
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol. , 21 February 2020
Sec. Pharmacology of Ion Channels and Channelopathies
Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01662
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a lethal inherited disease caused by mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, which result in impairment of CFTR mRNA and protein expression, function, stability or a combination of these. Although CF leads to multifaceted clinical manifestations, the respiratory disorder represents the major cause of morbidity and mortality of these patients. The life expectancy of CF patients has substantially lengthened due to early diagnosis and improvements in symptomatic therapeutic regimens. Quality of life remains nevertheless limited, as these individuals are subjected to considerable clinical, psychosocial and economic burdens. Since the discovery of the CFTR gene in 1989, tremendous efforts have been made to develop therapies acting more upstream on the pathogenesis cascade, thereby overcoming the underlying dysfunctions caused by CFTR mutations. In this line, the advances in cell-based high-throughput screenings have been facilitating the fast-tracking of CFTR modulators. These modulator drugs have the ability to enhance or even restore the functional expression of specific CF-causing mutations, and they have been classified into five main groups depending on their effects on CFTR mutations: potentiators, correctors, stabilizers, read-through agents, and amplifiers. To date, four CFTR modulators have reached the market, and these pharmaceutical therapies are transforming patients' lives with short- and long-term improvements in clinical outcomes. Such breakthroughs have paved the way for the development of novel CFTR modulators, which are currently under experimental and clinical investigations. Furthermore, recent insights into the CFTR structure will be useful for the rational design of next-generation modulator drugs. This review aims to provide a summary of recent developments in CFTR-directed therapeutics. Barriers and future directions are also discussed in order to optimize treatment adherence, identify feasible and sustainable solutions for equitable access to these therapies, and continue to expand the pipeline of novel modulators that may result in effective precision medicine for all individuals with CF.
In Memoriam: The author dedicates this review article to his youngest brother, Nilo Lopes Pacheco, who fought against CF for 26.5 years.
Mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene cause cystic fibrosis (CF)—the most common life-threatening autosomal recessive disease in Caucasian populations (Lopes-Pacheco, 2016). CFTR encodes a cAMP-dependent, phosphorylation-activated anion channel that transports chloride and bicarbonate across the apical plasma membrane (PM) of epithelial cells (Riordan, 2005; Saint-Criq and Gray, 2017). Furthermore, CFTR modulates the activity of other ion channels, such as the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) (Saint-Criq and Gray, 2017; Moore and Tarran, 2018). The absence or dysfunction of the CFTR protein at the PM leads to an impaired transepithelial balance of ions and fluid in cells of the sweat glands, airways, intestine, and pancreas, among other organs. Although CF is a multi-organ disease, the respiratory disorder represents the major cause of morbidity and mortality of these patients. A vicious cycle of mucus buildup in the airways, chronic inflammation, and recurrent infections leads to epithelial damage, tissue remodeling and progressive deterioration of lung function, ultimately resulting in respiratory failure (refer to Figure 4 in Lopes-Pacheco, 2016).
Archeological estimates indicate that the most prevalent CF-causing mutation, the deletion of a phenylalanine at position 508 (F508del), originated in Western Europe during the Early Bronze Age (Farrell et al., 2018). Although there are some archaic references regarding “children whose brow had salty taste when kissed and prematurely died”, CF remained uncharacterized until the 1930s. The first pathological description of the disease came in 1938 when Dorothy Anderson recognized CF as a separate entity from celiac syndrome after autopsy studies of malnourished infants, being then known as “cystic fibrosis of the pancreas” (Anderson, 1938). Another critical discovery was reported by Paul di Sant' Agnese in 1953 when he noticed that CF patients demonstrated an abnormal excess of salt in the sweat during a heat wave in New York (Di Sant'Agnese et al., 1953). Nevertheless, the decreased chloride transport and increased sodium reabsorption was described as a basic defect in CF epithelia in the 1980s by experiments using sweat duct cells (Knowles et al., 1983; Quinton, 1983; Boucher et al., 1986). Such findings served as basis for the sweat chloride test extensively used nowadays in CF diagnosis. Finally, the correlation between CF and the CFTR gene was discovered in 1989 when the gene was cloned by using chromosome walking and jumping, and linkage disequilibrium analysis (Kerem et al., 1989; Riordan et al., 1989; Rommens et al., 1989). Soon after, some reports demonstrated that CFTR-dependent chloride secretion could be restored by transfecting cells derived from CF patients with wild type (WT)-CFTR cDNA (Drumm et al., 1990; Rich et al., 1990).
The extensive knowledge obtained over this research path has enabled the early diagnosis and the discovery of more efficient and sophisticated therapies, resulting in increased life expectancy. In fact, the mean age of survival of CF has risen from early childhood in the 1960s to 40–50 years currently in several countries, although it still is much lower in certain regions worldwide. The “backbone” of CF treatment is symptomatic, focusing on the compensation of pancreatic insufficiency and intestinal malabsorption with pancreatic enzymes, fat-soluble vitamins, and high-calorie ingestion, as well as slowing lung function deterioration with physical and inhaled therapies to enhance airway clearance, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antibiotic therapy to eradicate infections (Cohen-Cymberknoh et al., 2011; Athanazio et al., 2017; Castellani et al., 2018). At late stages of disease, lung transplantation remains the only feasible intervention (Stephenson et al., 2017; Ramos et al., 2019), although still presenting a risk of cellular rejection (Calabrese et al., 2015). Furthermore, several comorbidities that were rare or not previously observed, including CF-related diabetes, metabolic bone and kidney disorders, and certain types of cancer, have become increasingly common as CF patients' lives have lengthened (Ronan et al., 2017). A tremendous effort has been made to continue optimizing the therapeutic regimens and the multidisciplinary healthcare in order to further enhance CF patients' life expectancy. Quality of life has also improved but patients are still subjected to substantial clinical, psychosocial and economic burdens.
Novel therapeutic approaches acting more upstream on the pathogenesis cascade have emerged (Lopes-Pacheco et al., 2019), including precision medicine with the discovery of drugs (termed CFTR modulators) that rectify the underlying defects of certain CFTR mutations. To date, four CFTR modulators have reached the market for the treatment of patients carrying specific CF-causing mutations and these breakthroughs have paved the way for the development of novel pharmacotherapies, which are currently under experimental and clinical investigations. This review provides a summary of recent developments in CFTR-directed therapeutics and sheds light on barriers that must be overcome for precision medicine efficiently to reach all individuals with CF.
CFTR is a long gene located on the long arm of chromosome 7, specifically in 7q31.2 (Figure 1). It is composed of 27 coding exons, spanning approximately 190 kb of human genomic DNA that is transcribed into a CFTR mRNA of 6.2 kb (Collins, 1992). Over 2,000 CFTR gene variants have been reported in the Cystic Fibrosis Mutation Database (CFTR1 Database). Many of them might be a variation in the DNA sequence eliciting neither a defect in CFTR mRNA or protein nor clinical symptoms. To date, 432 of these variants have been annotated in the Clinical and Functional Translation of CFTR (CFTR2 Database), of which 352 variants have confirmed disease liability and 46 variants have demonstrated variable clinical consequences. Many other variants are still uncharacterized, and in silico tools may be useful to predict the cellular and molecular consequences caused by these alterations (Michels et al., 2019; Pereira et al., 2019), while they are not confirmed in cell models. Some variants may also be pathogenic when two or more mutations are in cis, i.e., complex allele, thus contributing to the variable clinical phenotypes (Lucarelli et al., 2010; Diana et al., 2016; Pereira et al., 2019) and responsiveness to CFTR modulator therapies.
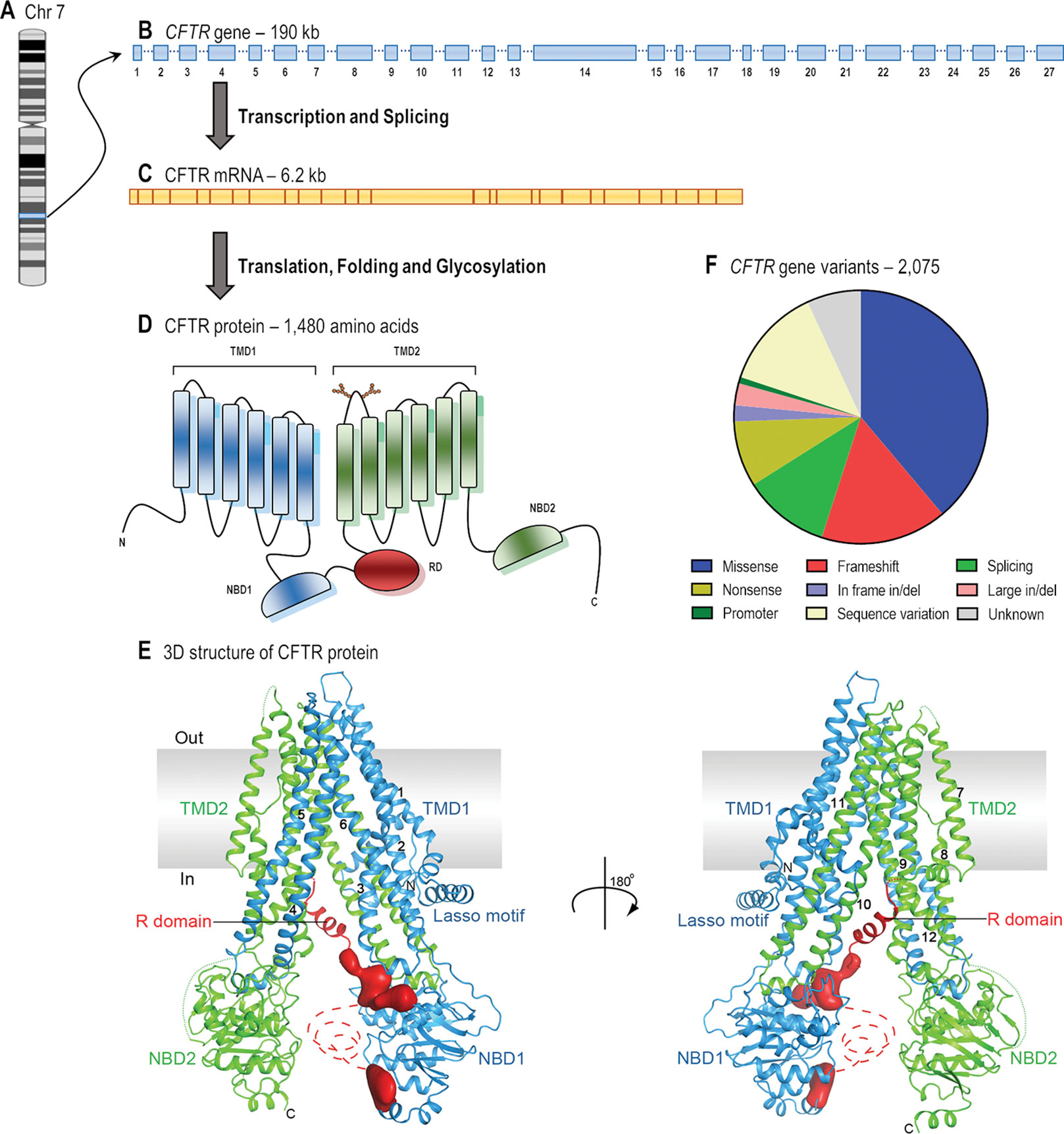
Figure 1 From gene to protein structure. (A) CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene is located on the long arm of chromosome (Chr) 7. (B) The gene contains 27 exons and spans approximately 190 kb of human genomic DNA. (C) The mRNA is 6.2 kb long including the untranslated regions (adapted from Collins, 1992). (D) The protein forms a chloride/bicarbonate channel composed of five domains: two transmembrane domains (TMD1 and TMD2), two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2) and a regulatory domain (RD) (adapted from Lopes-Pacheco, 2016). (E) The overall structure of human CFTR in the dephosphorylated, ATP-free conformation (adapted from Liu et al., 2017 with permission from Prof. J. Chen). (F) The 2,075 CFTR gene variants that have so far been reported consist of missense (38.9%), frameshift (16.1%), splicing (11.1%), and nonsense (8.4%) mutations; in-frame (2.1%) and large (2.8%) deletions or insertions; promoter mutations (0.9%); and possibly non-pathogenic variants (13.0%) (adapted from CFTR1 Database).
The CFTR mRNA translates into a 1,480-amino acid protein. Soon after co- and post-translational folding, and core glycosylation in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), CFTR protein traffics to the Golgi complex, where it is fully glycosylated. Thereafter, it is exported to the apical PM of epithelial cells, where it functions as a chloride and bicarbonate channel (Kim and Skach, 2012; Lukacs and Verkman, 2012).
The CFTR protein has five distinct domains: two transmembrane domains (TMD1 and TMD2), two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2), and a regulatory domain (RD). Each TMD contains six segments that completely cross the phospholipid bilayer and together they form the channel pore through which anions may flow (Riordan, 2005). The TM segments are joined by three extracellular loops and two intracellular loops in each TMD, and they have critical roles in CFTR biogenesis and in the post-translational folding in order to establish interdomain interactions required to achieve conformational stability (Kim and Skach, 2012). Furthermore, the fourth extracellular loop possesses two N-linked glycosylation sites (N894 and N900), which are assessed by the ER quality control during the protein folding process. These glycans are modified upon traversing the Golgi complex and may interact with extracellular macromolecules when the protein is located at the PM (Glozman et al., 2009; Lukacs and Verkman, 2012). The NBDs and the RD are exposed to the cytosol and are rich in charged residues. The NBDs present highly conserved sequence for ATP binding and hydrolysis, while the RD is highly disordered and has multiple consensus sequences containing serines and threonines for phosphorylation by protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC). ATP and cAMP-dependent PKA and PKC phosphorylation induce alterations in CFTR protein conformation, thus allowing anion conductance through the pore (Collins, 1992; Chappe et al., 2003; Saint-Criq and Gray, 2017). Among the 48 members of the human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family, CFTR (also known as ABCC7) is the unique one that possesses a RD and functions as an anion channel. Novel insights into channel opening and closure mechanisms have recently been elucidated with electron cryomicroscopy of the phosphorylated and dephosphorylated protein state (Liu et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2017; Fay et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2018; Liu F. et al., 2019). While these structures have not played a role in the development of CFTR modulators to date, such findings will be greatly useful for the identification of hotspots for drug-binding and for the application of rational design of next-generation modulator drugs based on the CFTR structure.
CF affects over 90,000 individuals and they are heterogeneously distributed worldwide (Figure 2). The F508del is the most prevalent CF-causing mutation, affecting approximately 82% of the CF population (Figures 3A, B). This mutation leads to CFTR protein misfolding that is arrested by the ER quality control, thus precluding its processing and trafficking to the PM, being instead targeted and prematurely degraded by proteasomes (Cheng et al., 1990; Jensen et al., 1995). Nevertheless, a small fraction of the mutant protein may evade the quality control checkpoints and reach the PM; however, it still presents a defective gating (Dalemans et al., 1991; Haws et al., 1996) and a considerable reduction in protein stability (Sharma et al., 2004; Swiatecka-Urban et al., 2005; Okiyoneda et al., 2010).
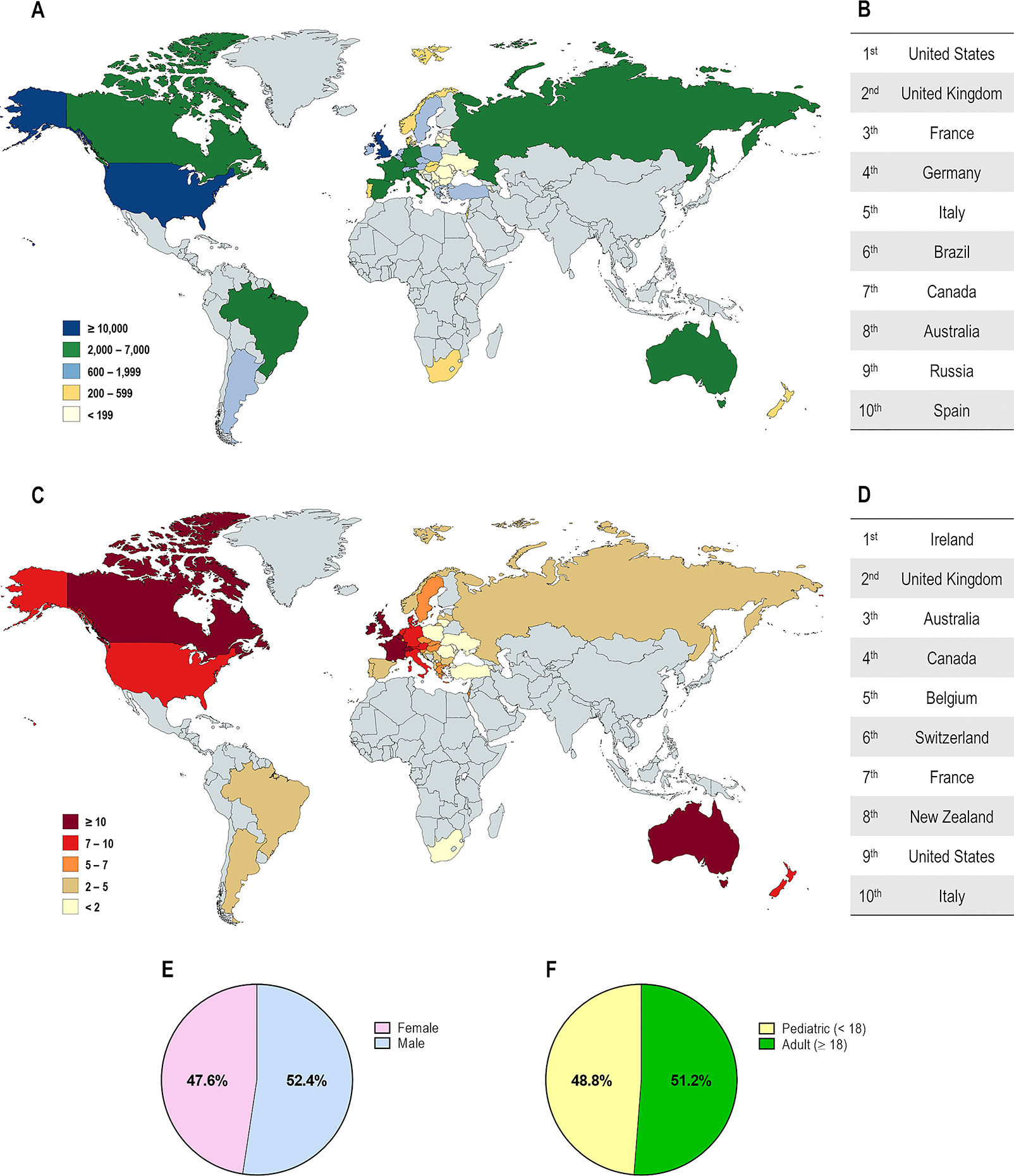
Figure 2 Demography of cystic fibrosis patients in different countries. (A) Distribution according to the total number of patients registered. (B) Top 10 countries with the highest number of patients registered. (C) Distribution according to the estimated prevalence of patients per 100,000 habitants. (D) Top 10 countries with the highest number of patients per 100,000 habitants. Global distribution by gender (E) and by age (F). [Data compiled from the last Patient Registry Report in Argentina (Pereyro et al., 2018), Australia (Cystic Fibrosis Australia, 2018), Brazil (Brazilian Cystic Fibrosis Study Group, 2019), Canada (Cystic Fibrosis Canada, 2019), Europe (European Cystic Fibrosis Society, 2019), New Zealand (Cystic Fibrosis New Zealand, 2019), South Africa (Zampoli et al., 2019), UK (Cystic Fibrosis Trust, 2019), and the USA (Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, 2019)].
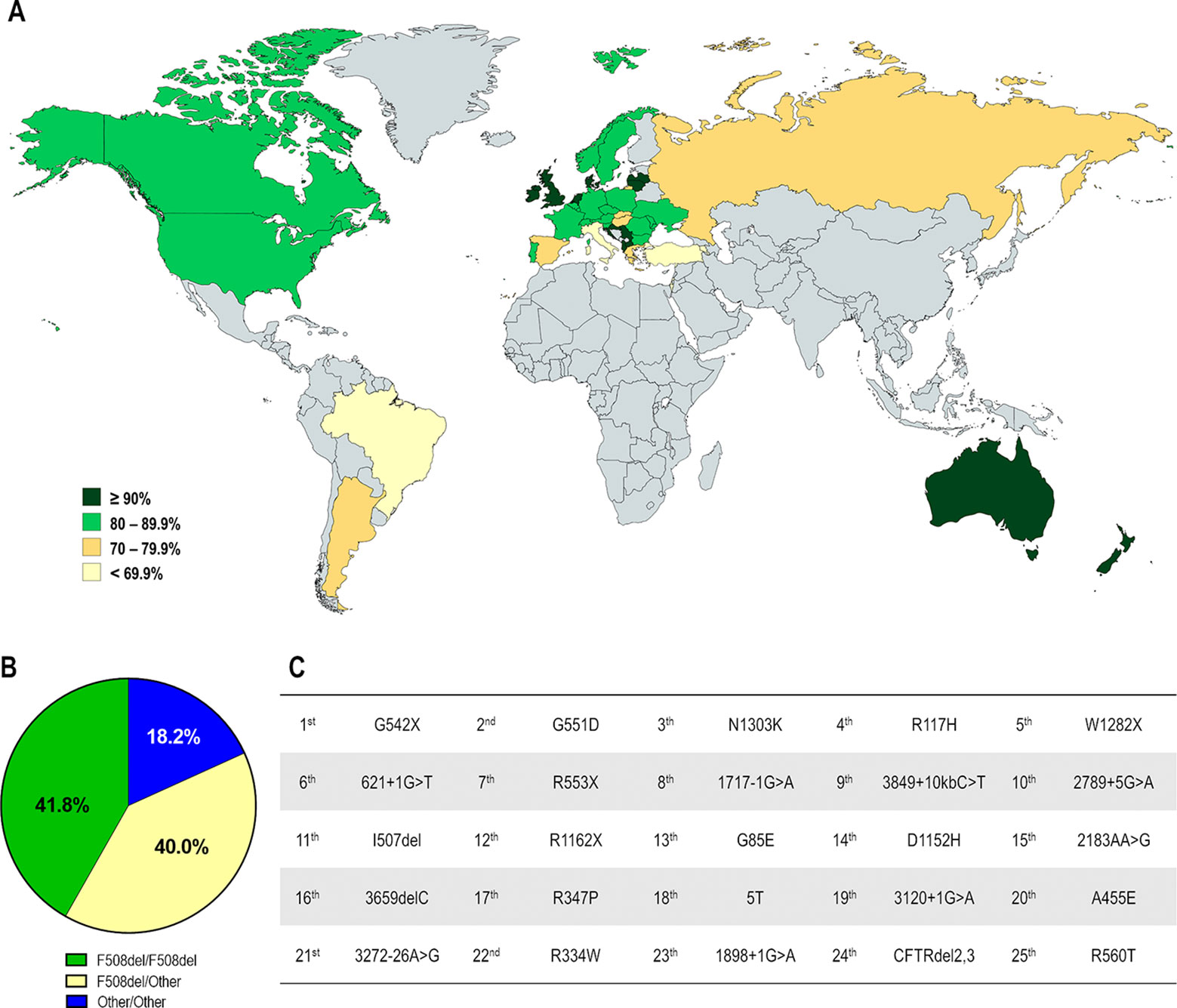
Figure 3 Demography of CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) mutations in different countries. (A) Distribution according to the percentage of patients carrying the F508del mutation in at least one allele. (B) Global distribution by CF genotype: F508del-homozygous, F508del-heterozygous and carrying non-F508del mutations in both alleles. (C) Top 25 most prevalent non-F508del CFTR mutations considering the whole CF population. [Data compiled from the last Patient Registry Report in Argentina (Pereyro et al., 2018), Australia (Cystic Fibrosis Australia, 2018), Brazil (Brazilian Cystic Fibrosis Study Group, 2019), Canada (Cystic Fibrosis Canada, 2019), Europe (European Cystic Fibrosis Society, 2019), New Zealand (Cystic Fibrosis New Zealand, 2019), UK (Cystic Fibrosis Trust, 2019), and the USA (Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, 2019), and CFTR2 Database].
