
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol., 09 March 2022
Sec. Breast Cancer
Volume 12 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.880458
This article is part of the Research TopicDrug Resistance in Breast Cancer – Mechanisms and Approaches to Overcome ChemoresistanceView all 15 articles
This article is a correction to:
STAT5a Confers Doxorubicin Resistance to Breast Cancer by Regulating ABCB1
 Zhaoqing Li1,2,3†
Zhaoqing Li1,2,3† Cong Chen2,3†
Cong Chen2,3† Lini Chen2,3†
Lini Chen2,3† Dengdi Hu2,3,4
Dengdi Hu2,3,4 Xiqian Yang2,3,5
Xiqian Yang2,3,5 Wenying Zhuo2,3,4
Wenying Zhuo2,3,4 Yongxia Chen2,3
Yongxia Chen2,3 Jingjing Yang2,3
Jingjing Yang2,3 Yulu Zhou2,3
Yulu Zhou2,3 Misha Mao2,3
Misha Mao2,3 Xun Zhang2,3
Xun Zhang2,3 Ling Xu2,3
Ling Xu2,3 Siwei Ju2,3
Siwei Ju2,3 Jun Shen2,3
Jun Shen2,3 Qinchuan Wang2,3
Qinchuan Wang2,3 Minjun Dong2,3
Minjun Dong2,3 Shuduo Xie2,3
Shuduo Xie2,3 Qun Wei2,3
Qun Wei2,3 Yunlu Jia6
Yunlu Jia6 Jichun Zhou2,3*
Jichun Zhou2,3* Linbo Wang2,3*
Linbo Wang2,3*A Corrigendum on
STAT5a Confers Doxorubicin Resistance to Breast Cancer by Regulating ABCB1
By Li Z, Chen C, Chen L, Hu D, Yang X, Zhuo W, Chen Y, Yang J, Zhou Y, Mao M, Zhang X, Xu L, Ju S, Shen J, Wang Q, Dong M, Xie S, Wei Q, Jia Y, Zhou J and Wang L (2021). Front. Oncol. 11:697950. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.697950
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 1 as published. In Figure 1F, the number “42” should be “38”. The corrected Figure 1 appears below.
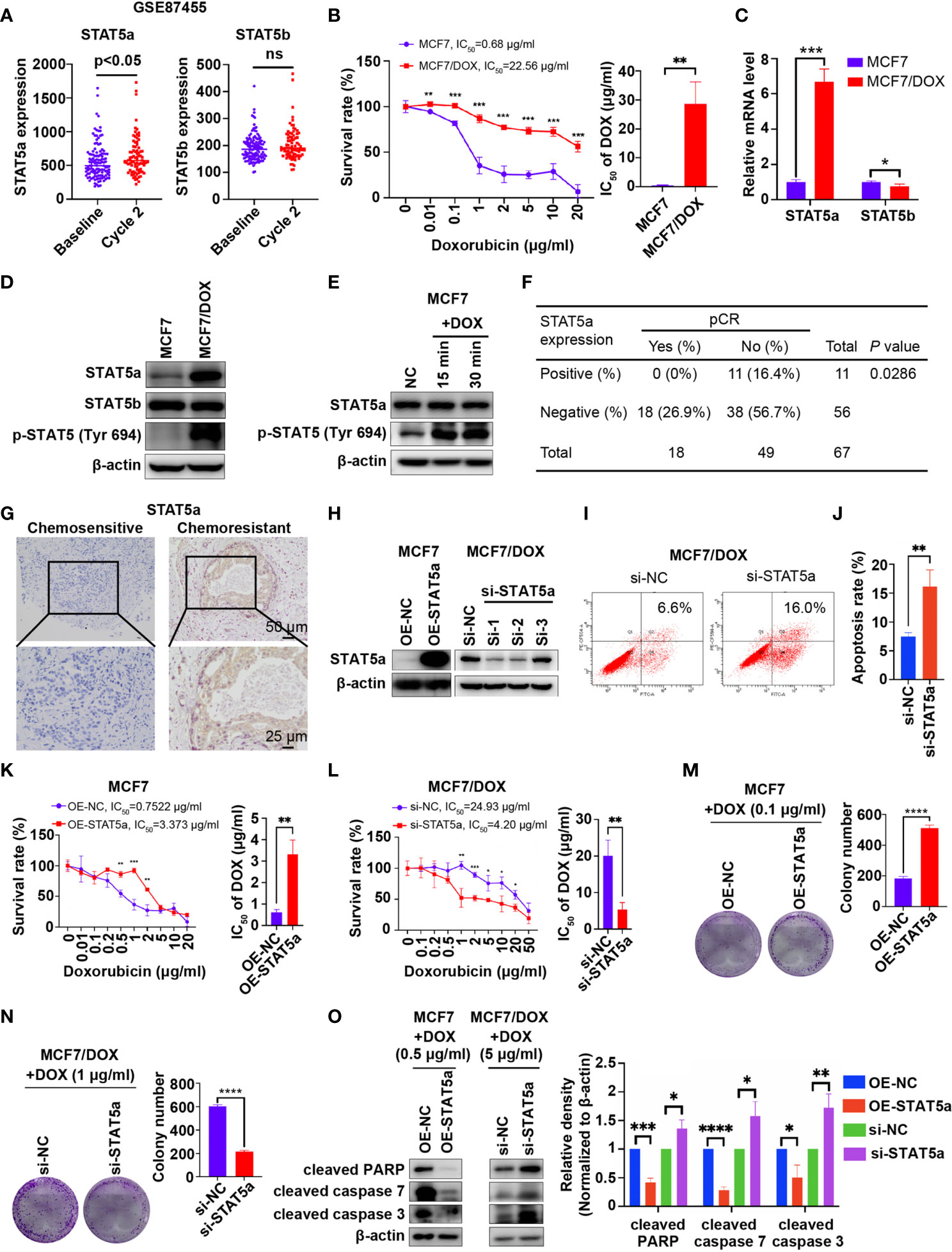
Figure 1 STAT5a is involved in chemoresistance in breast cancer. (A) Expression of STAT5a and STAT5b in breast cancer samples collected pre- and postchemotherapy in the dataset GSE87455. (B) Survival rates of MCF7 and MCF7/DOX cells after treatment with DOX for 48 h determined by a CCK8 assay. (C) mRNA levels of STAT5a and STAT5b in MCF7 and MCF7/DOX cells assessed via qPCR. (d) Protein levels of STAT5a, p-STAT5a (Tyr694) and STAT5b in MCF7 and MCF7/DOX cells determined by Western blotting. (E) Western blotting was performed to examine the expression of STAT5a and p-STAT5 (Tyr694) in CF7 cells upon treatment with DOX. (F) Correlation between the pCR rate and STAT5a expression in breast cancer samples obtained from 67 