
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Oncol., 25 May 2022
Sec. Gastrointestinal Cancers: Colorectal Cancer
Volume 12 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.812679
This article is part of the Research TopicEmerging Therapeutic Targets, Potential Diagnostic or Prognostic markers for Colorectal CancerView all 28 articles
It was highly controversial whether fermented dairy foods protect against colorectal cancer (CRC) because of conflicting results from current human epidemiologic studies; we therefore conducted this meta-analysis based on the case–control and cohort studies to estimate the holistic analyses. Finally, a total of seven case–control studies and ten cohort studies comprising a total of >20,000 cases were incorporated in the quantitative synthesis. Specifically, statistical evidence of significantly decreasing CRC risk in case–control studies was found to be associated with cheese intake (OR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.82–0.97). In a subgroup analysis, cheese intake was correlated with lower colon cancer (OR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.79–1.00) and rectal cancer (OR = 0.86, 95% CI = 0.74–1.00) risk in case–control studies. Furthermore, we also found that the higher intake of yogurt may lower the risk of rectal cancer (OR = 0.75, 95% CI = 0.65–0.88) in cohort studies. The consumption of fermented dairy foods may be relevant to decrease CRC risk in this meta-analysis.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42021269798, CRD42021269798.
In 2020, colorectal cancer (CRC) was the third most leading cause of cancer death in the Western world. Results of epidemiological studies show that a multitude of risk factors are relevant to colorectal cancer, including a lifestyle, diet, genetics, and obesity, and diet played a pivotal role for the disease (1). There was a general consensus in the diet with colorectal cancer—high red meat and processed meat consumption has been consistently associated with an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer; however, dietary fiber intake can protect from colorectal cancer (2). In addition, with the explosion of food processing in technologies, better seeking of new risk factors in diet associated with colorectal cancer is necessary to prevent the disease. Currently, a wide variety of milk and dairy products are consumed by over 6 billion people worldwide (3); against this background, greatly meeting the increasing demand for wide-ranging practical value in novel dairy products had attracted a great deal of attention in clinical practice. Fermented dairy foods were a traditional fresh dairy fermented by complex microorganisms, generating a significant amount of probiotics (4). The latter played an essential role in modulating the host gut microbiota for preventing carcinogenesis (5). Yogurt and cheese were exemplified in fermented dairy foods.
Increasing data had supported a role for the imbalances gut microbiota played on colorectal carcinogenesis (6). Multiple studies have lately shown that the gut microbiota dysbiosis can be remodeled through short-term effects of probiotic-enriched dietary intervention (7). Studies have also found recently that the consumption of fermented dairy foods was closely linked to colorectal cancer, yet the overwhelming majority of analyses were the consequences of negative or neutral results from the previous systematic review and meta-analysis (8–10). These apparent differences between theoretical and experimental results were intriguing but require validation. Since dietary interventions were the most practical and economical approach than other treatment modalities, further analysis was demanded.
In this study, yogurt and cheese were chosen typically represented on fermented dairy foods in order to ascertain the concrete links in colorectal cancer. We developed this comprehensive meta-analysis on published cohort and case–control studies according to the PROSPERO guidelines https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42021269798 to evaluate the impact of the fermented dairy foods intake on colorectal cancer (CRC).
Three databases (PubMed, Embase, Web of Science) were searched for all articles in English language since database inception in July 2021. We employed the following terms in the analysis: “fermented food or fermented milk or cultured milk or cheese or yogurt or lactic acid bacteria” and “Colorectal Neoplasm” or “Colorectal Cancer” or “Colonic Cancer” or “Rectum Cancers” and so on. The study design was not restricted during the retrieval of process in order to gain a comprehensive search of literature.
If a study meets the following criteria, the results could be incorporated for inclusion in the meta-analysis: (1) a topic of the association about yogurt or cheese consumption and CRC, colon, or rectal cancer risk; (2) the outcome relied on dietary information from questionnaires; (3) odds ratio (OR), hazard ratio (HR), and relative risk (RR) with 95% CIs can be acquired through reading full-text articles; (4) original articles were published in English; and (5) the study of design was a cohort or case–control study. In addition, we may exclude some articles that meet our exclusion criteria. (1) Duplicate articles in different databases; (2) cell or animal experiments; (3) meta-analysis studies; (4) reviews, letters, and commentaries; and (5) articles lacking specific data.
First of all, duplicate literature from the databases was removed from this study. Then, two authors (ZL and JW) independently screened the titles and abstracts to exclude some works of data that did not meet our eligibility. In parallel, based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the outcome of specific information can be acquired through reading the full texts, such as first author of the works, year of publication, sex, country of recruitment, follow-up period, dairy type, and the number of cases or controls.