The F508del mutation accounts for approximately 70% of CF alleles and other CFTR mutations are responsible for the remaining ones. Notably, most are rare or demonstrate a certain frequency in specific regions, and only six mutations present a prevalence ≥1% while approximately 50 mutations have a prevalence ≥0.1% considering the whole CF population (Figure 3C).
CFTR mutations may impair mRNA and protein expression, function, stability or a combination of these, and as such they have been stratified into different classes according to the primary molecular defect. The classification has historically been evolving according to the gained knowledge (Collins, 1992; Welsh and Smith, 1993; Wilschanski et al., 1995; Haardt et al., 1999; Rowe et al., 2005), and the current scheme is composed of six classes (Figure 4), although a seventh class has been proposed to separately consider large deletions that may abrogate production of CFTR mRNA (De Boeck and Amaral, 2016; Marson et al., 2016). Another system has also been proposed to take into account the pleiotropic defects of many CFTR mutations, including the F508del (Veit et al., 2016a). Although limitations in the classification system are evident, it has been useful in understanding the distinct cellular and molecular defects of different CFTR mutations as well as in the development of pharmacotherapies for specific defects (Figure 5).
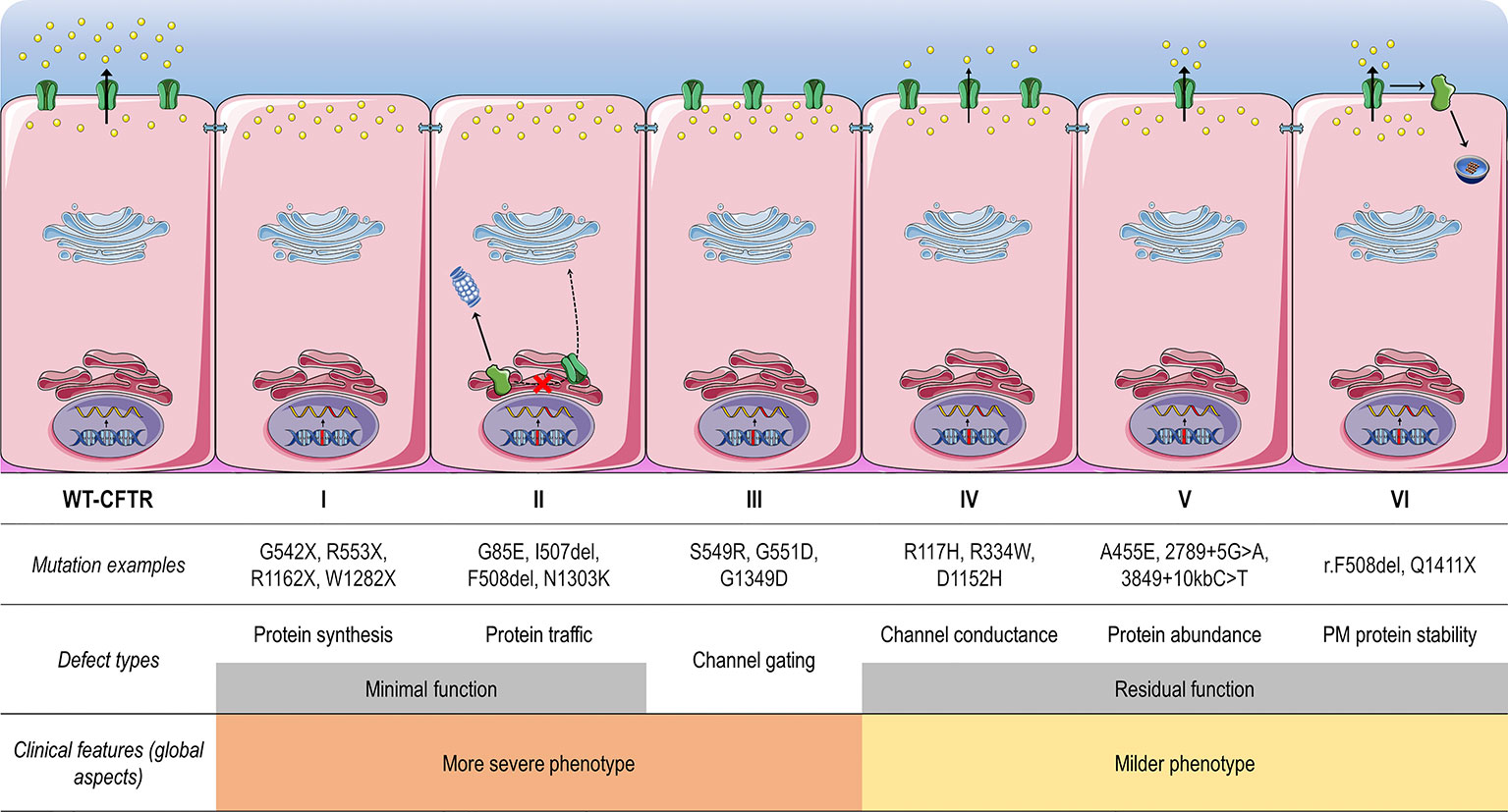
Figure 4 Classes of CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) mutations. Class I mutations lead to no protein synthesis or translation of shortened, truncated forms. They result from splice site abnormalities, frameshifts due to deletions or insertions, or nonsense mutations, which generate premature termination codons (PTCs). Class II mutations lead to a misfolding protein that fails to achieve conformational stability in the endoplasmic reticulum and then does not traffic to the plasma membrane (PM), being instead prematurely degraded by proteasomes. Class III mutations lead to a gating channel defect due to impaired response to agonists, although the protein is present at the PM. Class IV mutations lead to a channel conductance defect with a significant reduction in CFTR-dependent chloride transport. Class V mutations lead to a reduction in protein abundance of functional CFTR due to reduced synthesis or inefficient protein maturation. They result from alternative splicing, promoter or missense mutations. Class VI mutations lead to reduced protein stability at the PM, which results in increased endocytosis and degradation by lysosomes, and reduced recycling to the PM. Mutations in classes I and II are also known as minimal function mutations since they demonstrate no to very little CFTR function, while those in classes IV, V, and VI are known as residual function mutations since they demonstrate some CFTR function, although it is lower compared to the wild type (WT)-CFTR. (adapted from Lopes-Pacheco, 2016).
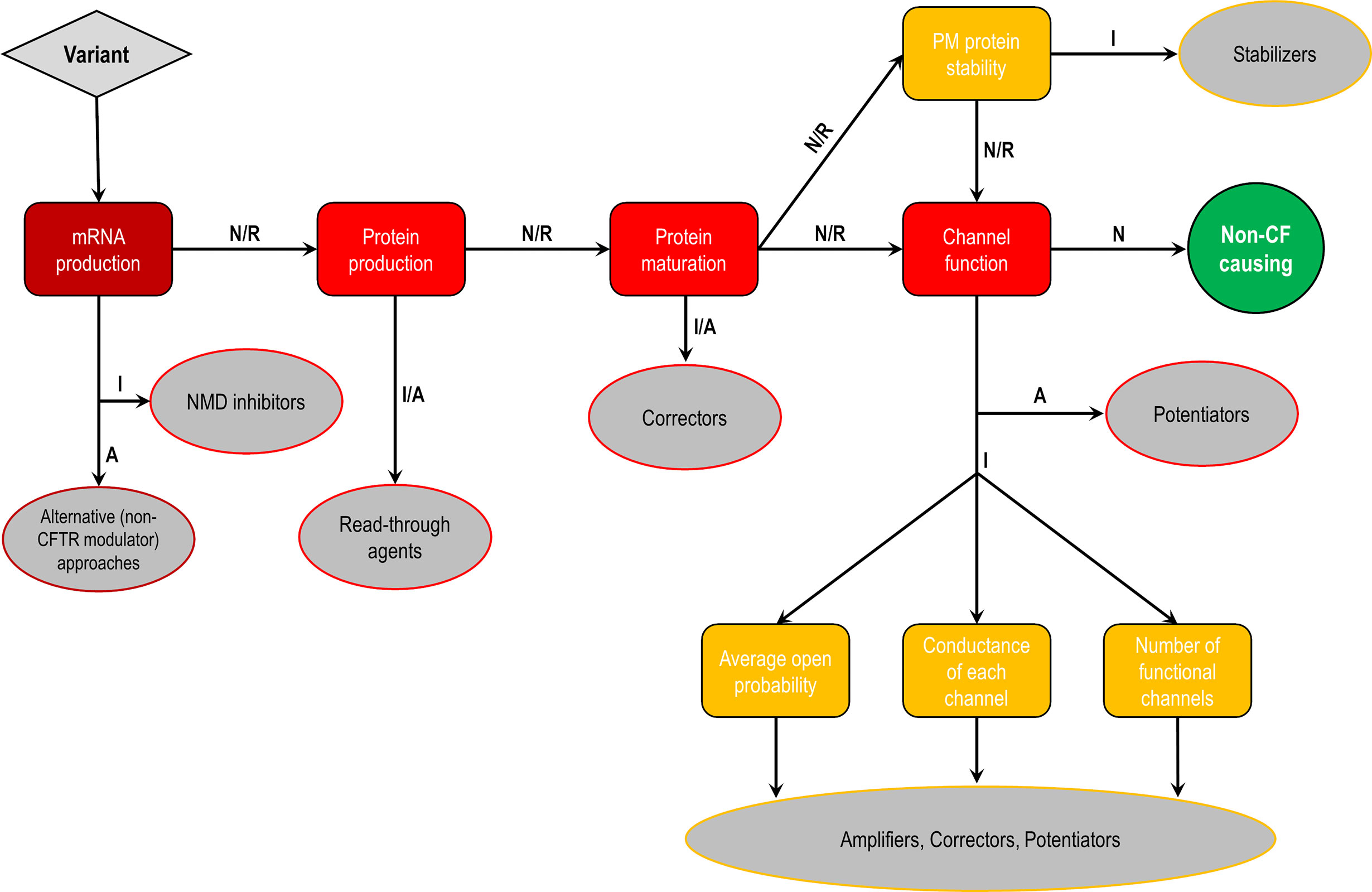
Figure 5 Cellular and molecular defects and potential CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulator approaches. Flowchart demonstrating the steps to identify each cellular and molecular defect of a CFTR gene variant and potential therapeutic approaches to correct each of these defects. Abbreviations: A, abrogated; I, impaired; N, normal; R, rescued.
Mutations in classes I, II, and III are usually associated with a classical and more severe disease, while those in classes IV, V, and VI are related to milder (or atypical) phenotypes. Individuals with CF may nevertheless carry different CFTR mutations on the two alleles, leading to thousands of possible combinations of CF genotypes. Noteworthy, CFTR mutations may differently respond to the same intervention (e.g., correction by low temperature or by chemical compounds), even for those classified as belonging to the same defect class (Rapino et al., 2015; Dekkers et al., 2016a; Dekkers et al., 2016b; Lopes-Pacheco et al., 2016; Lopes-Pacheco et al., 2017; Han et al., 2018; Awatade et al., 2019). Therapeutic responses may also differ between individuals carrying the same CF genotypes (Boyle et al., 2014; Donaldson et al., 2018a; Keating et al., 2018; Matthes et al., 2018). In fact, several other factors exert influence on disease severity beyond CFTR mutations, such as gene modifiers and epigenetic factors, social and economic status, patient's lifestyle, and adherence to therapies (Oates and Schechter, 2016; O'Neal and Knowles, 2018). Primary, reprogrammed and engineered human cell models have become important tools to identify novel pharmacotherapies. The effects of certain therapies may also be exploited at an individual level in ex vivo patient-derived specimens, such as primary bronchial/nasal epithelial cells, and intestinal/respiratory organoids (Fulcher and Randell, 2013; Dekkers et al., 2016a; Dekkers et al., 2016b; Pranke et al., 2017; Awatade et al., 2018; Brewington et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2018; Berkers et al., 2019; Merket et al., 2019). As these cell models recapitulate several features of the parental organ, they are useful to understand the impact of genetic factors on individual disease and predict clinical efficacy of therapies.
Numerous libraries of compounds have been screened by distinct high-throughput screening (HTS) methods and using several cell models. These experimental approaches have been contributing to the identification of small-molecules from different chemical series (Pedemonte et al., 2005a; Van Goor et al., 2009; Van Goor et al., 2011; Phuan et al., 2014; Phuan et al., 2015; Liang et al., 2017; Giuliano et al., 2018; Van der Plas et al., 2018; Veit et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2018; Berg et al., 2019; De Wilde et al., 2019; Merket et al., 2019) (Figure 6). Notably, as cell background may significantly influence the pharmacological rescue of CFTR mutants (Pedemonte et al., 2010), most promising hits should be further validated in well-differentiated cells in order to identify non-cytotoxic and effective compounds that might result in optimal therapeutic benefits in the clinical scenario.
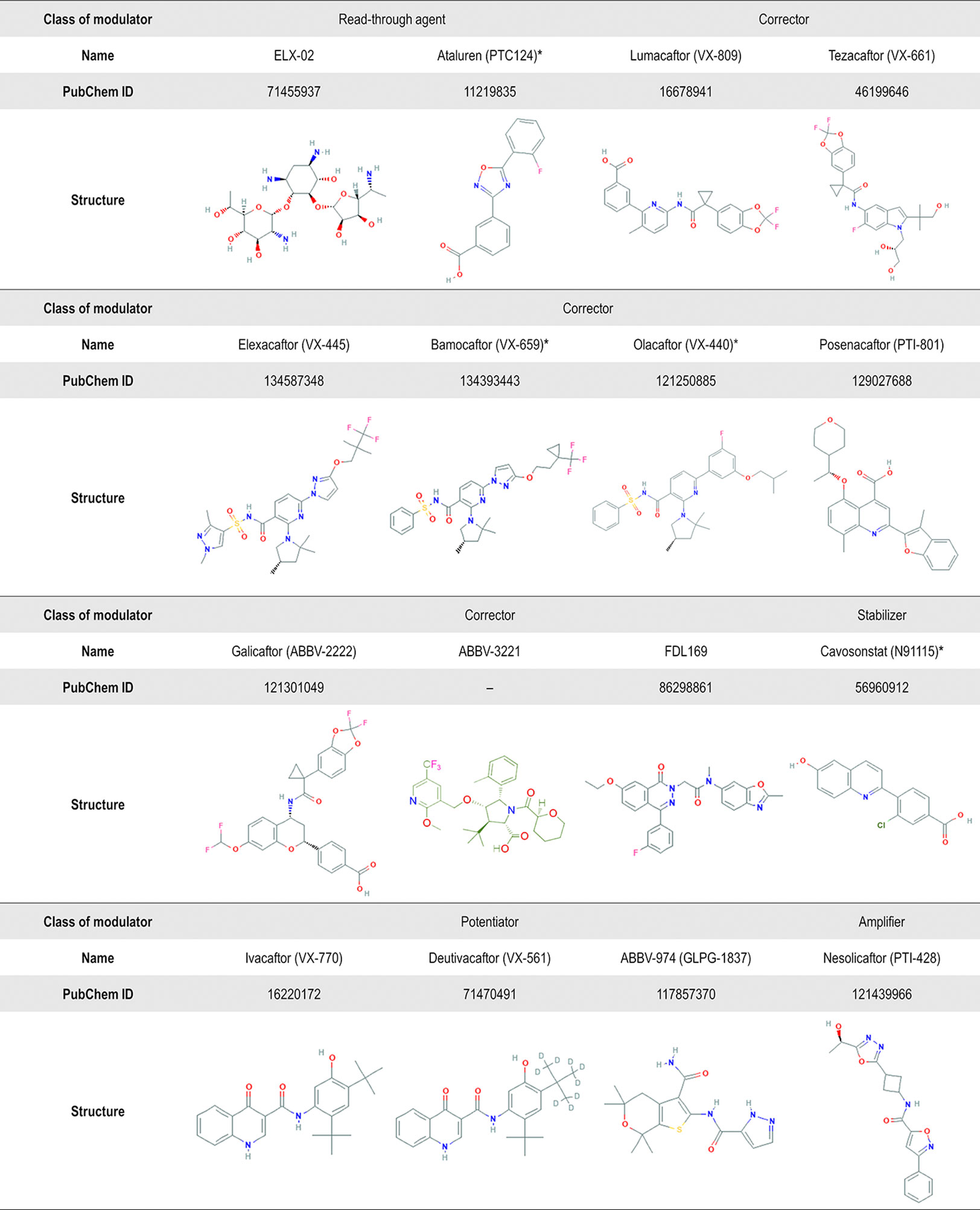
Figure 6 Chemical structure of several CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulators tested in clinical trials or currently in the market. Advances in high-throughput screening technologies have been enabling the identification of small-molecules from different chemical series. In addition to the compounds displayed in this figure, the compounds VX-121, ABBV-2737, ABBV-3067, FDL176, and PTI-808 are also under investigation in clinical trials, but the chemical structures are still not available on the PubChem or DrugBank. *Clinical development has been discontinued.
CFTR modulator drugs enhance or even restore the expression, function, and stability of a defective CFTR by distinct manners, and they have been classified into five main groups depending on their effects on CFTR mutations: potentiators, correctors, stabilizers, read-through agents, and amplifiers (Lopes-Pacheco, 2016). To date, four CFTR-directed modulators have reached the market for the treatment of CF patients carrying specific CFTR mutations (Ramsey et al., 2011; De Boeck et al., 2014; Wainwright et al., 2015; Rowe et al., 2017a; Taylor-Cousar et al., 2017; Heijerman et al., 2019; Middleton et al., 2019). Several clinical trials have been completed (Table 1) and many others are ongoing (Table 2) in extension/observational studies or to evaluate the safety and efficacy of novel modulators. As the experimental and clinical research in the CF field is moving at an accelerated pace, the most recent advances in precision medicine have been summarized below in order to update information previously published in the 2016 Review in Frontiers in Pharmacology (Lopes-Pacheco, 2016).
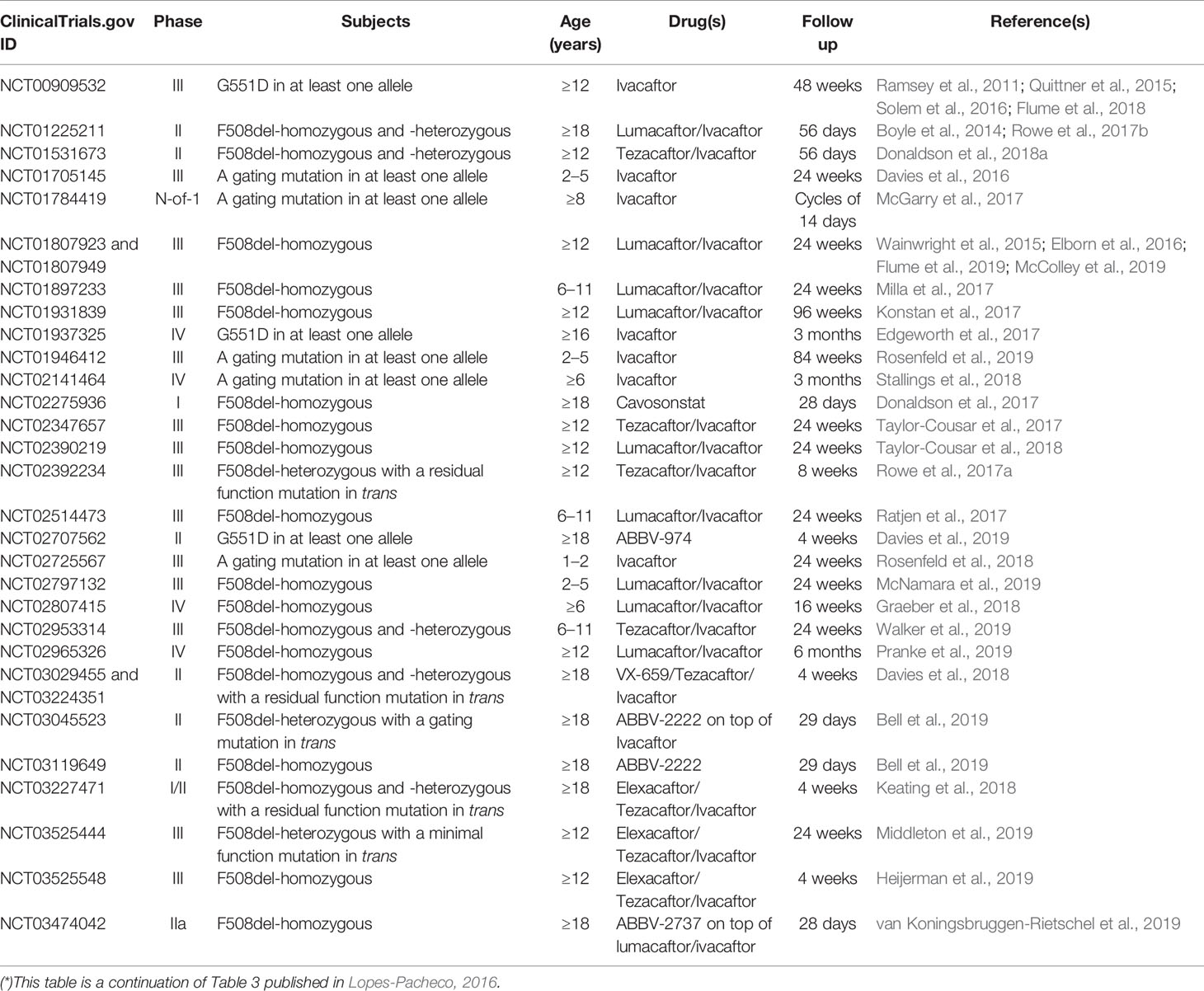
Table 1 Publications evaluating safety and efficacy and post-approval observational studies of CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulators in CF patients (*).
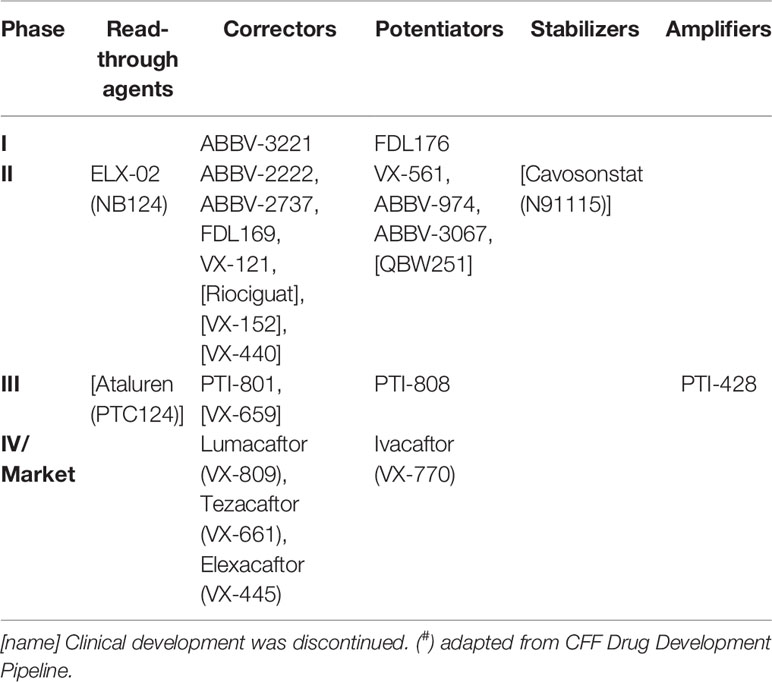
Table 2 Pipeline of CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulators in clinical trials and in the market (#).
Around 5% of CF-causing mutations lead to impaired CFTR channel gating or conductance as primary defects (Classes III and IV, Figure 4). The R117H, R334W, R347P, and G551D are among the most common mutations that cause such abnormalities and they are found in 1.3%, 0.3%, 0.4%, and 2.1% of CF alleles, respectively (CFTR2 Database). Potentiators are compounds that restore or even enhance the channel open probability, thus allowing for CFTR-dependent anion conductance (Lopes-Pacheco, 2016).
