- 1Laboratory of Cell Signal Transduction, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Henan University, Kaifeng, China
- 2School of Life Sciences, Henan University, Kaifeng, China
- 3Department of Basic Sciences Research, Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital and Research Centre (SKMCH&RC), Lahore, Pakistan
The discovery of circular RNAs and exploration of their biological functions are increasingly attracting attention in cell bio-sciences. Owing to their unique characteristics of being highly conserved, having a relatively longer half-life, and involvement in RNA maturation, transportation, epigenetic regulation, and transcription of genes, it has been accepted that circRNAs play critical roles in the variety of cellular processes. One of the critical importance of these circRNAs is the presence of small open reading frames that enable them to encode peptides/proteins. In particular, these encoded peptides/proteins mediate essential cellular activities such as proliferation, invasion, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and apoptosis and develop an association with the development and progression of cancers by modulating diverse signaling pathways. In addition, these peptides have potential roles as biomarkers for the prognosis of cancer and are being used as drug targets against tumorigenesis. In the present review, we thoroughly discussed the biogenesis of circRNAs and their functional mechanisms along with a special emphasis on the reported chimeric peptides/proteins encoded by circRNAs. Additionally, this review provides a perspective regarding the opportunities and challenges to the potential use of circRNAs in cancer diagnosis and therapeutic targets in clinics.
Introduction
Sequencing of the human genome has indicated that less than 2% of the human genome codes proteins while most of those remaining form the non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) (1). Therefore, by definition, ncRNAs are transcribed from the genomic DNA but lack the ability to encode proteins (2). Currently, the exact number of ncRNAs within the human genome remains uncertain, however, numerous studies have acknowledged their functional importance in regulating many vital cellular events, including the transcription of their host genes, chromatin modifications, messenger RNA (mRNA) splicing, RNA stability, DNA methylation, and translation (3–8). Classification of ncRNAs into the functional categories is still under different challenges; however, the published literature classifies the ncRNAs into two types: (A) regulatory ncRNAs, which are further subdivided into long ncRNAs (lncRNAs) (>200-nt) and small ncRNAs (<200-nt) consisting of piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), micro RNAs (miRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) and (B) housekeeper ncRNAs comprising transfer RNAs (tRNAs), ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), and small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) (4, 9–11) (Figure 1).
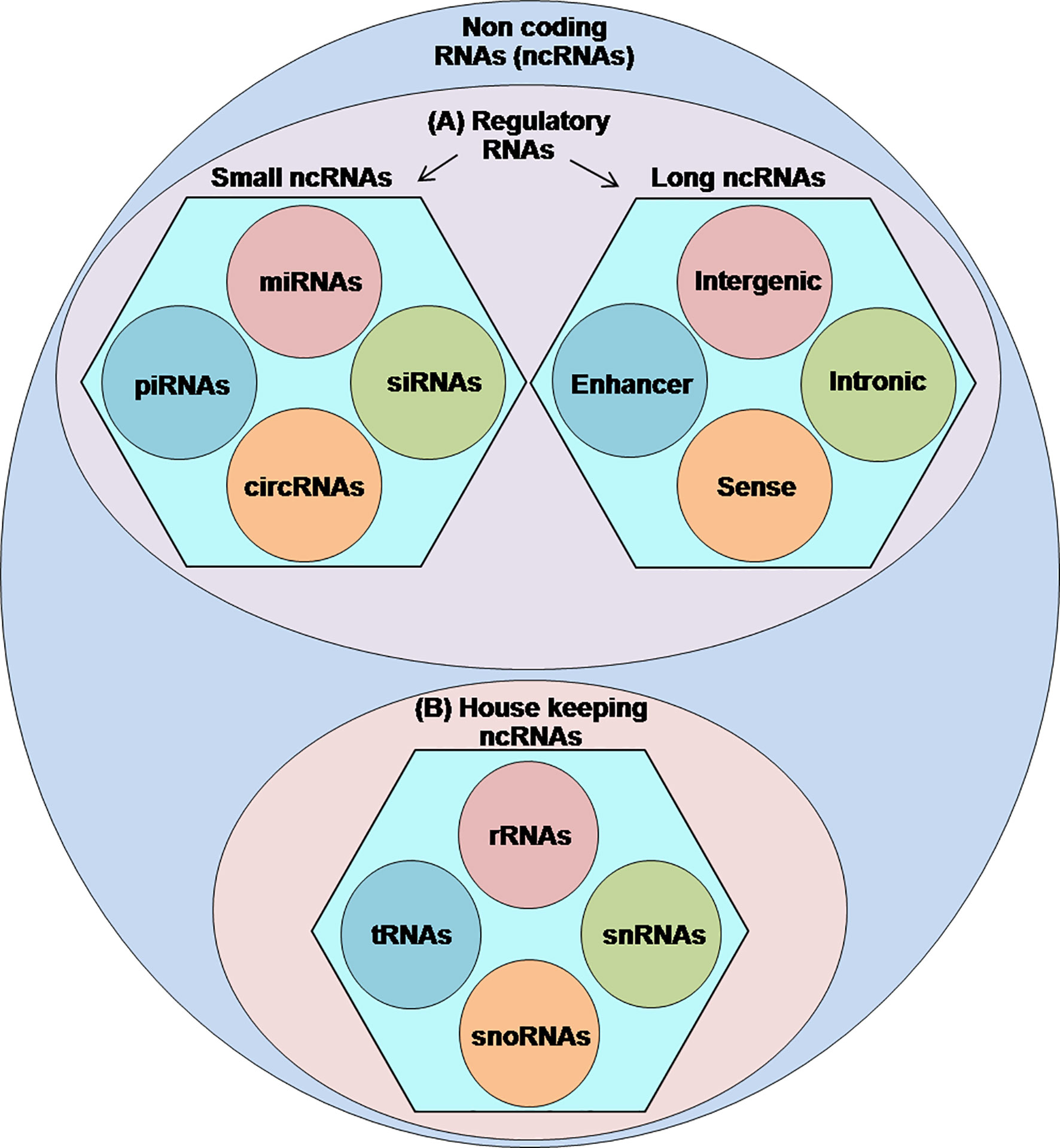
Figure 1 Classification of ncRNAs: a figurative discreption of ncRNAs into (A) regulatory ncRNAs and (B) housekeeping ncRNAs.
Endogenously expressed in the eukaryotic cells, circRNAs are mainly localized in the cytoplasm and characterized as a relatively stable, enriched in exosomes compared to linear RNAs, and highly conserved (4, 12–14). Anatomically, these circRNAs lack the 5ʹ and 3ʹ termini which confer them resistance to exonucleolytic degradation by RNase R (12). Based on their unique properties and functional involvement, literature categorizes the circRNAs into four subtypes: exonic circRNAs (ecircRNAs), which are made of exon(s) (>90% of all circRNAs); circular intronic RNAs (ciRNAs) composed of introns; exonic–intronic circRNAs (EIciRNAs) which contain both intron(s) and exon(s); and intergenic circRNAs composed of fragments of two intronic circRNAs or intergenic sequences (4, 15–17).
Since their discovery back in the 70s, circRNAs and their functional outcomes in the form of encoded peptides/proteins have attracted broad attention. Presently, circRNAs and their encoded peptides/proteins are among the hot topics to be explored for various cellular functions, where they determine the specific functions by regulating the expressions of the host and other genes. Taking part in the fundamental cellular process like gene expression, cell proliferation, and migration of cancer cells, the functional outcomes of these circRNAs in the form of encoded peptides/proteins are considered as a double-edge sword in cancer, where they determine prognosis in different cancers.
Here in this review, we sought to outline the recent advances in the therapeutic study of circRNAs and their peptides/proteins toward cancer therapy and diagnosis. Additionally, this review summarizes the current state of knowledge and future prospective about the use of circRNAs and their peptides/proteins in cancer clinics. We expect that this review could promote the blooming growth of research on circRNAs and their use in the cancer clinic in the near future.
Biogenesis of circRNAs
Although, there are very limited and incomplete data about the genesis of circRNAs, recent findings have shown that back splicing, intronic complementary sequences (ICSs), and RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are primary processes in the biogenesis of circRNAs and the hotspots of modern-day research in this domain (12, 18, 19) (Figure 2).
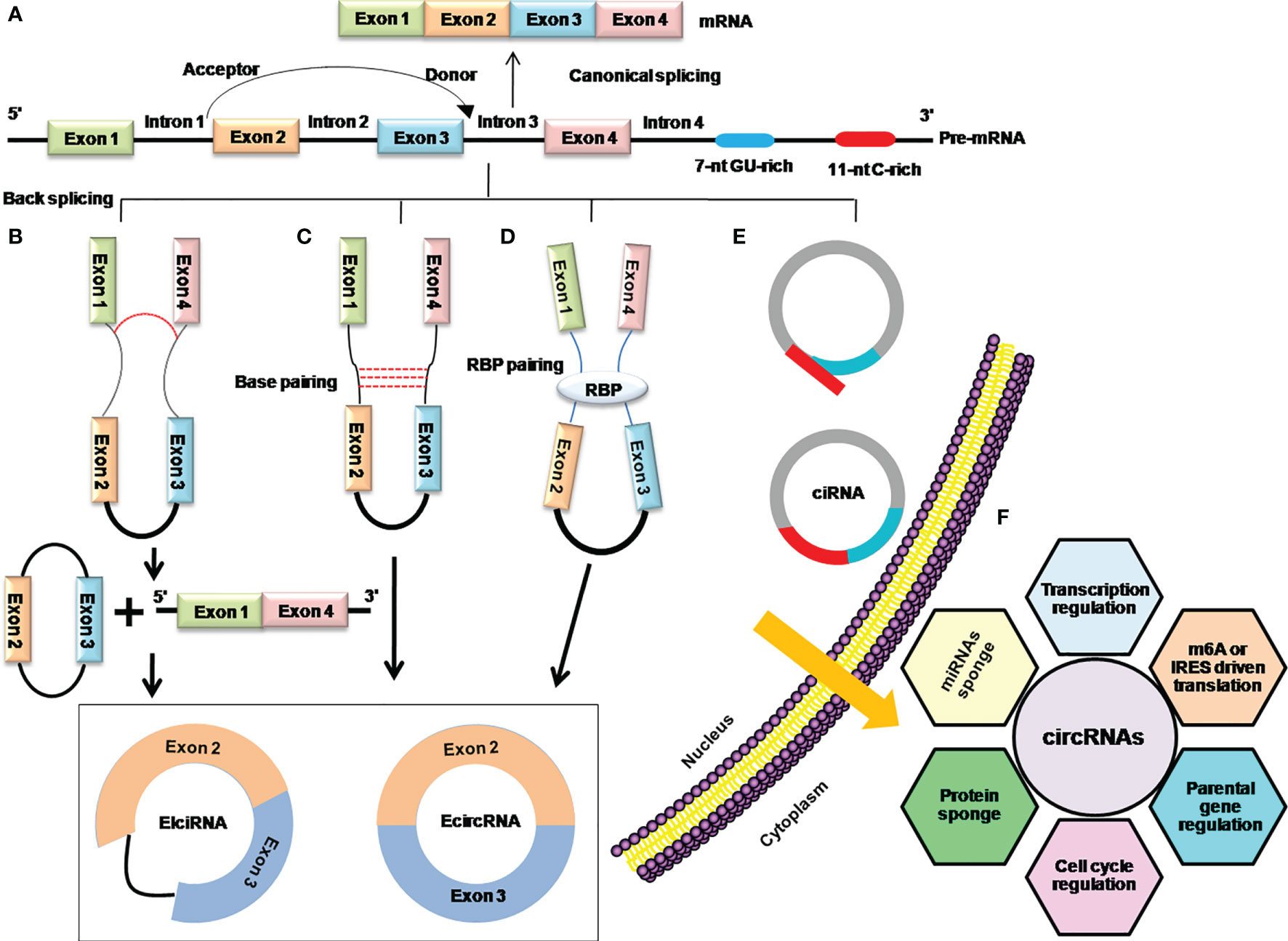
Figure 2 Mechanistic depiction of four circRNA biogenesis models. (A) Canonical splicing for the formation of linear mRNA. (B) Lariat-driven circularization model of internal splicing, either the removing of introns or retaining in the lariat. (C) Intron base-pairing-driven circularization through a base-pairing mechanism in which removing or retaining the introns generates ecircRNA, or EIciRNA especially. (D) RBP-driven circularization model in which RBPs shorten the distance between donor and acceptor sites and facilitate removing or retaining the introns to generate ecircRNA or EIciRNA. (E) The biosynthesis of stable ciRNA by debranching and exonucleolytic degradation. (F) Functions of circRNAs.
