
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 12 August 2022
Sec. Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs
Volume 12 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.989283
This article is a correction to:
Cucurbitacin B, Purified and Characterized From the Rhizome of Corallocarpus epigaeus Exhibits Anti-Melanoma Potential
 Sreekumar Usha Devi Aiswarya1,2
Sreekumar Usha Devi Aiswarya1,2 Gowda Vikas3
Gowda Vikas3 Nair Hariprasad Haritha2
Nair Hariprasad Haritha2 Vijayasteltar Belsamma Liju2,4
Vijayasteltar Belsamma Liju2,4 Anwar Shabna2
Anwar Shabna2 Mundanattu Swetha2
Mundanattu Swetha2 Tennyson Prakash Rayginia2
Tennyson Prakash Rayginia2 Chenicheri Kizhakkeveettil Keerthana2
Chenicheri Kizhakkeveettil Keerthana2 Lekshmi Raghu Nath2,5
Lekshmi Raghu Nath2,5 Mullan Vellandy Reshma6,7
Mullan Vellandy Reshma6,7 Sankar Sundaram8
Sankar Sundaram8 Nikhil Ponnoor Anto4
Nikhil Ponnoor Anto4 Ravi Shankar Lankalapalli3,7*
Ravi Shankar Lankalapalli3,7* Ruby John Anto2*
Ruby John Anto2* Smitha Vadakkeveettil Bava1*
Smitha Vadakkeveettil Bava1*A Corrigendum on:
Cucurbitacin B, purified and characterized from the rhizome of Corallocarpus epigaeus exhibits anti-melanoma potential
By Aiswarya SUD, Vikas G, Haritha NH, Liju VB, Shabna A, Swetha M, Rayginia TP, Keerthana CK, Nath LR, Reshma MV, Sundaram S, Anto NP, Lankalapalli RS, Anto RJ and Bava SV (2022). 12:903832. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.903832
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2 as published. The blot quantification graph of Figure 2C was duplicated in place of the graph for Figure 2D. The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
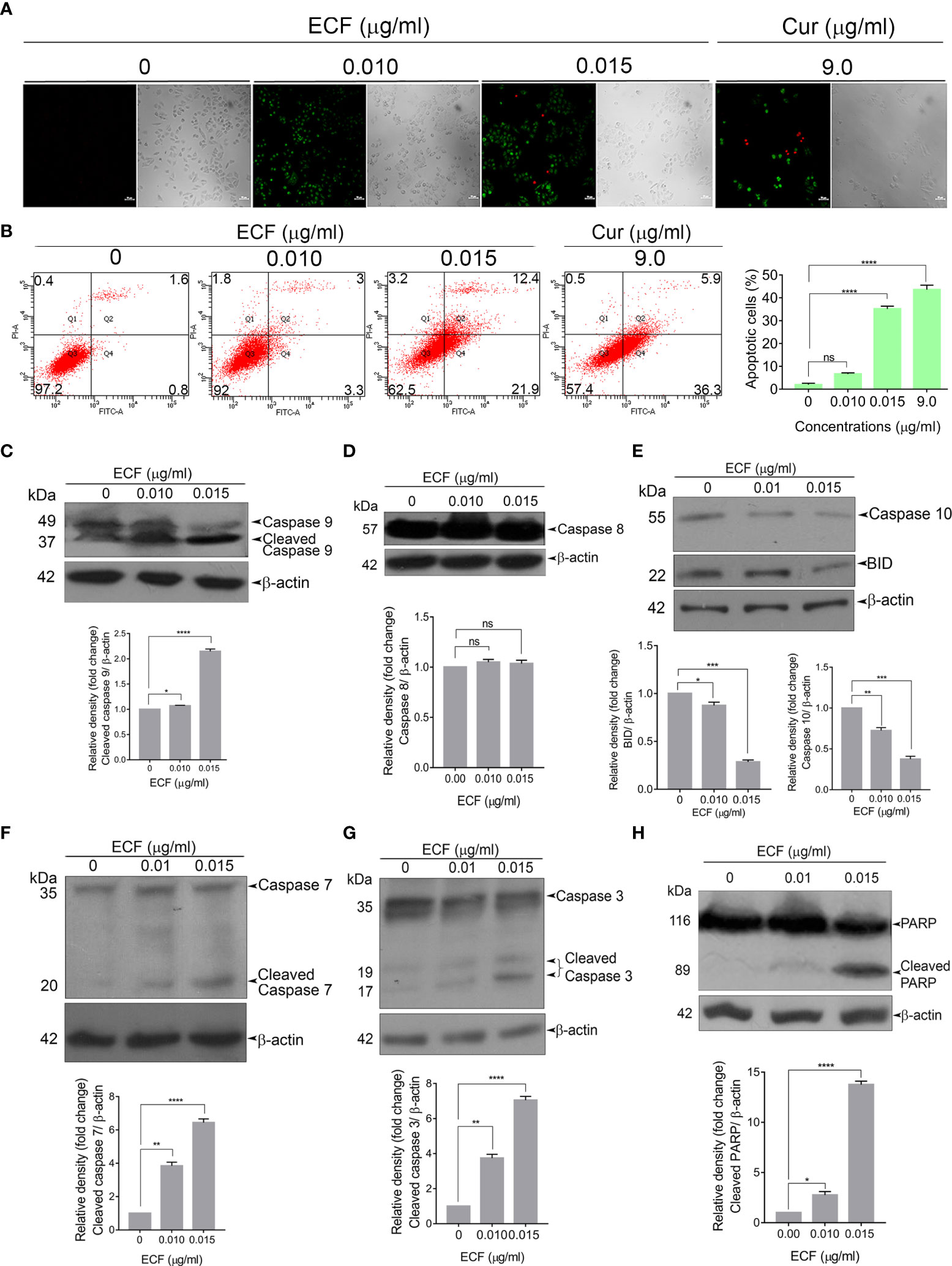
Figure 2 ECF triggers apoptotic mode of cell death in melanoma (A, B) ECF induces apoptosis in A375 cells as assessed by Annexin/PI staining, and was quantitated by FACS analysis. (C–H) ECF potentiates the activation of caspases and cleavage of PARP in A375 cells as analyzed by immunoblotting. Data are representative of three independent experiments (Mean ± SEM) and P-values are calculated using one-way ANOVA. ****P ≤ 0.0001, ***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.1and ns ≥ 0.05.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: corallocarpus epigaeus, cucurbitacin B, melanoma, apoptosis, NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry
Citation: Aiswarya SUD, Vikas G, Haritha NH, Liju VB, Shabna A, Swetha M, Rayginia TP, Keerthana CK, Nath LR, Reshma MV, Sundaram S, Anto NP, Lankalapalli RS, Anto RJ and Bava SV (2022) Corrigendum: Cucurbitacin B, purified and characterized from the rhizome of Corallocarpus epigaeus exhibits anti-melanoma potential. Front. Oncol. 12:989283. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.989283
Received: 08 July 2022; Accepted: 19 July 2022;
Published: 12 August 2022.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Balaji Krishnamachary, Johns Hopkins University, United StatesCopyright © 2022 Aiswarya, Vikas, Haritha, Liju, Shabna, Swetha, Rayginia, Keerthana, Nath, Reshma, Sundaram, Anto, Lankalapalli, Anto and Bava. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ravi Shankar Lankalapalli, cmF2aXNoYW5rYXJAbmlpc3QucmVzLmlu; Ruby John Anto, cmphbnRvQHJnY2IucmVzLmlu; Smitha Vadakkeveettil Bava, c21pdGhhbmlzaGFkQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.