels of cellular NADPH oxidase subunits (p47phox, p67phox, NOXJ2/gp91phox, and NOXJ4) and enhance superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, thereby providing a strong antioxidant effect. Additionally, Xinyi et al. (2020) found that cinnamon tannin D1, an A-type PCs oligomer derived from Cinnamomum cinnamomi, protects pancreatic β-cells against glucotoxicity induced by high glucose and palmitic acid, both in vitro and in vivo. The key process entails CD-1 initiating autophagy in pancreatic β-cells via the AMPK/mTOR/UNC-52-like kinase 1 (ULK1) pathway. This autophagic response reduces cell damage by activating the Keap1/Nrf2 antioxidant pathway, which is associated with Kelch-like ECH protein 1 and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, thereby mitigating inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis. Consequently, this lowers hyperglycemia and reduces glycotoxicity in diabetic db/db mice (Figure 5). A clinical study found (Hadi et al., 2020) that supplementation with epigallocatechin-3-gallate significantly increased serum total antioxidant capacity (TAC) levels in patients with type 2 diabetes, thereby enhancing the body’s overall antioxidant capacity.
In summary, this section systematically elucidates the mechanisms through which glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity impact pancreatic β-cell function and survival, leveraging both literature and experimental evidence to underscore the potential application of PCs in mitigating these pathological processes. In particular, PCs extracted from lychee pericarp and A-type PCs oligomers (CD-1) derived from cinnamon exhibit promising effects on autophagy activation, mitigation of β-cell damage, and enhancement of glucose metabolism. However, a notable gap remains between these findings and their clinical application. First, many uncertainties exist regarding the absorption, distribution, and metabolism of PCs in humans, including their bioavailability and potential side effects. Moreover, given the trend towards precision medicine, which accounts for individual differences, factors such as a patient’s disease stage, comorbidities, and genetic background must also be considered to fully assess the clinical translational potential of these active compounds in diabetes management. Only by bridging laboratory research with evidence-based medicine can we fully harness the potential of these active components in suppressing glucolipotoxicity and reducing the risk of diabetic complications.
Maintaining glucose homeostasis is crucial for providing energy to vital organs and sustaining overall health. The liver is key in this dynamic, participating in processes such as glucose synthesis, glycogenolysis, glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and glucose metabolism. Insulin, primarily stimulated by glucose, is secreted by beta cells under normal physiological conditions. During fasting, the liver generates glucose to fuel the brain, muscles, and adipose tissues, collectively regulating glucose uptake (Xinyi et al., 2020; Wei et al., 2017). PCs regulate glucose uptake, effectively lowering glucose levels through this mechanism (Montserrat et al., 2012). Recent research has underscored the importance of AMPK in managing metabolic conditions, including diabetes, obesity, and fatty liver disease (Sébastien and Reuben, 2017). Furthermore, AMPK boosts glucose absorption in insulin-responsive tissues such as adipocytes, muscle cells, and hepatocytes, proving effective in enhancing glucose uptake in vitro (Zhang et al., 2009; Yuta et al., 2013; Montserrat et al., 2004; Isabel et al., 2015). Elevated phosphorylation levels of AMPK were noted in the liver, muscle tissue, and adipocytes of mice subjected to insulin resistance from high-fat diets and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes models (Masahito et al., 2010; Peiling et al., 2013). Yuta et al. (2013), Ken-yu et al. (2022) utilized anthocyanins extracted from black beans to treat type 2 diabetic mice, activating AMPK in skeletal muscle cells to improve glucose utilization and decrease gluconeogenesis, while concurrently down-regulating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucokinase (GK) activities—crucial enzymes in glycolysis that boost intracellular glucose catabolism.
Glucose Transporter Type 4 (GLUT4), a crucial glucose transport regulator, is predominantly found in adipose, skeletal, and heart muscles. Significantly, skeletal muscle serves as a crucial target for managing hyperglycemia, accounting for roughly 80% of postprandial insulin-mediated glucose absorption and is essential for maintaining glucose equilibrium (Nia et al., 2002; Alan and Kahn, 2001). PCs enhance glucose absorption, facilitate GLUT4 translocation in mouse L6 myotubes, and promote glucose uptake within skeletal muscle via insulin and AMPK-dependent pathways (Miki et al., 2011). G Montagut et al. and HH Lee et al. showed that enhanced GLUT4 translocation increases Akt phosphorylation in adipocytes, further boosting a critical pathway in the insulin signaling cascade (Gemma et al., 2010b; Hee-Hyun et al., 2010). Additionally, PCs affect glucose synthesis and metabolism by boosting the functions of enzymes including glucokinase, hexokinase, and glycogen synthase, and reducing the functions of liver enzymes like glucose-6-phosphatase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Zhang et al., 2009; Gopalsamy Rajiv et al., 2011) (Figure 5).
GLP-1, a crucial hormone linked to intestinal insulin, is secreted by L-cells within the intestinal lining and remains vital for human glucose metabolism. Studies suggest that polyphenols can stimulate GLP-1 secretion, helping to manage insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and type 2 diabetes (Dao et al., 2011). Recent studies have demonstrated that botanical extracts emulate the actions of gut insulinotropic hormones. For example, PCs inhibit DPP-4 (the catabolic enzyme of GLP-1) expression, and tetrameric PCs cinnamon tannin A2 enhances GLP-1 secretion within 1 hour of ingestion (Noemi et al., 2012; Eun-Jung et al., 2011). Meanwhile, researchers noted that oligomers and polymers of PCs enhance GLP-1 activity and insulin secretion independently of glucose loading. This finding indicates that PCs may target L cells in the intestines as a crucial regulator of blood glucose, though the exact mechanism is yet to be elucidated and warrants further investigation (Yoko et al., 2019).
In summary, PCs regulate the function of glucose-targeting organs, modulate glucose metabolism and synthesis, and maintain glucose homeostasis through multiple pathways. However, the above studies have not clarified the differences in efficacy between PCs structures and total extracts, nor the specific targets of individual metabolites. Therefore, future research should focus on these aspects to provide more targeted options for clinical applications.
Insulin secretion by pancreatic β-cells is crucial for preserving glucose metabolic homeostasis. Research indicates that PCs modulate islet fibrosis, enhance pancreatic β-cell function and morphology, and promote insulin release in Wistar rats with high-fat-diet-induced diabetes (Anna et al., 2012). The amount of insulin secreted by β-cells hinges on the number of insulin-producing cells. Under insulin-resistant conditions, a direct relationship emerges between β-cell count and insulin demand. Often, a persistent imbalance between β-cell proliferation and cell death sets the stage for type 2 diabetes (Laura et al., 2007). The influence of PCs on apoptosis varies among different cell types. Research has shown that PCs display chemopreventive properties in cancer cells by enhancing apoptosis and suppressing proliferation (Giovanna et al., 2024). Similarly, PCs demonstrate parallel effects on pancreatic β-cell lines. Lídia et al. (2013) established an in vitro model of insulin resistance and diabetes using the pancreatic INS-1E β-cell line. This approach involved subjecting INS-1E β-cells to high glucose and fatty acid conditions to induce dysfunction. The researchers investigated how elevated glucose, fatty acids, and PCs affect glucose- and palmitate-induced apoptosis in INS-1E cells. They found that PCs amplified glucose-induced apoptosis yet did not alter palmitate-induced β-cell apoptosis. This discrepancy likely arises because these two triggers engage different mechanisms underlying INS-1E cell dysfunction. Research indicates that elevated glucose levels diminish glucokinase (Gck) protein expression in pancreatic islet cells, limiting its interaction with voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) in the mitochondrial outer membrane. Conversely, palmitic acid triggers apoptosis via LC-CoA or other metabolites, in conjunction with endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. The results suggest that PCs augment high glucose-induced apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells by increasing glucose uptake under high glucose conditions, potentially via a mechanism that downregulates Gck and promotes Bax protein translocation and oligomerization at the mitochondrial membrane. Furthermore, the study showed that PCs curtail cell proliferation induced by glucose, insulin, and palmitate, although the precise mechanism remains unclear. Meanwhile, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), used alone or together with GLP-1 agonist exendin-4, was shown to enlarge islet area and number, expand β-cell area, and boost pancreatic insulin content in diabetic and obese mouse models, thus demonstrating favorable therapeutic outcomes (Nupur et al., 2018).
The onset of diabetes and its associated complications are tightly linked to oxidative stress and inflammation. Elevated amounts of oxidative stressors and inflammatory cytokines are closely associated with pancreatic harm in diabetic laboratory rats. Therefore, reducing oxidative stress and cytokines could represent one pathway through which PCs safeguard pancreatic islet cells. Nrf2 is pivotal in the regulation of intracellular antioxidant defense mechanisms. Mahmoud MF and his team (Mona et al., 2021) noted significant elevations in Nrf2 and HO-1 levels within the pancreatic tissues of rats suffering from STZ-induced diabetes. Studies have demonstrated that catechin-rich PCs improve the functionality of isolated pancreatic β-cells from Wistar rats and primary rat islet cells. This improvement is realized by enhancing insulin secretion through a non-oxidative stress pathway involving the activation of MAPK/PI3K to phosphorylate Nrf2, facilitating its nuclear translocation, binding to the ARE promoter, and ultimately boosting antioxidant gene expression (Thomas et al., 2017). Ji-Hyun et al. (2009) showed that cytokines intensify inflammatory damage in isolated pancreatic islet cells, leading to disrupted insulin secretion. This result is attained by increasing nitric oxide (NO) production, enhancing NF-κB DNA binding, boosting inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression, and activating the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB) inflammatory pathway, leading to DNA damage and elevated levels of FAS and IL-1β. Wild PCs has successfully inhibited the phosphorylation of MAPKs and PI3K/Akt, thereby preventing lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced NFκB nuclear translocation. As a result, this leads to diminished production of NO, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and ROS, along with decreased levels of inducible iNOS, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and cytokines (Min-Ji et al., 2013).
The NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) comprises a large molecular weight protein assembly, incorporating NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1, which forms an inflammatory vesicle. This complex is responsible for releasing proinflammatory cytokines Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and Interleukin-18 (IL-18), fulfilling a critical function in regulating insulin resistance (Bo-Zong et al., 2015). Research has shown that silencing NLRP3 inhibits obesity-induced activation of inflammatory vesicles in adipose and hepatic tissues, thereby improving insulin sensitivity—a significant finding in this area (Bolormaa et al., 2011). Initiation of the NF-κB pathway is crucial for regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome, a vital element of the innate immune system. NF-κB is acknowledged as the primary mediator responsible for transcribing NLRP3 and generating precursors of IL-1β and IL-18 (Yuan et al., 2016). Yao et al. (2022) demonstrated that PCs treatment effectively reduces NF-κBp65 nuclear translocation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation, thereby inhibiting excessive NF-κB pathway activation due to high in sugar and fat. The intervention led to a marked decrease in the concentrations of inflammatory markers like IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, (TNF-α), IL-17, and CRP, and notably improved insulin sensitivity in gestational diabetic mice.
In summary, PCs can regulate pancreatic β-cell function and influence insulin secretion through apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory pathways. However, the retrieved literature mainly focuses on pancreatic cell lines, with limited studies on other cell lines. Future research could establish diverse cell models to investigate whether PCs exhibit similar effects on other cell lines (Figure 5).
Type 1 diabetes originates as an autoimmune disease involving the targeted destruction of pancreatic islet β-cells due to specific immune reactions. The β-cell primarily serves as the organ responsible for insulin secretion. Besides producing insulin, β-cells sense glucose levels and release insulin to maintain these levels within the normal physiological range (Jeffrey et al., 2010). Consequently, β-cells function not only as insulin producers but also as regulators—or “thermostats”—of glucose levels. Research indicates that key factors behind pancreatic islet β-cell dysfunction and structural damage include the presence of infiltrating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, along with macrophages (Alan et al., 1991). When β-cells are depleted, individuals with type 1 diabetes lose glycemic control, resulting in acute conditions like ketoacidosis and severe hypoglycemia, as well as chronic complications such as heart disease, blindness, and kidney failure (Maahs and Rewers, 2006). Hence, targeting macrophages may represent a promising strategy for managing type 1 diabetes.
Macrophages, key components of the innate immune system, maintain immune homeostasis and contribute to overall health. This regulatory function occurs via macrophage polarization in response to both internal and external environmental or pathological stimuli (Guillermo Arango and Albert, 2014). Ying et al. (2019) applied different concentrations of PCs to macrophages from db/db diabetic mice. Their findings indicated that PCs reduced M1 macrophage counts while elevating M2 macrophage markers such as Arginase 1, Ym1, and Fizz1. The proposed mechanism involves PCs activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in macrophages, upregulating PPARγ target genes (CD36 and ABCG1) and driving the transition from M1 to M2 phenotypes. Recently, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been recognized as a promising treatment alternative for diabetes. However, challenges such as oxidative stress and inflammation significantly limit the efficacy of bone marrow MSC transplantation therapy. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of PCs were validated through ex vivo experiments (Shuang et al., 2017; Min-Ji et al., 2013). Alyaa et al. (2022) administered a daily 300 mg/kg dose of PCs combined with bone marrow MSC transplantation to STZ-induced type 1 diabetic rats over a 30-day period, resulting in successful blood glucose management and enhanced insulin secretion. Furthermore, PCs mitigated oxidative stress and lowered the concentrations of inflammatory markers such as IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-12, and TLR-4, which were elevated by MSCs, while upregulating critical antioxidant enzymes, notably glutathione (GSH). This finding demonstrates that PCs provide substantial protection against oxidative stress and inflammatory responses triggered by diabetes and MSC differentiation (Figure 6).
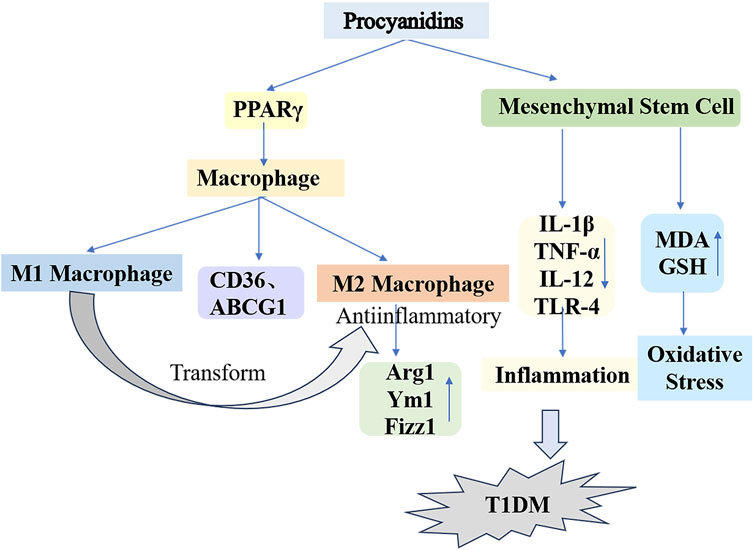
Figure 6. Mechanisms of Procyanidins in Counteracting Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. This figure illustrates how PCs reduce T1DM progression by modulating macrophage polarization and mesenchymal stem cell activity. PCs promote the shift from pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages to anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages, marked by increased Arg1, Ym1, and Fizz1 expression. Additionally, PCs reduce oxidative stress and inflammation by regulating cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-12) and enhancing antioxidant defenses (e.g., GSH, MDA).