Early days’ research on circRNAs found that the phenomena of lariat-driven circularization and intron base-pairing-driven circularization are responsible for the synthesis of circRNAs by catalyzing back splicing and joining the splicing donor and acceptor sites to form the ecircRNAs or EIciRNAs (12, 20). Later on, it was further explored that apart from the back-splicing way, ecircRNAs or EIciRNAs are generated by interactions of RBPs with introns flanking regions that connect the upstream and downstream introns (5). Moreover, the consensus motifs containing GU-rich and C-rich elements in the intronic region can produce the ciRNAs (16) (Figures 2B–E). The Quaking (QKI), Muscle blind (MBL/MBLN1), and adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADRA1) are among the key regulators of circRNA biogenesis. QKI has been shown to regulate the formation of circRNAs during human EMT by utilizing the QKI-binding domain located in the introns (5), while Muscle blind (MBL/MBLN1) is involved in the circularization of circRNAs in humans via its multiple MBL-binding domains in the flanking introns (19). Furthermore, it demonstrates that depletion of the double-strand RNA-editing enzyme–ADRA1 protein, is involved in converting adenosine to inosine on inverted ALU motif, and contributes to the promotion of circRNA production (21, 22).
Regulatory Roles of circRNAs
As mentioned above, with advancement in high-throughput RNA sequence techniques, and other genomic approaches, circRNAs are being explored for various cellular functions characterized by both tissue-specific and developmental stage-specific manners (23, 24). However, most functions of circRNAs reported are in a developmental stage-specific manner, where they have expression associations with parental genes, thus playing a role in protein coding gene functions.
Regulatory Roles of circRNAs in Host Gene Expression
Literature mining reveals that circRNAs regulate their host gene expression by epigenetic modulation, transcription, RNA splicing, and translation (8). The association of these circRNAs with parental gene expression has been explored well via silencing or depletion of specific circRNAs.
For example, the depletion of ciRNAs ci-mcm5 and ci-sirt7 significantly decreases the host gene expression and alters the cell physiology (25). Similarly, it has been found that depletion of ci-ankrd52 also reduces its parent mRNA expressions by accumulating in the transcription initiation site and by partially co-localizing with the polymerase-II (Pol II) enzyme (25). It has been revealed that the depletion of EIciRNAs circEIF3J and circPAIP2, located in the nucleus, resulted in a significant decrease in expressions of EIF3J and PAIP2 genes, respectively (17). According to Chen and colleagues, ecircRNA: circFECR have associations with the regulation of their parental gene FLI1 expression, where they interact with its promoter and incorporate TET1 demethylase to trigger the demethylation in the CpG islands (7). In the same way, circFECR1 also downregulates DNMT1, an enzyme that is responsible for sustaining DNA demethylation during DNA replication, thereby regulating TET1 and DNMT1, and their subsequent effects are observed in breast cancer (BC) progression (26). It has been found that, in a condition when circRNA and its parental gene have the same exons, the formation of circRNA will compete with the splicing of pre-mRNA, resulting in low linear mRNA levels (26).
Regulatory Roles of circRNAs in a Developmental Stage-Specific Manner
Increasing evidence are available on the functions of specific circRNAs in the development stages. Up till now, the vast number of identified circRNA expressions has been well explored in developmental stage-specific manner (27).
Recent findings reveal that circ-mbl, the highly abundant transcriptional product of the Drosophila muscle blind (mbl) gene, plays a regulatory role in the developmental process by competing with the linear mRNA production to regulate the expression of the mbl transcript (19). circ-sry circRNA consists of a single exon formed from the Sry gene and is mainly localized in the cytoplasm. It is abundantly expressed in adult testis and is generally implicated in sex determination (28). Another study has shown that ciRS-7 circRNA derived from the Cdr1 gene is highly expressed in the mammalian brain and associated with neuronal development (21). In zebrafish, miR-7 expression has an association with its normal development of the midbrain. It has been evaluated that when ciRS-7 is abnormally expressed in zebrafish, defects in the midbrain development are observed and vice versa in the revised case (4). Besides the association with those development-related genes, hsa_circ_2149 has been reported to be distinctively expressed in CD19+ but not in the CD34+ leukocytes, indicating that it may be involved in the CD19+ activities during normal development (4). However, there is a dearth of data on its exact function.
Regulatory Roles of circRNAs as miRNA Sponges
Along with their developmental stage-specific manner, circRNAs also function as a miRNA sponges. In human, miRNAs directly bind to the target sites primarily within the untranslated region (UTR) of mRNA and might play a vital role in post-transcriptional regulations of gene expression (29). Recently, it has been shown that the regulatory function of miRNAs is affected by the miRNA sponge sites presented in the competent endogenous RNA (ceRNAs) in human (30). The circRNAs are known as natural miRNA sponges due to the presence of multiple miRNA response elements (MRE) on their sequence, which regulates the expression of relevant genes (27).
CDR1as is a circRNA, with >70 conserved binding sites for mir-7 that suppresses its target gene activity. CDR1as is involved in altering miR-7 target gene expression and affects their functions in target cell lines (31). In another study, it has been observed that circTADA2A binds to miR-203a-3p, where it determines the expression of the SOCS3 gene and leads to the attenuation of cell migration, invasion, and clonogenicity in triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) (8). Testis-specific circSry contains 16 mir-138 target sites. It has been found that it modulates the mir-138 target gene expression and leads to abnormality in cell functioning (32). Furthermore, circRNA produced from ZNF91 contains >20 sites for miR-23 and miR-296, sequestering these miRNAs’ roles (32). Several other circRNAs that have been found to serve as miRNA sponges including circHRCR (heart-related circRNA) for miR-223 (33), hsa_circ_001569 for miR-148a (34), circITCH (itchy E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase) for miR-214, miR-17, and miR-7 (35), circ-foxo3 (forkhead box protein O3) for miR-29a-3p (36), circHIPK3 (homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3) for miR-558 (37), circMTO1 (mitochondrial tRNA translation optimization 1) for miR-9 (38), cirZNF609 (zinc finger protein 609) for miR-145 (39), and circBIRC6 (baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 6) for miR-34a and miR-145 (40). Additionally, it was found that the binding to miRNAs may not always lead to inhibition of target genes and the spongy properties of some circRNAs are limited (27).
Regulatory Role of circRNAs as RBP Sponges
In addition to serving as miRNA sponges, circRNAs also contain binding sites for RBPs and therefore act as protein sponges or decoys (8, 41). RBPs bind to the particular RNA sequences in their target genes and control all cycles of mRNA including splicing, stability, nuclear exportation, and subcellular localization (42). The current research exploration is mainly directed to investigate their potential role in regulating other oncogenes and tumor onset. A study reports that circ-Ccnb1 suppresses mutant p53 by binding to H2AX and interacts with Ccnb1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) proteins, resulting in the inhibition of tumor progression (43). The upregulation of circACC1 has also been associated with the activation of the AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) pathway in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues (44). Recently, Chen et al. have shown that ci-AGO2 binds to and interacts with human antigen R (HuR) protein, thereby repressing the functions of the AGO2–miRNA complex and promoting tumorigenesis and aggressiveness (45). Similarly, circPABPN1 can also bind to the HuR protein and inhibit the binding of HuR to PABPN1 mRNA. However, researchers are exploring furthermore about the intrinsic role of circRNAs in these critical molecular processes, expression, and regulation of genes involved in the cell cycle.
Mechanisms of circRNA Translation Into Peptides/Proteins
Considering the vitality of 5′ and 3′ UTR for the translation initiation in eukaryotic cells, in conventional opinions, lacking of 5′ and 3′ UTRs led researchers to consider circRNAs as ncRNAs for a long period of time. However, later on, studies have accumulated mounting evidence for circRNAs’ protein-coding potential. Sequence analysis demonstrates that there are some circRNAs which comprise the initiation codon AUG and stop codons followed by putative open reading frames (ORFs) with commendable length, which provides the circRNAs potential of translation (46–50).
There are explanations of circRNA translations via canonical cap-dependent translation in which a 7-methylguanosine cap is added to the 5′ end of mRNA for translation initiation. This initiation is mediated and guided by the unique set of eIF4E translation initiation factors, a protein complex including eIF4E, eIF4G, and eIF4A components (51–53). Another possible way of circRNA translations is cap-independent translation. It is a naturally occurring alternative mechanism employed in eukaryotes under certain conditions, such as cellular stress, viral infection, physiological stimulation in cell differentiation, and synapse network formation. In this mode of translation, a special sequence located in the 5′ UTR of mRNAs, such as an internal ribosome entry site (IRES), induces translation initiation (54, 55).
More recently, it has been found that majority of circRNAs originate from protein-coding genes containing IRES-like elements and N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications that initiate translation, suggesting that circRNAs can be translated into peptide/proteins (56). It has been categorized by two potential models which determine the regulation of circRNA translation initiation. In the first mechanism for circRNA translation initiation, coding circRNAs containing natural IRES-like elements can be directly recognized by a non-canonical eIF4G protein (eIF4G2 or DAP-5) and regulate the circRNA translation initiation (57). eIF4G2 contains the eIF4A- and eIF3-binding sites but lacks the eIF4E-binding region. Thus, in IRES-initiated translation, IRES can assemble the eIF4 complex in the absence of eIF4E, directly initiating translation (58–62). These findings were further endorsed by a study by Chen and Sarnow in which they found that engineered circRNAs in artificial constructs containing IRES-like elements could recruit the 40s ribosomal subunit, initiate translation, and produce a long repeating polypeptide chain with continuous ORFs in an in-vitro experiment (63). Another study has further confirmed that functional proteins can be translated from circRNAs by inserting the IRES-like elements into a minigene containing split green fluorescent proteins (GFP) (64). Similarly, Perriman and Ares show that artificial circular mRNA in Escherichia coli can be translated into long protein chains containing ORF for GFP, implying that bacterial ribosome can repeatedly induce the expression of GFP from circular mRNA (65) and yield a 795-nt-long circular mRNA containing ORF of 30-kDa peptide, representing that the bacterial ribosomes scanned the circular mRNA more than ten times. In summary, the studies above demonstrate that circRNAs can function as messenger RNA and be translated into proteins via IRES-like regions that are independent of 5ʹ cap and 3ʹ poly (A) tail.
The other important cap-independent translation mechanism is through methylated adenosine residues in the form of m6A in the 5′ UTR (66, 67). m6A is the common modification of mRNA, regulates many cellular events, such as tissue development, DNA damage response, and sex determination, and is also involved in tumorigenesis (68–70). Numerous translatable endogenous circRNAs enriched with consensus m6A motifs can promote efficient initiation of translation. Mechanistically, the m6A reading protein YTHDF3 (YTH domain family protein 3) recognizes m6A and recruits eIF4G2 to m6A, where eIF4G2 recognizes the IRES and initiates the assembly of the eIF4 complex, leading to the initiation of translation. Furthermore, m6A-initiated translation is cell-type independent and a single m6A site is sufficient to bypass the m7G cap recruitment and initiate the cap-independent model of translation (64, 71).
To date, some endogenous circRNAs have been linked with polysomes, implying that a considerable number of these molecules are able to be translated into peptides/proteins (64, 72, 73). Both IRESs and m6A-mediated translation initiation are considered as the most prevalent and essential components of circRNA translation initiation. Alternatively, rolling circle amplification (RCA) has been anticipated as another putative mechanism of circRNA translation (46, 74). Abe et al. have reported that circRNAs can efficiently be translated into peptides/proteins by a RCA mechanism with an infinite ORF either in a cell-free rabbit reticulocyte lysate system or in living human cells (46), suggesting that apart from IRESs and m6A, there are other elements that can initiate cap-independent translation within the circularized transcripts (46, 75). Although the above-listed mechanisms for circRNA translation provide enough explanation, researchers are still looking for further exploration to connect more dots.