Initial studies demonstrated an enhancement of the open probability of certain CFTR variants in cells by using either chemically modified analogs of ATP or compounds that increase intracellular cAMP levels (Drumm et al., 1991; Illek and Fischer, 1998; Zhuo et al., 2005). However, their use in the clinics is limited due to potential modulation of multiple signaling pathways and physiological functions. Genistein is an isoflavone that binds to and inhibits protein-tyrosine kinase, resulting in increased intracellular cAMP levels, which leads to potentiation of CFTR activity in cell models (Illek and Fischer, 1998). However, clinical benefits were not clearly demonstrated when it was used in combination with 4-phenylbutyrate (NCT00590538). Other potentiators have been identified by cell-based HTSs but did not reach the clinical investigation for CF, such as the phenylglycine molecule PG-01 (Pedemonte et al., 2005b) and VRT-532 (Van Goor et al., 2006).
Ivacaftor (VX-770; Vertex Pharmaceuticals) is a potentiator identified by HTS that partially restored CFTR activity in G551D-expressing cell lines and in primary bronchial epithelial cells (Van Goor et al., 2009). Although the mechanisms of action of ivacaftor are not entirely elucidated, it was demonstrated to mediate CFTR channel potentiation in a phosphorylation-dependent and ATP-independent manner (Eckford et al., 2012; Cui et al., 2019). It binds and potentiates CFTR function by promoting decoupling between ATP hydrolysis and gating cycles (Jih and Hwang, 2013). Several studies have been proposing the putative binding site for ivacaftor by distinct methods. Some initial reports indicated that ivacaftor might bind to a region of amino acids at the NBD1/2 interface and the coupling helix of intracellular loop 1 (Veit et al., 2014) and/or the ‘ball-and-socket’ joint close to intracellular loop 4 (Byrnes et al., 2018). More recent studies provided direct evidence of the binding site of ivacaftor at the interface between TMDs by using electron cryomicroscopy and electrophysiological assays (Liu F. et al., 2019; Yeh et al., 2019). As chemical interactions are dynamic and the protein undergoes multiple conformational changes during channel opening and closure, some binding sites might also differ depending on the protein conformational state.
In 2012, both the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved the use of ivacaftor (Kalydeco®, Vertex Pharmaceuticals) for CF patients aged ≥6 years carrying at least one G551D mutation after a phase III trial showing that ivacaftor has successfully improved clinical outcomes (sweat chloride concentration, percent predict forced expiratory volume in 1 sec [ppFEV1], and others) (Ramsey et al., 2011). A similar effectiveness was also observed in patients carrying one G551D mutation who had a more severe impairment in lung function (Barry et al., 2014). Ivacaftor is on the market for over 7 years, and it is transforming patients' lives with sustained and long-term benefits, including reduction in sweat chloride to normal levels, slower deterioration of lung function, reduction in the number of pulmonary exacerbation episodes, less frequent detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (McKone et al., 2014; Heltshe et al., 2015) and other common pathogens (Frost et al., 2019), better body mass index (BMI) (Borowitz et al., 2016), exercise capacity and well-being (Edgeworth et al., 2017), and quality of life (Quittner et al., 2015; Sawicki et al., 2015). Furthermore, observational studies have demonstrated that ivacaftor improved pancreatic function and mucociliary clearance. Reduction in the levels of blood inflammatory biomarkers, and smooth muscle and lung structure abnormalities have also been observed (Adam et al., 2016; Hisert et al., 2017; Donaldson et al., 2018b; Ronan et al., 2018).
A subsequent series of experimental and clinical studies led to the extended approval of ivacaftor to treat CF patients carrying other gating mutations (Yu et al., 2012; De Boeck et al., 2014). Thereafter, another extension has been approved to include CFTR mutations with residual function based on in vitro studies (Durmowicz et al., 2018), totalizing 38 eligible CF-causing mutations and increasing the number of patients who may benefit from ivacaftor treatment (Table 3). Notably, the membrane CFTR conductance depends on the number of functional channels, the average open probability and conductance of each CFTR channel (Figure 5). Therefore, some splicing mutations have shown to respond to ivacaftor treatment due to an improvement of the last two determinants, even though presenting less protein abundance at the PM. More recently, ivacaftor treatment has been extended for CF patients aged ≥6 months carrying at least one of the listed mutations (Table 3) (Davies et al., 2016; Rosenfeld et al., 2018; Rosenfeld et al., 2019). In an animal model of CF, intrauterine and postnatal administration of ivacaftor also demonstrated to protect ferrets (G551D/G551D genotype) against development of multi-organ disease (Sun et al., 2019), indicating that starting the treatment in newly diagnosed children may increase the chances of improving long-term outcomes or even preventing the appearance of certain symptoms. Long-term use of ivacaftor has also been associated with a decreased need for lung transplant and improved survival (Bessonova et al., 2018; Volkava et al., 2019). Despite all demonstrated benefits, patients receiving ivacaftor may eventually experience pulmonary exacerbations, thus requiring hospitalizations and worsening quality of life (Solem et al., 2016). Furthermore, ivacaftor treatment does not improve the rate of complete lung function recovery after an exacerbation episode (Flume et al., 2018). Lung function also declines in the long term, albeit at a slower rate.
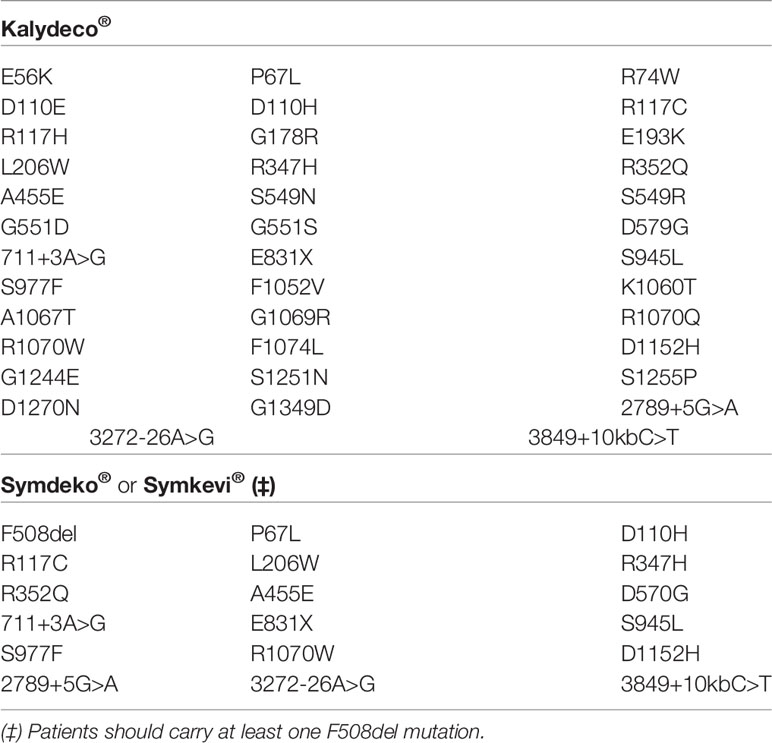
Table 3 List of CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) mutations eligible for the treatment with Kalydeco® and Symdeko®/Symkevi®.
Several novel potentiators have demonstrated promising effects and are currently under experimental and clinical investigations (Phuan et al., 2015; Park et al., 2016; Yeh et al., 2017; Gees et al., 2018). The potentiators VX-561 (deutivacaftor or formerly CTP-656; Vertex Pharmaceuticals) is a deuterated form of ivacaftor that demonstrated an enhanced stability in vitro and in healthy volunteers compared to ivacaftor (Harbeson et al., 2017), which would allow CF patients to take it once daily rather than twice as it has been the case with the ivacaftor. A phase II trial is in progress to comparatively evaluate the effects of VX-561 and ivacaftor in CF patients who have the following CFTR gating mutations in at least one allele: G178R, S549N, S549R, G551D, G551S, G1244E, S1251N, S1255P, or G1349D (NCT03911713).
The molecules ABBV-974, ABBV-2451, and ABBV-3067 (formerly GLPG-1837, GLPG-2451, and GLPG-3067, respectively) have been developed by Abbvie/Galapagos. ABBV-974 and ABBV-2451 have demonstrated greater and similar CFTR potentiation, respectively, in comparison with ivacaftor in R117H-, G178R-, S549N-, and G551D-expressing cells (Gees et al., 2018; Van der Plas et al., 2018). Interestingly, the simultaneous administration of ABBV-974 or ABBV-2451 with ivacaftor did not further enhance CFTR function, indicating that these molecules may act by the same mechanism of action (Yeh et al., 2017; Van der Plas et al., 2018). In fact, recent reports demonstrated that ABBV-974 and ivacaftor share a common binding site at the interface between the two TMDs near the kink of helix 8 (Liu F. et al., 2019; Yeh et al., 2019) (Figure 7). In a phase IIa trial, patients were subjected to a one-week ivacaftor washout before receiving three consecutive and increasing doses of ABBV-974. Although some adverse effects were observed in a dose-dependent manner, treatment was able to decrease sweat chloride concentration and improve ppFEV1 in CF patients carrying G551D-CFTR in at least one allele (Davies et al., 2019a).
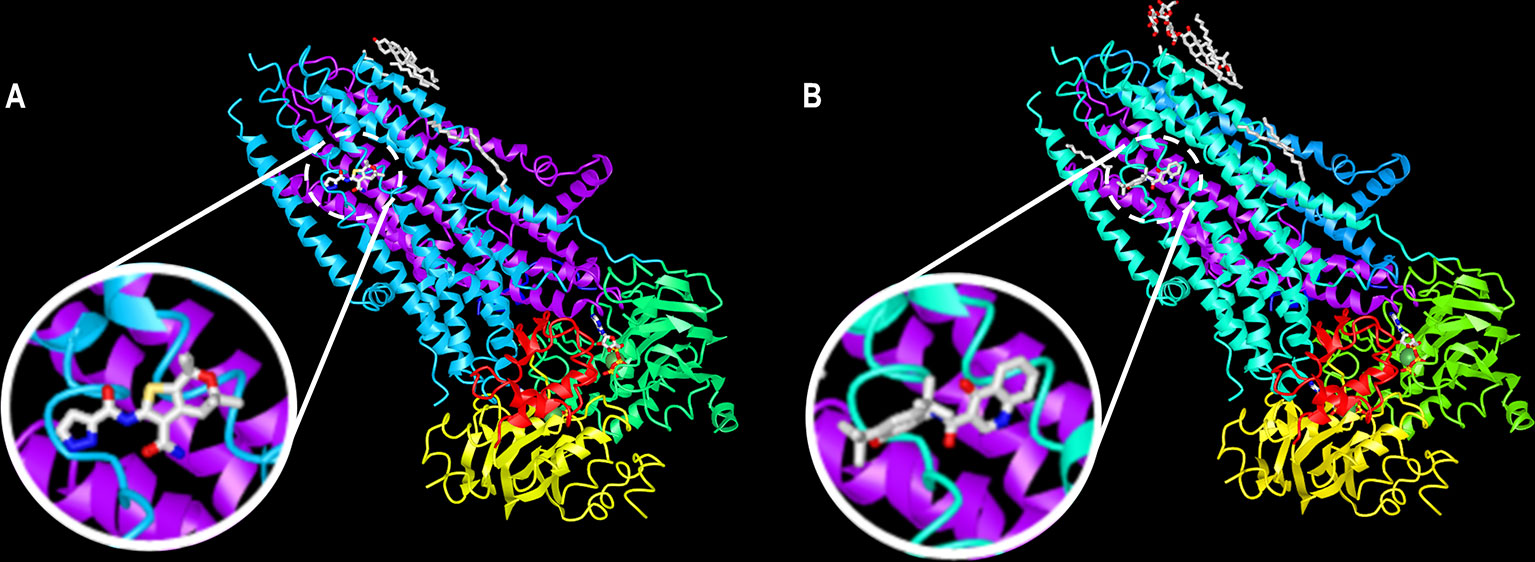
Figure 7 A common binding site for ABBV-974 and ivacaftor. Ribbon diagram of the phosphorylated, ATP-bound CFTR in complex with (A) ABBV-974 and (B) ivacaftor. These structures have been deposited on the Protein Data Bank under accession codes 6O1V (CFTR-ABBV-974) and 6O2P (CFTR-ivacaftor). (adapted from Liu F. et al., 2019 with permission from Prof. J. Chen).
The molecules FDL176 (Flatley Discovery Lab) and PTI-808 (dirocaftor; Proteostasis Therapeutics) are other potentiators being evaluated in early clinical trials (NCT03173573 and NCT03251092). The potentiator QBW251 (Novartis) was tested in both healthy volunteers and CF patients in a phase I/II clinical trial (NCT02190604). However, no significant improvements were observed in lung function of CF patients and adverse effects were also reported in many participants, resulting in early termination of this study. Recent studies have also demonstrated that co-administration of potentiators with complementary mechanisms of action may be an interesting approach for those CF-causing mutations in which CFTR gating/conductance is not completely restored by single potentiators (Phuan et al., 2018; Veit et al., 2019).
Most CF patients carry a mistrafficking CFTR mutation, since F508del is the most prevalent CF-causing mutation (Class II, Figure 4). Other common mutations that cause such abnormality are the G85E, I507del, R560T, and N1303K (found in 0.4%, 0.5%, 0.2%, and 1.6% CF alleles, respectively) (CFTR2 Database). Correctors are compounds that rescue folding, processing and trafficking to the PM of a CFTR mutant. While these compounds may act by distinct mechanisms, they usually enhance protein conformational stability during the ER folding process (Lopes-Pacheco, 2016).
New pharmacotherapies may target the defective CFTR structure directly by binding to the misfolding protein (termed as pharmacological chaperones) and/or indirectly by modulating its interaction with protein homeostasis (termed as proteostasis regulators), thus enabling the passage of CFTR protein through the ER quality control checkpoints (Lukacs and Verkman, 2012). Studies using genome- and proteome-wide association analyses have identified proteostasis components that could be targeted to rescue CFTR in F508del-expressing cells (Wang et al., 2006; Simpson et al., 2012; Tomati et al., 2018a). Furthermore, the recent identification of differences in WT- and F508del-CFTR interactomes unveiled several targets that could be exploited to rescue F508del (Pankow et al., 2015) and potentially other misfolding CFTR mutants (Hutt et al., 2018).
Initial studies were focused on certain proteostasis regulators, such as 4-phenylbutyrate (Rubenstein et al., 1997) and miglustat (Norez et al., 2006; Noël et al., 2008). Although these molecules demonstrated an increase in functional expression of F508del-CFTR in experimental models, only modest to no efficacy was found in early clinical studies (Zeitlin et al., 2002; Leonard et al., 2012). Several studies have also demonstrated a rescue of CFTR processing and trafficking to the PM in F508del-expressing cells by knocking down expression of certain proteostasis components, such as Aha1, an Hsp90 cochaperone (Wang et al., 2006), HDAC7 (Hutt et al., 2010), Hsp27 (Ahner et al., 2013; Lopes-Pacheco et al., 2015), and CFTR-associated ligand (CAL) (Bergbower et al., 2018), among others.
Advances in HTS technologies have been facilitating the fast-tracking of novel chemical compounds that act as proteostasis regulators and/or pharmacological chaperones (Pedemonte et al., 2005a; Van Goor et al., 2006; Noël et al., 2008; Kalid et al., 2010; Sampson et al., 2011). A classification of pharmacological chaperones has been proposed based on their molecular targets in the CFTR structure: class 1 correctors stabilize NBD1-TMD1 and/or NBD1-TMD2 interfaces; class 2 correctors stabilize NBD2 and its interfaces with other CFTR domains; and class 3 correctors directly stabilize NBD1 (Okiyoneda et al., 2013). This classification may be useful to evaluate corrector combinations with complementary mechanisms of action or targeting different defects in the mutant CFTR structure.
Lumacaftor (VX-809; Vertex Pharmaceuticals) is a first-generation corrector that demonstrated remarkable rescue of CFTR folding and function in F508del-expressing cell lines and primary bronchial epithelial cells (Van Goor et al., 2011). Other first-generation correctors had been identified previously but they were not suitable for the clinical practice due to a significant cytotoxicity and reduced efficacy (Pedemonte et al., 2005a; Van Goor et al., 2006). Some reports have suggested that lumacaftor has a putative binding site at the interface of NBD1 with the intracellular loop 4 in TMD2 (He et al., 2013; Okiyoneda et al., 2013; Hudson et al., 2017). Other studies have also indicated that lumacaftor acts on TMD1 and promote interactions between NBD1 and the intracellular loop 1 in TMD1 (Ren et al., 2013; Loo and Clarke, 2017; Laselva et al., 2018). While the identification of single putative binding site for small molecules, such as lumacaftor and ivacaftor, is important to unravel the mechanism(s) of action, multiple binding sites on the CFTR protein remain a possibility. Notably, lumacaftor was demonstrated to rescue ABCA4 trafficking mutants, another ABC transporter that shares approximately 45% homology with CFTR in NBDs (Sabirzhanova et al., 2015; Liu Q. et al., 2019).
Despite promising results in vitro, lumacaftor alone failed to demonstrate any improvement in lung function in F508del-homozygous patients in a phase IIa clinical study (Clancy et al., 2012). A significant, albeit modest, improvement in lung function (3%–4% in ppFEV1) was found only when lumacaftor was co-administered with ivacaftor in a following clinical trial (Boyle et al., 2014). Nevertheless, treatment with lumacaftor alone or in combination with ivacaftor was not able to improve ppFEV1 of F508del-heterozygous patients (Boyle et al., 2014; Rowe et al., 2017b). Certain adverse effects, such as chest tightness and dyspnea, have also been reported by both F508del-homozygous and -heterozygous patients in the early stage of the treatment.
In 2015, the FDA and the EMA approved the co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor (Orkambi®, Vertex Pharmaceuticals) for F508del-homozygous patients aged ≥12 years (Wainwright et al., 2015). Initial clinical trials usually tend to exclude patients with more severe disease, as they might present a more accelerated rate of decline in lung function (Habib et al., 2019). Nevertheless, F508del-homozygous patients with a more severe impairment of lung function were demonstrated to benefit from co-treatment initiation with lumacaftor/ivacaftor at a lower dose (Taylor-Cousar et al., 2019). Co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor was also demonstrated to benefit F508del-homozygous patients with distinct lung function impairment in a pooled analysis by subgrouping patients based on the FEV1 baseline (Elborn et al., 2016). Although the temporal process of recovery from pulmonary exacerbations may differ in each patient (Flume et al., 2019), co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor reduced the number of pulmonary exacerbation episodes even in patients without early lung function improvement (McColley et al., 2019). Furthermore, longer-term use of lumacaftor/ivacaftor has demonstrated continued benefits in patients, including improvement in BMI, reduction in the incidence of pulmonary exacerbations and hospitalizations, and slower deterioration of lung function (Konstan et al., 2017). Moreover, an observational study measured certain CFTR biomarkers — nasal potential differences and intestinal current measurements — and demonstrated that co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor results in partial correction of F508del-CFTR function to similar levels of the lower range of CFTR activity usually observed in patients with residual function mutations (Graeber et al., 2018). More recently, co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor has been extended for F508del-homozygous patients aged ≥2 years after phase III clinical trials demonstrating safety and efficacy in younger patients (Milla et al., 2017; Ratjen et al., 2017; McNamara et al., 2019). A clinical trial has also evaluated the effects of lumacaftor/ivacaftor in patients carrying A455E in at least one allele (NCT03061331), since this mutation has demonstrated an increase in CFTR PM abundance and function after corrector treatments in cell models (Dekkers et al., 2016a; Dekkers et al., 2016b; Lopes-Pacheco et al., 2016).
Lumacaftor has demonstrated different efficiency and potency in rescuing other CFTR mutations causing protein misfolding. In cell lines, lumacaftor was able to rescue CFTR function for E92K, L1077P, and M1101K, although it had no effect on G85E, R560S, and N1303K (Avramescu et al., 2017; Lopes-Pacheco et al., 2017; Awatade et al., 2019). The correction effects were also variable in patients-derived specimens carrying the F508del mutation in one allele and a minimal function mutation in trans (i.e., in the second allele); the mutants A561E, Y1092X, and W1282X demonstrated a response to lumacaftor treatment (Awatade et al., 2014; Haggie et al., 2017), but no effect was found for E60X, 394delTT, 711-1G>T, G542X, 1717-1G>A, and N1303K, among others (Awatade et al., 2014; Dekkers et al., 2016a; Pranke et al., 2017). Even for F508del-homozygous patients, co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor resulted in significant but variable clinical responsiveness (Boyle et al., 2014; Wainwright et al., 2015). The routine use of patient-specific biomarkers could be an effective approach to pre-clinically evaluate the safety and efficacy of certain pharmacotherapies and predict effectiveness at an individual level.
Notably, interaction between lumacaftor and ivacaftor revealed to negatively impact the rescue of F508del-CFTR protein. Chronic ivacaftor exposure (>1 µM) reduces lumacaftor-rescued CFTR in F508del-expressing cells (Cholon et al., 2014; Veit et al., 2014), although lower concentrations of ivacaftor (≤1 µM) may prevent such negative effect (Matthes et al., 2016). Lumacaftor also triggers cytochrome P450 3A4 activation, resulting in reduced plasma concentration of ivacaftor (Scheneider, 2018). Such findings might partially explain the modest efficacy observed in co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor in clinical trials. It also highlights the relevance of better evaluating drug-drug and drug-protein interactions for combined therapies. Recent studies have searched for potentiators of F508del-CFTR that do not interfere with lumacaftor actions (Phuan et al., 2015). Other studies have also identified genes of which either silencing or inhibition induce further lumacaftor-stimulated F508del-CFTR rescue, including RNF5 (Tomati et al., 2015; Sondo et al., 2018), FAU (Tomati et al., 2018a), and RFFL (Okiyoneda et al., 2018). Suppression of RPL12, a component of 60S subunit P stalk, was also demonstrated to rescue folding and function of F508del and other CFTR mutants by modulating ribosome velocity. CFTR rescue was increased when lumacaftor was concurrently administered (Veit et al., 2016b; Oliver et al., 2019).
Individuals with CF are susceptible to infection by distinct opportunistic pathogens, including Aspergillus spp., Burkholderia cepacia, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Some studies have demonstrated that CFTR modulator therapies may reduce P. aeruginosa infection in clinics (McKone et al., 2014; Heltshe et al., 2015; Wainwright et al., 2015). Co-administration of lumacaftor/ivacaftor in vitro also reduced pro-inflammatory responses induced by P. aeruginosa exoproducts in well-differentiated human bronchial epithelial cells (F508del/F508del genotype) (Ruffin et al., 2018). Nevertheless, P. aeruginosa infection was demonstrated to reduce lumacaftor- and lumacaftor/ivacaftor-stimulated CFTR activity in F508del-expressing cells (Stanton et al., 2015). On the other hand, exposure of cells to supernatant from mucopurulent material derived human CF lung resulted in greater rescue of F508del-CFTR by lumacaftor (Gentzsch et al., 2018). As both inflammation and infection may influence responses to modulator therapies, further research is needed to better understand such differences as well as to evaluate the effect of these therapies on infection caused by other pathogens.
Tezacaftor (VX-661; Vertex Pharmaceuticals) is a second-generation corrector developed based on lumacaftor structure but demonstrating better pharmacokinetic properties and fewer adverse effects. In clinical trials, co-treatment with tezacaftor/ivacaftor demonstrated comparable therapeutic outcomes (sweat chloride concentration, ppFEV1, and others) to those with lumacaftor/ivacaftor in F508del-homozygous patients (Taylor-Cousar et al., 2017; Donaldson et al., 2018a). For F508del-heterozygous patients with a residual function mutation in trans, co-treatment with tezacaftor/ivacaftor was more effective, demonstrating even better improvements in ppFEV1 in comparison to treatment with ivacaftor only (Rowe et al., 2017a). In 2018, the FDA and the EMA approved the co-treatment with tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Symdeko® or Symkevi®, Vertex Pharmaceuticals) for patients aged ≥12 years who are F508del-homozygous or F508del-heterozygous with a residual function mutation in trans (Table 3). In following phase III clinical trials, co-treatment of tezacaftor/ivacaftor was demonstrated to reduce sweat chloride concentration and preserve lung function with relatively low respiratory symptom burden (Walker et al., 2019). Such findings served as basis for the extended approval of tezacaftor/ivacaftor for patients aged ≥6 years. Extension clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate the longer-term effects of tezacaftor/ivacaftor (NCT03537651) and the safety and efficacy in younger children.