The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) was performed for some cohort or case–control studies. Two reviewers (ZL and JW) determined the quality of the included studies independently. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) of the maximum score was 9, and a high score (≥6) indicated high quality in this study. If there were any discrepancies, disagreements were addressed through discussion.
We calculated the consumption of yogurt or cheese in the highest compared with the lowest categories to computer odds ratios or (case–control studies) rr and hr (cohort studies) corresponding to the 95% confidence interval (95% CI). The study of heterogeneity was assessed with the Cochran’s Q statistic and I2 statistics. If I2 ≥ 50% from the statistics analysis, the fixed-effects model was performed for calculation; otherwise, the random-effects model was employed. In order to explore the sources of heterogeneity, we also performed a sensitivity analysis by logistic meta-regression analyses. In addition, we examined prespecified stratified analyses for different study characteristics: region, dairy type, sex, and tumor location (colorectal cancer, colon cancer, proximal or distal colon cancer, and rectal cancer). The funnel plot and Begg’s rank correlation method were employed to assess publication bias.
The statistical analyses were performed by STATA 16.0 software (Stata Corp, College Station, TX).
The flow diagram of the steps was presented as a flowchart in Figure 1. Of the 17 reports remaining after 2005 abstracts were screened, the studies were included in the meta-analysis: 10 prospective cohort studies (11–20) and 7 case–control studies (21–27).
The main characteristics of the studies are depicted in Table 1 and Table 2. Simultaneously, 6,968 cases and 8,536 controls were included in the case–control studies (Table 1). A total of 1,310,276 participants with 14,944 cases were recorded in this cohort studies (Table 2). The case–control studies were conducted in five countries (Netherland, Moroccan, France, the United States, Canada). In addition, for the cohort studies, many countries were incorporated in this analysis, including 2 from the United States, 3 from Sweden, 1 from Italy, 1 from Japan, and 2 from each of the 10 different European countries. Two types of studies were conducted in adults.
Yogurt The outcome of the high consumption compared with low consumption on yogurt is shown in Table 3 and Figure 2. In case–control studies, we included seven quantitative studies to assess the joint association of yogurt consumption with colorectal cancer which was not statistically significant in the outcome (OR = 0.91, 95% CI = 0.79–1.04), as is shown in Table 3, in terms of subgroup analysis by region, sex, and tumor location. The results from subgroups of region and sex had no statistical difference; however, there were two different outcomes on tumor location, rectal cancer (OR = 0.75, 95% CI = 0.65–0.88) and colon cancer (OR = 0.96. 95% CI = 0.77,1.19). In cohort studies, we enrolled 10 quantitative studies to analyze the incidence and mortality between consumption of yogurt and colorectal cancer. In addition, we also formed subgroups regarding region and tumor location, as shown in Table 3. Overall, yogurt intake levels were not statistically significant in mortality (HR = 1.09, 95% CI = 0.89,1.35) and incidence (RR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.77,1.03).

Figure 2 Yogurt: forest plot of case–control studies (A–G) and cohort studies (H–K) in yogurt examining the association between consumption of yogurt and risk of colorectal cancer as well as the consumption of yogurt in the mortality of colorectal cancer (L). CRC, colorectal cancer; CC, colon cancer; DC, distal colon cancer; R, rectal cancer; M, man; W, woman; NL, subjects in Newfoundland and Labrador; ON, subjects in Ontario. Case–control studies: (A) total CRC; (B) CRC in man; (C) CRC in woman; (D) US; (E) Canada; (F) colon cancer; (G) rectal cancer; Cohort studies: (H) total CRC; (I) Sweden; (J) colon cancer; (K) rectal cancer; (L) mortality of CRC.
Cheese The outcome of the high consumption compared with low consumption on yogurt is shown in Table 4 and Figure 3. In case–control studies, seven quantitative studies were included to analyze the joint association of cheese consumption with colorectal cancer. The result of the consumption of total cheese with colorectal cancer was a statistical difference (OR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.82,0.97). In addition, there was a statistically significant difference in tumor location with cheese of consumption between colon cancer (OR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.79,1.00) and rectal cancer (OR = 0.86, 95% CI = 0.74,1.00). However, systematic analyses of different countries based on extant data were not statistically significantly different. In cohort studies, interestingly, no statistically significant differences in outcome were found; only one country (Sweden) was a statistically significantly different in consumption of yogurt (RR = 0.72, 95% CI = 0.56,0.94).
