
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol., 12 April 2023
Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics
Volume 13 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1192526
This article is a correction to:
The MYC Paralog-PARP1 Axis as a Potential Therapeutic Target in MYC Paralog-Activated Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Xing Bian1,2,3,4
Xing Bian1,2,3,4 Xiaolin Wang1,2,3,4
Xiaolin Wang1,2,3,4 Qiuyan Zhang5
Qiuyan Zhang5 Liying Ma1,2,3,4
Liying Ma1,2,3,4 Guozhen Cao1,2,3,4
Guozhen Cao1,2,3,4 Ao Xu6,7
Ao Xu6,7 Jinhua Han8
Jinhua Han8 Jun Huang8
Jun Huang8 Wenchu Lin1,3,4*
Wenchu Lin1,3,4*A corrigendum on
The MYC paralog-PARP1 axis as a potential therapeutic target in MYC paralog-activated small cell lung cancer
by Bian X, Wang X, Zhang Q, Ma L, Cao G, Xu A, Han J, Huang J and Lin W (2020) Front. Oncol. 10:565820. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.565820
Error in Figure/Table
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3E as published. The representative picture of western blot bands of cleaved PARP1 of H446 cells were presented incorrectly. The corrected Figure 3E and its caption appear below.
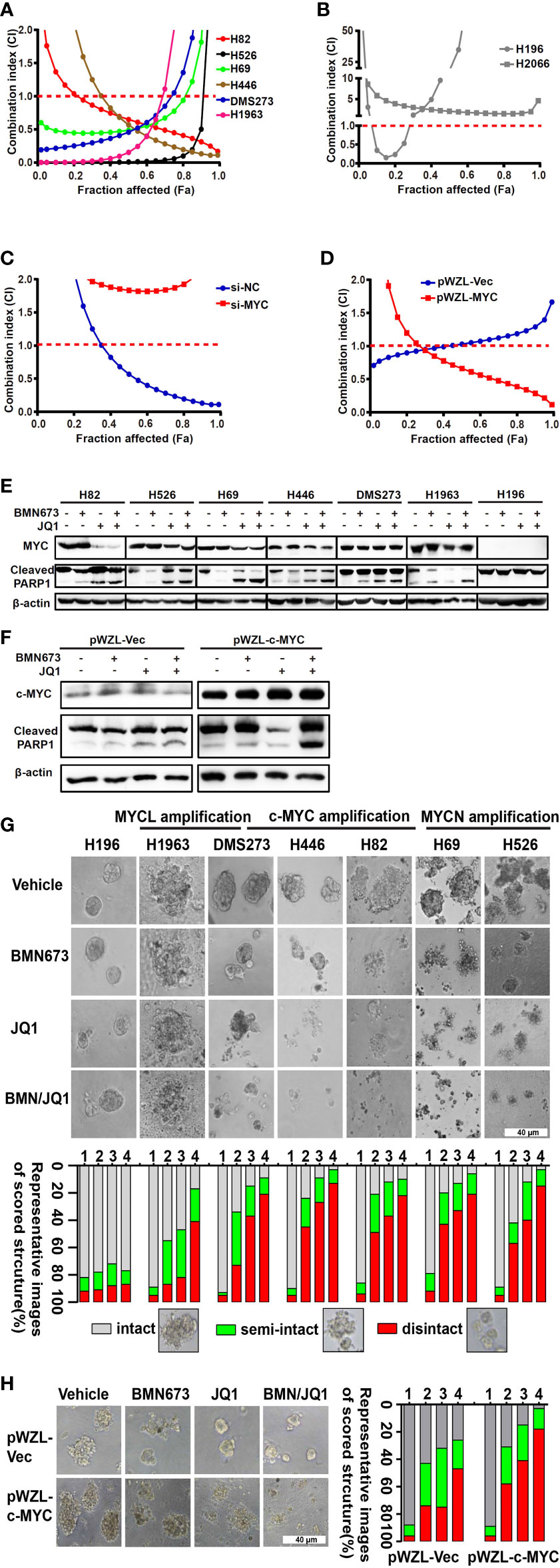
Figure 3 The combination effects of JQ1 and BMN673 in SCLC cells. (A–D) CellTiter-Glo Luminescent assays demonstrating the effects of JQ1 and BMN673 as single agents or in combination in MYC paralog-dependent (A), independent (B) SCLC cells, DMS53 cells with c-MYC knockdown (C), and SHP77 cells with c-MYC overexpression (D). A mathematical model was applied to calculate the combination index using the CalcuSyn software program. (E) Western blot analysis of cleaved PARP and MYC paralogs in SCLC cells treated with BMN673 or JQ1 alone or in combination for 24 h. c-MYC for H82, H446 and DMS273, MYCN for H526 and H69, MYCL for H1963. (F), Western blot analysis of cleaved PARP and c-MYC in SHP77 cells with c-MYC overexpression followed by BMN673 and JQ1 treatment alone or in combination for 24 h. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (G) Tumor sphere structures in 3D matrigel were captured under a phase-contrast microscope upon treatment of JQ1 and BMN673 as single agents or in combination for 10 to 15 days. Representative images of tumor spheres were shown in the top panel. Quantification of scored tumor sphere structures (disintegrated, semi-disintegrated, and intact) was shown in the bottom panel. Scale bar, 40 μm. (H) 3D matrigel assays showing the effect of JQ1 and BMN673 in SHP77 cells with or without c-MYC overexpression. 1, Vehicle; 2, BMN673; 3, JQ1; 4, JQ1+BMN673.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: small cell lung cancer, MYC paralog, PARP1, BET, DNA damage response
Citation: Bian X, Wang X, Zhang Q, Ma L, Cao G, Xu A, Han J, Huang J and Lin W (2023) Corrigendum: The MYC paralog-PARP1 axis as a potential therapeutic target in MYC paralog-activated small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 13:1192526. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1192526
Received: 23 March 2023; Accepted: 27 March 2023;
Published: 12 April 2023.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Shiv K. Gupta, Mayo Clinic, United StatesCopyright © 2023 Bian, Wang, Zhang, Ma, Cao, Xu, Han, Huang and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenchu Lin, d2VuY2h1QGhtZmwuYWMuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.