
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol. , 24 December 2024
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1510380
This article is part of the Research Topic Natural Products and Immune Inflammation: Mechanistic Understanding Based on Systems Biology View all 20 articles
Background: By far, one of the best treatments for myocardial ischemia is reperfusion therapy. The primary liposoluble component of Danshen, a traditional Chinese herbal remedy, Tanshinone ⅡA, has been shown to have cardiac healing properties. The purpose of this work is to investigate the processes by which Tanshinone ⅡA influences myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) in the H9C2 cardiac myoblast cell line, as well as the association between Tanshinone ⅡA and MIRI.
Methods and results: The cardiac cells were divided into a normal group, a model group and Tanshinone ⅡA treatment groups. After 4 h of culture with the deprivation of oxygen and glucose, the cells were incubated normally for 2 h. The success of the model and the capacity of Tanshinone ⅡA to heal cardiac damage were validated by the outcomes of cell viability, morphology, and proliferation. The efficacy of Tanshinone ⅡA in treating MIRI was further confirmed by the scratch assay and biomarker measurement. The differentially expressed genes were examined using transcriptome sequencing. The Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM)/Growth Arrest and DNA Damage (GADD45)/Origin Recognition Complex (ORC) signaling pathway was identified as being crucial to this process by KEGG pathway analysis and GO enrichment. Molecular docking and RT-qPCR were used to confirm our results. The crucial function of the ATM/GADD45/ORC pathway was further confirmed by the addition of an ATM inhibitor, which inhibited the expression of ATM.
Conclusion: Tanshinone ⅡA can relieve the myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in cardiac cells by activating the ATM/GADD45/ORC pathway.
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is an ischaemic heart disease caused by myocardial ischaemia and necrosis due to acute coronary artery congestion. It has become one of the greatest causes of mortality worldwide. Reperfusion, one of the most effective treatments for AMI, can help patients restore their coronary artery blood flow. However, increasing evidence shows that reperfusion treatment can cause myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI). MIRI has a complex pathomechanism involving metabolic disorders (Salameh et al., 2020), mitochondrial dysfunction (Tian et al., 2023), inflammation (Salameh et al., 2020; Tian et al., 2023), autophagy disorders and the release of high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) caused by oxidative stress (Yu et al., 2006). These injuries lead to myocardial damage and then aggravate heart failure or even lead to sudden cardiac death.
Among them, the excess ROS can attack DNA directly, causing base oxidation, glycation damage and DNA strand breaks. Massive release of inflammatory factors not only can increase oxidative stress but promote the expression of genes related to DNA damage. Furthermore, metabolic disorders can lead to a plunge in intracellular ATP levels, affecting the activity of DNA repair enzymes, exacerbating the consequences of DNA damage.
The ATM signaling pathway is a crucial signal transduction pathway that cells utilize to respond to DNA damage, particularly DNA double-strand breaks. Studies have shown that ATM activation can lead to Murine Double Minute 2 (MDM2) E3 phosphorylation and activity inhibition, which causes rapid accumulation of p53 (Chen, 2012). P53 activation can inhibit cell cycle progression (Chen, 2016). The cells arrest in the G2/M phase, and checkpoints are activated (St Clair et al., 2004). This arrest helps repair DNA damage, especially fatal double-strand breaks (Gatz and Wiesmüller, 2006).
Danshen is a traditional Chinese herb derived from the root and rhizome of Salvia miltiorrhiza, a Labiatae plant (Yuan et al., 2024). It promotes blood circulation to prevent blood stasis (Yuan et al., 2024; Cao et al., 2017). Danshen is frequently utilized in the clinical management of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular conditions (Qin et al., 2023). It can effectively relieve the clinical symptoms of ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and reduce complications and sequelae.
Tanshinone ⅡA, the main liposoluble constituent of Danshen (Yang et al., 2020), has garnered widespread attention for its efficacy in treating AMI. Studies have shown that Tanshinone ⅡA possesses significant anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic effects in cardiovascular protection. Ren et al. (2010) found that Tanshinone IIA effectively suppresses the release of inflammatory factors following myocardial infarction by reducing the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), thereby decreasing the infiltration of inflammatory cells. This anti-inflammatory property is also crucial in the treatment of MIRI, as post-reperfusion inflammation often leads to secondary myocardial damage.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, Tanshinone IIA demonstrates robust antioxidant potential. In AMI models, Tanshinone IIA enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and reduces the production of oxidative stress marker malondialdehyde (MDA), thereby alleviating oxidative stress-induced myocardial damage (Chen et al., 2021). During MIRI, the sudden increase in ROS directly damages myocardial cells activates inflammatory signaling pathways, such as the NF-κB pathway, promoting the release of inflammatory factors (Hu et al., 2015). Therefore, Tanshinone IIA may effectively interrupt the vicious cycle of MIRI injury by inhibiting both oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling pathways.
Myocardial fibrosis is a core manifestation of myocardial remodelling after AMI and MIRI and is a primary pathological mechanism leading to heart failure. During fibrosis, myocardial tissue gradually hardens due to the deposition of type I and III collagen, which impairs normal cardiac function. Gao et al. (2019) indicated that TIIA also has significant anti-fibrotic effects, inhibiting myocardial fibrosis by reducing the expression of TGF-β and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). This effect has potential application value in MIRI models, helping to prevent the progression of myocardial fibrosis and protecting cardiac function after myocardial infarction.
Previous studies have sufficiently demonstrated the therapeutic effects of Tanshinone IIA on AMI and MIRI. Therefore, we aim to investigate the regulatory role of Tanshinone on the ATM signaling pathway from the perspective of DNA damage, as well as the therapeutic mechanism in H9C2 cell ischemia-reperfusion injury. It provides experimental evidence supporting the usage of Tanshinone IIA in the prevention and treatment of ischemic cardiovascular diseases.
The rat-myocardium-derived cardiac myoblast cell line H9C2 was purchased from the Union Medical University Cell Experiment Center (lot No. SCSP-5211).