In literature, numerous methods have been listed for the identification of functional peptides/proteins encoded by circRNAs including the prediction of ORFs, IRES-like elements, m6A modification, conservation analysis, translation omics, proteomics, and experimental analysis (76).
Considering the rapid developments in the protein-coding circRNA field, the foremost aims of this review is to expand our current understanding of the protein-coding ability of circRNAs and the function of the peptides/proteins especially in cancer.
Peptides/Proteins Encoded by circRNAs
According to their effects and functions, circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins can be divided into four types: non-cancerous regulatory, promoting and inhibiting their full-length proteins, and signal transducer mediators. As per the study outlines, those peptides generated by circRNAs and having regulatory functions in other physiological processes except cancer are designated as non-cancerous regulatory peptides/proteins (61). The roles of circRNA-encoding peptides/proteins are up to the characteristic of overlapping amino acid sequence with their cognate linearly spliced protein isoforms, so it can act as a decoy to enhance their cognate linearly spliced protein isoform functions by releasing the proteins or protecting them from degradation, enhancing the expression of relevant proteins (77). Opposite to their role in enhancing the expression of relevant genes, there are other classes of circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins, which play an inhibitory role in reducing the activation of their cognate linearly spliced proteins (78). In the fourth category of translated peptides, there are some peptides taking part in signal transduction pathways to affect downstream targets but have no clear association with their full-length proteins (79).
Herein, we discussed some functional peptides/proteins encoded by the circRNAs and their possible mechanisms involved in regulating the various cellular activities such as proliferation, metastasis, and invasion (Figure 3).
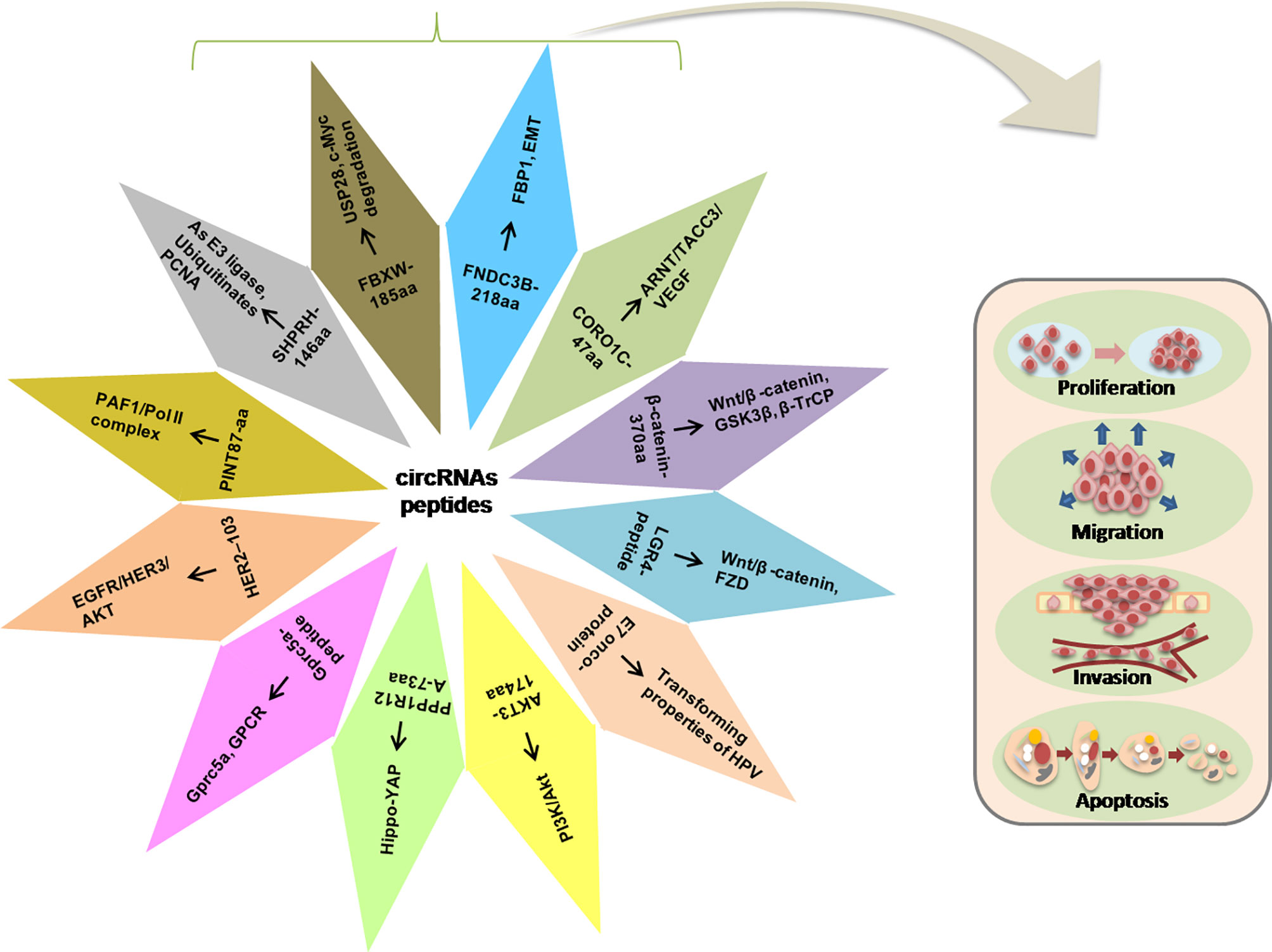
Figure 3 Illustration of the circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins and signaling pathways in the progression of tumorigenesis.
Non-cancerous Regulatory Peptides/Proteins
Translation of circMbl Regulates Neuronal Function
In the functional peptides encoded by circRNAs, circMbl is the firstly discovered peptide. circMbl originates from the second exon of mbl and regulates its parental gene expression by competing for the start codon with its canonical linear mRNA (19). Later on, it has been further detected that circMbl encodes a protein by using the cUTRs (UTR from circMbl) that act as IRES-like elements in a FOXO-dependent manner (61). The presence of MBL-binding sites in the flanking intronic sequences of the mbl gene promotes circMbl production from its exons. circMbl is present in neural related genes in the fly heads, providing a link between RBPs and brain functions. In addition, circMbl and their putative encoded isoforms are present in synaptosome fractions and regulate the synaptic functions induced by acute fasting through 4E-BP and FOXO (61). Despite the absence of signal peptide sequence detection, research reveals that circMbl is translated in the synapses, where they associate with RBPs and mediate the different roles in neurodegenerative disorders (80). However, to date, there is no available evidence on their involvement in tumorigenesis.
Translation of circ-ZNF609 Regulates Myoblast Proliferation
circ-ZNF609 (hsa_circ_0000615) is highly conserved, containing 753-nt ORF derived from the second exon circularization of its parental gene in muscle cells (81). The analysis of the protein-encoding ability of circ-ZNF609 using artificial vector P-circ3XF reveals that its UTR can drive IRES-dependent translation and encode a novel peptide isoform in a splicing-dependent manner, and mediates the regulation of myoblast proliferation (81). FOXP4 (Forkhead box P4) majorly reported in many cancers, is also regulated by circ-ZNF609 through sponging mir-138-5p in renal carcinoma, resulting in the downregulation of cell proliferation and invasion processes (82). Furthermore, circ-ZNF609 promotes the expression of p70S6K by binding to and sequestering miR-145-5p, thus elevating BC progression (39). Additionally, highly expressed circ-ZNF609 binds to and inhibits the activity of miRNA-150-5p, therefore upregulating the Sp1 expression and facilitating the metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells (83). According to the recent findings, it has been evaluated that circ-ZNF609 is an important regulator of G1/S transition circ-ZNF609 knockdown reduces the phosphorylated Rb : Rb ratio and E2F1 expression, which leads to cell cycle arrest at the G1/S transition. Conversely, the increased circ-ZNF609 expression in rhabdomyosarcoma promotes cell proliferation (84). Taken together, it can be concluded that Circ-ZNF609 is upregulated in different cancers, and its downregulation can inhibit cancer progression.
Promoting the Function of Full-length Proteins
Translation of circ-FBXW7 in Glioblastoma and TNBC
It has been demonstrated that circ-FBXW7 (hsa_circ_0001451) is formed by the exon 3 and exon 4 circularization of the FBXW7 gene in glioblastoma samples. circ-FBXW7 has to span the back-splice junction ORF of 620-nt encoding a 22-kDa novel protein driven by an IRES in a 5ʹ cap-independent translation manner, termed as FBXW7-185aa (77). The expression of circ-FBXW7 is positively associated with the overall survival of glioblastoma patients. It has been found that in glioblastoma patients, the overexpression of FBXW7-185aa inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells in vivo and in vitro (56). Furthermore, an isoform of the FBXW7 gene FBXW7α is also reported to target c-Myc for ubiquitination-induced degradation (85). Mechanistically, the de-ubiquitinating enzyme ubiquitin-specific protease 28 (USP28) binds to and stabilizes c-Myc by interacting with the N-terminus of FBXW7α. However, due to its high affinity, FBXW7-185aa binds to and inhibits USP28, thereby freeing FBXW7α to degrade c-Myc in cancer cells (77). The expression of circFBXW7 in TNBC is associated with poor clinical outcomes (86), whereas its upregulation suppresses TNBC progression by binding to the tumor-promoting miRNA (miR-197-3p) (87). circFBXW7 encodes the same protein (FBXW7-185aa) to repress malignant progression. FBXW7-185aa inhibits the proliferation and migration of TNBC cells by inducing c-Myc degradation (87). Based on this experimental evidence, it is reasonable to consider that circ-FBXW7 and FBXW7-185aa play an important role in glioblastoma and TNBC prognosis. Therefore, these might serve as independent prognostic, therapeutic markers in glioblastoma and TNBC.
Translation of circ-SHPRH in Glioblastoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
circ-SHPRH (hsa_circ_0001649) is formed after the back splicing of exons 26–29 of the SNF2 histone linker PHD RING helicase (SHPRH) gene and contains only 440-nt. The circularization of circ-SHPRH results in a tandem stop codon “UGAUGA”, starting the translation initiation and termination through the overlapping codon (88). circ-SHPRH encodes a 17-kDa protein named “SHPRH-146aa” formed by spinning the back-splice junction ORF and driven by IRES-like elements (88). Both circ-SHPRH and its transcripts are highly expressed in normal human brain cells, participating in the inhibition of central nervous system cancers through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathways triggered by SHPRH (88, 89). Recently, it has been found that the overexpression of SHPRH-146aa reduces the malignancy of glioblastoma cells with increased levels of SHPRH-146aa, and glioblastoma patients have increased survival time. Mechanistically, SHPRH-146aa acts as a protective decoy molecule to protect SHPRH from degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome. Full-length SHPRH ubiquitinates proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) as an E3 ligase, resulting in cell proliferation repression (56).
Moreover, circ-SHPRH harbors potential binding sites for RBPs (U2AF65, EIF4A3, UPF1), and miRNAs (miR-1283, miR-4310, miR-182-3p, miR-888-3p, miR-4502, miR-6811-5p, miR-6511b-5p, and miR-1972), and may act as a sponge and regulate the progression of HCC (90).
Translation of circE7 in Cervical Carcinoma
circE7, a 472-nt circRNA, contains the entire E7 ORF, originated via back splicing by human papillomaviruses (HPV). circE7 with modification of m6A is mainly localized in the cytoplasm, bearing polyribosome, and encodes the E7 oncoprotein (91). circE7 is predicted to have binding sites for multiple miRNAs, but none of these binding sites is conserved among HPV species. Cell stressors, such as heat shock (42°C), upregulate the E7 protein expression by a two- to four-fold increase (91). In addition, the depletion of circE7 in cervical carcinoma cells reduces E7 protein levels and inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. The circE7 knockdown by shRNA recovered circResist_WT but not circResist_noATG, confirming that the protein-coding ability of circE7 is required for its function in vivo. The above results provide the first evidence that protein-encoding circRNAs derived from a virus are biologically functional and link to the transforming properties of some HPV.