In conclusion, the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes involves the immune-mediated destruction of β-cells and abnormal activation of immune cells, with macrophage polarization playing a critical role in immune regulation, making it a promising therapeutic target. PCs, with their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, can amplify the therapeutic effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell combination therapy, alleviating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Although existing studies support its therapeutic potential, further investigation is necessary to clarify its mechanisms, optimize bioavailability, and identify specific targets, while large-scale clinical trials remain imperative to validate its efficacy.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is recognized as a metabolic syndrome, primarily marked by insufficient insulin caused by pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance in target organs (NCD Risk Factor Collaboration NCD-RisC, 2016; Sudesna et al., 2017). Multiple genes govern β-cell differentiation and function—for instance, GLP-1, which enhances insulin secretion while reducing glucagon secretion; PAX4, essential for islet development; and PDX1, vital for β-cell differentiation, growth, and the maintenance of mature function. Furthermore, elements including NF-κB, Toll-like receptors, and bone bridging proteins significantly affect insulin resistance, all of which are regulated by epigenetic mechanisms (Karina et al., 2021). Yoko et al. (2019) administered various doses of cocoa-derived proanthocyanidin extracts to ICR mice, observing that PCs with distinct structures enhanced GLP-1 secretion and reduced postprandial hyperglycemia. The probable pathway likely involves PCs augmenting GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle through an AMPK-dependent mechanism, subsequently enhancing GLP-1–activated insulin signaling and lowering postprandial hyperglycemia. In vitro studies show that a 10 µM concentration of PCs optimally attenuates bisphenol-induced islet cell damage, suppresses apoptosis, and improves insulin secretion. In bisphenol-induced T2DM mice, PCs reduced lipid peroxidation, boosted antioxidant enzymes (SOD and Gpx), upregulated mRNA levels of PDX1 and GUT2, and preserved glucose homeostasis. Furthermore, combined catechin and quercetin therapy demonstrated a stronger impact on elevating key enzymatic activities in hepatic glucose metabolism in diabetic rats relative to monotherapy (Byoung Rai and Pyoung Sim, 2022). Additionally, a double-blind clinical trial reported that continuous intake of a PCs-rich beverage, largely composed of catechin, stimulated insulin secretion and enhanced blood glucose control in individuals with type 2 diabetes (Tomonori et al., 2009). Collectively, these findings prevented BPA-induced islet cell apoptosis, hyperglycemia, and diabetic onset (Ahangarpour et al., 2016).
Insulin resistance is a major contributor to the development of type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, mitochondrial dysfunction plays a pivotal role in the progression of insulin resistance. Essential for maintaining normal mitochondrial function, mitochondrial biosynthesis is regulated by key factors such as Peroxisome receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) and silent information regulator factor 2-related enzyme1 (SirT1). PGC-1α acts as a coactivator for transcription factors that regulate mitochondrial genes, including nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) and mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM). Conversely, SirT1-mediated deacetylation activates PGC-1α (Helena et al., 2009; Bor Luen, 2016). In a dexamethasone-induced insulin resistance model using 3T3-L1 adipocytes, flavan-3-ols from PCs enhanced the expression of genes involved in mitochondrial biosynthesis (PGC-1α, SirT1, NRF1) and fusion proteins (Mfn1 and Mfn2). Furthermore, PCs reduced the expression of the fission protein Drp1, thereby improving mitochondrial defects in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by enhancing mitochondrial biosynthesis, dynamics, membrane potential, and antioxidant capacities, ultimately mitigating insulin resistance (Fangfang et al., 2020).
Hyperlipidemia substantially contributes to type 2 diabetes susceptibility. This condition arises from disrupted hepatic lipid metabolism, characterized by elevated triglyceride synthesis, increased cholesterol production, and reduced fatty acid oxidation. These processes drive excessive hepatic fat accumulation, culminating in steatosis (Lewis et al., 2002; David et al., 2007). Thus, optimizing lipid metabolism represents a viable strategy for both preventing and managing type 2 diabetes. In their research, Fangfang et al. (2020) used PCs to treat a T2DM mouse model induced by a high-fat diet (HFD) and STZ. PCs treatment significantly decreased hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia, as well as serum triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and AST-associated lipokines in T2DM mice compared to controls. PCs treatment enhanced diabetic hyperlipidemia and liver function in mice. Additionally, PCs suppressed adipogenic proteins (FAS, ACC) while upregulating lipolytic proteins (ATGL, HSL, CPT1A). The results indicate that PCs may suppress lipogenesis while enhancing lipid hydrolysis and β-oxidation processes for fatty acids. This effect likely occurs via AMPK/ACC/CPT1A pathway activation, enhancing hepatic lipid metabolism in HFD/STZ-induced diabetic mice. The degree of polymerization in PCs correlates with their biological potency. Zhao et al. (2024) administered equivalent doses of PCs exhibiting varying polymerization levels to HFD/STZ-induced diabetic mice. These PCs significantly lowered fasting blood glucose, improved glucose/insulin tolerance, and optimized lipid profiles (total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol), while reducing oil-red staining in hepatic and serum tissues. They significantly downregulated CHOP and GRP78 expression in diabetic mouse livers, implying a link between hepatic lipid dysregulation and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Furthermore, in vitro experiments showed that administering PCs of different polymerization degrees to palmitic acid–induced HepG2 cells markedly diminished intracellular GRP78 expression. Additionally, this approach activated the protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)/active transcription factor 4 (ATF4) signaling pathway, crucial for endoplasmic reticulum stress regulation, and partially mitigated hepatic lipid accumulation. These findings align with earlier investigations in high glucose–induced C57BL/6 mice treated with PB2, indicating that PCs regulate lipid metabolism in diabetes by targeting endoplasmic reticulum sensors such as PERK, IRE1, and ATF6 (Liu Z. et al., 2023; Nie et al., 2020). GSPE with varying polymerization degrees exhibit protective activity on blood glucose, lipid levels, and hepatic oxidative stress in diabetic rats (Zhaoxia et al., 2014). Notably, oligomers outperformed polymers, implying that the oligomeric form of GSPE might provide superior benefits over other forms. In conclusion, PCs and their derivatives, spanning different polymerization degrees, may influence the initiation and progression of T2DM via multiple pathways. Hence, these plant metabolites show promise as active agents for type 2 diabetes management (Figure 7).
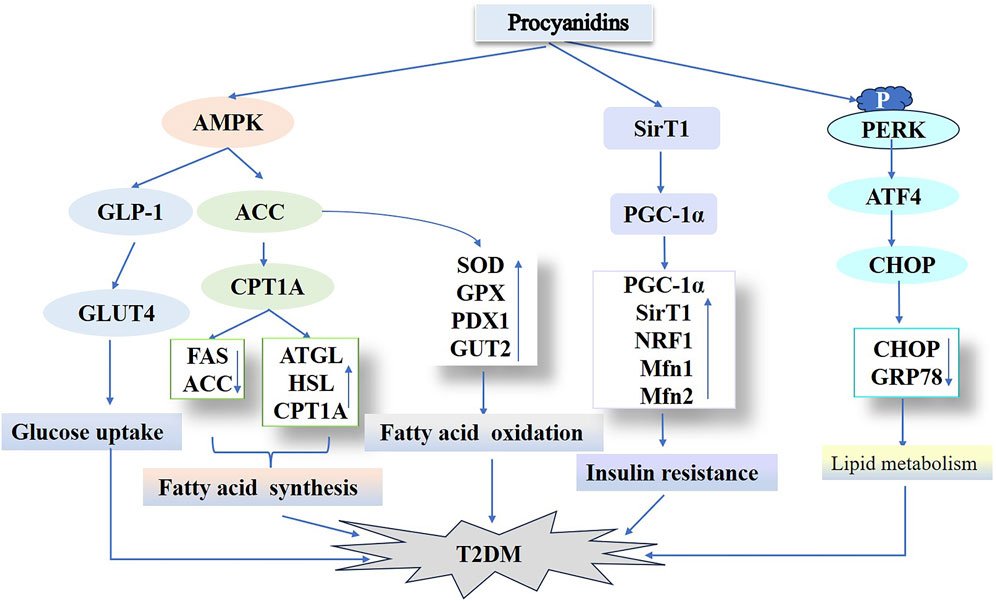
Figure 7. Procyanidins’ Role in Regulating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Pathways. This figure highlights how PCs improve T2DM by enhancing glucose uptake through AMPK activation and GLUT4 translocation, while modulating lipid metabolism via ACC, ATGL, and CPT1A. PCs also improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance by regulating SIRT1, PGC-1α, and NRF1. Additionally, PCs mitigate endoplasmic reticulum stress and associated T2DM progression through pathways involving PERK and CHOP.
In summary, PCs participate in T2DM pathophysiology via multiple mechanisms, such as enhancing insulin secretion, safeguarding pancreatic β-cells, optimizing mitochondrial function and insulin resistance, and regulating hepatic lipid metabolism. Their polyphenolic metabolites display significant potential in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipid metabolism. As natural plant metabolites, PCs hold considerable promise as a therapeutic option for T2DM, but their specific mechanisms and clinical applications demand further research.
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) emerges exclusively during pregnancy or is diagnosed when abnormal glucose tolerance is first identified (Sweeting et al., 2022). The pathogenesis of GDM is intricate, primarily involving impaired insulin secretion and reduced functionality. Insulin resistance gradually intensifies during pregnancy, ultimately leading to hyperglycemia (Jasmine et al., 2018; Kimber-Trojnar et al., 2018). Glucose, which traverses the placenta, serves as the primary energy source for the developing fetus (Ruszała et al., 2022). Furthermore, the overactivation of adipose tissue, which produces monocytes and macrophages that secrete inflammatory factors, contributes to the pathogenesis of GDM by initiating inflammatory responses. Growing evidence indicates that abnormal inflammatory responses are major contributors to the development of insulin resistance (Skórzyńska-Dziduszko et al., 2016; Akash et al., 2018; Gao et al., 2016). In a study utilizing a GDM mouse model induced by a high-fat diet and sugar, PCs (27.8 mg/kg/d) were administered from 4 weeks before pregnancy until delivery to evaluate their impact on insulin resistance, including during the postnatal period and in offspring. PCs effectively managed weight gain during pregnancy, decreased serum fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting insulin, oral glucose tolerance test area under the curve, and insulin tolerance test area under the curve levels, and enhanced the Homeostatic Model Assessment (HOMA) insulin sensitivity index. These interventions positively affected fasting glucose and insulin levels. Additionally, PCs improved glucose metabolism and reduced concentrations of inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, TNF-α, IL-17, and CRP, thereby diminishing inflammation and hepatic inflammatory infiltration in mice 4 weeks postnatally. However, these treatments did not significantly impact the offspring. In a related observation, PCs were used in a GDM mouse model with gut flora defects induced by a combination of broad-spectrum antibiotics and a high-fat, high-sugar diet. This treatment enhanced insulin resistance by inhibiting the NF-κB/NLRP3 activation pathway, thereby altering the levels of gut flora metabolites 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and 3- (4-hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid (Yao et al., 2022). In a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial on gestational diabetes (Zhang et al., 2017), it was observed that mothers in the epigallocatechin 3-gallate group showed significant improvements in diabetes parameters, with fewer cases of neonatal complications compared to the placebo group.
In conclusion, PCs exert significant protective effects on the pathogenesis of GDM by enhancing insulin sensitivity, lowering levels of inflammatory factors, and alleviating liver inflammation, while effectively regulating glucose metabolism during pregnancy and postpartum stages. Despite limited effects on offspring mice, PCs continue to show potential as a treatment for GDM, but their long-term safety and mechanisms require further research and verification.
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a primary microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus, characterized by proteinuria, glomerular enlargement, reduced tubular filtration, renal fibrosis, and renal dysfunction, ultimately leading to end-stage renal disease (Samsu, 2021). The progression of diabetic nephropathy is multifaceted, influenced by factors such as renal hemodynamic abnormalities, dyslipidemia, oxidative stress, and hormone synthesis, including Angiotensin II (Ang II). Additionally, its progression is influenced by inflammation, the renin-angiotensin system (RAAS), advanced glycation end-product (AGE) formation, and signaling molecules, including transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), PKC, MAPK, and ROS. Collectively, these factors accelerate the progression of diabetic nephropathy, making it a leading cause of end-stage renal disease (Javier et al., 2020; Su Woong and Jae-Young, 2021; Majid, 2013; Wei-Jian et al., 2015; Yashpal et al., 2011; Mandeep Kumar and Umesh Kumar, 2013). In a rat model induced by STZ, a 12-week regimen of PCs treatment resulted in improvements in proteinuria and podocyte injury. Its probable mechanism includes activation of renal AGE-RAGE signaling pathways, decreasing levels of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and PKC-A, which consequently reduces the production of slit diaphragm proteins such as nephrin and podocin, thereby mitigating the impact of AGE-mediated DN pathogenesis (Muthenna et al., 2014). Oral administration of PCs significantly enhanced kidney function and reduced pathological alterations in db/db mice. Proteomic evaluation revealed that following PCs administration, 53 proteins were downregulated and 60 upregulated, with milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8, (MFG-E8) as the most notably upregulated protein in diabetic kidneys. Inhibition of MFG-E8 via shRNA transfection decreased phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2, Akt, and GSK-3β in the kidneys of db/db mice, improving renal histopathology. Conversely, overexpression of MFG-E8 had opposite effects. PCs treatment reduced MFG-E8, phospho-ERK1/2, phospho-Akt, and phospho-GSK-3β levels in db/db mouse kidneys, indicating MFG-E8’s influence on the progression of diabetic nephropathy. PCs appear to mitigate diabetic nephropathy by reducing MFG-E8 levels and modulating the ERK1/2, Akt, and GSK-3β pathways (Zhang et al., 2013).
