
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 29 July 2024
Sec. Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1423402
This article is a correction to:
Methotrexate-conjugated zinc oxide nanoparticles exert a substantially improved cytotoxic effect on lung cancer cells by inducing apoptosis
 Prakriti Mishra1
Prakriti Mishra1 Mohammad Faizan Ali Ahmad1
Mohammad Faizan Ali Ahmad1 Lamya Ahmed Al-Keridis2*
Lamya Ahmed Al-Keridis2* Mohd Saeed3
Mohd Saeed3 Nawaf Alshammari3
Nawaf Alshammari3 Nadiyah M. Alabdallah4,5
Nadiyah M. Alabdallah4,5 Rohit Kumar Tiwari1,6
Rohit Kumar Tiwari1,6 Afza Ahmad1
Afza Ahmad1 Mahima Verma1
Mahima Verma1 Shireen Fatima1
Shireen Fatima1 Irfan Ahmad Ansari1*
Irfan Ahmad Ansari1*A Corrigendum on
Methotrexate-conjugated zinc oxide nanoparticles exert a substantially improved cytotoxic effect on lung cancer cells by inducing apoptosis
by Mishra P, Ali Ahmad MF, Al-Keridis LA, Saeed M, Alshammari N, Alabdallah NM, Tiwari RK, Ahmad A, Verma M, Fatima S and Ansari IA (2023). Front. Pharmacol. 14:1194578. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1194578
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 8 as published. Partial overlap between the IC50-ZnONPs, IC50-MTX, and IC50-MTX-ZnONPs panels were unintentionally duplicated. The corrected Figure 8 and its caption appear below.
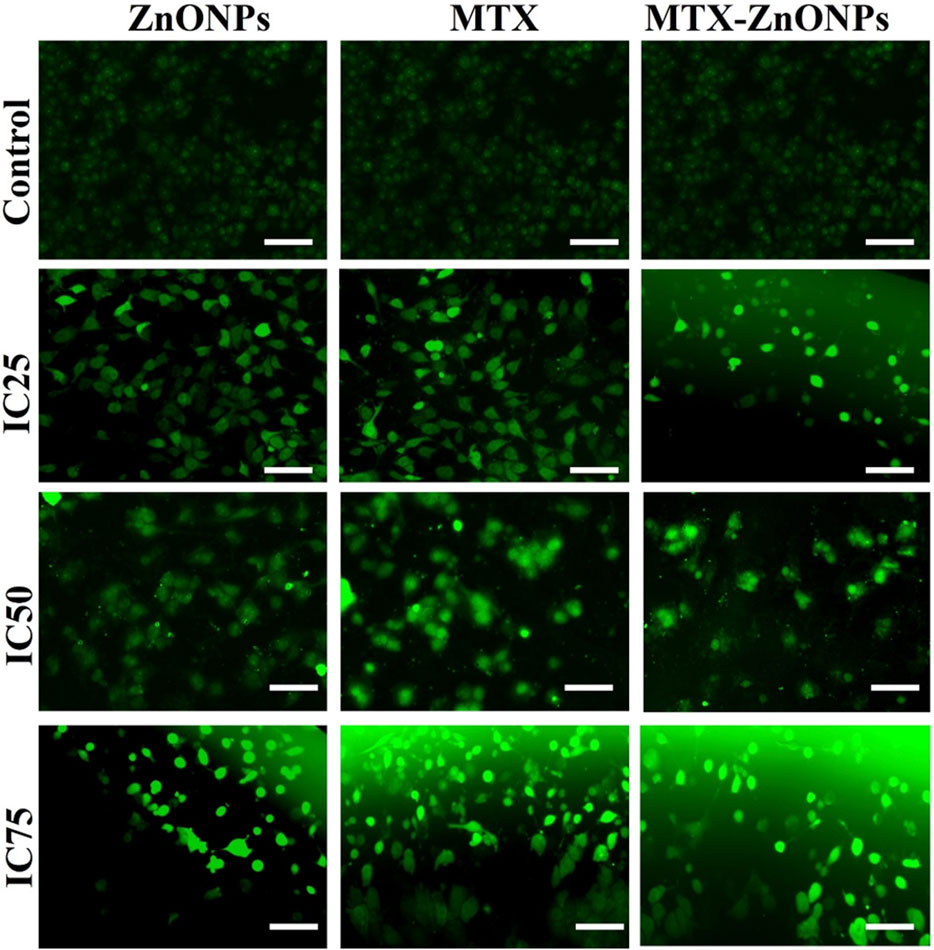
Figure 8. Qualitative evaluation of ROS in H2DCFDA-stained A549 cells treated at IC25 (ZnONPs 27.83 μg/mL; MTX 1.95 μg/mL; and MTX-ZnONPs 182 ng/mL), IC50 (ZnONPs 65.30 μg/mL; MTX 3.58 μg/mL; and MTX-ZnONPs 327 ng/mL), and IC75 (ZnONPs 70.41 μg/mL; MTX 6.57 μg/mL; and MTX-ZnONPs 588 ng/mL) concentrations for 24 h analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Images shown are representative of three independent experiments (scale bar: 100 μm; magnification: ×20). The control image was reused in each treatment group.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: zinc oxide, nanoparticles, methotrexate, lung cancer, A549, reactive oxygen species, caspases
Citation: Mishra P, Ali Ahmad MF, Al-Keridis LA, Saeed M, Alshammari N, Alabdallah NM, Tiwari RK, Ahmad A, Verma M, Fatima S and Ansari IA (2024) Corrigendum: Methotrexate-conjugated zinc oxide nanoparticles exert substantially improved cytotoxic effect on lung cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1423402. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423402
Received: 25 April 2024; Accepted: 16 July 2024;
Published: 29 July 2024.
Edited and reviewed by:
Vijayakumar Sekar, Shandong University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Mishra, Ali Ahmad, Al-Keridis, Saeed, Alshammari, Alabdallah, Tiwari, Ahmad, Verma, Fatima and Ansari. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lamya Ahmed Al-Keridis, bGFhbGtlcmlkaXNAcG51LmVkdS5zYQ==; Irfan Ahmad Ansari, YWhtYWRpcmZhbi5hbXVAZ21haWwuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.