- 1Department of Neuroscience, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
- 2Science for Life Laboratory, Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
- 3Science for Life Laboratory, Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
- 4Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Institute of Neuroscience, Faculty of Medicine, Autonomous University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
The A2A adenosine (A2AR) and D2 dopamine (D2R) receptors form oligomers in the cell membrane and allosteric interactions across the A2AR–D2R heteromer represent a target for development of drugs against central nervous system disorders. However, understanding of the molecular determinants of A2AR–D2R heteromerization and the allosteric antagonistic interactions between the receptor protomers is still limited. In this work, a structural model of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer was generated using a combined experimental and computational approach. Regions involved in the heteromer interface were modeled based on the effects of peptides derived from the transmembrane (TM) helices on A2AR–D2R receptor–receptor interactions in bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) and proximity ligation assays. Peptides corresponding to TM-IV and TM-V of the A2AR blocked heterodimer interactions and disrupted the allosteric effect of A2AR activation on D2R agonist binding. Protein–protein docking was used to construct a model of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer with a TM-IV/V interface, which was refined using molecular dynamics simulations. Mutations in the predicted interface reduced A2AR–D2R interactions in BRET experiments and altered the allosteric modulation. The heterodimer model provided insights into the structural basis of allosteric modulation and the technique developed to characterize the A2AR–D2R interface can be extended to study the many other G protein-coupled receptors that engage in heteroreceptor complexes.
Introduction
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) play essential roles in physiological processes and are important therapeutic targets (Lefkowitz, 2004; Lagerstrom and Schioth, 2008). The vast majority of the research efforts that have been made to understand GPCR signaling was performed under the assumption that these membrane proteins function as monomers. Contrary to this view, there is now evidence suggesting that many GPCRs form homo- and heteromers at the cell surface (Franco et al., 2000; Overton and Blumer, 2000; Angers et al., 2001; Han et al., 2009; Hasbi et al., 2009, 2017; Navarro et al., 2010; Vidi et al., 2010; Borroto-Escuela et al., 2014; Fuxe et al., 2014; Meng et al., 2014; Marsango et al., 2015; Martinez-Munoz et al., 2016; Rico et al., 2017). At the molecular level, GPCR signaling is hence not only determined by conformational changes induced by agonist binding, but is also allosterically modulated by interactions with other receptors. Further characterization of the influence of receptor–receptor interactions on signaling will be crucial for understanding GPCR function and could lead to development of novel drugs.
A prototypical GPCR heteromer is the one formed by the A2A adenosine receptors (A2AR) and D2 dopamine receptors (D2R) (Fuxe et al., 2010). In vitro experiments demonstrated that activation of the A2AR reduces D2R high affinity binding of agonists, suggesting that allosteric receptor–receptor interactions in the plasma membrane influence D2R signaling (Ferre et al., 1991). This was further supported by the demonstration that the A2AR and D2R form heteroreceptor complexes with antagonistic receptor–receptor interactions in living cells and in brain tissue (Hillion et al., 2002; Fuxe et al., 2005). A considerable amount of experimental data, including biophysical, biochemical, chemical neuroanatomical, and behavioral studies support the view that A2AR–D2R heteromerization plays an important functional role in the basal ganglia (Ferre et al., 1991; Yang et al., 1995; Dasgupta et al., 1996; Fenu et al., 1997; Hillion et al., 2002; Canals et al., 2003; Kamiya et al., 2003; Ciruela et al., 2004; Fuxe et al., 2005, 2007b, 2010; Azdad et al., 2009; Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010a,b, 2018; Navarro et al., 2010; Fernandez-Duenas et al., 2012; Cordomi et al., 2015; Feltmann et al., 2018). The negative allosteric modulation exerted by A2AR activation on D2R signaling provided one mechanism contributing to the motor activation observed with general adenosine receptor antagonists (e.g., caffeine) and the neuroleptic effects of A2AR agonists (Fuxe et al., 2007a). For this reason, the A2AR–D2R heteroreceptor complex represents a new therapeutic target for disorders treated with drugs interacting with the D2R, such as neurodegenerative diseases, schizophrenia, and drug addiction (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2016b). For example, A2AR antagonists should inter alia enhance dopaminergic signaling by blocking A2AR activation by endogenous adenosine in A2AR–D2R oligomers, thereby reducing the negative allosteric modulation of the D2R protomer (Fuxe et al., 2015). This may contribute to the antiparkinsonian effects observed after treatment with A2AR antagonists, such as reduction of bradykinesia, motor fluctuations, and dyskinesia associated with chronic L-DOPA treatment (Schwarzschild et al., 2006; Armentero et al., 2011).
Despite the thorough characterization of GPCR heteromers by biophysical and biochemical methods (Angers et al., 2001; Vidi et al., 2010; Fernandez-Duenas et al., 2012; Borroto-Escuela et al., 2013; Fuxe et al., 2014; Marsango et al., 2015; Fuxe and Borroto-Escuela, 2016), the understanding of the structural basis of GPCR heteromerization and the associated negative and positive cooperativity remains limited. A major advancement in this area was the recent determination of GPCR crystal structures, which enable generation of atomic resolution models for homo- and heteroreceptor complexes. Crystal structures for representative members from the adenosine (Liu et al., 2012) and dopamine (Chien et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2018) receptor families have recently been solved. In addition, a number of class A GPCRs have crystallized as homodimers (Murakami and Kouyama, 2008; Wu et al., 2010; Granier et al., 2012; Manglik et al., 2012; Huang et al., 2013), providing different plausible orientations of two monomers relative to each other. The rapidly increasing amount of structural data can now contribute to generation of models of GPCR dimers, which could improve understanding of allosteric modulation.
In this work, a combined computational and experimental approach to construct atomic resolution models of GPCR dimers was developed. In order to predict the structure of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer, regions involved in the interface were identified based on experiments utilizing peptides corresponding to the transmembrane (TM) helices of the A2AR and D2R. The effects of synthetic peptides corresponding to the seven TM helices of the A2AR on A2AR–D2R heteromerization were assessed using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2013) and proximity ligation assays (PLAs). Combined with the corresponding BRET data for the seven TM peptides derived from the D2R sequence (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010b), an initial model of the A2AR–D2R heteromer was constructed computationally using protein–protein docking. The predicted heterodimer structure was refined using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The resulting A2AR–D2R structure was subsequently used to predict mutations in the dimer interface, which were evaluated experimentally to assess the model.
Materials and Methods
Plasmid Constructs
The cDNA encoding the human D2R, human A2AR, and human A1R cloned in pcDNA3.1+ were subcloned (without stop codons) in humanized pGFP2-N1 (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, United States), pEYFP-N1 (Clontech, Germany), and pRluc-N3 vectors (Packard Bioscience, Spain). The cDNA encoding human 3xHA-D2R cloned in pcDNA3.1+ and human D2R cloned in pGFP2-N1 (Perkin-Elmer, Spain) were used as template to generate the two mutants, Tyr192Ala5.41x42 and Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60 [generic GPCR residue numbers indicated in superscript (Isberg et al., 2015)], by means of the QuickChangeTM site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, Netherlands) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The other constructs used have been described previously (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010a,b).
Cell Culture and Transfection
HEK293T cells (American Type Culture Collection, United States) were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 units/ml penicillin/streptomycin, and 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2. Cells were plated in 6-well plates at a concentration of 1 × 106 cells/well or in 75 cm2 flasks and cultured overnight prior to transfection. Cells were transiently transfected using linear polyethylenimine (Polysciences Inc., United States). Rat primary striatal neuronal cells purchased from QBM Cell Science (Montreal, QC, Canada) were cultured in Neuro basal medium supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM GlutaMAX-1, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 100 U/ml penicillin G, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin and B-27 supplement at 37°C in a humidified 10% CO2 environment according to manufacturer’s instructions.
TM Peptide Treatment
Synthetic peptides, representing each of the TM peptides for the human A2AR, were obtained from Lazarova et al. (2004), Thevenin et al. (2005), Thevenin and Lazarova (2008), CASLO (Denmark) or Ana Spec Inc. (CA, United States) with ≥90% purity. The A2AR TM-I peptide consisted of residues 8–32 (VYITVELAIAVLAILGNVLVCWAVW); TM-II peptide of residues 43–66 (YFVVSLAAADIAVGVLAIPFAITI); TM-III peptide of residues 78–100 (LFIACFVLVLTQSSIFSLLAIAI); TM-IV peptide of residues 121–143 (AKGIIAICWVLSFAIGLTPMLGW); TM-V peptide of residues 174–198 (MNYMVYFNFFACVLVPLLLMLGVYL); TM-VI peptide of residues 235–261 (LAIIVGLFALAWLPLHIINCFTFFAPD); and TM-VII peptide of residues 267–291 (LWLMYLAIVLSHTNSVVNPFIYAYR). A di, tri- or quatribasic sequence (KK, KKK, or RKKK) was introduced at the N- and C-terminal to ensure incorporation into the plasma membrane of cells, as demonstrated previously (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2012, 2018). The synthetic peptide representing TM-V of the 5-HT1A receptor was described previously (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2012, 2015a,b). Immediately before use, the peptides were solubilized in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and diluted in the corresponding cell culture medium to yield a final concentration of 1% DMSO. We verified that, for each tested concentration of DMSO alone, no effect on cell viability was observed. Cells were incubated with the above mentioned peptides at 37°C for 2 h prior to performing BRET analysis, in situ PLA assays or binding assays.
BRET1 Assays
In the BRET1 assays, the receptors of interest were fused to either Renilla luciferase (RLuc) or yellow fluorescent protein (YFP). Detection of dimer interactions is based on that RLuc oxidation of the substrate coelenterazine h leads to light emission with a peak at 480 nm, which results in excitation of YFP (excitation and emission maxima of 475 and 530 nm, respectively) if the receptors are in close proximity (Pfleger and Eidne, 2006). In the BRET1 saturation assays (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2013), HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with constant amounts (1 μg) of plasmids encoding for D2RRluc and increasing amounts (0.5–8 μg) of plasmids encoding for A2ARY FP. Forty-eight hours after transfection the cells were rapidly washed twice in PBS, detached, and resuspended in the same buffer. Cell suspensions (20 μg proteins) were distributed in duplicate into 96-well microplates; black plates with transparent bottom (Corning 3651, Corning, Stockholm, Sweden) for fluorescence measurement or white plates with white bottom (Corning 3600) for BRET determination. For BRET1 ratio measurement, coelenterazine h substrate (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, United States) was added at a final concentration of 5 μM. Readings were performed after 1 min and the BRET signal was detected using the POLARstar Optima plate reader (BMG Lab Technologies, Offenburg, Germany) that allows the sequential integration of the signals detected with two filter settings. Transfected HEK293T cells were incubated with 0.1 μM of the A2AR TM-V peptide at 37°C for 2 h prior to performing BRET1 analysis. Data were then represented as a normalized netBRET1 ratio versus the fluorescence value obtained from the YFP, normalized with the luminescence value of D2RRluc expression 10 min after h-coelenterazine incubation. The normalized netBRET1 ratio was defined as the BRET ratio for co-expressed Rluc and YFP constructs normalized against the BRET ratio for the Rluc expression construct alone in the same experiment: netBRET1 ratio = [(YFP emission at 530 ± 10 nm)/(Rluc emission 485 ± 10 nm)] – cf. The correction factor, cf. corresponds to (emission at 530 ± 10 nm)/(emission at 485 ± 10 nm) found with the receptor-Rluc construct expressed alone in the same experiment. BRET isotherms were fitted using a non-linear regression equation assuming a single binding site, which provided BRETmax and netBRETmax values. The maximal value of BRET (BRETmax or netBRETmax) corresponds to the situation when all available donor molecules are paired up with acceptor molecules.
To assess specificity of the peptides, HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with plasmids encoding for D2RRluc or A2ARRluc and A2ARY FP (pcDNA ratio 1:1, 1 μg cDNA each). Forty-eight hours after transfection the cells were incubated with 10 μM of the A2AR TM-IV peptide, or 0.1 μM of the A2AR TM-V peptide, or 0.1 μM of the 5-HT1A TM-V peptide at 37°C for 2 h prior to performing BRET1 analysis. The netBRET signal was detected as described above.
In the BRET1 competition assays, HEK293T cells transiently co-transfected with constant amounts (1 μg) of plasmids encoding for D2RRluc and A2ARY FP were incubated with each of the seven A2AR TM peptides at 37°C for 2 h prior to performing BRET1 analysis. The netBRET signal was detected as described above.
