C1q/TNF-Related Protein 9 Attenuates Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting Hyperglycemia-Induced Endothelial Cell Senescence Through the AMPKα/KLF4 Signaling Pathway
- 1The Key Laboratory of Myocardial Ischemia Organization, Chinese Ministry of Education, Harbin, China
- 2Department of Cardiology Organization, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 3Department of Cardiology, Harbin Yinghua Hospital, Harbin, China
by Wang, G., Han, B., Zhang, R., Liu, Q., Wang, X., Huang, X., Liu, D., Qiao, W., Yang, M., Luo, X., Hou, J., and Yu, B. (2021). Front. Pharmacol. 12:758792. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.758792
In the original article, there was a mistake in the artwork for Figure 2C as published. We made a careless mistake about p21 protein. The correct artwork appears below.
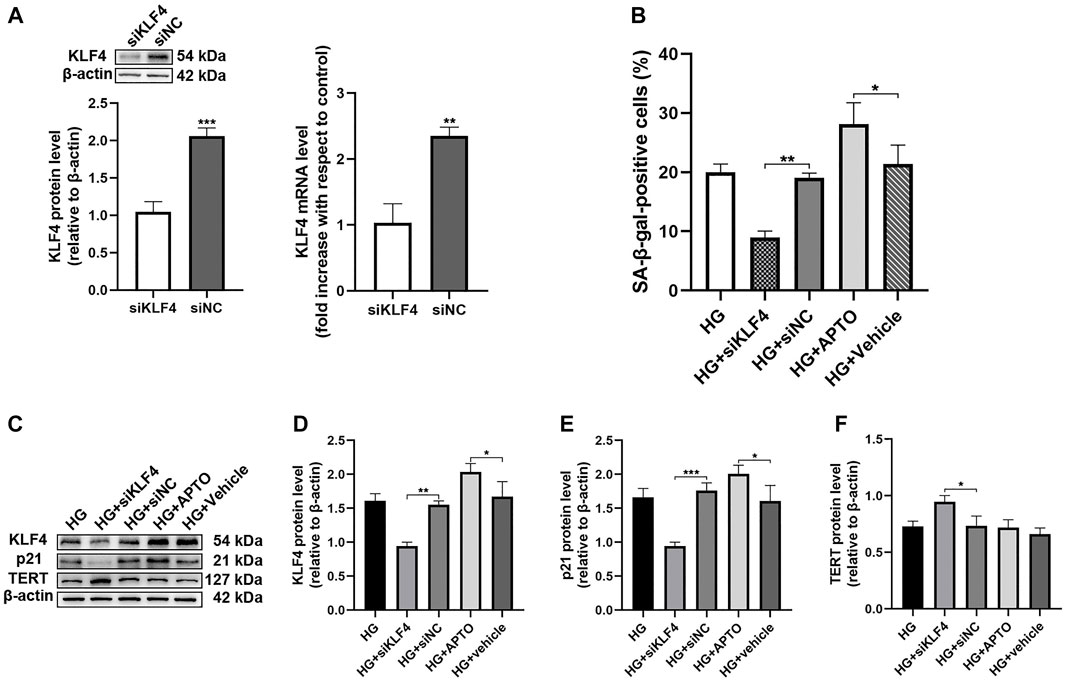
FIGURE 2. Hyperglycemia-induced HUVEC senescence is KLF4 dependent. (A) KLF4, as measured by immunoblotting and qRT-PCR in HUVECs after transfection with siNC or siKLF4 for 48 h. (B) Cells were fixed and stained for SA-β-gal activity and the histogram represents the percentage of SA-β-gal-positive cells per microscopic field. Values represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (C) KLF4, p21, and TERT protein levels were determined by immunoblotting. (D–F) Results were normalized to controls, and histograms represent the relative intensity of KLF4, p21, and TERT. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 3–4 per group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: CTRP9, atherosclerosis, senescence, hyperglycemia, AMPK, KLF4
Citation: Wang G, Han B, Zhang R, Liu Q, Wang X, Huang X, Liu D, Qiao W, Yang M, Luo X, Hou J and Yu B (2021) Corrigendum: C1q/TNF-Related Protein 9 Attenuates Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting Hyperglycemia-Induced Endothelial Cell Senescence Through the AMPKα/KLF4 Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12:812384. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.812384
Received: 10 November 2021; Accepted: 22 November 2021;
Published: 15 December 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Francesco Rossi, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, ItalyCopyright © 2021 Wang, Han, Zhang, Liu, Wang, Huang, Liu, Qiao, Yang, Luo, Hou and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jingbo Hou, jingbohou@163.com
 Gang Wang
Gang Wang Baihe Han1,2
Baihe Han1,2 Ruoxi Zhang
Ruoxi Zhang