
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 06 December 2024
Sec. Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1532291
This article is a correction to:
CDK4/6 inhibitors improve the anti-tumor efficacy of lenvatinib in hepatocarcinoma cells
 Graziana Digiacomo1†
Graziana Digiacomo1† Claudia Fumarola1†
Claudia Fumarola1† Silvia La Monica1*
Silvia La Monica1* Mara Bonelli1
Mara Bonelli1 Andrea Cavazzoni1*
Andrea Cavazzoni1* Maricla Galetti2
Maricla Galetti2 Rita Terenziani1
Rita Terenziani1 Kamal Eltayeb1
Kamal Eltayeb1 Francesco Volta1
Francesco Volta1 Silvia Zoppi1
Silvia Zoppi1 Patrizia Bertolini3
Patrizia Bertolini3 Gabriele Missale1,4
Gabriele Missale1,4 Roberta Alfieri1
Roberta Alfieri1 Pier Giorgio Petronini1
Pier Giorgio Petronini1A Corrigendum on
CDK4/6 inhibitors improve the anti-tumor efficacy of lenvatinib in hepatocarcinoma cells
By Digiacomo G, Fumarola C, La Monica S, Bonelli M, Cavazzoni A, Galetti M, Terenziani R, Eltayeb K, Volta F, Zoppi S, Bertolini P, Missale G, Alfieri R and Petronini PG (2022). Front. Oncol. 12:942341. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.942341
In the published article, there was an error in Figures 2B and 3D as published. Two representative images of colony formation were unintentionally inserted twice during the figure assembly for the manuscript preparation. The images of HepG2 cells shown in Figure 3D were inserted by mistake in Figure 2B (panel HepG2 cells). The images of HUH7 shown in Figure 2B were inserted by mistake in Figure 3D (panel SNU398 cells). The corrected Figure 2B and Figure 3D and their caption appear below.
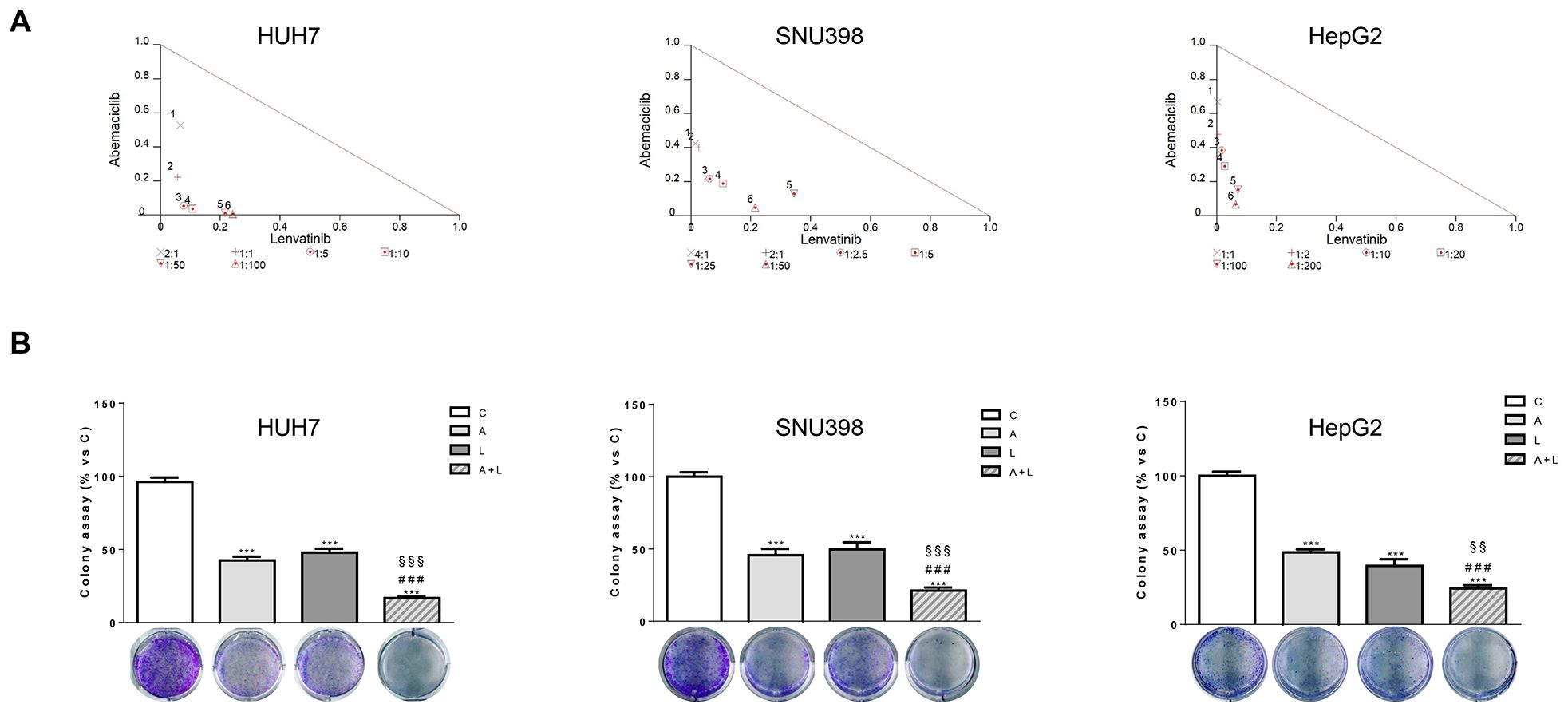
