Exogenous Let-7a-5p Induces A549 Lung Cancer Cell Death Through BCL2L1-Mediated PI3Kγ Signaling Pathway
- 1Key Laboratory of Birth Regulation and Control Technology of National Health Commission of China, Shandong Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, Jinan, China
- 2School of Public Health, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 3College of Jitang, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan, China
- 4School of Public Health, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
- 5School of Public Health and Management, Weifang Medical University, Weifang, China
A Corrigendum on
Exogenous let-7a-5p induces A549 lung cancer cell death through BCL2L1-mediated PI3Kγ signaling pathway
By Duan S, Yu S, Yuan T, Yao S, and Zhang L (2019) Front. Oncol. 9:808. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00808
In the published article, errors appeared in Figures 3B, C, 4E, F, and 7A, B. During the transwell assay and scratch test procedures, we used the equipment’s default image naming system for batch exports, which led to difficulties in distinguishing between intervention groups during image selection and resulted in incorrect image placement. Given that a significant amount of time has elapsed since publication, the original data associated with these results are no longer available. We therefore carried out independent repeat experiments and achieved outcomes consistent with the initial findings. As a result, the relevant images and their quantitative data in Figures 3B–E, 4E–H, and 7A, B have been updated.
The corrected Figure 3 and its caption are provided below.

Figure 3. Aberrant expression of let-7a-5p alters the growth, migration, and invasion of A459 lung cancer cells. (A) CCK8 assays show that let-7a-5p suppresses the growth of A549 lung cancer cells. (B, C) Transwell assays demonstrate that let-7a-5p inhibits the invasion (B) and migration (C) of A549 lung cancer cells. (D, E) Quantitative analysis of (B, C). NC represents the negative control. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group, using the pooled variance t-test.
The corrected Figure 4 and its caption are provided below.
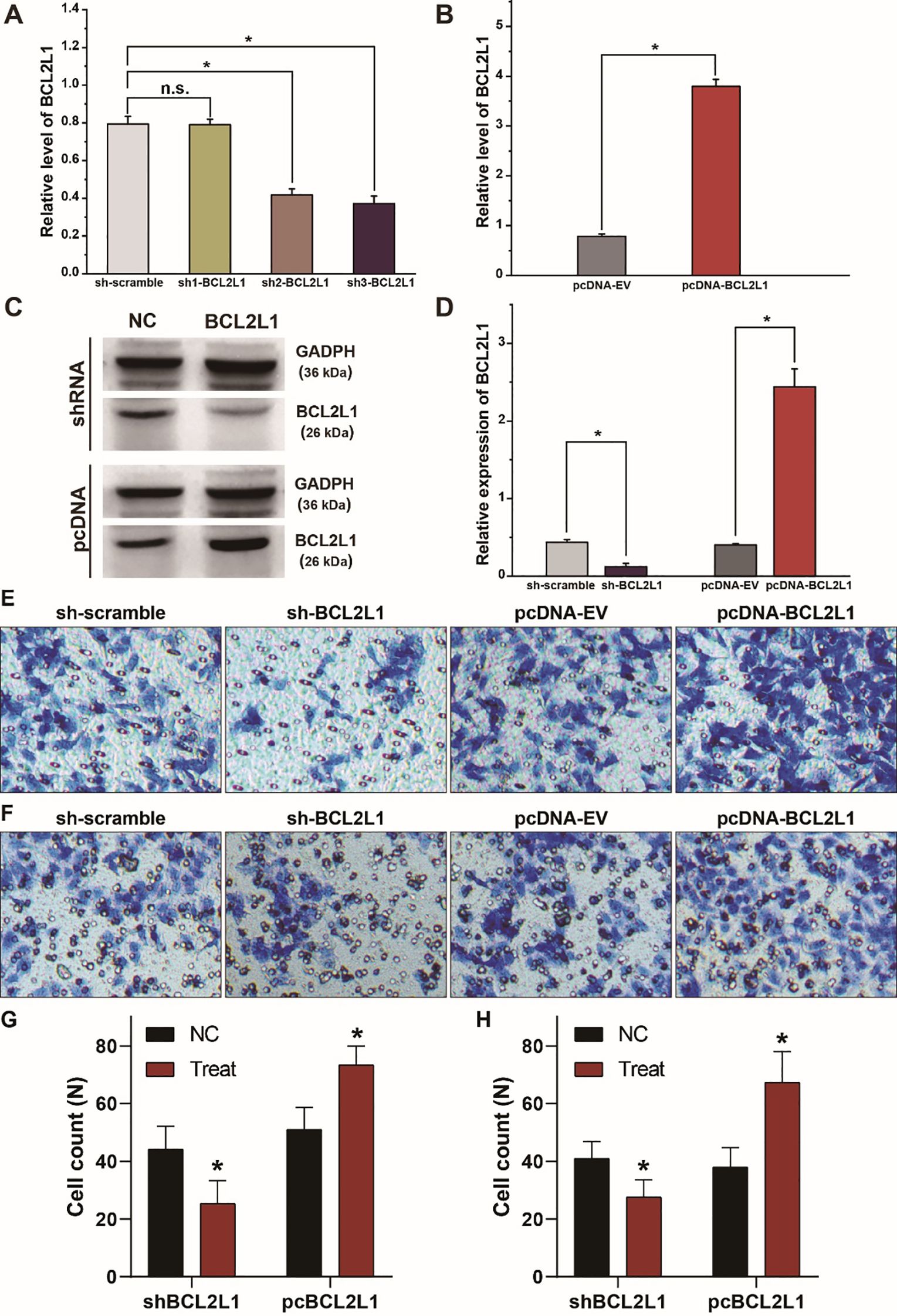
Figure 4. BCL2L1 modulates the migration and invasion of A549 lung cancer cells. (A) Examination of the knockdown efficiency of the sh-BCL2L1 plasmid using RT-qPCR. (B) RT-qPCR assays of BCL2L1 in A459 lung cancer cells transfected with pc-BCL2L1 or negative control. (C, D) Western blot gels and protein expression analysis of BCL2L1 in A459 lung cancer cells transfected with shRNAs or pcDNAs. (E, F), Transwell assays show the alterations of cell invasion (E) and migration (F) of A459 lung cancer cells. (G, H) Quantitative analysis of (E, F). NC, negative control. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group using the pooled variance t test.