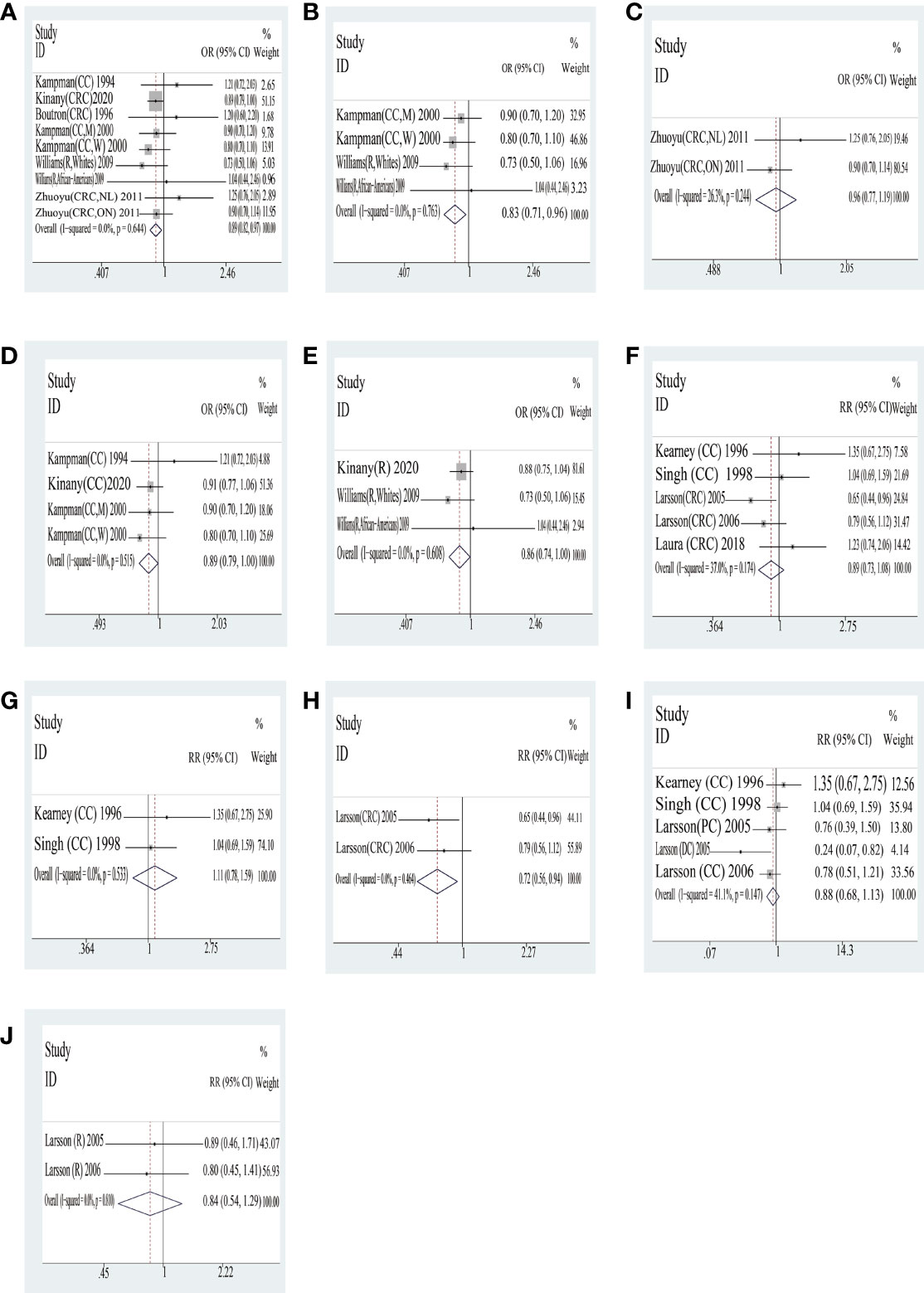
Figure 3 Cheese: forest plot of case–control studies (A–E) and cohort studies (F–J) in yogurt examining the association between consumption of yogurt and risk of colorectal cancer. CRC, colorectal cancer; CC, colon cancer; DC, distal colon cancer; R, rectal cancer; M, man; W, woman; NL, subjects in Newfoundland and Labrador; ON, subjects in Ontario. Case–control studies: (A) total CRC; (B) US; (C) Canada; (D) colon cancer; (E) rectal cancer. Cohort studies: (F) total CRC; (G) US; (H) Sweden; (I) colon cancer; (J) rectal cancer.
We will consider heterogeneity among studies in overall comparisons and choose the random-effects model (P heterogeneity< 0.001 and I2 > 50%.). In order to comprehensively analyze the outcome, we formed subgroups on sex, countries, and tumor location.
In order to understand the meta-stability of the associations observed, we omit one study at a time from the outcome in cohort and case–control studies. If the observation did not appreciably change, we confirmed the reliability of the data analysis.
The publication bias of selecting literature was evaluated by Begg’s test. Figure 4 exhibits two funnel plots of yogurt and cheese of case–control included in the meta-analysis. There was no apparent publication bias in yogurt (P = 1.000) and cheese (P = 0.251).
