
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 13 May 2024
Sec. Experimental Pharmacology and Drug Discovery
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1394151
This article is a correction to:
BM-MSCs alleviate diabetic nephropathy in male rats by regulating ER stress, oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptotic pathways
 Tarek Khamis1*
Tarek Khamis1* Adel Abdelkhalek2
Adel Abdelkhalek2 Hussein Abdellatif3,4
Hussein Abdellatif3,4 Nourelden Dwidar2
Nourelden Dwidar2 Ahmed Said2
Ahmed Said2 Rama Ahmed2
Rama Ahmed2 Kerolos Wagdy2
Kerolos Wagdy2 Rowina Elgarhy2
Rowina Elgarhy2 Rawan Eltahan2
Rawan Eltahan2 Hisham Mohamed2
Hisham Mohamed2 Eman Said Amer2
Eman Said Amer2 Maria Hanna2
Maria Hanna2 Tarek Ragab2
Tarek Ragab2 Abdallah Kishk2
Abdallah Kishk2 Judy Wael2
Judy Wael2 Eyad Sarhan2
Eyad Sarhan2 Linda Saweres2
Linda Saweres2 Mohamed Reda2
Mohamed Reda2 Sara Elkomy2
Sara Elkomy2 Abdalah Mohamed2
Abdalah Mohamed2 Abdullah Samy2
Abdullah Samy2 Ateya Khafaga2
Ateya Khafaga2 Youliana Shaker2
Youliana Shaker2 Hamdy Yehia2
Hamdy Yehia2 Asma Alanazi5,6
Asma Alanazi5,6 Mohammed Alassiri6,7,8
Mohammed Alassiri6,7,8 Emil Tîrziu9
Emil Tîrziu9 Iulia Maria Bucur9*
Iulia Maria Bucur9* Ahmed H. Arisha10,11*
Ahmed H. Arisha10,11*A Corrigendum on
BM-MSCs alleviate diabetic nephropathy in male rats by regulating ER stress, oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptotic pathways
by Khamis T, Abdelkhalek A, Abdellatif H, Dwidar N, Said A, Ahmed R, Wagdy K, Elgarhy R, Eltahan R, Mohamed H, Said Amer E, Hanna M, Ragab T, Kishk A, Wael J, Sarhan E, Saweres L, Reda M, Elkomy S, Mohamed A, Samy A, Khafaga A, Shaker Y, Yehia H, Alanazi A, Alassiri M, Tîrziu E, Bucur IM and Arisha AH (2023). Front. Pharmacol. 14:1265230. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1265230
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 1 as published. In the published version of the manuscript, there was an unintentional duplication of Figure 1E, which resulted in Figure 1D being covered. This duplication occurred due to a technical error during the formatting process. The corrected Figure 1 and its caption appear below.
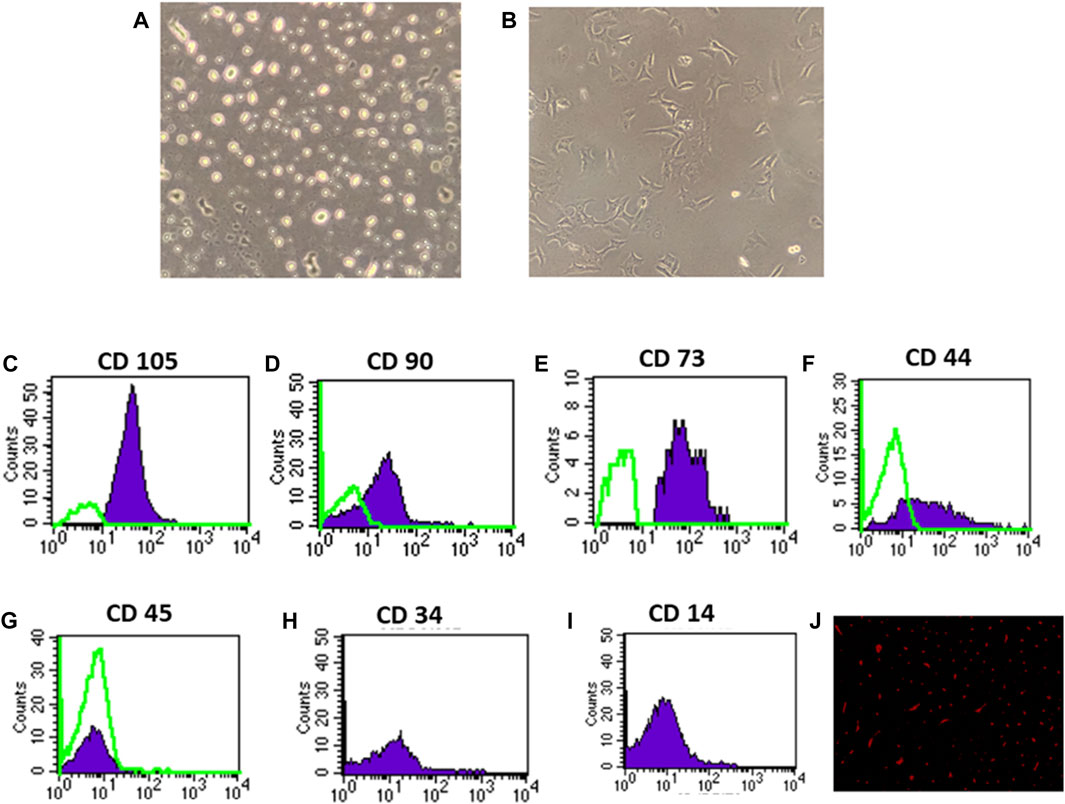