Diabetic glomerulosclerosis is a defining feature of diabetic nephropathy. A key process in glomerulosclerosis and tubular epithelial fibrosis involves the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by high glucose levels (Xu et al., 2017). PCs mitigate high glucose-triggered EMT within HK-2 cells by activating the TGF-β/Smads and P38/MAPK pathways, upregulating α-SMA, FN, and Waveform proteins, and downregulating E-cadherin levels (Li et al., 2015). Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in the progression of diabetic kidney injury. Research shows that PCs protect cells from the systemic high glucose impacts on mitochondria, preventing cellular dysfunction and cell death by activating the AMPK-SIRT1-PGC-1α pathway. This compound reduces ROS levels, enhances SOD antioxidant activity, and increases the expression of NRF-1 and TFAM genes (Cai et al., 2016). In diabetic nephropathy models, PCs attenuated renal cell apoptosis by enhancing p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activities and reducing Bcl-2 expression. GSPE also reduced thioredoxin-interactingprotein expression, facilitating intracellular ROS catabolism via the sulfhydryl antioxidant pathway to mitigate oxidative stress in diabetic kidneys (Wei et al., 2018). Additionally, PCs alleviated DN pathology, such as glomerular basement membrane thickening and central dilatation, by modulating mimecan protein expression through the NF-κB p65 pathway (Zhou et al., 2016) (Figure 8). The combined treatment of perindopril and catechin significantly improved mesangial matrix and podocyte function in diabetic rats, effectively preventing glomerular injury, with greater efficacy compared to monotherapy (Salime Pelin et al., 2014). A clinical study demonstrated (Tung-Sheng et al., 2011) that a 1:1 mixture of epigallocatechin-3-gallate and Amla (Emblica officinalis) significantly enhanced antioxidant defenses in patients with diabetic nephropathy, synergistically improving clinical outcomes.
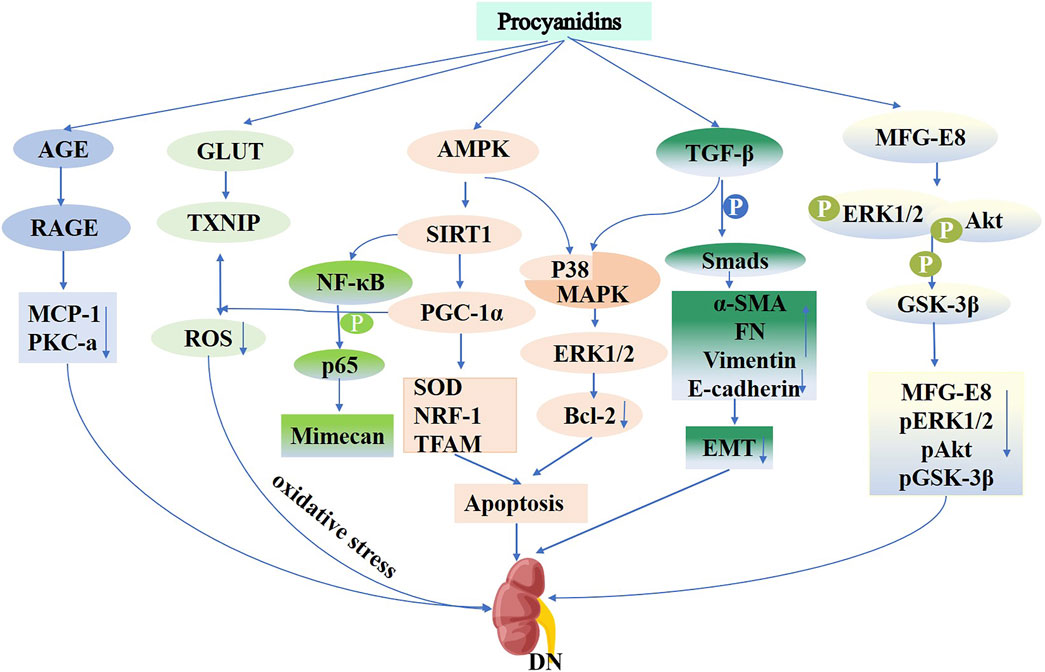
Figure 8. Mechanisms of Procyanidins in Diabetic Nephropathy. This figure highlights how PCs combat DN by reducing oxidative stress through AMPK activation and GLUT-mediated glucose uptake. PCs inhibit inflammation via the NF-κB and PKC-α pathways and attenuate renal fibrosis by modulating TGF-β/Smad signaling. Additionally, PCs prevent epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), preserving renal cell integrity and reducing apoptosis, thereby mitigating disease progression.
PCs and their metabolites exhibit significant therapeutic potential in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy through multiple mechanisms, including antioxidant and anti-fibrotic effects, as well as the regulation of key signaling pathways. They are particularly effective in reducing proteinuria, protecting mitochondrial function, and inhibiting inflammatory responses. Despite these promising findings, current research is largely confined to animal models and in vitro studies, with limited clinical investigations available. Therefore, further large-scale clinical trials are essential to confirm the safety and efficacy of PCs in managing diabetic nephropathy, thereby establishing a foundation for their clinical application.
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a significant microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus and a leading cause of vision loss worldwide (Tan and Wong, 2022; Liu and Wu, 2021; Joanne et al., 2012). DR stems from a complex pathology involving oxidative stress, inflammatory lesions, and the polyol pathway. Activation of hexosamine flux and advanced glycation end product (AGE) formation, driven by PKC isoform activation and related pathways, contributes to vascular dysfunction and tissue injury in the retina (Yau et al., 2012; Al-Shabrawey et al., 2015; Lu et al., 2018). Early and timely intervention is crucial to prevent retinal damage and vision impairment in individuals with diabetes.
Recent studies indicate that PCs exert protective effects on retinal cells by modulating autophagy, reducing oxidative stress, and attenuating inflammation (Rodríguez-Carrizalez et al., 2014; John et al., 2020). In high-glucose–challenged retinal pigment epithelial cells, PCs activate the p53/mTOR autophagy pathway, lowering apoptosis-related factors (e.g., Bax, Caspase-3, LC3-II/LC3-I, and phosphorylated p53) and elevating the levels of survival proteins (Bcl-2, p62, and phosphorylated mTOR) (Li et al., 2022). Additionally, the application of PCs to rat retinal capillary endothelial cells (TR-iBRB2) decreases oxidative stress and inflammasome activation, suggesting involvement of the oxidase/NF-κB/NLRP3 axis in mediating their cytoprotective effects (Zou et al., 2023). Further research reveals that PCs, alone or in combination with other phytoalexins, can activate the AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway and inhibit the miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 axis, thereby mitigating hyperglycemia-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in retinal cells (Liu et al., 2021) (Figure 9).
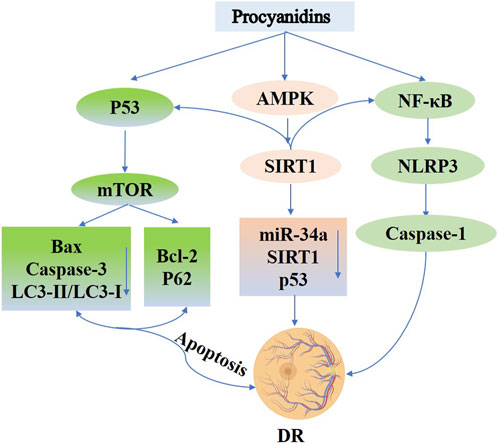
Figure 9. Procyanidins’ Role in Diabetic Retinopathy. This figure highlights how PCs alleviate DR by modulating key signaling pathways. PCs activate AMPK and SIRT1 to reduce oxidative stress and regulate apoptosis via p53, Bax, and Caspase-3. PCs also promote autophagy through mTOR signaling and inhibit inflammation by suppressing NF-κB and NLRP3 activation. Additionally, PCs regulate miR-34a and SIRT1 to protect retinal cells, reducing apoptosis and inflammation, thereby mitigating the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Moreover, mounting evidence highlights the anti-glycation and anti-dicarbonyl properties of PCs, which inhibit the formation of AGEs by scavenging reactive carbonyl species (e.g., methylglyoxal) (Qian et al., 2013). By reducing the burden of these glycation intermediates, PCs help maintain retinal integrity and limit the progression of DR.
In conclusion, PCs safeguard retinal cells and mitigate diabetic retinopathy through various molecular mechanisms, including autophagy activation, oxidative stress reduction, anti-glycation activity, and anti-inflammatory modulation. These pleiotropic actions underscore the potential of PCs as promising therapeutics for DR and warrant further investigation in both preclinical and clinical settings.
Diabetic neuropathy (DN), commonly presenting as a distal symmetrical polyneuropathy, is characterized by sensory deficits and pain in the extremities (Eva et al., 2019). Hyperglycemia-driven pathways accelerate DN progression, with AGEs and reactive dicarbonyl compounds exacerbating nerve injury through chronic inflammation and neuronal apoptosis (Stella et al., 2021; Ryuichi et al., 2001).
PCs have shown promising neuroprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress, preventing the accumulation of AGEs and other toxic intermediates, and mitigating glycation-induced damage. Moreover, their anti-glycation and anti-dicarbonyl properties lessen the accumulation of AGEs and other toxic intermediates, consequently protecting peripheral nerves from glycemic damage (Xiao-Fang et al., 2008; Xiao-Fang et al., 2010). Notably, in models of type 2 diabetes, PCs confer neuroprotection by modulating NF-E2/STAT1 signaling, attenuating Janus kinase activity, and inhibiting cell apoptosis, thereby reducing cerebrovascular lesions and associated neurological deficits (Wu et al., 2015; Yin et al., 2021) (Figure 10).
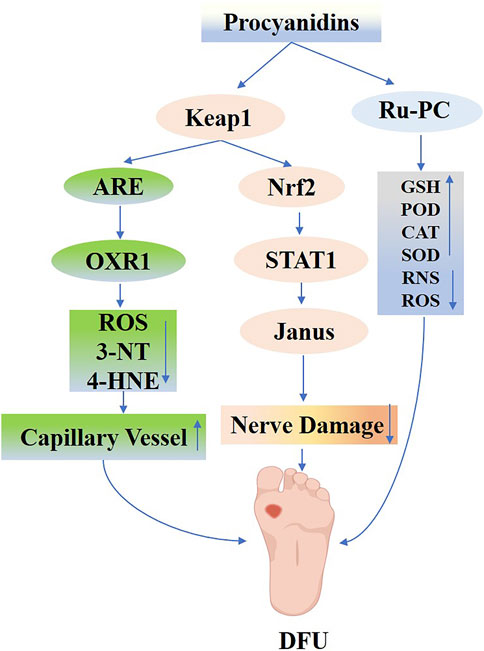
Figure 10. Mechanisms of Procyanidins in Diabetic Neuropathy and Diabetic Foot Ulcers. This figure shows how PCs alleviate DN and DFU by activating the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway, enhancing antioxidant defenses, and reducing oxidative damage (ROS, 3-NT, 4-HNE). PCs also regulate STAT1/JAK signaling to control inflammation and promote nerve repair while improving capillary function. Additionally, PCs support anti-inflammatory responses by modulating GSH, SOD, and other antioxidant systems, facilitating vascular and neural recovery critical for ulcer healing.
In summary, PCs offer a multifaceted neuroprotective effect in DN by targeting oxidative and inflammatory pathways, preventing glycation-related damage, and reducing neuronal apoptosis. Further clinical studies are needed to validate these findings and establish optimal dosing regimens for maximizing the therapeutic efficacy of PCs in managing DN.
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) are severe and common complications stemming from a multifactorial interplay of sensory, motor, autonomic, and vascular abnormalities, along with altered foot biomechanics (McDermott et al., 2023). Approximately 50%–60% of diabetic ulcer patients develop infections, and about 20% of these cases, involving moderate to severe infections, require lower extremity amputation (David et al., 2023). Patients with DFU face a 5-year mortality rate of about 30%, which rises to over 70% for those undergoing major amputations. Moreover, infected diabetic ulcers significantly heighten the risk of disability and mortality among these patients (Armstrong et al., 2020). Diabetic ulcer wounds that are resistant to healing markedly increase the risk of bacterial invasion and subsequent infection. Thus, prompt treatment and intervention aimed at promoting wound healing in diabetic ulcers are crucial for reducing infections and preventing amputations in diabetic patients. The wound healing process encompasses hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and wound remodeling. Hyperglycemia-induced cellular dysfunction, prolonged low-grade inflammation, and tissue ischemia and hypoxia are well-documented barriers to wound healing, further decelerating the repair of refractory diabetic wounds (Matoori et al., 2021).
Research increasingly indicates that plant-derived active ingredients support the differentiation and functional capabilities of various cell types, thereby promoting wound healing (Kisseih et al., 2015). Specifically, PCs have exhibited notable efficacy. Pimentel EF and their group (Pimentel et al., 2024) employed resonance mass spectrometry to analyze seed hulls, noting that PCs enhanced fibroblast functionality and migration, and increased the levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). These improvements supported the healing of wounds infected with Staphylococcus aureus. Subsequent experiments showed that PCs significantly enhanced the angiogenic, survival, and migration capabilities of human umbilical cord blood endothelial progenitor cells under high-glucose conditions, thus reducing glucose-induced damage. This protective action likely involves regulating antioxidant gene expression via Nrf2 activation, diminishing excessive ROS accumulation, and reducing oxidative damage markers (e.g., 3-NT and 4-HNE), as evidenced by J Fan et al.‘s study on STZ-induced diabetic mouse wounds treated with PCs (Fan et al., 2021). They found that PCs not only reduce oxidative stress in damaged skin via Nrf2 activation but also stimulate capillary formation and facilitate endothelial progenitor cell migration to the wound site, thereby accelerating wound healing and promoting neoangiogenesis.
The integration of nanomaterials and hydrogels with plant-derived active ingredients for wound healing has recently attracted significant interest among researchers. PCs, polyphenolic compounds derived from plants, exhibit antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties. When combined with ruthenium-liganded nano-enzymes, PCs are converted into potent antimicrobial agents that could potentially replace antibiotics in treating bacterial-infected wounds. Shan et al. (2024) combined RuCl₃ with polyvinylpyrrolidone to synthesize Ru-PVP, then mixed it with PCs in a methanol solution to formulate Ru-PC nano-enzymes exhibiting four enzymatic activities. The functional pathways of Ru-PC nano-enzymes varied significantly across different environments. In acidic environments, these nanoenzymes demonstrated effective antimicrobial properties through GSH reduction and peroxidase (POD) -mimetic activity. Under neutral conditions, Ru-PC nanoenzymes break down H2O2 into O2 via catalase (CAT) activity, thus alleviating wound healing complications due to hypoxia. Concurrently, Ru-PC exhibits SOD-like activity, efficiently eliminating excessive reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in neutral environments, thereby preserving antioxidant balance. Additionally, Ru-PC modulates the transition from M1 to M2 macrophage polarization, aiding in the management of inflammatory wound repair challenges. In conclusion, Ru-PC nanoenzymes expedite the healing of infected wounds by stimulating cell proliferation, eradicating bacteria, reducing inflammation, neutralizing free radicals, supplying oxygen, and promoting blood vessel growth. Liu K. et al. (2023) created a versatile PBOF hydrogel dressing composed of poly (vinyl alcohol) (P), borax (B), oligomeric PCs (O), and ferric ions (F). This hydrogel is characterized by its adhesive, shape-adapting, stretchable, self-healing, detachable, antioxidant, photothermal antimicrobial, hemostatic, and biocompatible properties, making it exceptionally suitable for managing wounds in highly active areas. In a mouse model with Staphylococcus aureus-induced cervical wound infections, the PBOF hydrogel dressing showed antimicrobial activity, utilizing the photothermal properties of ferric ions and polyphenol chelates, together with the hemostatic, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory qualities of PCs. These features aid in wound healing by minimizing oxidative stress, curbing inflammation, and enhancing angiogenesis (Figure 10).
