- 1Department of Surgery, Far Eastern Federal University, Vladivostok, Russia
- 2Medical Center, Far Eastern Federal University, Vladivostok, Russia
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, 1477th Naval Clinical Hospital, Vladivostok, Russia
Study design: Systematic review and update meta-analysis.
Purpose: The present systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to compare the efficacy and safety of the two approaches for HCC in adult patients (DEB-TACE vs cTACE).
Overview of literature: The TACE procedure is indicated for the treatment of HCC with intermediate (BCLC B) and early (BCLC A). Conflicting data obtained from earlier meta-analyses comparing DEB-TACE with cTACE prompted the updated meta-analysis.
Methods: The study included adult patients over the age of 18 with HCC. MEDLINE conducted a literature search using Pubmed and Google Scholar up to May 2024. The following parameters were evaluated: the effectiveness of the tumor response to treatment according to the mRECIST criteria (CR, PR, SD, PD), overall survival, progression-free survival, and complication rate. 32 retro- and prospective studies were analyzed.
Results: The study included 4,367 patients. The radiological response of the tumor in all four CR, PR, SD, and PD parameters in the DEB-TACE group showed the best response. The overall survival rate during the DEB-TACE procedure was higher by 3.54 months (p <0.00001), and progression-free survival (PFS) by 3.07 months (p <0.0001), respectively. The incidence of complications was comparable in both groups.
Conclusions: The results of the meta-analysis revealed clinically significant advantages of DEB-TACE in comparison with cTACE. Being comparable in terms of the frequency of complications, DEB-TACE demonstrated the best result in the radiological response of the tumor to the therapy, in terms of overall survival and progression-free survival.
1 Introduction
Liver cancer is the sixth most common in the world and ranks third as the cause of death from malignant neoplasms (MNP) (1).
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma are the two most common primary liver MNPs. Hepatocellular carcinoma develops from hepatocytes, and cholangiocarcinoma develops from bile duct cells (2).
HCC accounts for 75-85% of all primary liver MNPs, leading to the fourth most common cause of cancer-related death in the world (3).
Existing methods of treating HCC, such as surgical resection, transplantation, systemic drug therapy, and stereotactic irradiation, are complemented by the use of minimally invasive methods. One of these options is transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), which consists of the administration of chemotherapeutic drugs directly into the artery feeding the tumor under conditions of digital subtraction angiography.
TACE is performed in the treatment of HCC with intermediate (BCLC B) and early (BCLC A) stages according to the BCLC classification (4). Classical transarterial chemoembolization (cTACE) and transarterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting beads (DEB-TACE) are the two main options for locoregional treatment (5).
cTACE is a procedure that involves the sequential delivery of a chemotherapeutic drug and lipidol into the vessels feeding the tumor, followed by an embolic agent (6).
DEB-TACE is another type of TACE that contains beads saturated with the drug. The use of this technique makes it possible to increase the concentration of the drug in the tumor and reduce its systemic concentrations compared to cTACE (4). However, the disadvantages of DEB-TACE are the constant occlusion of the artery feeding the tumor due to non-degradable beads and a limited choice of therapeutic agents for loading (7, 8).
At the moment, the algorithms for selecting a chemotherapeutic drug and the method of its delivery based on the morphological subtype of the tumor and the stage of the disease remain the subject of active discussions. Conflicting data obtained from previously conducted meta-analyses (16–19) comparing DEB-TACE with cTACE led to the publication of new clinical studies, which prompted the implementation of an updated meta-analysis.
2 Materials and methods
This review was conducted in accordance with the recommendations of The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (9) and Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews AMSTAR. A systematic search was conducted via MEDLINE, PubMed, and Google Scholar. A highly sensitive search strategy using keywords was used for the search: hepatocellular carcinoma AND transarterial chemoembolization, hepatocellular carcinoma, AND chemoembolization, drug-eluting beads AND hepatocellular carcinoma. Irrelevant studies were excluded and duplicates were deleted. Only original articles from 2010 to 2024 were selected. Additional links were found by manually searching the literature lists of relevant studies, conference abstracts, and registered clinical trials. The search was limited to publications in English.
2.1 Selection criteria
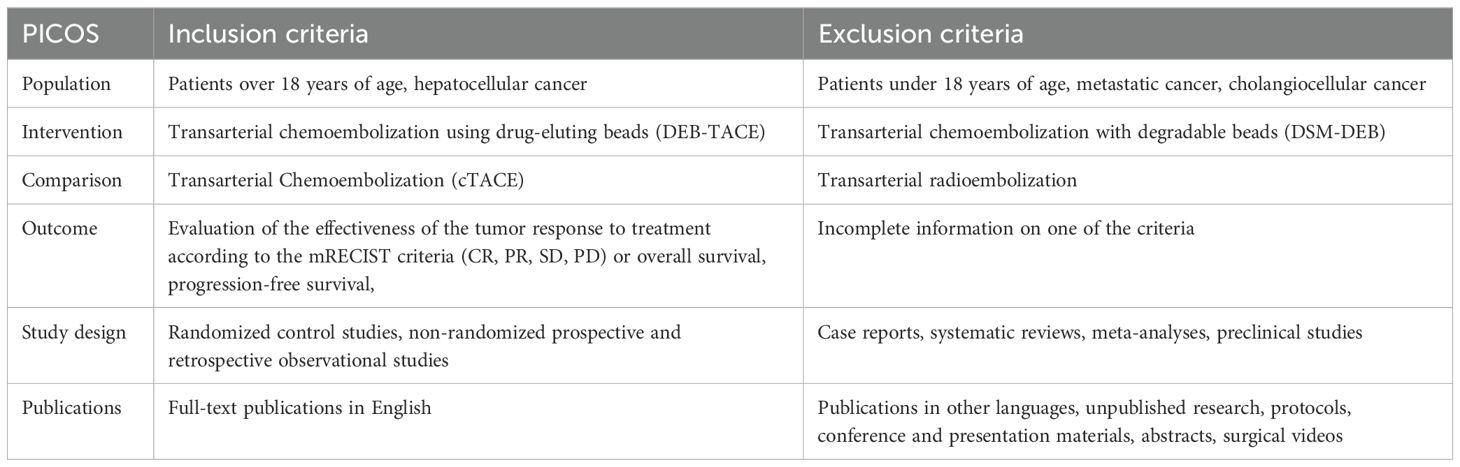
All articles were selected using previously specified keywords. The data were independently selected by two authors (TC, RP), who checked all relevant titles and abstracts of publications to exclude irrelevant ones. The researchers independently evaluated the complete reports, after which each selected article was independently evaluated by the entire author’s team using PICOS (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Study Design) (10) inclusion and exclusion criteria (Table 1).
2.2 Data extraction and quality assessment
The two above-mentioned authors independently extracted data using standardized forms. From publications that meet the inclusion criteria, information on the year, study design, type of emboli, intervention, comparative control, overall survival, mean and standard deviations (SD) or confidence interval (CI), as well as sample sizes were obtained. Modified scales were used to assess the methodological quality of research: Newcastle-Ottawa, NIH quality assessment tool for case series studies, and Cochrane Risk of Bias (ROB) 2.0 tool (11).
2.3 Evaluation of outcomes
The study primarily analyzed the following parameters: (1) median overall survival, (2) progression-free survival, (3) radiological response to treatment, according to the recommendations of the “Criteria for Evaluating Response in Solid Tumors” (RECIST) (12), the frequency of complications during hospitalization.
2.4 Statistical analysis
To analyze the data, we used the Review Manager ver. 5.4 (The Nordic Cochrane Center, The Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark). Risk ratio (RR), odds ratio (OR), and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated for dichotomous variables; standardized mean differences (SMD) and their 95% CI were used for continuous variables. The degree of heterogeneity was estimated using the coefficient I2. The fixed effects model was used for the absence of heterogeneity, and the random effects model was used if I2 was greater than 40%. A funnel-shaped graph was constructed and an Egger’s test was performed to assess the systematic error of the publication. A value of p <0.05 was used to indicate statistical significance. The standard deviations were calculated using the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (13).