Tanshinone ⅡA was purchased from the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control (lot No. WVH2-4LD1).
The rat cardiomyocytes, H9C2 cell line was cultivated in high-glucose DMEM (Gibco™, lot No. 8122512) supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS (Invitrogen™, lot No. 10099-141). The culture was then incubated at 37°C with 5% CO2. Several groups were created out of these cells: normal group, model group and Tanshinone ⅡA treatment groups.
For the normal group, the cells were cultured and incubated as normal. For the model group, the cells were first treated as described for the normal group. PBS was used to wash the cells once the density reached 80%. The glucose-free DMEM (Gibco™, lot No.2323012) without serum was introduced. For 4 h, the cells were incubated at 37°C with 85% N2, 10% H2, and 5% CO2. Then, the medium was replaced with high-glucose DMEM, and the cells were incubated with 5% CO2 at 37°C for 2 h.
For the treatment groups, the cells were treated as the model group. Different doses of Tanshinone ⅡA were added to the serum and glucose-free DMEM to final concentrations of 1, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160, 320, and 640 μmol/L.
For the inhibitor group, the ATM kinase inhibitor KU-55933 (Selleck, lot No. S1092) was added to the serum and glucose-free media together with Tanshinone ⅡA to a final concentration of 10 μmol/L.
Approximately 10⁴ cells were added to each well of a 96-well plate. After they reached 80%–90% confluence, the cells were cultured as described in Section 2.2. Each well received 10 μL of CCK-8 solution (DOJINDO, lot No. TR689), and the plate was incubated for an hour with 5% CO2 at 37°C. The absorbance was measured following incubation at a wavelength of 450 nm.
The morphology of the cultivated cells was observed using an inverted microscope (Olympus Corporation, TH4-200).
In a 6-well plate, about 2 × 10⁵ cells were put into each well. Following the outline described in Section 2.2, the cells were grown until they reached 80%–90% confluence. Culture media was used to dilute the EdU. The medium was supplemented with prewarmed EdU solution until the final concentration of EdU was 10 μmol/L. The cells underwent incubation in a CO2 environment at a temperature of 37°C for 2 h. Subsequently, the medium was substituted with a stationary medium, and the cells were cultured at room temperature for 15 min. Subsequently, the cells underwent a gentle wash with PBS, followed by the addition of 0.3% Triton X-100 to the cell suspension. The cells were cultivated for 10 min at room temperature, followed by a PBS wash and a further 20 min at room temperature with the blocking solution. Following washing, the cells were grown for 30 min at room temperature in the dark with 500 μL of Click solution added. Following a PBS wash, the cells were incubated for an additional 30 min at room temperature using 200 μL of streptavidin-HRP working solution. 200 μL of DAB colouring solution was applied after washing. After 10 min of RT culture, the cells were cleaned with PBS. DAPI was employed as the counterstain. A fluorescence microscope was used to observe and record the data. ImageJ was used to analyse the results.
The 6-well plate was filled with about 10⁵ H9C2 cells per well, and the cells were cultivated until they achieved 80%–90% confluence. The cells were subsequently incubated as described in Section 2.2. A vertical line scratch was made in the centre of each well using a sterile 200 μL pipette tip. The wells were washed gently with PBS to remove detached cells and debris. Images of the scratches were captured with an inverted microscope. The cells were subsequently incubated with serum-free medium in 5% CO2 at 37°C. Images were captured every 12 h. ImageJ was used to analyse these images.
The cellular supernatant was isolated to measure the levels of Aspartate transaminase (AST), Creatine kinase (CK) and Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) via ELISA (Jianglai, lot No. JL21297-96T, JL46377-96T, JL46377-96T). The cells were subsequently centrifuged at 2,500 rpm and 4°C for 10 min, after which the supernatant was collected according to the kit instructions.
The cells underwent a washing procedure using pre-cold PBS, followed by total RNA extraction utilizing TRIzol. Oligo (dT) Dynabeads were employed for the isolation of mRNA. A reverse transcription kit was employed to synthesize the first-strand cDNA. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) was subsequently used for cDNA amplification and cDNA library establishment. The Illumina sequencing platform was used to perform second-generation double-terminal sequencing.
TRIzol was employed to extract the total RNA from the cells. The extracted RNA was utilized for the synthesis of cDNA through the process of reverse transcription. Then, the PCR solution system was prepared, split into microcentrifuge tube and amplified in a real-time quantitative PCR instrument.
The PCR solution system employed consisted of the following components: Hieff qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix (10 μL), forward primer (0.4 μL), reverse primer (0.4 μL), cDNA (2 μL), and ddH2O (7.2 μL). The sequences of the forward primer and reverse primer are presented in Table 1. GAPDH served as the reference gene. The 2−ΔΔCT method was employed to determine the relative expression levels of mRNAs.
The reaction conditions were established as follows: an initial denaturation phase at 95°C for a duration of 10 min, followed by denaturation at 95°C for 10 s, and an annealing phase at 60°C for 30 s. Denaturation and annealing were regarded as one cycle. Forty cycles were performed in this reaction.
The three-dimensional structural files of the target proteins were acquired from the Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org/) and UniProt (https://www.uniprot.org/) databases. The molecular structures of the ligands were obtained from the PubChem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Coordinate files for the receptor and ligand were generated utilizing AutoDock Tools software. The receptor underwent the removal of water molecules, followed by the separation of the ligand from the receptor. Following the incorporation of nonpolar hydrogens, molecular docking was performed (Cao et al., 2023).
