- 1Department of Radiology, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Radiology, Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Computer Science and Technology, College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
- 4Department of Pathology, Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
A corrigendum on
Convolutional neural network-based diagnostic model for a solid, indeterminate solitary pulmonary nodule or mass on computed tomography
by Sun K, Chen S, Zhao J, Wang B, Yang Y, Wang Y, Wu C and Sun X (2021) Front. Oncol. 11:792062. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.792062
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 1 as published. Figure 1D2 and Figure 1C2 were duplicated by mistake. The corrected Figure 1 and its caption appear below.
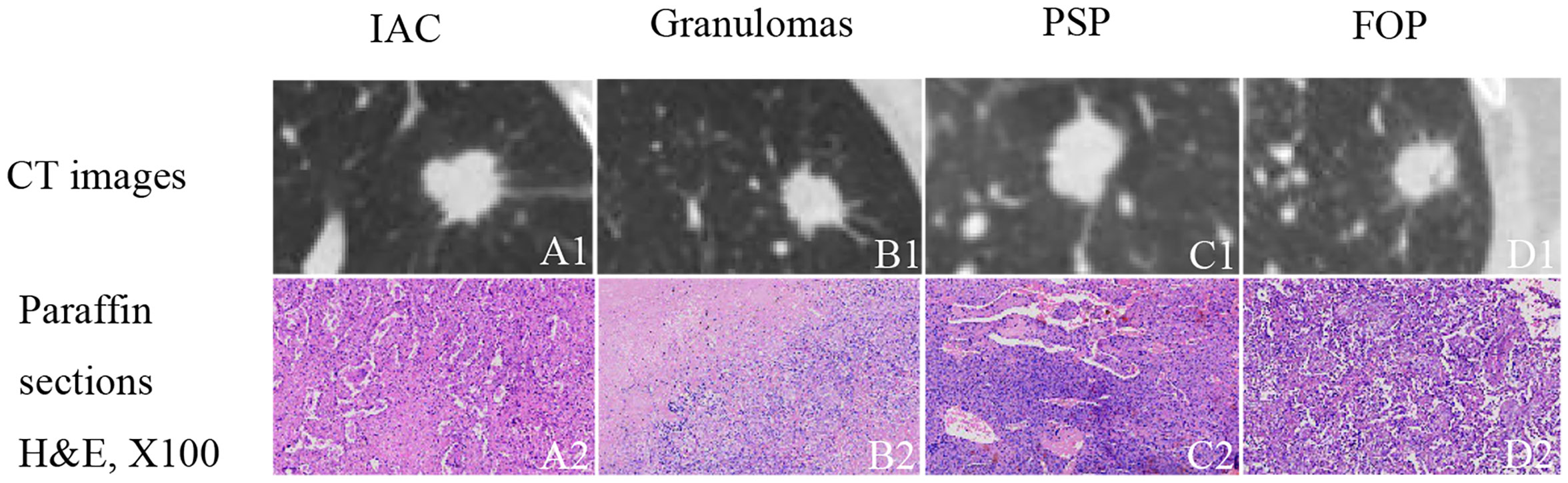
Figure 1 Examples of solid, indeterminate SPN/SPMs without features strongly suggestive of a benign etiology. (A1) Invasive adenocarcinoma (IAC); (B1) granuloma; (C1) pulmonary sclerosing pneumocytoma (PSP); (D1) focal organizing pneumonia (FOP). (A2–D2) paraffin section (hematoxylin and eosin [H&E], 100 ×) of IAC, granuloma, PSP, and FOP, respectively.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: neural network model, computed tomography, differential diagnosis, solid, indeterminate solitary pulmonary nodule, lung adenocarcinoma
Citation: Sun K, Chen S, Zhao J, Wang B, Yang Y, Wang Y, Wu C and Sun X (2023) Corrigendum: Convolutional neural network-based diagnostic model for a solid, indeterminate solitary pulmonary nodule or mass on computed tomography. Front. Oncol. 13:1302777. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1302777
Received: 28 September 2023; Accepted: 30 October 2023;
Published: 07 November 2023.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Abhishek Mahajan, The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre, United KingdomCopyright © 2023 Sun, Chen, Zhao, Wang, Yang, Wang, Wu and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chunyan Wu, d3VjaHVueWFuNTgxQHNpbmEuY29t; Xiwen Sun, c3VueGl3ZW41MjU2QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Ke Sun1,2†
Ke Sun1,2† Jiabi Zhao
Jiabi Zhao Yang Yang
Yang Yang Xiwen Sun
Xiwen Sun