3 Results
3.1 Systematic search results
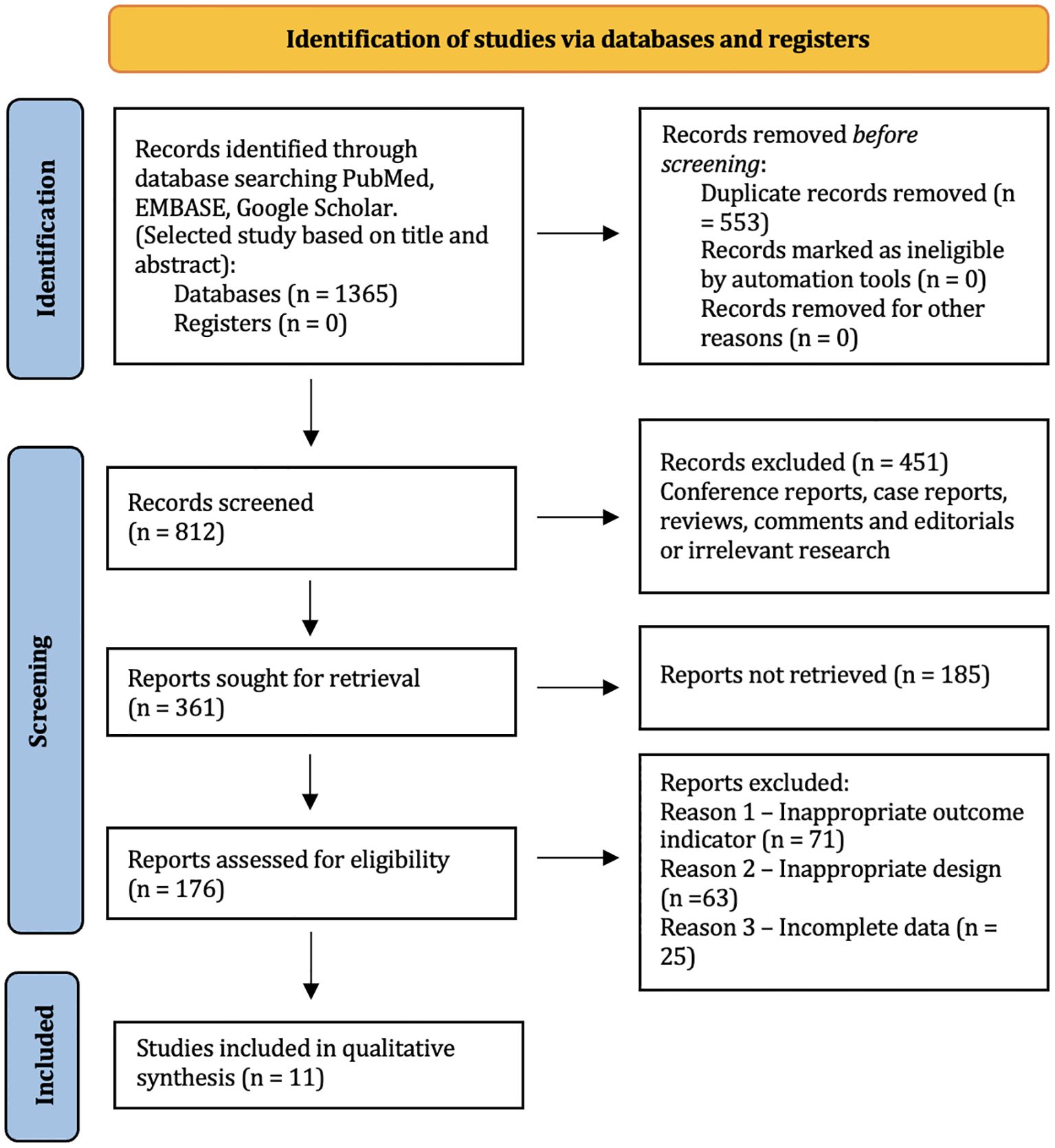
Figure 1 shows a brief description of the research selection process. In total, 1,365 articles were found in the databases of MEDLINE via PubMed, and Google Scholar. A total of 1,189 studies were excluded because they were duplicates, irrelevant studies, case reports, and reviews. A total of 176 potential articles were received for further full-text evaluation. Of these, 157 articles were excluded for non-compliance with the inclusion criteria. The final synthesis included 32 studies. 11 of them were added as a result of an updated systematic search. Table 2 summarizes the main characteristics of the included studies
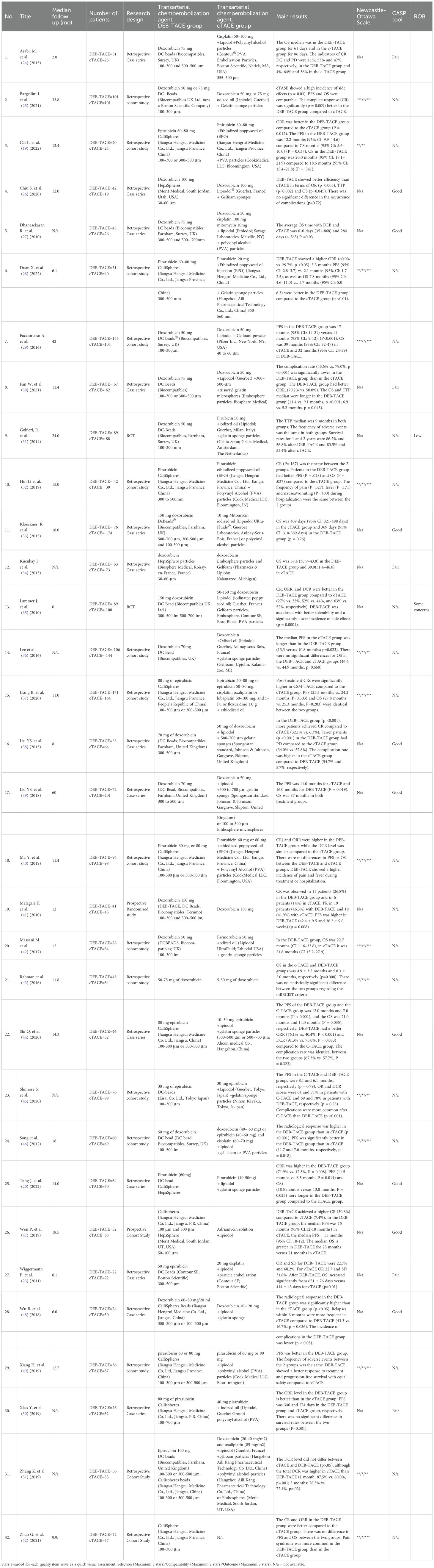
Table 2. General characteristics of the studies included in the systematic review and meta-analysis.
3.2 Initial characteristics and quality assessment
32 studies were included in this meta-analysis. These studies were published between 2010 and 2024. We have discovered and added 11 new studies. 3 scales were used to assess the methodological quality of articles: Newcastle-Ottawa, NIH quality assessment tool for case series studies and Cochrane Risk of Bias (ROB) 2.0 tool. The presented research quality was predominantly low and average (Table 2).
3.3 Clinical trial
3.3.1 Evaluation of the effectiveness of the procedure according to the mRECIST criteria
The effectiveness was assessed according to the mRECIST criteria: Complete Response (CR), Partial Response (PR), Stable Disease (SD), and Progressive Disease (PD). And was analyzed in two groups (455 patients with DEB-TACE and 502 cTACE patients).
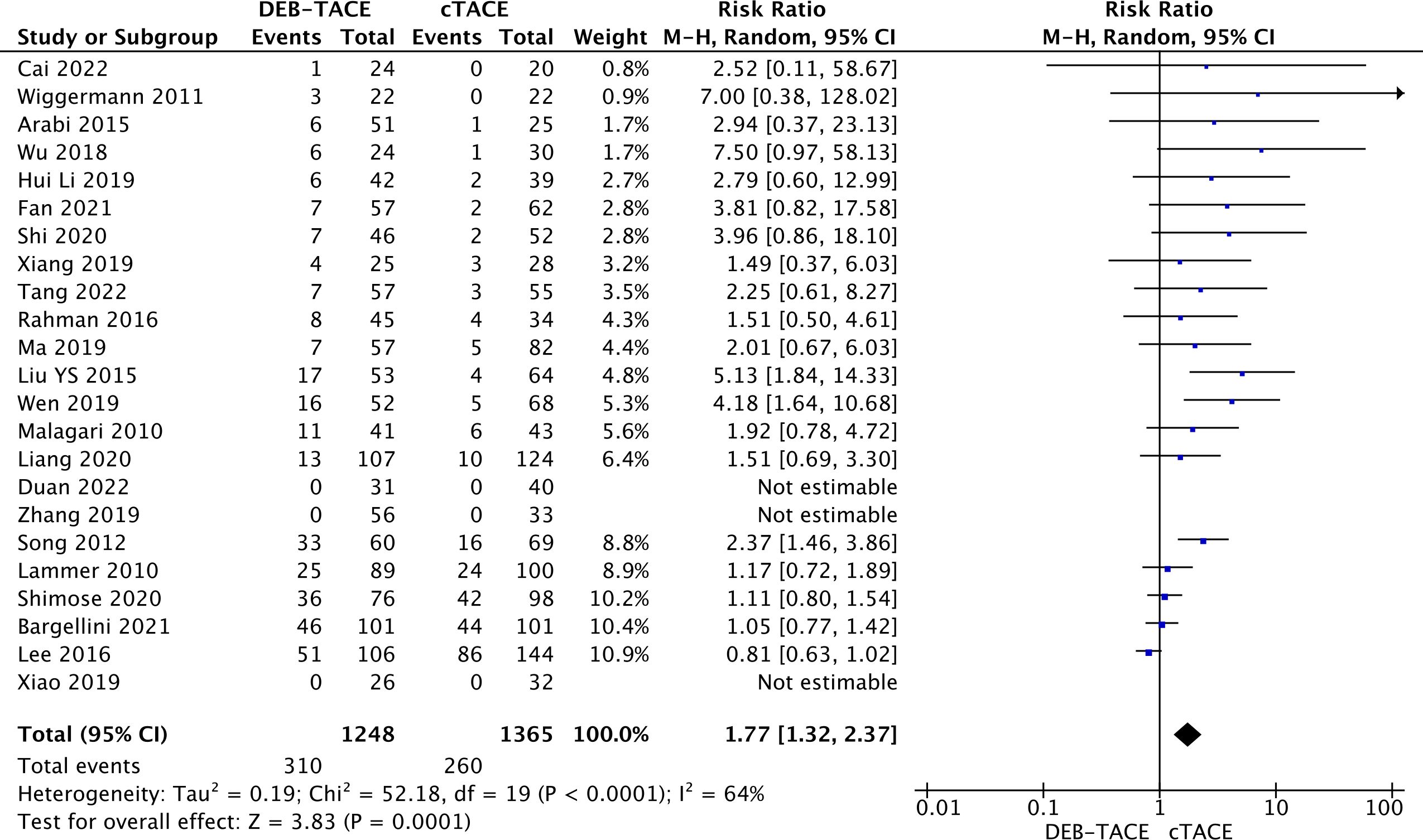
The complete response in the DEB-TACE group was obtained in most cases compared to cTACE (310/1248) versus (260/1365) (RR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.32 to 2.37; p=0.0001; I2 = 64%; random effects model (Figure 2).
