An Erratum on
Drug resistance mechanism of kinase inhibitors in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
by Jiang L, Li L, Liu Y, Lu L, Zhan M, Yuan S and Liu Y (2023). Front. Pharmacol. 14:1097277. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1097277
Due to an error in the editorial process, an incorrect version of the article was published. Significant textual revisions to the published article are detailed below.
The previous version is available in the Supplementary Material of this Erratum. The article has now been updated with the correct version. The publisher apologizes for this error.
A correction has been made to the section “Primary Drug Resistance”, subsection “Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)”. This section has been removed and its contents merged with the section entitled “Tumor heterogeneity and EGFR”.
A correction has been made to the section “Acquired Drug Resistance”, subsection “PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways”. This section has been removed and replaced with the section entitled “EGFR and HGF/cMet mediated signaling pathway”.
A spelling mistake was corrected in the keywords section of this article. “Carcinom” was corrected to “carcinoma”.
Additional references have been added to the published article. Details of these references can be found in the "References" section of this article.
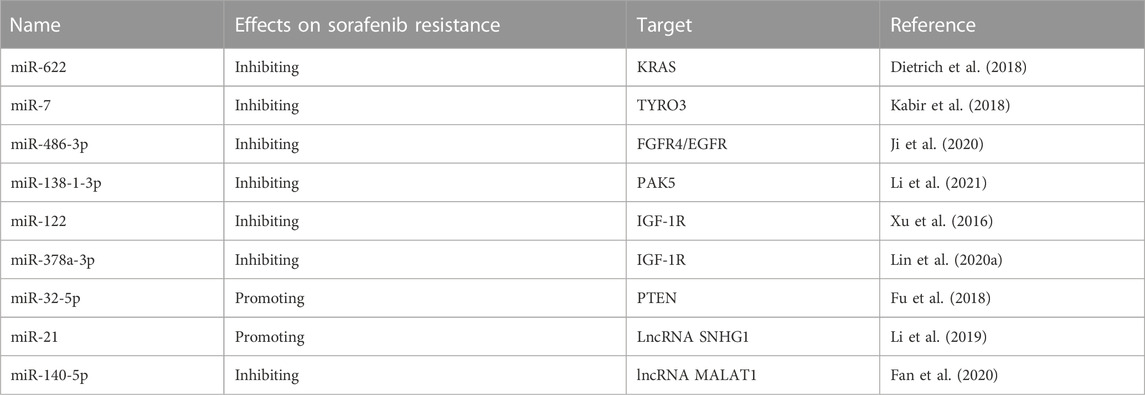
Tables 1, 2 have been added to the published article.
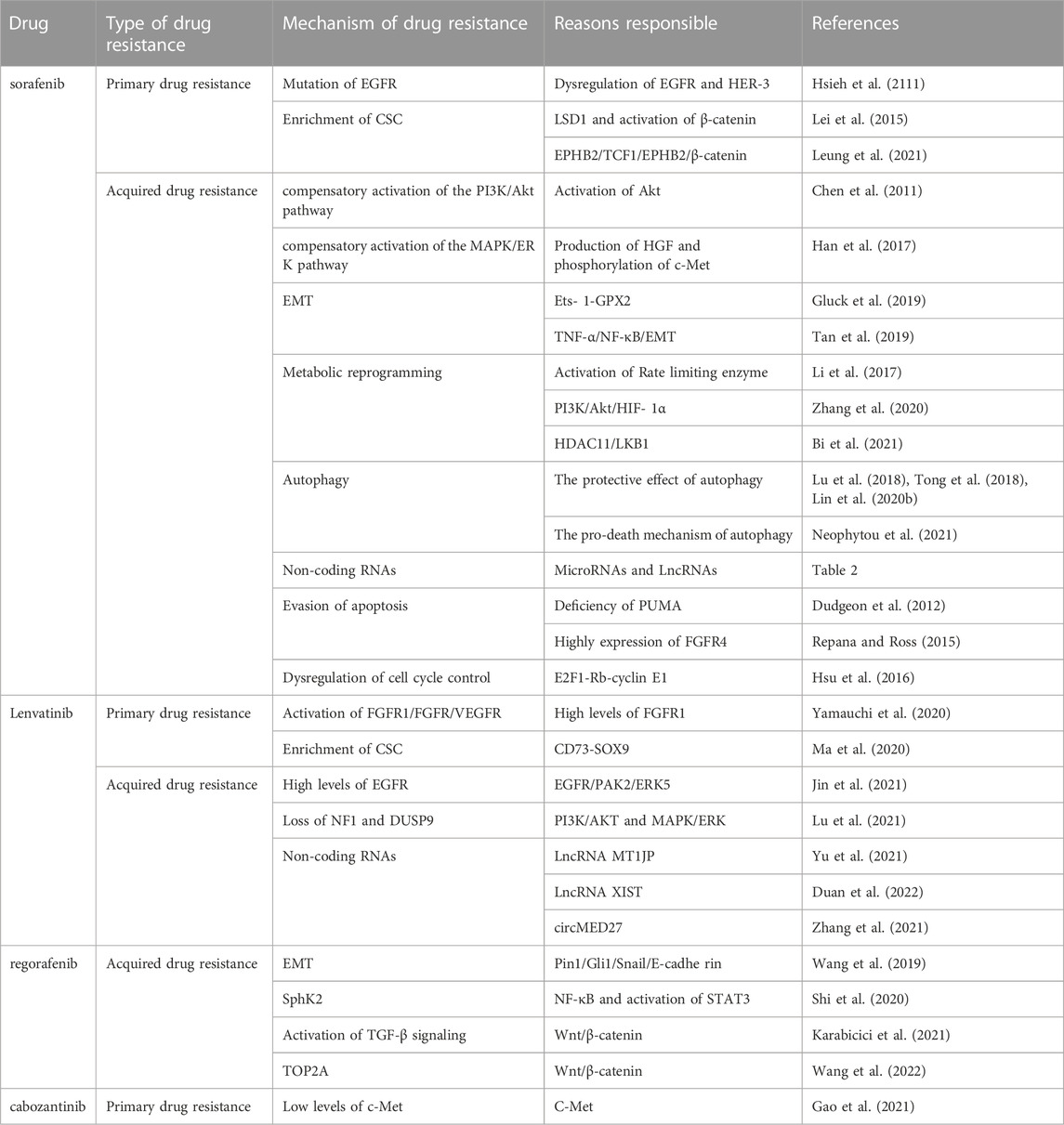
TABLE 1. Summary of previous studies with the mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase drug resistance in HCC.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2023.1188062/full#supplementary-material
References
Arai, H., Battaglin, F., Wang, J., Lo, J. H., Soni, S., Zhang, W., et al. (2019). Molecular insight of regorafenib treatment for colorectal cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 81, 101912. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.101912
Bi, L., Ren, Y., Feng, M., Meng, P., Wang, Q., Chen, W., et al. (2021). HDAC11 regulates glycolysis through the LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway to maintain hepatocellular carcinoma stemness. Cancer Res. 81 (8), 2015–2028. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3044
Chen, K. F., Chen, H. L., Tai, W. T., Feng, W. C., Hsu, C. H., Chen, P. J., et al. (2011). Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway mediates acquired resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Pharmacol. Ex. Ther. 337 (1), 155–161. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.175786
Dagogo-Jack, I., and Shaw, A. T. (2018). Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15 (2), 81–94. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.166
Dietrich, P., Koch, A., Fritz, V., Hartmann, A., Bosserhoff, A. K., and Hellerbrand, C. (2018). Wild type Kirsten rat sarcoma is a novel microRNA-622-regulated therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma and contributes to sorafenib resistance. Gut 67 (7), 1328–1341. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-315402