BRET2 Saturation Assays
In the BRET2 assays, the receptors of interest were fused to either RLuc or green fluorescent protein 2 (GFP2). Detection of dimer interactions is based on that Rluc oxidation of coelenterazine 400a (DeepBlueC) leads to light emission with a peak at 395 nm, which results in excitation of GFP2 (excitation and emission maxima of 400 and 510 nm, respectively) if the receptors are in close proximity (Pfleger and Eidne, 2006). The BRET2 saturation assays (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2013) were carried out using plasmids encoding for A2ARRluc and either 3xHA-D2RGFP2, 3xHA-D2RGFP2(Tyr192Ala5.41x42) or 3xHA-D2RGFP2(Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60), respectively. Forty-eight hours after transfection, HEK293T cells transiently transfected with constant (1 μg) or increasing amounts (0.12–7 μg) of plasmids encoding for A2ARRluc and either 3xHA-D2RGFP2, 3xHA-D2RGFP2(Tyr192Ala5.41x42) or 3xHA-D2RGFP2(Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60), respectively, were rapidly washed twice in PBS, detached, and resuspended in the same buffer. Cell suspensions (20 μg protein) were distributed in duplicate into the 96-well microplates; black plates with a transparent bottom (Corning 3651) (Corning, Stockholm, Sweden) for fluorescence measurement or white plates with a white bottom (Corning 3600) for BRET determination. For BRET2 measurement, DeepBlueC substrate (VWR, Sweden) was added at a final concentration of 5 μM, and readings were performed after 1 min using the POLARstar Optima plate-reader (BMG Lab Technologies, Offenburg, Germany) that allows the sequential integration of the signals detected with two filter settings. The netBRET2 ratio was defined as the BRET ratio for co-expressed Rluc and GFP2 constructs normalized against the BRET ratio for the Rluc expression construct alone: netBRET2 ratio = [(YFP emission at 515 ± 30 nm)/(Rluc emission 410 ± 80 nm)] – cf. The correction factor, cf, corresponds to (emission at 515 ± 30 nm)/(emission at 410 ± 80 nm) found with the receptor-Rluc construct expressed alone in the same experiment. The maximal value of BRET (BRET2max or netBRET2max) corresponds to the situation when all available donor molecules are paired up with acceptor molecules (Fuxe et al., 2010). The specificities of A2AR–D2R interactions were assessed by comparison with co-expression of A1RRluc and D2RGFP2.
In situ Proximity Ligation Assay
HEK293T cells transiently co-transfected with constant amounts (1 μg) of plasmids encoding for A2AR and D2R and rat primary striatal neuronal cells were employed to study the effect of TM peptides on A2AR–D2R complexes by means of in situ PLA. Furthermore, to study the effect of D2R mutants on A2AR–D2R complexes by means of in situ PLA, HEK293T cells were also transiently co-transfected with constant amounts (1 μg) of plasmids encoding for A2AR and 3xHA-D2R or 3xHA-D2R(Tyr192Ala5.41x42) or 3xHA-D2R(Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60). In situ PLA was performed using rabbit polyclonal anti-A2AR (Abcam: ab3461 or Millipore: AB1559) and mouse monoclonal anti-D2R (Millipore MABN53, clone 3D9) primary antibodies (for quality control of the antibodies, see Feltmann et al., 2018) and the Duolink in situ PLA detection kit (Sigma-Aldrich, Sweden), following the protocol described previously (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2012, 2016a, 2018; Feltmann et al., 2018). Primary striatal neuronal cells or transiently co-transfected HEK293T cells were incubated with 10 μM of the A2AR TM-IV peptide or 0.1 μM of the A2AR TM-V peptide at 37°C for 2 h prior to performing cell fixation with 3.7% formaldehyde solution (Sigma-Aldrich, Stockholm, Sweden). PLA control experiments employed only one primary antibody or cells transfected with cDNAs encoding only one type of receptor. The PLA signal was visualized and quantified by using a TCS-SL confocal microscope (Leica, United States) and the Duolink Image Tool software. High magnifications of the microphotograph were taken and visualized using multiple z-scan projection. It should be noted that if the confocal data acquisition is performed as a multiple z-scan some positive PLA blobs/clusters may appear to be inside the nuclear blue stained DAPI area despite being located on the cytoplasmic membrane.
Cell Surface Receptor Expression and Cellular Localization Analysis by Fluorescence Confocal Microscopy
HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with constant amounts (1 μg) of plasmids encoding for 3xHA-D2RGFP2, 3xHA-D2RGFP2(Tyr192Ala5.41x42) or 3xHA-D2RGFP2(Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60). Then, cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min, washed with PBS containing 20 mM glycine, and mounted in a Vectashield immunofluorescence medium (Vector Laboratories, United Kingdom). Microscope observations were performed with a 40× oil immersion objective in a Leica TCS-SL confocal microscope (Leica, United States).
[3H]-Raclopride Competition Experiments
[3H]-Raclopride binding was displaced by quinpirole to determine the proportion of receptors in the high affinity state (RH), the high affinity (Ki,High), and low affinity (Ki,Low) values for the agonist binding sites from competition curves in HEK cells expressing either A2AR/3xHA-D2R, A2AR/3xHA-D2R(Tyr192Ala5.41x42), or A2AR/3xHA-D2R(Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60). Membrane preparations (60 μg protein/ml) were incubated with increasing concentrations of quinpirole (0.001 nM to 1 μM) and 2 nM [3H]-raclopride (75 Ci/mmol, Novandi Chemistry AB, Sweden) in 250 μl of incubation buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 7 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 0.05% BSA, 1 mM DTT) and 0.3 IU/ml adenosine deaminase (EC 3.5.4.4, Sigma-Aldrich) for 90 min at 30°C in the presence or absence of 100 nM of the A2AR agonist CGS-21680. Non-specific binding was defined by radioligand binding in the presence of 10 μM (+) butaclamol (Sigma-Aldrich, Sweden). The incubation was terminated by rapid filtration Whatman GF/B filters (Millipore Corp, Sweden) using a MultiScreenTM Vacuum Manifold 96-well followed by three washes (∼250 μl per wash) with ice-cold washing buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4). The filters were dried, 5 ml of scintillation cocktail was added, and the amount of bound ligand was determined after 12 h by liquid scintillation spectrometry.
Statistical Analysis
The number of samples (n) in each experimental condition is indicated in figure legends. When two experimental conditions were compared, statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired t-test. Data from the competition experiments were analyzed by non-linear regression analysis. The changes induced by CGS-21680 on RH, Ki,High, and Ki,Low values were compared using one-way ANOVA. A p-value ≤ 0.05 was considered significant.
Homology Modeling
An atomic resolution structure of the D2R was constructed using homology modeling based on a crystal structure of the D3 subtype as template (PDB code 3PBL) (Chien et al., 2010). A set of 100 homology models was generated with MODELLER v9.10 (Sali and Blundell, 1993) based on a manually edited sequence alignment (Supplementary Figure S1) generated by the GPCR-ModSim webserver (Rodríguez et al., 2012). The D2R residues Arg311.29-Tyr361.34 were not present in the corresponding region of the template and alpha-helical restraints were added for these to extend TM-I. In addition, 140 residues from the intracellular loop 3 (IL3) of the D2R were omitted by introducing a chain break between Arg2225.71 and Leu3636.25. The ends of helices TM-V and TM-VI, which are connected by the IL3, were treated as independent. Selection of a final homology model was based on the DOPE scoring function (Shen and Sali, 2006), visual inspection, and the metrics available from the Molprobity server (Davis et al., 2007).
Protein–Protein Docking
A crystal structure of the A2AR (PDB code 4EIY) (Liu et al., 2012) and the D2R homology model were prepared for protein–protein docking with the program HADDOCK2.1 (Dominguez et al., 2003). The protonation states of ionizable residues (Asp, Glu, Arg, and Lys) were set to their most probable states at pH 7. Histidine protonation states were set by visual inspection on the basis of the hydrogen bonding network (Supplementary Table S1). Residues in the predicted dimer interface were used to guide protein–protein docking (Supplementary Table S2). A set of 1,000 configurations of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer was generated by rigid-body energy minimization. The 200 complexes with the best energy were refined and clustered by HADDOCK. Each A2AR–D2R complex was refined with MD sampling in the presence of explicit DMSO molecules to mimick the membrane environment. Subsequent to the determination of the first D2R crystal structure (PDB code 6CM4) (Wang et al., 2018), the protein–protein docking was repeated with the same parameters. In this case, 10,000 configurations of the A2AR–D2R dimer were generated and 1,000 of these were refined. The resulting models were clustered (Rodrigues et al., 2012) based on superimposition to the A2AR with a 7.5 Å RMSD cutoff and a minimum cluster size of four members.
MD Simulations
A model of the A2AR–D2R complex was prepared for all-atom MD simulations in GROMACS4.5.5 (Pronk et al., 2013). Prior to the MD simulations, the stretch of residues surrounding Ser1975.46x461 in the extracellular tip of TM-V of the D2R was modified to preserve the alpha-helical secondary structure present in the D3R template, which had slightly unfolded in the HADDOCK optimization of the heteromer complex. The dimer was inserted into a hydrated 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoylphosphatidylcholine (POPC) bilayer in gel phase (equilibrated at 260 K). Water and lipid atoms overlapping with the protein were removed, and the simulation box walls were set to be 12 and 35 Å from the protein atoms in the Z and XY dimensions, respectively. A 0.15 M sodium concentration and neutralization of the system were accomplished by adding 100 sodium and 118 chloride ions to the system. The resulting hexagonal prism-shaped simulation box comprised 145,260 atoms, including 36,889 water and 438 lipid molecules, and had an initial volume of 156 × 156 × 99 Å3. MD simulations were performed using the half-e double-pairlist method (Chakrabarti et al., 2010) to make the Berger parameters employed for the lipids (Berger et al., 1997) compatible with the OPLS-AA force field (Jorgensen et al., 1996) used for the protein atoms. As a part of the IL3 of the D2R was excluded from modeling, C-terminal amide and N-terminal acetyl caps were added to avoid charge–charge interactions between the termini of residues Arg222 and Leu363, respectively. Similarly, the N-termini of both the A2AR (Gly51x31) and D2R (Tyr341x32) were capped. The system was solvated with SPC waters (Jorgensen et al., 1983). Bond lengths and angles for these molecules were constrained with the SETTLE algorithm (Miyamoto and Kollman, 1992), whereas the LINCS algorithm (Hess et al., 1997) was used to constrain bond lengths of proteins and lipids. Periodic-boundary conditions were applied in the NPT ensemble using the semiisotropic Parinello-Raman barostat (Parrinello and Rahman, 1981) (1 atm, coupling constant of 2 ps, isothermal compressibility constant of 4.5 × 10-5 bar-1) and the Nose–Hoover thermostat (310 K with three independent coupling groups for proteins, lipids, and water plus ions). Lennard-Jones and coulombic interactions were explicitly considered within a 12 Å cutoff, whereas the particle mesh Ewald method was used for electrostatic interactions beyond that distance (Darden et al., 1993). The system was first minimized with the steepest descent algorithm and was then equilibrated using a time step of 2 fs by applying positional restraints only to protein atoms (Supplementary Table S3), which were gradually released during 10 ns. Three replicas with different initial random velocities were initiated from the last snapshot of the equilibration and 100 ns were then performed in each case.
Results
Mapping of the TM Helices Involved in the A2AR–D2R Heterodimer Interface
Peptides corresponding to TM helices have been found to disrupt receptor–receptor interactions for GPCRs that form oligomers (Hebert et al., 1996; Ng et al., 1996; Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010b, 2012; Guitart et al., 2014; Lee et al., 2014; Jastrzebska et al., 2015; Vinals et al., 2015). The proposed mechanism of inhibition is that the helices are part of the protein–protein interface and are able to block oligomerization through competition with the other protomer. Structural information could thus be deduced by investigating the effects of the individual 14 TM helices of the two involved GPCRs on dimerization. In previous work, the ability of the TM helices of the D2R to disrupt A2AR–D2R heteromerization was evaluated by means of quantitative BRET1 assays (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010b). The receptor–receptor interactions between the A2AR labeled with YFP (A2ARY FP) and D2R fused to RLuc (D2RRLuc) were characterized for the inhibition of the BRET1 signal by the seven TM helices (TM-ID2 to TM-VIID2) in concentration-response experiments. Addition of synthetic peptides TM-IVD2 and TM-VD2 resulted in a clear concentration-dependent reduction of the BRET1 signal, leading to a nearly complete blockade at 1 to 10 μM. TM-VID2 also achieved some inhibition at these concentrations, but not to the same extent as TM-IVD2 and TM-VD2. The remaining four peptides did not significantly influence A2AR–D2R heteromerization.
In the current work, the BRET1 experiments were performed for the seven TM peptides of the A2AR (TM-IA2A to TM-VIIA2A). TM-IVA2A, TM-VA2A, and TM-VIA2A displayed a concentration-dependent inhibition of the BRET1 signal (Figure 1A). TM-VA2A had the largest effect and A2AR–D2R dimerization was almost completely blocked at 1 μM. In a BRET saturation assay, TM-VA2A clearly resulted in a significant reduction of the netBRET1max values at 0.1 μM (Figure 1B). TM-IVA2A and TM-VIA2A also reduced the BRET1 signal and reached close to full inhibition at 10 and 100 μM, respectively. TM-IVA2A and TM-VA2A were also evaluated by in situ PLAs to characterize the disruption of A2AR–D2R heteroreceptor complexes in transiently co-transfected HEK293T cells (TM-IVA2A, TM-VA2A) and in rat striatal primary neuronal cell culture (TM-VA2A). In line with the BRET1 assays, the in situ PLA assay showed that the number of clusters of A2AR–D2R heteroreceptor complexes was reduced upon addition of 10 μM of TM-IVA2A and 0.1 μM TM-VA2A (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S2).
