Chloroquine Inhibits Stemness of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Through Targeting CXCR4-STAT3 Pathway
- 1Biotherapy Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Cancer Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 3Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 4Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 5Henan Key Laboratory for Esophageal Cancer Research and State Key Laboratory for Esophageal Cancer Prevention & Treatment of The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 6School of Life Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 7Henan Key Laboratory for Tumor Immunology and Biotherapy, Zhengzhou, China
A Corrigendum on:
Chloroquine Inhibits Stemness of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Through Targeting CXCR4-STAT3 Pathway
By Yue D, Zhang D, Shi X, Liu S, Li A, Wang D, Qin G, Ping Y, Qiao Y, Chen X, Wang F, Chen R, Zhao S, Wang L and Zhang Y (2020). Front. Oncol. 10:311. doi: .10.3389/fonc.2020.00311
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figures 3C and 5B as published. In Figure 3C, the representative image of the purity of the two sorted CXCR4 positive/negative subpopulations was inadvertently presented with an incorrect picture. In Figure 5B, incorrect image of western result of t-stat3 and p-stat3 were imported by mistake. The corrected Figures 3 and 5 appears below.
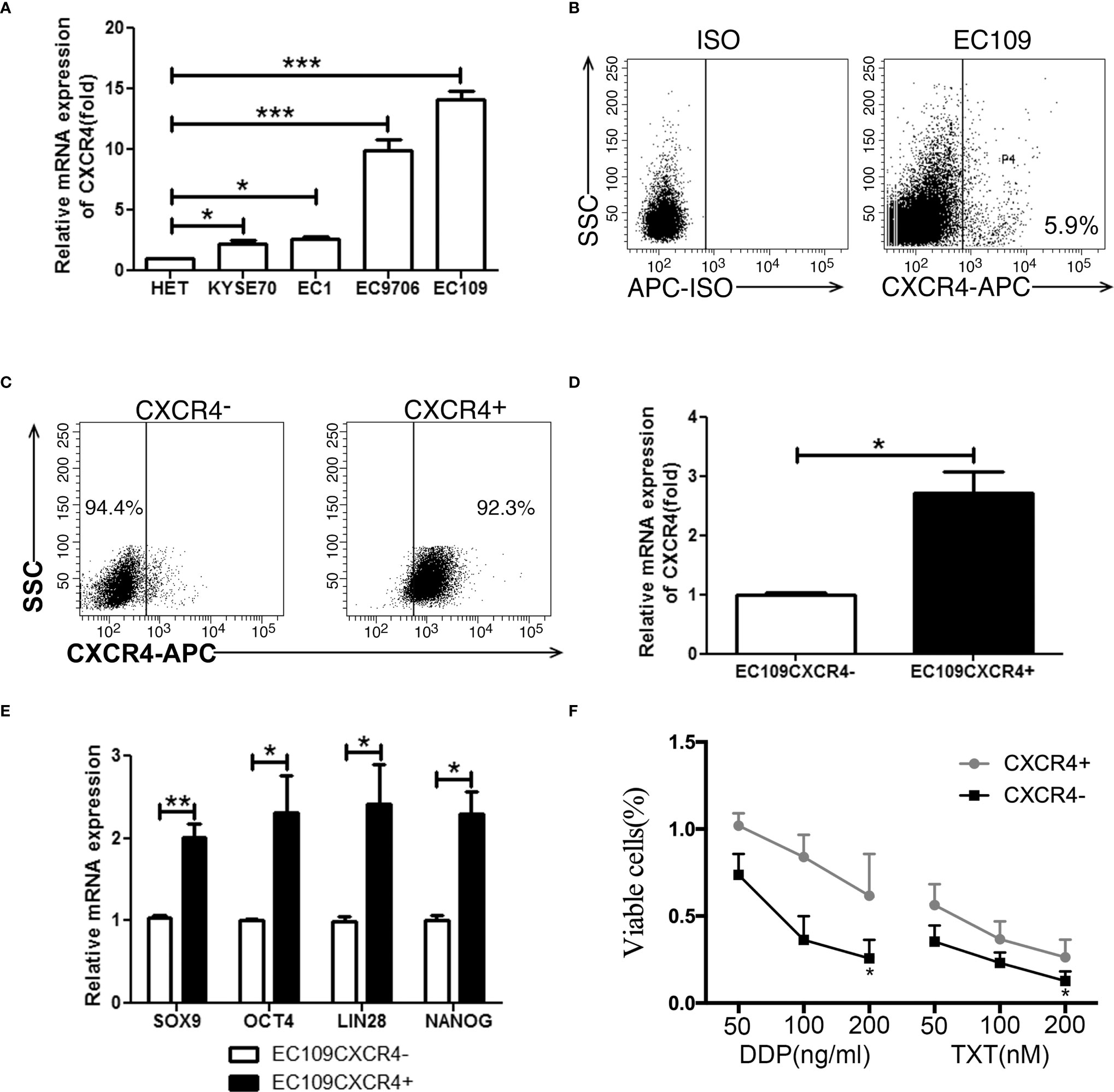
Figure 3 CXCR4 positive cells possessed stem-like properties. (A) The CXCR4 expression was detected by real time PCR in 1 immortalized esophageal cell line (Het-1a) and 4 ESCC cell lines. (B) The expression analysis of CXCR4 was detected by flow cytometry. (C) The purity of sorted EC109 cells with or without CXCR4 expression. (D) The expressio analysis of CXCR4 was detected by real time PCR. (E) The expression analysis of stemness-related transcription factors (SOX9, OCT4, LIN28, and NANOG) was detected by real time PCR. (F) Cell survival rate was tested by CCK-8 method. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