Duan, A., Li, H., Yu, W., Zhang, Y., and Yin, L. (2022). Long noncoding RNA XIST promotes resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via epigenetic inhibition of NOD2. J. Oncol. 2022, 4537343. doi:10.1155/2022/4537343
Dudgeon, C., Peng, R., Wang, P., Sebastiani, A., Yu, J., and Zhang, L. (2012). Inhibiting oncogenic signaling by sorafenib activates PUMA via GSK3β and NF-κB to suppress tumor cell growth. Oncogene 31 (46), 4848–4858. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.644
Duffy, A. G., and Greten, T. F. (2017). Liver cancer: Regorafenib as second-line therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14 (3), 141–142. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2017.7
Fan, L., Huang, X., Chen, J., Zhang, K., Gu, Y. H., Sun, J., et al. (2020). Long noncoding RNAMALAT1 contributes to sorafenib resistance by targeting miR-140-5p/aurora-A signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 19 (5), 1197–1209. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-0203
Fu, X., Liu, M., Qu, S., Ma, J., Zhang, Y., Shi, T., et al. (2018). Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 37 (1), 52. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0677-7
Gao, C., Wang, S., Shao, W., Zhang, Y., Lu, L., Jia, H., et al. (2021). Rapamycin enhances the anti-tumor activity of cabozantinib in cMet inhibitor-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Med.
Gluck, C., Glathar, A., Tsompana, M., Nowak, N., Garrett-Sinha, L. A., Buck, M. J., et al. (2019). Molecular dissection of the oncogenic role of ETS1 in the mesenchymal subtypes of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS Genet. 15, e1008250. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1008250
Han, P., Li, H., Jiang, X., Zhai, B., Tan, G., Zhao, D., et al. (2017). Dual inhibition of Akt and c-Met as a second-line therapy following acquired resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol. Oncol. 11 (3), 320–334. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.12039
Hsieh, S. Y., He, J. R., Hsu, C. Y., Chen, W. J., Bera, R., Lin, K. Y., et al. (2111). Neuregulin/erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 3 autocrine loop contributes to invasion and early recurrence of human hepatoma. Hepatology 53 (2), 504–516. doi:10.1002/hep.24083
Hsu, C., Lin, L. I., Cheng, Y. C., Feng, Z. R., Shao, Y. Y., Cheng, A. L., et al. (2016). Cyclin E1 inhibition can overcome sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through mcl-1 suppression. Clin. Cancer Res. 22 (10), 2555–2564. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0499
Huang, M., Chen, C., Geng, J., Han, D., Wang, T., Xie, T., et al. (2017). Targeting KDM1A attenuates Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to eliminate sorafenib-resistant stem-like cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 398, 12–21. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.038
Ippolito, M. R., Martis, V., Martin, S., Tijhuis, A. E., Hong, C., Wardenaar, R., et al. (2021). Gene copy-number changes and chromosomal instability induced by aneuploidy confer resistance to chemotherapy. Dev. Cell 56 (17), 2440–2454. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2021.07.006
