
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 22 February 2024
Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1381151
This article is a correction to:
ITGB5 promotes innate radiation resistance in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by promoting DNA damage repair and the MEK/ERK signaling pathway
 Xin Wen1,2†
Xin Wen1,2† Si Chen1,3†
Si Chen1,3† Xueting Chen1†
Xueting Chen1† Hui Qiu1
Hui Qiu1 Wei Wang1
Wei Wang1 Nie Zhang1
Nie Zhang1 Wanming Liu1
Wanming Liu1 Tingting Wang1
Tingting Wang1 Xin Ding1*
Xin Ding1* Longzhen Zhang1,2,4*
Longzhen Zhang1,2,4*A Corrigendum on
ITGB5 promotes innate radiation resistance in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by promoting DNA damage repair and the MEK/ERK signaling pathway
by Wen X, Chen S, Chen X, Qiu H, Wang W, Zhang N, Liu W, Wang T, Ding X and Zhang L (2022) Front. Oncol. 12:887068. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.887068
Error in Figure/Table
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5 and Figure 7 as published. Due to our careless work, we took multiple images of each group at the same time and saved all the images in the same folder. In Figure 5, images in pCDH were taken following taking images in sg-ITGB5, so that two images are confused partly. Similar mistake happened in Figure 7.]. The corrected [Figure 5 and Figure 7] and its caption [Figure 5 The effect of ITGB5 expression on migration and invasion on pancreatic cancer cells. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001] and [Figure 7 The effect of ITGB5 expression on radiation sensitization in pancreatic cancer cells. (A, C) The colony formation of PANC-1 (A) and BXPC3 (C) cells irradiated with different doses; (B, E) Plating efficiency (PE) of PANC-1 (B) and BXPC3 (E) cells; (C, F) Survival fraction (SF) of PANC-1 (C) and BXPC3 (F) cells; (G-H) Survival fraction curves of PANC-1 (G) and BXPC3 (H) cells according to Linear-quadratic model and Single-hit multitarget model. Values were presented as mean ± SD (n=3).] appear below.
