
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol., 19 May 2023
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1172950
This article is a correction to:
Effects of Poria cocos extract on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease via the FXR/PPARα-SREBPs pathway
 Jinbiao He†
Jinbiao He† Yu Yang†
Yu Yang† Fan Zhang
Fan Zhang Yanjuan Li
Yanjuan Li Xiaosi Li
Xiaosi Li Xuemei Pu
Xuemei Pu Xudong He
Xudong He Mei Zhang
Mei Zhang Xinxing Yang
Xinxing Yang Qiuman Yu
Qiuman Yu Yan Qi*
Yan Qi* Xuefang Li*
Xuefang Li* Jie Yu*
Jie Yu*A Corrigendum on
Effects of Poria coc os extract on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease via the FXR/PPARα-SREBPs pathway
by He J, Yang Y, Zhang F, Li Y, Li X, Pu X, He X, Zhang M, Yang X, Yu Q, Qi Y, Li X and Yu J (2022). Front. Pharmacol. 13:1007274. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1007274
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 2 as published. In the legend for Figure 2, “(N) Brown adipose tissue (BAT).” is a duplicate and needs to be deleted because the BAT is explained in the legend for Figure 2I. The corrected legend appears below.
“FIGURE 2 | EPC ameliorated MAFLD in rats. (A) Body weight (BW). (B) BW gain. (C–E) Organ wet weight. (F) Inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT). (G) Perirenal white adipose tissue (pWAT). (H) Epididymis white adipose tissue (eWAT). (I) Brown adipose tissue (BAT). (J) iWAT/BW ratio. (K) pWAT/BW ratio; (L) eWAT/BW rati. (M) BAT/BW ratio. (N) Representative rat liver images of hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) and Oil Red O staining per group (X200). (O) Representative iWAT, pWAT, eWAT, BAT. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted for the group comparison. n = 8, data are presented as mean ± SEM.*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. MOD group. EPC, P. cocos ethanol extract; CON, normal diet control group; MOD, high-fat diet group; FC, Fenofibrate capsules; EPC-L, low-dose P. cocos ethanol extract; EPC-H, high-dose P. cocos ethanol extract.].
Furthermore, there was an error in Figure 6P as published. The authors apologize for uploading the ERK protein image in Figure 6 incorrectly, with image of p-JNK, in this article. Furthermore, P-ERK should be p-ERK in Figure 6P. The corrected Figure 6 appears below.
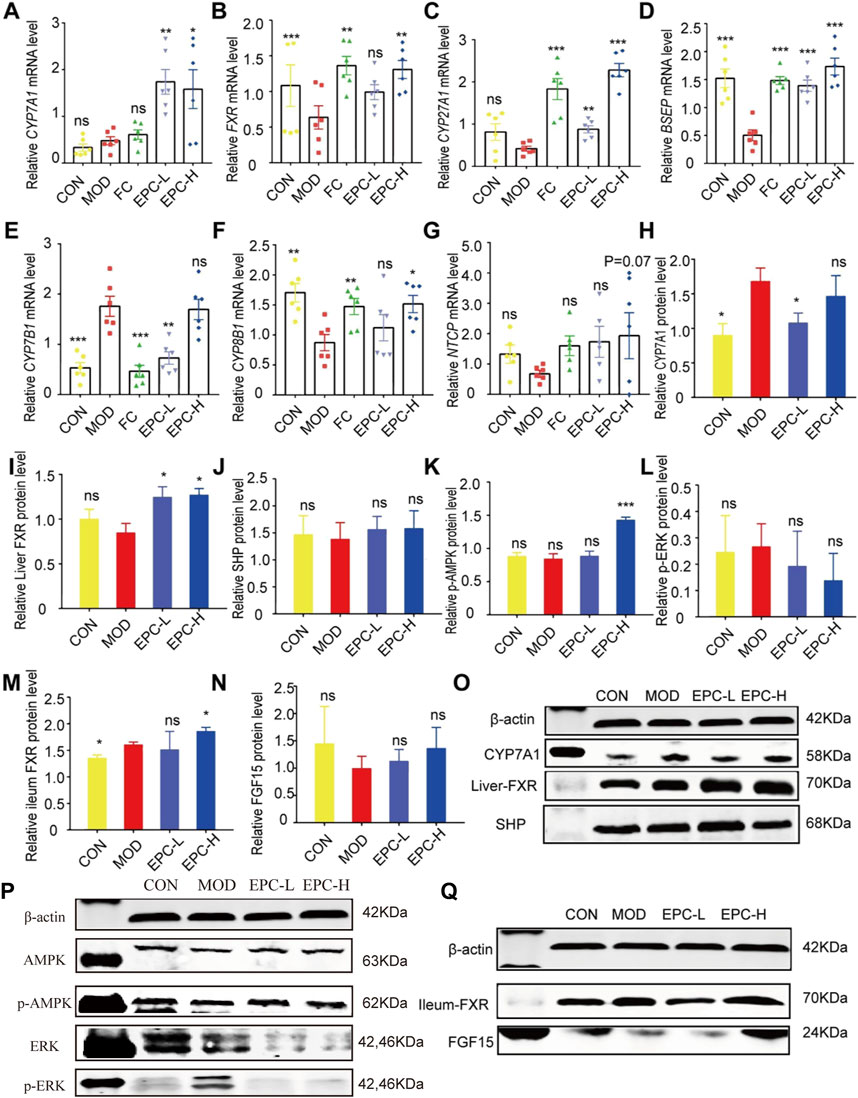
FIGURE 6. EPC ameliorated MAFLD formation in rats by regulating BA metabolism. (A–G) Relative expression of CYP7A1, FXR, CYP27A1, BSEP, CYP7B1, CYP8B1, NTCP mRNA in liver, n = 6; (H–L) Relative expression of protein CYP7A1, FXR, SHP, p-AMPK, and p-ERK in the liver, n = 4; (M–N) Relative expression of protein FXR and FGF15 in the ileum, n = 4. (O–P) Representative immunoblotting images of CYP7A1, FXR, SHP, p-AMPK,and p-ERK in the liver. (Q) Representative immunoblotting images of FXR and FGF15 in the ileum. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted for the group comparison. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. MOD group. CYP7A1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; CYP27A1, sterol 27-hydroxylase; BSEP, bile salt export protein; CYP7B1, oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase; CYP8B1, sterol 12αhydroxylase; NTCP, Na + -taurocholate co-transporting polypeptides; SHP, small heterodimer partner; AMPK, 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase; ERK, Extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: MAFLD (metabolic-associated fatty liver disease), Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf., bile acid metabolism, FXR/PPARα-SREBP pathway, lipid homeostasis, UPLC Q-TOF/MS
Citation: He J, Yang Y, Zhang F, Li Y, Li X, Pu X, He X, Zhang M, Yang X, Yu Q, Qi Y, Li X and Yu J (2023) Corrigendum: Effects of Poria cocos extract on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease via the FXR/PPARα-SREBPs pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1172950. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1172950
Received: 24 February 2023; Accepted: 15 May 2023;
Published: 19 May 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Michael Heinrich, University College London, United KingdomCopyright © 2023 He, Yang, Zhang, Li, Li, Pu, He, Zhang, Yang, Yu, Qi, Li and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Qi, cWl5YW5rbUB5bnV0Y20uZWR1LmNu; Xuefang Li, bGl4dWVmMTAwQDEyNi5jb20=; Jie Yu, Y3oueXVqaWVAZ21haWwuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.