Ito, Y., Takeda, T., Sakon, M., Tsujimoto, M., Higashiyama, S., Noda, K., et al. (2001). Expression and clinical significance of erb-B receptor family in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 84 (10), 1377–1383. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2000.1580
Ji, L., Lin, Z., Wan, Z., Xia, S., Jiang, S., Cen, D., et al. (2020). miR-486-3p mediates hepatocellular carcinoma sorafenib resistance by targeting FGFR4 and EGFR. Cell Death Dis. 11 (4), 250. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2413-4
Jin, H., Shi, Y., Lv, Y., Yuan, S., Ramirez, C. F. A., Lieftink, C., et al. (2021). EGFR activation limits the response of liver cancer to lenvatinib. Nature 595 (7869), 730–734. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03741-7
Kabir, T. D., Ganda, C., Brown, R. M., Beveridge, D. J., Richardson, K. L., Chaturvedi, V., et al. (2018). A microRNA-7/growth arrest specific 6/TYRO3 axis regulates the growth and invasiveness of sorafenib-resistant cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 67 (1), 216–231. doi:10.1002/hep.29478
Karabicici, M., Azbazdar, Y., Ozhan, G., Senturk, S., Firtina Karagonlar, Z., and Erdal, E. (2021). Changes in wnt and TGF-β signaling mediate the development of regorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HuH7. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 639779. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.639779
Lei, Z. J., Wang, J., Xiao, H. L., Guo, Y., Wang, T., Li, Q., et al. (2015). Lysine-specific demethylase 1 promotes the stemness and chemoresistance of Lgr5 + liver cancer initiating cells by suppressing negative regulators of β-catenin signaling. Oncogene 34 (24), 3188–3198. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.182
Leung, H. W., Leung, C. O. N., Lau, E. Y., Chung, K. P. S., Mok, E. H., Lei, M. M. L., et al. (2021). EPHB2 activates β-catenin to enhance cancer stem cell properties and drive sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 81 (12), 3229–3240. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0184
Li, S., Dai, W., Mo, W., Li, J., Feng, J., Wu, L., et al. (2017). By inhibiting PFKFB3, aspirin overcomes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 141 (12), 2571–2584. doi:10.1002/ijc.31022
Li, W., Dong, X., He, C., Tan, G., Li, Z., Zhai, B., et al. (2019). LncRNA SNHG1 contributes to sorafenib resistance by activating the Akt pathway and is positively regulated by miR-21 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 183. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1177-0
Li, T. T., Mou, J., Pan, Y. J., Huo, F. C., Du, W. Q., Liang, J., et al. (2021). MicroRNA-138-1-3p sensitizes sorafenib to hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PAK5 mediated β-catenin/ABCB1 signaling pathway. J. Biomed. Sci. 28 (1), 56. doi:10.1186/s12929-021-00752-4
Lin, Z., Xia, S., Liang, Y., Ji, L., Pan, Y., Jiang, S., et al. (2020a). LXR activation potentiates sorafenib sensitivity in HCC by activating microRNA-378a transcription. Theranostics 10 (19), 8834–8850. doi:10.7150/thno.45158