The cells were harvested and subjected to lysis with a suitable lysis buffer that included protease inhibitors, followed by the assessment of protein concentration utilizing a BCA kit. Equal volumes of protein were combined with loading buffer, subjected to boiling at 95°C for 5 min, subsequently loaded into 8% SDS-PAGE gels, and then electrophoresed to achieve separation of proteins according to their molecular weight. The proteins were subsequently transferred onto a PVDF membrane utilizing wet transfer techniques. The membrane underwent a blocking procedure using a blocking buffer composed of 5% non-fat milk in TBST for a duration of 90 min at room temperature, aimed at minimizing non-specific binding. The samples were incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies targeting ATM, GADD45, ORC, and β-actin (Cell Signalling, 2,873, 4,632, 4,731, 4,967), which served as the internal control, all diluted in blocking buffer at the concentration of 0.5 μL/mL. Following the washing procedure, the membrane underwent incubation with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies, which were diluted in blocking buffer for 1 h at room temperature. The membrane underwent a subsequent washing, followed by the application of enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) substrate, and the detection of protein bands was accomplished utilizing a chemiluminescence imaging system. The analysis of band intensities was conducted utilizing ImageJ for quantification.
For data analysis, GraphPad Prism 10.1.2 was utilised. The results were presented as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± sd). One-way ANOVA was employed to examine the differences between the two groups. When p < 0.05, the differences were considered statistically significant.
Cells in Tanshinone ⅡA treatment groups were treated as shown in Figure 1A. The model group exhibited a significant reduction in cell viability when compared to the normal group (p < 0.01). In contrast, the treatment groups receiving Tanshinone IIA exhibited a notable increase in cell viability at concentrations of 10 and 20 μmol/L (p < 0.01) and 40 μmol/L (p < 0.05) in comparison to the model group (Figure 1B).
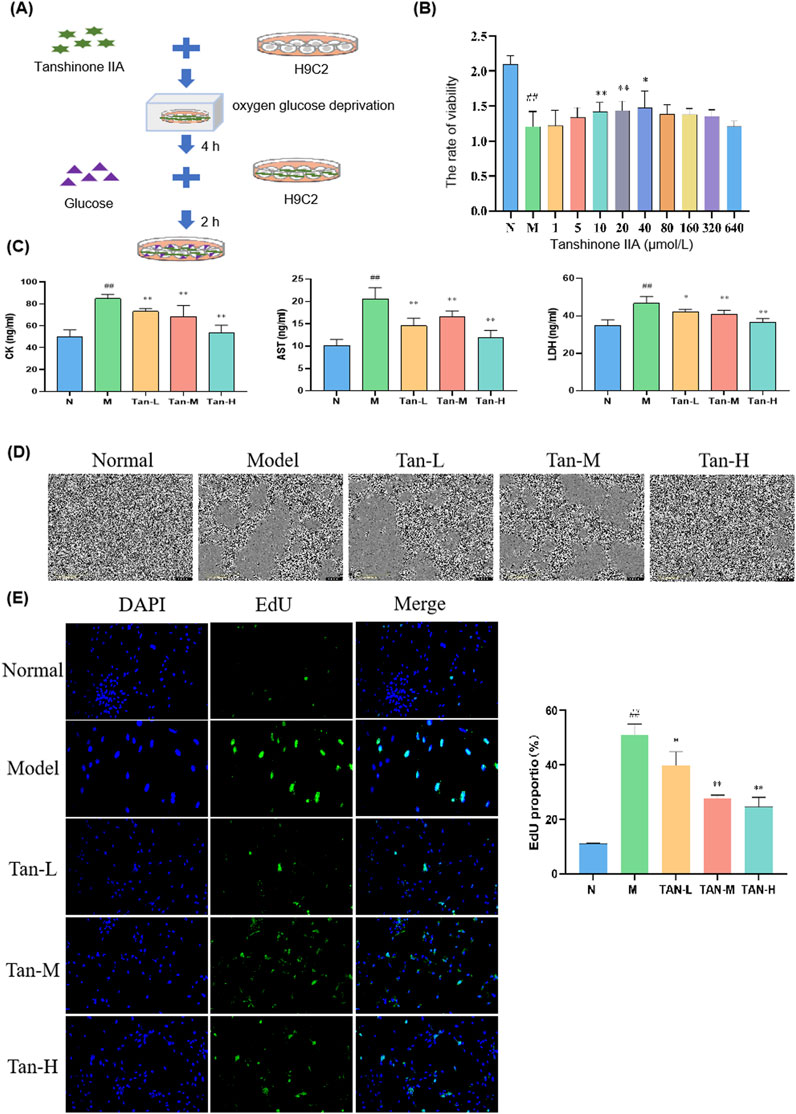
Figure 1. Effect of Tanshinone ⅡA on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in the H9C2. Notes: (A) Cell culture and treatment; (B) viability rate of H9C2; (C) changes in the level of CK, AST and LDH in H9C2; (D) morphology of H9C2 cells; (E) fluorescence staining of H9C2 cells. ##p < 0.01 vs. the normal group, *p < 0.05 vs. the model group, **p < 0.01 vs. the model group (n = 6, Mean ± sd).
Based on these cell viability results, concentrations of 10, 20, and 40 μmol/L were selected for further experiments. Figure 1C illustrates that the levels of CK, AST, and LDH were markedly elevated in the model group compared to the normal group (p < 0.01). In comparison to the model group, the levels of CK and AST were markedly reduced in the Tan-L (10 μmol/L), Tan-M (20 μmol/L), and Tan-H (40 μmol/L) groups (p < 0.01). Comparably, the levels of LDH exhibited a significant decrease in the Tan-L group (p < 0.05), Tan-M group (p < 0.01), and Tan-H group (p < 0.01) when contrasted with the model group.
Figure 1D shows that cells in the normal group were neatly arranged with regular shapes and small intercellular spaces. In contrast, cells in the model group varied in size, were loosely arranged with large intercellular spaces, and exhibited numerous pieces of cell debris. The Tan-L and Tan-M groups displayed more closely arranged cells with relatively regular shapes, though some irregular areas remained. Cells in the Tan-H group were tightly arranged with regular shapes and showed only mild signs of damage.
According to the DAPI and EdU staining results presented in Figure 1E, Tanshinone IIA treatment effectively alleviated the decrease in cell viability and abnormal proliferation caused by the model.