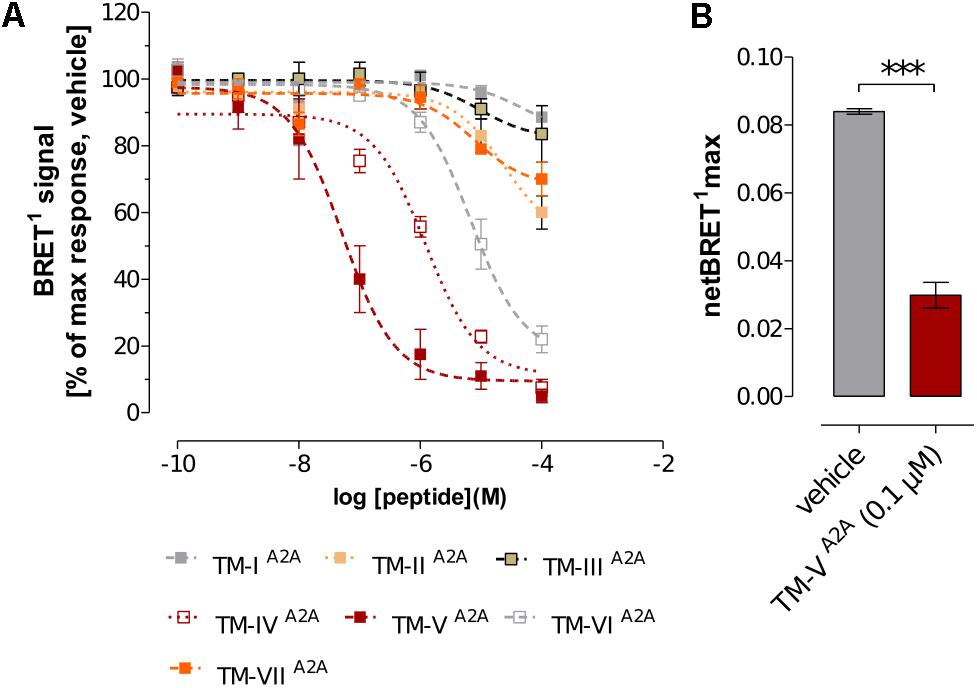
FIGURE 1. Effects of A2AR TM peptides on A2AR–D2R interactions. (A) The concentration-response effect of the individual A2AR TM peptides (TM-IA2A to TM-VIIA2A) on BRET1 signals of A2AR–D2R heteromers. Values represent percentages of maximal BRET1 responses in cells co-transfected with a 1:1 ratio of D2RRluc and A2ARY FP (1 μg cDNA each). Data are averages ± SEM; n = 6 experiments, 6 replicates (A2AR TM peptides I-III and V-VII); n = 6–10 experiments, 6 replicates (A2AR TM peptide IV). (B) Comparison of the effects of TM-VA2A peptide with the vehicle group on the netBRET1 max values obtained from BRET1 saturation curves for the A2AR–D2R heteromers. Co-transfected cells were incubated with 0.1 μM of TM-VA2A peptide or vehicle and studied by BRET1 saturation assays. Data are averages ± SEM; n = 4, eight replicates. ∗∗∗(TM-VA2A) significantly different compared to vehicle (P < 0.001) by unpaired t-test.
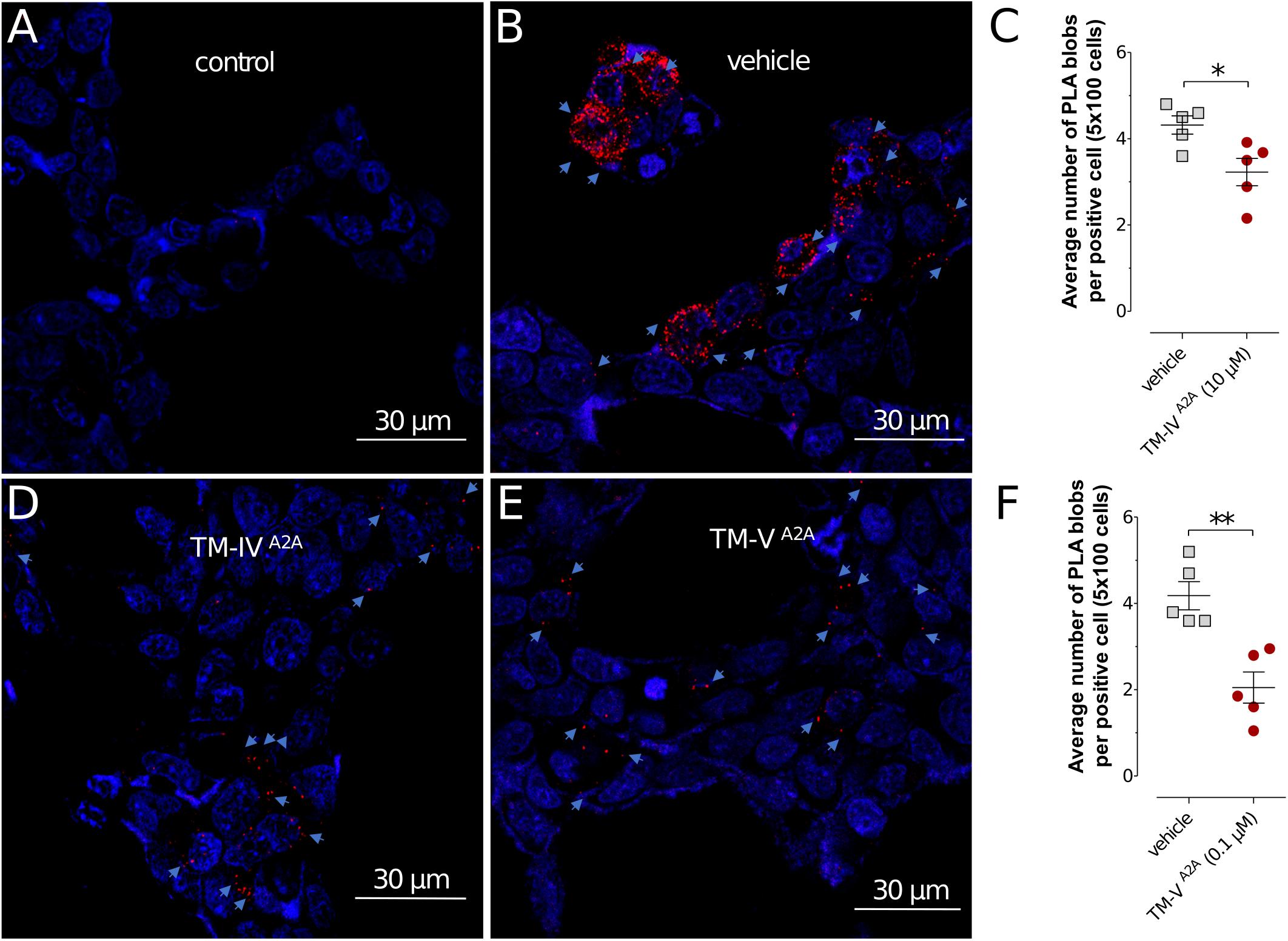
FIGURE 2. Detection of A2AR–D2R heteroreceptor complexes in transiently co-transfected HEK293T cells by in situ PLA. (A,B,D,E) The effects of A2AR TM peptides TM-IVA2A (10 μM), TM-VA2A (0.1 μM), and vehicle on the in situ PLA A2AR–D2R heteroreceptor complex signals are shown. Red clusters indicated by arrows represent heteroreceptor complexes and nuclei are shown in blue (DAPI). (C,F) Quantification of receptor complexes as the average number of PLA blobs (red clusters) per positive cell was determined using a confocal microscope Leica TCS-SL and the Duolink Image Tool software. Data are averages ± SEM (n = 5 experiments, 100 cells per experiment). Decreased A2AR–D2R heteroreceptor complex formation was observed upon cell incubation with TM-IVA2A (10 μM) and TM-VA2A (0.1 μM). These groups are significantly different compared to vehicle (∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01). Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired t-test.
To evaluate the impact of the interfering peptides on the allosteric modulation within the A2AR–D2R heteromer, the affinity values for D2R agonist quinpirole for D2R were examined in [3H]-raclopride/quinpirole competition assays in HEK293T cells. The high affinity value (Ki,High), the low affinity value (Ki,Low), and the proportion of receptors in the high affinity state (RH) were not significantly altered when cells expressing only the D2R were treated with the TM-IVA2A and TM-VA2A peptides compared with the vehicle by one-way ANOVA (Supplementary Figure S3). The A2AR agonist CGS-21680 decreased the affinity of the high affinity component of the D2R agonist quinpirole in membrane preparations expressing A2AR–D2R, but the Ki,Low and RH values were unaffected (Figure 3). Agonist binding to the high affinity state (Ki,High) was reduced from 1.05 ± 0.36 nM to 583 ± 27 nM by the A2A agonist CGS-21680. Thus, the strong negative allosteric modulation exerted by the A2AR agonist on the high affinity state of the wild type D2R was validated. In contrast, the allosteric modulation was significantly reduced in the experiments carried out in the presence of the TM-IVA2A and TM-VA2A peptides. TM-VA2A resulted in the strongest effect and there was a complete loss of allosteric modulation (Ki,High = 2.65 ± 0.52 nM). TM-IVA2A also counteracted the effect on the high affinity component, resulting in a Ki,High of 14.69 ± 0.35 nM. No differences in RH and Ki,Low values were observed after the A2AR agonist modulation or treatment of TM peptides (Figure 3).
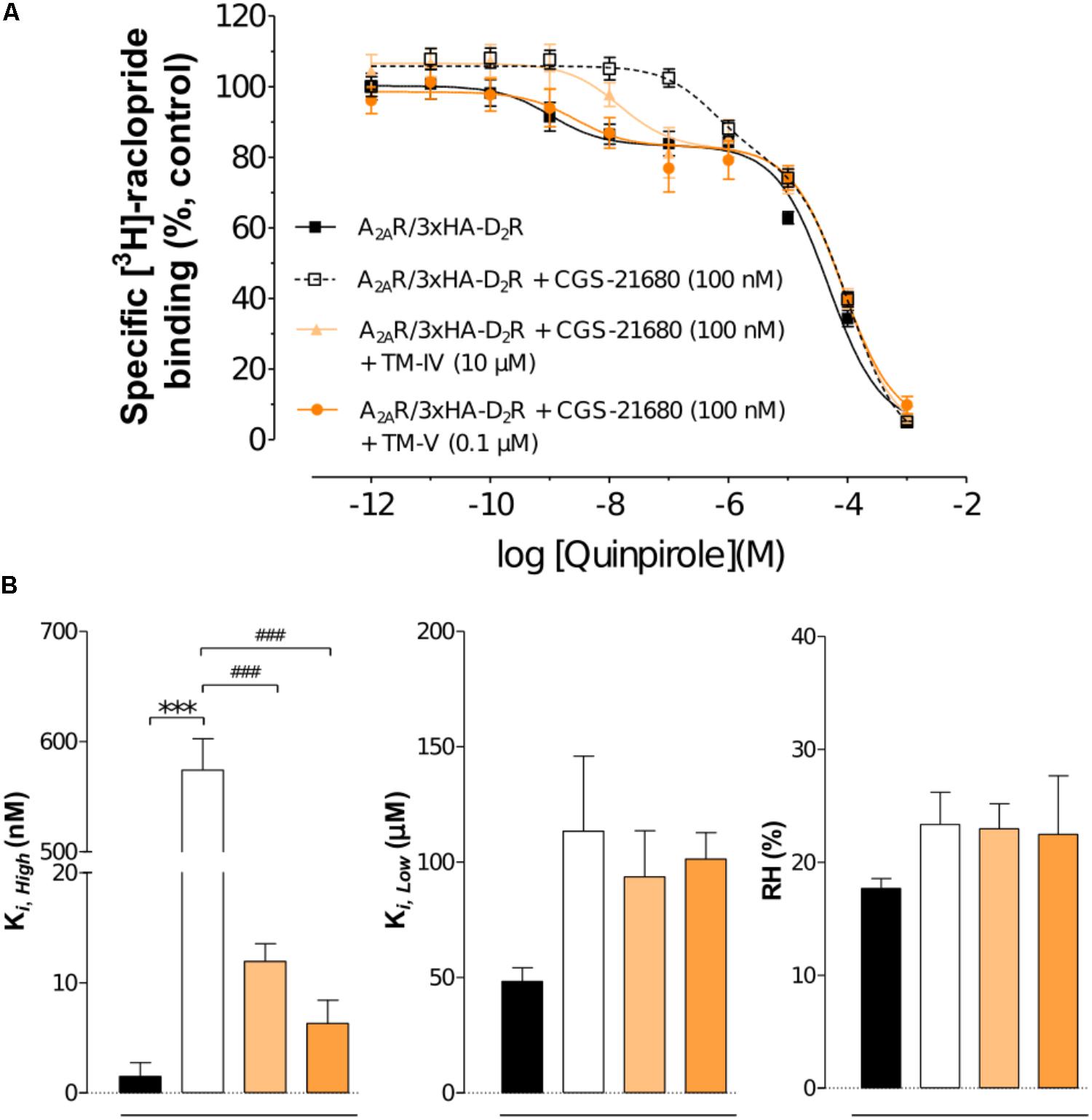
FIGURE 3. Experimental evaluation of TM peptides in radioligand binding assays. (A) Competition experiments involving D2R antagonist [3H]-raclopride binding versus increasing concentrations of quinpirole were performed in membrane preparation from HEK cells expressing A2AR–D2R in the presence of A2AR agonist CGS-21680 (100 nM), or A2AR agonist CGS-21680 (100 nM) + TM-IVA2A (10 μM), or A2AR agonist CGS-21680 (100 nM) + TM-VA2A (0.1 μM), or vehicle. Non-specific binding was defined as the binding in the presence of 10 μM (+)-butaclamol. The binding values (n = 3, in triplicate) are given in percent of specific binding at the lowest concentration of quinpirole employed. (B) Analysis and presentation of the high affinity values (Ki,High), low affinity values (Ki,Low), and the proportion of D2R in the high affinity state (RH). Averages ± SEM are given for three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison test. ∗∗∗Significant difference compared to vehicle (P < 0.001). ###Significant difference compared to the CGS-21680 treatment (P < 0.001).