In conclusion, the occurrence of DFU is closely related to cell dysfunction, low-grade inflammation, and tissue hypoxia induced by hyperglycemia. PCs significantly promote wound healing by alleviating oxidative stress, promoting endothelial progenitor cell migration, improving angiogenesis, and exerting anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. Moreover, the combination of nanomaterials and hydrogels with plant bioactive metabolites further enhances the therapeutic effect, suggesting that PCs hold great promise for the treatment of DFU.
Diabetic encephalopathy (DE), a diabetes-related complication marked by central nervous system damage, primarily results from cerebral microangiopathy, including conditions such as stroke, dementia, and depression (van Sloten et al., 2020). Numerous studies have confirmed that DM independently increases the risk of conditions such as ischemic stroke, transient ischemia, and vascular dementia (Antal et al., 2022). People with type 2 diabetes have a 2.5-fold increased risk of ischemic stroke and are 1.5 times more likely to experience hemorrhagic stroke and dementia than those without diabetes (Sarwar et al., 2010; Cheng et al., 2012). Potential mechanisms linking diabetes to stroke include vascular endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerosis, inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and alterations in blood-brain barrier permeability (van Sloten et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2016). Wu et al. (2015) employed PCs using a mouse model of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) to examine its impact. They observed that PCs reduced infarct size, cerebral swelling, and neurological impairments following MCAO. This effect is attributed to PCs’ role in facilitating nuclear translocation, enhancing levels of HO-1, GSTα, NQO1, and ZO-1 proteins in the ischemic zone to maintain blood-brain barrier integrity and mitigate damage to the nervous system. Similarly, PCs activated the TLR4-p38-NF-κB-NLRP3 signaling pathway, which decreases the production of inflammatory cytokines in response to MCAO/R and OGD/R both in vivo and in vitro. Furthermore, it exhibited neuroprotective properties by lessening cerebral edema, reducing infarct size, minimizing histological damage, and decreasing microglial cell death (Yang et al., 2020).
Oxidative stress acts as a critical factor in the onset of ischemic reperfusion damage. PCs derived from grape seeds significantly modulate oxidative stress responses. In experiments employing the MCAO/R model, PCs significantly reduced neurological impairment scores at various intervals—1, 24, 72 h, and 7 days post-MCAO. Additionally, PCs effectively reduced the volume of cerebral infarcts and curbed malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in brain tissues. Significantly, PCs lowered MDA levels and boosted glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activity in brain tissues relative to the control group. This protective effect was achieved by mitigating oxidative stress and apoptosis, promoting angiogenesis, and triggering the GSH-Px antioxidant pathway, thus defending against ischemia-reperfusion brain injury (Kong et al., 2017) (Figure 11).
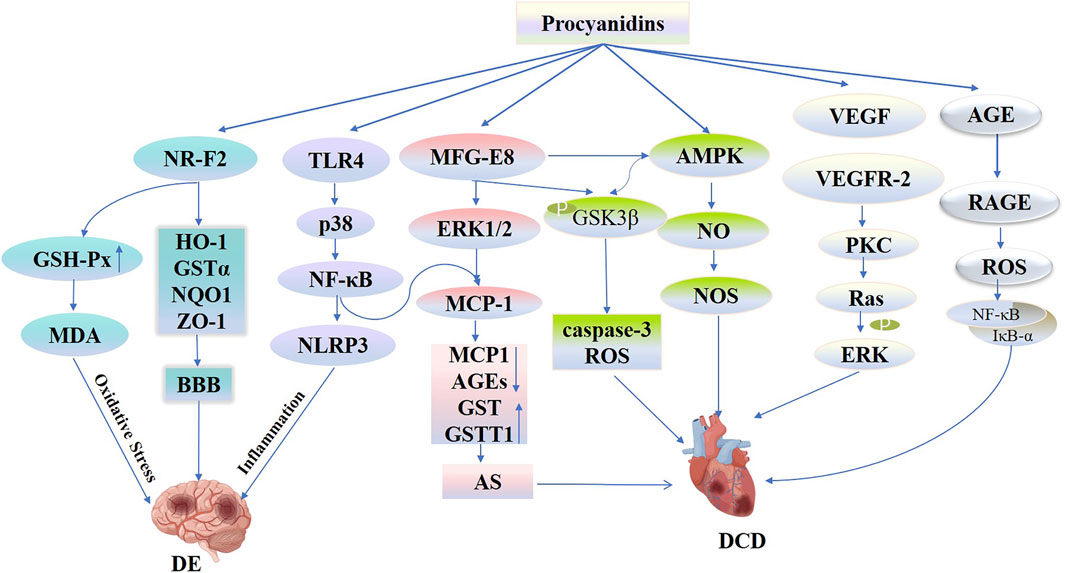
Figure 11. Procyanidins’ Mechanisms in Diabetic Encephalopathy and Cardiovascular Disease. This figure illustrates how PCs mitigate DE and DCD through multiple pathways. PCs activate NRF2 signaling, increasing antioxidant enzymes (e.g., HO-1, GSTα, NQO1) and strengthening the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in DE. PCs also regulate the TLR4-p38-NLRP3 pathway to suppress neuroinflammation. In the cardiovascular system, PCs modulate MFG-E8-ERK1/2 and AMPK-NO-NOS pathways to reduce MCP-1 levels, oxidative stress, and apoptosis, improving vascular function and preventing atherosclerosis and DCD progression.
In conclusion, PCs demonstrate significant neuroprotective effects through their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory properties, and maintenance of blood-brain barrier function. Additionally, PCs provide effective protection against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by alleviating oxidative stress, promoting angiogenesis, and activating antioxidant enzyme pathways. Both provide potential therapeutic strategies for treating brain injury caused by diabetes, but their clinical application requires further validation.
Diabetic cardiovascular disease (DCD) remains the primary cause of mortality among individuals with type 2 diabetes. Dysfunction of vascular endothelial cells is an initial contributor to cardiovascular disease (Strain and Paldánius, 2018). Nitric oxide is critical for regulating vasodilation. A diminished availability of nitric oxide can lead to endothelial dysfunction (Jeong et al., 2022). Elevated glucose levels activate the enzyme aldose reductase (AR), which transforms glucose to sorbitol, with NADPH serving as a coenzyme for this process. Depletion of NADPH impairs NO synthesis and lowers glutathione levels, causing an overproduction of oxygen free radicals, which compromises endothelial cell function in blood vessels (Belenichev et al., 2023). Clinical research has shown that PCs raise endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) levels, subsequently reducing systolic and diastolic blood pressure values (Odai et al., 2019; Schön et al., 2021). Simultaneously, PCs stimulate AMPK, which increases eNOS levels and nitric oxide production, thereby enhancing vascular endothelial performance (Cui et al., 2012). Research indicates that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in endothelial cell dysfunction and apoptosis (Silambarasan et al., 2016). PCs modulate glucose metabolism by regulating microRNA expression in the pancreas (Castell-Auví et al., 2013). Elevated blood sugar levels impair vasodilation by activating PKC in vascular cells, affecting the activities of ET-1, VEGF, NO, PDGF, ROS, and NF-κB in pericytes, leading to capillary myelopoietic thickening and increased endothelial cell proliferation (Barrett et al., 2017). Liu et al. (2016) demonstrated that PCs and their oligomers enhance cell proliferation, reducing oxidative damage in endothelial cells under high glucose conditions. This outcome is realized by enhancing VEGFR-2 expression and activating its downstream signaling pathways. Furthermore, glycated LDL, common in diabetic patients, substantially contributes to vascular endothelial cell dysfunction and apoptosis. Proteomic research reveals that extracts from grape seed PCs suppress apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells, initiated by glycated LDL, through the modulation of PIMT, a methyltransferase involved in protein repair (Li et al., 2013).
Considerable evidence indicates that the expansion of vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells, induced by AGEs, is vital for diabetic vasculopathy (Barbosa et al., 2008). The NF-κB signaling pathway substantially affects the movement, invasion, and growth of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). The interaction of AGEs with their receptor (RAGE) on VSMCs triggers intracellular oxidative stress by activating the transcription factor NF-κB (Yamagishi, 2011; San Martin et al., 2007). Experimental research has demonstrated that PCs therapy diminishes the proliferation and migration of human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMCs) triggered by AGEs by elevating UCH-L1 protein levels, reducing IκB-α degradation, and curtailing NF-κB nuclear translocation in a dose-responsive manner (Qian et al., 2011). GSK-3β, a pro-apoptotic kinase, is crucial in managing cell survival and apoptosis. Overexpression of GSK-3β increases cellular susceptibility to apoptosis, while inhibition of GSK-3β diminishes the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria (Ryu et al., 2021). Li et al. (2011) showed that low concentrations of PCs (<12.5 mmol/L) enhance cell viability and proliferation in HUVECs, while higher concentrations (>25.00 mmol/L) induce apoptosis. This effect is attributed to PCs dose-dependently enhancing GSK-3β phosphorylation, attenuating caspase-3 activation, and inhibiting lactic acid adhesion protein expression, thereby mitigating oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by AGEs in HUVECs. These protective mechanisms lead to decreased intracellular ROS production and reduced apoptotic damage.
Atherosclerosis is a key marker of diabetic cardiovascular lesions. Oxidative stress, induced by hyperglycemia, plays a significant role in advancing atherosclerosis (Chen et al., 2011). In individuals with diabetes, ROS facilitate atherosclerosis by damaging endothelial cells while promoting proliferation, movement, and phenotypic changes in smooth muscle cells (Jay et al., 2006). MFG-E8, also known as lactoadhesin, adversely affects diabetic vascular disease by playing a role in oxidative stress and inflammatory responses (Silvestre et al., 2005). Prior studies have demonstrated that elevated glucose levels enhance ROS production by increasing MFG-E8 expression in adipose tissue (Aoki et al., 2007). Within the db/db mouse model, PCs effectively reduced VSMC proliferation and endothelial cell damage by decreasing MCP-1 and AGEs in mouse serum. Additionally, it reduced oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cells and decelerated atherosclerosis progression by enhancing aortic glutathione S-transferase theta 1 (GSTT1) activity. The suggested mechanism includes PCs impacting MFG-E8 expression, which subsequently mitigates atherosclerosis in db/db mice by reducing the secretion of chemokines involved in inflammation and oxidative stress via the pathways of ERK1/2 and MCP-1 (Yu et al., 2012) (Figure 11). Clinical studies have found (Peter et al., 2013) that the combined intake of isoflavones and flavan-3-ols improves vascular function and arterial stiffness in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes, thereby slowing disease progression.
In conclusion, PCs improve diabetes-induced cardiovascular diseases through various mechanisms, particularly by regulating endothelial function, reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting inflammation, and modulating vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, exhibiting significant neuroprotective and cardiovascular protective effects. PCs can slow the formation of atherosclerosis and vascular endothelial cell damage by regulating multiple signaling pathways, including AGEs, MFG-E8, and GSK-3β. Although these studies support the application of PCs in diabetes-related cardiovascular diseases, further clinical trials and validation are required to promote their clinical application.
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DC) presents as abnormal cardiac structure and function in individuals with diabetes, occurring in the absence of significant coronary artery disease, hypertension, or valvular heart conditions (Jia et al., 2018; Dillmann, 2019). Recent research indicates that endothelial dysfunction is a key factor in the advancement of diabetic cardiomyopathy (Knapp et al., 2019). Several factors, including hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, lipid metabolism imbalances due to insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, decreased NO activity, elevated ROS, and inflammatory dysregulation, adversely affect endothelial function (Moran et al., 2022). This dysfunction can lead to cardiac fibrosis and structural changes through disrupted myocardial metabolism. The involved processes include improper handling of intracellular Ca2⁺, ER stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, the accumulation of AGEs, and the buildup of the extracellular matrix (ECM). These alterations can ultimately lead to both diastolic and systolic cardiac dysfunction, potentially resulting in heart failure (Moran et al., 2022). Quantitative proteomic analysis using iTRAQ revealed that PCs reverse s100A11 protein expression, a component in the S100 calcium-binding protein family involved in cellular regulation, and lower serum AGE levels in db/db mice. The hypothesis suggests that PCs activate the S100A11/RAGE/PPARγ signaling pathway, resulting in reduced RAGE expression and alleviation of cardiac fibrosis triggered by AGEs in type 2 diabetic rats (Luan et al., 2014). Mitochondria act as the primary sources of cellular energy and also produce ROS. A notable correlation exists between ROS production and the deterioration of cardiac function and structure (Bou-Teen et al., 2021). Dysfunctional mitochondrial activity due to hyperglycemia serves as an early sign of endothelial dysfunction, hastening the advancement of cardiovascular disease (Yuan et al., 2019). Normal mitochondrial function reduces myocardial oxidative damage, while abnormal mitochondrial function can cause chronic myocardial hypoxia and exacerbate myocardial fibrotic degeneration by impairing respiratory function. PCs stimulate myocardial mitochondrial phosphorylation, modulating mitochondrial uncoupling rates and affecting respiratory function (Kopustinskiene et al., 2015).
In conclusion, PCs can alleviate diabetes-induced myocardial hypertrophy, cardiac fibrosis, and heart failure, demonstrating potential cardioprotective effects by regulating the S100A11/RAGE/PPARγ signaling pathway, improving mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress, and inhibiting the formation of AGEs.
As a potent antioxidant, PCs exhibit significant therapeutic potential in the treatment of diabetes and its complications through their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-glycation properties. These plant metabolites improve endothelial function, reduce insulin resistance, and protect pancreatic β-cell function, offering a multidimensional strategy for diabetes treatment. However, current studies face several limitations. Most studies are restricted to in vitro experiments or animal models, lacking clinical trials in humans, particularly long-term efficacy and safety evaluations. Additionally, the low bioavailability of PCs, primarily due to poor gastrointestinal absorption, poses challenges for clinical application. The precise mechanisms of PCs remain unclear, necessitating further investigation into their molecular pathways.
