The Combination of Schisandrol B and Wedelolactone Synergistically Reverses Hepatic Fibrosis Via Modulating Multiple Signaling Pathways in Mice
- 1Department of Hepatology, The Fifth Medical Centre, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2Research Center for Clinical and Translational Medicine, The Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3China Military Institute of Chinese Materia, The Fifth Medical Centre, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
A corrigendum on
The Combination of Schisandrol B and Wedelolactone Synergistically Reverses Hepatic Fibrosis via Modulating Multiple Signaling Pathways in Mice
by Ai, Y., Shi, W., Zuo, X., Sun, X., Chen, Y., Wang, Z., Li, R., Song, X., Dai, W., Mu, W., Ding, K., Li, Z., Li, Q., Xiao, X., Zhan, X., Bai, Z. (2021). Front. Pharmacol. 12:655531. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.655531
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 5 as published. The symbols (*, **, ***, ns) of statistic differences in Figures 5B–F were wrongly labeled. The wrongly labeled Figure 5 was uploaded by accident when submitting the corrections of proof. The corrected Figure 5 appears below.
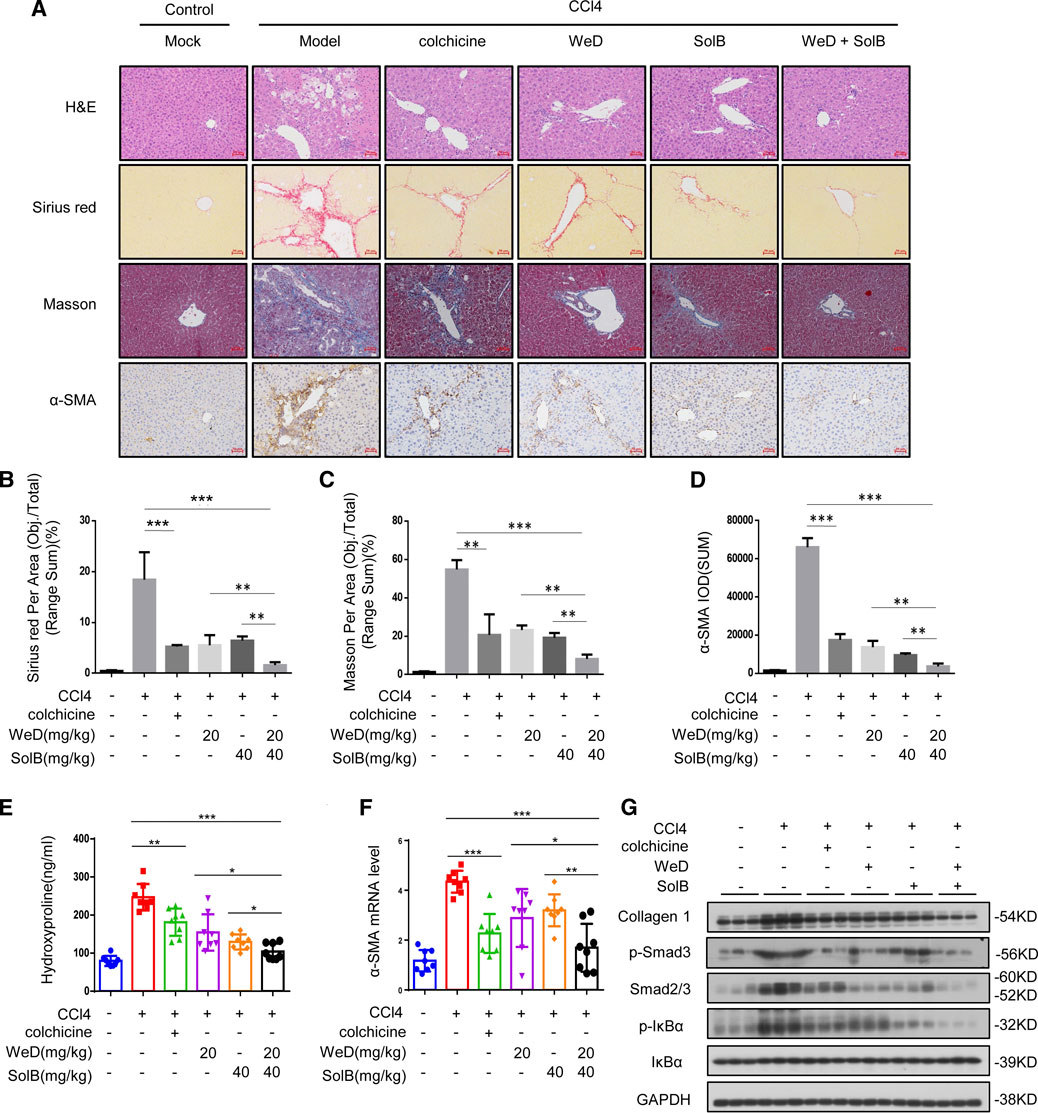
FIGURE 5. A combination of SolB and WeD treatment dramatically inhibits hepatic fibrosis and injury in CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice. (A) Images of livers from control, CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice, CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice treated with colchicine(0.2 mg/kg), SolB(40 mg/kg), WeD(20 mg/kg) or combination of SolB(40 mg/kg) and WeD(20 mg/kg). Representative micrographs of liver H&E staining, Sirius red, Masson and α-SMA staining were shown. Scale bars represent 50 μm. (B–D) Quantitative results of Sirius red(B), Masson(C) and α-SMA(D) staining sections. (E) Serum level of hydroxyproline of control, CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice, CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice treated with colchicine(0.2 mg/kg), SolB(40 mg/kg), WeD(20 mg/kg) or combination of SolB and WeD. (F) Quantitative PCR analysis of mRNA levels of α-SMA in livers from control, CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice, CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice treated with colchicine(0.2 mg/kg), SolB(40 mg/kg), WeD(20 mg/kg) or combination of SolB and WeD. (G) Western blot analysis of Collagen1, p-Smad3, Smad2/3, p-IκBα, IκBα and GAPDH in livers from control, CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice, CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mice treated with colchicine(0.2 mg/kg), SolB(40 mg/kg), WeD(20 mg/kg) or combination of SolB and WeD. Data are expressed as Mean ± SD (n = 8 or 3 mice). Statistics differences were analyzed using One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc tes: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. NS, no significance.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: schisandrol B, wedelolactone, hepatic fibrosis, combined pharmacotherapy, TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway
Citation: Ai Y, Shi W, Zuo X, Sun X, Chen Y, Wang Z, Li R, Song X, Dai W, Mu W, Ding K, Li Z, Li Q, Xiao X, Zhan X and Bai Z (2021) Corrigendum: The Combination of Schisandrol B and Wedelolactone Synergistically Reverses Hepatic Fibrosis via Modulating Multiple Signaling Pathways in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 12:777914. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.777914
Received: 16 September 2021; Accepted: 21 September 2021;
Published: 07 October 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Salvatore Salomone, University of Catania, ItalyCopyright © 2021 Ai, Shi, Zuo, Sun, Chen, Wang, Li, Song, Dai, Mu, Ding, Li, Li, Xiao, Zhan and Bai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhaofang Bai, baizf2008@hotmail.com; Xiaoyan Zhan, xyzhan123@163.com; Xiaohe Xiao, pharmacy_302@126.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yongqiang Ai1†
Yongqiang Ai1† Zhaofang Bai
Zhaofang Bai