Diplatin, a Novel and Low-Toxicity Anti-Lung Cancer Platinum Complex, Activation of Cell Death in Tumors via a ROS/JNK/p53-Dependent Pathway, and a Low Rate of Acquired Treatment Resistance
- 1Children’s Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 2Zhejiang Respiratory Drugs Research Laboratory of Food and Drug Administration of China, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 3Breath Smooth Biotech Hangzhou Co., LTD, Hangzhou, China
- 4Beijing Shuobai Pharmaceutical Co., LTD, Beijing, China
- 5Joinn Laboratories, BAD, Beijing, China
- 6Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
by Lin, X., Jia, Y., Dong, X., Shen, J., Jin, Y., Li, Y., Wang, F., Anenberg, E., Zhou, J., Zhu, J., Chen, X., Xie, Q., Xie, Y. (2019). Front. Pharmacol. 10:982. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00982
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 3H as published. An incorrect image for the p53 measurement in A549 was shown. The corrected Figure 3H appears below.
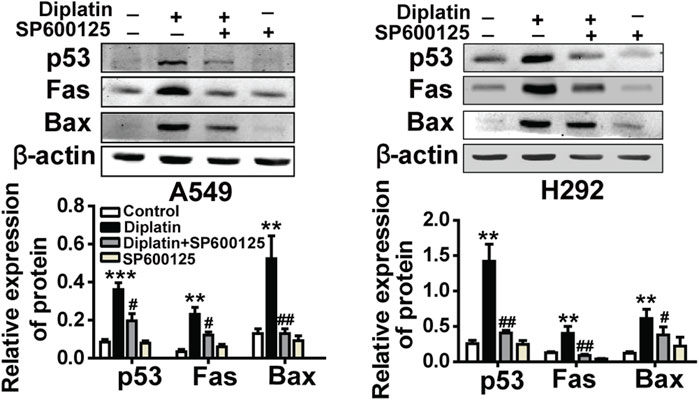
FIGURE 3. JNK/p53-mediated pathway is involved in diplatin-induced apoptosis of tumor cells. (H) Pretreatment (0.5 h) with 10 μM JNK inhibitor (SP600125) suppresses the 48 h time point 25 μM diplatin-induced p53, Fas, and Bax protein upregulation (n = 4 per group). The data are presented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments, one-way ANOVA followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test. Statistical significance is indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 for comparison with control and #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 for comparison with the diplatin-treated group.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: lung cancer, Platinum complex, Water solubility, ROS/p53 pathway, cisplatin resistance
Citation: Lin X, Jia Y, Dong X, Shen J, Jin Y, Li Y, Wang F, Anenberg E, Zhou J, Zhu J, Chen X, Xie Q and Xie Y (2022) Corrigendum: Diplatin, a Novel and Low-Toxicity Anti-Lung Cancer Platinum Complex, Activation of Cell Death in Tumors via a ROS/JNK/p53-Dependent Pathway, and a Low Rate of Acquired Treatment Resistance. Front. Pharmacol. 13:890886. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.890886
Received: 07 March 2022; Accepted: 05 April 2022;
Published: 28 April 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Fabrizio Marcucci, University of Milan, ItalyCopyright © 2022 Lin, Jia, Dong, Shen, Jin, Li, Wang, Anenberg, Zhou, Zhu, Chen, Xie and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yicheng Xie, eWN4aWVAemp1LmVkdS5jbg==
†Present Address: Xixi Lin, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children’s Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xixi Lin
Xixi Lin Yongliang Jia2,3‡
Yongliang Jia2,3‡ Eitan Anenberg
Eitan Anenberg Jiancang Zhou
Jiancang Zhou Qiangmin Xie
Qiangmin Xie Yicheng Xie
Yicheng Xie