Future research should focus on enhancing the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of PCs, potentially through novel delivery systems like nanoparticles or their combination with other plant bioactive metabolites, to optimize therapeutic outcomes. Large-scale randomized controlled trials are essential to validate their efficacy in patients with diabetic complications, particularly for clinical assessments of diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. Additionally, investigating the synergistic effects of PCs with other natural compounds or conventional drugs may unveil more comprehensive therapeutic strategies. More importantly, greater emphasis should be placed on studying their molecular mechanisms, especially their effects on inflammatory pathways and oxidative stress, to develop more targeted therapeutic approaches. Personalized medicine approaches, considering individual genetic and metabolic variations, may further optimize the clinical application of PCs in diabetes and its complications.
PCs are versatile bioactive compounds with significant potential in the prevention and management of diabetes and its related complications. They not only regulate glucose metabolism but also exhibit strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which enhance insulin sensitivity and improve endothelial function. Experimental studies have shown that PCs offer protective effects against diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular diseases. Despite these promising findings, most research has been limited to in vitro and animal models, highlighting the need for clinical validation.
Future research should prioritize comprehensive clinical trials to confirm the efficacy and safety of PCs in human subjects. Investigating synergistic interactions between PCs and existing antidiabetic therapies could lead to more effective treatment protocols with minimized side effects. Furthermore, advancements in delivery systems and the development of standardized formulations are crucial for enhancing the bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness of PCs. Establishing uniform criteria for PC purity, composition, and dosage will not only ensure reproducible and effective results but also streamline clinical trials and future regulatory approval processes.
In summary, PCs present a promising adjunctive option for diabetes management, contributing to better glycemic control and the mitigation of complications. Continued research and clinical investigations are essential to fully realize the therapeutic benefits of PCs, ultimately aiming to improve long-term outcomes and the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
YZ: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. ML: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. HaL: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. YF: Writing–review and editing, Validation. HuL: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
We acknowledge Figdraw for the creation of the figures, and we extend our gratitude to all staff members who contributed to this study for their dedicated efforts and support.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
PCs, Procyanidins; DM, Diabetes Mellitus; T1DM, Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus; T2DM, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; DN, Diabetic Nephropathy; DR, Diabetic Retinopathy; DN, Diabetic Neuropathy; CVD, Cardiovascular Disease; DFU, Diabetic Foot Ulcers; AGE, Advanced Glycation End-products; RAGE, Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-products; VEGF, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor; DCD, Diabetic Cardiomyopathy; GSH-Px, Glutathione Peroxidase; NQO1, NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1; ZO-1, Zonula Occludens-1; TLR4, Toll-like Receptor 4; MCP-1, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1; AMPK, AMP-activated Protein Kinase; GSK-3β, Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta; ERK1/2, Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases 1/2; ACC, Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase; GLUT4, glucose transporter type 4; ATGL, Adipose Triglyceride Lipase; CPT1A, Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1A; SIRT1, Sirtuin 1; NRF1, Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1; PERK, Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase; IRE1, Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1; ATF6, Activating Transcription Factor 6; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; TGF-β, Transforming Growth Factor Beta; EMT, Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition; MAPK, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; mTOR, Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; miR-34a, MicroRNA-34a; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; ARE, Antioxidant Response Element; 3-NT, 3-Nitrotyrosine; 4-HNE, 4-Hydroxynonenal; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase; CAT, Catalase; OXR1, Oxidation Resistance 1; NRF2, Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2; JAK, Janus Kinases; SOD, Superoxide Dismutase; RNS, Reactive Nitrogen Species; M1/M2, Macrophage phenotypes 1 and 2; IL-6, Interleukin 6; IL-17, Interleukin 17; IL-12, Interleukin 12; IL-1β, Interleukin 1 Beta; Arg1, Arginase 1; Ym1, Chitinase-Like Protein 3; Fizz1, Found in Inflammatory Zone 1; ABCG1, ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily G Member 1; CD36, Cluster of Differentiation 36.
Abdur, R., Muhammad, I., Tareq, A. I., Iahtisham-Ul, H., Seema, P., Xiaohong, P., et al. (2019). Proanthocyanidins: a comprehensive review. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 116, 108999. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108999
Ahangarpour, A., Afshari, G., Mard, S. A., Khodadadi, A., and Hashemitabar, M. (2016). Preventive effects of procyanidin A2 on glucose homeostasis, pancreatic and duodenal homebox 1, and glucose transporter 2 gene expression disturbance induced by bisphenol A in male mice. J. Physiology Pharmacol. Official J. Pol. Physiological Soc. 67 (2), 243–252.
Akash, M. S. H., Rehman, K., and Liaqat, A. (2018). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: role in development of insulin resistance and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Cell. Biochem. 119 (1), 105–110. doi:10.1002/jcb.26174
Alan, K. F., Margaret, M., and Farquharson, M. A. (1991). Insulitis in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in man—macrophages, lymphocytes, and interferon-γ containing cells. J. Pathology. doi:10.1002/path.1711650203
Alan, R. S., and Kahn, C. R. (2001). Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414, 799–806. doi:10.1038/414799a
Aleksey, V. M., and Peter, C. B. (2008). Relationship between β-cell mass and diabetes onset. Diabetes, Obes. Metabolism. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00939.x
Al-Shabrawey, M., Zhang, W., and McDonald, D. (2015). Diabetic retinopathy: mechanism, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. BioMed Res. Int., 2015, 854593. doi:10.1155/2015/854593
Alyaa, F., Hebatallah, H., Salma, A., Selim, A., and Gehan, S. (2022). Co-treatment with grape seed extract and mesenchymal stem cells in vivo regenerated beta cells of islets of Langerhans in pancreas of type I-induced diabetic rats. Stem Cell Res. and Ther. 13, 528. doi:10.1186/s13287-022-03218-y
André, S. (2019). SGLT2 inhibitor or GLP-1 receptor agonist in type 2 diabetes? Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinol. 7, 818–820. doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(19)30310-9
Andrei, I. O., George, B., Anthony, E. N., Emma, M. A., Christine, T., Edward, P., et al. (2007). Free fatty acid–induced reduction in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 56, 2927–2937. doi:10.2337/db07-0075
Anna, A., Marı́a-José, M., Aida, S., Mayte, B., and Montserrat, P. (2013). Procyanidins target mesenteric adipose tissue in Wistar lean rats and subcutaneous adipose tissue in Zucker obese rat. Food Chem. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.104
Anna, C.-A., Lídia, C., Víctor, P., Mayte, B., Montserrat, P., Marı́a-José, M., et al. (2012). Procyanidins modify insulinemia by affecting insulin production and degradation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 23, 1565–1572. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.10.010
Anoop, D. S., Claudia, L., Eleni, R., Spiros, D., Mar, P.-R., Chris, P. G., et al. (2015). Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: a cohort study in 1·9 million people. Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinol. 3, 105–113. doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(14)70219-0
Antal, B., McMahon, L. P., Sultan, S. F., Lithen, A., Wexler, D. J., Dickerson, B., et al. (2022). Type 2 diabetes mellitus accelerates brain aging and cognitive decline: complementary findings from UK Biobank and meta-analyses. ELife 11, e73138. doi:10.7554/eLife.73138
Antoni, C., Josep Maria del, B., Anna, C., and Lluı́s, A. (2012). Low doses of grape seed procyanidins reduce adiposity and improve the plasma lipid profile in hamsters. Int. J. Obes. doi:10.1038/ijo.2012.75
Antoni, C., Roger, M.-C., Noemí, B., Anna, C., Lluı́s, A., and Josep Maria del, B. (2017). Maternal intake of grape seed procyanidins during lactation induces insulin resistance and an adiponectin resistance-like phenotype in rat offspring. Sci. Rep. 7, 12573. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-12597-9
Aoki, N., Jin-no, S., Nakagawa, Y., Asai, N., Arakawa, E., Tamura, N., et al. (2007). Identification and characterization of microvesicles secreted by 3T3-L1 adipocytes: redox- and hormone-dependent induction of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8-associated microvesicles. Endocrinology 148 (8), 3850–3862. doi:10.1210/en.2006-1479
Armstrong, D. G., Swerdlow, M. A., Armstrong, A. A., Conte, M. S., Padula, W. V., and Bus, S. A. (2020). Five year mortality and direct costs of care for people with diabetic foot complications are comparable to cancer. J. Foot Ankle Res. 13 (1), 16. doi:10.1186/s13047-020-00383-2
Aurèle, B. P., Stewart, J., Philipa, L.-D., Blandine, S., Mathieu, L., and Jennifer, L. E. (2019). PGC1A regulates the IRS1:IRS2 ratio during fasting to influence hepatic metabolism downstream of insulin. doi:10.1073/pnas.1815150116
Aya, A. G., Nayira, A. A. B., Eman, A. M., and Heba, S. Z. (2020). Cardioprotective effect of pioglitazone and curcumin against diabetic cardiomyopathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus: impact on CaMKII/NF-κB/TGF-β1 and PPAR-γ signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives Pharmacol. 394, 349–360. doi:10.1007/s00210-020-01979-y
Barbara Di, C., Azzurra, C., Federica, E., and Gianna, T. (2016). A rule-based model of insulin signalling pathway. BMC Syst. Biol. doi:10.1186/s12918-016-0281-4
Barbosa, J. H. P., Oliveira, S. L., and Seara, L. T. e. (2008). O papel dos produtos finais da glicação avançada (AGEs) no desencadeamento das complicações vasculares do diabetes. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 52 (6), 940–950. doi:10.1590/s0004-27302008000600005
Barrett, E. J., Liu, Z., Khamaisi, M., King, G. L., Klein, R., Klein, B. E. K., et al. (2017). Diabetic microvascular disease: an endocrine society scientific statement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism 102 (12), 4343–4410. doi:10.1210/jc.2017-01922
Belenichev, I., Aliyeva, O., Popazova, O., and Bukhtiyarova, N. (2023). Molecular and biochemical mechanisms of diabetic encephalopathy. Acta Biochim. Pol. 70 (4), 751–760. doi:10.18388/abp.2020_6953
Benedetta, R., Fabiana, P., Ilaria, M., and Simona, F. (2019). Flavonoids and insulin-resistance: from molecular evidences to clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 2061. doi:10.3390/ijms20092061
Bolormaa, V., Yun-Hee, Y., Anthony, R., José, E. G., Krisztián, S., Randall, L. M., et al. (2011). The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 17, 179–188. doi:10.1038/nm.2279
Bou-Teen, D., Kaludercic, N., Weissman, D., Turan, B., Maack, C., Di Lisa, F., et al. (2021). Mitochondrial ROS and mitochondria-targeted antioxidants in the aged heart. Free Radic. Biol. and Med. 167, 109–124. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.02.043
Bo-Zong, S., Zuojun, X., Baohui, H., Ding-Feng, S., and Chong, L. (2015). NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: a review. Front. Pharmacol. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00262
Brigitte, V., Denis, G., Henri, P., Pourrat, A., Bastide, P., and Jeanine, B. (1989). Anti-ulcer activity of procyanidins preparation of water-soluble procyanidin-cimetidine complexes.