To investigate the specificity of the A2AR TM peptides, BRET1 experiments were also carried out for the A2AR homodimer with a receptor population labeled with either YFP (A2ARY FP) or Rluc (A2ARRLuc), which were compared to the results obtained for the A2AR–D2R heterodimer. Each peptide was assayed at a single-point concentration of 10 μM (TM-IVA2A) or 0.1 μM (TM-VA2A) and, interestingly, the results were different for the homo- and heterodimer. As expected, TM-IVA2A and TM-VA2A significantly reduced the population of A2AR–D2R complexes. However, no significant reduction of the BRET1 signal was observed for these two peptides in the case of A2AR homodimer. Similarly, the use of a peptide corresponding to TM-V of the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2012) did not have any significant effect on the A2AR–D2R heteromer or A2AR–A2AR homomer interactions (Figure 4).
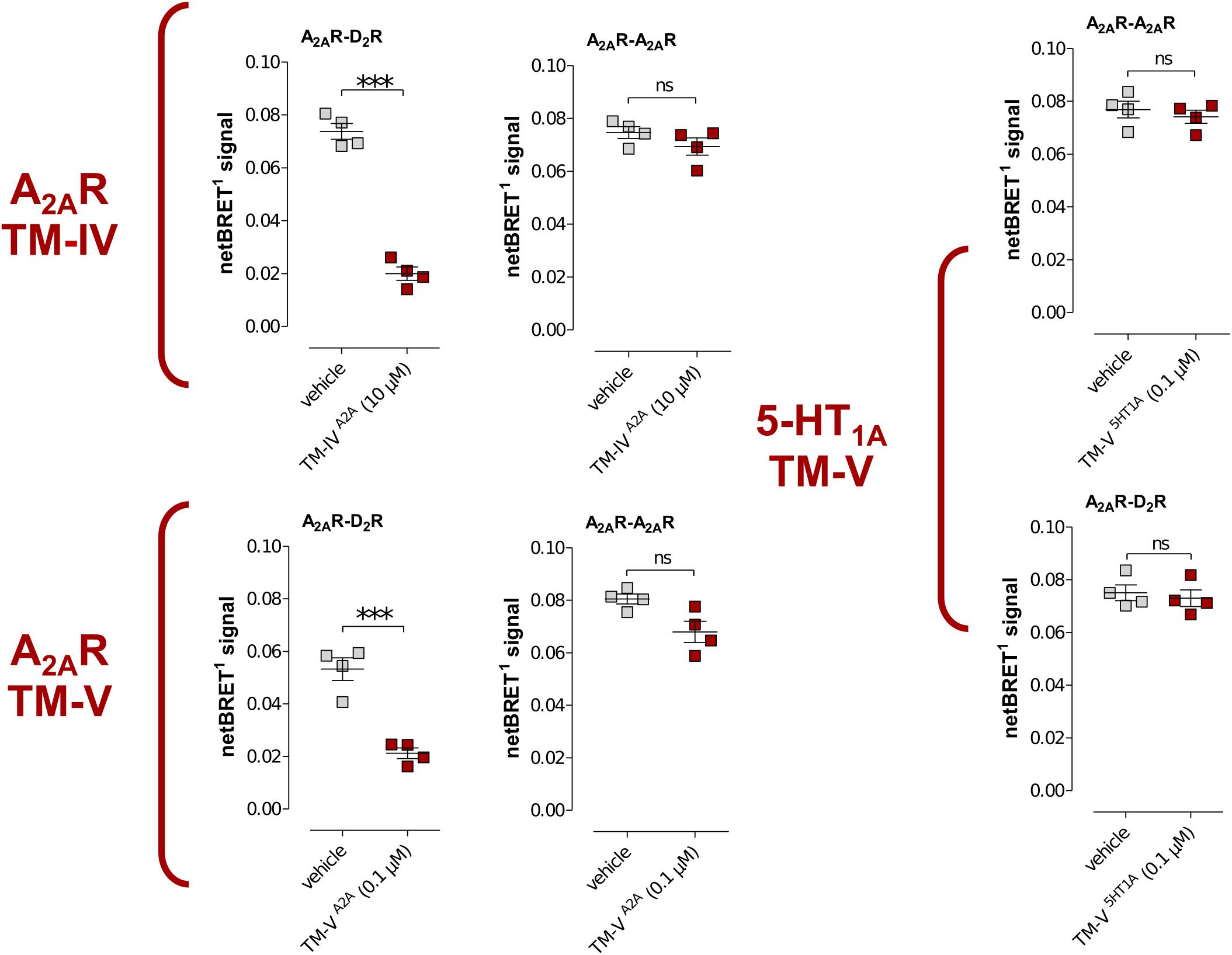
FIGURE 4. Effects of TM peptides on A2AR–D2R and A2AR–A2AR interactions. Cotransfected cells were incubated with either TM-IVA2A (10 μM) or TM-VA2A (0.1 μM) peptides or a peptide (0.1 μM) derived from TM-V of the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor and studied by BRET1. Values represent netBRET responses (Averages ± SEM; n = 4, six replicates). Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired t-test. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared to control group.
Experiment-Guided Modeling of the A2AR–D2R Heteroreceptor Complex
Modeling of the A2AR–D2R complex was guided by the BRET1 data for the 14 TM peptides of the two protomers and dimer interactions observed in crystal structures of GPCRs. No crystal structures were available for heterodimers, but several class A GPCRs have been crystallized in homomeric arrangements, revealing different potential interfaces (Figure 5A) (Murakami and Kouyama, 2008; Wu et al., 2010; Granier et al., 2012; Manglik et al., 2012; Huang et al., 2013). The first cluster of observed dimer interfaces mainly involved TM-I, TM-II, and helix VIII and has, for example, been identified in crystal structures of the β1 adrenergic (Huang et al., 2013), κ- and μ-opioid (Granier et al., 2012; Manglik et al., 2012) receptors. As no effects of TM-I or TM-II on A2AR–D2R heteromerization were observed in the BRET1 assays, this interface was not further considered. A second set of interfaces involving TM-V and either TM-IV or TM-VI has been revealed by, e.g., crystal structures of squid rhodopsin (Murakami and Kouyama, 2008), CXCR4 (Wu et al., 2010), μ-opioid (Manglik et al., 2012), and β1 adrenergic (Huang et al., 2013) receptors. The synthetic peptides corresponding to the same three helices of the D2R and A2AR disrupted A2AR–D2R heterodimerization in the BRET1 assays (Figure 1) (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010b). Visual inspection of the TM-IV/V/VI interfaces observed in the crystal structures of the CXCR4, μ-opioid, and β1 adrenergic receptors revealed that none of the observed dimers simultaneously involved all three helices to a significant extent. The μ-OR and squid rhodopsin receptor dimers had TM-V/VI and TM-V interfaces, respectively, but not TM-IV, which showed the largest effect among the synthetic peptides derived from the D2R. The β1 adrenergic receptor had a TM-IV/V interface, but the buried surface area (BSA) was relatively small (450 Å2). The CXCR4 receptor structure had strong interactions via TM-V and also involved TM-IV and TM-VI to a smaller extent, resulting in the largest BSA (∼1,100 Å2).
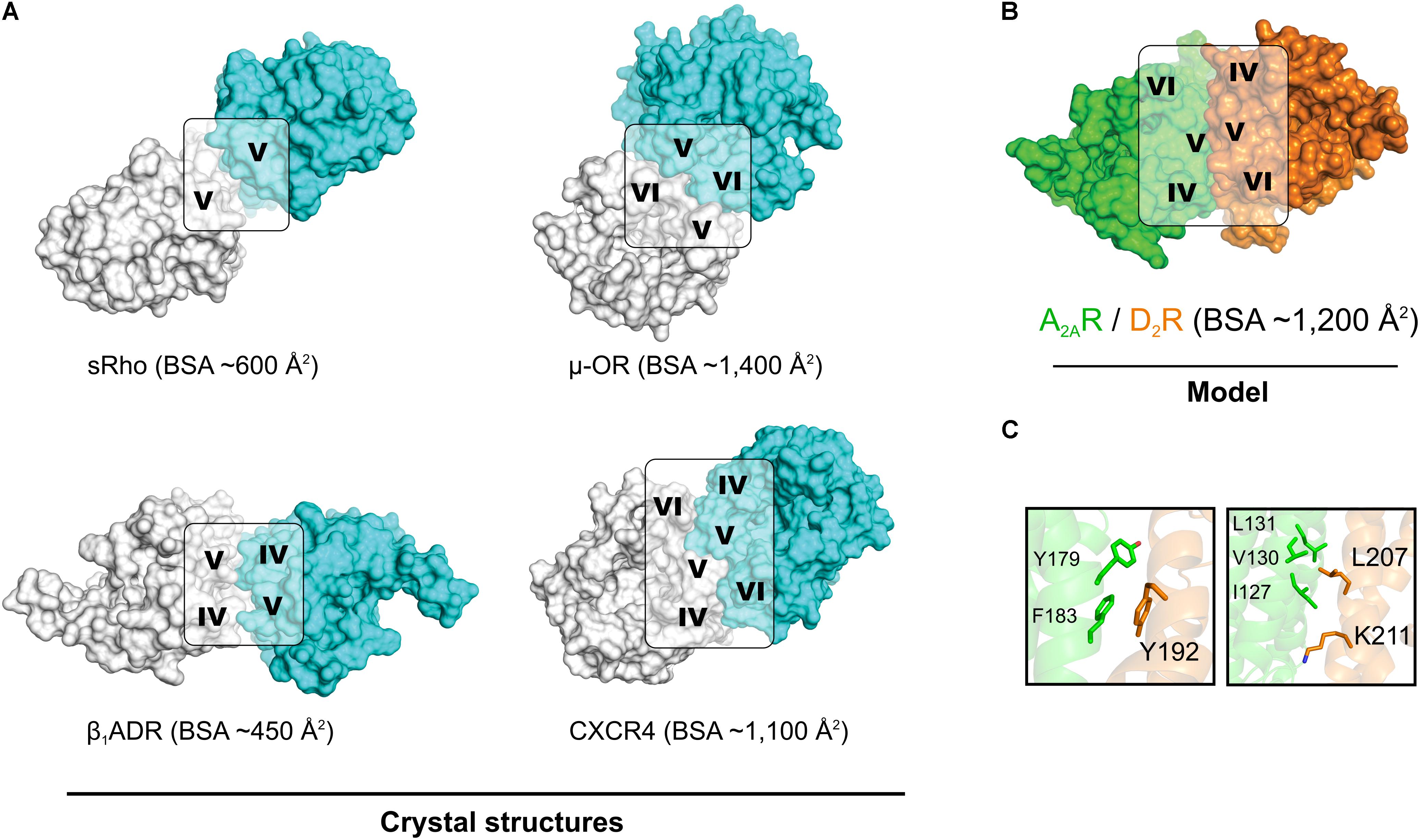
FIGURE 5. Crystal structures of GPCR homodimers with interfaces involving TM-IV, TM-V, and TM-VI and the model of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer. (A) Crystal structures of squid rhodopsin (sRho) (Murakami and Kouyama, 2008), μ-opioid (μ-OR) (Manglik et al., 2012), β1 adrenergic (β1ADR) (Huang et al., 2013), and CXCR4 (Wu et al., 2010) receptors. All these GPCRs crystallized as homodimers and have a large buried surface area (BSA). (B) Model of the heterodimer formed by the A2AR (green, crystal structure) and the D2R (orange, homology model). All structures are shown from the extracellular point of view and the TM helices involved in the dimerization interface are indicated. (C) Representative MD simulation snapshot of the mutated residues of the D2R (Top panel: Tyr1925.41x42, Bottom panel: Leu2075.56/Lys2115.60) with side chains of interacting residues shown as sticks.