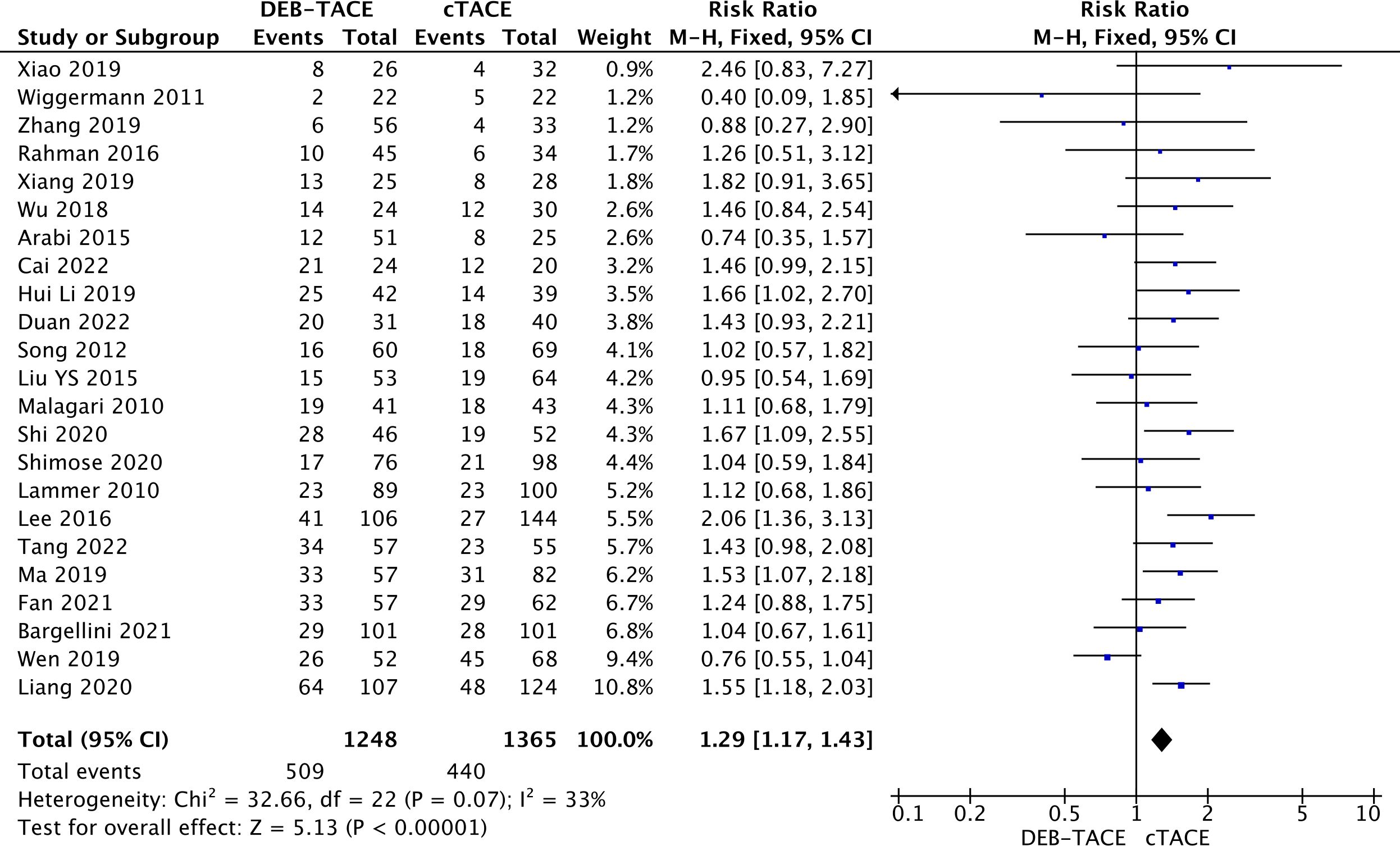
A partial response was also more often recorded in the DEB-TACE group (509/1248) versus (440/1365) (RR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.17 to 1.43; p <0.00001; I2 = 33%; fixed effects model) (Figure 3).
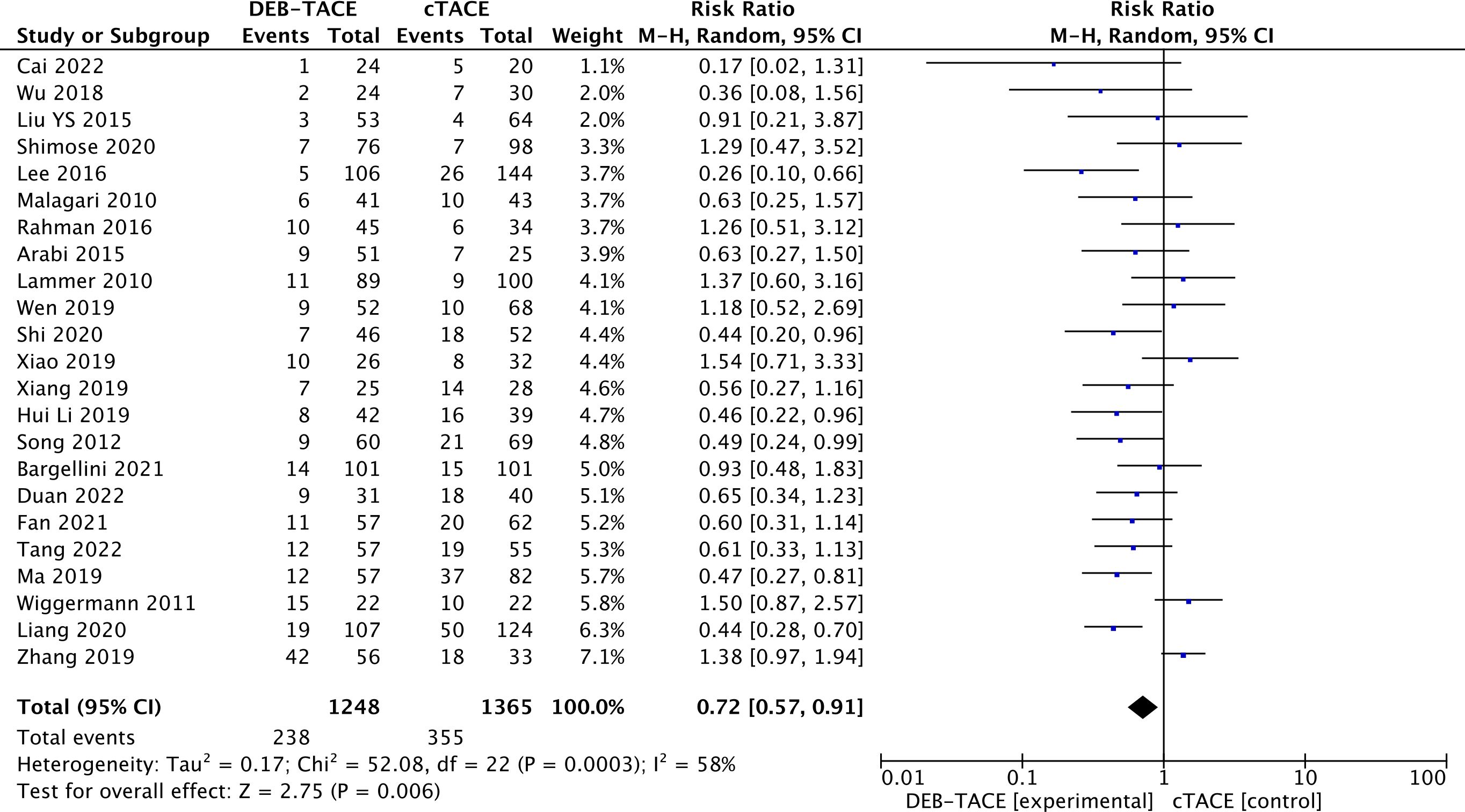
Stabilization of the disease prevailed in the cTACE group (238/1248) than in the DEB-TACE 355/1365 group (RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.57 to 0.91; p=0.006; I2 = 58%; random effects model) (Figure 4).