Byoung Rai, L., and Pyoung Sim, P. (2022). Effect of combined treatment with catechin and quercetin on hepatic glucose metabolism in diabetic rats. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. doi:10.3746/jkfn.2022.51.1.12
Cai, X., Bao, L., Ren, J., Li, Y., and Zhang, Z. (2016). Grape seed procyanidin B2 protects podocytes from high glucose-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis via the AMPK-SIRT1-PGC-1α axis in vitro. Food and Funct. 7 (2), 805–815. doi:10.1039/c5fo01062d
Castell-Auví, A., Cedó, L., Movassat, J., Portha, B., Sánchez-Cabo, F., Pallarès, V., et al. (2013). Procyanidins modulate microRNA expression in pancreatic islets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61 (2), 355–363. doi:10.1021/jf303972f
Chao, X., Mingxia, Z., Jiahui, W., and Zhenyu, W. (2021). Hawthorn polyphenols, D-chiro-inositol, and epigallocatechin gallate exert a synergistic hypoglycemic effect. J. Food Biochem. 45, e13771. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13771
Chen, J., Chen, X., Lei, Y., Wei, H., Xiong, C., Liu, Y., et al. (2011). Vascular protective potential of the total flavanol glycosides from Abacopteris penangiana via modulating nuclear transcription factor-κB signaling pathway and oxidative stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 136 (1), 217–223. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.04.052
Chen, R., Ovbiagele, B., and Feng, W. (2016). Diabetes and stroke: epidemiology, pathophysiology, pharmaceuticals and outcomes. Am. J. Med. Sci. 351 (4), 380–386. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2016.01.011
Cheng, G., Huang, C., Deng, H., and Wang, H. (2012). Diabetes as a risk factor for dementia and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Intern. Med. J. 42 (5), 484–491. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2012.02758.x
Christian, K. R., Andrea, L. H., and Barnard, R. J. (2013). Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance: underlying causes and modification by exercise training. Compr. Physiol. 3, 1–58. doi:10.1002/cphy.c110062
Chunhui, D. (2014). Protective effect of proanthocyanidins in cadmium induced neurotoxicity in mice. Drug Res. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1395544
Chuntang, M., Xuanzi, Z., Jianxin, Z., and Xiaoyan, H. (2022). Procyanidins regulate colonic metabolome, inflammatory response and antioxidant capacity in lambs fed a high-concentrate diet. J. Animal Physiology Animal Nutr. 107, 1006–1018. doi:10.1111/jpn.13790
Claudine, M., Gary, W., Christine, M., Augustin, S., and Christian, R. (2005). Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 81, 230S–242S. doi:10.1093/ajcn/81.1.230s
Constanze, C. M., Dina, C. S., Marco, G. A., Pedro, F. O., David Morritz de, K., and Thomas, L. (2017). Diabetes-induced hyperglycemia impairs male reproductive function: a systematic review. Hum. Reprod. Update 24, 86–105. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmx033
Cui, X., Liu, X., Feng, H., Zhao, S., and Gao, H. (2012). Grape seed proanthocyanidin extracts enhance endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression through 5'-AMP activated protein kinase/Surtuin 1-Krüpple like factor 2 pathway and modulate blood pressure in ouabain induced hypertensive rats. Biol. and Pharm. Bull. 35 (12), 2192–2197. doi:10.1248/bpb.b12-00598
Dandan, H., Guangjiang, S., Yaping, J., Chao, Y., and Chuanbing, Z. (2020). A review on the potential of Resveratrol in prevention and therapy of diabetes and diabetic complications. Biomed. and Pharmacother. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109767
Daniël, H. v. R., and Michaëla, D. (2011). Glucolipotoxicity and beta cells in type 2 diabetes mellitus: target for durable therapy? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 93, S37–S46. doi:10.1016/s0168-8227(11)70012-2
Daniel, J. D., and Michael, A. N. (2006). The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 368, 1696–1705. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(06)69705-5
Dao, T.-M. A., Waget, A., Klopp, P., Serino, M., Vachoux, C., Pechere, L., et al. (2011). Resveratrol increases glucose induced GLP-1 secretion in mice: a mechanism which contributes to the glycemic control. PloS One 6 (6), e20700. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020700
David, B. S., Kitt Falk, P., and Gerald, I. S. (2007). Disordered lipid metabolism and the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 87, 507–520. doi:10.1152/physrev.00024.2006
David, G. A., Tze-Woei, T., Andrew, J. M. B., and Sicco, A. B. (2023). Diabetic foot ulcers. Jama 330, 62. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.10578
Décio, L. E., Lorenzo, P., and Miriam, C. (2020). Pancreatic β-cells in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: different pathways to failure. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 16, 349–362. doi:10.1038/s41574-020-0355-7
Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus (2013). Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 37, S81–S90. doi:10.2337/dc14-s081
Dillmann, W. H. (2019). Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Circulation Res. 124 (8), 1160–1162. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314665
Eloisa Aparecida, V.-B., Davidson Correa, A., Letícia Prates, R., Fernanda, O., and Ângelo Rafael, C. (2021). Lipotoxicity and β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: oxidative stress linked to NADPH oxidase and ER stress. Cells. doi:10.3390/cells10123328
Eskandar, Q., Marwan, A., Bandar, A.-H., Abdullah, Q., Haneen, A., Ahmed, A.-M., et al. (2023). Procyanidins: a promising anti-diabetic agent with potential benefits on glucose metabolism and diabetes complications. Wound Repair Regen. 31, 688–699. doi:10.1111/wrr.13115
Eun-Jung, B., Hong Gyu, P., Choong Hwan, L., Tong Il, L., Gye Hyeong, W., Younghwa, N., et al. (2011). Effects of novel chalcone derivatives on α-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase-4, and adipocyte differentiation in vitro. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2011.44.6.410
Eva, L. F., Brian, C. C., Rodica, P. B., Douglas, W. Z., Douglas, E. W., David, B., et al. (2019). Diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 5, 41. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0092-1
Fan, J., Liu, H., Wang, J., Zeng, J., Tan, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Procyanidin B2 improves endothelial progenitor cell function and promotes wound healing in diabetic mice via activating Nrf2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 25 (2), 652–665. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16111
Fangfang, T., Jifei, W., Yuexin, L., Shujun, Z., Zhenhua, W., Gang, L., et al. (2020). Proanthocyanidins ameliorated deficits of lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus via inhibiting adipogenesis and improving mitochondrial function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 2029. doi:10.3390/ijms21062029
Feng, J., Xiaolu, Z., Yingya, L., Yingyu, C., and Yihan, C. (2016). Pinus massonianaBark extract: structure–activity relationship and biomedical potentials. Am. J. Chin. Med. 44, 1559–1577. doi:10.1142/s0192415x16500877
Gao, L., Gu, Y., and Yin, X. (2016). High serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis. PloS One 11 (10), e0164021. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0164021
Gaochao, Z., Robert, W. M., Ying, L., Yuli, C., Xiaolan, S., Judy, F.-M., et al. (2001). Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J. Clin. Investigation 108, 1167–1174. doi:10.1172/jci13505
Gary, F. L., and Patricia, L. B. (2021). The discovery of insulin revisited: lessons for the modern era. J. Clin. Investigation 131, e142239. doi:10.1172/jci142239
Gary, W., and Claudine, M. (2005). Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. II. Review of 93 intervention studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 81, 243S–255S. doi:10.1093/ajcn/81.1.243s
Gemma, M., Cinta, B., Mayte, B., Juan, F.-L., Gerard, P., Salvadó, M. J., et al. (2010a). Effects of a grapeseed procyanidin extract (GSPE) on insulin resistance. J. Nutr. Biochem. 21, 961, 967. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.08.001
Gemma, M., Sheela, O., Montserrat, V., Cinta, B., Mayte, B., Juan, F.-L., et al. (2010b). Oligomers of grape-seed procyanidin extract activate the insulin receptor and key targets of the insulin signaling pathway differently from insulin. J. Nutr. Biochem. 21, 476–481. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.02.003
Giovanna, B., Alessandra, A., Luca Della, V., Francesca, G., Quagliano, O., Sara, C., et al. (2024). Unraveling the parahormetic mechanism underlying the health-protecting effects of grapeseed procyanidins. Redox Biol. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102981
Gopalsamy Rajiv, G., Savarimuthu, I., and Michael Gabriel, P. (2011). Solanum torvum Swartz. fruit containing phenolic compounds shows antidiabetic and antioxidant effects in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.08.005
Guillermo Arango, D., and Albert, D. (2014). Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00491
Hadi, B., Seyed Ahmad, H., Sirous, S., Delsa, M., Mohammad, A., Maryam, L., et al. (2020). Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate of Camellia sinensis leaves on blood pressure, lipid profile, atherogenic index of plasma and some inflammatory and antioxidant markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a clinical trial. J. Complementary Integr. Med. 18, 405–411. doi:10.1515/jcim-2020-0090
Hee-Hyun, L., Kui-Jin, K., Ok-Hwan, L., and Boo-Yong, L. (2010). Effect of pycnogenol® on glucose transport in mature 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Phytotherapy Res. doi:10.1002/ptr.3193
Helena, Q., Josep Maria del, B., David, P., Sabina, D., Juan, F.-L., Montserrat, P., et al. (2009). Grape seed proanthocyanidins correct dyslipidemia associated with a high-fat diet in rats and repress genes controlling lipogenesis and VLDL assembling in liver. Int. J. Obes. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.136
Hong, S., Pouya, S., Suvi, K., Moritz, P., Katherine, O., Bruce Bartholow, D., et al. (2022). IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 183, 109119. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
Hsiang-Jung, T., Liang-Yi, W., and Lucy Sun, H. (2008). Effect of a proanthocyanidin-rich extract from longan flower on markers of metabolic syndrome in fructose-fed rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. doi:10.1021/jf801966y
Ill-Min, C., Govindasamy, R., Umadevi, S., Baskar, V., Venkatesan Gopiesh, K., and Muthu, T. (2020). Insights on the current status and advancement of diabetes mellitus type 2 and to avert complications: an overview. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. doi:10.1002/bab.1853
Isabel, C.-H., María Ángeles, M., Luis, G., and Sonia, R. (2014). Cocoa flavonoids attenuate high glucose-induced insulin signalling blockade and modulate glucose uptake and production in human HepG2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 64, 10–19. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.014
Isabel, C.-H., María Ángeles, M., Luis, G., and Sonia, R. (2015). Cocoa flavonoids protect hepatic cells against high-glucose-induced oxidative stress: relevance of MAPKs. Mol. Nutr. and Food Res. 59, 597–609. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201400492
Janika, S., Zi Yu, C., Bingyao, T., Damon Wing Kee, W., Xinyu, L., and Jacqueline, C. (2022). Dietary intake and diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review of the literature. Nutrients 14, 5021. doi:10.3390/nu14235021
Jasmine, F. P., John, C. S., Philip, N. B., Clare, M. R., and Mark, H. V. (2018). The pathophysiology of gestational diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3342. doi:10.3390/ijms19113342
Javier, D.-C., Desirée, L.-R., Ernesto, M. N., Víctor, G. T., Carolina, H.-C., Carla, F., et al. (2020). Inflammatory targets in diabetic nephropathy. J. Clin. Med. 9, 458. doi:10.3390/jcm9020458
Javier, I. O., Christian, H., Jeremy, P. E. S., Malte, K., and Hagen, S. (2018). Recommending flavanols and procyanidins for cardiovascular health: revisited. Mol. Aspects Med. 61, 63–75. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2018.02.001
Jay, D., Hitomi, H., and Griendling, K. K. (2006). Oxidative stress and diabetic cardiovascular complications. Free Radic. Biol. and Med. 40 (2), 183–192. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.06.018
Jeffrey, A. B., Kevan, C. H., and George, S. E. (2010). Genetics, pathogenesis and clinical interventions in type 1 diabetes. Nature 464, 1293–1300. doi:10.1038/nature08933
Jeong, H., Choi, D., Oh, Y., Heo, J., and Hong, J. (2022). A nanocoating Co-localizing nitric oxide and growth factor onto individual endothelial cells reveals synergistic effects on angiogenesis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 11 (6), e2102095. doi:10.1002/adhm.202102095
Jia, G., Hill, M. A., and Sowers, J. R. (2018). Diabetic cardiomyopathy: an update of mechanisms contributing to this clinical entity. Circulation Res. 122 (4), 624–638. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311586
Ji-Hyun, L., Mi-Young, S., Eunkyung, S., Min Jung, K., Woo Sung, M., Myung-Kwan, H., et al. (2009). Overexpression of SIRT1 protects pancreatic β-cells against cytokine toxicity by suppressing the nuclear factor-κb signaling pathway. Diabetes. doi:10.2337/db07-1795
Jiwon, K., and Kun-Ho, Y. (2011). Glucolipotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes and Metabolism J. doi:10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.444
Joanne, Y., Sophie, R., Ryo, K., Ecosse, L. L., Jonathan, W. K., Toke, B., et al. (2012). Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 35, 556–564. doi:10.2337/dc11-1909
John, V. F., Lucia, K., and Mirela, D. (2020). The role of inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Front. Immunol. 11, 583687. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.583687
Justin, B. E. T., Haolin, X., Adam, D. D., Phillip, J. S., Javed, B., Clyde, W. Y., et al. (2016). Temporal trends and factors associated with diabetes mellitus among patients hospitalized with heart failure: findings from Get with the Guidelines–Heart Failure registry. Am. Heart J. 182, 9–20. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2016.07.025
Karina, R. A., Montserrat, V., Lorena, M., Marcelo, V., Ahmed, A. H., Ahmed, A. R., et al. (2021). Phytochemicals as potential epidrugs in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 12, 656978. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.656978
Kathryn, P., Clara, W. R., Agnieszka, K. A., Garth, L. W., and Verchere, C. B. (2013). Death and dysfunction of transplanted β-cells: lessons learned from type 2 diabetes? Diabetes 63, 12–19. doi:10.2337/db12-0364
Kaul, R. K. (1996). Pflanzliche procyanidine vorkommen, klassifikation and pharmakologische wirkungen. Pharmazie unserer Zeit 25, 175–185. doi:10.1002/pauz.19960250406
Ken-yu, H., Hitoshi, A., and Yoko, Y. (2022). Black soybean seed coat polyphenol ameliorates the abnormal feeding pattern induced by high-fat diet consumption. Front. Nutr. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1006132
Kerry, L. D., Coleman, I. S., Sarah Jane, S., José, J., Mark, D. B., and Elizabeth, J. P. (2005). Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investigation 115, 1343–1351. doi:10.1172/jci23621
Kimber-Trojnar, Ż., Patro-Małysza, J., Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K. E., Oleszczuk, J., Trojnar, M., Mierzyński, R., et al. (2018). Ghrelin in serum and urine of post-partum women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (10), 3001. doi:10.3390/ijms19103001
Kisseih, E., Lechtenberg, M., Petereit, F., Sendker, J., Zacharski, D., Brandt, S., et al. (2015). Phytochemical characterization and in vitro wound healing activity of leaf extracts from Combretum mucronatum Schum. and Thonn.: oligomeric procyanidins as strong inductors of cellular differentiation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 174, 628–636. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.008
Knapp, M., Tu, X., and Wu, R. (2019). Vascular endothelial dysfunction, a major mediator in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 40 (1), 1–8. doi:10.1038/s41401-018-0042-6
Kong, X., Guan, J., Gong, S., and Wang, R. (2017). Neuroprotective effects of grape seed procyanidin extract on ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. Chin. Med. Sci. J. = Chung-kuo I Hsueh K'o Hsueh Tsa Chih 32 (2), 92–99. doi:10.24920/J1001-9294.2017.020
Kopustinskiene, D. M., Savickas, A., Vetchý, D., Masteikova, R., Kasauskas, A., and Bernatoniene, J. (2015). Direct effects of (-)-epicatechin and procyanidin B2 on the respiration of rat heart mitochondria. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 232836. doi:10.1155/2015/232836
