
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 15 December 2022
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1042762
This article is a correction to:
Xiaoyaosan Alleviates Hippocampal Glutamate-Induced Toxicity in the CUMS Rats via NR2B and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Xueming Zhou1,2†
Xueming Zhou1,2† Chenyue Liu1†
Chenyue Liu1† Yueyun Liu1
Yueyun Liu1 Qingyu Ma3
Qingyu Ma3 Xin Zhao1
Xin Zhao1 Youming Jiang1
Youming Jiang1 Xiaojuan Li3*
Xiaojuan Li3* Jia-Xu Chen1,3*
Jia-Xu Chen1,3*A Corrigendum on
Xiaoyaosan alleviates hippocampal glutamate-induced toxicity in the CUMS rats via NR2B and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
by Zhou X-M, Liu C-Y, Liu Y-Y, Ma Q-Y, Zhao X, Jiang Y-M, Li X-J and Chen J-X (2021). Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12: 586788. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.586788
In the published article, there was an error in Figures 5A, 8A as published. The wrong images were used in Figure 5A at the vehicle (W) and vehicle (D) group as well as Figure 8A. The correct version of the figure shows below. The corrected Figures 5, 8 and its caption appear below.
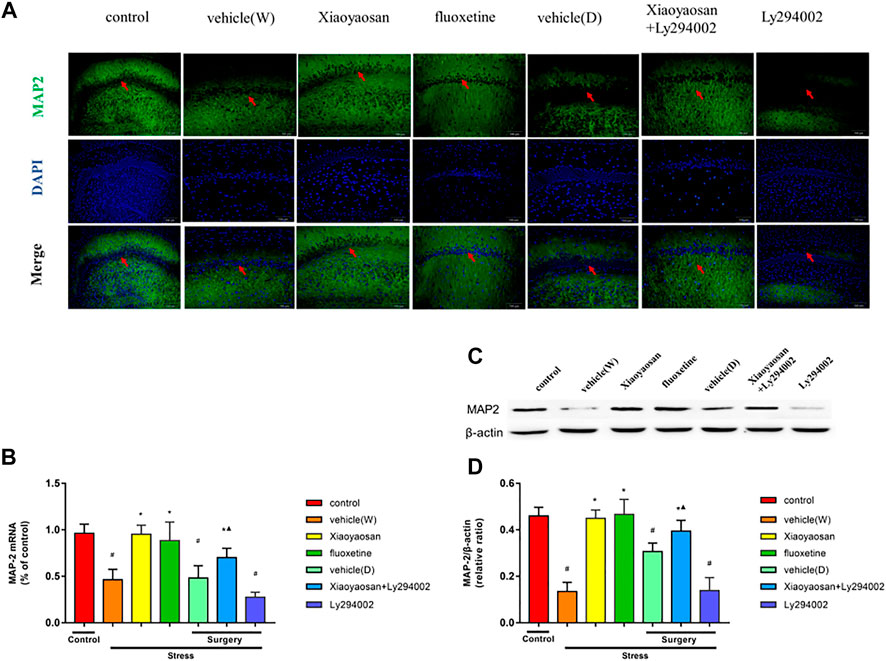
FIGURE 5. Xiaoyaosan elevates the expression of MAP2 in the hippocampal CA1 region of CUMS rats (A, original magnifification, ×200) Xiaoyaosan and Xiaoyaosan + Ly294002 promoted MAP2 expression in the CUMS rats. The green color represents MAP2 staining, and the blue color represents nuclear staining (C) Representative images and western blot analysis (D) of western blot assay showing the relative expression of MAP2 (B) Level of MAP2 mRNA in the hippocampal CA1 area of the rats in the treatment and control groups. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD. #p < 0.05 compared to the control group; *p < 0.05 compared to the vehicle (W) group; ▲p < 0.05 compared to the Ly294002 group, n = 6.
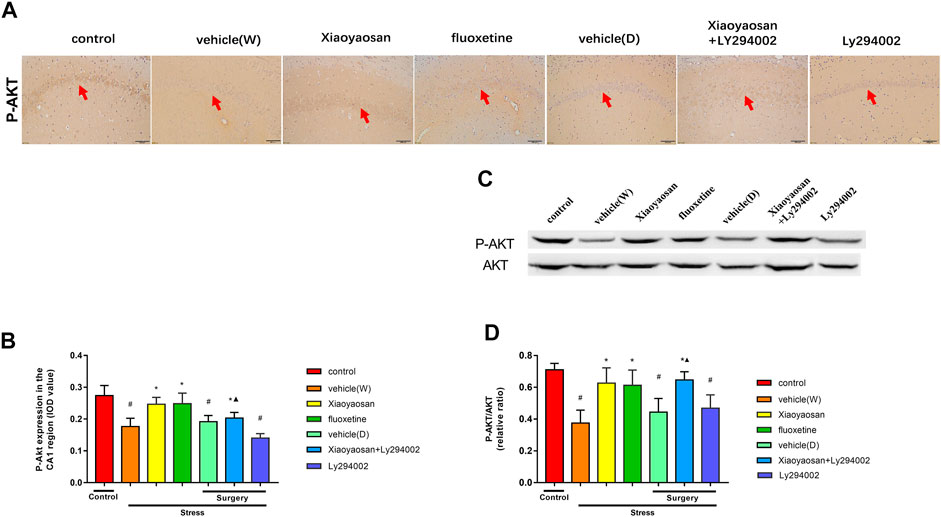
FIGURE 8. Xiaoyaosan elevates the expression of P-AKT/AKT in the hippocampal CA1 region of CUMS rats P-AKT/AKT in the hippocampal CA1 region of CUMS rats (A) Representative micrographs of immunohistochemical staining (sections were counterstained with hematoxylin; original magnifification, ×200) and (B) quantitative analysis showing the expression of P-AKT in the hippocampal CA1 region (C). Representative images and western blot analysis (D) of western blot assay showing the relative expression ratio of P-AKT/AKT in the hippocampal CA1 region. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD. #p < 0.05 compared to the control group; *p < 0.05, compared to the vehicle (W) group; ▲p < 0.05 compared to the Ly294002 group, n = 6.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: depression, xiaoyaosan, NR2B, PI3K/Akt pathway, hippocampal CA1 region, glutamate
Citation: Zhou X, Liu C, Liu Y, Ma Q, Zhao X, Jiang Y, Li X and Chen J-X (2022) Corrigendum: Xiaoyaosan alleviates hippocampal glutamate-induced toxicity in the CUMS rats via NR2B and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 13:1042762. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1042762
Received: 13 September 2022; Accepted: 05 December 2022;
Published: 15 December 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Yue Liu, Xiyuan Hospital, ChinaCopyright © 2022 Zhou, Liu, Liu, Ma, Zhao, Jiang, Li and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaojuan Li, bGl4aWFvanVhbkBqbnUuZWR1LmNu; Jia-Xu Chen, Y2hlbmppYXh1QGhvdG1haWwuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.