As indicated in Table 2, the relative wound density in the model group was significantly lower than that of the normal group (p < 0.01). Compared to the model group, the relative wound density significantly decreased at 60 h in both the medium-dose and high-dose Tanshinone IIA treatment groups (p < 0.01).
A correlation heatmap (Figure 2A) was used to visualize gene correlations between the groups. It revealed that all Pearson coefficients were greater than 0.9, indicative of strong positive correlations.
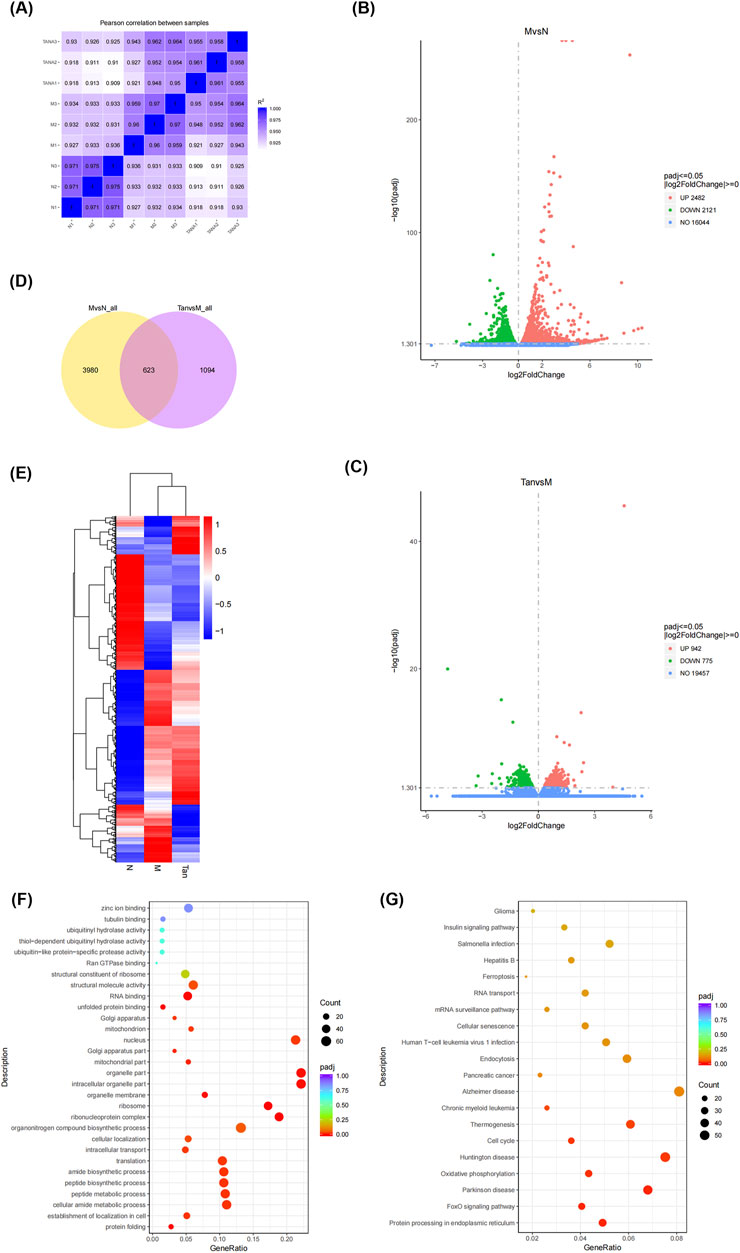
Figure 2. Gene differential expression analysis. Notes: (A) Gene correlation analysis between groups; (B) volcano plot of differentially expressed genes in the model group and normal group; (C) volcano plot of differentially expressed genes in the Tanshinone ⅡA treatment group and model group; (D) venn diagram of differentially expressed genes in the groups; (E) clustering heatmap of differentially expressed genes; (F) GO enrichment analysis; (G) KEGG pathway analysis.
The gene with a p-value threshold of less than 0.05 and a log2(FC) threshold less than or more than 0 was identified as a differentially expressed gene. Differentially expressed genes are illustrated in volcano plots (Figures 2B, C). In comparison to the control group, the experimental group demonstrated 4,603 differentially expressed genes, comprising 2,482 genes that were upregulated and 2,121 genes that were downregulated (Figure 2B). In the analysis of the Tanshinone IIA treatment group versus the model group, a total of 1,717 differentially expressed genes were identified, comprising 942 that were upregulated and 775 that were downregulated (Figure 2C).
A Venn diagram (Figure 2D) visualizes the distribution and overlap of the differentially expressed genes. Of the 4,603 genes differentially expressed between the normal and model groups and the 1,717 genes between the model and Tanshinone IIA treatment groups, 623 genes were commonly differentially expressed.
As shown in Figure 2F, the differentially expressed genes were enriched in Gene Ontology categories encompassing biological processes (BP), cellular components (CC), and molecular functions (MF). The main biological processes involved protein folding, peptide synthesis, and translation. The cellular components primarily included the ribosome, mitochondrial parts, and nucleus. Key molecular functions were unfolded protein binding, RNA binding, and structural molecule activity. The KEGG pathway analysis (Figure 2G) revealed that these genes were predominantly enriched in pathways associated with the cell cycle, Huntington’s disease, oxidative phosphorylation, Parkinson’s disease, the FoxO signaling pathway, and protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Based on the KEGG pathway analysis and literature review, the cell cycle has been identified as a key pathway through which Tanshinone IIA alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. As a result, the pathway genes in the cell cycle were imported into Cytoscpe. The core genes were screened using CytoHubba, and the top three genes, ATM,GADD45 and ORC, were selected for RT-qPCR analysis according to the Degree value. To verify the effectiveness of ATM/GADD45/ORC pathway (Figure 3A), follow-up experiments were conducted.