Although the circ-E7 and E7 peptides play an important role in the ability of HPV to transform cervical cells, the exact mechanism underlying the activity of the E7 peptide is unknown, and more studies are needed to understand the mechanism through which the E7 peptide exerts its function.
Translation of circß-catenin in HCC
circ-0004194 (termed as circβ-catenin) is derived through back splicing of six exons of the β-catenin gene containing 1,129-nt. Subsequent analysis shows that circβ-catenin is translated into a novel 370aa (40.8-kDa) peptide designated as β-catenin-370aa, mainly localized in the cytoplasm and positively correlated with its linear mRNA isoform in humans (92). circβ-catenin regulates the β-catenin expression at the protein level rather than its transcription level. circβ-catenin is significantly expressed in both HCC tissues and cell lines. The construction of the circβ-catenin knockdown expression vector inhibits the full-length β-catenin and β-catenin-370aa protein levels without affecting the β-catenin mRNA. Knockdown of circβ-catenin suppresses HCC cell growth and metastasis through the inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. The stability of β-catenin is strongly associated with its phosphorylation status. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) interacts with and phosphorylates β-catenin, and the ubiquitin ligase β-TrCP ubiquitinates the β-catenin, leading to degradation by the proteasome (93). Therefore, it is evaluated that β-catenin-370aa binds to GSK3β, which eventually leads to prevent the GSK3B from interacting with full-length β-catenin (92, 94).
Overviewing the four different forms of peptides which regulate the expression of genes in different cancers, it could be speculated that they may act as targets of drug designing for cancer treatment.
Inhibiting the Function of Full-length Protein
Translation of circ-AKT3 in Glioblastoma
circ-AKT3 (hsa_circ_0017250) is generated from circularization of exons 3–7 of the parent gene with 524-nt, localized in the cytoplasm (78). circ-AKT3 encodes a 174aa peptide (AKT3-174aa) through the overlapping start–stop codon UAAUGA driven by active IRES and contains a similar “aa” sequence to AKT3 residues from positions 62 to 232 (78).
AKT3-174aa expression is lowered in glioblastoma cells and is negatively associated with the diagnosis of the disease, suggesting that it may be a potential biomarker (78). In addition, the overexpression of AKT3-174aa diminishes glioblastoma cell proliferation, tumor growth, and radiation resistance, while its knockdown increases the malignant phenotypes, indicating that AKT3-174aa, but not circRNA itself, exerts a tumor-inhibiting role in glioblastoma cells (78). PI3K/Akt performs a key function in multiple oncogenic signaling pathways that drive the development and progression of glioblastoma (95). The activated PI3K recruits AKT to the plasma membrane through the PH domain and sequentially phosphorylates AKT at thr308 and ser473, respectively, to undergo a successive activation. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme 1 (PDK1) (another PH domain-containing kinase) directly phosphorylates AKT at thr308, the most critical step for AKT activation. The resemblance of the sequences between AKT3-174aa and AKT3 infers that AKT3-174aa can compete and bind to PDK1, thereby reducing the level of AKT3 thr308 phosphorylation, and executes a negative regulatory role in the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (78). Another circRNA, circAKT3 (hsa_circ_0000199), originated from exons 8–11 of the AKT3 gene (96). It is highly upregulated and associated with an aggressive phenotype in gastric cancer (GC) patients with resistance to cisplatin (CDDP) therapy. circAKT3 enhances DNA damage repair, inhibits the apoptosis of GC cells, and promotes PIK3R1 expression by sponging miR-198 through PI3K/AKT pathway activation in GC (96). Thus, the above data show that circAKT3 might be a potential therapeutic biomarker for GC patients receiving CDDP therapy (96).
Signal Transducer Peptides/Proteins
Translation of circPINTexon2 in Glioblastoma
Produced by self-circularization of exon 2 of the lncRNA LINC-PINT, circPINT (hsa_circ_0082389) contains 3ʹ AG and 5ʹ GT sequences required for back-splicing. circPINTexon2 has been determined endogenously in human cell lines, and its corresponding up-or downregulation has been confirmed by the artificial overexpression or junction siRNA transfection. It contains the ORF and IRES-like elements that initiate translation through 5ʹ cap-independent translation machinery to encode a 10-kDa protein designated as 87aa peptide (79). Both circPINTexon2 and its peptide “PINT87aa” are downregulated in glioblastoma tissue, with PINT87aa having a negative impact on clinical prognosis. PINT87aa localized in the nucleus, which plays a tumor-suppressive role in the control of cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. PINT87aa can interact with the PAF1 complex, inhibiting the transcriptional elongation of multiple oncogenes (50).
The polymerase-associated factor (PAF1) complex is an important component in RNA polymerase II, regulating gene transcription and elongation. It has been shown that the PINT87aa peptide interacts with PAF1, keeps the PAF1 complex on the target gene promoter, and regulates the formation of the PAF1/Pol II complex, thus controlling its downstream effects in the progression of several cancer types, including glioblastoma, BC, HCC, and GC (79). Loss of PINT87aa makes PAF1 lose its proper position, and the freed PAF1 is sequentially involved in many other biological processes such as cell cycle regulation, histone modification, and self-renewal of cancer stem cells (79).
Translation of circGprc5a in Bladder Cancer
circGprc5a (hsa_circ_02838) is commonly upregulated in cancer stem cells (CSCs) and advanced and metastatic bladder tumors with bad prognosis. It encodes a polypeptide of 11aa termed circGprc5a-peptide, which exerts its function through a peptide-dependent manner (97). Knockdown of circGpr5a and/or its peptide expression diminishes the proliferation and metastasis of bladder CSCs. In regulating self-renewal and metastasis of CSCs, circGprc5a-peptide binds to Gprc5a surface protein and activates the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling pathway involved in tumorigenesis (97, 98). Researchers have established circ-Gprc5a-mutant cells that cannot produce peptides, which in turn impair the function of circ-Gprc5a. These findings suggest that circGprc5a-peptide promote bladder tumorigenesis and metastasis.
Translation of circPPP1R12A in Colon Cancer (CC)
circPPP1R12A (hsa_circ_0000423) formed by back splicing of exon 24/25 of the PPP1R12A gene located at 12q21.2 contains a 216-nt small ORF that encodes a conserved protein of 10 kDa (circPPP1R12A-73aa) localized in the cytoplasm (99). circPPP1R12A is significantly upregulated in CC, and patients with highly expressed circRNA have a relatively shorter overall survival. It has been demonstrated that mutation of the start codon disrupts circPPP1R12A protein-encoding ability and represses CC proliferation, migration, and invasion both in vitro and in vivo, indicating that circPPP1R12A-73aa is involved in CC progression. Furthermore, the Hippo-Yes-associated protein (YAP), one of the most conserved tumor-repressor signaling pathways, can also be activated by circPPP1R12A-73aa resulting in the promotion of proliferation, migration, and invasion capability of cancer cells (99, 100). In addition, YAP-specific inhibitor peptide 17 has significantly reduced the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of CC promoted by upregulating circPPP1R12A-73aa. Collectively, a protein encoded by circRNA circPPP1R12A contributes to cell proliferation and provides an insight for the development of a novel therapeutic biomarker for CC patients.
Translation of circLgr4 in CRC
circLgr4 (hsa_circ_02276) is strongly expressed in advanced (metastatic) CRC with a poor prognosis. circLgr4 is translated into a 19aa (3-kDa) peptide, which plays an essential role in CSCs maintenance, renewal, and invasion (101).
A Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in colorectal CSCs tumorigenesis and metastasis (102). circLgr4-peptide interacts with Lgr4 to promote the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling through the ubiquitination of the Frizzled receptors (FZD), resulting in colorectal CSCs self-renewal and invasion. Both circLgr4 ASO (antisense oligo) and Lgr4 ASO can inhibit tumor proliferation (101). The CircLgr4-peptide-Lgr4 axis might be used as a therapeutic biomarker for colorectal CSCs and colorectal tumorigenesis.
Translation of circFNDC3B in GC and CC
circFNDC3B (hsa_circ_0006156) is structured through back splicing and circularization of exons 5–6 of the fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 3B (FNDC3B) gene. circFNDC3B possesses a potential IRES and an ORF of 218aa and encodes a 25-kDa peptide. circFNDC3B promotes cell migration and invasion in GC and is associated with EMT (103). EMT is a complex transformation process that drives epithelial carcinoma cells into malignant phenotype and enables tumor cells to migrate from the tumor’s primary site to distal metastasis (104). The downregulation of E-cadherin (epidermal phenotype protein E) and the upregulation of N-cadherin (mesenchymal phenotype N), Vimentin, and Snail enhance EMT in GC (105, 106). circFNDC3B promotes cell migration and invasion by inhibiting E-cadherin protein expression. circFNDC3B interacts with IGF2BP3 and promotes CD44 mRNA expression by forming a ternary complex of circFNDC3B–IGF2BP3–CD44 mRNA. However, FNDC3B has multiple domains which have been explored in cell adhesion, morphology, migration, and embryonic differentiation (107). While working on CC, Pan et al. evaluated that Circ-FNDC3B expression is associated with proliferation, invasion, and migration in CC. Mechanistically, circ-FNDC3B-218aa inhibits the expression of Snail and subsequently promotes the tumor-repressive effect of FBP1, which results in the suppression of tumor progression and EMT. Thus, the novel circ-FNDC3B-218aa might serve as a potential therapeutic target in CC (108). Further studies are required to elucidate the functional/regulatory role of peptides encoded by circFNDC3B in tumorigenesis.
Translation of circHER2 in TNBC
The novel circRNA of 103aa-long peptide (known as HER2-103) is formed from the circularization of exons 3–7 of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) gene in TNBC samples. It has been further evaluated that patients positive with circHER2/HER2-103 harbored a worse overall prognosis than circHER2/HER2-103-negative patients. HER2-103 promotes malignant phenotypes by interacting and activating the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/HER3 and promoting AKT phosphorylation (109). Further exploration is needed for its detailed functioning.
Translation of circ-0000437 in Endometrial Cancer
A solo study has been reported on CORO1C47aa. It originates from the circularization of exons 7–8 of its host gene CORO1C and has significantly reduced expression in endometrial cancer compared to matched precancerous tissue. Circ-0000437 contains a short ORF encoding a functional peptide named CORO1C47aa, and its overexpression mediates the inhibition of angiogenesis by suppressing endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation through competition with transcription factor TACC3 and suppresses VEGF signaling. Results also show that CORO1C47aa is directly bound to ARNT through the PAS-B domain and involved in blocking the association between ARNT and TACC3, which led to a reduced expression of VEGF and angiogenesis. The antitumor effects of CORO1C-47aa on endometrial cancer progression suggest that CORO1C-47aa has a potential role in anti-carcinoma treatment (110).
It is proposed that, in the near future, the ectopic expression and clinical association of these peptides in cancers will be a part of experimental and clinical examination, such as examination of body fluids or immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis of tumor tissues (76). Regarding this proposal, many novel studies have approved that some peptide-related drugs such as mifamurtide (111), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interferon-γ (INF- γ) (112), and interleukin-2 (IL-2) (113) cure human diseases including cancer and are found to be more effective (114). Compared to other traditional drugs, these peptide-related drugs hold distinctive advantages, including being highly specific and active, being less toxic, and having low immunogenicity (115, 116).
It has been also approved that some circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins (FBXW7-185aa and SHPRH-146aa) play a role in tumor inhibition. Approaches are now in process to rescue or strengthen these tumor-inhibiting peptides/proteins, including vaccination with artificially synthesized peptides or viral vector vaccines that encode the specific peptide sequences for cancer therapies (117–119). Additionally, these peptides modulate tumor energy metabolism, oncoprotein stability, and the EMT of cancer cells (11, 120).