As the dual combinations lumacaftor/ivacaftor and tezacaftor/ivacaftor demonstrated only modest efficacy in F508del-homozygous patients, Vertex Pharmaceuticals performed additional HTSs to identify next-generation correctors that act by different mechanisms and could therefore yield additive/synergistic effects in triple-combination regimens. Tezacaftor/ivacaftor was selected as the backbone for the triple combination based on the more favorable pharmacological properties, including lower cytochrome P450 3A activation (Rowe et al., 2017a; Taylor-Cousar et al., 2017; Donaldson et al., 2018a). Four novel correctors — VX-152, VX-440, VX-445, and VX-659 — demonstrated a pronounced improvement of CFTR activity when co-administered with tezacaftor/ivacaftor in human bronchial epithelial cells (F508del/F508del genotype). In early-stage clinical studies, all four triple combinations presented evidence of therapeutic benefits to relatively similar degrees (NCT02951195, NCT02951182, NCT3029455, and NCT03227471). Nevertheless, two compounds (VX-445 [or elexacaftor] and VX-659 [or bamocaftor]) demonstrated more suitable pharmacological properties and safety profiles for long-term use, making them better candidates for subsequent clinical studies. Both triple combinations — tezacaftor/ivacaftor/VX-445 and tezacaftor/ivacaftor/VX-659 — were safe, with most adverse effects being mild to moderate, and led to a reduction of sweat chloride concentration and incidence of pulmonary exacerbations in phase II and III trials. A significant increase in ppFEV1 was also found after triple-combination regimens in F508del-homozygous patients (up to 11.0% for the combination with VX-445 and 9.7% for the combination with VX-659 compared to tezacaftor/ivacaftor only) and F508del-heterozygous patients with a minimal function mutation in trans (up to 14.3% for the combination with VX-445 and 13.3% for the combination with VX-659 compared to placebo) (Davies et al., 2018; Keating et al., 2018; Heijerman et al., 2019; Middleton et al., 2019; Taylor-Cousar et al., 2019). In fact, the magnitude of therapeutic responses with triple-combination regimens was even greater than the benchmark achieved by ivacaftor alone in patients with a G551D-CFTR mutation (up to 10.6% in ppFEV1) (Ramsey et al., 2011; McKone et al., 2014; Donaldson et al., 2018a) or other gating mutations (De Boeck et al., 2014). The triple combination tezacaftor/ivacaftor/VX-445 (Trikafta™, Vertex Pharmaceuticals) has been recently approved by the FDA for the treatment of CF patients aged ≥12 years with the mutation F508del in at least one allele. Furthermore, other clinical trials are in progress to evaluate the long-term effects of this triple combination in patients who are F508del-homozygous or F508del-heterozygous with a minimal function mutation in trans (NCT03525574, NCT04043806, NCT04058366) as well as the safety and efficacy in younger patients (NCT03691779, NCT04183790). Another clinical study is also ongoing to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this triple-combination regimen in F508del-heterozygous patients with a gating or residual function mutation in trans (NCT04058353).
Other compound combinations have been evaluated in order to enhance the correction of F508del-CFTR, but only modest effects were observed in several experimental studies (Okiyoneda et al., 2013; Phuan et al., 2014; Lopes-Pacheco et al., 2015). A rational design for combinatory corrector therapy resulted in the discovery of small-molecule from different chemical series — 6258, 3151, and 4172 — that target defects at NBD1, NBD2, and TMD interfaces. Although the individual administration of these compounds was demonstrated to modestly rescue the functional expression of F508del-CFTR, the combination of three compounds resulted in greater effects than lumacaftor alone. The effects of this triple combination on F508del-CFTR reached ~50-100% of WT-level correction in cell lines, patient-derived specimens, and in mouse nasal epithelia. Moreover, this triple combination significantly increased protein folding efficacy of rare mutations across different CFTR domains (Veit et al., 2018).
Several novel correctors are being developed in collaboration between pharmaceutical companies and academic laboratories. The molecules FDL169 and FLD1737 have been investigated by Flatley Discovery Lab. FDL169 has demonstrated a rescue of CFTR PM expression in F508del-expressing cells with similar efficacy as lumacaftor but with no additive effects when they were co-administered, suggesting that these correctors may act by the same mechanisms. Nevertheless, ivacaftor had lesser inhibitory effect on FDL169 activity than on lumacaftor. The safety profile of FDL169 is under clinical investigation alone and in combination with the potentiator FDL176 (NCT02768297, NCT03093714, NCT03756922). Riociguat (Bayer), a soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator, was demonstrated to improve CFTR function in experimental studies. Although no safety concerns were identified in F508del-homozygous patients in a phase II trial (NCT02170025), the clinical development of this molecule has been terminated for CF.
The molecules ABBV-2222, ABBV-2737, ABBV-2851, ABBV-3221, and ABBV-3748 (formerly GLPG-2222, GLPG-2737, GLPG-2851, GLPG-3221, and GLPG-3748, respectively) are among the most promising correctors developed by Abbvie/Galapagos. ABBV-2222 (or galicaftor) has a similar chemical structure to lumacaftor and tezacaftor but was reported to be more potent. It was also highly functional in primary bronchial epithelial cells from a F508del-homozygous patient (Wang et al., 2018; Singh et al., 2019). ABBV-2737 was demonstrated to rescue functional expression of CFTR in F508del-expressing cells, and such effects were enhanced when it was co-administered with lumacaftor or ABBV-2222 (de Wilde et al., 2019). ABBV-3221 also rescued CFTR function in F508del-expressing cells with a greater effect in combination with ABBV-2222 and ABBV-974 (Scanio et al., 2019). In phase IIa clinical trials, ABBV-2222 reduced sweat chloride concentrations but did not improve ppFEV1 in F508del-homozygous patients or F508del-heterozygous patients with a gating mutation and receiving ivacaftor (Bell et al., 2019). Based on previous studies evaluating drugs with a similar mechanism of action in F508del-homozygous patients (Clancy et al., 2012; Boyle et al., 2014; Wainwright et al., 2015), a substantial improvement in lung function would be unusual for a single corrector. Nevertheless, such approach allows a better evaluation of the safety profile for the following studies with combined therapies. In this line, other clinical studies are in progress to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ABBV-2222 alone and in combination with ABBV-2737 and ABBV-2451 (NCT03540524) or with ABBV-3067 (NCT03969888). ABBV-2737 was also investigated for F508del-homozygous patients and on stable treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor in a phase IIa trial. A small improvement in ppFEV1 (3.6%) and a significant reduction in sweat chloride concentration were found in patients that received ABBV-2737 compared to placebo cohort (van Koningsbruggen-Rietschel et al., 2019).
The molecule PTI-801 (posenacaftor; Proteostasis Therapeutics) — a third-generation corrector — has demonstrated higher efficacy compared to first- and second-generation correctors (e.g., lumacaftor and tezacaftor) with additive/synergistic effects when they were co-administered in vitro. PTI-801 was also less sensitive to the ivacaftor-mediated decrease on CFTR function. In a phase I trial, PTI-801 was demonstrated to significantly reduce sweat chloride concentration, and improve ppFEV1 and BMI in F508del-homozygous patients receiving lumacaftor/ivacaftor therapy. Another phase I clinical trial is in progress in healthy volunteers and CF patients (NCT03140527). The corrector VX-121 (Vertex Pharmaceuticals) is also in early-stage clinical trials to evaluate the effects in CF patients receiving ivacaftor or tezacaftor/ivacaftor (NCT03768089) and in combination with tezacaftor, ivacaftor, and/or VX-561 (NCT03912233).
Although certain CFTR mutants are functional and present at the PM, the protein may still display a significant reduction in half-life (Haardt et al., 1999) (Class VI, Figure 4), probably due to accelerated endocytosis (Swiatecka-Urban et al., 2005) and/or reduced recycling (Sharma et al., 2004). Low temperature incubation rescues CFTR in F508del-expressing cells (r.F508del) (Denning et al., 1992), but the protein still demonstrates reduced stability and is rapidly removed by peripheral quality control mechanisms (Okiyoneda et al., 2010). In fact, environmental stresses may also lead to destabilization and internalization of WT-CFTR (Bomberger et al., 2012; Patel et al., 2019). Stabilizers are agents that anchor CFTR at the PM, thus preventing its removal and degradation by lysosomes (Fukuda and Okiyoneda, 2018).
Lumacaftor demonstrated to rescue functional expression of CFTR in F508del-expressing cells, but it does not confer long-term stability similar of that in WT-CFTR (He et al., 2013). Therefore, novel treatments have been investigated, alone or in combination, to rectify the intrinsic protein instability and thus prolong CFTR residence time at the PM (Fukuda and Okiyoneda, 2018). Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) was demonstrated to promote CFTR stabilization at the PM in F508del-expressing cells by activating Rac1 GTPase signaling and thus inducing CFTR interaction with Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 1 (NHERF1) (Moniz et al., 2013). Co-administration of HGF and lumacaftor has further enhanced CFTR maturation and anchoring at the PM (Loureiro et al., 2015). Prolonged HGF treatment also prevented ivacaftor-mediated destabilization of lumacaftor-rescued CFTR in F508del-expressing cells (Matos et al., 2018). Other strategies have demonstrated to enhance the PM stabilization of mutant CFTR protein, including administration of vasoactive intestine peptide (VIP) (Alshafie et al., 2014), activation of exchange factor directly activated by cAMP 1 (EPAC1) (Lobo et al., 2016), and inhibition of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase (Zaman et al., 2016) or CFTR-associated ligand (CAL) (Cusing et al., 2010; Bergbower et al., 2018). More recently, keratin-19 was also demonstrated to stabilize WT-CFTR and lumacaftor-rescued F508del at the PM by decreasing Rab7-mediated lysosomal degradation (Hou et al., 2019).
Cavosonstat (N91115; Nivalis) was the first CFTR stabilizer being tested in clinical trials. It was demonstrated to promote CFTR maturation and PM stability by inhibiting S-nitrosoglutathione reductase in vitro. In a phase I trial, cavosonstat demonstrated no safety concerns with the highest dose yet reducing sweat chloride concentration in F508del-homozygous patients (Donaldson et al., 2017). Nevertheless, cavosonstat failed to demonstrate any additional benefit in lung function and sweat chloride concentration when in combination with lumacaftor/ivacaftor or ivacaftor in phase II trials (NCT02589236 and NCT02724527). The clinical development of cavosonstat has been terminated for CF.
A significant fraction of the CF-causing mutations are in-frame nonsense, frameshift, and splicing variants that introduce a premature termination codon (PTC) into the CFTR mRNA, thus abrogating CFTR protein synthesis or resulting in translation of shortened, truncated forms (Class I, Figure 4). PTCs are also subjected to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), resulting in substantial decrease in the quantity of CFTR transcripts (Nguyen et al., 2014; Sharma N. et al., 2018). Around 10% of CF patients worldwide carry a PTC mutation, with G542X and W1282X being the most common PTC variants found in CF alleles (2.5% and 1.2%, respectively) (CFTR2 Database). Read-through agents are compounds that induce a ribosomal “over-reading” of a PTC, enabling the incorporation of a foreign amino acid in that place and thus the continued translation to the normal end of the transcript (Pranke et al., 2018).
Read-through effects were first found in aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as gentamicin and geneticin. Gentamicin is also commonly used to eradicate P. aeruginosa infection in CF patients. In both cell lines and transgenic mice, these compounds demonstrated the ability to promote expression of full-length CFTR and partially restore CFTR-dependent chloride secretion (Howard et al., 1996; Du et al., 2002). Furthermore, gentamicin improved nasal potential difference after administration either topically on the nasal mucosa (Wilschanski et al., 2003) or intravenously (Sermet-Gaudelus et al., 2007) in patients carrying a CFTR PTC mutation. Despite such findings, gentamicin and geneticin cannot be used as read-through agents in the clinics, since high systemic levels or long-term use may result in severe nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity (Prayle et al., 2010). Advances in the rational design of chemically modified aminoglycosides have enabled the identification of read-through agents with higher activity and less toxicity (Rowe et al., 2011; Kandasamy et al., 2012). In this line, ELX-02 (NB124; Eloxx Pharmaceuticals) has demonstrated to restore CFTR function in cells expressing any of the four most prevalent PTC mutations — G542X, R553X, R1162X, and W1282X. Moreover, ELX-02 was less cytotoxic than gentamicin in a model for ototoxicity (Xue et al., 2014). In phase I clinical trials with healthy volunteers, ELX-02 was well tolerated and exhibited a favorable safety profile, although mild side effects were also reported (Leubitz et al., 2019). Early-stage clinical trials are in progress to evaluate the effects of multiple dose escalation of ELX-02 in CF patients carrying the G542X mutation in at least one allele (NCT04126473, NCT04135495).
Ataluren (PTC124; PTC Therapeutics) was identified by HTS (Welch et al., 2007), and demonstrated to restore CFTR expression and function in transgenic mice expressing human G542X (Du et al., 2008). Despite therapeutic effects observed in phase II clinical trials (Sermet-Gaudelus et al., 2010; Wilschanski et al., 2011), ataluren treatment only demonstrated a favorable trend, albeit not significant, to improve ppFEV1 of CF patients carrying a nonsense CFTR mutation in at least one allele in a phase III clinical trial (Kerem et al., 2014). A new phase III trial was undertaken to exclude patients taking inhaled tobramycin, since it could interfere with ataluren actions on the ribosome; however, no improvements were observed in ppFEV1 and pulmonary exacerbations (NCT02139306). Although ataluren (Translarna®, PTC Therapeutics) is approved for the treatment of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, its clinical development has been terminated for CF. Other studies have performed HTSs to identify potential read-through agents for the various PTC mutations (Mutyam et al., 2016; Liang et al., 2017).
In addition to read-through agent-induced efficacy, the abundance of CFTR transcripts and the activity of the recoded protein are other factors that should be considered in order to efficiently rescue a PTC mutant (Pranke et al., 2018). The number of transcripts may considerably differ depending on the identity (amber, ochre, or opal) and position of the termination codon as well as cell type and patient's genetic background (Nguyen et al., 2014; Pranke et al., 2018; Sharma N. et al., 2018; Clarke et al., 2019), and association of an NMD inhibitor with a read-through agent may result in better therapeutic efficacy. In this line, amlexanox (Gonzalez-Hilarion et al., 2012) and escin (Mutyam et al., 2016) are drugs already approved for unrelated diseases that demonstrated dual activity by concomitantly increasing the abundance of target transcripts and read-through efficacy for certain CFTR PTC mutations. Furthermore, incorporation of a foreign amino acid may result in full-length but misfolded and/or nonfunctional proteins. PTC suppression in combination with other modulators, such as lumacaftor and/or ivacaftor, has demonstrated to promote a further rescue of expression and function of CFTR PTC mutations (Xue et al., 2014; Mutyam et al., 2016; Mutyam et al., 2017; Xue et al., 2017; Pranke et al., 2018; Sharma N. et al., 2018). These approaches should be exploited in future clinical studies.
A nucleic acid therapeutic has been developed for CF-causing nonsense mutations. RCT101 (ReCode Therapeutics) is a modified transfer RNA (tRNA) that is delivered into cells by nanoparticles to precisely recode the translating CFTR protein. In experimental studies, RCT101 demonstrated an increase in CFTR-dependent chloride secretion in primary bronchial epithelial cells carrying either G542X/G542X or G542X/F508del. Such effects were even greater when combined with lumacaftor/ivacaftor.
Some CF-causing mutations lead to reduction in the synthesis or maturation of CFTR protein. The 3849+10kbC>T, 2789+5G>A, and A455E are common mutations that cause such abnormalities (Class V, Figure 4) and are found in 0.8%, 0.7%, and 0.4% of the CF alleles, respectively (CFTR2 Database). Amplifiers are compounds that increase expression of CFTR mRNA and, consequently, biosynthesis of the CFTR protein (Giuliano et al., 2018).
The PTI-428 (nesolicaftor; Proteostasis Therapeutics) is the first-in-class amplifier investigated in clinical trials. It was demonstrated to selectively increase the expression of immature CFTR protein carrying different mutations without eliciting alteration in the expression of cellular stress response genes (Giuliano et al., 2018). PTI-428 also enhanced the rescue of CFTR in F508del- and ΔI1234_R1239-expressing cells when co-administered with lumacaftor/ivacaftor (Molinski et al., 2017; Giuliano et al., 2018). Furthermore, the triple combination PTI-428/PTI-808/PTI-801 enhanced the CFTR-dependent chloride secretion to almost normal levels in F508del-expressing cells. In phase I/II clinical trials (NCT03500263), this triple combination regimen resulted in significant reduction of sweat chloride concentration and improvement of lung function (8% in ppFEV1) compared to placebo in F508del-homozygous patients, being the greatest effects observed in those individuals with high disease burden. Based on these results, a phase III trial is planned to begin in early 2020. In F508del-heterozygous patients, the triple combination PTI-428/PTI-808/PTI-801 demonstrated a more variable change in sweat chloride concentration and lung function. These modulator drugs have also been tested in intestinal organoids of patients carrying rare CF genotypes in the HIT-CF project and the crossover clinical trial based on the individual responses is expected to initiate in the middle of 2020. Other early-stage clinical trials are in progress to evaluate the safety and efficacy of PTI-428 in CF patients on stable treatment with ivacaftor (NCT03258424), lumacaftor/ivacaftor (NCT02718495), or tezacaftor/ivacaftor (NCT03591094).
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are chemically-modified synthetic RNA-like molecules that act by complementary base pairing to the target sequence. ASOs have been demonstrating promising results to correct nonsense and splicing mutations or even to replace missing bases caused by deletion mutations, such as the F508del.
ASOs corrected the aberrant splicing in a cell line expressing the 2789+5G>A mutation minigene. Such correction resulted in recovery of CFTR protein levels at the PM (Igreja et al., 2016). Recently, ASOs developed by SpliSense have also demonstrated to correct aberrant splicing and restore CFTR function in a 3849+10kbC>T-expressing cell line and in primary bronchial epithelial cells (3849+10kbC>T/F508del genotype).
The mutant W1282X is subjected to NMD, thus resulting in significant reduction of CFTR mRNA abundance. Nevertheless, it still produces a certain amount of the truncated forms of both partially and fully glycosylated CFTR protein that may respond to CFTR modulators (Haggie et al., 2017; Aksit et al., 2019). ASOs designed to downregulate the serine/threonine-protein kinase SMG-1, a factor involved in the NMD pathway, led to upregulation of mRNA, protein maturation and traffic to the PM of the truncated CFTR products in W1282X-expressing cells. Furthermore, these ASOs increased CFTR-dependent chloride secretion in W1282X-homozygous cells (Keenan et al., 2019).
Eluforsen (QR-010; ProQR) is a modified RNA oligonucleotide that was demonstrated to restore CFTR function in a F508del-expressing cell line, patient-derived specimens and murine models (Beumer et al., 2019). Furthermore, eluforsen was able to efficiently diffuse through CF-like mucus layer on air-liquid interface cell cultures (Brinks et al., 2019). In an early-stage trial assessing single and multiple doses in F508del-homozygous patients, eluforsen was well tolerated and improved quality of life. Lung function also remained stable throughout the study (Drevinek et al., 2019). In a following clinical study, repeated intranasal administration of eluforsen resulted in improvement in the nasal potential difference in F508del-homozygous patients, but not in the F508del-heterozygous cohort (Sermet-Gaudelus et al., 2019). Although no severe safety concerns have been reported, the clinical development of eluforsen has been discontinued.
CFTR modulators have become transformative therapeutic approaches for many CF patients, as mentioned above. Despite several breakthroughs, further research is needed to continue optimizing therapies and to identify novel modulators for patients carrying rare, ultra-rare, or even unique CFTR mutations, who still face an unmet need for efficient, corrective therapies. Furthermore, some barriers still pose substantial challenges in the equitable availability of these pharmacotherapies, including the excessive costs and regulatory national issues. The collaborative environment composed by academic researchers, healthcare professionals, pharmaceutical companies, and patient representatives has been crucial in developing better treatments for people with CF.
The multifaceted nature of CF requires complex and time-consuming therapeutic regimens that should be periodically adapted according to disease progression. Furthermore, CF patients are subjected to substantial clinical, psychosocial, and economic burdens, which pose challenges to achieve optimal, lifelong treatment adherence. The adherence varies largely depending on treatment type, route of administration, duration, and number of distinct medications, as well as patient age and socioeconomic status (Sawicki et al., 2013; Angelis et al., 2015; Quittner et al., 2016; Narayanan et al., 2017). Moreover, CF patients usually spend twice and 20 times more time in daily treatment activities than diabetic and asthmatic patients, respectively (Ziaian et al., 2006), which may considerably affect adherence. Poor adherence has also been associated with higher healthcare costs, more frequent hospitalizations, and worse quality of life and clinical manifestations (Sawicki et al., 2013; Quittner et al., 2016; Narayanan et al., 2017). Establishing a closer relationship among patient, families/caregivers and the multidisciplinary healthcare team may be a first step to overcome key barriers to treatment adherence.
To date, only few publications have evaluated the adherence to ivacaftor treatment and adherence to modulator combinations remains yet to be demonstrated. From a clinical perspective, a life-transforming oral medication with a simple dosing schedule would supposedly be taken as prescribed. Adherence to ivacaftor has nevertheless varied from suboptimal (Siracusa et al., 2015) to optimal (Suthoff et al., 2016). As these studies had a small sample size and applied distinct methods, it is still difficult to extrapolate the results to a broader CF population, and further studies are needed to better address this issue. Certain therapeutic benefits may also be more modest in a real-world setting compared to clinical trials, as patients should take these oral medications following specific recommendations, including dietary to ensure better drug absorption and availability in the body. Furthermore, recent studies have demonstrated that abrupt interruption of CFTR modulator therapy may cause severe clinical consequences. Ivacaftor withdrawal resulted in accelerated deterioration of lung function consistent with a pulmonary exacerbation episode in a case series (Trimble and Donaldson, 2018). Patients who discontinued treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor, mainly due to early adverse effects, also demonstrated a higher risk of worsening clinical manifestations compared to patients who continued treatment or those who restarted it after temporary discontinuation in a real-world study (Burgel et al., 2020). As patients have different lifestyles and socioeconomic conditions, the development of educational and motivational interventions at an individual level may help in ensuring optimal adherence to achieve the greatest clinical outcomes.
CFTR modulators have been added to therapeutic regimens of eligible patients, rather than replacing some symptomatic therapies. This appears to be the optimal approach for most CF patients, although it also increases the burden of medications in use. Once the safety and efficacy of novel therapies are demonstrated in adults, extension clinical trials are pursued to evaluate the effects on younger patients, as adverse effects may vary across distinct age groups (Davies et al., 2016; Rosenfeld et al., 2018; McNamara et al., 2019; Rosenfeld et al., 2019). Starting these transformative therapies in milder disease severity and earlier in life may offer more chances of significantly improving long-term outcomes or even preventing certain injury of affected organs, which may also result in a lower burden of medications in a long-term perspective. Some reports have also demonstrated that younger patients are more adherent to therapies than adolescents and adults, possibly due to higher parental supervision (Quittner et al., 2014; Shakkottai et al., 2014). Providing educational and supporting approaches to young children and their parents may result in optimal, lifelong treatment adherence. As patients should be transferred from pediatric to adult care at a certain age (generally between 18 and 21 years old), a planned transition is greatly helpful to maximize independence, minimize chances of interruption in the therapies and continue improving their quality of life (Goralski et al., 2017).