Figure 1. Identification and homing of BM-MSCs in diabetic rat renal tissue (A–J). (A) BM-MSC isolation on the third day of culture; (B) BM-MSC isolation on the seventh day of culture (C–I). Flow cytometric detection of BM-MSCs: (C) BM-MSC cell populations were +ve for CD105; (D) BM-MSCS cell populations were +ve for CD90; (E) BM-MSC cell populations were +ve for CD73; (F) BM-MSC cell populations were +ve for CD44; (G) BM-MSC cell populations were −ve for CD45; and (H) BM-MSC cell populations were −ve for CD34. (I) BM-MSC cell populations were −ve for CD14, and (J) PKH26 was used to identify BM-MSC homing in renal tissue.
In the published article, the Supplementary Table S2 was mistakenly not included in the publication. The missing material contains the raw data of the article. This is now published alongside the original article.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy, mesenchymal stem cells, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, diabetes, apoptosis, ER stress, inflammation, intermediate filament proteins
Citation: Khamis T, Abdelkhalek A, Abdellatif H, Dwidar N, Said A, Ahmed R, Wagdy K, Elgarhy R, Eltahan R, Mohamed H, Said Amer E, Hanna M, Ragab T, Kishk A, Wael J, Sarhan E, Saweres L, Reda M, Elkomy S, Mohamed A, Samy A, Khafaga A, Shaker Y, Yehia H, Alanazi A, Alassiri M, Tîrziu E, Maria Bucur I and Arisha AH (2024) Corrigendum: BM-MSCs alleviate diabetic nephropathy in male rats by regulating ER stress, oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptotic pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1394151. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1394151
Received: 01 March 2024; Accepted: 30 April 2024;
Published: 13 May 2024.
Edited and reviewed by:
Md Abdul Hye Khan, University of Missouri, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Khamis, Abdelkhalek, Abdellatif, Dwidar, Said, Ahmed, Wagdy, Elgarhy, Eltahan, Mohamed, Said Amer, Hanna, Ragab, Kishk, Wael, Sarhan, Saweres, Reda, Elkomy, Mohamed, Samy, Khafaga, Shaker, Yehia, Alanazi, Alassiri, Tîrziu, Maria Bucur and Arisha. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tarek Khamis, dC5raGFtaXNAdmV0Lnp1LmVkdS5lZw==; Iulia Maria Bucur, aXVsaWEuYnVjdXJAdXNhYi10bS5ybw==; Ahmed H. Arisha, dmV0YWhtZWRoYW1lZEB6dS5lZHUuZWc=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.