In order to generate a model of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer, atomic resolution structures for the monomeric forms of each protomer were required. Multiple crystal structures of the A2AR in monomeric form were available and the one with the highest resolution, which represented an inactive state conformation, was selected (Liu et al., 2012). At the initiation of this study, no crystal structure of the D2R was available. Thus, a crystal structure of the D3R (Chien et al., 2010) was used to generate a set of homology models of the D2R in an inactive-like state. Due to the high sequence similarity to the D3R, which shared 71% of the amino acids in the TM region with the D2 subtype (Supplementary Figure S1), there was only a small variation among the models generated. The three best models, as judged by DOPE score (Shen and Sali, 2006), were analyzed manually and one of these was selected as a starting point for modeling of the heterodimer. Models of the A2AR–D2R complex were first generated by structural superimposition of the monomers onto the available homodimer crystal structures with interfaces that involved TM-IV and TM-V. CXCR4 (Wu et al., 2010) was considered to be the best template for the A2AR–D2R heterodimer based on the large contact interface involving TM-V, but the resulting model only had weak interactions with TM-IV. Protein–protein docking with the program HADDOCK (Dominguez et al., 2003) was performed to identify interfaces that were in better agreement with the experimental data for the TM peptides. HADDOCK allows inclusion of experimental data to focus the docking calculation on a specific interface. Residues in TM-IV and TM-V were defined as being involved in the interface based on the BRET data and CXCR4-based model (Supplementary Table S2). The protein–protein docking was used to generate 200 models of the A2AR–D2R complex, which were clustered based on RMSD. The 10 most populated clusters are shown in Supplementary Figure S4 and were analyzed based on four criteria (Supplementary Table S4). The first two criteria required the receptors to be oriented in a parallel manner and correctly aligned with the plane of the membrane-solvent interface, which was fulfilled by 133 models from four different clusters. Among these, the heterodimer models in the sixth cluster were found to have the most extensive contacts involving TM-IV and TM-V and its centroid was selected for further consideration (Figure 5B and Supplementary Figure S5). The predicted A2AR–D2R interface had a total BSA of ∼1,200 Å2 and was overall similar, but not identical, to the model obtained by aligning to the CXCR4 homodimer crystal structure (Supplementary Figure S6). TM-V was the helix with the highest contribution to the dimer interface for both protomers. However, the selected structure had some rearrangements compared to CXCR4-based model that led to higher involvement of TM-IV.
MD Simulation Refinement of the A2AR–D2R Heterodimer Model
The A2AR–D2R heterodimer predicted by protein–protein docking was further explored using all-atom MD simulations in a hydrated lipid bilayer. The time-scales reachable by MD simulations are too short to observe major rearrangements of the dimer interface, structural changes related to activation of the receptors, or the influence of oligomerization on ligand binding. Therefore the goal of these calculations was to refine the predicted interface using a more realistic model of the biological environment. Three independent trajectories of the dimer model were generated, resulting in a total of 0.3 μs of unrestrained simulation. After a short equilibration (Supplementary Table S3), the overall root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the Cα atoms of the dimer increased slightly during the first ∼40 ns of unrestrained simulation and then stabilized at an average of 3.3 Å, which is similar to the results obtained for a simulation study on the crystal structure of the CXCR4 homodimer (Rodriguez and Gutierrez-De-Teran, 2012). The largest structural changes were observed in TM-VII of the A2AR and TM-I of the D2R whereas the dimer interface remained stable. The BSA changed only slightly during the simulation, with an average of 1,163 Å2 for the last 50 ns of the three simulation replicas (Supplementary Figure S7 and Supplementary Table S5).
Snapshots from the MD simulations were analyzed to identify interactions between specific residues in the interface. To further evaluate the model, two D2R mutants that probed interactions in either the N- or C-terminal ends of these helices were predicted (Figure 5C). The interaction interface at the top of TM-V was close to the orthosteric binding sites of both receptors. Tyr1925.41x42 of the D2R was located just one helical turn from a set of residues (Ser1935.42x43, Ser1945.43x44, and Ser1975.46x461) that has been proposed to play a role in the activation mechanism for monoamine-recognizing GPCRs (Warne et al., 2011). The side chain of Tyr1925.41x42 formed stacking interactions with a cluster of aromatic residues formed by Tyr1795.40x411 and Phe1835.44x45 in TM-V of the A2AR, which were located only ∼10 Å from the adenosine binding site. At the intracellular end of TM-V of the D2R, interactions with residues in TM-IV and TM-V of the A2AR were formed. Leu2075.56 of the D2R interacted with Ile1274.48, Val1305.51, and Leu1314.52 of the A2AR whereas the alkyl chain of Lys2115.60 formed van der Waals interactions with Ile1274.48 of the A2AR. Based on these results, two mutants of the D2R, Tyr192Ala5.41x42 and Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60, were predicted to reduce favorable dimer interactions and were selected for experimental evaluation.
Experimental Evaluation of D2R Mutations in the Predicted Heteromer Interface
To further probe the predicted role of TM-V of the D2R in A2AR–D2R heteromerization, the Tyr192Ala5.41x42 and Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60 D2R mutants were evaluated experimentally in BRET2, in situ PLA, and binding assays. No differences in cellular localization at the membrane level between the wild type and mutants of the D2R were observed (Supplementary Figure S8). The interactions between the wild type and mutant D2Rs labeled with GFP2 with the A2ARRLuc were first assessed in BRET2 saturation assays. Both the Tyr192Ala5.41x42 and Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60 mutations reduced A2AR–D2R interactions and the largest effect was observed for the double mutant (p < 0.01, Figure 6). In contrast, no significant differences were observed between the wild type and mutant D2Rs with the A2AR protomer if the in situ PLA method was used (Supplementary Figure S9). In binding assays, the high affinity value (Ki,High) for D2R agonist quinpirole for 3xHA-D2R, 3xHA-D2R(Tyr192Ala5.41x42), and 3xHA-D2R(Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60) were determined in [3H]-raclopride/quinpirole competition assays (1.65 ± 0.21 nM, 1.08 ± 0.34 nM, and 1.80 ± 0.22 nM, respectively). The high affinity value (Ki,High), the low affinity value (Ki,Low) and the proportion of receptors in the high affinity state (RH) were not significantly altered for the two D2R mutants compared with the wild type D2R by one-way ANOVA (Supplementary Figure S10). As expected, the A2AR agonist CGS-21680 decreased the affinity of the high affinity component of the D2R agonist quinpirole in membrane preparations expressing A2AR/3xHA-D2R whereas the Ki,Low and RH values were not significantly altered. The D2R agonist binding to the high affinity state was reduced 300-fold by the A2A receptor agonist CGS-21680 to 533 ± 23 nM. Significant A2AR agonist induced reductions of the Ki,High value for quinpirole were also observed for the D2R mutants, but not to the same degree as found in the wild type. The Tyr192Ala5.41x42 and Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60 mutants had (Ki,High) values equal to 129 ± 21 nM and 90 ± 2 nM in the presence of A2AR agonist, respectively. The ability of 3xHA-D2R(Tyr192Ala5.41x42) and 3xHA-D2R(Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60) to respond to the negative allosteric modulation induced by the A2AR agonist was hence significantly lower than for the wild type A2AR/3xHA-D2R complex. No significant differences in RH and Ki,Low values were observed (Figure 7).
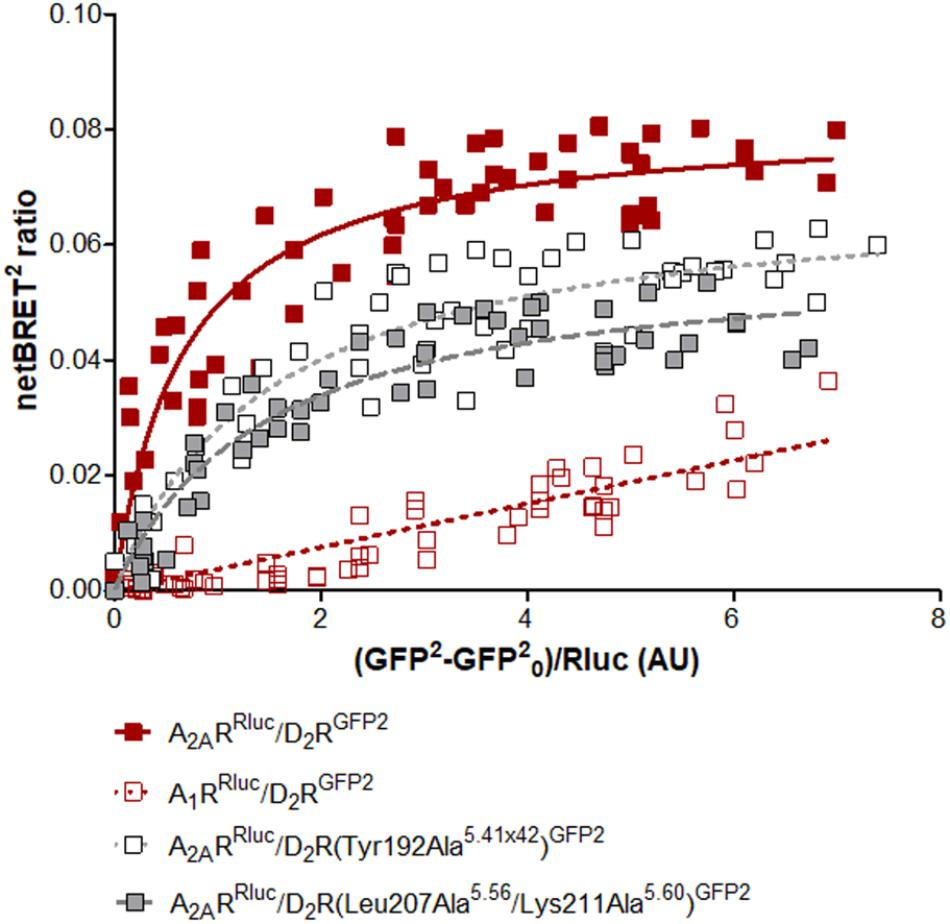
FIGURE 6. Experimental evaluation of mutations in the A2AR–D2R dimer interface by BRET2. BRET2 saturation curves for the A2AR–D2R heterodimer for wild type and mutants of the D2R. The normalized BRET2 ratio, which was defined as the netBRET2 ratio for co-expressed Rluc and GFP2 constructs normalized against the netBRET2 ratio for the Rluc expression construct alone in the same experiment, is plotted on the y-axis. The fluorescence value obtained from the GFP2, normalized with the luminescence value of A2ARRluc or A1RRluc expression 10 min after DeepBlueC incubation, is plotted on the x-axis. GFP0 is defined as the fluorescent emission values at 515 ± 30 nm of the cells which only expressed the Rluc construct. Data are averages ± SEM; n = 5, eight replicates. Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired t-test. The netBRETmax values of A2AR–D2R(Tyr192Ala5.41x42) are significantly different compared to A2AR–D2R (P < 0.05) and the netBRETmax values of A2AR–D2R(Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60) are significantly different compared to A2AR–D2R (P < 0.01).