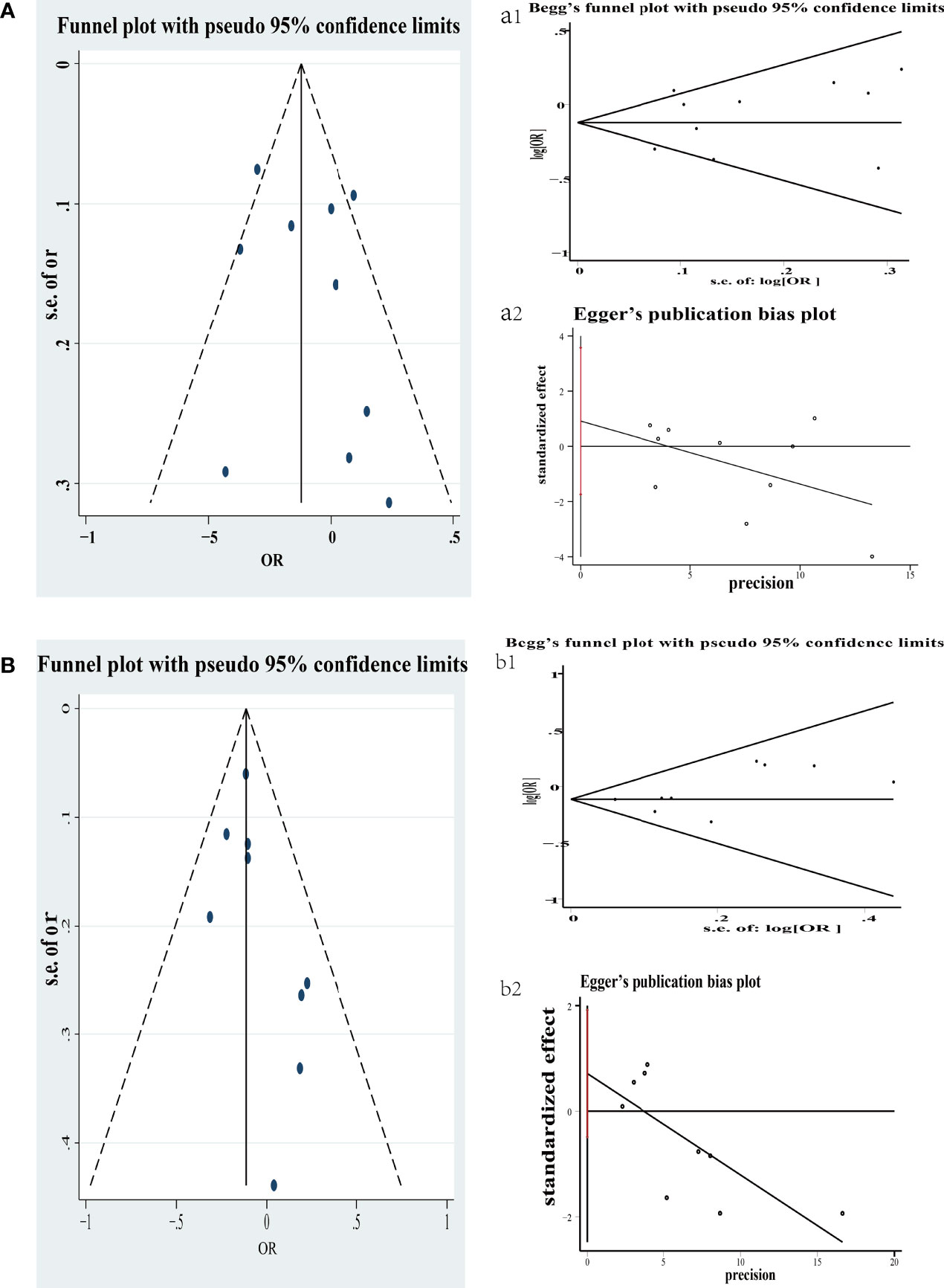
Figure 4 Funnel plot of colorectal cancer risk associated with consumption of yogurt in case–control (A); Begg’s and Egger’s funnel plot for publication bias test on consumption of yogurt in case–control (a1 and a2). Each point represents a separate study for the indicated association. s.e., standardized effect. Funnel plot of colorectal cancer risk associated with consumption of cheese in case–control (B); Begg’s and Egger’s funnel plot for publication bias test on consumption of cheese in case–control (b1 and b2). Each point represents a separate study for the indicated association. s.e., standardized effect.
Here, we developed this meta-analysis on 17 cohorts and case–control studies with more than 1,310,276 participants and 14,944 cases. By comparing the high consumption with low consumption in two distinct study designs, we attempted to identify the link of fermented food such as yogurt and cheese in association with colorectal cancer. We discovered new associations, some of which have not previously been published. In general, whereas our results from this meta-analysis are consistent with the observation that the consumption of yogurt and cheese remained unclear connection for previous studies, we discovered some novel links in different study designs and subgroups.