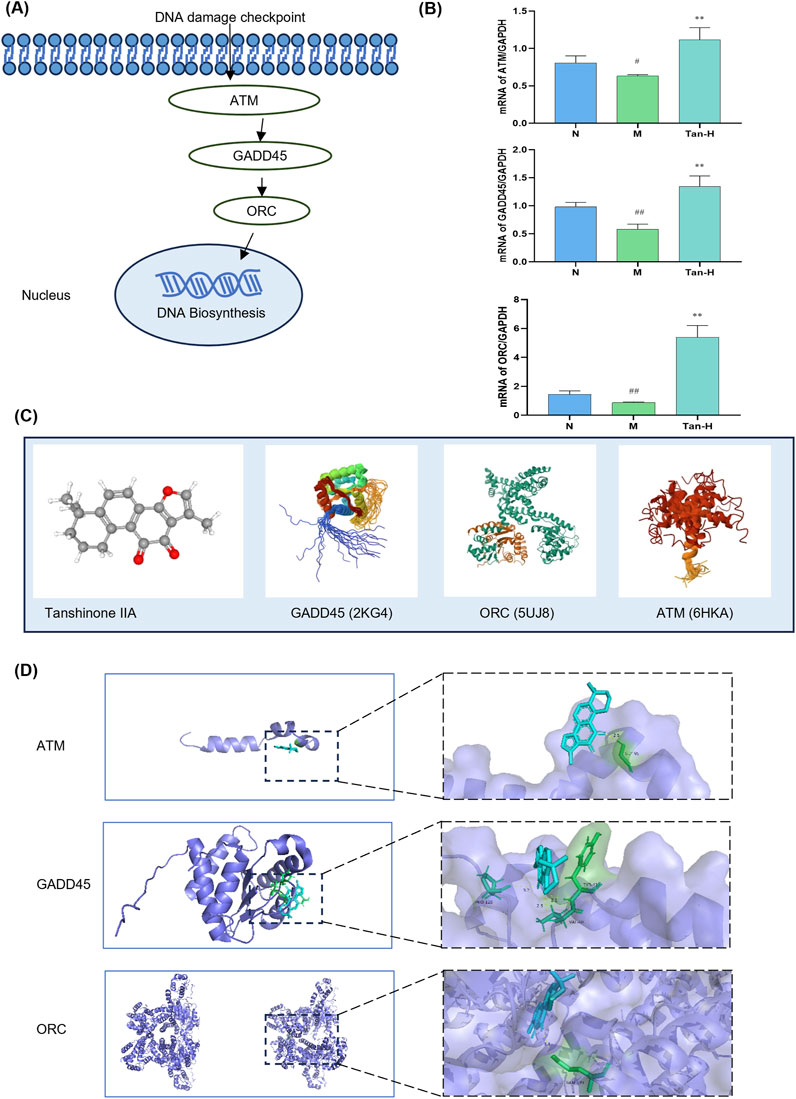
Figure 3. Pathway validation. Notes: (A) ATM/GADD45/ORC pathway; (B) mRNA expression of ATM, GADD45 and ORC in H9C2; (C) molecular structure of Tanshinone ⅡA and pathway-related proteins; (D) molecular docking image of Tanshinone ⅡA and pathway-related protein. #p < 0.05 vs. the normal group, ##p < 0.01 vs. the normal group, **p < 0.01 vs. the model group (n = 6, mean ± sd).
Figure 3B illustrates that the model group exhibited a notable reduction in ATM expression relative to the normal group (p < 0.05), alongside significant decreases in GADD45 and ORC expressions (p < 0.01). Moreover, the Tan-H group demonstrated significantly reduced expression levels of ATM, GADD45, and ORC compared to the model group (p < 0.01).
Figure 3C presents the molecular structure of Tanshinone IIA alongside the 3D structures of GADD45, ORC, and ATM. The docking results in Figure 3D indicate that Tanshinone IIA can interact with GADD45, ORC, and ATM. Specifically, it binds to ATM and ORC via hydrogen bonds with GLY-95 and GLN-399, respectively, and forms three hydrogen bonds with GADD45 involving VAL-40, TYR-41, and PRO-120.
To further validate the involvement of the ATM/GADD45/ORC pathway, the ATM inhibitor KU-55933 was introduced into the model system (Figure 4A).
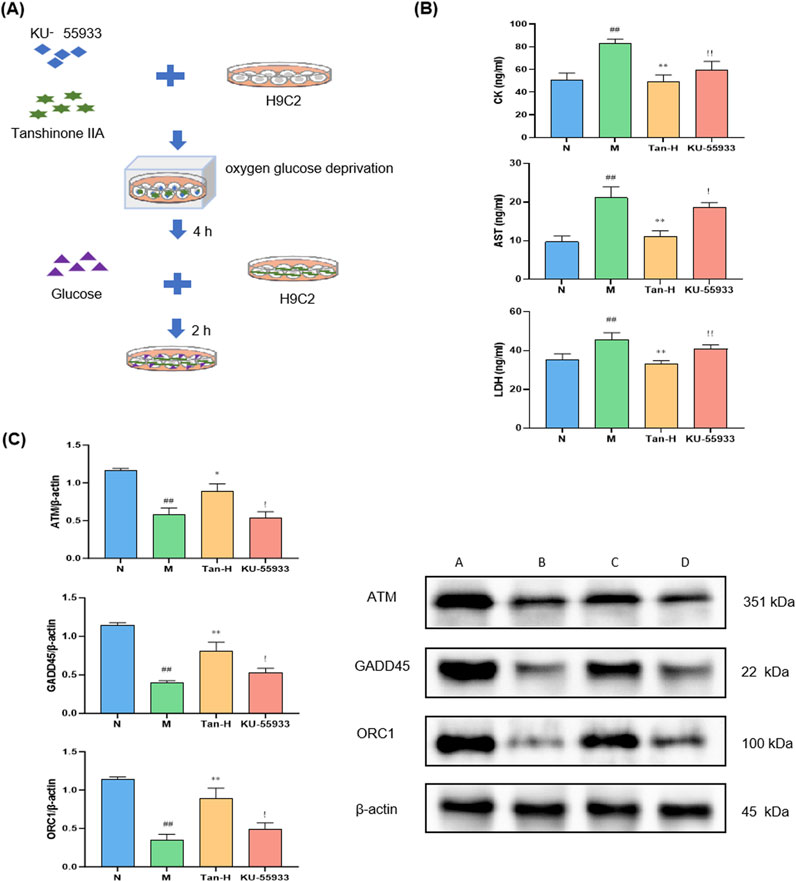
Figure 4. Pathway validation through ATM inhibitor. Notes: (A) Cell culture and treatment; (B) changes in the level of CK, AST and LDH in H9C2; (C) expression of ATM, GADD45 and ORC in H9C2. #p < 0.05 vs. the normal group, ##p < 0.01 vs. the normal group; *p < 0.05 vs. the model group, **p < 0.01 vs. the model group; !p < 0.05 vs. the Tanshinone ⅡA treatment group, !!p < 0.01 vs. the Tanshinone ⅡA treatment group (n = 6, mean ± sd).