Most development programs of CFTR modulators has been initially focused on the correction of F508del mutation, since fully overcoming the defects in this mutation would result in an effective therapy for approximately 82% of the CF patient population worldwide. There are still nevertheless 10%–18% of patients without any CFTR-directed therapeutics. This percentage is even higher in countries where the prevalence of F508del is much lower, such as Brazil, Israel, Italy and Turkey (Figure 3).
Identifying the putative binding sites of CFTR-directed modulators using the novel insights of CFTR structure may facilitate the rational design of novel compounds with enhanced pharmacological properties. The pipeline of CFTR modulators continues to expand and some recent drug development programs have also been pursuing the identification of modulators to less common CF-causing mutations. Identification of specific therapies for rare and ultra-rare mutations poses nevertheless several challenges due to the great variability of CF-causing mutations and the very small number of patients. In addition to CFTR-directed modulators, CFTR dysfunction might be compensated by targeting alternative ion channels, such as ENaC (Moore and Tarran, 2018), the calcium-activated chloride channel transmembrane protein membrane 16A (TMEM16A) (Sondo et al., 2014), and the solute carrier 26A9 (SLC26A9) (Balázs and Mall, 2018). Strategies that modulate these alternative ion channels might be efficient therapies for all patients, regardless of their CF genotypes. These strategies might also be used alone or in combination with CFTR modulators to enhance clinical outcomes. Nevertheless, as CF patients are already subjected to a substantial burden of medications, drug-drug interaction profiles should be further exploited to avoid adverse effects or inhibitory effects of one therapy on another. In this line, itraconazole, an antifungal commonly used for the treatment of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, was demonstrated to significantly increase systemic exposures of tezacaftor and ivacaftor (Garg et al., 2019). Caution and appropriate monitoring are recommended when these therapies are used at the same period.
Traditional trials with a placebo-controlled design have been providing evidence for the safety and efficacy of CFTR modulators (Habib et al., 2019) (Table 1); however, alternatives will be needed in the near future, as more modulator options become available and the number of patients without any modulator therapy will certainly reduce. Furthermore, clinical trials in sicker or younger patients, and those carrying rarer CFTR mutations are more challenging due to small sample size, specific inclusion/exclusion criteria, or even for some hesitation on the part of the investigators. Strategies to adapt and optimize trial design and deliver for speed and efficacy have been discussed, including the use of patient-derived specimens, power calculations to compensate for group sampling, and N-of-1 and “basket” trials (Matthes et al., 2018; Amaral et al., 2019; Davies et al., 2019b).
The use of patient-derived specimens to comparatively evaluate drug efficacies may be a feasible starting point to identify the best candidate drug(s) in vitro and predict the magnitude of therapeutic responses for following clinical testing (Strauss and Blinova, 2017; Amaral et al., 2019). In fact, a significant but variable clinical responsiveness was observed in clinical trials with CFTR modulators in patients carrying at least one G551D mutation (Ramsey et al., 2011; Rowe et al., 2014) or in F508del-homozygous patients (Boyle et al., 2014; Wainwright et al., 2015; Donaldson et al., 2018a), which suggests that patient responsiveness to a certain therapy is influenced not only by the CF genotype but also by the genetic background and/or epigenetic factors. In this line, some reports have demonstrated that single nucleotide polymorphisms in SLC26A9 gene contribute to heterogeneity in inter-individual responsiveness to CFTR modulator therapies (Strug et al., 2016; Corvol et al., 2018). Such findings denote the relevance of assessing the drug effectiveness at an individual level in patient-derived specimens.
A report pairing in vitro measurement of CFTR function in cell lines and clinical features demonstrated a strong correlation between CFTR function and sweat chloride concentration, and to a lesser extent but still significant with lung function and pancreatic status (McCague et al., 2019). Correlations between responses in patient-derived specimens and clinical parameters/biomarkers have been investigated to establish reliable prediction of drug effectiveness. A consistent correlation was found among forskolin-induced swelling of intestinal organoids, sweat chloride concentration and intestinal current measurements of infants with CF (de Winter-de Groot et al., 2018). Despite the clinical heterogeneity in adults with CF and homozygous for F508del mutation, forskolin-induced swelling of intestinal organoids positively correlated with FEV1 and BMI (de Winter-de Groot et al., 2019). Responses from intestinal organoids were also demonstrated to correlate with intestinal current measurements, reduction in sweat chloride concentration and improvement in lung function of patients after CFTR modulator therapies (Dekkers et al., 2016a; Berkers et al., 2019). In N-of-1 trial series, an increase in CFTR-dependent chloride transport in nasal epithelial cell cultures was only found in the three patients who also demonstrated a reduction in sweat chloride concentration after ivacaftor treatment (McGarry et al., 2017). Furthermore, responses in F508del-homozygous patient-derived nasal epithelial cells were correlated to improvements in ppFEV1 and intestinal current measurements, but not with nasal potential difference after co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor (Pranke et al., 2019). Nevertheless, no significant correlations were found among responses in intestinal current measurement, nasal potential difference and sweat chloride concentration, despite high concordance for all CFTR-dependent biomarkers in another study evaluating the co-treatment with lumacaftor/ivacaftor (Graeber et al., 2018). Further studies are certainly needed to better correlate and validate drug effectiveness in patient-derived specimens with clinical features, and identification of novel biomarkers may also enrich strategies in efficacy trials.
In an era of drugs targeting the underlying defects in CF-causing mutations, the development of symptomatic therapies might appear less attractive. Nevertheless, these therapies must continue to be developed as most (if not all) existing CF population will need them at some point, and CFTR modulators are very unlikely to reverse lung tissue remodeling already established (Davies et al., 2019b). A recent study demonstrated that six months of ivacaftor treatment was unable to significantly change airway microbiome and several inflammation measurements in patients carrying at least one G551D mutation. Such findings indicate that antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs will still be required to control disease symptoms and prevent complications (Harris et al., 2019). As the disease progresses, patients may also develop comorbidities and thus require even more complex therapeutic regimens, adding further burdens. Ivacaftor treatment was demonstrated to improve exocrine pancreatic function as well as insulin secretion profile, which may alleviate or even reverse CF-related diabetes (Hayes et al., 2014; Davies et al., 2016; Tsabari et al., 2016; Kelly et al., 2019). Ivacaftor treatment was also demonstrated to improve bone health (Sermet-Gaudelus et al., 2016) and vascular tone abnormalities (Adam et al., 2016). A recent review nicely summarizes the current understanding of CFTR modulators on extra-pulmonary complications in CF (Sergeev et al., 2019). Nevertheless, most studies are case reports or have a small sample size, and further studies are warranted to investigate the impact of CFTR modulator therapies on CF comorbidities.
Treatment with more than one CFTR modulator appears to be the optimal approach for many CF-causing mutations. As heterozygous carriers are asymptomatic, fully overcoming CFTR dysfunction in one allele might be enough to halt disease progression, if treatment is started early in life and before severe lung injury occurs. Based on in vitro evidence (Zhang et al., 2009), rescue of 25-50% of WT-CFTR function in both alleles might also be sufficient to restore normal rates of mucociliary clearance. It remains nevertheless unclear how many CFTR modulators would be needed to reach such threshold in patients. In addition to CFTR modulators, progress has been made in developing cell-based (Barical et al., 2019; Hayes et al., 2019) and gene-based therapies (Donnelley and Parsons, 2018; Duncan et al., 2018; Lopes-Pacheco et al., 2018; Osman et al., 2018) for CF lung disease.
A major limitation of these novel pharmaceutical treatments for CF patients, such as the CFTR modulators, is the excessive costs when they reach the market (over US$250,000 per patient per year), which renders difficulties in their availability for many patients worldwide (O'Sullivan et al., 2013; Ferkol and Quinton, 2015; Orestein et al., 2015), especially for those living in low- and middle-income countries (Cohen-Cymberknoh et al., 2016). In developed countries, certain health authorities have also been slow in approving reimbursement (Bush and Simmonds, 2012; Whiting et al., 2014; Sharma D. et al., 2018) and the cost-effectiveness of these pharmacotherapies has yet been questioned (Gulland, 2016; Balk et al., 2018). Even though the quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) analysis might not adequately address all concerns for rare diseases, such as CF (Schlander et al., 2014; Pearson et al., 2018), these therapies pose a substantial burden on national healthcare systems, as they are expensive and lifelong. It remains nevertheless unclear if such prices will persist over time, as several novel molecules are on the horizon and probably will reach the market over the next years, if they prove to be safe and to have efficacy in clinical studies. Further discussion should certainly be undertaken with patient representatives, healthcare providers, policymakers, government authorities and pharmaceutical companies to identify feasible and sustainable solutions that would enable equitable access to eligible patients for these “on-target” therapies. Hopefully, market competition will also reduce modulator prices with the approval of novel ones.
Over the past three decades, the human disease target landscape considerably expanded, as approximately 40% of approved pharmaceuticals received an orphan designation (Attwood et al., 2018). Drug discovery and development for a new molecule may be nevertheless far slower than expected, as it is a costly process with high attrition rates that also depends on several regulatory requirements. Drug repurposing (also known as drug repositioning or reprofiling) has become an increasingly attractive strategy that may save valuable time and funding investments in drug development for common and rare diseases. As approved drugs have already undergone extensive toxicological evaluations in both experimental and early-stage clinical studies, the time frame to obtain a new disease indication may be reduced, if safety and efficacy is demonstrated for the repurposed use in late-stage clinical studies (Pushpakom et al., 2019). Furthermore, drug repurposing may unravel effective therapies for patients with common and rare CF-causing mutations in an expedited way and at a feasible cost for national healthcare systems. In experimental models, certain underlying defects in CFTR mutations have been rectified by administering clinically approved drugs, such as gentamicin (Howard et al., 1996), amlexanox (Gonzalez-Hilarion et al., 2012), escin (Mutyam et al., 2016), ibuprofen (Carlile et al., 2015), and genistein (Illek and Fischer, 1998). These findings indicate that other existing and approved drugs for unrelated disease indications might have the potential to correct or circumvent CFTR dysfunction and should be exploited in the pre-clinical setting. Both cysteamine and thymosin α-1 were also claimed to restore functional expression of F508del-CFTR (Tosco et al., 2016; Romani et al., 2017). Nevertheless, several independent CF research groups failed to demonstrate rescue of F508del-CFTR PM expression and function by either cysteamine or thymosin α-1 (Tomati et al., 2018b; Armirotti et al., 2019; Awatade et al., 2019). Although the immunomodulatory effect of these molecules in CF remains to be further exploited, they did not demonstrate F508del-CFTR correction. As the identification of highly efficient treatments often draws the attention of both scientific and lay audiences, a note of caution should be considered before such findings are diffused in the press to avoid creating premature expectations, especially in CF patients and their relatives.
Thirty years have passed since the discovery of the CFTR gene, and numerous milestones in experimental and clinical research of CF have been achieved during this period (Figure 8). Understanding the cellular and molecular basis of the disease has paved the way for the development of therapeutic strategies targeting the underlying dysfunctions caused by CF mutations. CFTR modulator therapies are in clinics and they represent a landmark in patients' lives, demonstrating short- and long-term benefits in clinical outcomes. Nevertheless, strategies to achieve optimal, lifelong adherence to treatments should be optimized. Several barriers have still been preventing equitable access worldwide of the current CFTR modulators, including the costs and regulatory national issues, and as such further discussions are needed to identify feasible and sustainable solutions for these therapies to achieve all eligible patients. Furthermore, many rare and ultra-rare CF-causing mutations are still without any efficient, corrective therapy. Novel tools have been developed to accelerate and continue to expand the pipeline of CFTR modulators. From a translational perspective, the use of patient-derived specimens would ensure a comparative evaluation of drug efficacies in vitro to select the best candidate(s) and predict the therapeutic responses at an individual level. Every patient is unique, but everyone certainly wants the same: to have a longer and healthier life (ideally, with no symptoms or complications). Hopefully, precision medicine will enable “the highest attainable standard of health” for all patients with CF, and then we will see “all our brothers and sisters breathing free.”
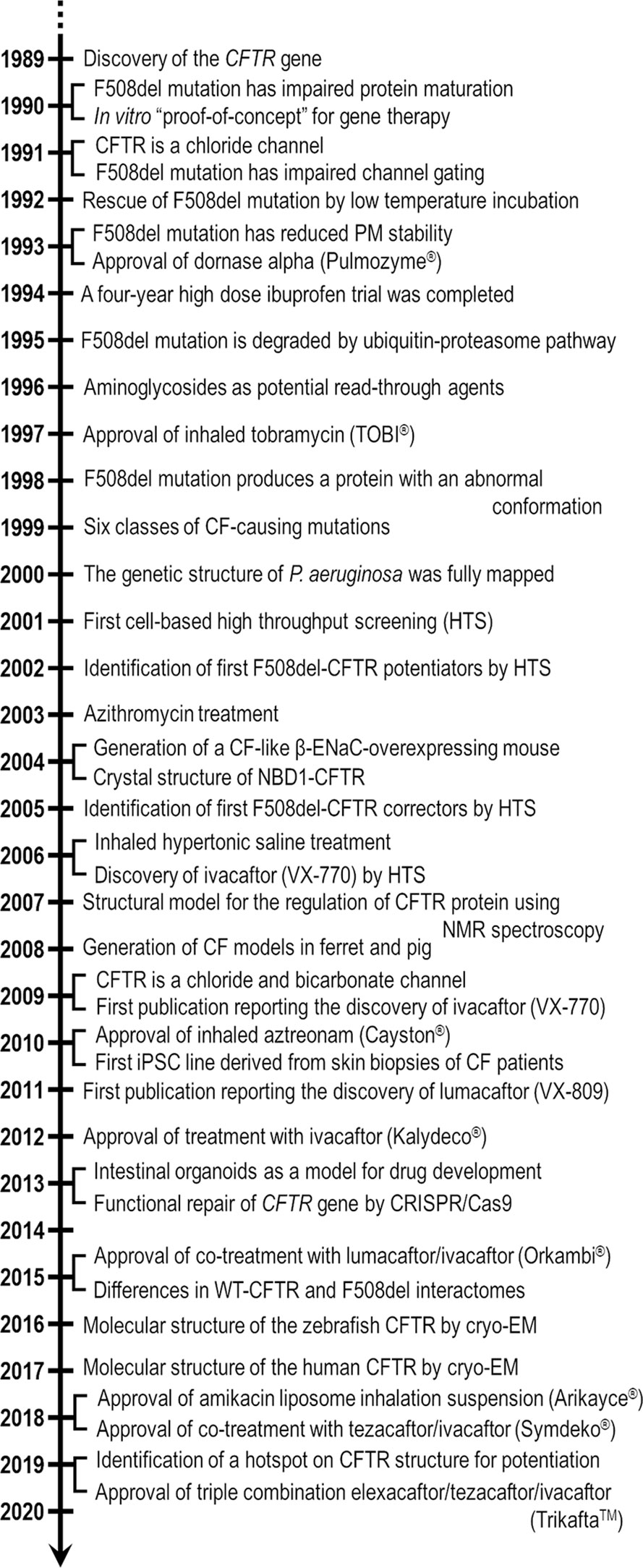
Figure 8 Timeline with several milestones in experimental and clinical research for cystic fibrosis since the discovery of CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene in 1989. The knowledge accumulated over these 30 years has been ensuring a better understanding of the molecular biology and protein structure of CFTR, and the pathophysiology of CF in order to translate the basic sciences into clinical practice. More than 10 novel CF therapies have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) during this period with four of these being CFTR modulator drugs.
CF patients under care at accredited care centers in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Europe, New Zealand, South Africa, United Kingdom, and United States of America. Figures 2 and 3 are data compiled from the last Patient Registry Report in Australia (Cystic Fibrosis Australia), Brazil (Brazilian Cystic Fibrosis Study Group), Canada (Cystic Fibrosis Canada), Europe (European Cystic Fibrosis Society), New Zealand (Cystic Fibrosis New Zealand), UK (Cystic Fibrosis Trust), and USA (Cystic Fibrosis Foundation). Data from Argentina (Associación Argentina de Lucha contra la Enfermedad Fibroquística del Páncreas) and South Africa (South Africa Cystic Fibrosis Association) have been obtained from Annals of scientific events. A citation with the link to access each Registry Report has been provided.
The author confirms being the sole contributor of this work and has approved it for publication.
The author is a recipient of the 2018 Gilead Sciences Research Scholars for Cystic Fibrosis.
The author declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author is grateful to Solon Leite (Pharm.D.), Susana Igreja (Ph.D.), and Iris Silva (Ph.D.) for the comments and suggestions during the manuscript writing and editing. The author also thanks Nicoletta Pedemonte (Ph.D.) for the help in preparing Figure 8.
Adam, R. J., Hisert, K. B., Dodd, J. D., Grogan, B., Launspach, J. L., Barnes, J. K., et al. (2016). Acute administration of ivacaftor to people with cystic fibrosis and a G551D-CFTR mutation reveals smooth muscle abnormalities. JCI Insight 1, e86183. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.86183
Ahner, A., Gong, X., Schmidt, B. Z., Peters, K. W., Rabeh, W. M., Thibodeau, P. H., et al. (2013). Small heat shock proteins target cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator for degradation via a small ubiquitin-like modifier-dependent pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell. 24 (2), 74–84. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e12-09-0678
Aksit, M. A., Bowling, A. D., Evans, T. A., Joynt, A. T., Osorio, D., Patel, S., et al. (2019). Decreased mRNA and protein stability of W1282X limits response to modulator therapy. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (5), 606–613. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.02.009
Alshafie, W., Chappe, F. G., Li, M., Anini, Y., Chappe, V. M. (2014). VIP regulates CFTR membrane expression and function in Calu-3 cells by increasing its interaction with NHERF1 and P-ERM in a VPAC1- and PKCϵ-dependent manner. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 307 (1), C107–C119. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00296.2013
Amaral, M. D., de Boeck, K., ECFS Strategic Planning Task Force on ‘Speeding up access to new drugs for CF' (2019). Theranostics by testing CFTR modulators in patients-derived materials: The current status and a proposal for subjects with rare CFTR mutations. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (5), 685–6925. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.06.010
Anderson, D. H. (1938). Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas and its relation to celiac disease. Am. J. Dis. Child. 56, 344. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1938.01980140114013
Angelis, A., Tordrup, D., Kanavos, P. (2015). Socio-economic burden of rare diseases: A systematic review of cost of illness evidence. Health Policy 119 (7), 964–979. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2014.12.016
Armirotti, A., Tomati, V., Matthes, E., Veit, G., Cholon, D. M., Phuan, P. W., et al. (2019). Bioactive thymosin alpha-1 does not influence F508del-CFTR maturation and activity. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 10310. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46639-1
Athanazio, R. A., Silva Filho, L. V. R. F., Vergara, A. A., Ribeiro, A. F., Riedi, C. A., Procianoy, E. D. F. A., et al. (2017). Brazilian guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic fibrosis. J. Bras. Pneumol. 43 (3), 219–245. doi: 10.1590/s1806-37562017000000065
Attwood, M. M., Rask-Andersen, M., Schiöth, H. B. (2018). Orphan drugs and their impact on pharmaceutical development. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 39 (6), 525–535. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.03.003
Avramescu, R. G., Kai, Y., Xu, H., Bidaud-Meynard, A., Schnúr, A., Frenkiel, S., et al. (2017). Mutation-specific downregulation of CFTR2 variant by gating potentiators. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26 (24), 4873–4885. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx367
Awatade, N. T., Ulyiakina, I., Farinha, C. M., Clarke, L. A., Mendes, K., Solé, A., et al. (2014). Measurements of functional responses in human primary lung cells as a basis for personalized therapy for cystic fibrosis. EBioMedicine 2 (2), 147–153. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2014.12.005
Awatade, N. T., Wong, S. L., Hewson, C. K., Fawcett, L. K., Kicic, A., Jaffe, A., et al. (2018). Human primary epithelial cell models: Promising tools in the era of cystic fibrosis personalized medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1429. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01429
Awatade, N. T., Ramalho, S., Silva, I. A. L., Felício, V., Botelho, H. M., de Poel, E., et al. (2019). R560S: a class II CFTR mutation that is not rescued by current modulators. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (2), 182–189. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2018.07.001
Balázs, A., Mall, M. A. (2018). Role of the SLC26A9 chloride channel as disease modifier and potential therapeutic target in cystic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1112. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01112
Balk, E. M., Trikalinos, T. A., Mickle, K., Cramer, G., Chapman, R., Khan, S., et al. (2018). Modulator treatments for cystic fibrosis: effectiveness and value – Evidence report May 3, 2018. Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) Available at: https://icer-review.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/CF_Evidence_Report_05222018.pdf (accessed Nov 09, 2019).
Barical, A., Lee, R. E., Randell, S. H., Hawkins, F. (2019). Challenges facing airway epithelial cell-based therapy for cystic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 74. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00074
Barry, P. J., Plant, B. J., Nair, A., Bicknell, S., Simmonds, N. J., Bell, N. J., et al. (2014). Effects of ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis who carry the G551D mutation and have severe lung disease. Chest 146 (1), 152–158. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-2397
Bell, S. C., Barry, P. J., De Boeck, K., Drevinek, P., Elborn, J. S., Plant, B. J., et al. (2019). CFTR activity is enhanced by the novel GLPG222, given with and without ivacaftor in two randomized trials. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (5), 700–707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.04.014
Berg, A., Hallowell, S., Tivvetts, M., Beasley, C., Brown-Philips, T., Healy, A., et al. (2019). High-throughput surface liquid absorption and secretion assays to identify F508del CFTR correctors using patient primary airway epithelial cultures. SLAS Discovery 24 (7), 724–737. doi: 10.1177/2472555219849375
Bergbower, E., Boinot, C., Sabirzhanova, I., Guggino, W., Cebotaru, L. (2018). The CFTR-associated ligand arrests the trafficking of the mutant ΔF508 CFTR chnnel in the ER contributing to cystic fibrosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 45 (2), 639–655. doi: 10.1159/000487120
Berkers, G., van Mourik, P., Vonk, A. M., Kruisselbrink, E., Dekkers, J. F., de Winter-de Groot, K. M., et al. (2019). Rectal organoids enable personalized treatment of cystic fibrosis. Cell Rep. 26 (7), 1701–1708.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.068
Bessonova, L., Volkova, N., Higgins, M., Bengtsson, L., Tian, S., Simard, C., et al. (2018). Data from US and UK cystic fibrosis registries support disease modification by CFTR modulation with ivacaftor. Thorax 73 (8), 731–740. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2017-210394
Beumer, W., Swildens, J., Leal, T., Noel, S., Anthonijsz, H., van der Horst, G., et al. (2019). Evaluation of eluforsen, a novel RNA oligonucleotide for restoration of CFTR in in vitro and murine model of p.Phe508del cystic fibrosis. PloS One 14 (6), e0219182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219182
Bomberger, J. M., Coutermarsh, B. A., Barnaby, R. L., Stanton, B. A. (2012). Arsenic promotes ubiquitinylation and lysosomal degradation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) chloride channels in human epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 17130–17139. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.338855
Borowitz, D., Lubarsky, B., Wilschanski, M., Munck, A., Gelfond, D., Bodewes, F., et al. (2016). Nutritional status improves in cystic fibrosis patients with the G551D mutation after treatment with ivacaftor. Dig. Dis. Sci. 61 (1), 198–207. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3834-2
Boucher, R. C., Stutts, M. J., Knowles, M. R., Cantley, L., Gatzy, J. T. (1986). Na+ transport in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelial. Abnormal basal rate and response to anenylate cyclase activation. J. Clin. Invest. 78 (5), 1245–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI112708
Boyle, M. P., Bell, S. C., Konstan, M. W., McColley, S. A., Rowe, S. M., Rietschel, E., et al. (2014). A CFTR corrector (lumacaftor) and a CFTR potentiator (ivacaftor) for treatment of patients with cystic fibrosis who have a phe508del CFTR mutation: a phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 20142 (7), 527–538. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70132-8
Brazilian Cystic Fibrosis Study Group (2019). Relatório do Registro Brasileiro de Fibrose Cística 2017, Available at: http://portalgbefc.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/Registro2017.pdf.