Disease progression was 310/1365 (22.7%) in the cTACE group and 191/1248 (15.3%) in the DEB-TACE group (RR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.54 to 0.74 p <0.00001; I2 = 20%; fixed effects model) (Figure 5).
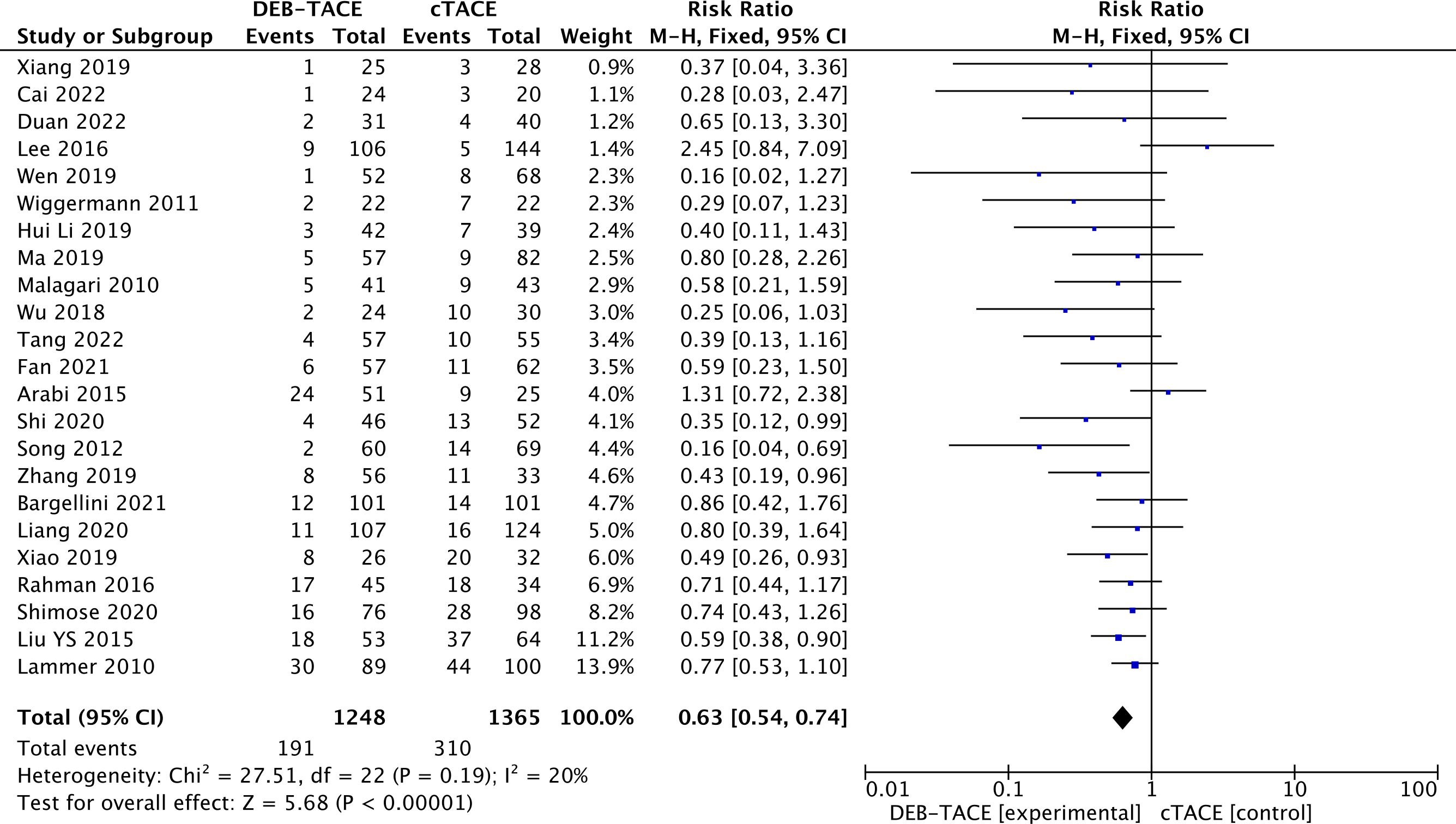
Figure 5. Forest plot of the frequency of Progressive Disease (PD) according to the mRECIST criteria.
3.3.2 Overall survival rate
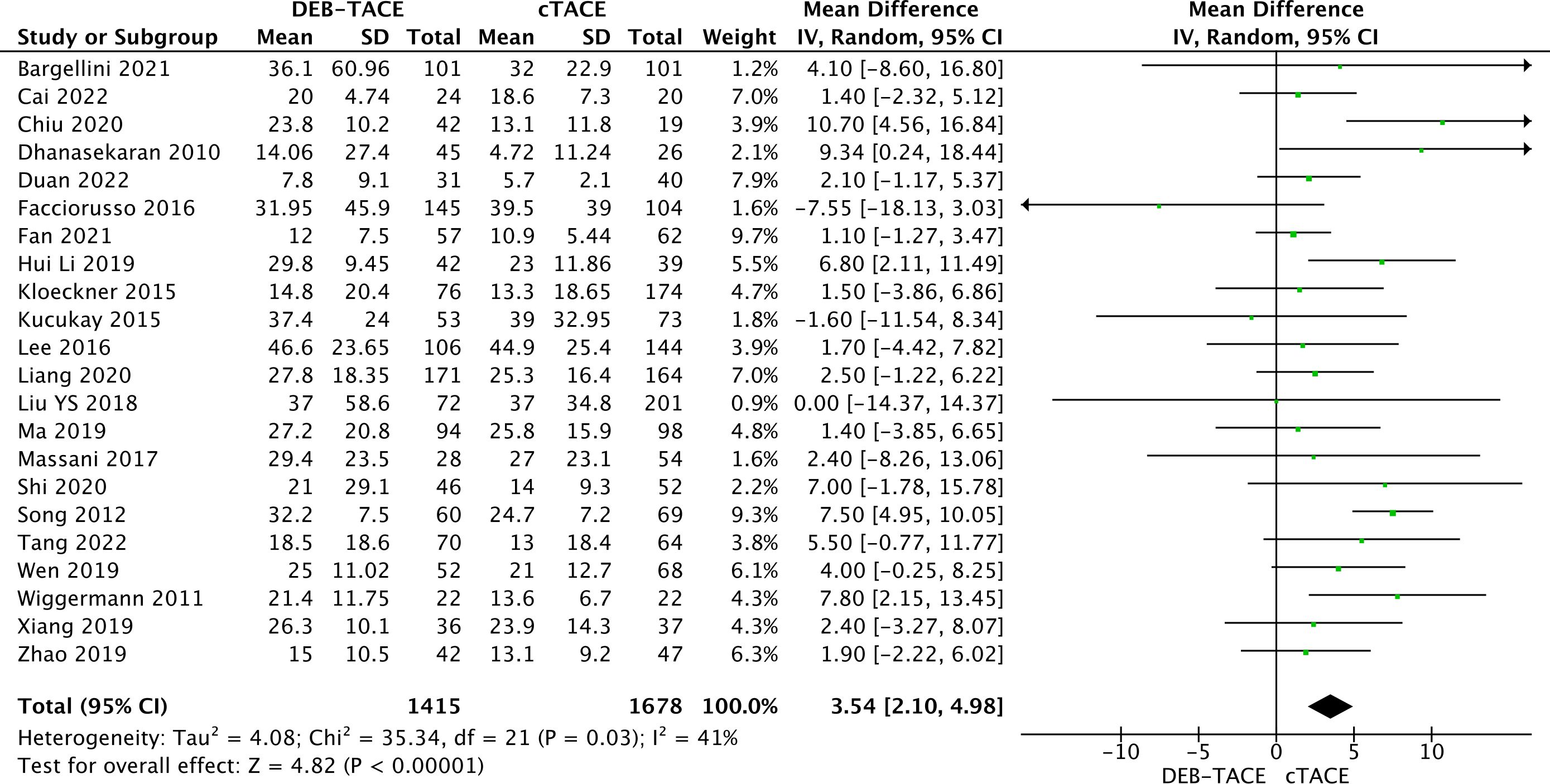
Information on overall survival is presented in 22 studies. The analysis obtained a statistically significant result in the form of better overall survival in the DEB-TACE group over cTACE (MD, 3.54; 95% CI, 2.10 to 4.98; p <0.00001; I2 = 41%; random effects model) (Figure 6).