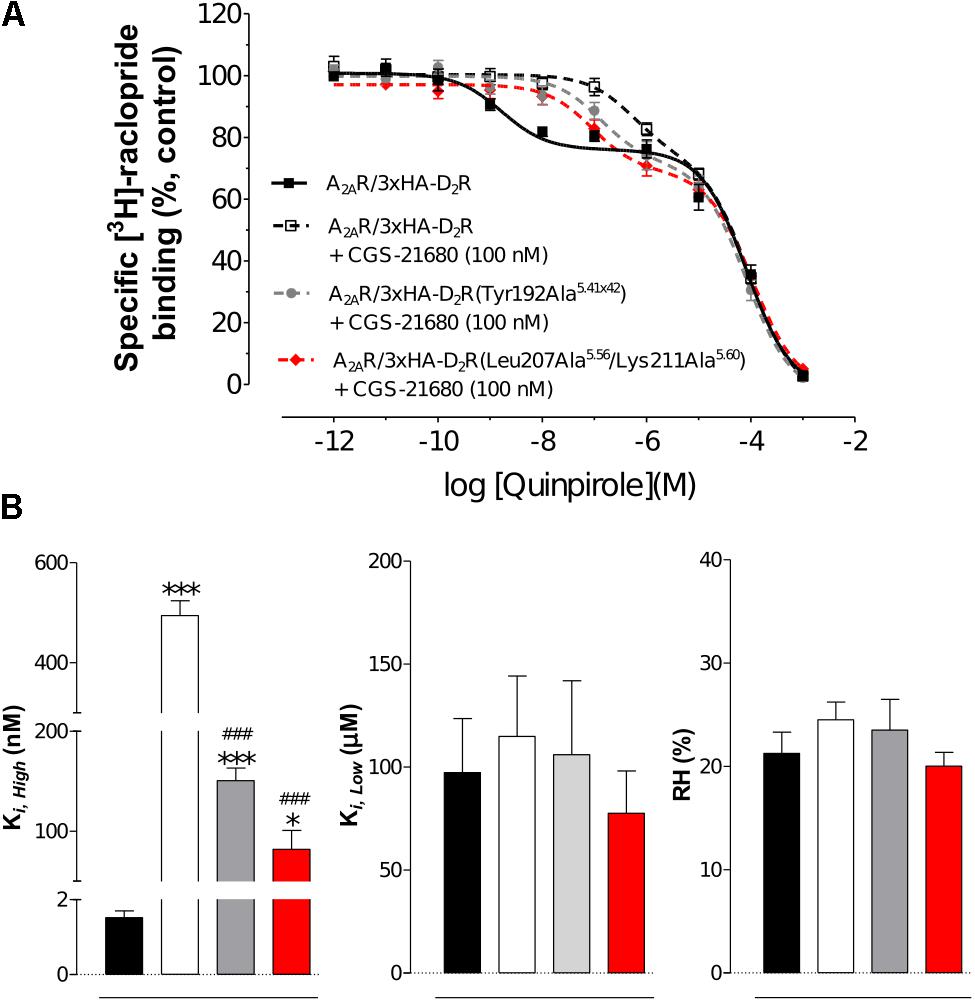
FIGURE 7. Experimental evaluation of mutations in the A2AR–D2R dimer interface by radioligand binding assays. (A) Competition experiments involving D2R antagonist [3H]-raclopride binding versus increasing concentrations of quinpirole were performed in membrane preparation from HEK cells expressing A2AR/3xHA-D2R or A2AR/3xHA-D2R(T192A5.41x42), or A2AR/3x-HA-D2R(L207A5.56/K211A5.60) in the presence or absence of A2AR agonist CGS-21680 (100 nM). Non-specific binding was defined as the binding in the presence of 10 μM (+)-butaclamol. The binding values (n = 4, in triplicate) are given in percent of specific binding at the lowest concentration of quinpirole employed. (B) Analysis and presentation of the CGS-21680 induced changes in the high affinity values (Ki,High), low affinity values (Ki,Low) and in the proportion of D2R in the high affinity state (RH) after incubation of the membrane preparations with A2AR agonist CGS-21680 (100 nM). Data are averages ± SEM of four independent experiments, each one performed in triplicate. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison test. ∗∗∗P < 0.001 and ∗P < 0.05; Significant difference compared to wild-type without CGS-21680. ###P < 0.001; The results for the two mutants were significantly different compared to wild-type with CGS-21680.
Model of the A2AR–D2R Complex Based on Crystal Structures of Both Protomers
After the initial review of this paper, the first crystal structure of the D2R was determined (Wang et al., 2018). This allowed us to assess the accuracy of the D2R model and generate alternative interfaces of the A2AR–D2R dimer using protein–protein docking based on crystal structures of both receptors. Alignment of the D2R homology model and crystal structure showed that the D3R subtype was a good template for the prediction of the TM region (backbone RMSD = 1.2 Å). To assess the influence of using a D2R homology model on our results and to further improve our model of the A2AR–D2R complex, the protein–protein docking calculations were carried out with the crystal structures. A total of 1,000 models were generated and the resulting clusters of potential interfaces were assessed using the same criteria as for the D2R homology model (Supplementary Table S6). The third most populated cluster was compatible with membrane insertion and had a TM-IV/V interface. The interface RMSD between the cluster center obtained from docking with the D2R homology model (cluster 6, Supplementary Table S4) and crystal structure (cluster 3, Supplementary Table S6) was 4.6 Å. These models hence belonged to the same cluster of solutions (HADDOCK clustering cut-off < 7.5 Å) and the interfaces were very similar based on our criteria (Supplementary Figure S11). On the residue level, there were some differences in the interactions predicted by the two cluster centers, but the contacts made by the residues evaluated by mutagenesis (Tyr192Ala5.41x42 and Leu207Ala5.56/Lys211Ala5.60) were maintained in the A2AR–D2R complex obtained using the crystal structures (Supplementary Figure S11). A representative A2AR–D2R model obtained using crystal structures of both receptors is shown in Figure 8.
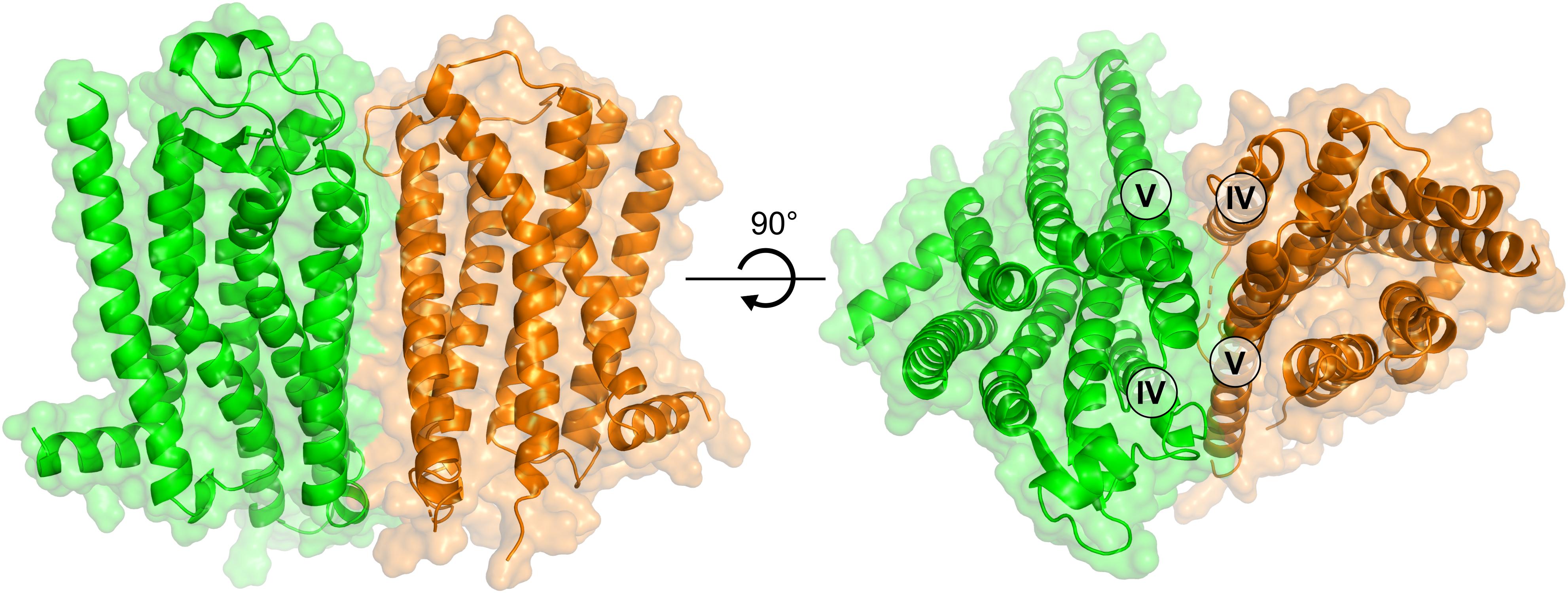
FIGURE 8. Model of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer based on crystal structures of both receptors. The structure of the A2AR–D2R heteroreceptor complex is based on protein–protein docking with the A2AR (green) and D2R (orange) depicted as cartoons.
Discussion
The main result of this study is that identification of dimer disrupting peptides derived from TM helices in combination with crystal structure data for GPCRs enabled the generation of atomic-resolution models of the A2AR–D2R heteroreceptor complex. A representative A2AR–D2R model was refined using MD simulations and mutations in the predicted interface reduced the propensity of the receptors to dimerize.
A key step toward understanding GPCR heteromerization is the identification of the regions involved in receptor–receptor interactions (Meng et al., 2014; Cordomi et al., 2015). In the membrane-spanning region, essentially every TM helix has been proposed as a potential interface (Selent and Kaczor, 2011; Ferre et al., 2014). For example, in the case of the A2AR–D2R heteromer, Canals et al. (2003) proposed that the TM interface was mainly composed of TM-V/VI/VII (D2R) and TM-III/IV (A2AR) whereas the study by Borroto-Escuela et al. (2010b) predicted that TM-IV/V (D2R) interacted with either TM-IV/V (A2AR) or TM-I/VII (A2AR). In the current work, the interface of the A2AR–D2R heteromer was further characterized by probing the ability of peptides based on the TM helices of the A2AR to interfere with receptor–receptor interactions. The TM-IV and TM-V peptides had the strongest effect on A2AR–D2R interactions. Combined with the corresponding data for the D2R (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010b), the results pointed to a primary interface involving TM-IV/V for both the A2AR and D2R, but may also involve interactions with TM-VI. This model is in agreement with the work of Canals et al. (2003), in which a chimera of the D1- and D2R subtypes was characterized. To probe the role of the TM region of the D2R in heteromerization, Canals et al. (2003) replaced TM-V/VI and IL3 with the corresponding sequence of the D1 subtype, which does not dimerize with the A2AR. The D2/D1 chimera did not interact with the A2AR, supporting a TM interface involving either TM-V, TM-VI, IL3 or a combination of these regions. These results are consistent with our experimental data for peptides corresponding to TM-V of the D2R, which resulted in a reduction of heteromerization in BRET assays (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010b). As TM-IV, TM-V, and TM-VI cannot be part of a single interface, TM-IV/V interactions were prioritized over those involving TM-V/VI based on the fact that the TM-VI peptide resulted in the smallest effects experimentally. In addition, the fact that the degree of A2AR–D2R heteromerization is not affected by receptor activation (Canals et al., 2003) makes an TM-V/VI interface less likely because this complex would not allow the large conformational changes in TM-VI required for G protein binding (Rasmussen et al., 2011b). An alternative interpretation is that the dimer interface changes upon activation, as proposed for the D2R (Guo et al., 2005) and metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 homodimers (Xue et al., 2015). Although this is a more complex model, it is possible that there is an equilibrium between the TM-IV/V and TM-V/VI interfaces, which may be influenced by activation of either protomer. The results for the TM peptides and predicted interactions are also in agreement with the recent findings by Navarro et al. (2018), which also identified TM-IV/V as the primary interface of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer.
With a more detailed map of the helices involved in A2AR–D2R heteromerization, specific residue interactions and their role in allosteric modulation of ligand binding can be probed. Previous studies have investigated the role of intracellular regions in A2AR–D2R heteromerization by site directed mutagenesis. Based on pulldown and mass spectrometry experiments, negatively charged residues in the C-terminal tail of the A2AR were proposed to form strong interactions with an arginine rich region in IL3 of the D2R (Ciruela et al., 2004). Mutagenesis of the set of arginine residues in IL3 of the D2R (217–222 and 267–269) to alanine abolished the negative allosteric modulation of D2R agonist on activation of the A2AR (Fernandez-Duenas et al., 2012). Similarly, site-directed mutagenesis for three residues in the C-terminal tail of the A2AR (Ser374, Asp401, and Asp402) supported a role of this intracellular region in heteromerization. Loss of heteromerization for the alanine mutant of phosphorylated Ser374, the double mutant Asp401Ala/Asp402Ala as well as the combination of these three mutations were demonstrated in BRET assays. The two mutants involving Ser374 also disrupted the negative allosteric modulation mediated by the A2AR on high-affinity agonist binding to the D2R (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2010a). The C-terminal of the A2AR and IL3 of the D2R were not included in our proposed heterodimer model because of the lack of reliable templates to predict these regions. However, it should be noted that the positively charged region in IL3 of the D2R is close to our proposed TM-IV/V interface as these residues are located at the intracellular part of TM-V. Considering that the three negatively charged residues of the A2AR are located at the end of the long C-terminal tail, interactions between these two regions are also compatible with our proposed model.
To further test the predicted TM interface of the A2AR–D2R complex, two D2R variants with mutations in either the N- or C-terminal end of TM-V were evaluated experimentally. None of these mutations disrupted dimerization completely, which was expected considering the large predicted contact surface and the involvement of intracellular regions in receptor–receptor interactions. The BRET data indicated a reduced population of heteroreceptor complexes, which supports the view that TM-V of the D2R is part of the interface. The lack of effect in the PLA experiments may be due to a combination of the relatively modest impact of the mutants on dimerization and high receptor expression, which can lead to saturation effects that influence quantification of small differences in the level of receptor–receptor interactions using this technique (Mocanu et al., 2011). Based on the binding data, the predicted TM-IV/V interactions between the two receptors could contribute to the negative allosteric modulation across the A2AR–D2R heterodimer. Interestingly, crystal structures of the A2AR in active- and inactive-like conformations suggest that TM-V shifts slightly inward upon activation by adenosine (Lebon et al., 2011). A similar inward contraction of TM-V was observed for monoamine-recognizing GPCRs that are homologous to the D2R (e.g., for the β1 and β2 adrenergic receptors) (Rasmussen et al., 2011a; Warne et al., 2011). The negative allosteric modulation across the A2AR–D2R heterodimer may thus be partly accomplished via interactions across the TM-V interface. The reduction of agonist binding to the D2R observed upon activation of the A2AR may be due to altered helix–helix interactions when TM-V shifts inward in response to adenosine receptor activation. In the complex with an A2AR antagonist, TM-V can instead contribute to stabilizing the high affinity state conformation of the D2R binding site, leading to the increased dopaminergic D2R signaling sought in treatment of Parkinson’s disease (Fuxe et al., 2007b; Armentero et al., 2011).
