
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 04 March 2024
Sec. Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1334971
This article is a correction to:
In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Activity of Cucurbitacin C, a Novel Natural Product From Cucumber
 Dinglan Wu1†
Dinglan Wu1† Zhu Wang2†
Zhu Wang2† Muqi Lin3†
Muqi Lin3† Yi Shang4
Yi Shang4 Fei Wang5
Fei Wang5 JiaYi Zhou1
JiaYi Zhou1 Fei Wang1
Fei Wang1 Xiantong Zhang1
Xiantong Zhang1 Xiaomin Luo1*
Xiaomin Luo1* Weiren Huang6*
Weiren Huang6*A Corrigendum on
In Vitro and In Vivo antitumor activity of cucurbitacin C, a novel natural product from cucumber
by Wu D, Wang Z, Lin M, Shang Y, Wang F, Zhou J, Wang F, Zhang X, Luo X and Huang W (2019). Front. Pharmacol. 10:1287. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01287
In the published article, there was an error in Figures 4, 8 as published. The incorrect images were erroneously inserted.
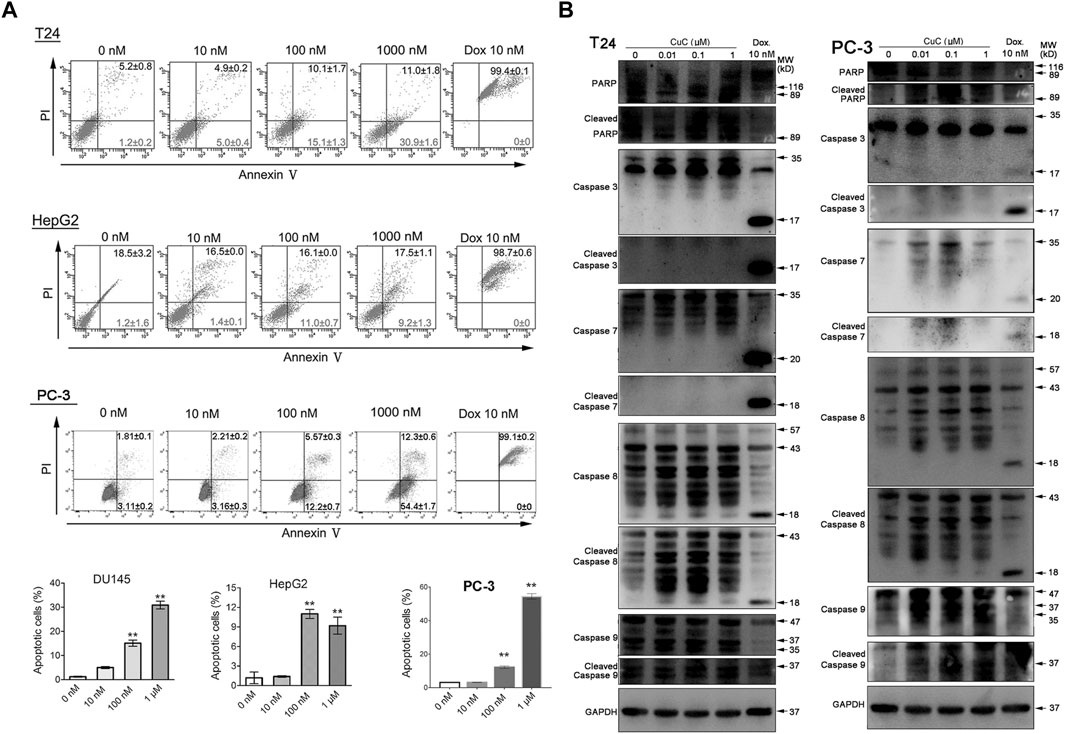
FIGURE 4. CuC induces cell apoptosis. (A) Apoptosis assay of cancer cells with CuC treatment by annexin V-FITC and PI staining. CuC induced significant early apoptosis at 100 mM and 1 µM treatment in T24, HepG2 and PC-3 cells (**, p < 0.01). (B) Western blot (WB) analysis of indicated apoptotic markers after 48 h dosage of serial CuC in T24 and PC-3 cells.
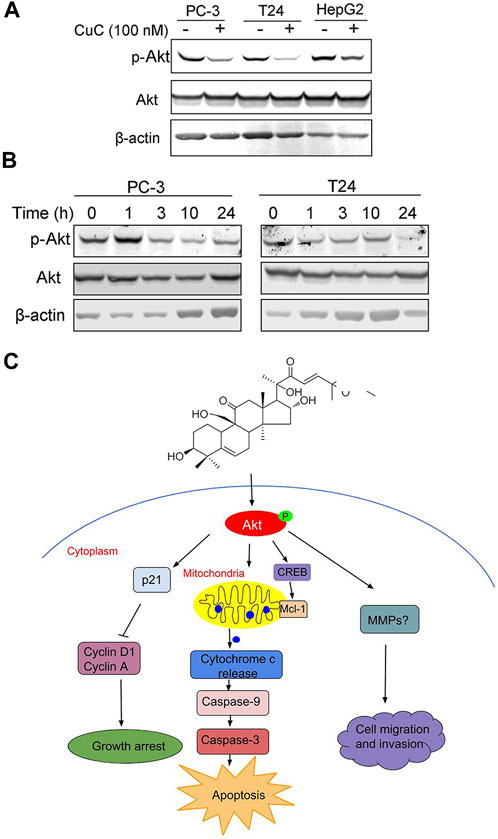
FIGURE 8. Molecular working model of CuC in cancer cells. (A) Western blot (WB) analysis of p-Akt and Akt in PC-3, T24, and HepG2 cells with or without CuC. p-Akt (Ser473) was significantly decreased in the presence of 100 nM CuC. Cells were treated for 24 h (B) p-Akt (Ser473) and Akt expression in PC-3 and T24 cells under CuC (100 nM) treatment at different time points (0, 1, 3, 10, and 24 h). (C) Schematic diagram illustrated the bio-relevant context of antitumor activities of CuC, and the proposed cell growth arrest, apoptosis, and cell migration inhibition are illustrated.
Specifically, in Figure 4B, the blot of Caspase 3 of PC-3 cell was inadvertently displayed as the cleaved caspase-3. In Figure 8A, the blot of β-actin image was mistakenly showed, due to the carelessness of the picture combination and image processing. Additionally, there is an error in the caption of Figure 8A. The published legend states: “Western blot (WB) analysis of p-Akt and Akt in PC-3, T24, and LNCaP cells with or without CuC”. The legend of Figure 8A is corrected as: “Western blot (WB) analysis of p-Akt and Akt in PC-3, T24, and HepG2 cells with or without CuC.” Finally, in the caption of Figure 4A, “T-24” is corrected as “T24.”
The corrected Figures 4, 8 and their captions appear below.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: cucurbitacin C, natural product, anti-cancer, growth arrest, apoptosis, Akt pathway
Citation: Wu D, Wang Z, Lin M, Shang Y, Wang F, Zhou J, Wang F, Zhang X, Luo X and Huang W (2024) Corrigendum: In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of cucurbitacin C, a novel natural product from cucumber. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1334971. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1334971
Received: 08 November 2023; Accepted: 01 February 2024;
Published: 04 March 2024.
Edited and reviewed by:
Christian Celia, University of Studies G. d’Annunzio Chieti and Pescara, ItalyCopyright © 2024 Wu, Wang, Lin, Shang, Wang, Zhou, Wang, Zhang, Luo and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaomin Luo, TWlsbG9yZUAxNjMuY29t; Weiren Huang, cG9ueTg5ODBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.