The corrected Figure 7 and its caption are provided below.
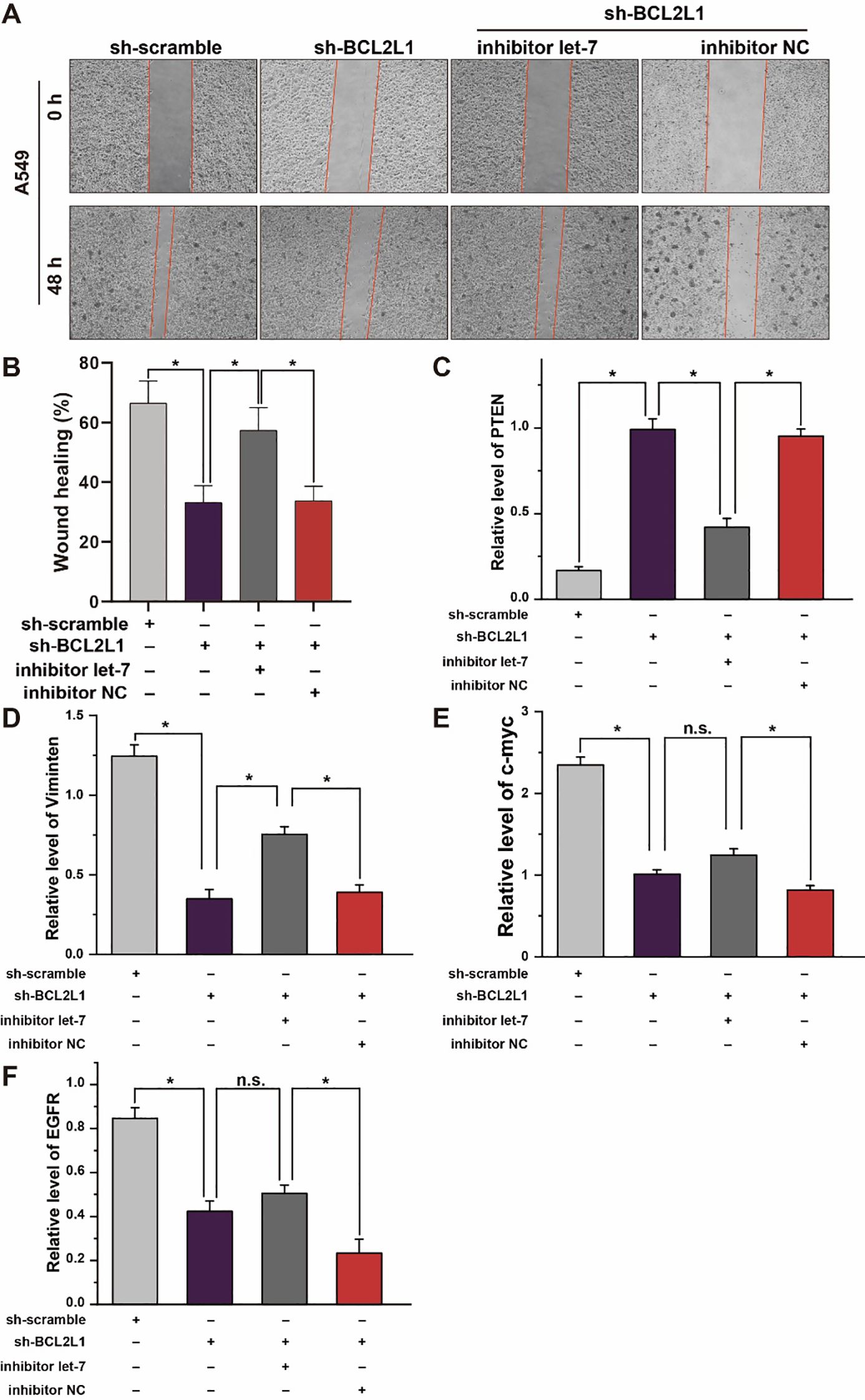
Figure 7. Effect of let-7a-5p-BCL2L1 crosstalk on lung cancer cells in vitro. (A) Wound healing assays exhibit the effect of let-7a-5p-BCL2L1 crosstalk on the migration of A459 lung cancer cells. (B) Quantitative analysis of (A). (C–F) RT-qPCR analysis of lung cancer biomarkers. let-7, let-7a-5p; NC, negative control. *p < 0.05 compared with the indicated group, using the pooled variance t-test.
The authors apologize for these errors and confirm that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: lung cancer, macrophage, exosome, BCL2L1, let-7a-5p, autophagy
Citation: Duan S, Yu S, Yuan T, Yao S and Zhang L (2024) Corrigendum: Exogenous let-7a-5p induces A549 lung cancer cell death through BCL2L1-mediated PI3Kγ signaling pathway. Front. Oncol. 14:1513956. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1513956
Received: 19 October 2024; Accepted: 13 November 2024;
Published: 02 December 2024.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Saverio Marchi, Marche Polytechnic University, ItalyCopyright © 2024 Duan, Yu, Yuan, Yao and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sanqiao Yao, c2FucWlhb3lhb0AxMjYuY29t; Lin Zhang, emhhbmdsaW44OTAxQDE2My5jb20=
 Shuyin Duan
Shuyin Duan Songcheng Yu2
Songcheng Yu2 Lin Zhang
Lin Zhang