Figure 4B illustrates that the model group demonstrated markedly elevated levels of CK, AST, and LDH in comparison to the normal group (p < 0.01). Conversely, the Tan-H group exhibited markedly lower levels of these enzymes in comparison to the model group (p < 0.01). In comparison to the Tan-H group, the inhibitor group exhibited a statistically significant elevation in CK levels (p < 0.05) and notably higher concentrations of AST and LDH (p < 0.01).
Figure 4C demonstrates that the model group exhibited markedly reduced expression levels of ATM, GADD45, and ORC1 in comparison to the normal group (p < 0.05). The Tan-H group demonstrated a notable enhancement in the expression of these genes in comparison to the model group (p < 0.05). Nonetheless, the inhibitor group exhibited markedly lower expression levels of ATM, GADD45, and ORC1 in comparison to the Tan-H group (p < 0.05).
Acute myocardial infarction is a global ischemic cardiovascular disease with high mortality and morbidity (Li et al., 2023). As of 2020, approximately 1.72% of the global population was plagued with AMI (Khan et al., 2020). Reperfusion therapy is an effective treatment for ischemic diseases. However, ischemia-reperfusion injury after reperfusion is also fatal (Verma et al., 2002). As a result, prevention and treatment of MIRI have become a key procedure during AMI treatment. It always causes myocardial necrosis, endothelial dysfunction, inflammation and oxidative stress (Yao et al., 2023).
Pharmacological studies have shown that Danshen promotes coronary artery expansion, improves myocardial ischemia and repairs myocardial damage. It can also increase the hypoxia tolerance of myocardial cells, thereby protecting the anoxic myocardium (Feng et al., 2022). The effective constituent Tanshinone ⅡA has the effects of heart protection, coronary dilation, anti-atherosclerosis, anti-platelet, anticoagulant, anti-thrombosis and inhibition of myocardial hypertrophy (Cao et al., 2017; Feng et al., 2022).
According to the previous research, Tanshinone ⅡA has a great therapeutic effect to MIRI. Hu et al. used rat cardiomyocytes, H9C2, to establish MIRI cell model (Hu et al., 2023) and found that Tanshinone ⅡA effectively attenuated H9c2 cardiomyocyte damage through inhibiting ferroptosis in the MIRI injury model. Li et al. used SD rats to establish MIRI rat model (Li et al., 2016) and found that Tanshinone IIA could activate the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to relieve MIRI in rats. Pan et al. used C57BL/6 mice to establish MIRI mouse model (Zhai et al., 2024) and found that Tanshinone IIA contributed to the improvement of the area of myocardial infarction, reducing myocardial enzyme levels, and promoting myocardial contractility recovery. Liu et al. used Japanese white rabbits to establish MIRI rabbit model (Liu et al., 2017) and found that Tanshinone IIA can significantly enhance the secretion of VEGF and the activity of oxygen free radical scavenging enzymes, accelerate the neovascularization of vascular endothelium in ischemic myocardium, promote angiogenesis, inhibit lipid peroxidation reactions during MIRI and alleviate the inflammatory response of myocardial vascular endothelium. Thus, it improves the function of damaged vascular endothelium after I/R injury and has a definite protective effect on acute MIRI in rabbits. Researchers have used various cells and experimental animals to establish different models of MIRI, and all have shown that Tanshinone IIA has a preventive and therapeutic effect on MIRI. It is considered that the effect of Tanshinone IIA to this disease model has been proved and there is no need to add a positive drug to certify its therapeutic effect. Besides, the mechanisms of commonly used positive drugs in ischemic cardiovascular disease are not accordant with the mechanism studied in the research. As a result, the positive control was not mentioned in the whole study.
In this study, the myoblast cell line H9C2 was deprived of oxygen and glucose to establish an MIRI model in vitro. Tanshinone ⅡA was added at the same time to simulate MIRI. In terms of cell viability, morphology and migration, significant differences were detected between the normal group and the model group, indicating the success of the cell model. A statistically significant difference existed between the model group and the Tanshinone ⅡA treatment groups. These findings suggest that Tanshinone ⅡA can reduce myocardial apoptosis caused by MIRI. In addition, the EdU staining results revealed that Tanshinone ⅡA treatment relieved the decrease in myocardial cell viability and abnormal proliferation caused by MIRI.
After modelling, cardiac biomarkers were measured to verify the effect of Tanshinone ⅡA on myocardial protection from MIRI. CK, AST and LDH are cardiac markers commonly used in the clinic. The expression levels can be used to quantify the extent of MIRI (Toldo et al., 2018). In this study, the levels of CK, AST and LDH decreased, and the cell viability increased significantly after treatment. These findings suggest that Tanshinone ⅡA may reduce inflammation, improve myocardial cell apoptosis and thereby protect against MIRI.
Then, transcriptomic sequencing was performed to analyse the differences in gene expression between the groups. According to the transcriptomic sequencing results, many genes exhibited differences among the groups. Many genes were enriched in the cell cycle pathway. ATM, GADD45 and ORC are key genes in the cell cycle pathway, and their transcriptomic sequencing results also differ greatly.