Brewington, J. J., Filbrandt, E. T., LaRosa, F. J., Moncivaiz, J. D., Ostmann, A. J., Strecker, L. M., et al. (2018). Brushed nasal epithelial cells are a surrogate for bronchial epithelial CFTR studies. JCI Insight 3 (13), 99385. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.99385
Brinks, V., Lipinska, K., de Jager, M., Beumer, W., Button, B., Livraghi-Butrico, A., et al. (2019). The cystic fibrosis-like airway surface layer is not a significant barrier for delivery of eluforsen to airway epithelial cells. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 32 (5), 303–315. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2018.1502
Burgel, P. R., Munck, A., Durieu, I., Chiron, R., Mely, L., Prevotat, A., et al. (2020). Real-life safety and effectiveness of lumacaftor-ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 201 (2), 188–197. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201906-1227OC
Bush, A., Simmonds, N. J. (2012). Hot off the breath: ‘I've a cost for'—the 64 milion dollar question. Thorax 67 (5), 382–384. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-201798
Byrnes, L. J., Xu, Y., Qiu, X., Hall, J. D., West, G. M. (2018). Sites associated with Kalydeco binding on human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator revealed by hydrogen/deuterium exchange. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 4664. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22959-6
Calabrese, F., Lunardi, F., Nannini, N., Balestro, E., Loy, M., Marulli, G., et al. (2015). Higher risk of acute cellular rejection in lung transplant recipients with cystic fibrosis. Ann. Transplant. 20, 769–776. doi: 10.12659/AOT.894785
Carlile, G. W., Robert, R., Goepp, J., Matthes, E., Liao, J., Kus, B., et al. (2015). Ibuprofen rescues mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator trafficking. J. Cyst. Fibros. 14 (1), 16–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2014.06.001
Castellani, C., Duff, A. J. A., Bell, S. C., Heijerman, H. G. M., Munck, A., Ratjen, F., et al. (2018). ECFS best practice guidelines: the 2018 version. J. Cyst. Fibros. 17 (2), 153–178. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2018.02.006
CFTR1 Database. Cystic Fibrosis Mutation Database. http://www.genet.sickkids.on.ca/Home.html. (accessed Nov 09th, 2019).
CFTR2 Database. Clinical and Functional Translation of CFTR. https://www.cftr2.org/. (accessed Nov 09th, 2019).
Chappe, V., Hinkson, D. A., Zhu, T., Chang, X. B., Riordan, J. R., Hanrahan, J. W. (2003). Phosphorylation of protein kinase C sites in NBD1 and the R domain control CFTR channel activation by PKA. J. Physiol. 548 (Pt 1), 39–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.035790
Chen, K. G., Mallon, B. S., Park, K., Robey, P. G., McKay, R. D. G., Gottesman, M. M., et al. (2018). Pluripotent stem cell platforms for drug discovery. Trends Mol. Med. 24 (9), 805–820. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.06.009
Cheng, S. H., Gregory, R. J., Marshall, J., Paul, S., Souza, D. W., White, G. A., et al. (1990). Defective intracellular transport and processing of CFTR is the molecular basis of the most cystic fibrosis. Cell 63 (4), 827–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90148-8
Cholon, D. M., Quinney, N. L., Fulcher, M. L., Esther, C. R., Jr., Das, J., Dokholyan, N. V., et al. (2014). Potentiator ivacaftor abrogates pharmacological correction of ΔF508 CFTR in cystic fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 6 (246), 246ra96. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008680
Clancy, J. P., Rowe, S. W., Accurso, F. J., Aitken, M. L., Amin, R. S., Ashlock, M. A., et al. (2012). Results of a phae IIa study of VX-809, an investigational CFTR corrector compound, in subjects with cystic fibrosis homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation. Thorax 67 (1), 12–18. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200393
Clarke, L. A., Awatade, N. T., Felício, V. M., Silva, I. A., Calucho, M., Pereira, L., et al. (2019). The effect of premature termination códon mutations on CFTR mRNA abundance in human nasal epithelial and intestinal organoids: a basis for read-through therapies in cystic fibrosis. Hum. Mutat. 40 (3), 326–334. doi: 10.1002/humu.23692
Cohen-Cymberknoh, M., Shoseyov, D., Kerem, E. (2011). Managing cystic fibrosis: strategies that increase life expectancy and improve quality of life. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 183 (11), 1463–14715. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201009-1478CI
Cohen-Cymberknoh, M., Shoseyov, D., Breuer, O., Shamali, M., Wilschanski, M., Kerem, E. (2016). Treatment of cystic fibrosis in low-income countries. Lancet Respir. Med. 4 (2), 91–92. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00507-X
Collins, F. S. (1992). Cystic fibrosis: molecular biology and therapeutic implications. Science 256 (5058), 774–779. doi: 10.1126/science.1375392
Corvol, H., Mésinèle, J., Douksieh, I. H., Strug, L. J., Boëlle, P. Y., Guillot, L. (2018). SLC26A9 gene is associated with lung function response to ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 828. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00828
Cui, G., Stauffer, B. B., Imhoff, B. R., Rab, A., Hong, J. S., Sorscher, E. J., et al. (2019). VX-770-mediated potentiation of numerous human CFTR disease mutants is influenced by phosphorylation level. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 13460. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49921-4
Cusing, P. R., Vouilleme, L., Pellegrini, M., Boisguerin, P., Madden, D. R. (2010). A stabilizing influence: CAL PDZ inhibition extends the half-life of ΔF508-CFTR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49 (51), 9907–9911. doi: 10.1002/anie.201005585
Cystic Fibrosis Australia. (2018). Australian Cystic Fibrosis Data Registry – Annual Report 2016, Available at: https://www.cysticfibrosis.org.au/getmedia/a3b28200-caeb-4c5a-ad15-98c71a8c7dc8/ACFDR-2016-Annual-Report-Final-Copy-Single-Page-Version.pdf.aspx.
Cystic Fibrosis Canada. (2019). The canadian cystic fibrosis registry – 2018 annual data report, Available at: https://www.cysticfibrosis.ca/uploads/RegistryReport2018/2018RegistryAnnualDataReport.pdf.
Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. (2019). 2018 patient registry – annual data report, Available at: https://www.cff.org/Research/Researcher-Resources/Patient-Registry/2018-Patient-Registry-Annual-Data-Report.pdf.
Cystic Fibrosis New Zealand. (2019). PORT NZ – 2015 National Data Registry, Available at: https://www.cfnz.org.nz/assets/Reports/849f16f667/2015-PORT-CF_Registry-Report.pdf.pdf.
Cystic Fibrosis Trust. (2019). UK Cystic Fibrosis Registry – Annual Data Report 2018, Available at: https://www.cysticfibrosis.org.uk/~/media/documents/the-work-we-do/uk-cf-registry/2018-registry-annual-data-report.ashx?la=en.
Dalemans, W., Barbry, P., Champigny, G., Jallat, S., Dott, K., Dreyer, D., et al. (1991). Altered chloride ion channe kinetics associated with delta F508 cystic fibrosis mutation. Nature 354 (6354), 526–528. doi: 10.1038/354526a0
Davies, J. C., Cunningham, S., Harris, W. T., Lapey, A., Regelmann, W. E., et al. (2016). Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of ivacaftor in patients in patients aged 2-5 years with cystic fibrosis and a CFTR gating mutation (KIWI): an open-label, single-arm study. Lancet Respir. Med. 4 (2), 107–115. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00545-7
Davies, J. C., Moskowitz, S. M., Brown, C., Horsley, A., Mall, M. A., McKone, E. F., et al. (2018). VX-659-tezacaftor-ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis and one or two phe508del alleles. N. Eng. J. Med. 379 (17), 1599–1611. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1807119
Davies, J. C., Van de Seen, O., van Koningsbruggen-Ritschel, S., Drevinek, P., Derichs, N., McKone, E. F., et al. (2019a). GLPG1837, a CFTR potentiator, in p.Gly551Asp (G551D)-CF patients: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2a study (SAPHIRA1). J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (5), 693–699. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.05.006
Davies, J. C., Drevinek, P., Elborn, J. S., Kerem, E., Lee, .T, ECFS Strategic Planning Task Force on ‘Speeding up access to new drugs for CF'. (2019b). Speeding up access to new drugs for CF: considerations for clinical trial design and delivery. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (5), 677–6845. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.06.011
De Boeck, K., Amaral, M. D. (2016). Progress in therapies for cystic fibrosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 4 (8), 662–674. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)00023-0
De Boeck, K., Munck, A., Walker, S., Faro, A., Hiatt, P., Gilmartin, G., et al. (2014). Efficacy and safety of ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis and a non-G551D gating mutation. J. Cyst. Fibros. 13 (6), 674–680. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2014.09.005
De Wilde, G., Gees, M., Musch, S., Verdonck, K., Jans, M., Wesse, A. S., et al. (2019). Identification of GLPG/ABBV-2737, a novel class of corrector, which exerts functional synergy with other CFTR modulators. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 514. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00514
De Winter-de Groot, K. M., Janssens, H. M., van Uum, R. T., Dekkers, J. F., Berkers, G., Vonk, A., et al. (2018). Stratifying infants with cystic fibrosis for disease severity using intestinal organoids swelling as a biomarker of CFTR function. Eur. Respir. J. 52 (3), 1702529. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02529-2017
De Winter-de Groot, K. M., Berkers, G., Marck-van der Wilt, R. E. F., van der Meer, R., Vonk, A., Dekkers, J. F., et al. (2019). Foskolin-induced swelling of intestinal organoids correlated with disease severity in adults with cystic fibrosis and homozygous F508del mutations. J. Cyst. Fibros. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.10.022
Dekkers, J. F., Berkers, G., Kruisselbrink, E., Vonk, A., de Jonge, H. R., Janssens, H. N., et al. (2016a). Characterizing responses to CFTR-modulating drugs using rectal organoids derived from subjects with cystic fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 8 (344), 344ra84. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad8278
Dekkers, J. F., Gogorza Gondra, R. A., Kruisselbrink, E., Bonk, A. M., Janssens, H. M., de Winter-de Groot, K. M., et al. (2016b). Optimal correction of distinct CFTR fonding mutants in rectal cystic fibrosis organoids. Eur. Respir. J. 48 (2), 451–458. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01192-2015
Denning, G. M., Anderson, M. P., Amara, J. F., Marshall, J., Smith, A. E., Welsh, M. J. (1992). Processing of mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is temperature-sensitive. Nature 358 (6389), 761–764. doi: 10.1038/358761a0
Di Sant' Agnese, P. A., Darling, R. C., Perera, G. A., Shea, E. (1953). Abnormal electrolyte composition of sweat in cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. Clinical significance and relationship to disease. Pediatrics 12, 549–563.
Diana, S., Polizzi, A. M., Santostasi, T., Ratclif, L., Pantaleo, M. G., Leonetti, G., et al. (2016). The novel complex allele [A238V;F508del] of the CFTR gene: clinical phenotype and possible implications for cystic fibrosis etiological therapies. J. Hum. Genet. 61 (6), 473–481. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.15
Donaldson, S. H., Solomon, G. M., Zeitlin, P. L., Flume, P. A., Casey, A., McCoy, K., et al. (2017). Pharmacokinetics and safety of cavosonstat (N91115) in health and cystic fibrosis adults homozygous for F508del-CFTR. J. Cyst. Fibros. 16 (3), 371–379. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2017.01.009
Donaldson, S. H., Pilewski, J. M., Griese, M., Cooke, J., Viswanathan, L., Tullis, E., et al. (2018a). Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor in subjects with cystic fibrosis and F508del/F508del-CFTR or F508del/G551D-CFTR. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 197 (2), 214–224. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201704-0717OC
Donaldson, S. H., Laube, B. L., Corcoran, T. E., Bhambhvani, P., Zeman, K., Ceppe, A., et al. (2018b). Effect of ivacaftor on mucociliary clearance and clinical outcomes in cystic fibrosis patients with G551D-CFTR. JCI Insight 3 (24), 122695. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.122695
Donnelley, M., Parsons, D. W. (2018). Gene therapy for cystic fibrosis lung disease: overcoming the barriers to translation to the clinic. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1381. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01381
Drevinek, P., Pressler, T., Cipolli, M., De Boeck, K., Schwarz, C., Bouisset, F., et al. (2019). Antisense oligonucleotide eluforsen id safe and improves respiratory symptoms in F508del cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.05.014
Drumm, M. L., Pope, H. A., Cliff, W. H., Rommens, J. M., Marvin, S. A., Tsui, L. C., et al. (1990). Correction of the cystic fibrosis defect in vitro by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Cell 62 (6), 1227–1233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90398-X
Drumm, M. L., Wilkinson, D. J., Smit, L. S., Worrell, R. T., Strong, T. V., Frizzell, R. A., et al. (1991). Choride condunctance expressed by delta F508 and other mutant CFTRs in Xenopus oocytes. Science 254 (5039), 1797–1799. doi: 10.1126/science.1722350
Du, M., Jones, J. R., Lanier, J., Keeling, K. M., Lindsey, J. R., Tousson, A., et al. (2002). Aminoglycoside suppression of a premature stop mutation in a Cftr-/I mouse carrying a human CFTR-G542X- transgene. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 80 (9), 595–604. doi: 10.1007/s00109-002-0363-1
Du, M., Lui, X., Welch, E. M., Hirawat, S., Peltz, S. W., Bedwell, D. M. (2008). PTC124 is an orally bioavailable compound that promotes suppression of the human CFTR-G542X nonsense allele in a CF mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105 (6), 2064–2069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711795105
Duncan, G. A., Kim, N., Colon-Cortes, Y., Rodriguez, J., Mazur, M., Birket, S. E., et al. (2018). An adeno-associated viral vector capable of penetrating the mucus barrier to inhaled gene therapy. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 9, 296–304. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2018.03.006
Durmowicz, A. G., Lim, R., Rogers, H., Rosebraugh, C. J., Chowdhury, B. A. (2018). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration's experience with ivacaftor in cystic fibrosis. Establishing efficacy using in vitro data in lieu if a clinical trial. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc 15 (1), 1–2. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201708-668PS
Eckford, P. D., Li, C., Ramjeesingh, M., Bear, C. E. (2012). Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) potentiator VX-770 (ivacaftor) opens the defective channel gate of mutant CFTR in a phosphorylation-dependent but ATP-independent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 287 (44), 36639–36649. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.393637
Edgeworth, D., Keating, D., Ellis, M., Button, M., Williams, E., Clark, D., et al. (2017). Improvement in exercise duration, lung function and well-being in G551D-cystic fibrosis patients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, cross-over study with ivacaftor treatment. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 131 (15), 2037–2045. doi: 10.1042/CS20170995
Elborn, J. S., Ramsey, B. W., Boyle, M. P., Konstan, M. W., Huang, X., Marigowda, G., et al. (2016). Efficacy and safety of lumacaftor/ivacaftor combination therapy in patients with cystic fibrosis homozygous for phe508del CFTR by pulmonary function subgroup: a pooled analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 4 (8), 617–626. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30121-7
European Cystic Fibrosis Society. (2019). ECFS Patient Registry – 2017 Annual Data Report, Available at: https://www.ecfs.eu/sites/default/files/general-content-images/working-groups/ecfs-patient-registry/ECFSPR_Report2017_v1.3.pdf.
Farrell, P., Férec, C., Macek, M., Frischer, T., Renner, S., Riss, K., et al. (2018). Estimating the age of p.(phe508del) with family studies of geographically distinct European populations and the early spread of cystic fibrosis. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 26 (12), 1832–1839. doi: 10.1038/s41431-018-0234-z
Fay, J. F., Aleksandrov, L. A., Jensen, T. J., Cui, L. L., Kousouros, J. N., He, L., et al. (2018). Cryo-EM visualization of an active high open probability CFTR anion channel. Biochemistry 57 (43), 6234–6246. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00763
Ferkol, T., Quinton, P. (2015). Precision medicine: at what price? Am. J. Respir. Care Med. 192 (6), 658–659. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201507-1428ED
Flume, P. A., Wainwright, C. E., Elizabeth Tullis, D., Rodriguez, S., Niknian, M., Higgins, M., et al. (2018). Recovery of lung function following a pulmonary exacerbation in patients with cystic fibrosis and the G551D-CFTR mutation treated with ivacaftor. J. Cyst. Fibros. 17 (1), 83–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2017.06.002
Flume, P. A., Suthoff, E. D., Kosinski, M., Marigowda, G., Quittner, A. L. (2019). Measuring recovery in health-related quality of life during and after pulmonary exacerbations in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (5), 737–742. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2018.12.004
Frost, F. J., Nazareth, D. S., Charman, S. C., Winstanley, C., Walshaw, M. J. (2019). Ivacaftor is associated with reduced lung infection by key cystic fibrosis pathogens. A cohort study using national registry report. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc 16 (11), 1375–1382. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201902-122OC
Fukuda, R., Okiyoneda, T. (2018). Peripheral protein quality control as a novel drug target for CFTR stabilizer. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1100. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01100
Fulcher, M. L., Randell, S. H. (2013). Human nasal and trachea-bronchial respiratory epithelial cell culture. Methods Mol. Biol. 945, 109–121. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-125-7_8
Garg, V., Shen, J., Li, C., Agarwal, S., Gebre, A., Robertson, S., et al. (2019). Pharmacokinetic and drug-drug interaction profiles of the combination of tezacaftor/ivacaftor. Clin. Transl. Sci. 12 (3), 267–275. doi: 10.1111/cts.12610
Gees, M., Much, S., Van der Plas, S., Wesse, A. S., Vandevelde, A., Verdonck, K., et al. (2018). Identification and characterization of novel CFTR potentiators. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1221. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01221
Gentzsch, M., Cholon, D. M., Quinney, N. L., Boyles, S. E., Martino, M. E. B., Ribeiro, C. M. P. (2018). The cystic fibrosis airway milieu enhances rescue of F508del in a pre-clinical model. Eur. Respir. J. 52 (6), 1801133. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01133-2018
Giuliano, K. A., Wachi, S., Drew, L., Dukovski, D., Green, O., Bastos, C., et al. (2018). Use of a high-throughput phenotypic screening strategy to identify amplifiers, a novel pharmacological class of small molecules that exhibit functional synergy with potentiators and correctors. SLAS Discovery 23 (2), 111–121. doi: 10.1177/2472555217729790
Glozman, R., Okiyoneda, T., Mulvihill, C. M., Rini, J. M., Barriere, H., Lukacs, G. L. (2009). N-glycans are direct determinants of CFTR folding and stability in secretory and endocytic membrane traffic. J. Cell. Biol. 184 (6), 847–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200808124
Gonzalez-Hilarion, S., Beghyn, T., Jia, J., Debreuck, N., Berte, G., Mamchaoui, K., et al. (2012). Rescue of nonsense mutations by amlexanox in human cells. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 7, 58. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-7-58
Goralski, J. L., Nasr, S. Z., Uluer, A. (2017). Overcoming barriers to a successful transition from pediatric to adult care. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 52 (S48), S52–S60. doi: 10.1002/ppul.23778
Graeber, S. Y., Dopfer, C., Naehrlich, L., Gyulumyan, L., Scheuermann, H., Hirtz, S., et al. (2018). Effects of lumacaftor-ivacaftor therapy on cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function in phe508del homozygous patients with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 197 (11), 1433–1442. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201710-1983OC
Gulland, A. (2016). Cystic fibrosis drug is not cost effective, says NICE. BMJ 353, i3409. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i3409
Haardt, M., Benharouga, M., Lechardeur, D., Kartner, N., Lukacs, G. L. (1999). C-terminal truncations destabilize the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator without impairing its biogenesis. A novel class of mutation. J. Biol. Chem. 274 (31), 21873–21877. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.31.21873
Habib, A. R., Kajbafzadeh, M., Desai, S., Yang, C. L., Skolnik, K., Quon, B. S. (2019). A systematic review of clinical efficacy and safety of CFTR modulators in cystic fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 7234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43652-2
Haggie, P. M., Phuan, P. W., Tan, J. A., Xu, H., Avramescu, R. G., Perdomo, D., et al. (2017). Correctors and porentiators rescue function of the truncated W1282X-cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) translation product. J. Biol. Chem. 292 (3), 771–785. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.764720
Han, S. T., Rab, A., Pellicore, M. J., Davis, E. F., McCague, A. F., Evans, T. A., et al. (2018). Residual function of cystic fibrosis mutants predicts response to small molecule CFTR modulators. JCI Insight 3 (14), 121159. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121159
Harbeson, S. L., Morgan, A. J., Liu, J. F., Aslanian, A. M., Nguyen, S., Bridson, G. W., et al. (2017). Altering metabolic profiles of drugs by precision deuteration 2: discovery of a deuterated analog of ivacaftor with differentiated pharmacokinetics for clinical development. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 362 (2), 359–367. doi: 10.1124/jpet.117.241497
Harris, J. K., Wagner, B. D., Zemanick, E. T., Robertson, C. E., Stevens, M. J., Heltshe, S. L., et al. (2019). Changes in airway microbiome and inflammation with ivacaftor treatment in patients with cystic fibrosis and the G551D mutation. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201907-493OC
Haws, C. M., Nepomuceno, I. B., Krouse, M. E., Wakelee, H., Law, T., Xia, Y., et al. (1996). Delta F508del-CFTR channels: kinetics, activation by forskolin, and potentiation by xanthines. Am. J. Physiol. 270 (5 Pt 1), 1544–1555. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.270.5.C1544
Hayes, D., Jr., McCoy, K. S., Sheikh, S. I. (2014). Resolution of cystic fibrosis-related diabetes with ivacaftor therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 190 (5), 590–591. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201405-0882LE
