
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 20 March 2025
Sec. Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1417603
This article is a correction to:
Astragalus–Scorpion Drug Pair Inhibits the Development of Prostate Cancer by Regulating GDPD4-2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and Autophagy
A Corrigendum on
Astragalus–scorpion drug pair inhibits the development of prostate cancer by regulating GDPD4-2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and autophagy
by You X, Wu Y, Li Q, Sheng W, Zhou Q and Fu W (2022). Front. Pharmacol. 13:895696. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.895696
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 4 as published. The original description has ambiguity, which may cause readers to misunderstand. The corrected legend appears below.
FIGURE 4 | In PCa tissues and LNCaP cells, GDPD4-2 expression was decreased compared to non-tumorigenic prostate epithelial cells but increased following treatment with the herb pair Astragalus IV and PESV. (A) Volcano plot showed the lncRNA expression. (B) The differential lncRNA expression in RWPE-1 and LNCaP cells, *p < 0.05 vs. RWPE-1 group. (C) The differential lncRNA expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR in LNCaP cells after treatment with Astragaloside IV-PESV. *p < 0.05 vs. control group, #p < 0.05 vs. Astragaloside IV group, &p < 0.05 vs. PESV group.
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 5 as published. The original description was not consistent with its results. The corrected legend appears below.
FIGURE 5 | Astragaloside IV- PESV regulates PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling via GDPD4-2. (A) The expression level of GDPD4-2. (B) LC3 and DAPI immunofluorescence staining were performed to detect autophagy. (C) The LC3, Beclin1, and P62 expression were determined by Western blot. (D) The protein expression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. (E) Cell activity was determined by the CCK8 assay. *p < 0.05 vs. NC group, #p < 0.05 vs. sh-GDPD4-2 group, &p < 0.05 vs. Astragaloside IV-PESV group.
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3 as published. The WB blot image of p-PI3K was mistakenly added in place of p-AKT and PI3K. The corrected Figure 3 and its caption appear below.
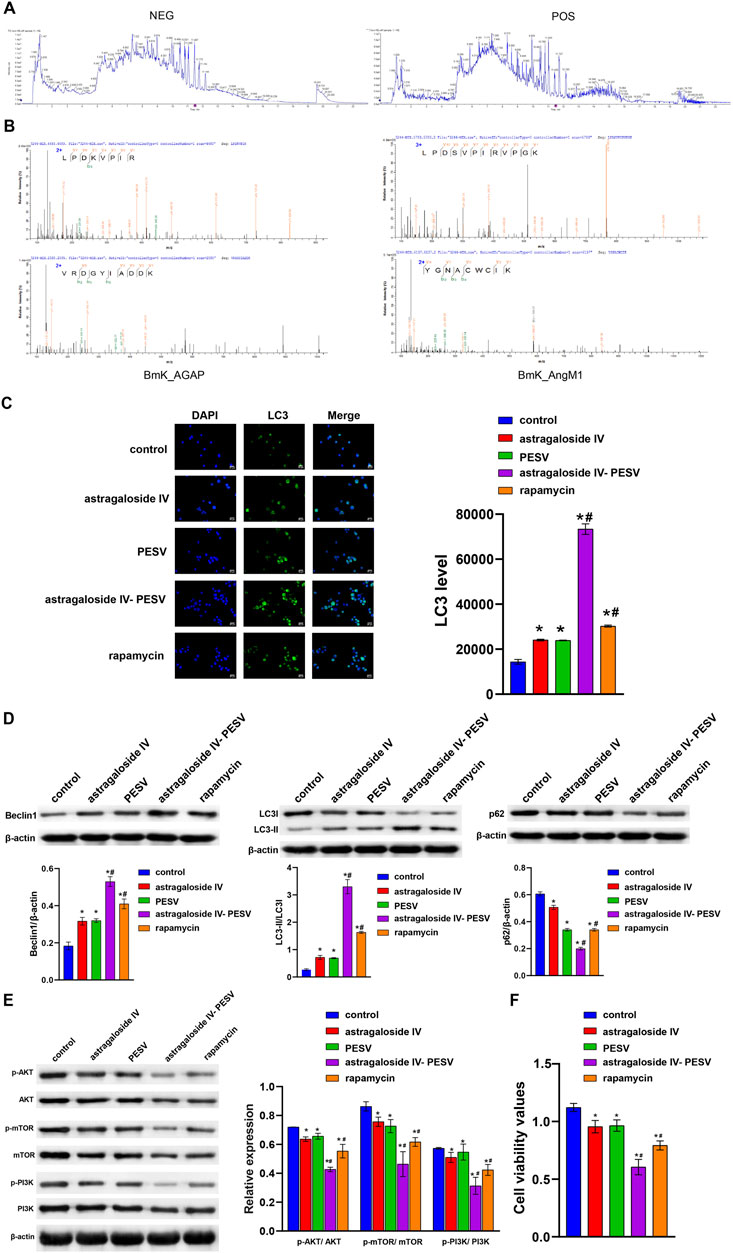
Figure 3. The main bio-active components in the herb pair A–S suppressed LNCaP cell proliferation and migration through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. (A) LC–MS/MS chromatogram of the bio-active components in Astragalus. (B) The LC-MS/MS analysis of PESV in scorpion. (C) LC3 and DAPI immunofluorescence staining were performed to detect autophagy. (D) The LC3, Beclin1, and P62 expression were determined by Western blot. (E) The protein expression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. (F) Cell activity was determined by the CCK8 assay. *p < 0.05 vs. control group, #p < 0.05 vs. Astragaloside IV or PESV groups.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Astragalus–Scorpio, prostate cancer, PI3K/AKT, Astragaloside IV, polypeptide extract from scorpion venom, autophagy
Citation: You X, Wu Y, Li Q, Sheng W, Zhou Q and Fu W (2025) Corrigendum: Astragalus–Scorpion drug pair inhibits the development of prostate cancer by regulating GDPD4-2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1417603. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1417603
Received: 15 April 2024; Accepted: 05 March 2025;
Published: 20 March 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Olivier Feron, Université catholique de Louvain, BelgiumCopyright © 2025 You, Wu, Li, Sheng, Zhou and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qing Zhou, MzEwMDk0QGhudWNtLmVkdS5jbg==; Wei Fu, NTk4MzU2MDAxQHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.