Figure 2. Abemaciclib and lenvatinib combination exerts additive anti-proliferative effects in HCC cells and inhibits colony formation more strongly than single agents. (A) Cells were treated with A, L or the combination. The growth medium with drugs was refreshed every 3 days. After 6 days, cell proliferation was assessed by CV assay. Combination indexes were calculated with Calcusyn software. (B) HUH7, SNU398, and HepG2 cells were treated with A or L at their corresponding IC50 values alone or in combination. After 6 days, colony formation was assessed by CV assay. Representative images of crystal violet staining of colonies are shown. ***p<0.001 vs C, ###p<0.001 vs A; §§p< 0.01, §§§p<0.001 vs L. Data in A are representative of three independent experiments. Data in B are mean values ± SD of three independent experiments.
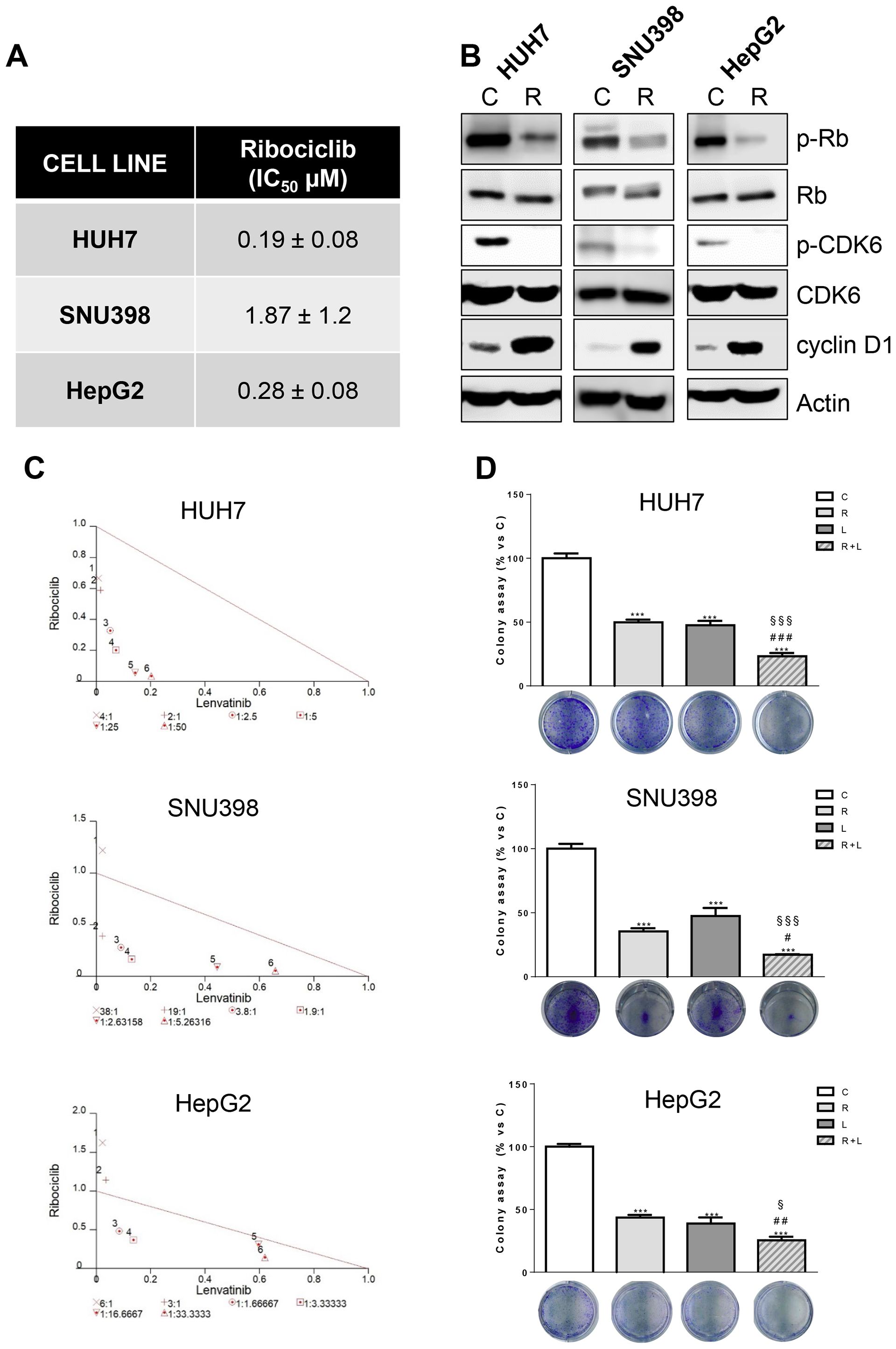
Figure 3. Ribociclib and lenvatinib combination exerts additive anti-proliferative effects in HCC cells and inhibits colony formation more strongly than single agents. (A) After 24h from seeding, HUH7, SNU398, and HepG2 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of ribociclib (R) for 6 days. Cells proliferation was evaluated by CV assay and the IC50 values were calculated using GraphPad Prism 6.00 software. (B) HCC cells were untreated (C) or treated with 1 μM R for 24h. The cells were lysed and the expression of the indicated proteins was evaluated by Western blot analysis. (C) Cells were treated with R, L or the combination. The growth medium with drugs was refreshed every 3 days. After 6 days, cell proliferation was assessed by CV assay. Combination indexes were calculated