For example, we observed that different primary tumor sites were associated with yogurt consumption. Results of the case–control study found yogurt intake to be associated with a decreased risk of rectal cancer, but not colon cancer. The reason for this disparity in the outcome was unclear. Furthermore, we found that there is an inverse association between dietary intake of cheese in case–control and the risk of colorectal cancer. There are several reasons that could account for these outcomes. Compared to other fermentation products such as yogurt, having greater viable probiotics in cheese is advantageous. The reason for these differences was interpreted with unique characteristics in higher pH and buffering capacity and lower oxygen and salt levels. In these settings, the long-term survival of probiotics was observed in the center of the cheese. Theoretically, it may also play a protective role in storage and passage through the gastrointestinal tracts (28). From the field of microbial ecology perspective, it is suggested that the administration of sufficient amounts of diet rich in probiotics may be associated with a lower incidence of colorectal cancer (29). There was a marked regional difference in consumption of cheese such as Sweden from Europe which was distinct from other countries. Simultaneously, consumption of cheese in a cohort study is negatively associated with the risk of colorectal cancer. Swedish people are well known to have healthy and fixed dietary habits, particularly breakfast, at which they prefer to consume them as daily dietary activities, so they gain more probiotics from cheese compared to other countries. This resulted in a lower incidence of CRC in Swedish people.
Epidemiologic studies have shown that fermented dairy foods such as yogurt and cheese, the main sources of probiotics in human diets, have proved to be one source of calcium in Western populations (30). Therefore, there are several possible reasons that could explain the consumption of fermented dairy foods associated with CRC. A recent meta-analysis showed that dietary patterns rich in calcium in dairy foods may decrease the incidence of colorectal adenomas, which was precancerous lesions of colorectal cancer (31). The underlying mechanism could arrest excessive proliferation and mutation in the gut epithelium by binding to toxic bile acids and long-chain fatty acids (32). Some studies argued that high physiological concentrations of bile acids in the colorectal epithelium may initiate carcinogenesis (Figure 5) (33). Moreover, probiotics in fermented dairy foods may also play a pivotal role in colorectal cancer. There have been some animal models of evidence which have suggested that probiotics can competitively adhere to intestinal mucus to prevent colonization of pathogens (34). Probiotics may regulate the imbalance of intestinal microflora to suppress tumorigenesis via multiple mechanisms (Figure 5) (35–40). Hence, consumption of calcium in fermented dairy foods may decrease the incidence of CRC and lower the risk of developing colorectal tumors.
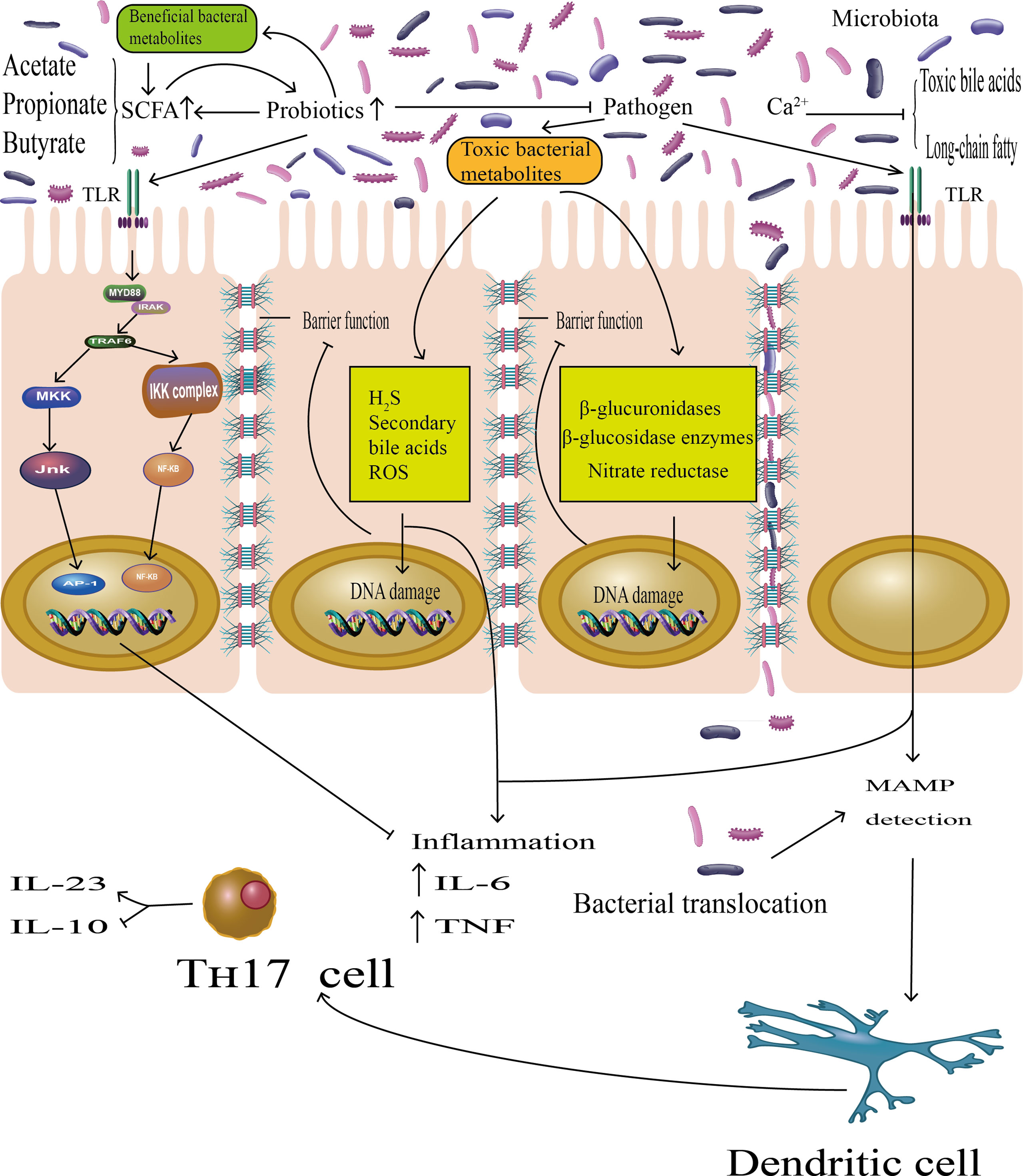
Figure 5 The probiotics play essential roles in host metabolism, immune modulation, and colonization resistance to pathogens, suppressing the CRC progression. On the one hand, there were studies demonstrating that probiotics can prevent the attachment of pathogenic bacteria to gut epithelia. On the other hand, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), mainly acetate, butyrate, and propionate, are major metabolic products of probiotics, promoting probiotics growth and reproduction, protecting the intestinal barrier function. Probiotics may represses toxic bacterial metabolites by indirectly inhibiting the growth of pathogens. Toxic bacterial metabolites can induce DNA damage in epithelial cells; indirectly impaired barrier function was among the constellation of accepted pathologies in CRC and generated local or chronic inflammation by producing inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF). In addition, pathogenic bacteria may also exert pro-inflammatory effects via microorganism-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) by Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which lead to detection by dendritic cells (DC) as well as activation of Th-17 cells, and the latter will promote the expression of the pro-inflammatory mediator IL-23 and block the expression of the anti-inflammatory mediator IL-10. However, probiotics also bound the Toll-like receptor (TLR), which activated the TLR–NF-kB signal transduction pathway to inhibit the inflammatory effects.
