
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 23 October 2020
Sec. Experimental Pharmacology and Drug Discovery
Volume 11 - 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01312
This article is part of the Research Topic Apoptosis Induction/Suppression: A Feasible Approach for Natural Products to Treatment of Diseases View all 29 articles
A correction has been applied to this article in:
Corrigendum: Ginsenoside Re attenuates high glucose-induced RF/6A injury via regulating PI3K/AKT inhibited HIF-1a/VEGF signaling pathway
 Weijie Xie1†
Weijie Xie1† Ping Zhou1†
Ping Zhou1† Muwen Qu2
Muwen Qu2 Ziru Dai1
Ziru Dai1 Xuelian Zhang1
Xuelian Zhang1 Chenyang Zhang1
Chenyang Zhang1 Xi Dong1
Xi Dong1 Guibo Sun1*
Guibo Sun1* Xiaobo Sun1*
Xiaobo Sun1*A Corrigendum on
Ginsenoside Re Attenuates High Glucose-Induced RF/6A Injury via Regulating PI3K/AKT Inhibited HIF-1a/VEGF Signaling Pathway
By: Xie W, Zhou P, Qu M, Dai Z, Zhang X, Zhang C, Dong X, Sun G and Sun X (2020). Front. Pharmacol. 11:695. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00695