3.3.3 Progression-free survival
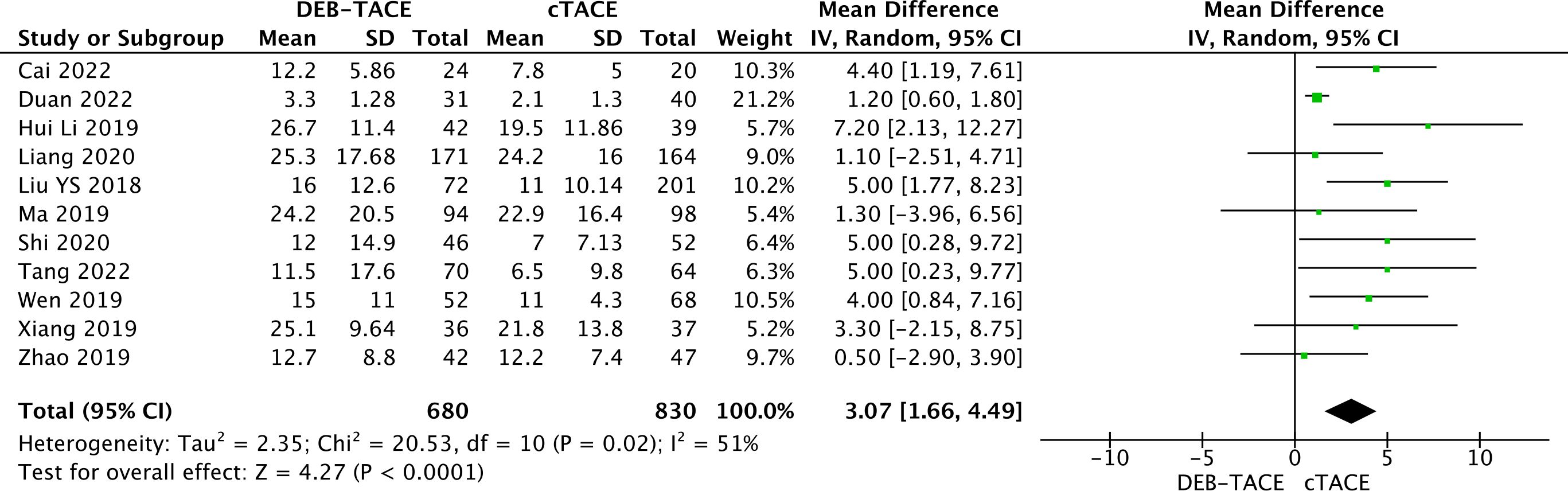
The analysis obtained a statistically significant result in the form of better progression-free survival in the DEB-TACE group over cTACE (MD, 3.07; 95% CI, 1.66 to 4.49; p <0.0001; I2 = 51%; random effects model) (Figure 7).
3.3.4 Complications
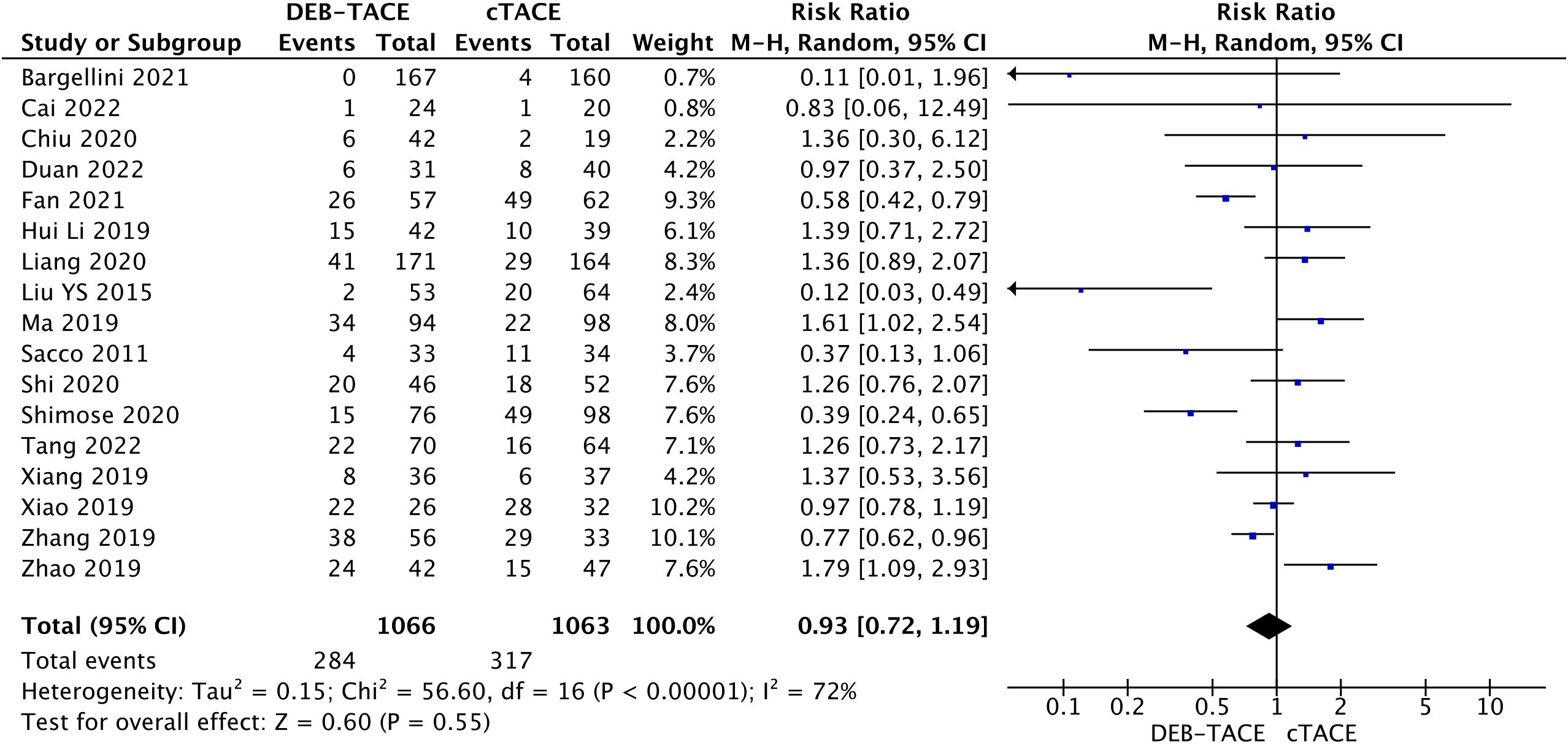
17 studies reported complications after treatment 284/1122(25.31%) in the DEB-TACE group and 317/1117 (28.38%) in the cTACE group (RR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.19; p=0.55; I2 = 72%; random effects model (Figure 8).