The A2AR and D2R exist both as homo- and heteromers in the brain and alteration of the balance between these receptor complexes influences intracellular signaling and could lead to development of neurological diseases (Fuxe and Borroto-Escuela, 2016). The heteromer interface between the A2AR and D2R was the main focus of this work. Future studies need to consider potential changes to the interface upon receptor activation, the influence of homodimers on A2AR–D2R interactions, and the existence of tetramers composed by A2AR–A2AR and D2R–D2R complexes (Bonaventura et al., 2015). As a first step toward characterizing the A2AR homodimer, the effects of peptides derived from TM-IV and TM-V of the A2AR on this complex were evaluated experimentally. In contrast to the strong inhibition of dimerization observed with these peptides for the A2AR–D2R heteromer, there were no effects on A2AR homomerization. The TM-IVA2A and TM-VA2A peptides hence selectively modulate the A2AR–D2R heteromer, which supports the view that the A2AR homo- and A2AR–D2R heteromerization involve different helices.
In this work, we developed an approach for mapping the interfaces of GPCR dimers based on biophysical experiments in combination with protein–protein docking and MD simulations. The modeling of the A2AR–D2R heterodimer was guided by information from low-resolution experiments that identified helices involved in receptor–receptor interactions and led to a potential TM-IV/V interface. The proposed A2AR–D2R structure provides a starting-point for designing new experiments that can contribute to further refinement of the model and understanding of allosteric modulation at the molecular level. The same approach can likely be extended to the large number of class A GPCRs that have been shown to engage in receptor–receptor interactions.
Author Contributions
DR, JK, MJ, AR, and JC designed, performed, analyzed, and interpreted all the molecular modeling studies. DB-E, WR-F, TL, and KF designed, performed, analyzed, and interpreted all laboratory experiments. All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council (2013-5708 and 2017-4676), Åke Wibergs Stiftelse, and the Science for Life Laboratory to JC. The Sven och Lilly Lawski Foundation supported DR with a Postdoctoral Fellowship. This work was also supported by grants from the Swedish Medical Research Council (04X-715 and VR-link) to KF, and by Hjärnfonden (FO2016-0302) to DB-E. Computational resources were provided by the Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing (SNIC).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2018.00829/full#supplementary-material
References
Angers, S., Salahpour, A., and Bouvier, M. (2001). Biochemical and biophysical demonstration of GPCR oligomerization in mammalian cells. Life Sci. 68, 2243–2250. doi: 10.1016/S0024-3205(01)01012-8
Armentero, M. T., Pinna, A., Ferre, S., Lanciego, J. L., Muller, C. E., and Franco, R. (2011). Past, present and future of A(2A) adenosine receptor antagonists in the therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 132, 280–299. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.07.004
Azdad, K., Gall, D., Woods, A. S., Ledent, C., Ferre, S., and Schiffmann, S. N. (2009). Dopamine D2 and adenosine A2A receptors regulate NMDA-mediated excitation in accumbens neurons through A2A-D2 receptor heteromerization. Neuropsychopharmacology 34, 972–986. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.144
Berger, O., Edholm, O., and Jähnig, F. (1997). Molecular dynamics simulations of a fluid bilayer of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine at full hydration, constant pressure, and constant temperature. Biophys. J. 72, 2002–2013. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78845-3
Bonaventura, J., Navarro, G., Casado-Anguera, V., Azdad, K., Rea, W., Moreno, E., et al. (2015). Allosteric interactions between agonists and antagonists within the adenosine A2A receptor-dopamine D2 receptor heterotetramer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, E3609–E3618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1507704112
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Brito, I., Romero-Fernandez, W., Di Palma, M., Oflijan, J., Skieterska, K., et al. (2014). The G protein-coupled receptor heterodimer network (GPCR-HetNet) and its hub components. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 8570–8590. doi: 10.3390/ijms15058570
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Flajolet, M., Agnati, L. F., Greengard, P., and Fuxe, K. (2013). Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer methods to study G protein-coupled receptor-receptor tyrosine kinase heteroreceptor complexes. Methods Cell Biol. 117, 141–164. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-408143-7.00008-6
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Hagman, B., Woolfenden, M., Pinton, L., Jiménez-Beristain, A., Oflijan, J., et al. (2016a). “In situ proximity ligation assay to study and understand the distribution and balance of GPCR homo- and heteroreceptor complexes in the brain,” in Receptor and Ion Channel Detection in the Brain, eds R. Lujan and F. Ciruela (Berlin: Springer), 109–126.
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Marcellino, D., Narvaez, M., Flajolet, M., Heintz, N., Agnati, L., et al. (2010a). A serine point mutation in the adenosine A2AR C-terminal tail reduces receptor heteromerization and allosteric modulation of the dopamine D2R. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 394, 222–227. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.168
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Narvaez, M., Perez-Alea, M., Tarakanov, A. O., Jimenez-Beristain, A., Mudo, G., et al. (2015a). Evidence for the existence of FGFR1-5-HT1A heteroreceptor complexes in the midbrain raphe 5-HT system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 456, 489–493. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.11.112
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Perez-Alea, M., Narvaez, M., Tarakanov, A. O., Mudo, G., Jimenez-Beristain, A., et al. (2015b). Enhancement of the FGFR1 signaling in the FGFR1-5-HT1A heteroreceptor complex in midbrain raphe 5-HT neuron systems. Relevance for neuroplasticity and depression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 463, 180–186. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.04.133
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Pintsuk, J., Schafer, T., Friedland, K., Ferraro, L., Tanganelli, S., et al. (2016b). Multiple D2 heteroreceptor complexes: new targets for treatment of schizophrenia. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 6, 77–94. doi: 10.1177/2045125316637570
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Romero-Fernandez, W., Tarakanov, A. O., Gomez-Soler, M., Corrales, F., Marcellino, D., et al. (2010b). Characterization of the A2AR-D2R interface: focus on the role of the C-terminal tail and the transmembrane helices. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 402, 801–807. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.10.122
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Romero-Fernandez, W., Mudo, G., Perez-Alea, M., Ciruela, F., Tarakanov, A. O., et al. (2012). Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1- 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A heteroreceptor complexes and their enhancement of hippocampal plasticity. Biol. Psychiatry 71, 84–91. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.09.012
Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Wydra, K., Li, X., Rodriguez, D., Carlsson, J., Jastrzebska, J., et al. (2018). Disruption of A2AR-D2R heteroreceptor complexes after A2AR transmembrane 5 peptide administration enhances cocaine self-administration in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0887-1 [Epub ahead of print].
Canals, M., Marcellino, D., Fanelli, F., Ciruela, F., De Benedetti, P., Goldberg, S. R., et al. (2003). Adenosine A2A-dopamine D2 receptor-receptor heteromerization: qualitative and quantitative assessment by fluorescence and bioluminescence energy transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 46741–46749. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306451200
Chakrabarti, N., Neale, C., Payandeh, J., Pai, E. F., and Pomès, R. (2010). An iris-like mechanism of pore dilation in the CorA magnesium transport system. Biophys. J. 98, 784–792. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.11.009
Chien, E. Y., Liu, W., Zhao, Q., Katritch, V., Han, G. W., Hanson, M. A., et al. (2010). Structure of the human dopamine D3 receptor in complex with a D2/D3 selective antagonist. Science 330, 1091–1095. doi: 10.1126/science.1197410
Ciruela, F., Burgueno, J., Casado, V., Canals, M., Marcellino, D., Goldberg, S. R., et al. (2004). Combining mass spectrometry and pull-down techniques for the study of receptor heteromerization. Direct epitope-epitope electrostatic interactions between adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors. Anal. Chem. 76, 5354–5363. doi: 10.1021/ac049295f
Cordomi, A., Navarro, G., Aymerich, M. S., and Franco, R. (2015). Structures for G-protein-coupled receptor tetramers in complex with G proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 40, 548–551. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.07.007
Darden, T., York, D., and Pedersen, L. (1993). Particle mesh Ewald: an N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 98, 10089–10089. doi: 10.1063/1.464397
Dasgupta, S., Ferre, S., Kull, B., Hedlund, P. B., Finnman, U. B., Ahlberg, S., et al. (1996). Adenosine A2A receptors modulate the binding characteristics of dopamine D2 receptors in stably cotransfected fibroblast cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 316, 325–331. doi: 10.1016/S0014-2999(96)00665-6
Davis, I. W., Leaver-Fay, A., Chen, V. B., Block, J. N., Kapral, G. J., Wang, X., et al. (2007). MolProbity: all-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, W375–W383. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm216
Dominguez, C., Boelens, R., and Bonvin, A. M. (2003). HADDOCK: a protein-protein docking approach based on biochemical or biophysical information. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 1731–1737. doi: 10.1021/ja026939x
Feltmann, K., Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Ruegg, J., Pinton, L., De Oliveira Sergio, T., Narvaez, M., et al. (2018). Effects of long-term alcohol drinking on the dopamine D2 receptor: gene expression and heteroreceptor complexes in the striatum in rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 42, 338–351. doi: 10.1111/acer.13568
Fenu, S., Pinna, A., Ongini, E., and Morelli, M. (1997). Adenosine A2A receptor antagonism potentiates L-DOPA-induced turning behaviour and c-fos expression in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 321, 143–147. doi: 10.1016/S0014-2999(96)00944-2
Fernandez-Duenas, V., Gomez-Soler, M., Jacobson, K. A., Kumar, S. T., Fuxe, K., Borroto-Escuela, D. O., et al. (2012). Molecular determinants of A2AR-D2R allosterism: role of the intracellular loop 3 of the D2R. J. Neurochem. 123, 373–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07956.x
Ferre, S., Casado, V., Devi, L. A., Filizola, M., Jockers, R., Lohse, M. J., et al. (2014). G protein-coupled receptor oligomerization revisited: functional and pharmacological perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 66, 413–434. doi: 10.1124/pr.113.008052
Ferre, S., Von Euler, G., Johansson, B., Fredholm, B. B., and Fuxe, K. (1991). Stimulation of high-affinity adenosine A2 receptors decreases the affinity of dopamine D2 receptors in rat striatal membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 7238–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7238
Franco, R., Ferre, S., Agnati, L., Torvinen, M., Gines, S., Hillion, J., et al. (2000). Evidence for adenosine/dopamine receptor interactions: indications for heteromerization. Neuropsychopharmacology 23, S50–S59. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00144-5
Fuxe, K., and Borroto-Escuela, D. O. (2016). Heteroreceptor complexes and their allosteric receptor-receptor interactions as a novel biological principle for integration of communication in the CNS: targets for drug development. Neuropsychopharmacology 41, 380–382. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.244
Fuxe, K., Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Romero-Fernandez, W., Palkovits, M., Tarakanov, A. O., Ciruela, F., et al. (2014). Moonlighting proteins and protein-protein interactions as neurotherapeutic targets in the G protein-coupled receptor field. Neuropsychopharmacology 39, 131–155. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.242
Fuxe, K., Ferre, S., Canals, M., Torvinen, M., Terasmaa, A., Marcellino, D., et al. (2005). Adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 heteromeric receptor complexes and their function. J. Mol. Neurosci. 26, 209–220. doi: 10.1385/JMN
Fuxe, K., Ferre, S., Genedani, S., Franco, R., and Agnati, L. F. (2007a). Adenosine receptor-dopamine receptor interactions in the basal ganglia and their relevance for brain function. Physiol. Behav. 92, 210–217. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.05.034
Fuxe, K., Guidolin, D., Agnati, L. F., and Borroto-Escuela, D. O. (2015). Dopamine heteroreceptor complexes as therapeutic targets in Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 19, 377–398. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.981529
Fuxe, K., Marcellino, D., Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Guescini, M., Fernandez-Duenas, V., Tanganelli, S., et al. (2010). Adenosine-dopamine interactions in the pathophysiology and treatment of CNS disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 16, e18–e42. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2009.00126.x
Fuxe, K., Marcellino, D., Genedani, S., and Agnati, L. (2007b). Adenosine A(2A) receptors, dopamine D(2) receptors and their interactions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 22, 1990–2017. doi: 10.1002/mds.21440
Granier, S., Manglik, A., Kruse, A. C., Kobilka, T. S., Thian, F. S., Weis, W. I., et al. (2012). Structure of the delta-opioid receptor bound to naltrindole. Nature 485, 400–404. doi: 10.1038/nature11111