Hayes, D., Jr., Kopp, B. T., Hill, C. L., Lallier, S. W., Schwartz, C. M., Tadesse, M., et al. (2019). Cell therapy for cystic fibrosis lung disease: regenerative basal cell amplification. Stem Cells Trans. Med. 8 (3), 225–235. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0098
He, L., Kota, P., Aleksandrov, A. A., Cui, L., Jensen, T., Dokholyan, N. V., et al. (2013). Correctors of ΔF508 CFTR restore global conformational maturation without thermally stabilizing the mutant protein. FASEB J. 27 (2), 536–545. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-216119
Heijerman, H. G. M., McKone, E. F., Downey, D. G., Van Braeckel, E., Rowe, S. M., Tullis, E., et al. (2019). Efficacy and safety of the elexacaftor plus tezacaftor plus ivacaftor combination regimen in people with cystic fibrosis homozygous for the F508del mutation: a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 394 (10212), 1940–1948. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32597-8
Heltshe, S. L., Mayer-Hamblett, N., Burns, J. L., Khan, U., Baines, A., Ramsey, B. W., et al. (2015). Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis with G551D-CFTR treated with ivacaftor. Clin. Infect. Dis. 60 (5), 703–712. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu944
Hisert, K. B., Heltshe, S. L., Pope, C., Jorth, P., Wu, X., Edward, R. M., et al. (2017). Restoring cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function reduces airway bacteria and inflammation in people with cystic fibrosis and chronic lung infections. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 195 (12), 1617–1628. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201609-1954OC
Hou, X., Wu, Q., Rajagopalan, C., Zhang, C., Boubamdan, M., Wei, H., et al. (2019). CK19 stabilizes CFTR at the cell surface by limiting its endocytic pathway degradation. FASEB J. 33 (11), 12602–12615. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901050R
Howard, M., Frizzell, R. A., Bedwell, D. M. (1996). Aminoglycoside antibiotics restore CFTR function by overcoming premature stop mutations. Nat. Med. 2 (4), 467–469. doi: 10.1038/nm0496-467
Hudson, R. P., Dawson, J. E., Chong, P. A., Yang, Z., Millen, L., Thomas, P. J., et al. (2017). Direct binding of the corrector VX-809 to human CFTR NBD1: Evidence of an allosteric coupling between the binding site and the NBD1:CL4 interface. Mol. Pharmacol. 92 (2), 124–135. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.108373
Hutt, D. M., Herman, D., Rodrigues, A. P., Noel, S., Pilewski, J. M., Matteson, J., et al. (2010). Reduced histone deacetylase 7 activity function to misfolded CFTR in cystic fibrosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 6 (1), 25–33. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.275
Hutt, D. M., Loguercio, S., Campos, A. R., Balch, W. E. (2018). A proteomic variant approach (ProVarA) for personalized medicine of inherited and somatic disease. J. Mol. Med. 430 (18 Pt A), 2951–2973. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.06.017
Igreja, S., Clarke, L. A., Botelho, H. M., Marques, L., Amaral, M. D. (2016). Correction of a cystic fibrosis splicing mutation by antisense oligonucleotides. Hum. Mutat. 37 (2), 209–215. doi: 10.1002/humu.22931
Illek, B., Fiscker, H. (1998). Flavonoids stimulate Cl conductance of human airway epithelium in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. 275 (5), L902–L910. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1998.275.5.L902
Jensen, T. J., Loo, M. A., Pind, S., Williams, D. B., Goldberg, A. L., Riordan, J. R. (1995). Multiple proteolytic systems, including the proteasome, contribute to CFTR processing. Cell 83 (1), 129–135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90241-4
Jih, K. Y., Hwang, T. C. (2013). VX-770 potentiates CFTR function by promoting decoupling between the gating cycle and ATP hydrolysis cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110 (11), 4404–4409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215982110
Kalid, O., Mense, M., Fischman, S., Shitrit, A., Bihler, H., Ben-Zeev, E., et al. (2010). Small molecule correctors of F508del-CFTR discovered by structure-based virtual screening. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 24 (12), 971–991. doi: 10.1007/s10822-010-9390-0
Kandasamy, J., Atia-Glikin, D., Shulman, E., Shapira, K., Shavit, M., Belakhov, V., et al. (2012). Increased selectivity toward cytoplasmic versus mitochondrial ribosome confers improved efficiency of synthetic aminoglycosides in fixing damaged genes: a strategy for treatment of genetic disease caused by nonsense mutations. J. Med. Chem. 55 (23), 10630–10643. doi: 10.1021/jm3012992
Keating, D., Marigowda, G., Burr, L., Daines, C., Mall, M. A., NcKone, E. F., et al. (2018). VX-445-tezacaftor-ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis and one or two phe508del alleles. N. Engl. J. Med. 379 (17), 1612–1620. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1807120
Keenan, M. M., Huang, L., Jordan, N. J., Wong, E., Cheng, Y., Valley, H. C., et al. (2019). Nonsense mediated RNA decay pathway inhibition restores expression and function of W1282X CFTR. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 61 (3), 290–300. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0316OC
Kelly, A., De Leon, D. D., Sheikh, S., Cambum, D., Kubrak, C., Peleckis, A. J., et al. (2019). Islet hormone and incretin secretion in cystic fibrosis after four months of ivacaftor therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 199 (3), 342–351. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201806-1018OC
Kerem, B., Rommens, J. M., Buchanan, J. A., Markiewicz, D., Cox, T. K., Chakravarti, A., et al. (1989). Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science 245 (4922), 1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460
Kerem, E., Konstan, M. W., De Boeck, K., Accurso, F. J., Sermet-Gaudelus, I., Wilschanski, M., et al. (2014). Ataluren for the treatment of nonsense-mutation cystic fibrosis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2 (7), 539–547. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70100-6
Kim, S. J., Skach, W. R. (2012). Mechanisms of CFTR folding at the endoplasmic reticulum. Front. Pharmacol. 3, 201. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00201
Knowles, M. R., Stutts, M. J., Spock, A., Fischer, N., Gatzy, J. T., Boucher, R. C. (1983). Abnormal ion permeation through cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelium. Science 221 (4615), 1067–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6308769
Konstan, M. W., McKone, E. F., Moss, R. B., Marigowda, G., Tian, S., Waltz, D., et al. (2017). Assessment of safety and efficacy of long-term treatment with combination lumacaftor and ivacaftor therapy in patients with cystic fibrosis homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation (PROGRESS): a phase 2, extension study. Lancet Respir. Med. 5 (2), 107–118. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30427-1
Laselva, O., Molinski, S., Casavola, V., Bear, C. E. (2018). Correctors of the major cystic fibrosis mutant interact through membrane-spanning domains. Mol. Pharmacol. 93 (6), 612–618. doi: 10.1124/mol.118.111799
Leonard, A., Lebecque, P., Dingemanse, J., Leal, T. (2012). A randomized placebo-controlled trial of miglustat in cystic fibrosis based on nasal potential difference. J. Cyst. Fibros. 11 (3), 231–236. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2011.12.004
Leubitz, A., Frydman-Marom, A., Sharpe, N., van Duzer, J., Campbell, K. C. M., Vanhoutte, F. (2019). Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of single ascending dose of ELX-02, a potential treatment for genetic disorder caused by nonsense mutations, in healthy volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 8 (8), 984–994. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.647
Liang, F., Shang, H., Jordan, N. J., Wong, E., Mercadante, D., Saltz, J., et al. (2017). High-throughput screening for readthrough modulators of CFTR PTC mutations. SLAS Technol. 22 (3), 315–324. doi: 10.1177/2472630317692561
Liu, F., Zhang, Z., Csanády, L., Gadsby, D. C., Cheng, J. (2017). Molecular structure of the human CFTR ion channel. Cell 169 (1), 85–95.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.024
Liu, F., Zhang, Z., Levit, A., Levring, J., Touhara, K. K., Shoichet, B. K., et al. (2019). Structural identification of a hotspot on CFTR for potentiation. Science 364 (6446), 1184–1188. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw7611
Liu, Q., Sabirzhanova, I., Bergbower, E. A. S., Yanda, M., Guggino, W. B., Cebotaru, L. (2019). The CFTR corrector, VX-809 (lumacaftor), rescues ABCA4 trafficking mutants: a potential treatment for Stargardt disease. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 53 (2), 400–412. doi: 10.33594/000000146
Lobo, M. J., Amaral, M. D., Zaccolo, M., Farinha, C. M. (2016). EPAC1 activation by cAMP stabilizes CFTR at the membrane by promoting its interaction with NHERF1. J. Cell Sci. 129 (13), 2599–2612. doi: 10.1242/jcs.185629
Loo, T. W., Clarke, D. M. (2017). Corrector VX-809 promotes interactions between cytoplasmic loop one and the first nucleotide-binding domain of CFTR. Biochem. Pharmacol. 136, 24–31. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.03.020
Lopes-Pacheco, M., Boinot, C., Sabirzhanova, I., Morales, M. M., Guggino, W. B., Cebotaru, L. (2015). Combination of correctors rescue ΔF508del-CFTR by reducing its association with Hsp40 and Hsp27. J. Biol. Chem. 290 (42), 25636–25645. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.671925
Lopes-Pacheco, M., Sabirzhanova, I., Rapino, D., Morales, M. M., Guggino, W. B., Cebotaru, L. (2016). Correctors rescue CFTR mutations in nucleotide-binding domain 1 (NBD1) by modulating proteostasis. Chembiochem 17 (6), 493–505. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201500620
Lopes-Pacheco, M., Boinot, C., Sabirzhanova, I., Rapino, D., Cebotaru, L. (2017). Combination of correctors rescues CFTR transmembrane-domain by mitigating their interactions with proteostasis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 41 (6), 2194–2210. doi: 10.1159/000475578
Lopes-Pacheco, M., Kitoko, J. Z., Morales, M. M., Petrs-Silva, H., Rocco, P. R. M. (2018). Self-complementary and tyrosine-mutant rAAV vectors enhance transduction in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 372 (2), 99–107. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.09.015
Lopes-Pacheco, M., Pedemonte, N., Kicic, A. (2019). Editorial: Emerging therapeutic approaches for cystic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 1440. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01440
Lopes-Pacheco, M. (2016). CFTR Modulators: Shedding light on precision medicine for cystic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 7, 275. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00275
Loureiro, C. A., Matos, A. M., Dias-Alvez, Â., Pereira, J. F., Uliyakina, I., Barros, P., et al. (2015). A molecular switch in the scaffold NHERF1 enables misfolded CFTR to evade the peripheral quality control checkpoint. Sci. Signal. 8 (377), ra48. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa1580
Lucarelli, M., Narzi, L., Pierandrei, S., Bruno, S. M., Stamato, A., d'Avanzo, M., et al. (2010). A new complex allele of the CFTR gene partially explains the variable phenotype of the L997F mutation. Genet. Med. 12 (9), 548–555. doi: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181ead634
Lukacs, G. L., Verkman, A. S. (2012). CFTR: folding, misfolding and correcting the ΔF508 conformational defect. Trends Mol. Med. 18 (2), 81–91. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.10.003
Marson, F. A. L., Bertuzzo, C. S., Ribeiro, J. D. (2016). Classification of CFTR mutation classes. Lancet Respir. Med. 4 (8), e37–e38. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30188-6
Matos, A. M., Gomes-Duarte, A., Faria, M., Barros, P., Jordan, P., Amaral, M. D., et al. (2018). Prolonged co-treatment with HGF sustains epithelial integrity and improves pharmacological rescue of phe508del-CFTR. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 13026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31514-2
Matthes, E., Goepp, J., Carlile, G. W., Luo, Y., Dejgaard, K., Billet, A., et al. (2016). Low free drug concentration prevents inhibition of F508del CFTR functional expression by the potentiator VX-770 (ivacaftor). Br. J. Pharmacol. 173 (3), 459–470. doi: 10.1111/bph.13365
Matthes, E., Goepp, J., Martini, C., Shan, J., Liao, J., Thomas, D. Y., et al. (2018). Variable responses to CFTR correctors in vitro: estimating the design effect in precision medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1490. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01490
McCague, A. F., Raraigh, K. S., Pellicore, M. J., Davis-Marcisak, E. F., Evans, T. A., Han, S. T., et al. (2019). Correlating cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function with clinical features to inform precision treatment of cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 199 (9), 1116–1126. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201901-0145OC
McColley, S. A., Konstan, M. W., Ramsey, B. W., Stuart Elborn, J., Boyle, M. P., Wainwright, C. E., et al. (2019). Limacaftor/ivacaftor pulmonary exacerbations in patients irrespective of initial changes in FEV1. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (1), 94–101. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2018.07.011
McGarry, M. E., Illek, B., Ly, N. P., Zlock, L., Olshansky, S., Moreno, C., et al. (2017). In vivo and in in vitro ivacaftor response in cystic fibrosis patients with residual CFTR function: N-of-1 studies. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 52 (4), 472–479. doi: 10.1002/ppul.23659
McKone, E. F., Borowitz, D., Devinek, P., Griese, M., Konstan, M. W., Wainwright, C., et al. (2014). Long-term safety and efficacy of ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis who have the Gly551Asp-CFTR mutation: a phase 3, open-label extension study (PERSIST). Lancet Respir. Med. 2, 902–910. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70218-8
McNamara, J. J., McColley, S. A., Marigowda, G., Liu, F., Tian, S., Owen, C. A., et al. (2019). Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lumacaftor and ivacaftor combination therapy in children aged 2-5 years with cystic fibrosis homozygous for F508del-CFTR: ah open-label phase 3 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 7 (4), 325–335. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30460-0
Merket, S., Schubert, M., Olmer, R., Engles, L., Radetzki, S., Veltman, M., et al. (2019). High-throughput screening for modulators of CFTR activity based on genetically engineered cystic fibrosis disease-specific iPSCs. Stem Cell Rep. 12 (6), 1389–1403. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.04.014
Michels, M., Matte, U., Fraga, L. R., Mancuso, A. C. B., Ligabue-Braun, R., Berneira, E. F. R., et al. (2019). Determining the pathogenicity of CFTR missense variants: multiple comparison of in silico predictors and variant annotation data bases. Genet. Mol. Biol. 42 (3), 560–570. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-gmb-2018-0148
Middleton, P. G., Mall, M. A., Drevínek, P., Lands, L. C., McKone, E. F., Polineni, D., et al. (2019). Elexacaftor-tezacaftor-ivacaftor for cystic fibrosis with a single phe508del allele. N. Eng. J. Med. 381 (19), 1809–1819. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908639
Milla, C. E., Ratjen, F., Marigowda, G., Liu, F., Waltz, D., Rosenfeld., M. (2017). Lumacaftor/ivacaftor in patients aged 6-11 years with cystic fibrosis and homozygous for F508del-CFTR. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 195 (7), 912–920. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201608-1754OC
Molinski, S. V., Ahmadi, S., Ip, W., Ouyang, H., Villella, A., Miller, J. P., et al. (2017). Orkambi® and amplifier co-therapy improves function from a rare CFTR mutation in gene-edited cells and patient tissue. EMBO Mol. Med. 9 (9), 1224–1243. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201607137
Moniz, S., Sousa, M., Moraes, B. J., Mendes, A. I., Palma, M., Barreto, C., et al. (2013). HGF stimulation of Rac1 signaling enhances pharmacological correction of the most prevalent cystic fibrosis mutant F508del-CFTR. ACS Chem. Biol. 8 (2), 432–442. doi: 10.1021/cb300484r
Moore, P. J., Tarran, R. (2018). The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) as a therapeutic target for cystic fibrosis lung disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 22 (8), 687–701. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1501361
Mutyam, V., Du, M., Xue, X., Keeling, K. M., White, E. L., Bostwick, J. R., et al. (2016). Discovery of clinically approved agents that promote suppression of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator nonsense mutations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 194 (9), 1092–1103. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201601-0154OC
Mutyam, V., Libby, E. F., Peng, N., Hadjiliadis, D., Bonk, M., Solomon, G. M., et al. (2017). Therapeutic benefit observed with the CFTR potentiator, ivacaftor, in a CF patient homozygous for the W1282X CFTR nonsense mutation. J. Cyst. Fibros. 16 (1), 24–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2016.09.005
Narayanan, S., Mainz, J. G., Gala, S., Tabori, H., Grossoehme, D. (2017). Adherence to therapies in cystic fibrosis: a targeted literature review. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 11 (2), 129–145. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2017.1280399
Nguyen, L. S., Wilkinson, M. F., Gecz, J. (2014). Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: inter-individual variability and human disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 46 (Pt 2), 175–186. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.10.016
Noël, S., Wilke, M., Bot, A. G., De Jonge, H. R., Becq, F. (2008). Parallel improvement of sodium and chloride transport defect by miglustat (n-butyldeoxyjyrimicin) in cystic fibrosis epithelial cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 325 (3), 1016–10235. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.135582
Norez, C., Noel, S., Wilke, M., Bijvelds, M., Jorna, H., Melin, P., et al. (2006). Rescue of functional delF508-CFTR channels in cystic fibrosis epithelial cells by the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor miglustat. FEBS Lett. 580 (8), 2081–2086. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.03.010
O'Neal, W. K., Knowles, M. R. (2018). Cystic fibrosis disease modifiers: complex genetics defines the phenotypic diversity in a monogenic disease. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 19, 201–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-083117-021329
O'Sullivan, B. P., Orenstein, D. M., Milla, C. E. (2013). Pricing for orphan drugs: will the market bear what society cannot? JAMA 310 (13), 1343–1344. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.278129
Oates, G. R., Schechter, M. S. (2016). Socioeconomic status and health outcomes: cystic fibrosis as a model. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 10 (9), 967–977. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2016.1196140
Okiyoneda, T., Barrière, H., Bagdány, M., Rabeh, W. M., Du, K., Höhfeld, J., et al. (2010). Peripheral protein quality control removes unfolded CFTR from the plasma membrane. Science 329, 805–810. doi: 10.1126/science.1191542
Okiyoneda, T., Veit, G., Dekkers, J. F., Bagdany, M., Soya, N., Roldan, A., et al. (2013). Mechanism-based corrector combination restores ΔF508-CFTR folding and function. Nat. Chem. Biol. 9 (7), 444–454. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1253
Okiyoneda, T., Veit, G., Sakai, R., Aki, M., Pujihara, T., Higashi, M., et al. (2018). Chaperone-independent peripheral quality control of CFTR by RFFL E3 ligase. Del. Cell 44 (6), 694–708. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.02.001
Oliver, K. E., Rauscher, R., Mijnders, M., Wang, W., Wolpert, M. J., Maya, J., et al. (2019). Slowing ribosome velocity restores folding and function of mutant CFTR. J. Clin. Invest. 129 (2), 5236–5253. doi: 10.1172/JCI124282
Orestein, D. M., O'Sullivan, B. P., Quinton, P. M. (2015). Cystic fibrosis: breakthrough drugs at break-the-bank prices. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 4 (6), 8–9. doi: 10.7453/gahmj.2015.123
Osman, G., Rodriguez, J., Chan, S. Y., Chisholm, J., Duncan, G., Kim, N., et al. (2018). PEGylated enhanced cell penetration peptide nanoparticles for lung gene therapy. J. Control. Release 285, 35–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.07.001
Pankow, S., Bamberger, C., Calzolari, D., Martínez-Bartolomé, S., Lavallée-Adam, M., Balch, W. E., et al. (2015). ΔF508 CFTR interactome remodeling promotes rescue of cystic fibrosis. Nature 528 (7583), 510–516. doi: 10.1038/nature15729
Park, J., Khloya, P., Seo, Y., Kumar, S., Lee, H. K., Jeon, D. K., et al. (2016). Potentiaton of ΔF508- and G551D-CFTR-mediated Cl- current by novel hydroxypyrazolines. PloS One 11 (2), e0149131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149131
Patel, W., Moore, P. J., Sassano, M. F., Lopes-Pacheco, M., Aleksandrov, A. A., Amaral, M. D., et al. (2019). Increased in cytosolic Ca2+ induce dynamin and calcineurin-dependent internalisation of CFTR. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 76 (5), 977–994. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2989-3
Pearson, I., Rothwell, B., Olaye, A., Knight, C. (2018). Economic modeling considerations for rare diseases. Value Health 21 (5), 515–524. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2018.02.008
Pedemonte, N., Lukacs, G. L., Du, K., Caci, E., Zegarra-Moran, O., Galietta, L. J., et al. (2005a). Small-molecule correctors of defective deltaF508-CFTR cellular processing identified by high-throughput screening. J. Clin. Invest. 115 (9), 2564–2571. doi: 10.1172/JCI24898
Pedemonte, N., Sonawane, N. D., Taddei, A., Hu, J., Zegarra-Moran, O., Suen, Y. F., et al. (2005b). Phenylglycine and sulfonamide correctors of defective delta F508 and G551D cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride-channel gating. Mol. Pharmacol. 67 (5), 1797–1807. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.010959
Pedemonte, N., Tomati, V., Sondo, E., Galietta, L. J. (2010). Influence of cell background on pharmacological rescue of mutant CFTR. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 298 (4), C866–C874. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00404.2009
Pereira, S. V., Ribeiro, J. D., Ribeiro, A. F., Bertuzzo, C. S., Marson, F. A. L. (2019). Novel, rare and common pathogenic variants in the CFTR gene screened by high-throughput sequencing technology and predicted by in silico tools. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 6234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42404-6
Pereyro, S., on behalf of Associación Argentina de Lucha contra la Enfermedad Fibroquística del Páncreas [FIPAN] (2018). Registro de Fibrosis Quística, Available at: https://www.sap.org.ar/docs/congresos_2018/Neumonolog%C3%ADa/Pereyro_fibrosis_quistica.pdf.