In this meta-analysis, there were some inadequacies, although we enrolled a great deal of high-quality studies. No apparent publication bias has not been perceived, yet its impact may remain. Besides this, there was a marked heterogeneity throughout this analysis. The reason could be attributed to the difference in food products, regular and prolonged dietary habits, and the sample size of this study. Finally, the smaller sample sizes of the relevant analysis allows us not to fully account for mortality in colorectal cancer. We hope more experimental and theoretical evidence will be able to verify the outcome.
In conclusion, our meta-analysis suggests that fermented dairy food intake may have an impact on the incidence of colorectal cancer. Besides, the economic approach applied to convey health benefits by way of modifying the gut microbiota has been used to ferment dairy foods, which could markedly prevent colorectal cancer in the near future. It may thus be an effective strategy to integrate fermented dairy foods into eating habits for the early prevention of colorectal cancer. In parallel, we wished to see what role this meta-analysis could play in the dietary management of future outbreaks in colorectal neoplasms.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
LL , JW, and XS conceived and designed the study. ZL and JH selected the studies and collected the data. RW, PL, and ZD analyzed data. All authors interpreted the results. ZL and JW drafted the paper. All authors revised the draft paper. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Hyuna S, Jacques F, Rebecca LS, Mathieu L, Isabelle S, Ahmedin J, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Mingyang S, Kana W, Meyerhardt JA, Shuji O, Molin W, Fuchs CS, et al. Fiber Intake and Survival After Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis. JAMA Oncol (2018) 4:71–9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3684
3. Cécile V, Laurie J-C, Manon L, Emmanuel C, Lemlih O, Jocelyne D, et al. Milk Polar Lipids Reduce Lipid Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Overweight Postmenopausal Women: Towards a Gut Sphingomyelin-Cholesterol Interplay. Gut (2020) 69:487–501. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-318155.4
4. Aryana KJ, Olson DW. A 100-Year Review: Yogurt and Other Cultured Dairy Products. J Dairy Sci (2017) 100:9987–10013. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-12981
5. Winnie F, Qing L, Jun Y. Gut Microbiota Modulation: A Novel Strategy for Prevention and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Oncogene (2020) 39:4925-43. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1341-1
6. Cao Y, Wu K, Mehta R, Drew DA, Song M, Lochhead P, et al. Long-Term Use of Antibiotics and Risk of Colorectal Adenoma. Gut (2018) 67:672–8. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313413
7. Zhenjiang X, Rob K. Dietary Effects on Human Gut Microbiome Diversity. Br J Nutr (2015) 113 Suppl:1–5. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514004127
8. Laura B, Nancy B, Nerea B-T, Núria R-E, Jordi S-S. Association Between Dairy Product Consumption and Colorectal Cancer Risk in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiologic Studies. Adv Nutr (2019) 10:190–211. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa071
9. Ralston RA, Truby H, Palermo C, Walker KZ. Colorectal Cancer and Nonfermented Milk, Solid Cheese, and Fermented Milk Consumption: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr (2014) 54:1167–79. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2011.629353
10. Mazidi M, Mikhailidis DP, Sattar N, Howard G, Graham I, Banach M. Consumption of Dairy Product and its Association With Total and Cause Specific Mortality - A Population-Based Cohort Study and Meta-Analysis. Clin Nutr (Edinburgh Scotland) (2019) 38:2833–45. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.12.015