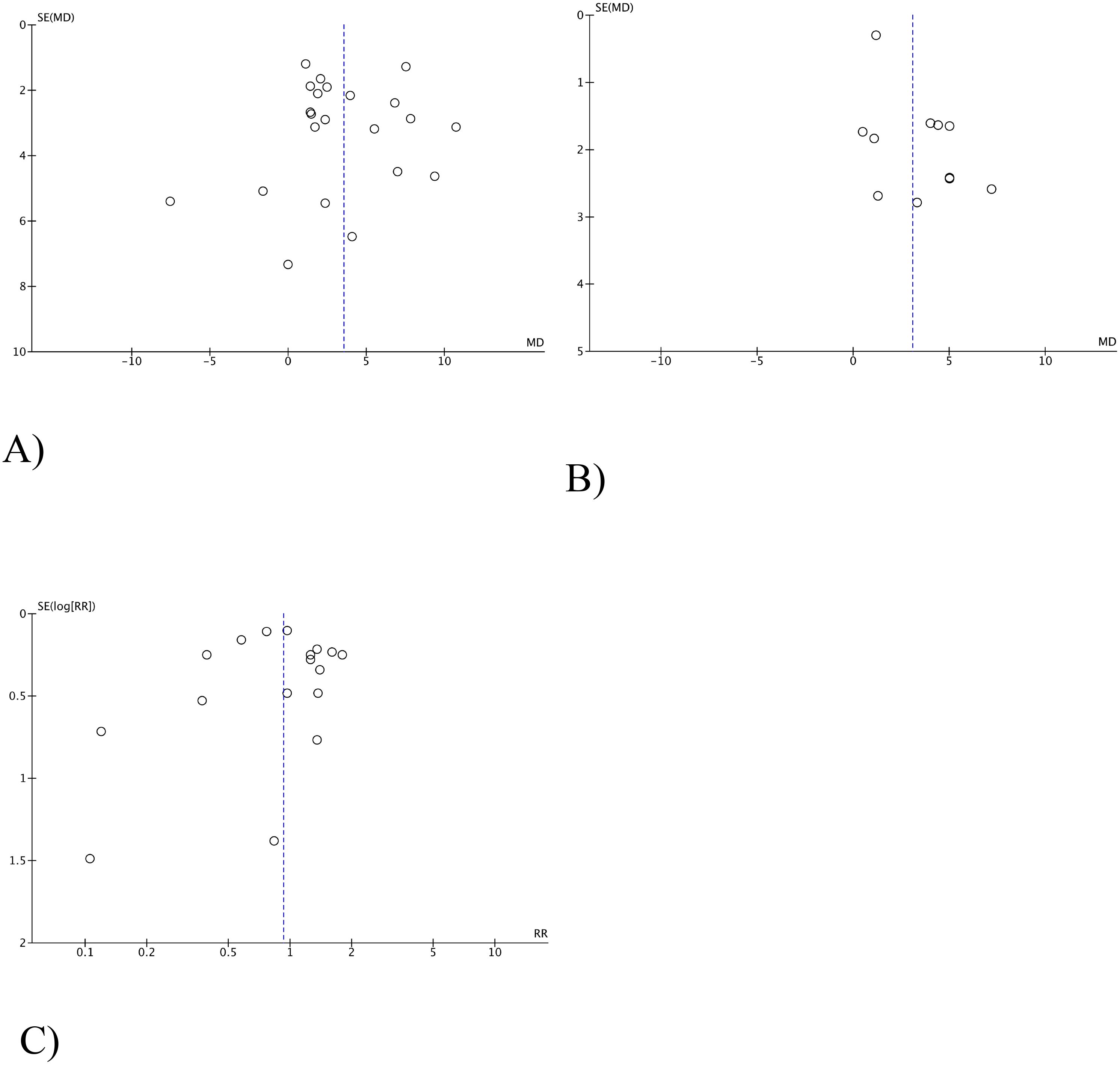
3.4 Evaluation of the publication bias
The estimation of the publication bias for each research parameter was performed using a visual analysis of the funnel diagram. The studies were almost symmetrically distributed on both sides of the vertical line, which indicates a relatively small distortion of publications (Figures 9, 10).

Figure 9. Funnel-shaped diagrams of tumor efficacy. (A) Complete Response. (B) Partial Response. (C) Stable Disease. (D) Progressive Disease .
4 Discussion
In recent years, indications for the TACE procedure have expanded. Starting from treatment as a first-line for the intermediate stage of HCC and ending with palliative care for late-stage patients (14). Various embolic agents for transarterial embolization have been developed, the improvement of the properties of which improved clinical results (7) and dictated the need to study the dependence of the drug delivery method and its effectiveness. Previous meta-analyses (15–18) did not demonstrate definitive conclusions and led to the continuation of the publication of comparative clinical studies (19–21). Our meta-analysis is a summary of the intermediate outcome of these efforts.
According to the results of our study, it was revealed that patients in the DEB-TACE group had a clinically and statistically significantly better radiological tumor response according to the mRECIST criteria compared with cTACE. The overall survival and progression-free survival rates were significantly higher in the DEB-TACE group. At the same time, DEB-TACE did not have an increased complication rate compared to cTACE. The results obtained in the DEB-TACE group may influence the selection of patients for surgical resection, transplantation and chemotherapy line.
Previous meta-analyses comparing treatment responses between DEB-TACE and cTACE in HCC have yielded contradictory results (15–18), which is probably caused by differences between the included studies and population heterogeneity. The initial meta-analysis by Wang et al. (2020) (16) did not reveal any differences in overall survival, radiological response, and complication rates in the cTACE and DEB-TACE groups. Subsequently, Bzeizi et al. (2021) (17) evaluated the safety profile and found that DEB-TACE is associated with a better objective response (CR+PR) (OR: 1.33, 95% CI: 0.99–1.79, p<0.01), lower mortality (OR: 0.32, 95% CI: 0.16-1.17, p=0.04), fewer side effects (OR: 0.74, 95% CI: 0.24-2.24, p<0.01). However, the safety results were based on very limited data. In a meta-analysis by Wang et al. (2023) (15), the best tumor response (OR) was obtained in the DEB-TACE group (RR: 1.27, 95% CI: 1.08–1.48; p = 0.003). The overall survival time was slightly longer in the DEB-TACE group (RR: 1.05, 95% CI: 0.99–1.11, p=0.08), but the result was not statistically significant. The incidence of adverse events was slightly higher in the cTACE group (RR: 1.11, 95% CI: 0.99–1.26; p=0.08). Liang et al. (2021) (18) showed that patients who underwent DEB-TACE had the best complete response (CR) (OR: 2.00, 95% CI: 1.29–3.09, p=0.89), objective response (ORR) (OR: 2.87, 95% CI: 2.15–3.83, p=0,96). Four studies presented PFS and OS data and were included in the combined analysis. The combined results showed a tendency towards longer duration of PFS (HR: 0.86, 95% CI: 0.67–1.11, p=0.16) and OS (HR: 0.79, 95% CI: 0.59–1.07, p=0.58) with DEB-TACE compared to cTACE, although these differences did not reach statistical significance. The analysis of the safety profile revealed no differences in the frequency of adverse events.
Previous studies have not shown that DEB-TACE demonstrates a significant improvement in overall survival or tumor response rate compared to cTACE, calling into question the broader clinical benefits of this technique despite targeted drug delivery. However, the presence of a statistically significant advantage of DEB-TACE in overall survival and tumor response rate in some studies gave impetus to further research in this area, which led to the need to conduct an updated meta-analysis. Our work is the result of efforts and summarizing the results of previous research. The results obtained are statistically and clinically significant. The radiological response of the tumor in all four parameters CR, PR, SD, PD in the DEB-TACE group showed the best response (RR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.32 to 2.37; p =0.0001; I2 = 64%; RR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.17 to 1.43; p <0.00001; I2 = 33%; RR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.57 to 0.91; p =0.006; I2 = 58%; RR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.54 to 0.74 p <0.00001; I2 = 20%; respectively). The overall survival rate during the DEB-TACE procedure was higher by 3.54 months (p <0.00001), and progression-free survival (PFS) by 3.07 months (p <0.0001), respectively. At the same time, the incidence of complications was comparable in both groups. Although, in some cases DEB-TACE can cause more serious side effects such as bile duct damage (60, 61). Controlled, sustained drug release can lead to prolonged local toxicity, which should be considered when administering DEB-TACE (62).
The results obtained during the meta-analysis can significantly affect the practice of using TACE. Thus, when using TACE as a Bridge therapy, in order to reduce tumor progression and the frequency of patients dropping out of the waiting list for liver transplantation, the overall survival of the patient is crucial. Choosing DEB-TACE technology can clinically significantly increase the survival time and increase the chances of liver transplantation. The best radiological response in the DEB-TACE group can be used in down-standing therapy to lower the tumor stage, which can increase the patient’s chances of resection surgery. The radiological response and increased survival time in the DEB-TACE group can significantly affect the use of antitumor drug therapy, changing the choice of therapy line, the algorithm of further management and the timing of follow-up. And also better integrate the use of image segmentation with deep learning technologies in the evaluation of treatment results (58, 59).
