
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 30 September 2024
Sec. Cancer Genetics
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1476128
This article is a correction to:
A Novel LncRNA, AC091729.7 Promotes Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinomas Proliferation and Invasion Through Binding SRSF2
 Boyu Yu1†
Boyu Yu1† Linmei Qu2†
Linmei Qu2† Tianyi Wu3
Tianyi Wu3 Bingrui Yan1
Bingrui Yan1 Xuan Kan1
Xuan Kan1 Xuehui Zhao1
Xuehui Zhao1 Like Yang1
Like Yang1 Yushan Li1
Yushan Li1 Ming Liu1
Ming Liu1 Linli Tian1
Linli Tian1 Yanan Sun1*
Yanan Sun1* Qiuying Li1*
Qiuying Li1*A Corrigendum on
A Novel LncRNA, AC091729.7 promotes sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas proliferation and invasion through binding SRSF2
By Yu B, Qu L, Wu T, Yan B, Kan X, Zhao X, Yang L, Li Y, Liu M, Tian L, Sun Y and Li Q (2020). . 9:1575. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01575
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 3F Transwell invasion assay as published. The corrected Figure 3 and its legend appear below.
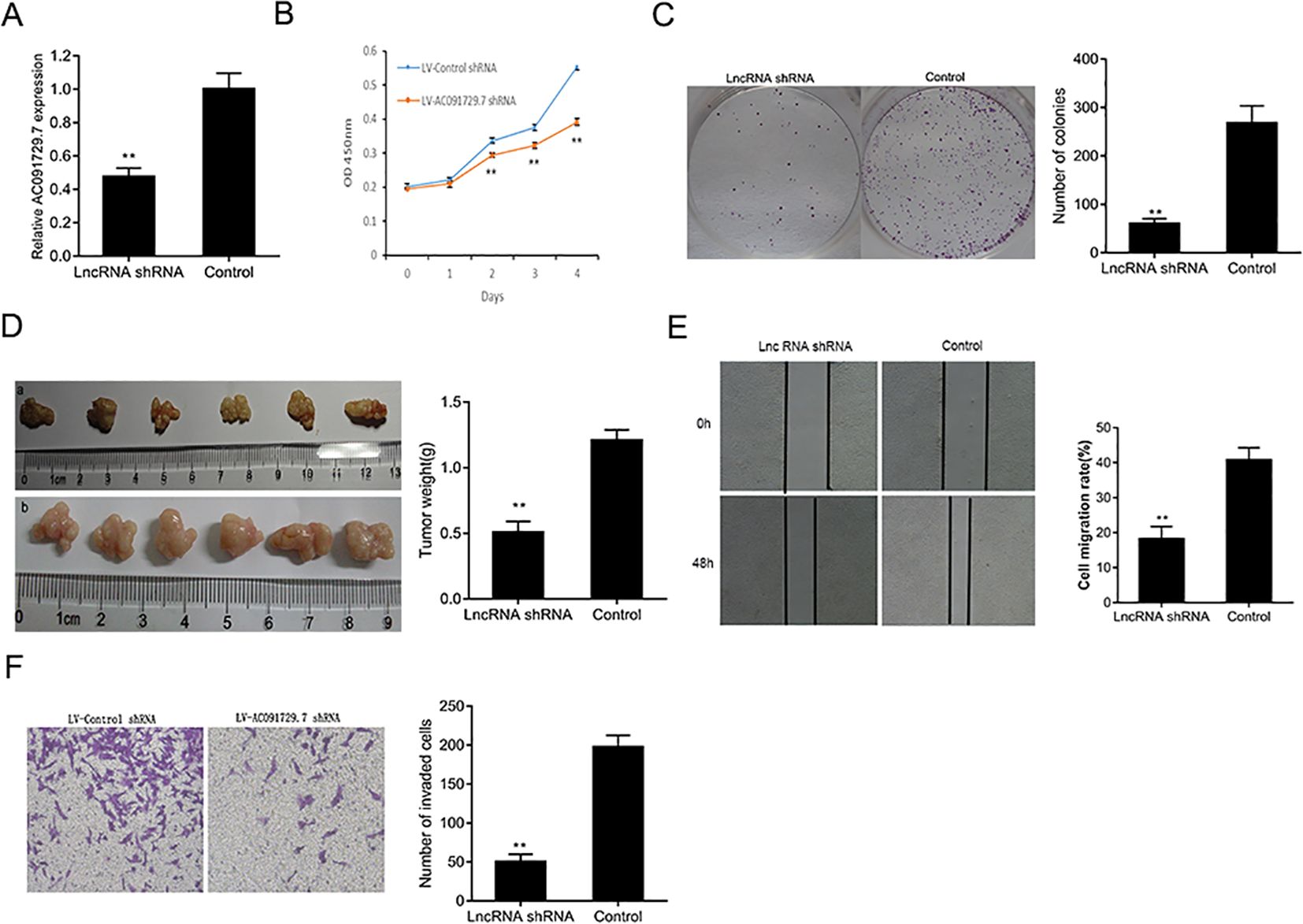
Figure 3. The knockdown of AC091729.7 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of SNSCC cells. (A) Relative RNA level of AC091729.7 was decreased in SNSCC cells with AC091729.7 knockdown. (B) CCK-8 showed that the viability of SNSCC cells was inhibited after the downregulation of AC091729.7 expression. (C) Colony-formation assay suggested that SNSCC cell proliferation was inhibited after AC091729.7 knockdown. (D) Subcutaneous xenograft SNSCC tumors developed in nude mice after RPMI-2650 cells were transfected with lentivirus encoding (a) AC091729.7 shRNA; (b) control shRNA. (E) Wound healing cell migration assay. (F) Transwell invasion assay (**p < 0.01).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: long non-coding RNA, AC091729.7, sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas, serine/arginine rich splicing factor 2, prognosis
Citation: Yu B, Qu L, Wu T, Yan B, Kan X, Zhao X, Yang L, Li Y, Liu M, Tian L, Sun Y and Li Q (2024) Corrigendum: A novel LncRNA, AC091729.7 promotes sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas proliferation and invasion through binding SRSF2. Front. Oncol. 14:1476128. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1476128
Received: 05 August 2024; Accepted: 23 August 2024;
Published: 30 September 2024.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Meng Zhou, Wenzhou Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Yu, Qu, Wu, Yan, Kan, Zhao, Yang, Li, Liu, Tian, Sun and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanan Sun, c3luMjc2N0AxMjYuY29t; Qiuying Li, cWl1eWluZzA5MTJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.