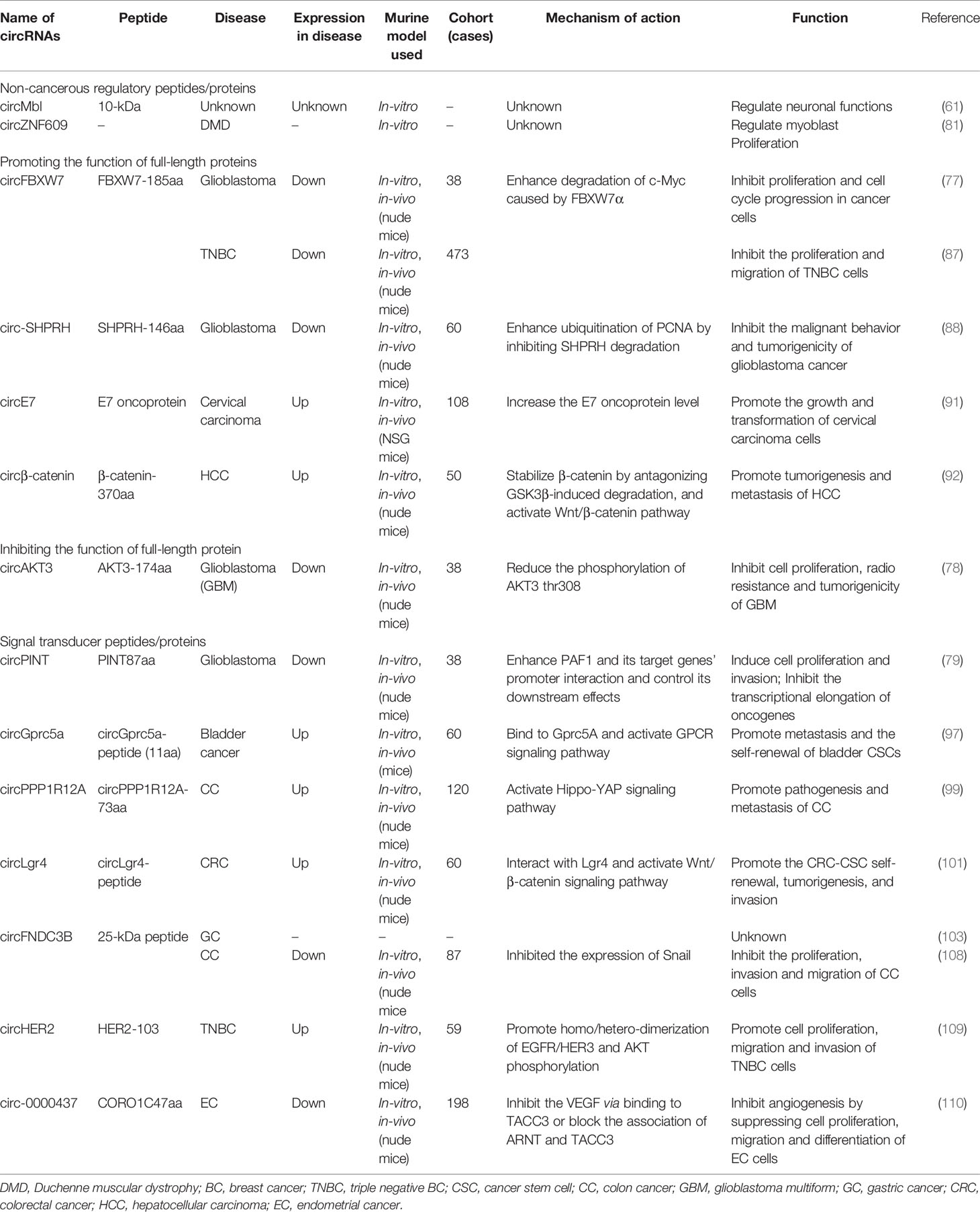
A summary of recently reported studies on the altered expression of peptides encoded by circRNAs as potential biomarkers for different malignancies is listed in Table 1.
circRNA-Encoded peptides/Proteins as Therapeutic Target/Biomarkers
Owing to the distinctive back-splice junction features, high stability, and specificity in tissues and body fluids, circRNAs and their encoded peptides/proteins are considered as therapeutic targets/biomarkers in cancer studies (121–123).
Several techniques have been developed to study/target circRNAs and their encoded peptides/proteins for therapeutic purposes in vivo. Here we proposed some possible strategies that could be operational via over-expressing or knock down the circRNA encoding peptides, as summarized in Figure 4.
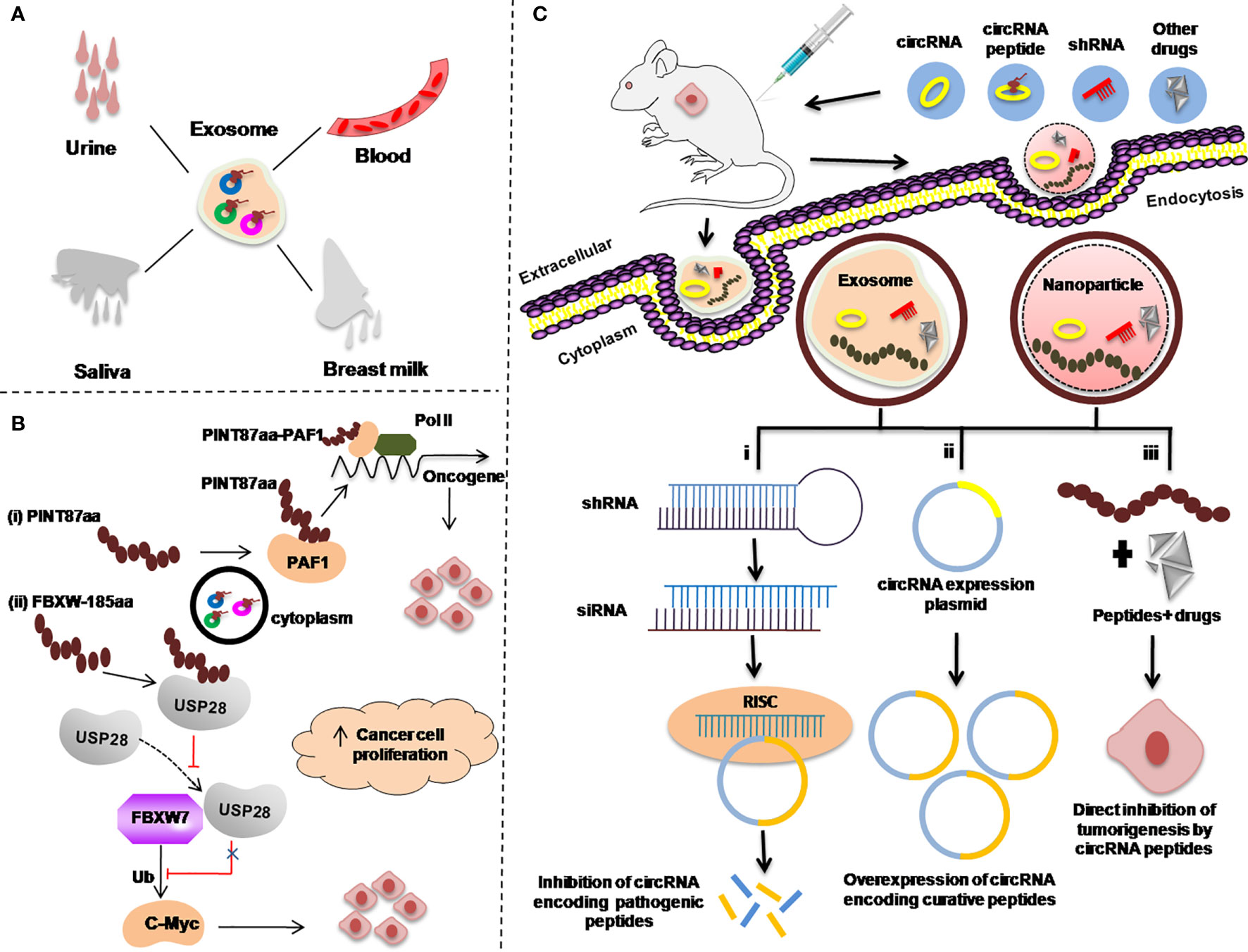
Figure 4 Re-proposed possible applications of circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins in cancers as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers. (A) Body fluids, such as urine, blood, saliva, and breast milk as a sample for examining exosome-circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins for cancer diagnosis. (B) Regulation of the expression of circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins to inhibit transcriptional elongation of oncogenes. (C) Strategies used to target circRNA peptides as a therapeutic approach in animal mouse models. Exosome-mediated delivery of small hairpin RNA (shRNA) (i). circRNA expression plasmid to overexpress circRNA-encoding curative peptides/proteins (ii). Gold nanoparticle-mediated delivery of shRNA targeting the back-splice junction of circRNAs for treating different malignancies (i–iii).
Studies have demonstrated that circRNAs in the exosome and other body liquids such as in blood, urine, saliva, and breast milk have provided a new direction for the uncovering of new biomarkers for cancer diagnosis (124–126) (Figure 4A).
Secondly, as it has been reported in many studies that there are several circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins such as PINT87A and FBXW7-185aa which are involved in regulating the expression of different oncogenes (77, 79). Possible strategies to use these peptides/proteins as targets to control the expression of those oncogenic proteins, is to design the corresponding target drugs as summerized in Figures 4B, C.
In cancer treatment, knockdown of the circRNAs encoding pathogenic peptides/proteins is the most efficient way to develop circRNA-based therapies (127) [Figure 4C(i)].
There are various circRNAs that encode curative peptides/proteins and are downregulated in various malignancies and can be exploited as potential targets for cancer treatment (88, 92). A proposed strategy for these curative peptides/proteins against cancer is explained in Figure 4C(ii).
In addition to the knockdown of pathogenic peptides/proteins and overexpression of curative circRNAs encoding peptides/proteins, the third important strategy is to use these peptides/proteins along with anticancer drugs. The combination of these peptides/proteins with other anticancer drugs can be directly delivered to the cancer cells via exosome or nanoparticle via injecting into the patients as anticancer therapy [Figure 4C(iii)].
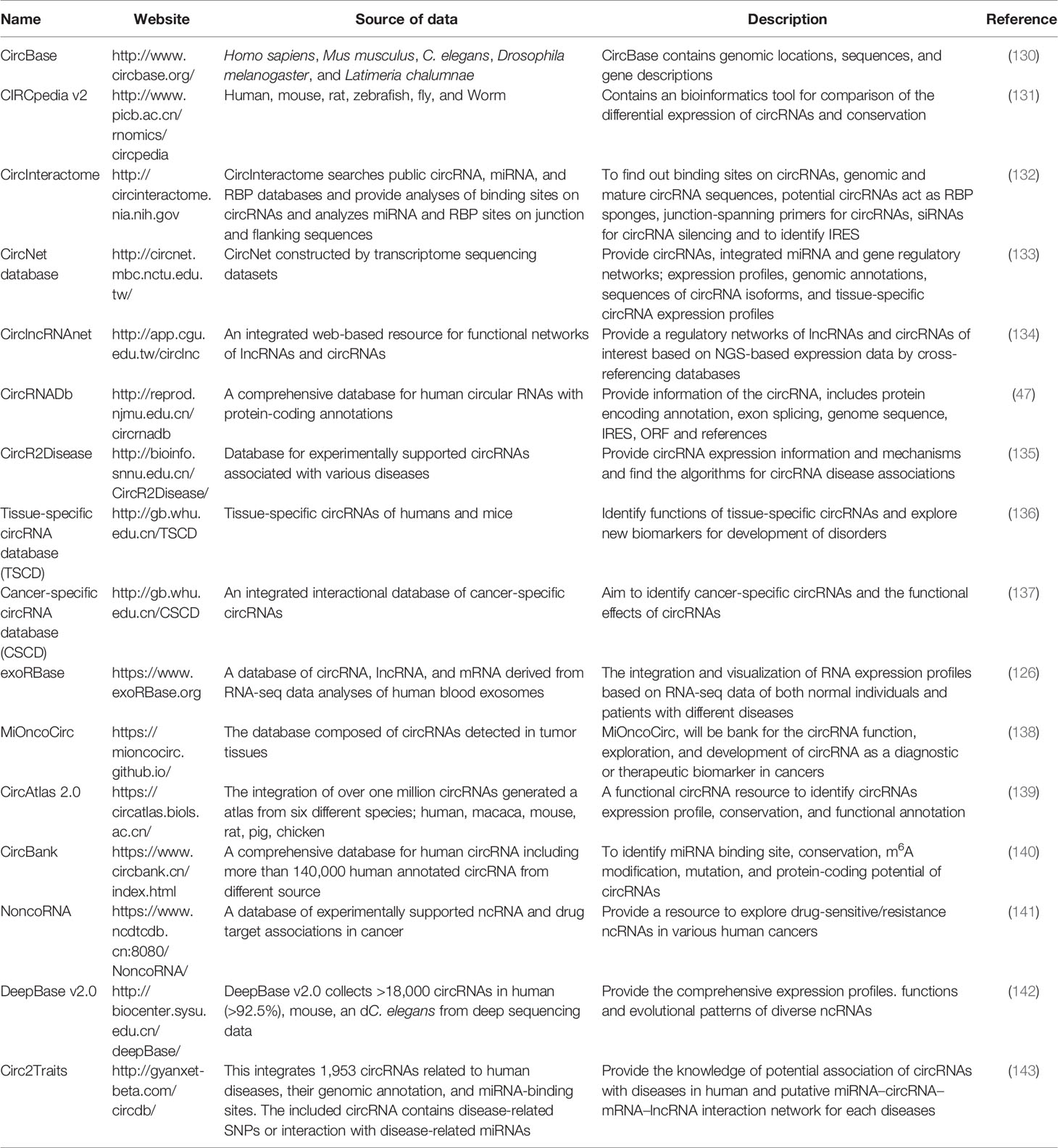
Despite the huge volume of publications on circRNA involvement in tumorigenesis, the underlying mechanisms are still not completely clear. Exploring the hidden mechanisms of circRNAs and circRNA-encoded peptides will recognize their importance in human cancers (128, 129). In the future, more studies on the development of effective technologies to target circRNAs in vivo will lead to the clinical revolution of circRNA-based therapeutics. In this regard, circRNAs databases play an important role and provide valuable information; improvements in these databases and other detection technologies will provide new strategies for cancer treatment. Some circRNAs databases are summarized here in Table 2.