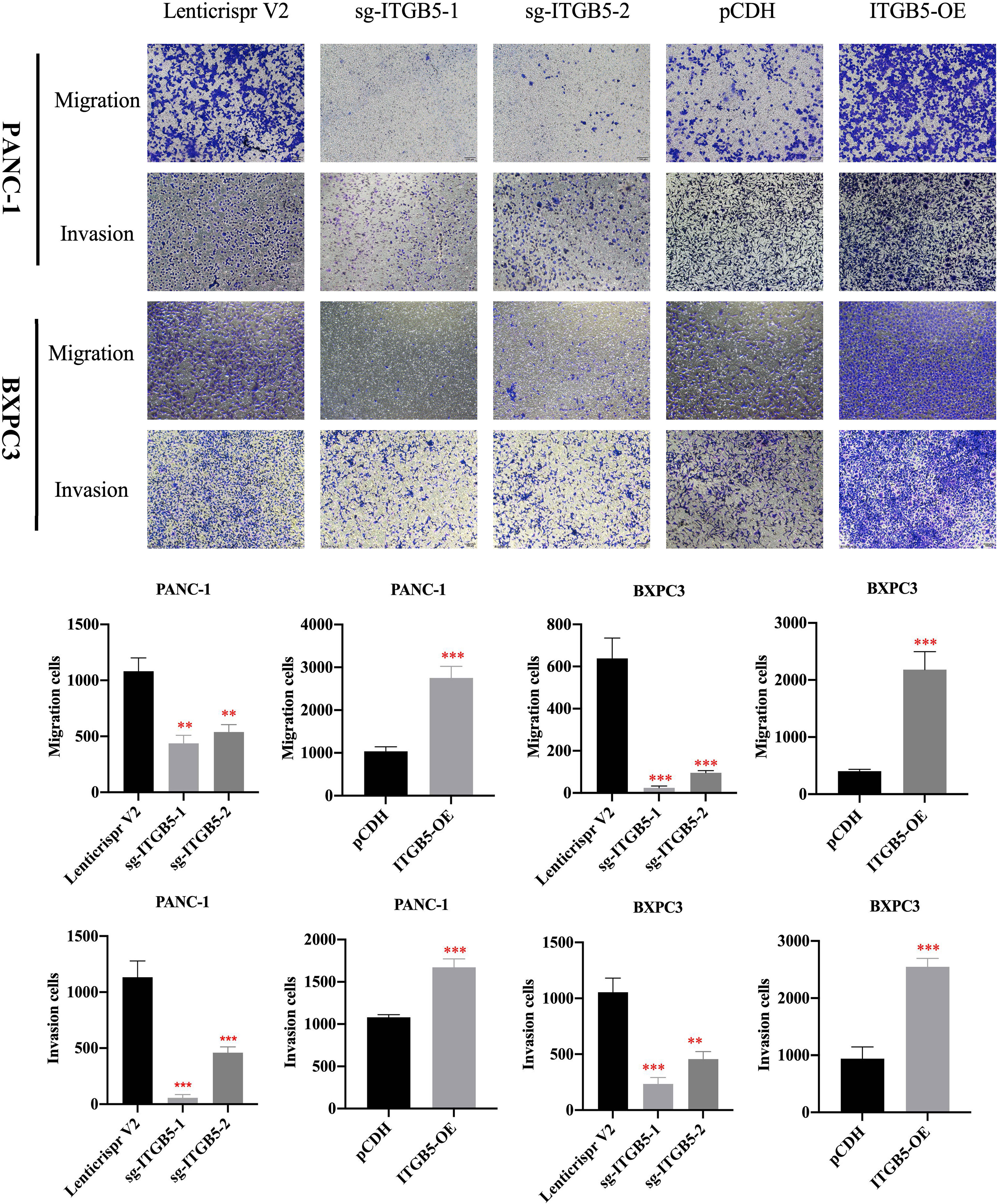
Figure 5 The effect of ITGB5 expression on migration and invasion on pancreatic cancer cells. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
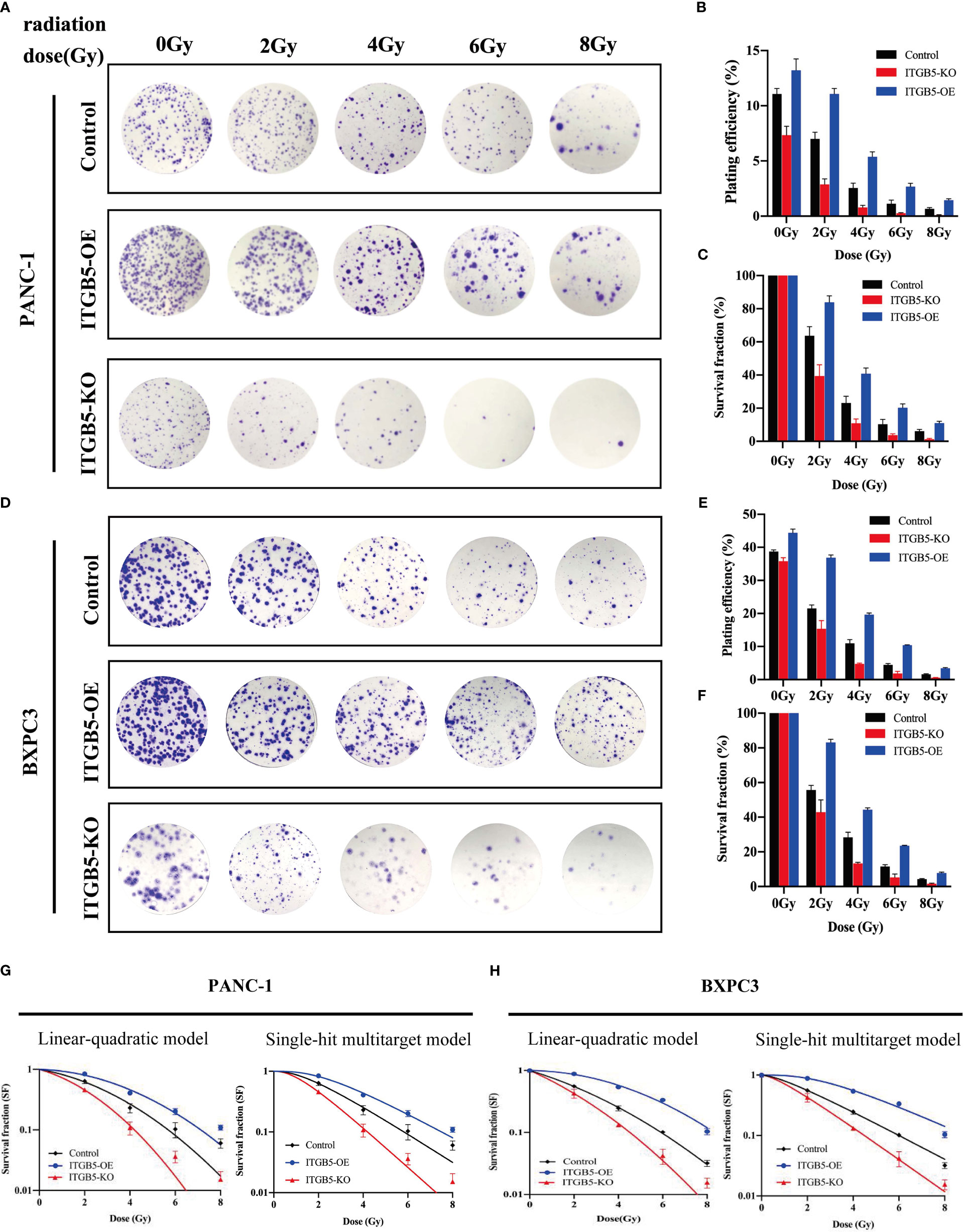
Figure 7 The effect of ITGB5 expression on radiation sensitization inpancreatic cancer cells. (A, C) The colony formation of PANC-1 (A) and BXPC3 (C) cells irradiated with different doses; (B, E) Plating efficiency (PE) of PANC-1 (B) and BXPC3 (E) cells; (C, F) Survival fraction (SF) of PANC-1 (C) and BXPC3 (F) cells; (G-H) Survival fraction curves of PANC-1 (G) and BXPC3 (H) cells according to Linear-quadratic model and Single-hit multitarget model. Values were presented as mean ± SD (n=3).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD), ITGB5, radio-sensitivity, MEK/ERK signaling pathway, DNA damage repair
Citation: Wen X, Chen S, Chen X, Qiu H, Wang W, Zhang N, Liu W, Wang T, Ding X and Zhang L (2024) Corrigendum: ITGB5 promotes innate radiation resistance in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by promoting DNA damage repair and the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Front. Oncol. 14:1381151. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1381151
Received: 02 February 2024; Accepted: 07 February 2024;
Published: 22 February 2024.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Sumitra Deb, Virginia Commonwealth University, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Wen, Chen, Chen, Qiu, Wang, Zhang, Liu, Wang, Ding and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Ding, ZGluZ3hpbjgxQDE2My5jb20=; Longzhen Zhang, anN4eWZ5emx6QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.