Lin, Z., Niu, Y., Wan, A., Chen, D., Liang, H., Chen, X., et al. (2020b). RNA m6 A methylation regulates sorafenib resistance in liver cancer through FOXO3-mediated autophagy. EMBO J. 39 (12), e103181. doi:10.15252/embj.2019103181
Lu, S., Yao, Y., Xu, G., Zhou, C., Zhang, Y., Sun, J., et al. (2018). CD24 regulates sorafenib resistance via activating autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 9 (6), 646. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0681-z
Lu, Y., Shen, H., Huang, W., He, S., Chen, J., Zhang, D., et al. (2021). Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in hepatocellular carcinoma with lenvatinib resistance. Cell Death Discov. 7 (1), 359. doi:10.1038/s41420-021-00747-y
Ma, X. L., Hu, B., Tang, W. G., Xie, S. H., Ren, N., Guo, L., et al. (2020). CD73 sustained cancer-stem-cell traits by promoting SOX9 expression and stability in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13 (1), 11. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-0845-z
McGranahan, N., and Swanton, C. (2017). Clonal heterogeneity and tumor evolution: Past, present, and the future. Cell 168 (4), 613–628. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.018
Negrini, S., Gorgoulis, V. G., and Halazonetis, T. D. (2010a). Genomic instability-an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11 (3), 220–228. doi:10.1038/nrm2858
Negrini, S., Gorgoulis, V. G., and Halazonetis, T. D. (2010b). Clonal heterogeneity and tumor evolution: Past, present, and the future. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11 (3), 220–228. doi:10.1038/nrm2858.14.McGranahan
Neophytou, C. M., Trougakos, I. P., Erin, N., and Papageorgis, P. (2021). Apoptosis deregulation and the development of cancer multi-drug resistance. Cancers (Basel) 13 (17), 4363. doi:10.3390/cancers13174363
O'Connor, R., Clynes, M., Dowling, P., O'Donovan, N., and O'Driscoll, L. (2007). Drug resistance in cancer - searching for mechanisms, markers and therapeutic agents. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 3 (6), 805–817. doi:10.1517/17425255.3.6.805
Pan, J., Zhang, M., Dong, L., Ji, S., Zhang, J., Zhang, S., et al. (2022). Genome-Scale CRISPR screen identifies LAPTM5 driving lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Autophagy 7, 1–15. doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2117893
Repana, D., and Ross, P. (2015). Targeting FGF19/FGFR4 pathway: A novel therapeutic strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Diseases 3 (4), 294–305. doi:10.3390/diseases3040294
Shi, W., Zhang, S., Ma, D., Yan, D., Zhang, G., Cao, Y., et al. (2020). Targeting SphK2 reverses acquired resistance of regorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 10, 694. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.00694
Tan, W., Luo, X., Li, W., Zhong, J., Cao, J., Zhu, S., et al. (2019). TNF-α is a potential therapeutic target to overcome sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 40, 446–456. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.047