Phuan, P. W., Veit, G., Tan, J., Roldan, A., Finkbeiner, W. E., Lukacs, G. L., et al. (2014). Synergy-based small-molecule screen using a human lung epithelial cell line yields ΔF508-CFTR correctors that augment VX-809 maximal efficacy. Mol. Pharmacol. 86 (1), 42–51. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.092478
Phuan, P. W., Veit, G., Tan, J. A., Finkbeiner, W. E., Lukacs, G. L., Verkman, A. S. (2015). Potentiators of defective ΔF508-CFTR gating that do not interfere with corrector action. Mol. Pharmacol. 88 (4), 791–799. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.099689
Phuan, P. W., Son, J. H., Tan, J. A., Musante, I., Zlock, L., Nielson, D. W., et al. (2018). Combination potentiator (‘co-potentiator') therapy for CF caused CFTR mutants, including N1303K, that are poorly responsive to single potentiators. J. Cyst. Fibros. 17 (5), 595–606. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2018.05.010
Pranke, I., Hatton, A., Simonin, J., Jais, J. P., Le Pimpec-Barthes, F., Carsin, A., et al. (2017). Correction of CFTR function in nasal epithelial cells from cystic fibrosis predicts improvement of respiratory function by CFTR modulators. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 7375. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07504-1
Pranke, I., Bidou, L., Martin, N., Blanchet, S., Hatton, A., Karri, S., et al. (2018). Factors influencing readthrough therapy for frequent cystic fibrosis premature termination codons. ERJ Open Res. 4 (1), 00080–02017. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00080-2017
Pranke, I., Hatton, A., Masson, A., Flament, T., Le Bourgeois, M., Chedevergne, F., et al. (2019). Might brushed nasal cells be a surrogate for CFTR modulator clinical response? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 199 (1), 123–126. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201808-1436LE
Prayle, A., Watson, A., Fortnum, H., Smyth, A. (2010). Side effects of aminoglycosides on the kidney, ear and balance in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 65 (7), 654–658. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.131532
Pushpakom, S., Iorio, F., Eyers, P. A., Escott, K. J., Hopper, S., Wells, A., et al. (2019). Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 18 (1), 41–58. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.168
Quinton, P. M. (1983). Chloride impermeability in cystic fibrosis. Nature 301, 421–422. doi: 10.1038/301421a0
Quittner, A. L., Zhang, J., Marynchenko, M., Chopra, P. A., Signorovitch, J., Yushkina, Y., et al. (2014). Pulmonary medication adherence and health-care use in cystic fibrosis. Chest 146 (1), 142–151. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-1926
Quittner, A., Suthoff, E., Rendas-Baum, R., Bayliss, M. S., Sermet-Gaudelus, I., Castiglione, B., et al. (2015). Effect of ivacaftor treatment in patients with cystic fibrosis and the G551D-CFTR mutation: patient-reported outcomes in the STRIVE randomized, controlled trial. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 13, 93. doi: 10.1186/s12955-015-0293-6
Quittner, A. L., Saez-Flores, E., Barton, J. D. (2016). The psychological burden of cystic fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 22 (2), 187–191. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000244
Ramos, K. J., Smith, P. J., McKone, E. F., Pilewski, J. M., Lucy, A., Hempstead, S. E., et al. (2019). Lung transplant referral for individuals with cystic fibrosis: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus guidelines. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (3), 321–333. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.03.002
Ramsey, B. W., Davies, J., McElvaney, N. G., Tullis, E., Bell, S. C., Drevínek, P., et al. (2011). A CFTR potentiator in patients with cystic fibrosis and the G551D mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 365 (18), 1663–1672. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1105185
Rapino, D., Sabirzhanova, I., Lopes-Pacheco, M., Grover, R., Guggino, W. B., Cebotaru, L. (2015). Rescue of NBD2 mutants N1303K and S1235R of CFTR by small-molecule correctors and transcomplementation. PloS One 10 (3), e0119796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119796
Ratjen, F., Hug, C., Marigowda, G., Tian, S., Huang, X., Stanojevic, S., et al. (2017). Efficacy and safety of lumacaftor and ivacaftor in patients aged 6-11 with cystic fibrosis homozygous for F508del-CFTR: a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 5 (7), 557–567. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30215-1
Ren, H. Y., Grove, D. E., De La Rosa, O., Houck, S. A., Sopha, P., Van Goor, F., et al. (2013). VX-809 corrects folding defects in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator through action on membrane-spanning domain 1. Mol. Biol. Cell 24 (19), 3016–3024. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e13-05-0240
Rich, D. P., Anderson, M. P., Gregory, R. J., Cheng, S. H., Paul, S., Jefferson, D. M., et al. (1990). Expression of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator corrects defective chloride channel regulation in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Nature 347 (6291), 358–363. doi: 10.1038/347358a0
Riordan, J. R., Rommens, J. M., Kerem, B., Alon, N., Rozmahel, R., Grzelczak, Z., et al. (1989). Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science 245 (4922), 1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911
Riordan, J. R. (2005). Assembly of functional CFTR chloride channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 67, 701–718. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.67.032003.154107
Romani, L., Oikonomou, V., Moretti, S., Iannitti, R. G., D'Adamo, M. C., Villella, V. R., et al. (2017). Thymosin α1 represents a potential single-molecule-based therapy for cystic fibrosis. Nat. Med. 23 (5), 590–600. doi: 10.1038/nm.4305
Rommens, J. M., Ianuzzi, M. C., Drumm, M. L., Melmer, G., Dean, M., Rozmahel, R., et al. (1989). Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science 245 (4922), 1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657
Ronan, N. J., Elborn, J. S., Plant, B. J. (2017). Current and emerging comorbidities in cystic fibrosis. Presse Med. 46 (6 Pt 2), e125–e138. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2017.05.011
Ronan, N. J., Einarsson, G. G., Twomey, M., Mooney, D., Mullane, D., NiChroinin, M., et al. (2018). CORK Study in cystic fibrosis: sustained improvement in ultra-low-dose chest CT scores after CFTR modulation with ivacaftor. Chest 153 (2), 395–403. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.10.005
Rosenfeld, M., Wainwright, C. E., Higgins, M., Wang, L. T., McKee, C., Campbell, D., et al. (2018). Ivacaftor treatment of cystic fibrosis in children aged 12 to <24 months and with a CFTR gating mutation (ARRIVAL): a phase 3 single-arm study. Lance Respir. Med. 6 (7), 545–553. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30202-9
Rosenfeld, M., Cunningham, S., Harris, W. T., Lapey, A., Regelmann, W. E., Sawicki, G. S., et al. (2019). An open-label extension study of ivacaftor in children with CF and a CFTR gating mutation initiating treatment at age 2-5 years (KLIMB). J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (6), 838–843. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.03.009
Rowe, S. M., Miller, S., Sorscher, E. J. (2005). Cystic fibrosis. N. Eng. J. Med. 352 (19), 1992–2001. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra043184
Rowe, S. M., Sloane, P., Tang, L. P., Backer, K., Mazur, M., Buckley-Lanier, J., et al. (2011). Suppression of CFTR premature termination codons and rescue of CFTR protein and function by the synthetic aminoglycoside NB54. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 89 (11), 1149–1161. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0787-6
Rowe, S. M., Heltshe, S. L., Gonska, T., Donaldson, S. H., Borowitz, D., Gelfond, D., et al. (2014). Clinical mechanism of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator potentiator ivacaftor in G551D-mediated cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 190 (2), 175–184. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201404-0703OC
Rowe, S. M., Daines, C., Ringshausen, F. C., Kerem, E., Tullis, E., Nair, N., et al. (2017a). Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in residual-function heterozygotes with cystic fibrosis. N. Eng. J. Med. 377 (21), 2024–2034. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709847
Rowe, S. M., McColley, S. A., Rietschel, E., Li, X., Bell, S. C., Konstan, M. W., et al. (2017b). Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor treatment of patients with cystic fibrosis heterozygous for F508del-CFTR. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc 14 (2), 213–219. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201609-689OC
Rubenstein, R. C., Egan, M. E., Zeitlin, P. L. (1997). In vitro pharmacologic restoration of CFTR-mediated chloride transport with sodium 4-phenylbutyrate in cystic fibrosis epithelial cells containing delta F508-CFTR. J. Clin. Invest. 100 (10), 2457–2465. doi: 10.1172/JCI119788
Ruffin, M., Roussel, L., Maillé, É., Rousseau, S., Bronchiero, E. (2018). VX-809/VX-770 treatment reduces inflammatory response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa inprimary differentiated cystic fiborisis bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Phyiol. Lun Cell. Mol. Physiol. 314 (4), L635–L641. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00198.2017
Sabirzhanova, I., Lopes-Pacheco, M., Rapino, D., Grover, R., Handa, J. T., Guggino, W. B., et al. (2015). Rescuing trafficking mutants of the ATP-binding cassette protein, ABCA4, with small molecule correctors as a treatment for Stargardt eye disease. J. Biol. Chem. 290 (32), 19743–19755. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.647685
Saint-Criq, V., Gray, M. A. (2017). Role of CFTR in epithelial physiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 74 (1), 93–115. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2391-y
Sampson, H. M., Robert, R., Liao, J., Matthes, E., Carlile, G. W., Hanrahan, J. W., et al. (2011). Identification of a NBD1-binding pharmacological chaperone that corrects the trafficking defect of F508del-CFTR. Chem. Biol. 18 (2), 231–242. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.11.016
Sawicki, G. S., Ren, C. L., Konstan, M. W., Millar, S. J., Pasta, D. J., Quittner, A. L., et al. (2013). Treatment complexity in cystic fibrosis: trends over time and associations with site-specific outcomes. J. Cyst. Fibros. 12 (5), 461–467. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2012.12.009
Sawicki, G. S., McKone, E. F., Pasta, D. J., Millar, S. J., Wagener, J. S., Johnson, C. A., et al. (2015). Sustained benefit from ivacaftor demonstrated by combining clinical trial and cystic fibrosis patient registry data. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 192, 836–842. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201503-0578OC
Scanio, M. J. C., Searle, X. B., Liu, B., Koenig, J. R., Altenbach, R., Gfesser, G. A., et al. (2019). Discovery of ABBV-GLPG-3221, a potent corrector of CFTR for the treatment of cystic fibrosis. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 10 (11), 1543–1548. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00377
Scheneider, E. K. (2018). Cytochrome P450 3A4 induction: lumacaftor versus ivacaftor potentially resulting in significantly reduced plasma concentration of ivacaftor. Drug Metab. Lett. 12 (1), 71–74. doi: 10.2174/1872312812666180328105259
Schlander, M., Garattini, S., Holm, S., Kolominsky-Rabas, P., Nord, E., Persson, U., et al. (2014). Incremental cost per quality-adjuested life year gained? The need for alternative methods to evaluate medical interventions for ultra-rare disorders. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 3 (4), 399–422. doi: 10.2217/cer.14.34
Sergeev, V., Chou, F. Y., Lam, G. Y., Hamilton, C. M., Wilcox, P. G., Quon, B. S. (2019). The extra-pulmonary effects of CFTR modulators in cystic fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201909-671CME
Sermet-Gaudelus, I., Renouil, M., Fajac, A., Bidou, L., Parbaille, B., Pierrot, S., et al. (2007). In vitro prediction of stop-codon suppression by intravenous gentamicin in patients with cystic fibrosis: a pilot study. BMC Med. 5, 5. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-5-5
Sermet-Gaudelus, I., Boeck, K. D., Casimir, G. J., Bermeulen, F., Leal, T., Mogenet, A., et al. (2010). Ataluren (PTC124) induced cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein expression and activity in children with nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 182 (10), 1262–1272. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201001-0137OC
Sermet-Gaudelus, I., Delion, M., Durieu, I., Jacquot, J., Hubert, D. (2016). Bone demineralization is improved by ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis carrying the p.Gly551Asp mutation. J. Cyst. Fibros. 15 (6), e67–e69. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2016.09.003
Sermet-Gaudelus, I., Clancy, J. P., Nichols, D. P., Nick, J. A., De Boeck, K., Solomon, G. M., et al. (2019). Antisense oligonucleotide eluforsen improves CFTR function in F508del cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (4), 536–542. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2018.10.015
Shakkottai, A., Kidwell, K. M., Townsend, M., Nasr, S. Z. (2014). A five-year retrospective analysis of adherence in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 50 (12), 1224–1229. doi: 10.1002/ppul.23307
Sharma, M., Pampinella, F., Nemes, C., Benharouga, M., So, J., Du, K., et al. (2004). Misfolding diverts CFTR from recycling to degradation: quality control at early endosomes. J. Cell Biol. 164 (6), 923–933. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200312018
Sharma, D., Xing, S., Hung, Y. T., Caskey, R. N., Dowell, M. L., Touchette, D. R. (2018). Cost-effectiveness analysis of lumacaftor and ivacaftor combination for the treatment of patients with cystic fibrosis in the United States. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 13 (1), 172. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0914-3
Sharma, N., Evans, T. A., Pellicore, M. J., Davis, E., Aksit, M. A., McCague, A. F., et al. (2018). Capitalizing on the heterogeneous effects of CFTR nonsense and frameshift variants to inform therapeutic strategy for cystic fibrosis. PloS Genet. 14 (11), e1007723. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007723
Simpson, J. C., Joggerst, B., Laketa, V., Verissimo, F., Cetin, C., Erfle, H., et al. (2012). Genome-wide RNAi screening identified human proteins with a regulatory function in the early secretory pathway. Nat. Cell. Biol. 14 (7), 764–774. doi: 10.1038/ncb2510
Singh, A. K., Fan, Y., Balut, C., Alani, S., Manelli, A., Swensen, A. M., et al. (2019). Biological characterization of F508delCFTR protein processing by the CFTR corrector ABBV-2222/GLPG2222. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 372 (1), 107–118. doi: 10.1124/jpet.119.261800
Siracusa, C. M., Ryan, J., Burns, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, N., Clancy, J. P., et al. (2015). Eletronic monitoring reveals highly variable adherence patterns in patients prescribed ivacaftor. J. Cyst. Fibros. 14 (5), 621–626. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2015.05.009
Solem, C. T., Vera-Llonch, M., Liu, S., Botteman, M., Castiglione, B. (2016). Impact of pulmonary exacerbations and lung function on generic health-related quality of life in patients with cystic fibrosis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 14, 63. doi: 10.1186/s12955-016-0465-z
Sondo, E., Caci, E., Galietta, L. J. (2014). The TMEM16A chloride channel as an alternative therapeutic target in cystic fibrosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 52, 73–76. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.03.022
Sondo, E., Falchi, F., Caci, E., Ferrera, L., Giacomini, E., Pesce, E., et al. (2018). Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin ligase RNF5 rescues F508del-CFTR in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Cell Chem. Biol. 25 (7), 891–905. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.04.010
Stallings, V. A., Sainath, N., Oberle, M., Bertolaso, C., Schall, J. I. (2018). Energy balance and mechanisms of weight gating with ivacaftor treatment of cystic fibrosis gating mutations. J. Pediatr. 201, 229–237.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.05.018
Stanton, B. A., Coutermarsh, B., Bsrnaby, R., Hogan, D. (2015). Pseudomonas aeruginosa reduced VX-809 stimulates F508del-CFTR chloride secretion by airway epithelial cells. PloS One 10 (5), e0127742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127742
Stephenson, A. L., Sykes, J., Stanojevic, S., Quon, B. S., Marshall, B. C., Petren, K., et al. (2017). Survival comparison of patients with cystic fibrosis in Canada and the United States: a population-based cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 166 (8), 537–546. doi: 10.7326/M16-0858
Strauss, D. G., Blinova, K. (2017). Clinical trials in a dish. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 38 (1), 4–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2016.10.009
Strug, L. J., Gonska, T., He, G., Keenan, K., Ip, W., Boëlle, P. Y., et al. (2016). Cystic fibrosis gene modifier SLC26A9 modulates airway response to CFTR-directed therapeutics. Hum. Mol. Genet. 25 (50), 2590–4600. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw290
Sun, X., Yi, Y., Yan, Z., Rosen, B. H., Liang, B., Winter, M. C., et al. (2019). In utero and postnatal VX-770 administration rescues multiorgan disease in a ferret model of cystic fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 11 (485), eaau7531. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau7531
Suthoff, E. D., Bonafede, M., Limone, B., O'Callaghan, L., Sawicki, G. S., Wagener, J. S. (2016). Healthcare resource utilization associated with ivacaftor use in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Med. Econ. 19 (9), 845–851. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2016.1178125
Swiatecka-Urban, A., Brown, A., Moreau-Marquis, S., Renuka, J., Coutermarsh, B., Barnaby, R., et al. (2005). The short apical membrane half-life of rescue {Delta}F508-cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) results from accelerated endocytosis of {Delta}F508-CFTR in polarized human airway epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 36762–36772. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508944200
Taylor-Cousar, J. L., Munck, A., McKone, E. F., van der Ent, C. K., Moeller, A., Simard, C., et al. (2017). Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis homozygous for Phe508del. N. Eng. J. Med. 377 (21), 2013–2023. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709846
Taylor-Cousar, J. L., Jain, M., Barto, T. L., Haddad, T., Atkinson, J., Tian, S., et al. (2018). Lumacaftor/ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis and advanced lung disease homozygous for F508del-CFTR. J. Cyst. Fibros. 17 (2), 228–235. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2017.09.012
Taylor-Cousar, J. L., Mall, M. A., Ramsey, B. W., McKone, E. F., Tullis, E., Marigowda, G., et al. (2019). Clinical development of triple-combination CFTR modulators for cystic fibrosis patients with one or two F508del alleles. ERJ Open Res. 5 (2), 00082–02019. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00082-2019
Tomati, V., Sondo, E., Armirotti, A., Caci, E., Pesce, E., Marini, M., et al. (2015). Genetic inhibition of the ubiquitin ligase Rnf5 attenuates phenotypes associated to F508del cystic fibrosis mutation. Sci. Rep. 5L, 12138. doi: 10.1038/srep12138
Tomati, V., Pesce, E., Caci, E., Sondo, E., Scudieri, P., Marini, M., et al. (2018a). High-throughput screening identifies FAU protein as a regulator of mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator channel. J. Biol. Chem. 293 (4), 1203–1217. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.816595
Tomati, V., Caci, E., Ferrera, L., Pesce, E., Sondo, E., Cholon, D. M., et al. (2018b). Thymosin α-1 does not correct F508del-CFTR in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. JCI Insight 3 (3), e98699. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.98699
Tosco, A., De Gregorio, F., Esposito, S., De Stefano, D., Sana, I., Ferrari, E., et al. (2016). A novel treatment of cystic fibrosis acting on-target: cysteamine plus epigallocatechin gallate for autophagy-dependent recue of class II-mutated CFTR. Cell Death Differ. 23 (8), 1380–1393. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.22
Trimble, A. T., Donaldson, S. H. (2018). Ivacaftor withdrawal syndrome in cystic fibrosis patients with the G551D mutation. J. Cyst. Fibros. 17 (2), e13–e16. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2017.09.006
Tsabari, R., Elyashar, H. I., Cymberknowh, M. C., Breuer, O., Armoni, S., Livnat, F., et al. (2016). CFTR potentiator therapy ameliorates impaired insulin secretion in CF patients with a gating mutation. J. Cystic Fibros. 15 (3), e25–e27. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2015.10.012
Van der Plas, S. E., Kelgtermans, H., De Munck, T., Martina, S. L. X., Dropsit, D., Quinton, E., et al. (2018). Discovery of N-(3-Carbamoyl-5,5,7,7-tetramethyl-5,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-c]pyran-2-yl)-lH-pyrazole-5-carboxamide. J. Med. Chem. 61 (4), 1425–1435. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01288
Van Goor, F., Straley, K. S., Cao, D., González, J., Hadida, S., Hazlewood, A., et al. (2006). Rescue of deltaF508-CFTR trafficking and gating in human cystic fibrosis airway primary cultures by small molecules. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 290 (6), L1117–L1130. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00169.2005
Van Goor, F., Hadida, S., Gootenhuis, P. D., Burton, B., Cao, D., Neuberger, T., et al. (2009). Rescue of CF airway epithelial cell function in vitro by a CFTR potentiator, VX-770. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106 (44), 18825–18830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904709106
Van Goor, F., Hadida, S., Gootenhuis, P. D., Burton, B., Stack, J. H., Straley, K. S., et al. (2011). Correction of the F508del-CFTR protein processing defect in vitro by investigational drug VX-809. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (46), 18843–18848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105787108
Van Koningsbruggen-Rietschel, S., Conrath, K., Fischer, R., Sutharsan, S., Kempa, A., Gleiber, W., et al. (2019). GLPG2737 in lumacaftor/ivacaftor-treated CF subjects homozygous for the F508del mutation: A randomized phase 2A trial (PELICAN). J. Cyst. Fibros. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.09.006
Veit, G., Avramescu, R. G., Perdomo, D., Phuan, P. W., Bagdany, M., Apaja, P. M., et al. (2014). Some gating potentiators, including VX-770, diminish ΔF508-CFTR functional expression. Sci. Transl. Med. 6 (246), 246ra97. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008889
Veit, G., Avramescu, R. G., Chiang, A. N., Houck, S. A., Cai, Z., Peters, K. W., et al. (2016a). From CFTR biology toward combinatorial pharmacotherapy: expanded classification of cystic fibrosis mutations. Mol. Biol. Cell. 27 (3), 424–433. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e14-04-0935
Veit, G., Oliver, K., Apaja, P. M., Perdomo, D., Bidaud-Meynard, A., Lin, S. T., et al. (2016b). Ribosomal stalk protein silencing partially corrects the ΔF508del-CFTR function expression defect. PLoS. Biol. 14 (5), e1002462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002462
Veit, G., Xu, H., Dreano, E., Avramescu, R. G., Bagdany, N., Beitel, L. K., et al. (2018). Structure-guided combination therapy to potently improve the function of mutant CFTRs. Nat. Med. 24 (11), 1732–1742. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0200-x
Veit, G., da Fonte, D. F., Avramescu, R. G., Premchandar, A., Bagdany, M., Xu, H., et al. (2019). Mutation-specific dual potentiators maximize rescue of CFTR gating mutants. J. Cyst. Fibros. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.10.011
Volkava, N., Moy, K., Evans, J., Campbell, D., Tian, S., Simard, C., et al. (2019). Disease progression in patients with cystic fibrosis treated with ivacaftor: Data from national US and UK registries. J. Cyst. Fibros. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.05.015
Wainwright, C. E., Elborn, J. S., Ramsey, B. W., Marigowda, G., Huang, X., Cipolli, M., et al. (2015). Lumacaftor-ivacaftor in patients with cystic fibrosis homozygous for phe508del CFTR. N. Engl. J. Med. 373 (3), 220–231. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1409547
Walker, S., Glume, P., McNamara, J., Solomon, M., Chilvers, M., Chmiel, J., et al. (2019). A phase 3 study of tezacaftor in combination with ivacaftor in children aged 6 through 11 years with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 18 (5), 708–713. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.06.009
Wang, X., Venable, J., LaPointe, P., Hutt, D. M., Koulov, A. V., Coppinger, J., et al. (2006). Hsp90 cochaperone Aha1 downregulation rescues misfolding of CFTR in cystic fibrosis. Cell 127 (4), 803–815. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.043
Wang, X., Liu, B., Searle, X., Yeung, C., Bogdan, A., Greszler, S., et al. (2018). Discovery of 4-[(2R,4R)-4-({[1-(2,2-Difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)cyclopropyl]carbonyl}amino)-7-(difluoromethoxy)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl]benzoic Acid (ABBV/GLPG-2222), a potent cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) corrector for the treatment of cystic fibrosis. J. Med. Chem. 61 (4), 1436–1449. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01339
Welch, E. M., Barton, E. R., Zhuo, J., Tomizawa, Y., Friesen, W. J., Trifillis., P., et al. (2007). PTC124 targets genetic disorders caused by nonsense mutations. Nature 447 (7140), 87–91. doi: 10.1038/nature05756
Welsh, M. J., Smith, A. E. (1993). Molecular mechanisms of CFTR chloride channel dysfunction in cystic fibrosis. Cell 73 (7), 1251–1254. doi: 10.1038/nature05756
Whiting, P., Al, M., Burgers, L., Weswood, M., Ryder, S., Hoogendoorn, M., et al. (2014). Ivacaftor for the treatment of patients with cystic fibrosis and the G551D mutation: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol. Assess. 18 (18), 1–106. doi: 10.3310/hta18180
Wilschanski, M., Zielenski, J., Markiewicz, D., Tsui, L. C., Corey, M., Levison, H., et al. (1995). Correlation of sweat chloride concentration with classes of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene mutations. J. Pediatr. 127 (5), 705–710. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(95)70157-5
Wilschanski, M., Yahav, Y., Yaacov, Y., Blau, H., Bentur, L., Rivlin, J., et al. (2003). Gentamicin-induced correction of CFTR function in patients with cystic fibrosis and CFTR stop mutations. N. Eng. J. Med. 349 (15), 1433–1441. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022170
Wilschanski, M., Miller, L. L., Shoseyov, D., Blau, H., Rivlin, J., Aviram, M., et al. (2011). Chronic ataluren (PTC124) treatment of nonsense mutation cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 38 (1), 59–69. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00120910
Xue, X., Mutyam, V., Tang, L., Biswas, S., Du, M., Jackson, L. A., et al. (2014). Synthetic aminoglycosides efficiently suppress cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator nonsense mutations and are enhanced by ivacaftor. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 50 (4), 805–816. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0282OC
Xue, X., Mutyam, V., Thakerar, A., Mobley, J., Bridges, R. J., Rowe, S. M., et al. (2017). Identification of the amino acids inserted during suppression of CFTR nonsense mutations and determination of their functional consequences. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26 (16), 3116–3129. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx196
Yeh, H. I., Sohma, Y., Conrath, K., Hwang, T. C. (2017). A common mechanism for CFTR potentiators. J. Gen. Physiol. 149 (12), 1105–1118. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201711886
Yeh, H. I., Qui, L., Sohma, Y., Conrath, K., Zou, X., Hwang, T. C. (2019). Identifying the molecular target sites for CFTR potentiators GLPG1837 and VX-770. J. Gen. Physiol. 151 (7), 912–928. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201912360
Yu, H., Burton, B., Huang, C. J., Worley, J., Cao, D., Johnson, J. P., Jr., et al. (2012). Ivacaftor potentiation of multiple CFTR channels with gating mutations. J. Cyst. Fibros. 11 (3), 237–245. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2011.12.005
Zaman, K., Sawczak, V., Zaidi, A., Butler, M., Bennett, D., Getsy, P., et al. (2016). Augmentation of CFTR maturation by S-nitroglutathione reductase. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 310 (3), L263–L270. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00269.2014
Zampoli, M., Zar, H., Morrow, B., The South African Cystic Fibrosis Registry Steering Committee. (2019). The South African Cystic Fibrosis Registry Initiative (SACFRI): Implementation challenges and initial data. Abstracts of the joint ALLSA, SATS and CWIG Congress in Petroria, July 2019. Afr. J. Thoracic Crit. Care Med. 25 (2), 675. Available at: http://www.ajtccm.org.za/index.php/SARJ/article/view/236/242 (accessed Nov 09th, 2019).
Zeitlin, P. L., Diener-West, M., Rubenstein, R. C., Boyle, M. P., Lee, C. K., Brass-Ernst, L. (2002). Evidence of CFTR function in cystic fibrosis after systemic administration of 4-phenylbutyrate. Mol. Ther. 6 (1), 119–124. doi: 10.1006/mthe.2002.0639
Zhang, L., Button, B., Gabriel, S. E., Burkett, S., Yan, Y., Skiadopoulos, M. H., et al. (2009). CFTR delivery to 25% of surface epithelial cells restores normal rates of mucus transport to human cystic fibrosis airway epithelium. PloS Biol. 7 (7), e1000155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000155
Zhang, Z., Liu, F., Chen, J. (2017). Conformation changes of CFTR upon phosphorylation and ATP binding. Cell 170 (3), 483–491. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.041
Zhang, Z., Liu, F., Chen, J. (2018). Molecular structure of the ATP-bound, phosphorylated human CFTR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115 (50), 12757–12762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815287115
Zhuo, Z., Wang, X., Li, M., Sohma, Y., Zou, X., Hwang, T. C. (2005). High affinity ATP/ADP analogues as new tools for studying CFTR gating. J. Physiol. 569 (Pt 2), 447–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.095083
Keywords: cystic fibrosis, CFTR mutations, personalized medicine, drug development, high-throughput screening, cell models, clinical trials, lung
Citation: Lopes-Pacheco M (2020) CFTR Modulators: The Changing Face of Cystic Fibrosis in the Era of Precision Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 10:1662. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01662
Received: 24 September 2019; Accepted: 19 December 2019;
Published: 21 February 2020.
Edited by:
Hugues Abriel, University of Bern, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2020 Lopes-Pacheco. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Miquéias Lopes-Pacheco, bWxvcGVzMDgxMUBnbWFpbC5jb20=; bWxwYWNoZWNvQGZjLnVsLnB0
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.