11. Kearney J, Giovannucci E, Rimm EB, Ascherio A, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, et al. Calcium, Vitamin D, and Dairy Foods and the Occurrence of Colon Cancer in Men. Am J Epidemiol (1996) 143:907–17. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a008834
12. Singh PN, Gary FE. Dietary Risk Factors for Colon Cancer in a Low-Risk Population. Am J Epidemiol (1998) 148:761–74. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009697
13. Terry P, Baron JA, Bergkvist L, Holmberg L, Wolk A. Dietary Calcium and Vitamin D Intake and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Prospective Cohort Study in Women. Nutr Cancer (2002) 43:39–46. doi: 10.1207/S15327914NC431_4
14. Larcsson SC, Bergkvist L, Wolk A. High-Fat Dairy Food and Conjugated Linoleic Acid Intakes in Relation to Colorectal Cancer Incidence in the Swedish Mammography Cohort. Am J Clin Nutr (2005) 82:894–900. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/82.4.894
15. Larcsson SC, Leif B, Jörgen R, Edward G, Alicja W. Calcium and Dairy Food Intakes are Inversely Associated With Colorectal Cancer Risk in the Cohort of Swedish Men. Narnia (2006) 83:667–73. doi: 10.1093/ajcn.83.3.667
16. Valeria P, Sabina S, Franco B, Paolo V, Carlotta S, Domenico P, et al. Yogurt Consumption and Risk of Colorectal Cancer in the Italian European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer and Nutrition Cohort. Int J Cancer (2011) 129:2712–9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26193
17. Neil M, Teresa N, Pietro F, Mazda J, Bas B, Guri S, et al. Consumption of Dairy Products and Colorectal Cancer in the European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). PloS One (2013) 8:e72715–5. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072715
18. Laura B, Nancy B, Guillermo M-S, Estefania T, Ramírez-Sabio JB, Ramón E, et al. Dairy Product Consumption and Risk of Colorectal Cancer in an Older Mediterranean Population at High Cardiovascular Risk. Int J Cancer (2018) 143:1356–66. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31540
19. Matsumoto M, Ishikawa S, Nakamura Y, Kayaba K, Kajii E. Consumption of Dairy Products and Cancer Risks. Japan Epidemiol Assoc (2007) 17:38–44. doi: 10.2188/jea.17.38
20. Dik VK, Murphy N, Siersema PD, Fedirko V, Jenab M, Kong SY, et al. Prediagnostic Intake of Dairy Products and Dietary Calcium and Colorectal Cancer Survival–Results From the EPIC Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev (2014) 23:1813–23. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965
21. Kampman E, van ‘t Veer P, Hiddink GJ, van Aken-Schneijder P, Kok FJ, Hermus RJ. Fermented Dairy Products, Dietary Calcium and Colon Cancer: A Case-Control Study in The Netherlands. Int J Cancer (1994) 59:170–6. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910590205
22. Kinany KE, Deoula MMS, Hatime Z, Boudouaya HA, Huybrechts I, Asri AE, et al. Consumption of Modern and Traditional Moroccan Dairy Products and Colorectal Cancer Risk: A Large Case Control Study. Eur J Nutr (2020) 59:953–63. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-01954-1
23. Shannon J, White E, Shattuck AL, Potter JD. Relationship of Food Groups and Water Intake to Colon Cancer Risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev (1996) 5:495–502. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4878(97)00007-0
24. Boutron MC, Faivre J, Marteau P, Couillault C, Senesse P, Quipourt V. Calcium, Phosphorus, Vitamin D, Dairy Products and Colorectal Carcinogenesis: A French Case–Control Study. Br J Cancer (1996) 74:145–51. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.330
25. Kampman E, Slattery ML, Caan B, Potter JD. Calcium, Vitamin D, Sunshine Exposure, Dairy Products and Colon Cancer Risk (United States). Cancer Causes Control (2000) 11:459–66. doi: 10.1023/a:1008914108739
26. Williams DC, Satia JA, Adair LS, Steven J, Galanko J, Keku TO, et al. Dietary Patterns, Food Groups, and Rectal Cancer Risk in Whites and African-Americans. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev Publ Am Assoc Cancer Res Cosponsored by Am Soc Prev Oncol (2009) 18:1552–61. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-1146