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figures 3, 5 and 7 as published. The marked symbols “+” and “-”in Figures 3B, C, Figures 5C, D and Figure 7C were misplaced. The corrected Figures 3, 5 and 7 appear below.
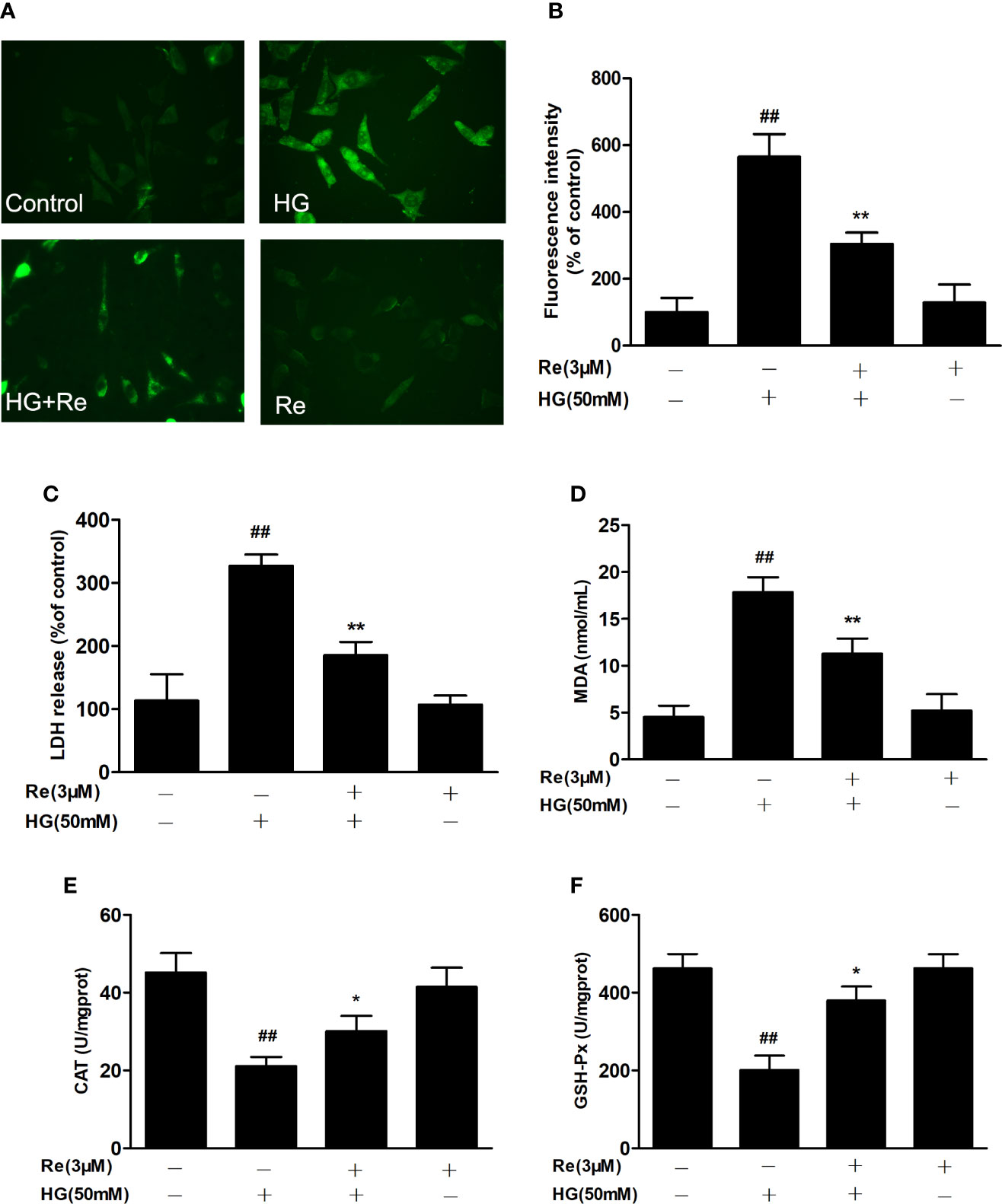
Figure 3 Ginsenoside Re attenuated HG-induced RF/6A cell injury and oxidative stress. (A) ROS levels were monitored using a fluorescence microscope. (B) Statistical analysis of ROS fluorescence intensity. The enzymatic activities of LDH (C), MDA (D), CAT (E), and GSH-Px (F) were detected by spectrophotometry. The data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 5). ##P < 0.01 versus the control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus the HG group. Scale bar, 50 μm.
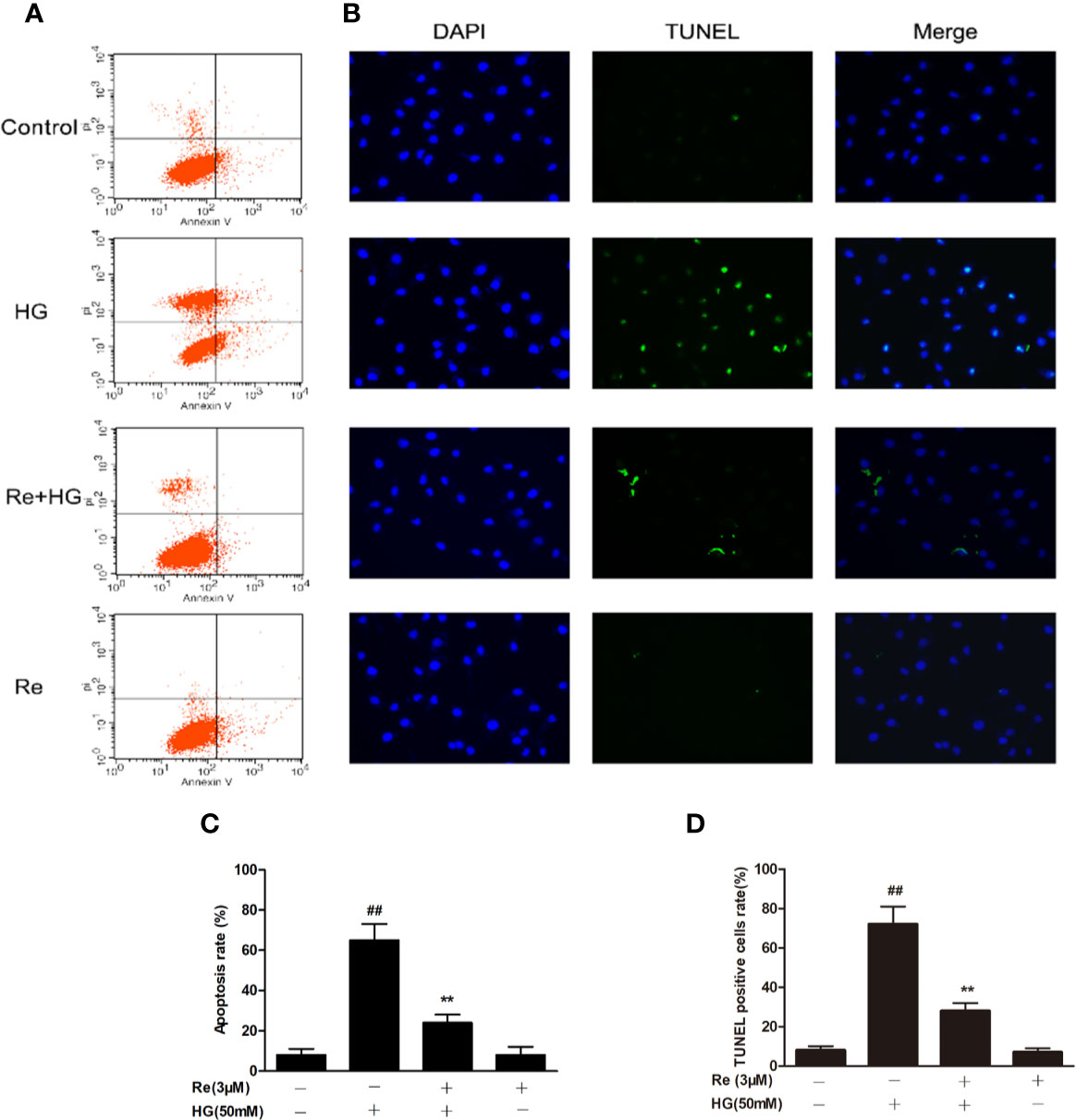