Kyle, D. C., and Morris, F. W. (2012). Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2. Diabetologia. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2644-8
Laura, A., Takuya, Y., Pili, Z., Donald, K. S., Seung, K. K., Christopher, P. O. D., et al. (2007). Glucose infusion in mice. Diabetes 56, 1792–1801. doi:10.2337/db06-1513
Lewis, G. F., Carpentier, A., Adeli, K., and Giacca, A. (2002). Disordered fat storage and mobilization in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 23 (2), 201–229. doi:10.1210/edrv.23.2.0461
Li, B.-y., Li, X.-l., Gao, H.-q., Zhang, J.-h., Cai, Q., Cheng, M., et al. (2011). Grape seed procyanidin B2 inhibits advanced glycation end product-induced endothelial cell apoptosis through regulating GSK3β phosphorylation. Cell Biol. Int. 35 (7), 663–669. doi:10.1042/CBI20100656
Li, D., Zhao, T., Meng, J., Jing, Y., Jia, F., and He, P. (2015). Procyanidin B2 inhibits high glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HK-2 human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 12 (6), 8148–8154. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.4445
Li, R., Li, H., and Zhang, Q. (2022). Procyanidin protects human retinal pigment epithelial cells from high glucose by inhibiting autophagy. Environ. Toxicol. 37 (2), 201–211. doi:10.1002/tox.23389
Li, X.-l., Li, B.-y., Cheng, M., Yu, F., Yin, W.-b., Cai, Q., et al. (2013). PIMT prevents the apoptosis of endothelial cells in response to glycated low density lipoproteins and protective effects of grape seed procyanidin B2. PloS One 8 (7), e69979. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069979
Liang, C., Peng, S., Ting, W., Kaixian, C., Qi, J., He-Yao, W., et al. (2012). Diverse mechanisms of antidiabetic effects of the different procyanidin oligomer types of two different cinnamon species on db/db mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 9144–9150. doi:10.1021/jf3024535
Liang, Z., Yijun, W., Daxiang, L., Chi Tang, H., Junsong, L., and Xiaochun, W. (2016). The absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of procyanidins. Food and Funct. 7, 1273–1281. doi:10.1039/c5fo01244a
Lídia, C., Anna, C.-A., Víctor, P., Mayte, B., Anna, A., Lluı́s, A., et al. (2013). Grape seed procyanidin extract modulates proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cells. Food Chem. 138, 524–530. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.088
Linards, K., Ingus, P. r., Mārcis, M., Artūrs, V., and Māris, K. (2022). Procyanidins from cranberry press residues—extraction optimization, purification and characterization. Plants 11, 3517. doi:10.3390/plants11243517
Liu, K., Zhang, C., Chang, R., He, Y., Guan, F., and Yao, M. (2023b). Ultra-stretchable, tissue-adhesive, shape-adaptive, self-healing, on-demand removable hydrogel dressings with multiple functions for infected wound healing in regions of high mobility. Acta Biomater. 166, 224–240. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2023.05.025
Liu, S., Fang, Y., Yu, J., and Chang, X. (2021). Hawthorn polyphenols reduce high glucose-induced inflammation and apoptosis in ARPE-19 cells by regulating miR-34a/SIRT1 to reduce acetylation. J. Food Biochem. 45 (2), e13623. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13623
Liu, Y., Liao, W. J., Zhu, Z., Zeng, H., He, H. Q., Sun, X. L., et al. (2016). Effect of procyanidine on VEGFR-2 expression and transduction pathway in rat endothelial progenitor cells under high glucose conditions. Genet. Mol. Res. GMR 15 (1). doi:10.4238/gmr.15016925
Liu, Y., and Wu, N. (2021). Progress of nanotechnology in diabetic retinopathy treatment. Int. J. Nanomedicine 16, 1391–1403. doi:10.2147/IJN.S294807
Liu, Z., Liu, G., Ha, D. P., Wang, J., Xiong, M., and Lee, A. S. (2023a). ER chaperone GRP78/BiP translocates to the nucleus under stress and acts as a transcriptional regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120 (31), e2303448120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2303448120
Liwei, G., Mark, A. K., John, F. H., Gary, R. B., David, C., Sarah, V., et al. (2002). Fractionation of polymeric procyanidins from lowbush blueberry and quantification of procyanidins in selected foods with an optimized normal-phase HPLC−MS fluorescent detection method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 4852–4860. doi:10.1021/jf020214v
Lu, L., Lu, Q., Chen, W., Li, J., Li, C., and Zheng, Z. (2018). Vitamin D3 protects against diabetic retinopathy by inhibiting high-glucose-induced activation of the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J. Diabetes Res., 2018, 8193523. doi:10.1155/2018/8193523
Luan, S.-s., Yu, F., Li, B.-y., Qin, R.-j., Li, X.-l., Cai, Q., et al. (2014). Quantitative proteomics study of protective effects of grape seed procyanidin B2 on diabetic cardiomyopathy in db/db mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 78 (9), 1577–1583. doi:10.1080/09168451.2014.930320
Maahs, D. M., and Rewers, M. (2006). Editorial: mortality and renal disease in type 1 diabetes mellitus-progress made, more to be done. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism 91 (10), 3757–3759. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-1730
Maaike, M. A., Jean-Paul, V., Anna-Marja, A., Hollman, P. C. H., and Harry, G. (2009). Procyanidin dimers are metabolized by human microbiota with 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acetic acid and 5-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone as the major metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 1084–1092. doi:10.1021/jf803059z
Majid, T. (2013). Diabetic nephropathy and antioxidants. J. Nephropathol. 2, 20–27. doi:10.5812/nephropathol.9093
Mandeep Kumar, A., and Umesh Kumar, S. (2013). Molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: an update. Vasc. Pharmacol. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2013.01.001
Maria, L., Anne-Laure, C., Vincent, P., and Miriam, C. (2020). Recent insights into mechanisms of β-cell lipo- and glucolipotoxicity in type 2 diabetes. J. Mol. Biol. 432, 1514–1534. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2019.09.016
Marinko, M., Matej, P., Mia, K., and Ana-Marija Liberati, P. (2021). NAFLD, insulin resistance, and diabetes mellitus type 2. Can. J. Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2021, 6613827. doi:10.1155/2021/6613827
Marta, M., Gabriele, W., Reinhard, W., and Philip, N. (2010). Effects of pharmacological inhibition of NADPH oxidase or iNOS on pro-inflammatory cytokine, palmitic acid or H2O2-induced mouse islet or clonal pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Biosci. Rep. 30, 445–453. doi:10.1042/bsr20090138
Mary, T. K. (2004). Sulfonylurea treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: focus on glimepiride. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 24, 606–620. doi:10.1592/phco.24.6.606.34752
Mary, W.-L., Xiaohui, L. W., Brian, K. L., Robert, K. H., Masao, N., and Daryl, K. G. (2002). Epigallocatechin gallate, a constituent of green tea, represses hepatic glucose production. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 34933–34940. doi:10.1074/jbc.m204672200
Masahito, T., Seiya, I., Fumihiko, H., and Takanori, T. (2010). Dietary anthocyanin-rich bilberry extract ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in diabetic mice. J. Nutr. 140, 527–533. doi:10.3945/jn.109.118216
Matoori, S., Veves, A., and Mooney, D. J. (2021). Advanced bandages for diabetic wound healing. Sci. Transl. Med. 13 (585), eabe4839. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abe4839
McDermott, K., Fang, M., Boulton, A. J. M., Selvin, E., and Hicks, C. W. (2023). Etiology, epidemiology, and disparities in the burden of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 46 (1), 209–221. doi:10.2337/dci22-0043
Michael, N. C. (2004). Diet-derived phenols in plasma and tissues and their implications for health. Planta Medica. doi:10.1055/s-2004-835835
Miki, M., Atutoshi, K., Yutaka, M., and Kazumi, Y. (2011). Hypoglycemic effect of resveratrol in type 2 diabetic model db/db mice and its actions in cultured L6 myotubes and RIN-5F pancreatic β-cells. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 48, 237–244. doi:10.3164/jcbn.10-119
Min, L., Bijun, H., Li, W., Qun, L., and Rui, L. (2022). Peanut skin procyanidins ameliorate insulin resistance via modulation of gut microbiota and gut barrier in type 2 diabetic mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 102, 5935–5947. doi:10.1002/jsfa.11945
Min-Ji, B., Van Long, T., Hey-Sook, K., Mira, J., and Woo-Sik, J. (2013). Anti-inflammatory effect of procyanidins from wild grape (vitis amurensis) seeds in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. doi:10.1155/2013/409321
Mona, F. M., Shimaa, A., Heba Osama, M., Assem, M. E.-S., Rachid, D., Mohamed, A. O. A., et al. (2021). Syzygium aqueum (Burm.f.) alston prevents streptozotocin-induced pancreatic beta cells damage via the TLR-4 signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 769244. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.769244
Montserrat, P., Lídia, C., Gemma, M., Mayte, B., and Anna, A. (2012). Procyanidins improve some disrupted glucose homoeostatic situations: an analysis of doses and treatments according to different animal models. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 52, 569–584. doi:10.1080/10408398.2010.501533
Montserrat, P., Mayte, B., Cinta, B., Salvadó, M. J., Lluı́s, A., and Anna, A. (2004). Grape seed-derived procyanidins have an antihyperglycemic effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and insulinomimetic activity in insulin-sensitive cell lines. Endocrinology. doi:10.1210/en.2004-0764
Moran, W., Yongsheng, L., Sheng, L., and Jiagao, L. (2022). Endothelial dysfunction and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 851941. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.851941
Mota, M., Banini, B. A., Cazanave, S. C., and Sanyal, A. J. (2016). Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism Clin. Exp. 65 (8), 1049–1061. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2016.02.014
Muthenna, P., Raghu, G., Kumar, P. A., Surekha, M. V., and Reddy, G. B. (2014). Effect of cinnamon and its procyanidin-B2 enriched fraction on diabetic nephropathy in rats. Chemico-biological Interact. 222, 68–76. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2014.08.013
Najim, A.-A., Caroline, A., Aurélie, B., Sandrine, D., Jean-Paul, C., Nathalie, L., et al. (2004). Extracts enriched in different polyphenolic families normalize increased cardiac NADPH oxidase expression while having differential effects on insulin resistance, hypertension, and cardiac hypertrophy in high-fructose-fed rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 151–157. doi:10.1021/jf048919f
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration NCD-RisC (2016). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet London, Engl. 387 (10027), 1513–1530. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00618-8
Nia, J. B., Roland, G., and David, E. J. (2002). Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 267–277. doi:10.1038/nrm782
Nie, X., Tang, W., Zhang, Z., Yang, C., Qian, L., Xie, X., et al. (2020). Procyanidin B2 mitigates endothelial endoplasmic reticulum stress through a PPARδ-Dependent mechanism. Redox Biol. 37, 101728. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101728
Noemi, G.-A., Neus, M.-M., Mayte, B., Gerard, P., Santiago, G. a.-V., Montserrat, P., et al. (2012). Grape seed-derived procyanidins decrease dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 activity and expression. J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 9055–9061. doi:10.1021/jf3010349
Nupur, P., Paul, M., Varun, P., Peter, R. F., and Victor, G. (2018). Beneficial metabolic effects of dietary epigallocatechin gallate alone and in combination with exendin-4 in high fat diabetic mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 460, 200–208. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2017.07.024
Odai, T., Terauchi, M., Kato, K., Hirose, A., and Miyasaka, N. (2019). Effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on vascular endothelial function in participants with prehypertension: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutrients 11 (12), 2844. doi:10.3390/nu11122844
Peiling, H., Chin-Wen, C., and Tsung-Yun, L. (2013). Areca nut procyanidins ameliorate streptozocin-induced hyperglycemia by regulating gluconeogenesis. Food Chem Toxicol. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.12.057
Peter, J. C., John, F. P., Paul, A. K., Paddy, W., Ketan, D., Mike, S., et al. (2013). Vascular function and atherosclerosis progression after 1 y of flavonoid intake in statin-treated postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 97, 936–942. doi:10.3945/ajcn.112.043745
Peter, J. C., Mike, S., John, F. P., Ketan, D., Paul, A. K., and Aedín, C. (2012). Chronic ingestion of flavan-3-ols and isoflavones improves insulin sensitivity and lipoprotein status and attenuates estimated 10-year CVD risk in medicated postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 35, 226–232. doi:10.2337/dc11-1443
Pimentel, E. F., de Oliveira, B. G., Pereira, A. C. H., Figueira, M. M., Portes, D. B., Scherer, R., et al. (2024). Polyphenols, antioxidants, and wound healing of lecythis pisonis seed coats. Planta Medica 90 (3), 243–251. doi:10.1055/a-2212-0262
Qian, C., Baoying, L., Haiqing, G., Jianhua, Z., Junfu, W., Fei, Y., et al. (2011). Grape seed procyanidin B2 inhibits human aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration induced by advanced glycation end products. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 75, 1692–1697. doi:10.1271/bbb.110194
Qian, W., Fen, Z., Mengyao, N., Yan, J., Lin, S., Yinggang, L., et al. (2023). Extraction methods, properties, functions, and interactions with other nutrients of Lotus procyanidins: a review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 14413–14431. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05305
Qian, W., Hengye, C., Zhejuan, L., Shuyi, L., Bei, H., Yan-Qing, G., et al. (2013). Oligomeric procyanidins of lotus seedpod inhibits the formation of advanced glycation end-products by scavenging reactive carbonyls. Food Chem. 138, 1493–1502. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.111
Ramesh, C. K., Luke, R. H., Samuel, E. W., Theodore, J. R., and Ronald, L. P. (2012). Effect of dietary blueberry pomace on selected metabolic factors associated with high fructose feeding in growing sprague–dawley rats. J. Med. Food 15, 802–810. doi:10.1089/jmf.2011.0212
Ramesh, C. K., Theodore, J. R., Samuel, E. W., Luke, R. H., and Ronald, L. P. (2010). Effects of dietary consumption of cranberry powder on metabolic parameters in growing rats fed high fructose diets. Food and Funct. 1, 116–123. doi:10.1039/c0fo00089b
Rebecca, A. H., Timothy, E. M., and Domenico, A. (2017). Biochemical and cellular properties of insulin receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 31–44. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.89
Reuben, J. S., Katja, L., Debbie, S. V., Seung Hoi, K., Nabeel, B., Ronald, A. D., et al. (2005). The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science 310, 1642–1646. doi:10.1126/science.1120781
Rodríguez-Carrizalez, A. D., Castellanos-González, J. A., Martínez-Romero, E. C., Miller-Arrevillaga, G., Villa-Hernández, D., Hernández-Godínez, P. P., et al. (2014). Oxidants, antioxidants and mitochondrial function in non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy. J. Diabetes 6 (2), 167–175. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.12076
Rosalyn, S. Y., and Solomon, A. B. (1960). Plasma insulin concentrations in nondiabetic and early diabetic subjects: determinations by a new sensitive immuno-assay technic. Diabetes 9, 254–260. doi:10.2337/diab.9.4.254
Rui, X., Xiuling, W., Jianming, W., Yong, T., Wen-Qiao, Q., Xin, S., et al. (2020). Polyphenols isolated from lychee seed inhibit Alzheimer's disease-associated Tau through improving insulin resistance via the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 251, 112548. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.112548
Ruszała, M., Pilszyk, A., Niebrzydowska, M., Kimber-Trojnar, Ż., Trojnar, M., and Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. (2022). Novel biomolecules in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus 2.0. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (8), 4364. doi:10.3390/ijms23084364
Ryu, H. Y., Kim, L. E., Jeong, H., Yeo, B. K., Lee, J.-W., Nam, H., et al. (2021). GSK3B induces autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1. Exp. and Mol. Med. 53 (3), 369–383. doi:10.1038/s12276-021-00570-6
Ryuichi, W., Yusuke, N., Norito, Y., Masayoshi, T., Yuichi, I., Koichi, Y., et al. (2001). Effects of OPB-9195, anti-glycation agent, on experimental diabetic neuropathy. Eur. J. Clin. Investigation. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2362.2001.00826.x