The RT‒qPCR results revealed that Tanshinone ⅡA can increase the mRNA expression of ATM, GADD45 and ORC in cardiomyocytes damaged by MIRI. On the basis of the gene differential analysis and RT‒qPCR results, we can speculate that Tanshinone ⅡA can repair DNA damage and promote DNA biosynthesis by stimulating key factors involved in the ATM/GADD45/ORC pathway (Figure 5). The molecular docking results revealed the combination of Tanshinone ⅡA with these three proteins, which may provide additional evidence supporting the above conjecture.
ATM, GADD45 and ORC are key proteins involved in ATM signaling pathway. ATM is a serine‒threonine protein kinase. It is the key factor in the DNA damage response. It can phosphorylate p53 and Chk2 (Li and Stern, 2005; Meulmeester et al., 2005). Therefore, the interaction between MDM2 and p53 is inhibited, which can increase p53 levels, inhibit the cell cycle, and trigger checkpoint and DNA repair activation (Kastan and Lim, 2000). P53 can bind with GADD45 in the promoter region and transcriptionally activate it (Kim et al., 2013). GADD45 is also a crucial protein in DNA repair. It can stimulate p38-JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), mediating the immune response (Rodríguez-Jiménez et al., 2021). GADD45 expression is related to ROS production and the activation of NADPH oxidase, which potentially promotes the counter-regulation of oxidative damage (Wan et al., 2000; De La Fuente et al., 2009). On the other hand, active Chk2 can amplify DNA damage signals (Li and Stern, 2005). Its key substrate, CDC25A, can activate CDK2 (Ditano et al., 2021), thereby activating ORC. The ORC is the origin of DNA replication and can regulate the cell cycle (Ohta et al., 2003). The increased expression of these three genes can improve DNA repair and new DNA biosynthesis. To verify the above findings, an ATM inhibitor was used for cell treatment. KU-55933 was used in cell culture together with Tanshinone ⅡA to inhibit the expression of ATM. The levels of CK, AST, and LDH in the cell supernatant of the inhibitor group were markedly elevated compared to those observed in the Tan-H group. Furthermore, the Western blot analysis demonstrated that Tanshinone ⅡA markedly enhanced the protein expression levels of ATM, GADD45, and ORC1 through ATM activating.
The experimental findings indicate that Tanshinone ⅡA mitigates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in cardiac cells. The mechanism could be linked to the activation of the ATM/GADD45/ORC pathway.
The data presented in the study are deposited in Zenodo, accession DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.14284052. It can be accessed through the URL: https://zenodo.org/records/14284052.
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
YS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JD: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. DZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. ZS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Cao, C., Qi, Y. T., Wang, A. A., Wang, Z. Y., Liu, Z. X., Meng, H. X., et al. (2023). Huoxin pill reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats via TLR4/NFκB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 29 (12), 1066–1076. doi:10.1007/s11655-023-3640-1
Cao, H., Wu, J., Jia, L., and Yang, G. (2017). Progress in study of tanshinone IIA'S pharmacological effects on cardiovascular system. World J. traditional Chin. Med. 12 (07), 1718–1722. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2017.07.059
Chen, J. (2012). The roles of MDM2 and MDMX phosphorylation in stress signaling to p53. Genes and Cancer 3 (3-4), 274–282. doi:10.1177/1947601912454733
Chen, J. (2016). The cell-cycle arrest and apoptotic functions of p53 in tumor initiation and progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 6 (3), a026104. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a026104
Chen, R., Chen, W., Huang, X., and Rui, Q. (2021). Tanshinone IIA attenuates heart failure via inhibiting oxidative stress in myocardial infarction rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 23 (6), 404. doi:10.3892/mmr.2021.12043
De La Fuente, H., Lamana, A., Mittelbrunn, M., Perez-Gala, S., Gonzalez, S., García-Diez, A., et al. (2009). Identification of genes responsive to solar simulated UV radiation in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 4 (8), e6735. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006735
Ditano, J. P., Sakurikar, N., and Eastman, A. (2021). Activation of CDC25A phosphatase is limited by CDK2/cyclin A-mediated feedback inhibition. Cell Cycle 20 (13), 1308–1319. doi:10.1080/15384101.2021.1938813
Feng, K., Li, W., Wang, X., Wu, Y., Zhang, H., Liu, X., et al. (2022). Chemical components and pharmacological action for Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and predictive analysis on quality markers. Chin. Traditional Herb. Drugs 53 (02), 609–618. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.02.031
Gao, S., Li, L., Li, L., Ni, J., Guo, R., Mao, J., et al. (2019). Effects of the combination of tanshinone IIA and puerarin on cardiac function and inflammatory response in myocardial ischemia mice. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 137, 59–70. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.09.012
Gatz, S. A., and Wiesmüller, L. (2006). p53 in recombination and repair. Cell Death Differ. 13 (6), 1003–1016. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401903
Hu, H., Zhai, C., Qian, G., Gu, A., Liu, J., Ying, F., et al. (2015). Protective effects of tanshinone IIA on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress, HMGB1 expression, and inflammatory reaction. Pharm. Biol. 53 (12), 1752–1758. doi:10.3109/13880209.2015.1005753
Hu, T., Zou, H. X., Le, S. Y., Wang, Y. R., Qiao, Y. M., Yuan, Y., et al. (2023). Tanshinone IIA confers protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and apoptosis via VDAC1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 52 (5), 109. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2023.5312
Kastan, M. B., and Lim, D. S. (2000). The many substrates and functions of ATM. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1 (3), 179–186. doi:10.1038/35043058
Khan, M. A., Hashim, M. J., Mustafa, H., Baniyas, M. Y., Al Suwaidi, S. K. B. M., AlKatheeri, R., et al. (2020). Global epidemiology of ischemic heart disease: results from the global burden of disease study. Cureus 12 (7), e9349. doi:10.7759/cureus.9349