Figure 5 Effects of Ginsenoside Re on HG-triggered apoptosis in RF/6A cells. (A) Distribution map of apoptotic cells detected by annexin V/PI double staining. (B) Representative images captured with fluorescence microscopy showing TUNEL-stained RF/6A cells. (C) Quantitative analysis of the ratio of annexin V/PI-positive cells to total cells. (D) The ratio of TUNEL-positive cells. The results are expressed as the mean ± SE of the mean (n = 5). ##P < 0.01 versus the control group; **P < 0.01 versus the HG group. Scale bar, 50 μm.
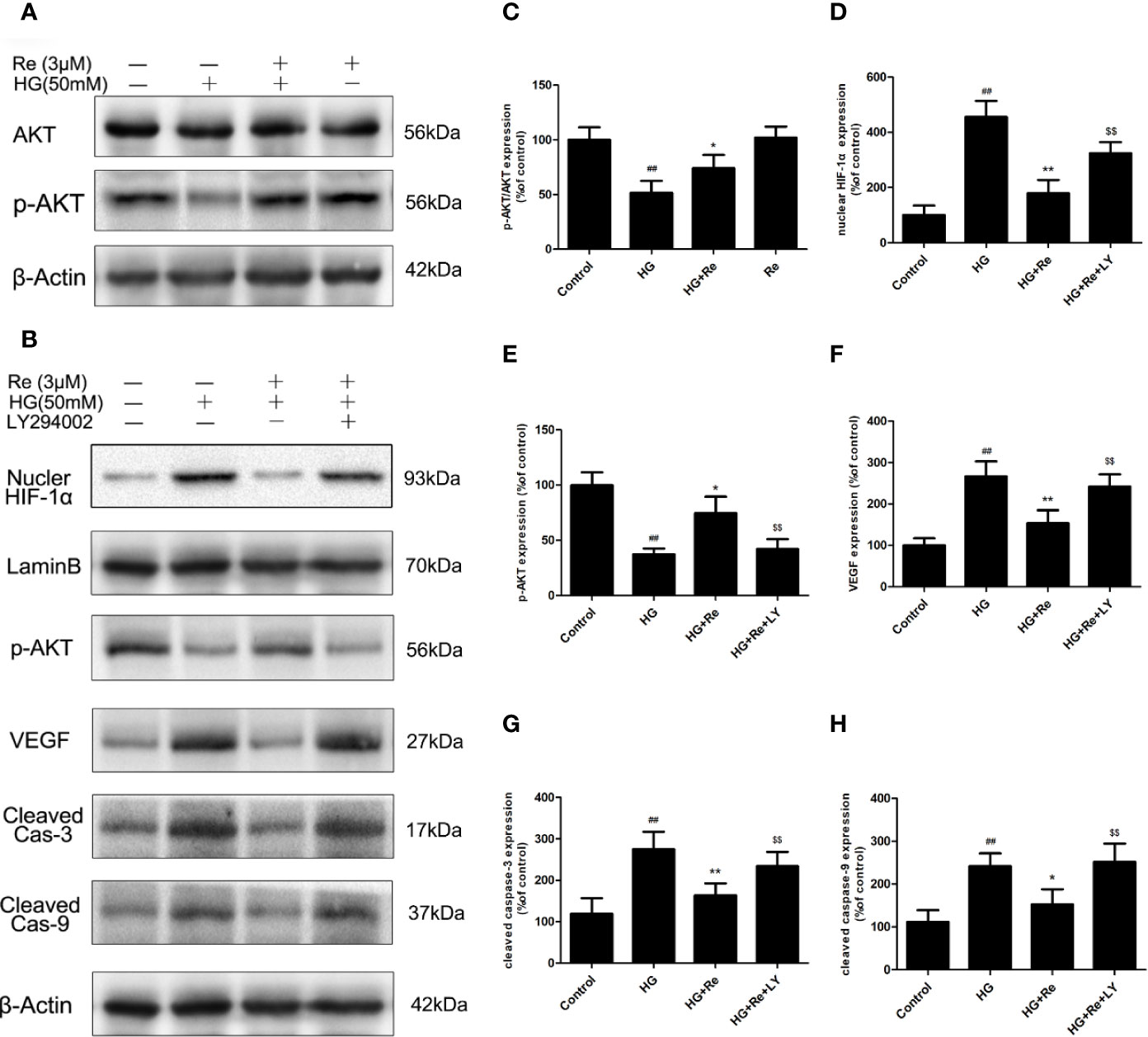
Figure 7 Re protects RF/6A cells via regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. (A) Akt and p-AKT expression detected by western blot. (B) The changes of related proteins after LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor) incubation. (C) Analysis of Akt and p-Akt expression. (D–H) Statistic analysis of related protein levels. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM percentage of the control from three independent tests. ##P < 0.01 versus the control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus the HG group; $$P < 0.01 versus the HG+Re group.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: ginsenoside Re, diabetic retinopathy, oxidative stress, apoptosis, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKTT, hypoxia-inducible factor-1-alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor
Citation: Xie W, Zhou P, Qu M, Dai Z, Zhang X, Zhang C, Dong X, Sun G and Sun X (2020) Corrigendum: Ginsenoside Re Attenuates High Glucose-Induced RF/6A Injury via Regulating PI3K/AKT Inhibited HIF-1a/VEGF Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 11:1312. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01312
Received: 01 July 2020; Accepted: 07 August 2020;
Published: 23 October 2020.
Edited and reviewed by: Wei Peng, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2020 Xie, Zhou, Qu, Dai, Zhang, Zhang, Dong, Sun and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guibo Sun, c3VuZ3VpYm9AMTI2LmNvbQ==; Xiaobo Sun, c3VueGlhb2JvcGFwZXJAMTYzLmNv
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.