Salime Pelin, E., Murat, B., Matem, T. r., and İsmail, S. (2014). The comparative effects of perindopril and catechin on mesangial matrix and podocytes in the streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Pharmacol. Rep. doi:10.1016/j.pharep.2013.09.010
Samsu, N. (2021). Diabetic nephropathy: challenges in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. BioMed Res. Int., 2021, 1497449. doi:10.1155/2021/1497449
San Martin, A., Foncea, R., Laurindo, F. R., Ebensperger, R., Griendling, K. K., and Leighton, F. (2007). Nox1-based NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide is required for VSMC activation by advanced glycation end-products. Free Radic. Biol. and Med. 42 (11), 1671–1679. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.02.002
Sarwar, N., Gao, P., Seshasai, S. R. K., Gobin, R., Kaptoge, S., Di Angelantonio, E., et al. (2010). Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet London, Engl 375 (9733), 2215–2222. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60484-9
Schön, C., Allegrini, P., Engelhart-Jentzsch, K., Riva, A., and Petrangolini, G. (2021). Grape seed extract positively modulates blood pressure and perceived stress: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in healthy volunteers. Nutrients 13 (2), 654. doi:10.3390/nu13020654
Sébastien, H., and Reuben, J. S. (2017). AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 121–135. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.95
Shan, J., Jin, X., Zhang, C., Huang, M., Xing, J., Li, Q., et al. (2024). Metal natural product complex Ru-procyanidins with quadruple enzymatic activity combat infections from drug-resistant bacteria. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 14 (5), 2298–2316. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.12.017
Shuang, R., Xueqiang, H., Siqi, Z., Yong, Z., Xiao, X., Wei, B., et al. (2017). Procyanidins extracted from the litchi pericarp ameliorate atherosclerosis in ApoE knockout mice: their effects on nitric oxide bioavailability and oxidative stress. Food and Funct. 8, 4210–4216. doi:10.1039/c7fo00747g
Silambarasan, M., Tan, J. R., Karolina, D. S., Armugam, A., Kaur, C., and Jeyaseelan, K. (2016). MicroRNAs in hyperglycemia induced endothelial cell dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17 (4), 518. doi:10.3390/ijms17040518
Silvestre, J.-S., Théry, C., Hamard, G., Boddaert, J., Aguilar, B., Delcayre, A., et al. (2005). Lactadherin promotes VEGF-dependent neovascularization. Nat. Med. 11 (5), 499–506. doi:10.1038/nm1233
Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K. E., Kimber-Trojnar, Ż., Patro-Małysza, J., Olszewska, A., Zaborowski, T., and Małecka-Massalska, T. (2016). An interplay between obesity and inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 17 (7), 603–613. doi:10.2174/1389201017666160127105926
Stella, P., Kalliopi, P., Grigorios, T., Dimitrios, P., Κonstantinos, V., and Νικόλαος, Π. (2021). Skin advanced glycation end products among subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus with or without distal sensorimotor polyneuropathy. J. diabetes Res. 2021, 6045677. doi:10.1155/2021/6045677
Stergios, A. P., Jannis, K., and Christos, Z. (2009). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the pathogenetic roles of insulin resistance and adipocytokines. Curr. Mol. Med. 9, 299–314. doi:10.2174/156652409787847191
Strain, W. D., and Paldánius, P. M. (2018). Diabetes, cardiovascular disease and the microcirculation. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 17 (1), 57. doi:10.1186/s12933-018-0703-2
Sudesna, C., Kamlesh, K., and Melanie, J. D. (2017). Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 389, 2239–2251. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)30058-2
Su Woong, J., and Jae-Young, M. (2021). The role of inflammation in diabetic kidney disease. Korean J. Intern. Med. doi:10.3904/kjim.2021.174
Suzanne, M. B., William, T. M., Ryan, P. M., Melanie, R. D., Katheryn, M. G., Liyun, Y., et al. (2017). High-molecular-weight cocoa procyanidins possess enhanced insulin-enhancing and insulin mimetic activities in human primary skeletal muscle cells compared to smaller procyanidins. J. Nutr. Biochem. 39, 48–58. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.10.001
Sweeting, A., Wong, J., Murphy, H. R., and Ross, G. P. (2022). A clinical update on gestational diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 43 (5), 763–793. doi:10.1210/endrev/bnac003
Takako, Y., Hyun Ju, K., and Eun Ju, C. (2008). Gravinol ameliorates high-fructose-induced metabolic syndrome through regulation of lipid metabolism and proinflammatory state in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 5026–5032. doi:10.1021/jf800213f
Tan, T.-E., and Wong, T. Y. (2022). Diabetic retinopathy: looking forward to 2030. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 1077669. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1077669
Teri, G. B., Steven, H. N., David, J. R., Nancy, Y. I., Elizabeth, R., Sharon, D. M., et al. (1991). ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell 65, 663–675. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j
Thomas, J. R., Benjamin, F. B., Jason, D. R., Daniel, R. L., Andrew, T. S., Blake, D., et al. (2017). Monomeric cocoa catechins enhance β-cell function by increasing mitochondrial respiration. J. Nutr. Biochem. 49, 30–41. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.07.015
Tomonori, N., Shu, M., Tadashi, H., Kazuhiro, O., Masanori, K., Ichiro, T., et al. (2009). A catechin-rich beverage improves obesity and blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Obesity 17, 310–317. doi:10.1038/oby.2008.505
Tung-Sheng, C., Show Yih, L., Hsi Chin, W., Fuu Jen, T., Chang Hai, T., Chih Yang, H., et al. (2011). Efficacy of epigallocatechin-3-gallate and Amla (emblica officinalis) extract for the treatment of diabetic-uremic patients. J. Med. Food. doi:10.1089/jmf.2010.1195
Van Long, T., Min Ji, B., Mira, J., Ah Ng Tony, K., Chi Tang, H., and Woo-Sik, J. (2014). Antioxidant defense and hepatoprotection by procyanidins from almond (prunus amygdalus) skins. J. Agric. Food Chem. doi:10.1021/jf5027247
van Sloten, T. T., Sedaghat, S., Carnethon, M. R., Launer, L. J., and Stehouwer, C. D. A. (2020). Cerebral microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes: stroke, cognitive dysfunction, and depression. Lancet. Diabetes and Endocrinol. 8 (4), 325–336. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30405-X
Wei, J., Wu, H., Zhang, H., Li, F., Chen, S., Hou, B., et al. (2018). Anthocyanins inhibit high glucose-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis caused by oxidative stress in db/db mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 41 (3), 1608–1618. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2018.3378
Wei, T., Chen, L., Zhang, L., Wang, B., Li, X. B., Kai, F., et al. (2017). Effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on glucose metabolism and liver injury in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Genet. Mol. Res. doi:10.4238/gmr16019463
Wei-Jian, N., Hai-Hua, D., and Ling-Zhi, T. (2015). Berberine as a promising anti-diabetic nephropathy drug: an analysis of its effects and mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 760, 103–112. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.04.017
Wenqian, G., Andreas, R., Kjeld, H., Søren, G., and Per Bendix, J. (2018). The dynamic effects of isosteviol on insulin secretion and its inability to counteract the impaired β-cell function during gluco-lipo-and aminoacidotoxicity: studies in vitro. Nutrients 10, 127. doi:10.3390/nu10020127
Wu, S., Yue, Y., Li, J., Li, Z., Li, X., Niu, Y., et al. (2015). Procyanidin B2 attenuates neurological deficits and blood-brain barrier disruption in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Mol. Nutr. and Food Res. 59 (10), 1930–1941. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201500181
Xiao-Fang, P., Jinyu, M., Jianfei, C., Zheng, S., Raymond Chuen-Chung, C., Iris Mei Ying, T., et al. (2010). Beneficial effects of cinnamon proanthocyanidins on the formation of specific advanced glycation endproducts and methylglyoxal-induced impairment on glucose consumption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 6692–6696. doi:10.1021/jf100538t
Xiao-Fang, P., Ka-Wing, C., Jinyu, M., Bo, C., Chi-Tang, H., Clive, L., et al. (2008). Cinnamon bark proanthocyanidins as reactive carbonyl scavengers to prevent the formation of advanced glycation endproducts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 1907–1911. doi:10.1021/jf073065v
Xinyi, W., Bo-Rong, Z., Qi, J., Yiming, L., Ting, W., and He-Yao, W. (2020). Cinnamtannin D1 protects pancreatic β-cells from glucolipotoxicity-induced apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy in vitro and in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04898
Xu, J., Hu, X. F., Huang, W., Shen, P. Y., Zhang, W., Ren, H., et al. (2017). The clinicopathological characteristics of diabetic nephropathy and non-diabetic renal diseases in diabetic patients. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 56 (12), 924–929. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2017.12.007
Yamagishi, S.-i. (2011). Role of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and receptor for AGEs (RAGE) in vascular damage in diabetes. Exp. Gerontol. 46 (4), 217–224. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2010.11.007
Yang, B., Sun, Y., Lv, C., Zhang, W., and Chen, Y. (2020). Procyanidins exhibits neuroprotective activities against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting TLR4-NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway. Psychopharmacology 237 (11), 3283–3293. doi:10.1007/s00213-020-05610-z
Yao, L., Ruifang, S., Xiaoping, L., Lei, W., Hengying, C., Siwen, S., et al. (2022). Procyanidins and its metabolites by gut microbiome improves insulin resistance in gestational diabetes mellitus mice model via regulating NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 151, 113078. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113078
Yashpal, S. K., Lin, S., Ping, X., Fu You, L., and Sheldon, C. (2011). A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. Annu. Rev. Pathology-mechanisms Dis. 6, 395–423. doi:10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092150
Yau, J. W. Y., Rogers, S. L., Kawasaki, R., Lamoureux, E. L., Kowalski, J. W., Bek, T., et al. (2012). Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 35 (3), 556–564. doi:10.2337/dc11-1909
Yin, Q., Wang, L., Yu, H., Chen, D., Zhu, W., and Sun, C. (2021). Pharmacological effects of polyphenol phytochemicals on the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 716672. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.716672
Ying, T., Chunmiao, Y., Qinyu, Y., Qian, L., Jia, L., Xinya, X., et al. (2019). Procyanidin B2 activates PPARγ to induce M2 polarization in mouse macrophages. Front. Immunol. 10, 1895. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01895
Ying Yng, C., Paola, Q. R., Dirk, M. H., Steven, A. F., Calvert, C. C., David, A. M., et al. (2014). Phenolic metabolites and substantial microbiome changes in pig feces by ingesting grape seed proanthocyanidins. Food and Funct. doi:10.1039/c4fo00325j
Yiqi, Y., Yixuan, L., Minqi, W., Kai, Y., Qishan, W., Pei, M., et al. (2022). Targeting ferroptosis suppresses osteocyte glucolipotoxicity and alleviates diabetic osteoporosis. Bone Res. 10, 26. doi:10.1038/s41413-022-00198-w
Yoko, Y., Masaru, O., Mitsutaka, N., and Hitoshi, A. (2019). Cacao liquor procyanidins prevent postprandial hyperglycaemia by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 activity and AMP-activated protein kinase in mice. J. Nutr. Sci. 8, e2. doi:10.1017/jns.2018.28
Yu, F., Li, B.-y., Li, X.-l., Cai, Q., Zhang, Z., Cheng, M., et al. (2012). Proteomic analysis of aorta and protective effects of grape seed procyanidin B2 in db/db mice reveal a critical role of milk fat globule epidermal growth factor-8 in diabetic arterial damage. PloS One 7 (12), e52541. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052541
Yuan, H., Hideki, H., and Gabriel, N. (2016). Mechanism and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 41, 1012–1021. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2016.09.002
Yuan, T., Yang, T., Chen, H., Fu, D., Hu, Y., Wang, J., et al. (2019). New insights into oxidative stress and inflammation during diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis. Redox Biol. 20, 247–260. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2018.09.025
Yue, W., Chi, L., Yuxu, N., Jiamin, X., Liwen, F., Yun, W., et al. (2021). Procyanidins mediates antineoplastic effects against non-small cell lung cancer via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Transl. cancer Res. 10, 2023–2035. doi:10.21037/tcr-20-3018
Yuta, K., Yuki, S., Seiya, I., Minoru, S., Masahito, T., Chiaki, I., et al. (2013). Black soybean seed coat extract ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity via the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in diabetic mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61, 5558–5564. doi:10.1021/jf401190y
Zhang, H., Sheng-Chiang, S., Xiaoxi, Y., and Li, Y. (2017). Dietary epigallocatechin 3-gallate supplement improves maternal and neonatal treatment outcome of gestational diabetes mellitus: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. J. Hum. Nutr. Dietetics 30, 753–758. doi:10.1111/jhn.12470
Zhang, H. J., Baoping, J., Chen, G., Feng, Z., Yangchao, L., Han-Qing, Y., et al. (2009). A combination of grape seed-derived procyanidins and gypenosides alleviates insulin resistance in mice and HepG2 cells. J. Food Sci. 74, H1–H7. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00976.x
Zhang, Z., Li, B.-Y., Li, X.-L., Cheng, M., Yu, F., Lu, W.-d., et al. (2013). Proteomic analysis of kidney and protective effects of grape seed procyanidin B2 in db/db mice indicate MFG-E8 as a key molecule in the development of diabetic nephropathy. Biochimica Biophysica Acta 1832 (6), 805–816. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.02.022
Zhao, T., Liu, D., Liu, Y., Deng, J., and Yang, H. (2024). Comparisons of procyanidins with different low polymerization degrees on prevention of lipid metabolism in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Food Res. Int. Ott. Ont. 188, 114508. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114508
Zhaoxia, W., Siyao, S., Jiaqian, J., Tan, D., Donghua, J., Bing, B., et al. (2014). Protective effects of grape seed extract fractions with different degrees of polymerisation on blood glucose, lipids and hepatic oxidative stress in diabetic rats. Nat. Prod. Res. 29, 988–992. doi:10.1080/14786419.2014.965165
Zhimei, L., Ning, L., Yaping, J., Jiamei, Y., Jie, Z., Miao, S., et al. (2019). Vitexin alleviates streptozotocin-induced sexual dysfunction and fertility impairments in male mice via modulating the hypothalamus–pituitary–gonadal axis. Chemico-Biological Interact. 297, 119–129. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2018.10.013
Zhiwei, Z., Xiaowei, Z., Lei, M., Mengqi, G., Jian, L., Wen, S., et al. (2021). Pioglitazone inhibits diabetes-induced atrial mitochondrial oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial biogenesis, dynamics, and function through the PPAR-γ/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 658362. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.658362
Zhou, Y., Li, B.-Y., Li, X.-L., Wang, Y.-J., Zhang, Z., Pei, F., et al. (2016). Restoration of mimecan expression by grape seed procyanidin B2 through regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB in mice with diabetic nephropathy. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 10 (5), 325–331.
Zou, W., Lu, Q., Zhu, X., Pan, Y., Xu, Q., and Wang, K. (2023). Procyanidin B2 protects TR-iBRB2 cells against hyperglyc emia stress by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammasome activation via regulation of redoxosomes/NF-kB signaling. Curr. Mol. Med. 23 (10), 1095–1103. doi:10.2174/1566524023666221017120334
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, procyanidins, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, insulin sensitivity
Citation: Zhang Y, Li M, Liu H, Fan Y and Liu HH (2025) The application of procyanidins in diabetes and its complications: a review of preclinical studies. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1532246. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532246
Received: 21 November 2024; Accepted: 14 January 2025;
Published: 10 February 2025.
Edited by:
Ramith Ramu, JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research, IndiaReviewed by:
Jin-Long Tian, Shenyang Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Li, Liu, Fan and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongfu Fan, ZnlmODAzMUAxNjMuY29t; Huan Huan Liu, MTU2Mzg5NDM3NTNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.