
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 13 April 2023
Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics
Volume 13 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1163510
This article is a correction to:
Improving anti-tumor efficacy of low-dose Vincristine in rhabdomyosarcoma via the combination therapy with FOXM1 inhibitor RCM1
 Johnny Donovan1†
Johnny Donovan1† Zicheng Deng1,2,3†
Zicheng Deng1,2,3† Fenghua Bian1
Fenghua Bian1 Samriddhi Shukla1
Samriddhi Shukla1 Jose Gomez-Arroyo1,4
Jose Gomez-Arroyo1,4 Donglu Shi2
Donglu Shi2 Vladimir V. Kalinichenko1,3
Vladimir V. Kalinichenko1,3 Tanya V. Kalin1*
Tanya V. Kalin1*A corrigendum on
Improving anti-tumor efficacy of low-dose Vincristine in rhabdomyosarcoma via the combination therapy with FOXM1 inhibitor RCM1
by Donovan J, Deng Z, Bian F, Shukla S, Gomez-Arroyo J, Shi D, Kalinichenko VV and Kalin TV (2023) Front. Oncol. 13:1112859. doi: .10.3389/fonc.2023.1112859
Error in Figure/Table
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3, panel J as published. We inadvertently used the incorrect image for the RCM1-NPFA IVIS image on Day 9 in panel 3J. The corrected Figure 3 and its caption appear below.
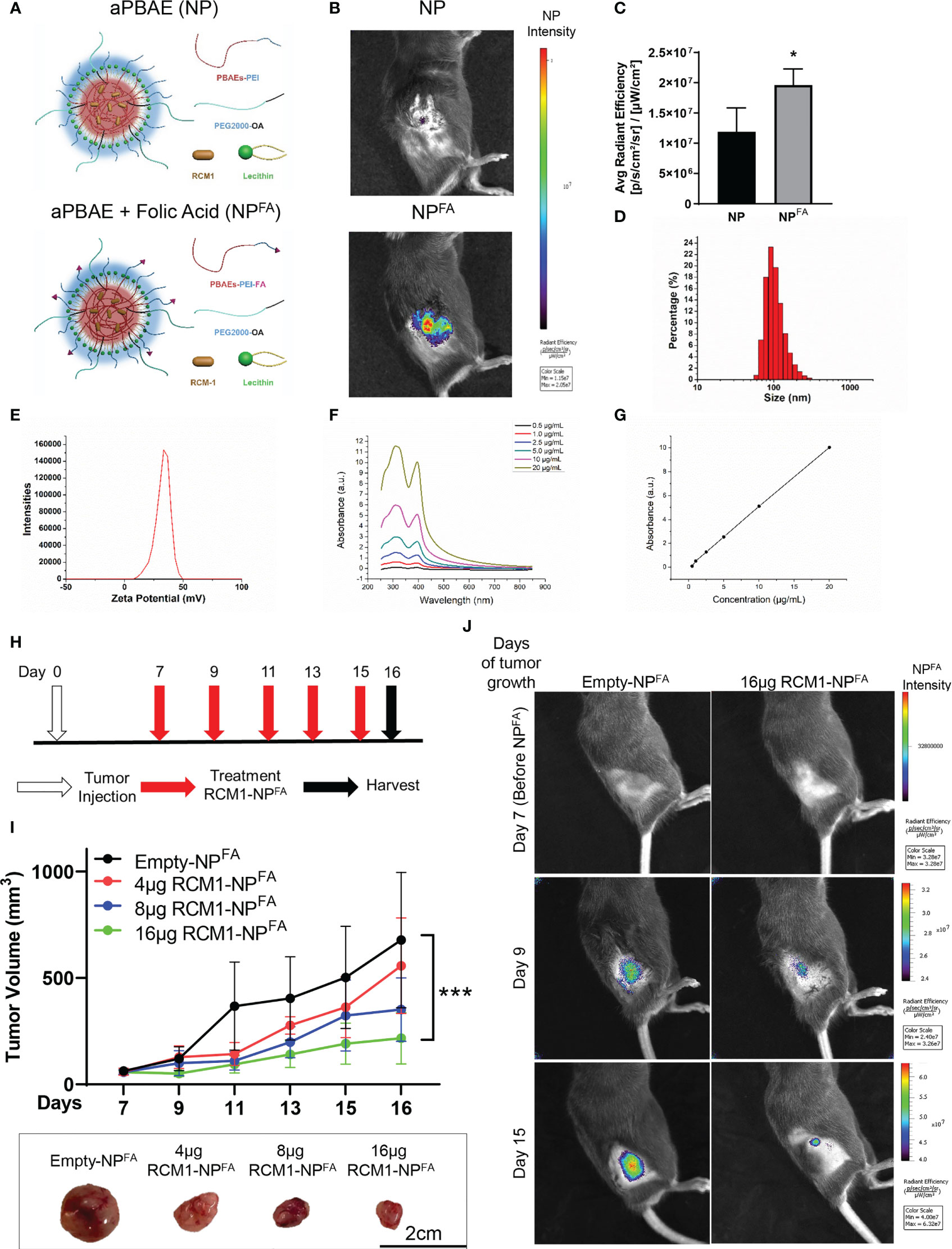
Figure 3 Generation of nanoparticle to deliver RCM1 to tumors. (A), Graphic of amphiphilic poly-beta amino ester (aPBAE) nanoparticles without folic acid (NP, top) and with folic acid (NPFA, bottom). (B), Highly efficient delivery of NPFA, compared to NP into the tumors is shown using IVIS imaging. Mice bearing Rd76-9 subcutaneous RMS tumors were injected with NP or NPFA labeled with DyLight 800. NPFA are present in the tumor 48 hours after i.v. injection. (C), Average radiant efficiency indicating NPFA have a higher intensity compared to NP. (D), The sizes of NPFA were measured and the hydrodynamic average diameter of NPFA is 160.67nm. (E), The surface charge of NPFA is 38.13mV. (F), The UV/Vis