There are a number of fundamental limitations in our work. Most of the studies were not randomized and were retrospective in nature, which can lead to a variety of systematic biases, including selection bias, attrition bias, reporting bias and other systematic and random errors. In the included trials, patients were selected according to the BCLC classification with stages A and B. Some studies included only patients in stage B, while others included both B and A. These selection criteria may influence the heterogeneity of the patient groups, which may affect prognosis and overall survival rates. Many aspects of the technical implementation of both types of chemoembolization were not taken into account in the meta-analysis process. The type of embolizing agent material leads to a different ability to adsorb the chemotherapy drug and retain it for a long time in the bloodstream during embolization, which affects the local concentration of the chemotherapy drug and systemic toxicity. In addition, DEB-TACE may require more precise planning and monitoring because of the sustained release mechanism of the beads and the possibility of embolization complications. Furthermore, the size of the emboli reflects the selectivity of delivery of the chemotherapy drug to the tumor, determining the degree of ischemia of healthy tissue. While DEB-TACE offers the advantage of customizable bead sizes, selecting the wrong size can lead to suboptimal outcomes, including inadequate embolization or excessive tissue ischemia (53, 54). However, given the different size of the emboli used, we did not consider this factor in our analysis. Further studies are needed to assess the risks of non-targeted obstruction (55). In addition, in some clinical cases, a differentiated approach to transarterial chemoembolization techniques is required. For example, DEB-TACE releases chemotherapeutic agents in a controlled manner, but this may limit the extent of drug distribution compared to the oil-based emulsions used in cTACE. It may also affect treatment efficacy in larger or more vascularized tumors (56, 57). The chemotherapy drug group also affects the level of response to HCC. Systemic administration of different groups of drugs causes a heterogeneous tumor response. Local administration of the same drugs can similarly lead to different changes in tumor cells, which can affect the overall survival and radiological response (22, 23). These features were not taken into account during the meta-analysis, and there was significant heterogeneity in the presented works with respect to the emboli and chemotherapeutic drugs used. In addition, DEB-TACE uses drug-eluting beads, which are more expensive than the materials used in cTACE. This may make it less affordable in resource-limited settings. This should be taken into account when comparing treatment effects and planning oncology programs. Another limitation of our research was the analysis of publications in English only.
5 Conclusion
The results of the meta-analysis revealed clinically significant advantages of DEB-TACE in comparison with cTACE. Being comparable in the frequency of complications, DEB-TACE demonstrated the best results in the radiological response of the tumor to the therapy, in terms of overall survival and progression-free survival, which may affect the selection of patients for surgical treatment, as well as the choice of a line of chemotherapy. Thus, DEB-TACE may have an advantage over сTACE in increasing the overall life expectancy of patients with HCC.
The data obtained as a result of the meta-analysis are subject to distortions and systematic errors due to the small sample size, lack of randomization and the predominantly retrospective nature of the studies. To improve the methodological quality of studies, as well as an objective comparison of the effectiveness of DEB-TACE and cTACE, it is necessary to conduct prospective randomized trials on a large cohort of patients comparing the effectiveness and safety of these procedures in patients with HCC.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
TC: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ED: Data curation, Project administration, Software, Writing – review & editing. VS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. RG: Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the academic committee of School of Medicine and Life Sciences Far Eastern Federal University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M, Colombet M, Mery L, et al. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer (2024).
2. Mejia JC, Pasko J. Primary liver cancers. Surg Clinics North America. (2020) 100:535–49. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2020.02.013
3. Singal AG, Lampertico P, Nahon P. Epidemiology and surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: New trends. J Hepatol. (2020) 72:250–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.08.025
4. Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:681–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018
5. Lawson A, Kamarajah SK, Parente A, Pufal K, Sundareyan R, Pawlik TM, et al. Outcomes of transarterial embolization (TAE) vs. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers. (2023) 15:3166–6. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123166
6. Mosconi C, Solaini L, Vara G, Brandi N, Cappelli A, Modestino F, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization and radioembolization for unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma-a systemic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Interventional Radiol. (2021) 44:728–38. doi: 10.1007/s00270-021-02800-w
7. Rana M, Melancon M. Emerging polymer materials in trackable endovascular embolization and cell delivery: from hype to hope. Biomimetics. (2022) 7:77–7. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics7020077
8. Jia G, Valkenburgh J, Chen AZ, Chen Q, Li J, Zuo C, et al. Recent advances and applications of microspheres and nanoparticles in transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. (2021) 14(2). doi: 10.1002/wnan.1749
9. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. (2021) 88:105906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
10. Amir-Behghadami M, Janati A. Population, intervention, comparison, outcomes and study (PICOS) design as a framework to formulate eligibility criteria in systematic reviews. Emergency Med J. (2020) 37:387–7. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2020-209567
11. Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non-randomized studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa (ON): Ottawa Hospital Research Institute (2000).
12. Lencioni R, Llovet J. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Disease. (2010) 30:052–60. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-124713
13. Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester, Uk: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd (2008).
14. Zhong BY, Jin Z, Chen JJ, Zhu HD, Zhu XL. Role of transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Trans Hepatol. (2022). doi: 10.14218/jcth.2022.00293
15. Wang ZY, Xie CF, Feng KL, Xiong CM, Huang JH, Chen QL, et al. Drug-eluting beads versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Medicine. (2023) 102:e34527–7. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000034527
16. Liu Y, Zhai B, Wang H, et al. A comparison between drug-eluting bead-transarterial chemoembolization and conventional transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis of six randomized controlled trials. J Cancer Res Ther. (2020) 16:243. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_504_19
17. Bzeizi KI, Arabi M, Jamshidi N, Albenmousa A, Sanai FM, Al-Hamoudi W, et al. Conventional transarterial chemoembolization versus drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers. (2021) 13(24):6172–2. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246172
18. Liang B, Makamure J, Shu S, Zhang L, Sun T, Zheng C. Treatment response, survival, and safety of transarterial chemoembolization with calliSpheres® Microspheres versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:576232. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.576232
19. Cai L, Li H, Guo J, Zhao W, Duan Y, Hou X, et al. Treatment efficacy and safety of drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with arterioportal fistula. Cancer Biol Ther. (2022) 23:89–95. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2021.2020059
20. Tang J, Huang Z, Xu J, Lv Q, Wang P. Drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) exhibits superior efficacy and equal tolerance to conventional TACE in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with conventional TACE history. Clinics Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2022) 46:101814. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2021.101814
21. Domaratius C, Settmacher U, Malessa C, Teichgräber U. Transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: response analysis with mRECIST. Diagn Interventional Radiol. (2020) 27(1):85. doi: 10.5152/dir.2020.19439
22. Bi Y, Jiao D, Ren J, Han X. Clinical outcomes of drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization loaded with raltitrexed for the treatment of unresectable or recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 2022:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2022/2602121
23. Wiggermann P, Sieron D, Brosche C, Brauer T, Scheer F, Platzek I, et al. Transarterial Chemoembolization of Child-A hepatocellular carcinoma: Drug-eluting bead TACE (DEB TACE) vs. TACE with Cisplatin/Lipiodol (cTACE). Med Sci Monitor. (2011) 17:CR189–95. doi: 10.12659/msm.881714
24. Arabi M, BenMousa A, Bzeizi K, Garad F, Ahmed I, Al-Otaibi M. Doxorubicin-loaded drug-eluting beads versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization for nonresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Saudi J Gastroenterol. (2015) 21:175. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.157571
25. Bargellini I, Lorenzoni V, Lorenzoni G, Scalise P, Andreozzi G, Bozzi E, et al. Duration of response after DEB-TACE compared to lipiodol-TACE in HCC-naïve patients: a propensity score matching analysis. Eur Radiol. (2021) 31:7512–22. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07905-x
26. Chiu SH, Chang PY, Shih YL, Huang WY, Ko KH, Chang WC, et al. Efficacy and safety of supplemental transarterial chemoembolization through extrahepatic collateral arteries with drug-eluting beads: treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Design Dev Ther. (2020) 14:5029–41. doi: 10.2147/dddt.s26647
27. Dhanasekaran R, Kooby DA, Staley CA, Kauh JS, Khanna V, Kim HS. Comparison of conventional transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and chemoembolization with doxorubicin drug eluting beads (DEB) for unresectable hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC). J Surg Oncol. (2010) 101:476–80. doi: 10.1002/jso.21522
28. Duan X, Liu J, Han X, Ren J, Li H, Li F, et al. Comparison of treatment response, survival profiles, as well as safety profiles between calliSpheres® Microsphere transarterial chemoembolization and conventional transarterial chemoembolization in huge hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2022) 11:793581. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.793581
29. Facciorusso A, Mariani L, Sposito C, Spreafico C, Bongini M, Morosi C, et al. Drug-eluting beads versus conventional chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2016) 31:645–53. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13147
30. Fan W, Guo J, Zhu B, Wang S, Yu L, Huang W, et al. Drug-eluting beads TACE is safe and non-inferior to conventional TACE in HCC patients with TIPS. Eur Radiol. (2021) 31:8291–301. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07834-9
31. Golfieri R, Giampalma E, Renzulli M, Cioni R, Bargellini I, Bartolozzi C, et al. Randomized controlled trial of doxorubicin-eluting beads vs conventional chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. (2014) 111:255–64. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.199
32. Li H, Wu F, Duan M, Zhang G. Drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) vs conventional TACE in treating hepatocellular carcinoma patients with multiple conventional TACE treatments history. Medicine. (2019) 98:e15314. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000015314
33. Kloeckner R, Weinmann A, Prinz F, Pinto dos Santos D, Ruckes C, Dueber , et al. Conventional transarterial chemoembolization versus drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. (2015) 15:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1480-x
34. Küçükay F, Badem S, Karan A, Ozdemir M, Okten RS, Ozbulbul NI, et al. A single-center retrospective comparison of doxorubicin-loaded hepaSphere transarterial chemoembolization with conventional transarterial chemoembolization for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interventional Radiol. (2015) 26:1622–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2015.07.01
35. Lammer J, Malagari K, Vogl T, Pilleul F, Denys A, Watkinson A, et al. Prospective randomized study of doxorubicin-eluting-bead embolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: results of the PRECISION V study. Cardiovasc Interventional Radiol. (2009) 33:41–52. doi: 10.1007/s00270-009-9711-7
36. Lee YK, Jung KS, Kim DY, Choi JY, Kim BK, Kim SU, et al. Conventional versus drug-eluting beads chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Emphasis on the impact of tumor size. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 32:487–96. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13501
37. Liang B, Xiang H, Ma C, Xiong B, Ma Y, Zhao C, et al. Comparison of chemoembolization with CalliSpheres® microspheres and conventional chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective study. Cancer Manage Res. (2020) 12:941–56. doi: 10.2147/cmar.s187203
38. Liu YiS, Ou MC, Tsai YiS, Lin XZ, Wang CK, Tsai HM, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization using gelatin sponges or microspheres plus lipiodol-doxorubicin versus doxorubicin-loaded beads for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. (2015) 16(1):125–5. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.1.125
39. Liu YS, Lin CY, Chuang MT, Lin CY, Tsai YS, Wang CK, et al. Five-year outcome of conventional and drug-eluting transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. (2018) 18:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12876-018-0848-1
40. Ma Y, Zhao C, Zhao H, Li H, Chen C, Xiang H, et al. Comparison of treatment efficacy and safety between drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization with CalliSpheres® microspheres and conventional transarterial chemoembolization as first-line treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. PubMed. (2019) 11(12):7456–70.