Conclusion and Future Prospective
CircRNAs are a highly stable class of ncRNAs and are directly involved in gene-cell cycle regulation that makes them flashy targets for cancer studies. circRNAs and their encoding peptides/proteins take part in fundamental cellular processes like gene expression, cell proliferation, and migration of cancer cells, which are considered as the hallmark of cancer development through suppressing or promoting the different cancers either in differential peptides or in miRNA sponges. However, this bifunctionality of circRNAs needs further in-depth exploration.
The current assessment of the literature on circRNAs demonstrates an expanding body of data supporting the effectiveness of circRNAs encoding peptides/proteins in clinical practice for different malignancies. The current research established a significant relationship between the ectopic expression of circRNA-encoded peptides and prognostic as well as diagnostic values in oncology. For their effective involvement in cell cycle, drug resistance, and functioning in protein translation, circRNAs provide a new avenue of clinical research to identify new peptide-based cancer biomarkers for diagnosis and potential use to generate circRNA-peptide-based targeted therapeutic drugs.
Although ongoing research on circRNA-encoded peptides’ role in progression and as diagnostic targets for different medical illnesses including cancer holds great promise, especially in terms of precision medicines and to design multi-marker approaches toward cancer diagnosis and treatments, it is still in its early stages of exploration. Summarizing the research on classification, biogenesis, peptide translation, and the clinical applications of circRNAs, we come to conclude with some prospect points here.
Firstly, only a handful of functional circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins have been characterized yet. We endorse more extensive studies on the biology of circRNAs especially about protein-coding ability and their interactions with gene expression will be launched. We also endorse to develop an academic standardized nomenclature system for circRNAs. Secondly, except as miRNA sponges, it is imperative to elucidate other possible mechanisms underlying circRNAs participating in regulation of gene expression. Third, there is a need to implement large multiethnic studies before recommending specific circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins for related cancer diagnosis or treatment. Fourth, for the ultimate goal of using circRNAs as a potential target for cancer diagnoses or therapy, future research should be directed to deal with host immune rejection and delivery of circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins to the particular sites in vitro. Fifth, the discovery of dysregulated circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins should be mainly carried out in clinical tissue samples. In the future, the expression of circRNA-encoded peptides/proteins should be discovered in more clinical samples associated with a specific disease, such as blood, urine, saliva, breast milk, and other body fluids.
We anticipate that the coming days’ in-depth new research will strengthen the applications to develop circRNA-encoded peptide-based diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. This review could promote the blooming growth of research on circRNAs and their clinical application in the cancer clinics.
Author Contributions
FAK write the first draft, refined, edited, and revised the manuscript, designed the tables and figures. NHK, BN, SZ, EEN, YW formatted and contributed to the materials organization and final editing of the manuscript. WZ and SJ conceptualized and designed the study. All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work and approved for publication.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31371386 SP.J).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary

References
1. Anastasiadou E, Jacob LS, Slack FJ. Non-Coding RNA Networks in Cancer. Nat Rev Cancer (2018) 18(1):5–18. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.99
2. Guttman M, Russell P, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Lander ES. Ribosome Profiling Provides Evidence That Large Noncoding RNAs do Not Encode Proteins. Cell (2013) 154(1):240–51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.009
3. Pelechano V, Steinmetz LM. Gene Regulation by Antisense Transcription. Nat Rev Genet (2013) 14(12):880–93. doi: 10.1038/nrg3594
4. Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, et al. Circular RNAs are a Large Class of Animal RNAs With Regulatory Potency. Nature (2013) 495(7441):333–8. doi: 10.1038/nature11928
5. Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM, Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, et al. The RNA Binding Protein Quaking Regulates Formation of circRNAs. Cell (2015) 160(6):1125–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.014
6. Huang C, Shan G. What Happens at or After Transcription: Insights Into circRNA Biogenesis and Function. Transcription (2015) 6(4):61–4. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2015.1071301
7. Chen N, Zhao G, Yan X, Lv Z, Yin H, Zhang S, et al. A Novel FLI1 Exonic Circular RNA Promotes Metastasis in Breast Cancer by Coordinately Regulating TET1 and DNMT1. Genome Biol (2018) 19(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1594-y
8. Zhao X, Cai Y, Xu J. Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function in Human Cancers. Int J Mol Sci (2019) 20(16):3926. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163926
9. McMahon M, Contreras A, Ruggero D. Small RNAs With Big Implications: New Insights Into H/ACA snoRNA Function and Their Role in Human Disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA (2015) 6(2):173–89. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1266
10. Pasut A, Matsumoto A, Clohessy JG, Pandolfi PP. The Pleiotropic Role of non-Coding Genes in Development and Cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol (2016) 43:104–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2016.10.005
11. Zhu S, Wang J, He Y, Meng N, Yan GR. Peptides/Proteins Encoded by Non-Coding RNA: A Novel Resource Bank for Drug Targets and Biomarkers. Front Pharmacol (2018) 9:1295. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01295
12. Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, et al. Circular RNAs are Abundant, Conserved, and Associated With ALU Repeats. RNA (2013) 19: (2):141–57. doi: 10.1261/rna.035667.112
13. Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, Li S, Guo W, Zhao J, et al. Circular RNA is Enriched and Stable in Exosomes: A Promising Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis. Cell Res (2015) 25(8):981–4. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.82
14. Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO. Cell-Type Specific Features of Circular RNA Expression. PloS Genet (2013) 9(9):e1003777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003777 Erratum in: PLoS Genet (2013) 9(12). doi:10.1371/annotation/f782282b-eefa-4c8d-985c-b1484e845855.
15. Hsu MT, Coca-Prados M. Electron Microscopic Evidence for the Circular Form of RNA in the Cytoplasm of Eukaryotic Cells. Nature (1979) 280(5720):339–40. doi: 10.1038/280339a0
16. Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, Xiang JF, Yin QF, Xing YH, et al. Circular Intronic Long Noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell (2013) 51(6):792–806. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.017
17. Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang X, et al. Exon-Intron Circular RNAs Regulate Transcription in the Nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol (2015) 22(3):256–64. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2959 Erratum in: Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017 Feb 6;24(2):194.
18. Chen LL, Yang L. Regulation of circRNA Biogenesis. RNA Biol (2015) 12(4):381–8. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1020271
19. Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, et al. circRNA Biogenesis Competes With pre-mRNA Splicing. Mol Cell (2014) 56(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.019
20. Zaphiropoulos PG. Circular RNAs From Transcripts of the Rat Cytochrome P450 2C24 Gene: Correlation With Exon Skipping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (1996) 93(13):6536–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.13.6536
21. Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glažar P, Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol Cell (2015) 58(5):870–85. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.027
22. Ivanov A, Memczak S, Wyler E, Torti F, Porath HT, Orejuela MR, et al. Analysis of Intron Sequences Reveals Hallmarks of Circular RNA Biogenesis in Animals. Cell Rep (2015) 10(2):170–7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.12.019
23. Wang F, Nazarali AJ, Ji S. Circular RNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Am J Cancer Res (2016) 6(6):1167–76.