Tong, M., Che, N., Zhou, L., Luk, S. T., Kau, P. W., Chai, S., et al. (2018). Efficacy of annexin A3 blockade in sensitizing hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib and regorafenib. J. Hepatol. 69 (4), 826–839. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.034
Vasan, N., Baselga, J., and Hyman, D. M. (2019). A view on drug resistance in cancer. Nature 575 (7782), 299–309. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1730-1
Vishnoi, K., Ke, R., Viswakarma, N., Srivastava, P., Kumar, S., Das, S., et al. (2022). Ets1 mediates sorafenib resistance by regulating mitochondrial ROS pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 13 (7), 581. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05022-1
Wang, J., Zhang, N., Han, Q., Lu, W., Wang, L., Yang, D., et al. (2019). Pin1 inhibition reverses the acquired resistance of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to Regorafenib via the Gli1/Snail/E-cadherin pathway. Cancer Lett. 444, 82–93. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2018.12.010
Wang, Z., Zhu, Q., Li, X., Ren, X., Li, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). TOP2A inhibition reverses drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to regorafenib. Am. J. Cancer Res. 12 (9), 4343–4360.
Xu, Y., Huang, J., Ma, L., Shan, J., Shen, J., Yang, Z., et al. (2016). MicroRNA-122 confers sorafenib resistance to hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting IGF-1R to regulate RAS/RAF/ERK signaling pathways. Cancer Lett. 371 (2), 171–181. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.034
Yamauchi, M., Ono, A., Ishikawa, A., Kodama, K., Uchikawa, S., Hatooka, H., et al. (2020). Tumor fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 level predicts the efficacy of lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 11 (5), e00179. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000179
Yu, T., Yu, J., Lu, L., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Y., Zhou, Y., et al. (2021). MT1JP-mediated miR-24-3p/BCL2L2 axis promotes Lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting apoptosis. Cell Oncol. (Dordr). 44 (4), 821–834. doi:10.1007/s13402-021-00605-0
Zhang, X., Wu, L., Xu, Y., Yu, H., Chen, Y., Zhao, H., et al. (2020). Microbiota-derived SSL6 enhances the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib by down-regulating glycolysis. Cancer Lett. 481, 32–44. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.03.027
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, drug resistance, sorafenib, lenvatinib, regorafenib, cabozantinib
Citation: Frontiers Production Office (2023) Erratum: Drug resistance mechanism of kinase inhibitors in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1188062. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1188062
Received: 16 March 2023; Accepted: 16 March 2023;
Published: 03 April 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Frontiers Production Office. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Frontiers Production Office, cHJvZHVjdGlvbi5vZmZpY2VAZnJvbnRpZXJzaW4ub3Jn
 Frontiers Production Office
Frontiers Production Office