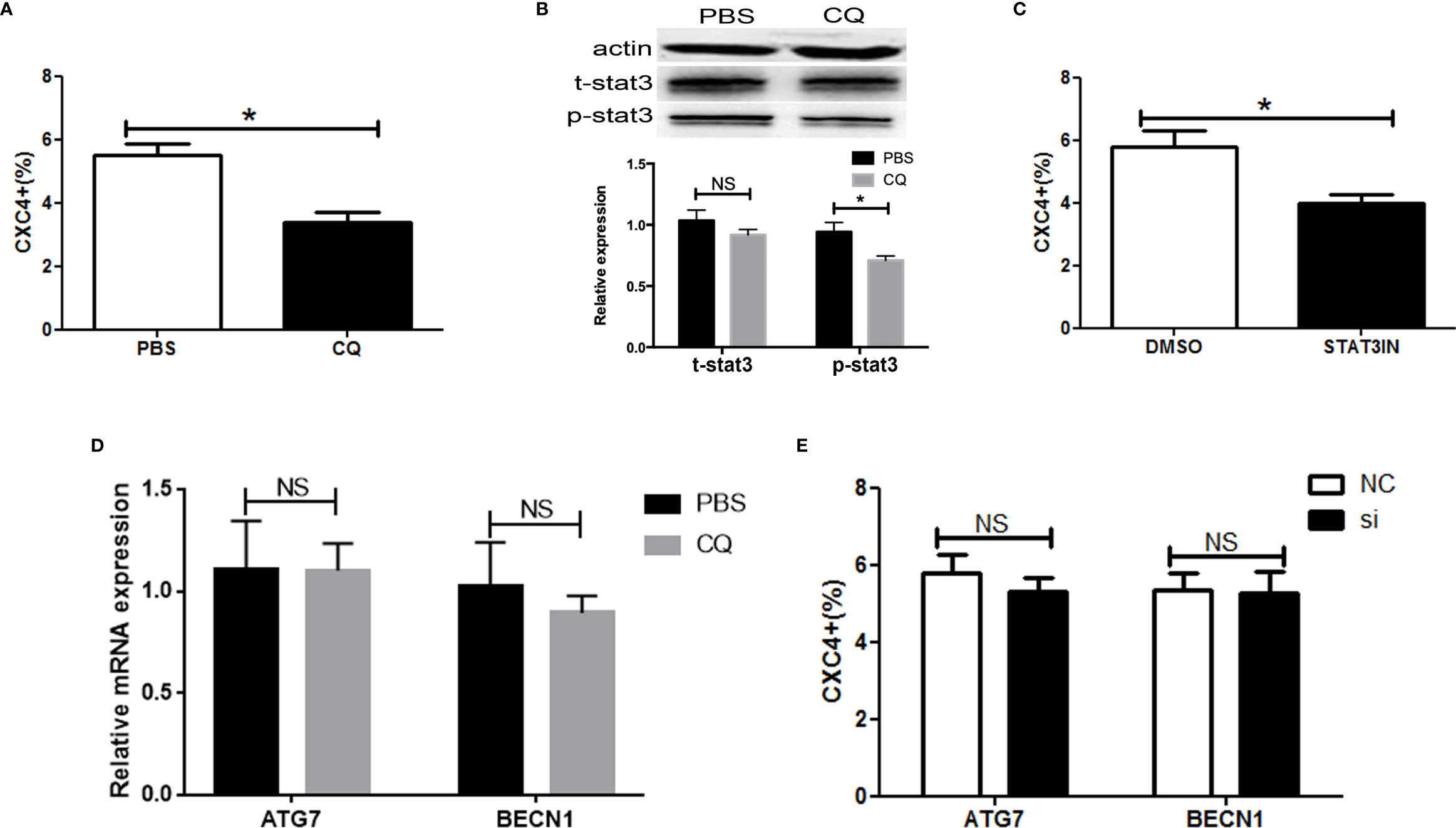
Figure 5 Chloroquine targeted CXCR4-positive ESCC cells via STAT3. (A) The expression of CXCR4 was analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) The activity of pSTAT3 and tSTAT3 were measured by western blotting in ESCC cells with or without CQ treatment (5µM). (C) The expression of CXCR4 was analyzed by flow cytometry in ESCC cells with or without STAT3 inhibitor (S3I-201, Sigma, USA) treatment. (D) The expression analysis of ATG7 and BECN1 was detected by real time PCR in ESCC cells with or without CQ treatment (5µM). (E) The expression of CXCR4 was analyzed by flow cytometry in ESCC cells after ATG7 or BECN1 knockdown. *P < 0.05.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), cancer stem cells (CSCs), CXCR4, chloroquine (CQ), STAT3
Citation: Yue D, Zhang D, Shi X, Liu S, Li A, Wang D, Qin G, Ping Y, Qiao Y, Chen X, Wang F, Chen R, Zhao S, Wang L and Zhang Y (2022) Corrigendum: Chloroquine Inhibits Stemness of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Through Targeting CXCR4-STAT3 Pathway. Front. Oncol. 12:860158. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.860158
Received: 24 January 2022; Accepted: 28 January 2022;
Published: 24 February 2022.
Copyright © 2022 Yue, Zhang, Shi, Liu, Li, Wang, Qin, Ping, Qiao, Chen, Wang, Chen, Zhao, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Zhang, eWl6aGFuZ0B6enUuZWR1LmNu
 Dongli Yue1,2
Dongli Yue1,2 Daiqun Zhang
Daiqun Zhang Shasha Liu
Shasha Liu Yu Ping
Yu Ping Xinfeng Chen
Xinfeng Chen Song Zhao
Song Zhao Lidong Wang
Lidong Wang Yi Zhang
Yi Zhang