24. Wawrzyniak O, Zarębska Ż, Kuczyński K, Gotz-Więckowska A, Rolle K. Protein-Related Circular RNAs in Human Pathologies. Cells (2020) 9(8):1841. doi: 10.3390/cells9081841
25. Li LJ, Huang Q, Pan HF, Ye DQ. Circular RNAs and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Exp Cell Res (2016) 346(2):248–54. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.07.021
26. Zhao W, Dong M, Pan J, Wang Y, Zhou J, Ma J, et al. Circular RNAs: A Novel Target Among non−Coding RNAs With Potential Roles in Malignant Tumors (Review). Mol Med Rep (2019) 20(4):3463–74. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10637
27. Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J. Circular RNAs: Promising Biomarkers for Human Diseases. EBioMedicine (2018) 34:267–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.036
28. Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, Hacker A, Walter M, Koopman P, et al. Circular Transcripts of the Testis-Determining Gene Sry in Adult Mouse Testis. Cell (1993) 73(5):1019–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90279-y
29. Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Most Mammalian mRNAs Are Conserved Targets of microRNAs. Genome Res (2009) 19(1):92–105. doi: 10.1101/gr.082701.108
30. Tay Y, Kats L, Salmena L, Weiss D, Tan SM, Ala U, et al. Coding-Independent Regulation of the Tumor Suppressor PTEN by Competing Endogenous mRNAs. Cell (2011) 147(2):344–57. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.029
31. Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA Circles Function as Efficient microRNA Sponges. Nature (2013) 495(7441):384–8. doi: 10.1038/nature11993
32. Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H, Bartel DP. Expanded Identification and Characterization of Mammalian Circular RNAs. Genome Biol (2014) 15(7):409. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0409-z
33. Wang K, Long B, Liu F, Wang JX, Liu CY, Zhao B, et al. A Circular RNA Protects the Heart From Pathological Hypertrophy and Heart Failure by Targeting miR-223. Eur Heart J (2016) 37(33):2602–11. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv713
34. Xie H, Ren X, Xin S, Lan X, Lu G, Lin Y, et al. Emerging Roles of circRNA_001569 Targeting miR-145 in the Proliferation and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget (2016) 7(18):26680–91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8589
35. Wan L, Zhang L, Fan K, Cheng ZX, Sun QC, Wang JJ. Circular RNA-ITCH Suppresses Lung Cancer Proliferation via Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. BioMed Res Int (2016) 2016:1579490. doi: 10.1155/2016/1579490
36. Kong Z, Wan X, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Xu Y, et al. Circular RNA Circfoxo3 Promotes Prostate Cancer Progression Through Sponging miR-29a-3p. J Cell Mol Med (2020) 24(1):799–813. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14791
37. Li Y, Zheng F, Xiao X, Xie F, Tao D, Huang C, et al. CircHIPK3 Sponges miR-558 to Suppress Heparanase Expression in Bladder Cancer Cells. EMBO Rep (2017) 18(9):1646–59. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643581
38. Han D, Li J, Wang H, Su X, Hou J, Gu Y, et al. Circular RNA Circmto1 Acts as the Sponge of microRNA-9 to Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Hepatology (2017) 66(4):1151–64. doi: 10.1002/hep.29270
39. Wang S, Xue X, Wang R, Li X, Li Q, Wang Y, et al. CircZNF609 Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Growth, Migration, and Invasion by Elevating P70s6k1 via Sponging miR-145-5p. Cancer Manag Res (2018) 10:3881–90. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S174778
40. Xu Z, Li P, Fan L, Wu M. The Potential Role of circRNA in Tumor Immunity Regulation and Immunotherapy. Front Immunol (2018) 9:9. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00009
41. Yi Z, Hongjie W, Xiaoyi G, Li P, Yijie D, Jijun T, et al. MK-FSVM-SVDD: A Multiple Kernel-Based Fuzzy SVM Model for Predicting DNA-Binding Proteins via Support Vector Data Description. Curr Bioinf (2021) 16(2):274–83. doi: 10.2174/1574893615999200607173829
42. Haque S, Harries LW. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) in Health and Disease. Genes (Basel) (2017) 8(12):353. doi: 10.3390/genes8120353
43. Fang L, Du WW, Awan FM, Dong J, Yang BB. The Circular RNA Circ-Ccnb1 Dissociates Ccnb1/Cdk1 Complex Suppressing Cell Invasion and Tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett (2019) 459:216–26. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.05.036
44. Li Q, Wang Y, Wu S, Zhou Z, Ding X, Shi R, et al. CircACC1 Regulates Assembly and Activation of AMPK Complex Under Metabolic Stress. Cell Metab (2019) 30(1):157–173.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.05.009
45. Chen Y, Yang F, Fang E, Xiao W, Mei H, Li H, et al. Circular RNA Circago2 Drives Cancer Progression Through Facilitating HuR-Repressed Functions of AGO2-miRNA Complexes. Cell Death Differ (2019) 26(7):1346–64. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0220-6
46. Abe N, Matsumoto K, Nishihara M, Nakano Y, Shibata A, Maruyama H, et al. Rolling Circle Translation of Circular RNA in Living Human Cells. Sci Rep (2015) 5:16435. doi: 10.1038/srep16435
47. Chen X, Han P, Zhou T, Guo X, Song X, Li Y. circRNADb: A Comprehensive Database for Human Circular RNAs With Protein-Coding Annotations. Sci Rep (2016) 6:34985. doi: 10.1038/srep34985
48. Granados-Riveron JT, Aquino-Jarquin G. The Complexity of the Translation Ability of circRNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta (2016) 1859(10):1245–51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.07.009
49. Wilusz JE. Circular RNAs: Unexpected Outputs of Many Protein-Coding Genes. RNA Biol (2017) 14(8):1007–17. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1227905
50. Lei M, Zheng G, Ning Q, Zheng J, Dong D. Translation and Functional Roles of Circular RNAs in Human Cancer. Mol Cancer (2020) 19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1135-7
51. Gross JD, Moerke NJ, von der Haar T, Lugovskoy AA, Sachs AB, McCarthy JE, et al. Ribosome Loading Onto the mRNA Cap is Driven by Conformational Coupling Between Eif4g and Eif4e. Cell (2003) 115(6):739–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00975-9
52. Schütz P, Bumann M, Oberholzer AE, Bieniossek C, Trachsel H, Altmann M, et al. Crystal Structure of the Yeast Eif4a-Eif4g Complex: An RNA-Helicase Controlled by Protein-Protein Interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2008) 105(28):9564–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800418105
53. Marintchev A, Edmonds KA, Marintcheva B, Hendrickson E, Oberer M, Suzuki C, et al. Topology and Regulation of the Human Eif4a/4G/4H Helicase Complex in Translation Initiation. Cell (2009) 136(3):447–60. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.014
54. Fitzgerald KD, Semler BL. Bridging IRES Elements in mRNAs to the Eukaryotic Translation Apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta (2009) 1789(9-10):518–28. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.07.004
55. Godet AC, David F, Hantelys F, Tatin F, Lacazette E, Garmy-Susini B, et al. IRES Trans-Acting Factors, Key Actors of the Stress Response. Int J Mol Sci (2019) 20(4):924. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040924
56. Zhou B, Yang H, Yang C, Bao YL, Yang SM, Liu J, et al. Translation of Noncoding RNAs and Cancer. Cancer Lett (2021) 497:89–99. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.002
57. Yang Y, Wang Z. IRES-Mediated Cap-Independent Translation, a Path Leading to Hidden Proteome. J Mol Cell Biol (2019) 11(10):911–9. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz091
58. Petkovic S, Müller S. RNA Circularization Strategies in-Vivo and in-Vitro. Nucleic Acids Res (2015) 43(4):2454–65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv045
59. Wang Y, Wang Z. Efficient Backsplicing Produces Translatable Circular mRNAs. RNA (2015) 21(2):172–9. doi: 10.1261/rna.048272.114
60. Liberman N, Gandin V, Svitkin YV, David M, Virgili G, Jaramillo M, et al. DAP5 Associates With Eif2β and Eif4ai to Promote Internal Ribosome Entry Site Driven Translation. Nucleic Acids Res (2015) 43(7):3764–75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv205
61. Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M, Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol Cell (2017) 66(1):9–21.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.021
62. Morino S, Imataka H, Svitkin YV, Pestova TV, Sonenberg N. Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4E (Eif4e) Binding Site and the Middle One-Third of Eif4gi Constitute the Core Domain for Cap-Dependent Translation, and the C-Terminal One-Third Functions as a Modulatory Region. Mol Cell Biol (2000) 20(2):468–77. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.2.468-477.2000
63. Chen CY, Sarnow P. Initiation of Protein Synthesis by the Eukaryotic Translational Apparatus on Circular RNAs. Science (1995) 268(5209):415–7. doi: 10.1126/science.7536344
64. Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, Song X, Wu P, Zhang Y, et al. Extensive Translation of Circular RNAs Driven by N6-Methyladenosine. Cell Res (2017) 27(5):626–41. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.31
65. Perriman R, Ares M. Circular mRNA can Direct Translation of Extremely Long Repeating-Sequence Proteins in-Vivo. RNA (1998) 4(9):1047–54. doi: 10.1017/s135583829898061x
66. Meyer KD, Patil DP, Zhou J, Zinoviev A, Skabkin MA, Elemento O, et al. 5’ UTR M(6)A Promotes Cap-Independent Translation. Cell (2015) 163(4):999–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.012
67. Zou Q, Xing P, Wei L, Liu B. Gene2vec: Gene Subsequence Embedding for Prediction of Mammalian N6-Methyladenosine Sites From mRNA. RNA (2019) 25(2):205–18. doi: 10.1261/rna.069112.118(66
68. Robinson M, Shah P, Cui YH, He YY. The Role of Dynamic M6 A RNA Methylation in Photobiology. PhotochemPhotobiol (2019) 95(1):95–104. doi: 10.1111/php.12930
69. Berlivet S, Scutenaire J, Deragon JM, Bousquet-Antonelli C. Readers of the M6a Epitranscriptomic Code. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech (2019) 1862(3):329–42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.12.008
70. Chen J, Zou Q, Li J. DeepM6ASeq-EL: Prediction of Human N6-Methyladenosine (M6a) Sites With LSTM and Ensemble Learning. Front Comput Sci (2022) 16. doi: 10.1007/s11704-020-0180-0
71. Shi Y, Jia X, Xu J. The New Function of circRNA: Translation. Clin Transl Oncol (2020) 22(12):2162–9. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02371-1
72. Greco S, Cardinali B, Falcone G, Martelli F. Circular RNAs in Muscle Function and Disease. Int J Mol Sci (2018) 19(11):3454. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113454
73. Feng Z, Meng S, Zhou H, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P, et al. Functions and Potential Applications of Circular RNAs in Cancer Stem Cells. Front Oncol (2019) 9:500:500. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00500
74. AbouHaidar MG, Venkataraman S, Golshani A, Liu B, Ahmad T. Novel Coding, Translation, and Gene Expression of a Replicating Covalently Closed Circular RNA of 220 Nt. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2014) 111(40):14542–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402814111 Erratum in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2016) 113(35):E5252-3.
75. Abe N, Hiroshima M, Maruyama H, Nakashima Y, Nakano Y, Matsuda A, et al. Rolling Circle Amplification in a Prokaryotic Translation System Using Small Circular RNA. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl (2013) 52(27):7004–8. doi: 10.1002/anie.201302044
76. Wu P, Mo Y, Peng M, Tang T, Zhong Y, Deng X, et al. Emerging Role of Tumor-Related Functional Peptides Encoded by lncRNA and circRNA. Mol Cancer (2020) 19(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1147-3
77. Yang Y, Gao X, Zhang M, Yan S, Sun C, Xiao F, et al. Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst (2018) 110(3):304–15. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx166
78. Xia X, Li X, Li F, Wu X, Zhang M, Zhou H, et al. A Novel Tumor Suppressor Protein Encoded by Circular AKT3 RNA Inhibits Glioblastoma Tumorigenicity by Competing With Active Phosphoinositide-Dependent Kinase-1. Mol Cancer (2019) 18(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1056-5 Erratum in: Mol Cancer. 2019 Oct 29;18(1):149.