spectrum for RCM1 at increasing concentrations in DMSO determined RCM1 has an absorbance peak at 310nm and 395nm. (G), Data from the UV/VIS spectra was used to generate a standard concentration curve that was used to determine RCM1 concentration in the nanoparticles. Adjusted R2 = 0.99944. (H), Schematic diagram showing treatment strategy of tumor bearing mice. Rhabdomyosarcoma Rd76-9 cells were inoculated subcutaneously. Animals were treated with 4µg, 8µg, or 16µg RCM1- NPFA. (I), Treatment with RCM1-NPFA reduced tumor burden in a dose-dependent manner in animals. Mice were treated with 4µg, 8µg, or 16µg of RCM1-NPFA or with empty-NPFA. Tumor volumes were measured at different time points compared to empty-NPFA (top panel). Representative tumors per group are shown (bottom panel). Values are shown as mean ± SD. n=3-7, *P<0.05; ***P<0.001. (J), Presence of Empty-NPFA and RCM1-NPFA nanoparticles in the tumors are shown at days 9 and 15 after treatment. Nanoparticles were labeled with DyLight 800 and visualized using IVIS.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: FOXM1 inhibitor, combination therapy, rhabdomyosarcoma, nanoparticles, animal models
Citation: Donovan J, Deng Z, Bian F, Shukla S, Gomez-Arroyo J, Shi D, Kalinichenko VV and Kalin TV (2023) Corrigendum: Improving anti-tumor efficacy of low-dose Vincristine in rhabdomyosarcoma via the combination therapy with FOXM1 inhibitor RCM1. Front. Oncol. 13:1163510. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1163510
Received: 10 February 2023; Accepted: 30 March 2023;
Published: 13 April 2023.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Keqiang Zhang, City of Hope National Medical Center, United StatesCopyright © 2023 Donovan, Deng, Bian, Shukla, Gomez-Arroyo, Shi, Kalinichenko and Kalin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tanya V. Kalin, dGF0aWFuYS5rYWxpbkBjY2htYy5vcmc=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.