Kim, Y.-A., Kim, M. Y., Yu, H. Y., Mishra, S. K., Lee, J. H., Choi, K. S., et al. (2013). Gadd45β is transcriptionally activated by p53 via p38α-mediated phosphorylation during myocardial ischemic injury. J. Mol. Med. 91 (11), 1303–1313. doi:10.1007/s00109-013-1070-9
Li, J., and Stern, D. F. (2005). DNA damage regulates Chk2 association with chromatin. J. Biol. Chem. 280 (45), 37948–37956. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509299200
Li, Q., Shen, L., Wang, Z., Jiang, H. P., and Liu, L. X. (2016). Tanshinone IIA protects against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed. and Pharmacother. = Biomedecine and Pharmacother. 84, 106–114. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.014
Li, X., Ou, W., Xie, M., Yang, J., Li, Q., and Li, T. (2023). Nanomedicine-based therapeutics for myocardial ischemic/reperfusion injury. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 12 (20), e2300161. doi:10.1002/adhm.202300161
Liu, J., Wu, S., Li, L., and Ao, J. (2017). Protective effect of danshen A sodium sulfonate injection on vascular endothelial injury after ischemic preconditioning in rabbits with myocardial ischemia preconditioning. WORLD Chin. Med. 12 (03), 618–622. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2017.03.036
Meulmeester, E., Pereg, Y., Shiloh, Y., and Jochemsen, A. G. (2005). ATM-mediated phosphorylations inhibit Mdmx/Mdm2 stabilization by HAUSP in favor of p53 activation. Cell CycleGeorget. Tex. 4 (9), 1166–1170. doi:10.4161/cc.4.9.1981
Ohta, S., Tatsumi, Y., Fujita, M., Tsurimoto, T., and Obuse, C. (2003). The ORC1 cycle in human cells: II. Dynamic changes in the human ORC complex during the cell cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 278 (42), 41535–41540. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307535200
Qin, W., Xu, J., Yang, T., and Wang, P. (2023). Research progress of tanshinone IIA signaling pathway in the treatment of nerve injury after ischemic stroke. Chin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 28 (06), 705–713. doi:10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2023.06.014
Ren, Z. H., Tong, Y. H., Xu, W., Ma, J., and Chen, Y. (2010). Tanshinone II A attenuates inflammatory responses of rats with myocardial infarction by reducing MCP-1 expression. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytotherapy Phytopharm. 17 (3-4), 212–218. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2009.08.010
Rodríguez-Jiménez, P., Fernández-Messina, L., Ovejero-Benito, M. C., Chicharro, P., Vera-Tomé, P., Vara, A., et al. (2021). Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible proteins (GADD45) in psoriasis. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 14579. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-93780-x
Salameh, A., Dhein, S., Mewes, M., Sigusch, S., Kiefer, P., Vollroth, M., et al. (2020). Anti-oxidative or anti-inflammatory additives reduce ischemia/reperfusions injury in an animal model of cardiopulmonary bypass. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 27 (1), 18–29. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.04.003
St Clair, S., Giono, L., Varmeh-Ziaie, S., Resnick-Silverman, L., Liu, W. J., Padi, A., et al. (2004). DNA damage-induced downregulation of Cdc25C is mediated by p53 via two independent mechanisms: one involves direct binding to the cdc25C promoter. Mol. Cell 16 (5), 725–736. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.11.002
Tian, J., Zheng, Y., Mou, T., Yun, M., Tian, Y., Lu, Y., et al. (2023). Metformin confers longitudinal cardiac protection by preserving mitochondrial homeostasis following myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 50 (3), 825–838. doi:10.1007/s00259-022-06008-z
Toldo, S., Mauro, A. G., Cutter, Z., and Abbate, A. (2018). Inflammasome, pyroptosis, and cytokines in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiology. Heart Circulatory Physiology 315 (6), H1553–H1568. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00158.2018
Verma, S., Fedak, P. W. M., Weisel, R. D., Butany, J., Rao, V., Maitland, A., et al. (2002). Fundamentals of reperfusion injury for the clinical cardiologist. Circulation 105 (20), 2332–2336. doi:10.1161/01.cir.0000016602.96363.36
Wan, Y., Wang, Z., Shao, Y., Xu, Y., Voorhees, J., and Fisher, G. (2000). UV-induced expression of GADD45 is mediated by an oxidant sensitive pathway in cultured human keratinocytes and in human skin in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 6 (6), 683–688. doi:10.3892/ijmm.6.6.683
Yang, Y., Wei, Y., and Fang, F. (2020). Advances in the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza against cardiovascular diseas. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 12 (21), 37–40+56.
Yao, L., He, F., Zhao, Q., Li, D., Fu, S., Zhang, M., et al. (2023). Spatial multiplexed protein profiling of cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Circulation Res. 133 (1), 86–103. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322620
Yu, S.-W., Andrabi, S. A., Wang, H., Kim, N. S., Poirier, G. G., Dawson, T. M., et al. (2006). Apoptosis-inducing factor mediates poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymer-induced cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103 (48), 18314–18319. doi:10.1073/pnas.0606528103
Yuan, Q., Wang, T., Fu, H., Li, X., and Lei, P. (2024). Research progress on the active ingredients and pharmacological effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 26 (09), 172–179. doi:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2024.09.033
Keywords: myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, H9C2, ATM, GADD45, ORC
Citation: Sang Y, Du J, Zulikala D and Sang Z (2024) Mechanistic analysis of Tanshinone IIA’s regulation of the ATM/GADD45/ORC signaling pathway to reduce myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1510380. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1510380
Received: 12 October 2024; Accepted: 12 December 2024;
Published: 24 December 2024.
Edited by:
Boyang Ji, BioInnovation Institute (BII), DenmarkReviewed by:
Hong-he Xiao, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Sang, Du, Zulikala and Sang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhongqiang Sang, c2FuZ3pob25ncWlhbmcyMDI0QDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.