
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 21 June 2022
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 12 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.927917
This article is a correction to:
Anti-Tumoral Effect and Action Mechanism of Exosomes Derived From Toxoplasma gondii-Infected Dendritic Cells in Mice Colorectal Cancer
 Shilan Zhu1,2
Shilan Zhu1,2 Jinmiao Lu1,2
Jinmiao Lu1,2 Zhibing Lin3*
Zhibing Lin3* Asmaa M. I. Abuzeid1,4
Asmaa M. I. Abuzeid1,4 Xiaoyu Chen1,2
Xiaoyu Chen1,2 Tingting Zhuang1
Tingting Zhuang1 Haiyan Gong2
Haiyan Gong2 Rongsheng Mi2
Rongsheng Mi2 Yan Huang2
Yan Huang2 Zhaoguo Chen2*
Zhaoguo Chen2* Guoqing Li1*
Guoqing Li1*A Corrigendum on:
Anti-Tumoral Effect and Action Mechanism of Exosomes Derived From Toxoplasma gondii-Infected Dendritic Cells in Mice Colorectal Cancer
By Zhu S, Lu J, Lin Z, Abuzeid AMI, Chen X, Zhuang T, Gong H, Mi R, Huang Y, Chen Z and Li G (2022). Front. Oncol. 12:870528. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.870528
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 2 as published. 1. Figure 2A (left) missed to indicate the corresponding groups for the panels. The corresponding groups are now correctly indicated. 2. Figure 2B: The representative flow cytometry plot was repeated two times (same flow cytometry image shown in the third column). The flow cytometry image are the results of flow cytometry detection of anti-CD86-PC7 in the Me49 group.We replaced the lower flow cytometry image in the third column with a representative flow-cytometry plot of anti-CD206-APC in the Me49 group. The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
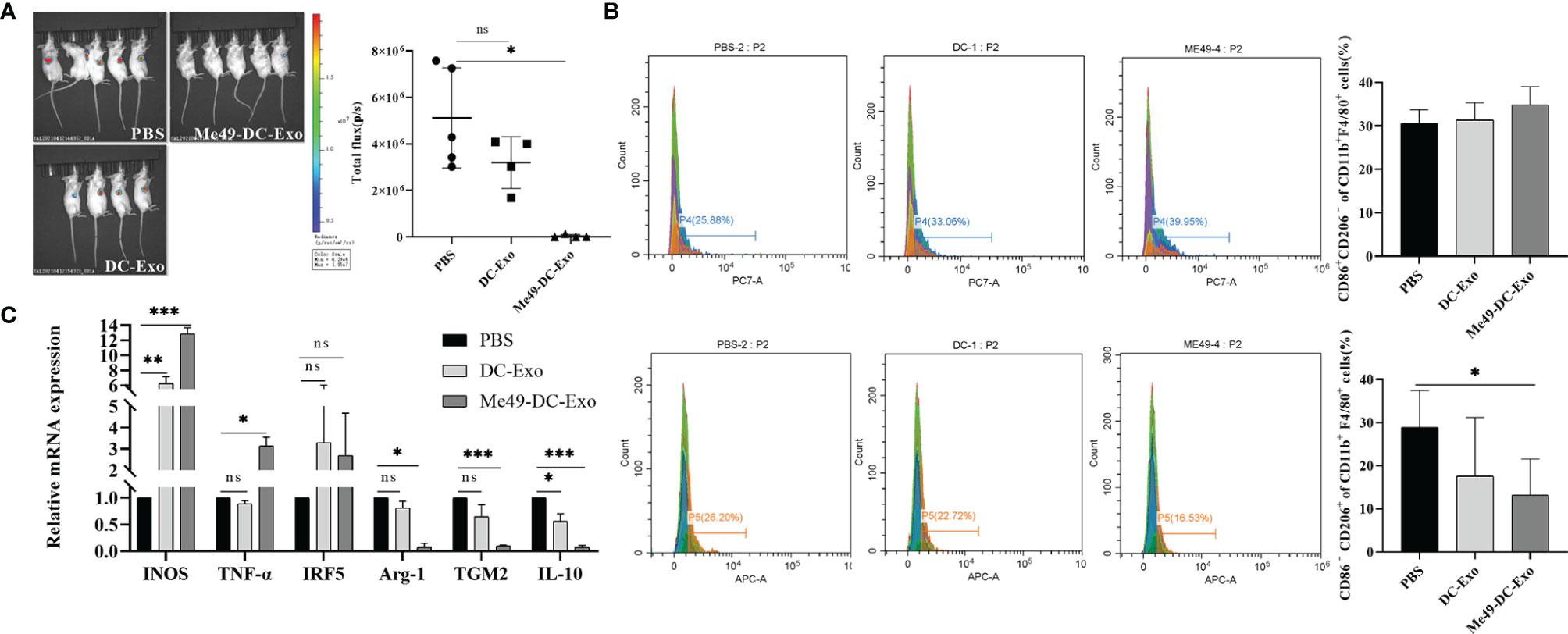
Figure 2 Me49-DC-Exo inhibited tumor growth in mouse and regulated macrophage polarization. (A) On day 4 after treatment, the IVIS imager detected bioluminescence images in tumors of mouse and quantified the bioluminescence signal intensity of each tumor in mouse. (B) Flow cytometry was used to label CD86 + or CD206 +, and CD45 + CD11b + F4/80 + macrophages in blood of mice injected with DC-Exo and Me49-DC-Exo were stained to detect the percentage of CD86+ CD206 − M1 macrophages and CD86 − CD206 + M2 macrophages. (C) mRNA levels of M1 macrophage specific genes (INOS, TNF-a, and IRF5) and M2 macrophage specific genes (TGM2, Arg-1 and IL10) in blood of tumor-bearing mice injected intratumorally with PBS, DC-Exo and Me49-DC-Exo were detected by qRT-PCR. The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and the independent sample t-test was used to compare the statistical differences between two groups. ns (p ≥ 0.05), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii, dendritic cells, exosome, miRNA, macrophage, miR-155-5p
Citation: Zhu S, Lu J, Lin Z, Abuzeid AMI, Chen X, Zhuang T, Gong H, Mi R, Huang Y, Chen Z and Li G (2022) Corrigendum: Anti-Tumoral Effect and Action Mechanism of Exosomes Derived From Toxoplasma gondii-Infected Dendritic Cells in Mice Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 12:927917. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927917
Received: 25 April 2022; Accepted: 31 May 2022;
Published: 21 June 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Anil Shanker, Meharry Medical College, United StatesCopyright © 2022 Zhu, Lu, Lin, Abuzeid, Chen, Zhuang, Gong, Mi, Huang, Chen and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guoqing Li, Z3FsaUBzY2F1LmVkdS5jbg==; Zhaoguo Chen, emhhb2d1b2NoZW5Ac2h2cmkuYWMuY24=; Zhibing Lin, bWR6aGliaW5nQDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.