with Calcusyn software. (D) HUH7, SNU398, and HepG2 cells were treated with R or L at their corresponding IC50 values alone or in combination. After 6 days, colony formation was assessed by CV assay. Representative images of crystal violet staining of colonies are shown. ***p<0.001 vs C; #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 ###p<0.001 vs R; §p< 0.05, §§§p<0.001 vs L. Data in A are mean values ± SD of three independent experiments. Data in B-C are representative of two independent experiments. Data in D are mean values ± SD of two independent experiments.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: hepatocarcinoma (HCC), CDK4/6 inhibition, abemaciclib, lenvatinib, senescence
Citation: Digiacomo G, Fumarola C, La Monica S, Bonelli M, Cavazzoni A, Galetti M, Terenziani R, Eltayeb K, Volta F, Zoppi S, Bertolini P, Missale G, Alfieri R and Petronini PG (2024) Corrigendum: CDK4/6 inhibitors improve the anti-tumor efficacy of lenvatinib in hepatocarcinoma cells. Front. Oncol. 14:1532291. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1532291
Received: 21 November 2024; Accepted: 26 November 2024;
Published: 06 December 2024.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Tong-Chuan He, University of Chicago Medicine, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Digiacomo, Fumarola, La Monica, Bonelli, Cavazzoni, Galetti, Terenziani, Eltayeb, Volta, Zoppi, Bertolini, Missale, Alfieri and Petronini. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Silvia La Monica, c2lsdmlhLmxhbW9uaWNhQHVuaXByLml0; Andrea Cavazzoni, YW5kcmVhLmNhdmF6em9uaUB1bmlwci5pdA==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.