27. Zhuoyu S, Peizhong PW, Barbara R, Michelle C, Roger G, Sharon B, et al. Calcium and Vitamin D and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: Results From a Large Population-Based Case-Control Study in Newfoundland and Labrador and Ontario. Can J Public Health (2011) 102:382–9. doi: 10.1007/BF03404181
28. Plessas S, Bosnea L, Alexopoulos A, Bezirtzoglou E. Potential Effects of Probiotics in Cheese and Yogurt Production: A Review. Eng Life Sci (2012) 12:433–40. doi: 10.1002/elsc.201100122
29. Konishi H, Fujiya M, Tanaka H, Ueno N, Moriichi K, Sasajima J, et al. Probiotic-Derived Ferrichrome Inhibits Colon Cancer Progression via JNK-Mediated Apoptosis. Nat Commun (2016) 7:91–6. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12365
30. Qibiao W, LaiHan LE. Association of Dietary Fiber and Yogurt Consumption With Lung Cancer Risk. JAMA Oncol (2020) 6:91–6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0261
31. Hassan EM, Mansoor S, Ammar HK, Marjan M, Samaneh M, Fatemeh M. Calcium and Dairy Products in the Chemoprevention of Colorectal Adenomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr (2021), 21–5. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1911927
32. Lamprecht SA, Lipkin M. Cellular Mechanisms of Calcium and Vitamin D in the Inhibition of Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Ann New York Acad Sci (2001) 952:73–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb02729.x
33. Zhou X, Cao L, Jiang C, Xie Y, Cheng X, Krausz KW, et al. Pparα-UGT Axis Activation Represses Intestinal FXR-FGF15 Feedback Signalling and Exacerbates Experimental Colitis. Nat Commun (2014) 5:4573. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5573
34. Young HI, Elvin K, Adison W, March JC, Bentley WE, Seng LY, et al. Engineered Probiotic Escherichia Coli can Eliminate and Prevent Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Gut Infection in Animal Models. Nat Commun (2017) 8:15028. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15028
35. González S, Fernández-Navarro T, Arboleya S, de los Reyes-Gavilán CG, Salazar N, Gueimonde M. Fermented Dairy Foods: Impact on Intestinal Microbiota and Health-Linked Biomarkers. Front Microbiol (2019) 10:1046. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01046
36. Louis P, Hold GL, Flint HJ. The Gut Microbiota, Bacterial Metabolites and Colorectal Cancer. Nat Rev Microbiol (2014) 12:661–72. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3344
37. Tianyu L, Xueli S, Samiullah K, Yun L, Zixuan G, Chuqiao L, et al. The Gut Microbiota at the Intersection of Bile Acids and Intestinal Carcinogenesis: An Old Story, Yet Mesmerizing. Int J Cancer (2020) 146:1780–90. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32563
38. Quigley EMM. Prebiotics and Probiotics in Digestive Health. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol (2019) 17:333–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.09.028
39. Gori S, Inno A, Belluomini L, Bocus P, Bisoffi Z, Russo A, et al. Gut Microbiota and Cancer: How Gut Microbiota Modulates Activity, Efficacy and Toxicity of Antitumoral Therapy. Crit Rev Oncol / Hematol (2019) 143:139–47. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.09.003
Keywords: fermented dairy foods, yogurt, cheese, probiotics, colorectal cancer, meta-analysis
Citation: Liang Z, Song X, Hu J, Wu R, Li P, Dong Z, Liang L and Wang J (2022) Fermented Dairy Food Intake and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 12:812679. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.812679
Received: 10 November 2021; Accepted: 14 April 2022;
Published: 25 May 2022.
Edited by:
Zhanlong Shen, Peking University People’s Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Sudabeh Alatab, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, IranCopyright © 2022 Liang, Song, Hu, Wu, Li, Dong, Liang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jijun Wang, d2FuZ2ppanVuMjAyMkAxMjYuY29t; Lu Liang, MTI5MTIwMTM2NEBxcS5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.