41. Malagari K, Pomoni M, Kelekis A, Pomoni A, Dourakis S, Spyridopoulos T, et al. Prospective randomized comparison of chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting beads and bland embolization with beadBlock for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc Interventional Radiol. (2009) 33:541–51. doi: 10.1007/s00270-009-9750-0
42. Massani M, Stecca T, Ruffolo C, Bassi N. Should we routinely use DEBTACE for unresectable HCC? cTACE versus DEBTACE: a single-center survival analysis. Updates Surgery. (2017) 69:67–73. doi: 10.1007/s13304-017-0414-3
43. Rahman FA, Ngiu CS, Yaakob Y, Mohamed Z, Othman H, Jarmin R, et al. Conventional versus doxorubicin-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a tertiary medical centre experience in Malaysia. PubMed. (2016) 17:4037–41. doi: 10.14456/apjcp.2016.211/APJCP.2016.17.8.4037
44. Shi Q, Chen D, Zhou C, Liu J, Huang S, Yang C, et al. Drug-eluting beads versus lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma: A single-center retrospective study. Cancer Manage Res. (2020) 12:5461–8. doi: 10.2147/cmar.s255960
45. Shimose S, Iwamoto H, Tanaka M, Niizeki T, Shirono T, Nakano M, et al. Increased arterio-portal shunt formation after drug-eluting beads TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. (2020) 98(8):558–65. doi: 10.1159/000507262
46. Song MJ, Chun HJ, Kim HY, Yoo SH, Park CH, Bae SH, et al. Comparative study between doxorubicin-eluting beads and conventional transarterial chemoembolization for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2012) 57(6):1244–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.07.017
47. Wen P, Chen SD, Wang JR, Zeng YH. Comparison of treatment response and survival profiles between drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization and conventional transarterial chemoembolization in Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A prospective cohort study. Oncol Res Featuring Preclinical Clin Cancer Ther. (2019) 27(5):583–92. doi: 10.3727/096504018x15368325811545
48. Wu B, Zhou J, Ling G, Zhu D, Long Q. CalliSpheres drug-eluting beads versus lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a short-term efficacy and safety study. World J Surg Oncol. (2018) 16:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1368-8
49. Xiang H, Long L, Yao Y, Fang Z, Zhang Z, Zhang Y. CalliSpheres drug-eluting bead transcatheter arterial chemoembolization presents with better efficacy and equal safety compared to conventional TACE in treating patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2019) 18:153303381983075. doi: 10.1177/1533033819830751
50. Xiao YD, Ma C, Zhang ZS, Liu J. Safety and efficacy assessment of transarterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and arterioportal shunt: a single-center experience. Cancer Manage Res. (2019) 11:1551–7. doi: 10.2147/cmar.s193948
51. Zhang Z, Li H, Ma C, Xiao Y. Conventional versus drug-eluting beads chemoembolization for infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparison of efficacy and safety. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6386-6
52. Zhao G, Liu S, Chen S, Ren Z, Li C, Bian J, et al. Assessment of efficacy and safety by CalliSpheres versus HepaSpheres for drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in unresectable large hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Drug Delivery. (2021) 28:1356–62. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1943057
53. Al-Thani A, Sharif A, El Borgi S, Abdulla S, Ahmed Saleh MR, Al-Khal R, et al. Development of a flexible liver phantom for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment planning: a useful tool for training & education. 3D Printing Med. (2024) 10:24. doi: 10.1186/s41205-024-00228-9
54. Mangalote IAC, Aboumarzouk O, Al-Ansari AA, Dakua SP. A comprehensive study to learn the impact of augmented reality and haptic interaction in ultrasound-guided percutaneous liver biopsy training and education. Artif Intell Rev. (2024) 57:186. doi: 10.1007/s10462-024-10791-6
55. Rai P, Ansari MY, Warfa M, Al‐Hamar H, Abinahed J, Barah A, et al. Efficacy of fusion imaging for immediate post-ablation assessment of Malignant liver neoplasms: A systematic review. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:14225–51. doi: 10.1002/cam4.v12.13
56. Zhu SL, Zhong JH, Ke Y, Ma L, You XM, Li LQ. Efficacy of hepatic resection vs transarterial chemoembolization for solitary huge hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. (2015) 21:9630–7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9630
57. Schicho A, Hellerbrand C, Krüger K, Beyer LP, Wohlgemuth W, Niessen C, et al. Impact of different embolic agents for transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) procedures on systemic vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels. J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2016) 4:288–92. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2016.00058
58. Al-Kababji A, Bensaali F, Dakua SP, Himeur Y. Automated liver tissues delineation techniques: A systematic survey on machine learning current trends and future orientations. Eng Appl Artif Intell. (2023) 117:105532. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105532
59. Ansari MY, Mangalote IAC, Meher PK, Aboumarzouk O, Al-Ansari A, Halabi O, et al. Advancements in deep learning for B-mode ultrasound segmentation: A comprehensive review. IEEE Trans Emerging Topics Comput Intell. (2024) 8–3. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3377676
60. Rai P, Dakua S, Abinahed J, Balakrishnan S. Feasibility and efficacy of fusion imaging systems for immediate post ablation assessment of liver neoplasms: protocol for a rapid systematic review. Int J Surg Protoc. (2021) 25:209–15. doi: 10.29337/ijsp.162
61. Dakua SP, Nayak A. A review on treatments of hepatocellular carcinoma—role of radio wave ablation and possible improvements. Egyptian Liver J. (2022) 12:30. doi: 10.1186/s43066-022-00191-2
Keywords: transarterial chemoembolization, drug-eluting beads, hepatocellular carcinoma, systematic review, meta-analysis
Citation: Chernyshenko T, Polkin R, Dvoinikova E, Shepelev V and Goncharuk R (2025) Drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization vs conventional transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in adult patients: a systematic review and update meta-analysis of observational studies. Front. Oncol. 14:1526268. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1526268
Received: 11 November 2024; Accepted: 31 December 2024;
Published: 12 February 2025.
Edited by:
Francisco Tustumi, University of São Paulo, BrazilReviewed by:
David Sacerdoti, University of Verona, ItalySarada Prasad Dakua, Hamad Medical Corporation, Qatar
Copyright © 2025 Chernyshenko, Polkin, Dvoinikova, Shepelev and Goncharuk. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Roman Polkin, cm9tYW4ucG9sa2luQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Tatiana Chernyshenko
Tatiana Chernyshenko Roman Polkin
Roman Polkin Ekaterina Dvoinikova1,2
Ekaterina Dvoinikova1,2