patients. (G) Representative images of IHC staining for STAT5a in chemoresistant and chemosensitive breast cancer samples. (H) Efficiency of vector transfection for overexpression of STAT5a in MCF7 cells and siRNA transfection for knockdown of STAT5a in MCF7/DOX cells determined by Western blotting. (I, J) Flow cytometry was performed to assess apoptosis in MCF7/DOX cells after knocking down STAT5a or control treatment (I). Bar graphs showing the percentage of apoptotic cells (J, K) Survival rate and IC50 of MCF7 cells transfected with an empty vector or a STAT5a vector after treatment with DOX for 48 h determined by a CCK8 assay. (L) Survival rate and IC50 of MCF7/DOX cells transfected with scramble siRNA or STAT5a-targeting siRNA after treatment with DOX for 48 h determined by a CCK8 assay. (M, N) Representative images and quantification of colonies formed by MCF7 cells transfected with the empty vector or STAT5a vector (M) and MCF7/DOX cells transfected with scramble siRNA or STAT5a-targeting siRNA (N) in medium containing the indicated concentration of DOX. (O) The expression levels of apoptosis markers in MCF7 cells transfected with the empty vector or STAT5a vector and MCF7/DOX cells transfected with scramble siRNA or STAT5a-targeting siRNA under treatment with the indicated concentration of DOX determined by Western blotting. ns, p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: breast cancer, STAT5A, ABCB1, pimozide, doxorubicin resistance
Citation: Li Z, Chen C, Chen L, Hu D, Yang X, Zhuo W, Chen Y, Yang J, Zhou Y, Mao M, Zhang X, Xu L, Ju S, Shen J, Wang Q, Dong M, Xie S, Wei Q, Jia Y, Zhou J and Wang L (2022) Corrigendum: STAT5a Confers Doxorubicin Resistance to Breast Cancer by Regulating ABCB1. Front. Oncol. 12:880458. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.880458
Received: 21 February 2022; Accepted: 23 February 2022;
Published: 09 March 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Dayanidhi Raman, University of Toledo, United StatesCopyright © 2022 Li, Chen, Chen, Hu, Yang, Zhuo, Chen, Yang, Zhou, Mao, Zhang, Xu, Ju, Shen, Wang, Dong, Xie, Wei, Jia, Zhou and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Linbo Wang, bGluYm93YW5nQHpqdS5lZHUuY24=; Jichun Zhou, amljaHVuLXpob3VAemp1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.