Guitart, X., Navarro, G., Moreno, E., Yano, H., Cai, N. S., Sanchez-Soto, M., et al. (2014). Functional selectivity of allosteric interactions within G protein-coupled receptor oligomers: the dopamine D1-D3 receptor heterotetramer. Mol. Pharmacol. 86, 417–429. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.093096
Guo, W., Shi, L., Filizola, M., Weinstein, H., and Javitch, J. A. (2005). Crosstalk in G protein-coupled receptors: changes at the transmembrane homodimer interface determine activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 17495–17500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508950102
Han, Y., Moreira, I. S., Urizar, E., Weinstein, H., and Javitch, J. A. (2009). Allosteric communication between protomers of dopamine class A GPCR dimers modulates activation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 5, 688–695. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.199
Hasbi, A., Fan, T., Alijaniaram, M., Nguyen, T., Perreault, M. L., O’dowd, B. F., et al. (2009). Calcium signaling cascade links dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer to striatal BDNF production and neuronal growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 21377–21382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903676106
Hasbi, A., Perreault, M. L., Shen, M. Y. F., Fan, T., Nguyen, T., Alijaniaram, M., et al. (2017). Activation of dopamine D1-D2 receptor complex attenuates cocaine reward and reinstatement of cocaine-seeking through inhibition of DARPP-32, ERK, and DeltaFosB. Front. Pharmacol. 8:924. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00924
Hebert, T. E., Moffett, S., Morello, J. P., Loisel, T. P., Bichet, D. G., Barret, C., et al. (1996). A peptide derived from a beta2-adrenergic receptor transmembrane domain inhibits both receptor dimerization and activation. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 16384–16392. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.27.16384
Hess, B., Bekker, H., Berendsen, H. J. C., and Fraaije, J. G. E. M. (1997). LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 18, 1463–1472. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(199709)18:12<1463::AID-JCC4>3.0.CO;2-H
Hillion, J., Canals, M., Torvinen, M., Casado, V., Scott, R., Terasmaa, A., et al. (2002). Coaggregation, cointernalization, and codesensitization of adenosine A2A receptors and dopamine D2 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 18091–18097. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107731200
Huang, J., Chen, S., Zhang, J. J., and Huang, X. Y. (2013). Crystal structure of oligomeric beta1-adrenergic G protein-coupled receptors in ligand-free basal state. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 419–425. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2504
Isberg, V., De Graaf, C., Bortolato, A., Cherezov, V., Katritch, V., Marshall, F. H., et al. (2015). Generic GPCR residue numbers - aligning topology maps while minding the gaps. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 36, 22–31. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2014.11.001
Jastrzebska, B., Chen, Y., Orban, T., Jin, H., Hofmann, L., and Palczewski, K. (2015). Disruption of rhodopsin dimerization with synthetic peptides targeting an interaction interface. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 25728–25744. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.662684
Jorgensen, W., Chandrasekhar, J., Madura, J., Rw, I., and Klein, M. (1983). Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 79, 926–935. doi: 10.1063/1.445869
Jorgensen, W. L., Maxwell, D. S., and Tirado-Rives, J. (1996). Development and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 11225–11236. doi: 10.1021/ja9621760
Kamiya, T., Saitoh, O., Yoshioka, K., and Nakata, H. (2003). Oligomerization of adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors in living cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 306, 544–549. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00991-4
Lagerstrom, M. C., and Schioth, H. B. (2008). Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 7, 339–357. doi: 10.1038/nrd2518
Lazarova, T., Brewin, K. A., Stoeber, K., and Robinson, C. R. (2004). Characterization of peptides corresponding to the seven transmembrane domains of human adenosine A2A receptor. Biochemistry 43, 12945–12954. doi: 10.1021/bi0492051
Lebon, G., Warne, T., Edwards, P. C., Bennett, K., Langmead, C. J., Leslie, A. G., et al. (2011). Agonist-bound adenosine A2A receptor structures reveal common features of GPCR activation. Nature 474, 521–525. doi: 10.1038/nature10136
Lee, L. T. O., Ng, S. Y. L., Chu, J. Y. S., Sekar, R., Harikumar, K. G., Miller, L. J., et al. (2014). Transmembrane peptides as unique tools to demonstrate the in vivo action of a cross-class GPCR heterocomplex. FASEB J. 28, 2632–2644. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-246868
Lefkowitz, R. J. (2004). Historical review: a brief history and personal retrospective of seven-transmembrane receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 25, 413–422. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2004.06.006
Liu, W., Chun, E., Thompson, A. A., Chubukov, P., Xu, F., Katritch, V., et al. (2012). Structural basis for allosteric regulation of GPCRs by sodium ions. Science 337, 232–236. doi: 10.1126/science.1219218
Manglik, A., Kruse, A. C., Kobilka, T. S., Thian, F. S., Mathiesen, J. M., Sunahara, R. K., et al. (2012). Crystal structure of the micro-opioid receptor bound to a morphinan antagonist. Nature 485, 321–326. doi: 10.1038/nature10954
Marsango, S., Varela, M. J., and Milligan, G. (2015). Approaches to characterize and quantify oligomerization of GPCRs. Methods Mol. Biol. 1335, 95–105. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2914-6-7
Martinez-Munoz, L., Rodriguez-Frade, J. M., and Mellado, M. (2016). Use of resonance energy transfer techniques for in vivo detection of chemokine receptor oligomerization. Methods Mol. Biol. 1407, 341–359. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3480-5-24
Meng, X. Y., Mezei, M., and Cui, M. (2014). Computational approaches for modeling GPCR dimerization. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 15, 996–1006. doi: 10.2174/1389201015666141013102515
Miyamoto, S., and Kollman, P. A. (1992). Settle: an analytical version of the SHAKE and RATTLE algorithm for rigid water models. J. Comput. Chem. 13, 952–962. doi: 10.1002/jcc.540130805
Mocanu, M. M., Varadi, T., Szollosi, J., and Nagy, P. (2011). Comparative analysis of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and proximity ligation assay (PLA). Proteomics 11, 2063–2070. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100028
Murakami, M., and Kouyama, T. (2008). Crystal structure of squid rhodopsin. Nature 453, 363–367. doi: 10.1038/nature06925
Navarro, G., Cordomi, A., Casado-Anguera, V., Moreno, E., Cai, N. S., Cortes, A., et al. (2018). Evidence for functional pre-coupled complexes of receptor heteromers and adenylyl cyclase. Nat. Commun. 9:1242. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03522-3
Navarro, G., Ferre, S., Cordomi, A., Moreno, E., Mallol, J., Casado, V., et al. (2010). Interactions between intracellular domains as key determinants of the quaternary structure and function of receptor heteromers. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 27346–27359. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115634
Ng, G. Y., O’dowd, B. F., Lee, S. P., Chung, H. T., Brann, M. R., Seeman, P., et al. (1996). Dopamine D2 receptor dimers and receptor-blocking peptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 227, 200–204. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1489
Overton, M. C., and Blumer, K. J. (2000). G-protein-coupled receptors function as oligomers in vivo. Curr. Biol. 10, 341–344. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00386-9
Parrinello, M., and Rahman, A. (1981). Polymorphic transitions in single-crystals - a new molecular-dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 7182–7190. doi: 10.1063/1.328693
Pfleger, K. D., and Eidne, K. A. (2006). Illuminating insights into protein-protein interactions using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). Nat. Methods 3, 165–174. doi: 10.1038/nmeth841
Pronk, S., Páll, S., Schulz, R., Larsson, P., Bjelkmar, P., Apostolov, R., et al. (2013). GROMACS 4.5: a high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics 29, 845–854. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt055
Rasmussen, S. G., Choi, H. J., Fung, J. J., Pardon, E., Casarosa, P., Chae, P. S., et al. (2011a). Structure of a nanobody-stabilized active state of the beta(2) adrenoceptor. Nature 469, 175–180. doi: 10.1038/nature09648
Rasmussen, S. G., Devree, B. T., Zou, Y., Kruse, A. C., Chung, K. Y., Kobilka, T. S., et al. (2011b). Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. Nature 477, 549–555. doi: 10.1038/nature10361
Rico, A. J., Dopeso-Reyes, I. G., Martinez-Pinilla, E., Sucunza, D., Pignataro, D., Roda, E., et al. (2017). Neurochemical evidence supporting dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromers in the striatum of the long-tailed macaque: changes following dopaminergic manipulation. Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 1767–1784. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1306-x
Rodrigues, J. P., Trellet, M., Schmitz, C., Kastritis, P., Karaca, E., Melquiond, A. S., et al. (2012). Clustering biomolecular complexes by residue contacts similarity. Proteins 80, 1810–1817. doi: 10.1002/prot.24078
Rodríguez, D., Bello, X., and Gutiérrez-De-Terán, H. (2012). Molecular modelling of G protein-coupled receptors through the web. Mol. Inform. 31, 334–341. doi: 10.1002/minf.201100162
Rodriguez, D., and Gutierrez-De-Teran, H. (2012). Characterization of the homodimerization interface and functional hotspots of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor. Proteins 80, 1919–1928. doi: 10.1002/prot.24099
Sali, A., and Blundell, T. L. (1993). Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 234, 779–815. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1626
Schwarzschild, M. A., Agnati, L., Fuxe, K., Chen, J. F., and Morelli, M. (2006). Targeting adenosine A2A receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 29, 647–654. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2006.09.004
Selent, J., and Kaczor, A. A. (2011). Oligomerization of G protein-coupled receptors: computational methods. Curr. Med. Chem. 18, 4588–4605. doi: 10.2174/092986711797379320
Shen, M. Y., and Sali, A. (2006). Statistical potential for assessment and prediction of protein structures. Protein Sci. 15, 2507–2524. doi: 10.1110/ps.062416606
Thevenin, D., and Lazarova, T. (2008). Stable interactions between the transmembrane domains of the adenosine A2A receptor. Protein Sci. 17, 1188–1199. doi: 10.1110/ps.034843.108
Thevenin, D., Roberts, M. F., Lazarova, T., and Robinson, C. R. (2005). Identifying interactions between transmembrane helices from the adenosine A2A receptor. Biochemistry 44, 16239–16245. doi: 10.1021/bi051422u
Vidi, P. A., Przybyla, J. A., Hu, C. D., and Watts, V. J. (2010). Visualization of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) interactions in living cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC). Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 51, 5.29.1–5.29.15. doi: 10.1002/0471142301.ns0529s51
Vinals, X., Moreno, E., Lanfumey, L., Cordomi, A., Pastor, A., De La Torre, R., et al. (2015). Cognitive impairment induced by Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol occurs through heteromers between cannabinoid CB1 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptors. PLoS Biol. 13:e1002194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002194
Wang, S., Che, T., Levit, A., Shoichet, B. K., Wacker, D., and Roth, B. L. (2018). Structure of the D2 dopamine receptor bound to the atypical antipsychotic drug risperidone. Nature 555, 269–273. doi: 10.1038/nature25758
Warne, T., Moukhametzianov, R., Baker, J. G., Nehme, R., Edwards, P. C., Leslie, A. G., et al. (2011). The structural basis for agonist and partial agonist action on a beta(1)-adrenergic receptor. Nature 469, 241–244. doi: 10.1038/nature09746
Wu, B., Chien, E. Y., Mol, C. D., Fenalti, G., Liu, W., Katritch, V., et al. (2010). Structures of the CXCR4 chemokine GPCR with small-molecule and cyclic peptide antagonists. Science 330, 1066–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.1194396
Xue, L., Rovira, X., Scholler, P., Zhao, H., Liu, J., Pin, J. P., et al. (2015). Major ligand-induced rearrangement of the heptahelical domain interface in a GPCR dimer. Nat. Chem. Biol. 11, 134–140. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1711
Yang, S. N., Dasgupta, S., Lledo, P. M., Vincent, J. D., and Fuxe, K. (1995). Reduction of dopamine D2 receptor transduction by activation of adenosine A2a receptors in stably A2a/D2 (long-form) receptor co-transfected mouse fibroblast cell lines: studies on intracellular calcium levels. Neuroscience 68, 729–736. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00171-E
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor, D2 dopamine receptor, A2A adenosine receptor, heteroreceptor complex, dimerization, dimer interface, allosteric modulation
Citation: Borroto-Escuela DO, Rodriguez D, Romero-Fernandez W, Kapla J, Jaiteh M, Ranganathan A, Lazarova T, Fuxe K and Carlsson J (2018) Mapping the Interface of a GPCR Dimer: A Structural Model of the A2A Adenosine and D2 Dopamine Receptor Heteromer. Front. Pharmacol. 9:829. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00829
Received: 08 February 2018; Accepted: 10 July 2018;
Published: 30 August 2018.
Edited by:
Dominique Massotte, UPR3212 Institut des Neurosciences Cellulaires et Intégratives (INCI), FranceReviewed by:
Peter Vanhoutte, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), FranceAhmed Hasbi, University of Toronto, Canada
Juan Fernandez-Recio, Barcelona Supercomputing Center, Spain
Francesca Fanelli, Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia, Italy
Copyright © 2018 Borroto-Escuela, Rodriguez, Romero-Fernandez, Kapla, Jaiteh, Ranganathan, Lazarova, Fuxe and Carlsson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kjell Fuxe, a2plbGwuZnV4ZUBraS5zZQ== Jens Carlsson, amVucy5jYXJsc3NvbkBpY20udXUuc2U=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Dasiel O. Borroto-Escuela
Dasiel O. Borroto-Escuela David Rodriguez2†
David Rodriguez2† Kjell Fuxe
Kjell Fuxe Jens Carlsson
Jens Carlsson