79. Zhang M, Zhao K, Xu X, Yang Y, Yan S, Wei P, et al. A Peptide Encoded by Circular Form of LINC-PINT Suppresses Oncogenic Transcriptional Elongation in Glioblastoma. Nat Commun (2018) 9(1):4475. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06862-2
80. Buratti E, Baralle FE. TDP-43: New Aspects of Autoregulation Mechanisms in RNA Binding Proteins and Their Connection With Human Disease. FEBS J (2011) 278(19):3530–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08257.x
81. Legnini I, Di Timoteo G, Rossi F, Morlando M, Briganti F, Sthandier O, et al. Circ-ZNF609 Is a Circular RNA That Can Be Translated and Functions in Myogenesis. Mol Cell (2017) 66(1):22–37.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.017
82. Xiong Y, Zhang J, Song C. CircRNA ZNF609 Functions as a Competitive Endogenous RNA to Regulate FOXP4 Expression by Sponging miR-138-5p in Renal Carcinoma. J Cell Physiol (2019) 234(7):10646–54. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27744
83. Zhu L, Liu Y, Yang Y, Mao XM, Yin ZD. CircRNA ZNF609 Promotes Growth and Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Competing With microRNA-150-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci (2019) 23(7):2817–26. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201904_17558
84. Rossi F, Legnini I, Megiorni F, Colantoni A, Santini T, Morlando M, et al. Circ-ZNF609 Regulates G1-S Progression in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene (2019) 38(20):3843–54. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0699-4
85. Yada M, Hatakeyama S, Kamura T, Nishiyama M, Tsunematsu R, Imaki H, et al. Phosphorylation-Dependent Degradation of C-Myc is Mediated by the F-Box Protein Fbw7. EMBO J (2004) 23(10):2116–25. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600217
86. Tang T, Cheng Y, She Q, Jiang Y, Chen Y, Yang W, et al. Long non-Coding RNA TUG1 Sponges miR-197 to Enhance Cisplatin Sensitivity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. BioMed Pharmacother (2018) 107:338–46. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.076
87. Ye F, Gao G, Zou Y, Zheng S, Zhang L, Ou X, et al. Circfbxw7 Inhibits Malignant Progression by Sponging miR-197-3p and Encoding a 185-Aa Protein in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids (2019) 18:88–98. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.07.023
88. Zhang M, Huang N, Yang X, Luo J, Yan S, Xiao F, et al. A Novel Protein Encoded by the Circular Form of the SHPRH Gene Suppresses Glioma Tumorigenesis. Oncogene (2018) 37(13):1805–14. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0019-9
89. Unk I, Hajdú I, Fátyol K, Szakál B, Blastyák A, Bermudez V, et al. Human SHPRH is a Ubiquitin Ligase for Mms2-Ubc13-Dependent Polyubiquitylation of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2006) 103(48):18107–12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608595103
90. Qin M, Liu G, Huo X, Tao X, Sun X, Ge Z, et al. Hsa_circ_0001649: A Circular RNA and Potential Novel Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer biomark (2016) 16(1):161–9. doi: 10.3233/CBM-150552
91. Zhao J, Lee EE, Kim J, Yang R, Chamseddin B, Ni C, et al. Transforming Activity of an Oncoprotein-Encoding Circular RNA From Human Papillomavirus. Nat Commun (2019) 10(1):2300. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10246-5
92. Liang WC, Wong CW, Liang PP, Shi M, Cao Y, Rao ST, et al. Translation of the Circular RNA Circβ-Catenin Promotes Liver Cancer Cell Growth Through Activation of the Wnt Pathway. Genome Biol (2019) 20(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1685-4
93. Fatima S, Lee NP, Luk JM. Dickkopfs and Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling in Liver Cancer. World J Clin Oncol (2011) 2(8):311–25. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i8.311
94. Wang Y, Wang F. Post-Translational Modifications of Deubiquitinating Enzymes: Expanding the Ubiquitin Code. Front Pharmacol (2021) 12:685011. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.685011
95. Wang YA, Li XL, Mo YZ, Fan CM, Tang L, Xiong F, et al. Effects of Tumor Metabolic Microenvironment on Regulatory T Cells. Mol Cancer (2018) 17(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0913-y
96. Huang X, Li Z, Zhang Q, Wang W, Li B, Wang L, et al. Circular RNA AKT3 Up-Regulates PIK3R1 to Enhance Cisplatin Resistance in Gastric Cancer via miR-198 Suppression. Mol Cancer (2019) 18(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0969-3
97. Gu C, Zhou N, Wang Z, Li G, Kou Y, Yu S, et al. Circgprc5a Promoted Bladder Oncogenesis and Metastasis Through Gprc5a-Targeting Peptide. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids (2018) 13:633–41. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.10.008
98. Dorsam RT, Gutkind JS. G-Protein-Coupled Receptors and Cancer. Nat Rev Cancer (2007) 7(2):79–94. doi: 10.1038/nrc2069
99. Zheng X, Chen L, Zhou Y, Wang Q, Zheng Z, Xu B, et al. A Novel Protein Encoded by a Circular RNA Circppp1r12a Promotes Tumor Pathogenesis and Metastasis of Colon Cancer via Hippo-YAP Signaling. Mol Cancer (2019) 18(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1010-6
100. Wu WK, Wang XJ, Cheng AS, Luo MX, Ng SS, To KF, et al. Dysregulation and Crosstalk of Cellular Signaling Pathways in Colon Carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol (2013) 86(3):251–77. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2012.11.009
101. Zhi X, Zhang J, Cheng Z, Bian L, Qin J. Circlgr4 Drives Colorectal Tumorigenesis and Invasion Through Lgr4-Targeting Peptide. Int J Cancer (2019) 150(5):E3. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32549
102. Vermeulen L, De Sousa E Melo F, van der Heijden M, Cameron K, de Jong JH, Borovski T, et al. Wnt Activity Defines Colon Cancer Stem Cells and is Regulated by the Microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol (2010) 12(5):468–76. doi: 10.1038/ncb2048
103. Hong Y, Qin H, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhuang X, Liu L, et al. FNDC3B Circular RNA Promotes the Migration and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells via the Regulation of E-Cadherin and CD44 Expression. J Cell Physiol (2019) 234(11):19895–910. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28588
104. Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA, Thiery JP. EMT: 2016. Cell (2016) 166(1):21–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.028
105. Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell (2009) 139(5):871–90. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.007
106. Jolly MK, Boareto M, Huang B, Jia D, Lu M, Ben-Jacob E, et al. Implications of the Hybrid Epithelial/Mesenchymal Phenotype in Metastasis. Front Oncol (2015) 5:155. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00155
107. Leahy DJ, Hendrickson WA, Aukhil I, Erickson HP. Structure of a Fibronectin Type III Domain From Tenascin Phased by MAD Analysis of the Selenomethionyl Protein. Science (1992) 258(5084):987–91. doi: 10.1126/science.1279805
108. Pan Z, Cai J, Lin J, Zhou H, Peng J, Liang J, et al. A Novel Protein Encoded by Circfndc3b Inhibits Tumor Progression and EMT Through Regulating Snail in Colon Cancer. Mol Cancer (2020) 19(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01179-5
109. Li J, Ma M, Yang X, Zhang M, Luo J, Zhou H, et al. Circular HER2 RNA Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer is Sensitive to Pertuzumab. Mol Cancer (2020) 19(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01259-6
110. Li F, Cai Y, Deng S, Yang L, Liu N, Chang X, et al. A Peptide CORO1C-47aa Encoded by the Circular non-Coding RNA Circ-0000437 Functions as a Negative Regulator in Endometrium Tumor Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem (2021) 14:101182. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101182
111. Brosa M, García del MX, Mora J, Villacampa A, Pozo T, Adán C, et al. Economic Considerations On the Use of Mifamurtide In the Treatment of Osteosarcoma In Spain. Value Health (2014) 17(7):A526–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2014.08.1662
112. Berek JS. Interferon Plus Chemotherapy for Primary Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Lancet (2000) 356(9223):6–7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02422-3
113. Liang X, De Vera ME, Buchser WJ, Romo de Vivar Chavez A, Loughran P, Beer Stolz D, et al. Inhibiting Systemic Autophagy During Interleukin 2 Immunotherapy Promotes Long-Term Tumor Regression. Cancer Res (2012) 72(11):2791–801. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0320
114. Brogden KA, Ackermann M, McCray PB Jr, Tack BF. Antimicrobial Peptides in Animals and Their Role in Host Defences. Int J Antimicrob Agents (2003) 22(5):465–78. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(03)00180-8
115. Leader B, Baca QJ, Golan DE. Protein Therapeutics: A Summary and Pharmacological Classification. Nat Rev Drug Discov (2008) 7(1):21–39. doi: 10.1038/nrd2399
116. Xu Q, Guo Q, Wang CX, Zhang S, Wen CB, Sun T, et al. Network Differentiation: A Computational Method of Pathogenesis Diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on Systems Science. Artif Intell Med (2021) 118:102134. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102134
117. Efremova M, Finotello F, Rieder D, Trajanoski Z. Neoantigens Generated by Individual Mutations and Their Role in Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy. Front Immunol (2017) 8:1679. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01679
118. Radvanyi LG. Targeting the Cancer Mutanome of Breast Cancer. Nat Med (2018) 24(6):703–4. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0065-z
119. Zhao B, Zhang X, Yu T, Liu Y, Zhang X, Yao Y, et al. Discovery of Thiosemicarbazone Derivatives as Effective New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-1 (NDM-1) Inhibitors Against NDM-1 Producing Clinical Isolates. Acta Pharm Sin B (2021) 11(1):203–21. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.005
120. Papatsirou M, Artemaki PI, Scorilas A, Kontos CK. The Role of Circular RNAs in Therapy Resistance of Patients With Solid Tumors. Per Med (2020) 17(6):469–90. doi: 10.2217/pme-2020-0103
121. Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Venø MT, Kjems J. Circular RNAs in Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges in the Field. Oncogene (2018) 37(5):555–65. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.361
122. Panda AC, Gorospe M. Detection and Analysis of Circular RNAs by RT-PCR. Bio Protoc (2018) 8(6):e2775. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2775
123. Xu T, Wang M, Jiang L, Ma L, Wan L, Chen Q, et al. CircRNAs in Anticancer Drug Resistance: Recent Advances and Future Potential. Mol Cancer (2020) 19(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01240-3
124. Wang Y, Liu J, Ma J, Sun T, Zhou Q, Wang W, et al. ExosomalcircRNAs: Biogenesis, Effect and Application in Human Diseases. Mol Cancer (2019) 18(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1041-z
125. Fanale D, Taverna S, Russo A, Bazan V. Circular RNA in Exosomes. Adv Exp Med Biol (2018) 1087:109–17. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_9
126. Li S, Li Y, Chen B, Zhao J, Yu S, Tang Y, et al. Exorbase: A Database of circRNA, lncRNA and mRNA in Human Blood Exosomes. Nucleic Acids Res (2018) 46(D1):D106–12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx891
127. Bennett CF, Swayze EE. RNA Targeting Therapeutics: Molecular Mechanisms of Antisense Oligonucleotides as a Therapeutic Platform. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol (2010) 50:259–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.010909.105654
128. Wang J, Zhu S, Meng N, He Y, Lu R, Yan GR. ncRNA-Encoded Peptides or Proteins and Cancer. Mol Ther (2019) 27(10):1718–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.09.001
129. Ma S, Kong S, Wang F, Ju S. CircRNAs: Biogenesis, Functions, and Role in Drug-Resistant Tumours. Mol Cancer (2020) 19(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01231-4
130. Glažar P, Papavasileiou P, Rajewsky N. Circbase: A Database for Circular RNAs. RNA (2014) 20(11):1666–70. doi: 10.1261/rna.043687.113
131. Dong R, Ma XK, Li GW, Yang L. CIRCpedia V2: An Updated Database for Comprehensive Circular RNA Annotation and Expression Comparison. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf (2018) 16(4):226–33. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.08.001
132. Dudekula DB, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, De S, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M. CircInteractome: A Web Tool for Exploring Circular RNAs and Their Interacting Proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biol (2016) 13(1):34–42. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1128065
133. Liu YC, Li JR, Sun CH, Andrews E, Chao RF, Lin FM, et al. CircNet: A Database of Circular RNAs Derived From Transcriptome Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res (2016) 44(D1):D209–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv940
134. Wu SM, Liu H, Huang PJ, Chang IY, Lee CC, Yang CY, et al. Circlncrnanet: An Integrated Web-Based Resource for Mapping Functional Networks of Long or Circular Forms of Noncoding RNAs. Gigascience (2018) 7(1):1–10. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/gix118
135. Fan C, Lei X, Fang Z, Jiang Q, Wu FX. CircR2Disease: A Manually Curated Database for Experimentally Supported Circular RNAs Associated With Various Diseases. Database (Oxf) (2018) 2018:bay044. doi: 10.1093/database/bay044
136. Xia S, Feng J, Lei L, Hu J, Xia L, Wang J, et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Tissue-Specific Circular RNAs in the Human and Mouse Genomes. Brief Bioinform (2017) 18(6):984–92. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw081
137. Xia S, Feng J, Chen K, Ma Y, Gong J, Cai F, et al. CSCD: A Database for Cancer-Specific Circular RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res (2018) 46(D1):D925–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx863
138. Vo JN, Cieslik M, Zhang Y, Shukla S, Xiao L, Zhang Y, et al. The Landscape of Circular RNA in Cancer. Cell (2019) 176(4):869–881.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.021
139. Wu W, Ji P, Zhao F. CircAtlas: An Integrated Resource of One Million Highly Accurate Circular RNAs From 1070 Vertebrate Transcriptomes. Genome Biol (2020) 21(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02018-y
140. Liu M, Wang Q, Shen J, Yang BB, Ding X. Circbank: A Comprehensive Database for circRNA With Standard Nomenclature. RNA Biol (2019) 16(7):899–905. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1600395
141. Li L, Wu P, Wang Z, Meng X, Zha C, Li Z, et al. NoncoRNA: A Database of Experimentally Supported non-Coding RNAs and Drug Targets in Cancer. J Hematol Oncol (2020) 13(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00849-7
142. Zheng LL, Li JH, Wu J, Sun WJ, Liu S, Wang ZL, et al. Deepbase V2.0: Identification, Expression, Evolution and Function of Small RNAs, LncRNAs and Circular RNAs From Deep-Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res (2016) 44(D1):D196–202. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1273
Keywords: circRNAs, chimeric peptides/proteins, cancer, biomarkers, therapeutic target
Citation: Khan FA, Nsengimana B, Khan NH, Song Z, Ngowi EE, Wang Y, Zhang W and Ji S (2022) Chimeric Peptides/Proteins Encoded by circRNA: An Update on Mechanisms and Functions in Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 12:781270. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.781270
Received: 22 September 2021; Accepted: 10 January 2022;
Published: 11 February 2022.
Edited by:
Lianying Jiao, Xi’an Jiaotong University, ChinaCopyright © 2022 Khan, Nsengimana, Khan, Song, Ngowi, Wang, Zhang and Ji. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weijuan Zhang, endqdWFuMTk2NUBoZW51LmVkdS5jbg==; Shaoping Ji, c2hhb3BpbmdqaUBoZW51LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Faiz Ali Khan1,2,3
Faiz Ali Khan1,2,3 Bernard Nsengimana
Bernard Nsengimana Weijuan Zhang
Weijuan Zhang Shaoping Ji
Shaoping Ji