- 1Research Studio of Traditional Chinese Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, School of Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, China
- 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, School of Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, China
A Corrigendum on
Shu-Xie decoction alleviates oxidative stress and colon injury in acute sleep-deprived mice by suppressing p62/KEAP1/NRF2/HO1/NQO1 signaling
by Wang M, Li B, Liu Y, Zhang M, Huang C, Cai T, Jia Y, Huang X, Ke H, Liu S and Yang S (2023). Front. Pharmacol. 14:1107507. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1107507
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 6 as published. The pictures for ASD + S-z groups in Figure 6 were erroneously presented after being redrawn and submitted. The corrected Figure 6 and its caption appear below.
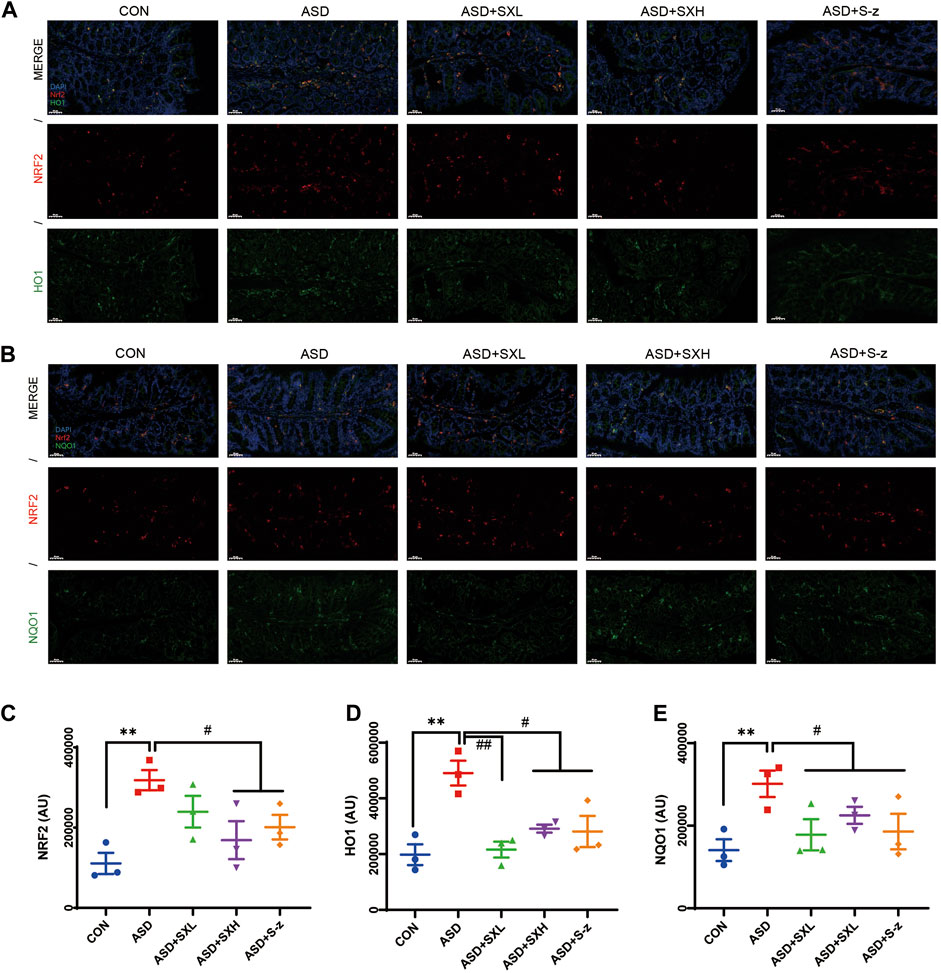
FIGURE 6. Immunofluorescence analysis of NRF2 (red), HO1 and NQO1 (green) in colon mucosal layers (×400 magnification). (A) Representative fluorescence confocal images show NRF2 and HO1 staining in the colon sections of mice belonging to the CON, ASD, ASD + SXL, ASD + SXH, and ASD + S-z groups. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) Representative fluorescence confocal images show NRF2 and NQO1 staining in the colon sections of mice belonging to the CON, ASD, ASD + SXL, ASD + SXH, and ASD + S-z groups. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (C) Quantitative analysis of NRF2 fluorescence. (D) Quantitative analysis of HO1 fluorescence. (E) Quantitative analysis of NQO1 fluorescence. The immunofluorescence signal intensity in the images was quantified using the ImageJ software. n = 3 per group. The experiment was repeated three times. The data are shown as mean ± S.E.M. **p < 0.01 vs CON group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs ASD group. Scale bar: 50 μm.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: sleep deprivation, oxidative stress, NRF2, traditional Chinese medicine, ROS
Citation: Wang M, Li B, Liu Y, Zhang M, Huang C, Cai T, Jia Y, Huang X, Ke H, Liu S and Yang S (2023) Corrigendum: Shu-Xie decoction alleviates oxidative stress and colon injury in acute sleep-deprived mice by suppressing p62/KEAP1/NRF2/HO1/NQO1 signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1199204. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1199204
Received: 03 April 2023; Accepted: 25 May 2023;
Published: 30 May 2023.
Edited by:
Feng Li, Baylor College of Medicine, United StatesReviewed by:
Michael McMahon, Penman Consulting, United KingdomCopyright © 2023 Wang, Li, Liu, Zhang, Huang, Cai, Jia, Huang, Ke, Liu and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bo Li, dGp1dGNtbGlib0BxcS5jb20=; Suhuan Liu, bGl1c3VodWFuQHhtdS5lZHUuY24=; Shuyu Yang, eG15YW5nc2h1eXVAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Mengyuan Wang
Mengyuan Wang Bo Li
Bo Li Yijiang Liu
Yijiang Liu Mengting Zhang1
Mengting Zhang1 Caoxin Huang
Caoxin Huang Teng Cai
Teng Cai Yibing Jia
Yibing Jia Xiaoqing Huang
Xiaoqing Huang Suhuan Liu
Suhuan Liu Shuyu Yang
Shuyu Yang