
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CASE REPORT article
Front. Oncol. , 05 January 2023
Sec. Genitourinary Oncology
Volume 12 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.1042459
This article is part of the Research Topic Case Reports in Genitourinary Oncology : 2022 View all 38 articles
Primary bladder mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma is an extremely rare bladder tumor. Only scarce reports have been reported. We hereby report a case of an 81-year-old female patient with bladder tumor presenting with frequent urination and dysuria, whose pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) considered bladder cancer. She underwent transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT), and histopathology confirmed the mass to be bladder MALT lymphoma. The patient refused further treatment, and no disease recurrence one year after surgery. The current data are insufficient to draw conclusions about the long-term efficacy of treatment for this tumor, regular follow-up is necessary. To further understand the clinical features, pathology, treatment and prognosis of this tumor, we have searched the literature from 1990 to the present, analyzing a total of 64 cases of primary MALT lymphoma.
Primary extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (NHLs) comprise approximately 10-20% of all NHL cases (1). The most common site of involvement is the gastrointestinal tract, followed by the head and neck, central nervous system, breast, thyroid, skin, bones, and testes. Primary lymphoma involving the bladder is very uncommon, accounting for less than 1% of all bladder tumors and only 0.2% of extranodal lymphomas (2). Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma is a unique subtype of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, which accounts for 7% to 8% of all B-cell lymphomas (3). Therefore, this tumor can easily be misdiagnosed until histologically confirmed. It needs to be clinically differentiated from other diseases including inflammatory lesions, bladder cancer and infection. There is no consensus on the optimal treatment strategy for primary bladder MALT lymphoma. Clinicians can choose surgery or/and radiation or/and chemotherapy based on the patient’s specific situation and their own clinical experience. Although the prognosis of primary bladder MALT lymphoma is good, the current data are insufficient to draw conclusions about the long-term efficacy of treatment for this tumor, regular follow-up is necessary. The present study reported a case of a bladder MALT lymphoma and reviewed the relevant literature to further understand the clinical characteristics, pathology, treatment and prognosis of primary MALT lymphoma, and to strengthen the awareness of this rare disease.
An 81-year-old woman was admitted with symptoms of frequent urination and painful urination. The patient’s symptoms started one month prior to her presentation, and she had no other symptoms. The patient did not undergo relevant examination and treatment. She follows a healthy daily diet, and no relatives in her family had similar illnesses. The patient’s vital signs were normal. Lymph node and abdomen physical examination showed no abnormalities. Urine analysis showed a red blood cell count of 79.4 cells/µl and a white blood cell count of 5071 cells/µl. Urine culture indicated Escherichia coli, and other indices were normal. Colour ultrasound showed a 29 mm×9 mm×19 mm hypoechoic mass in the posterior wall of the bladder, with a clear boundary and a regular form. CDFI: no blood flow signal in the mass was noted (Figure 1). Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging indicated bladder cancer (Figures 2A–H). Computed tomography (CT) of the chest and abdomen revealed no enlarged lymph nodes. The patient underwent transurethral resection of the bladder tumor after the use of antibiotics to control the urinary tract infection. During the operation, the right side and posterior bladder wall showed two nodular lesions with a size of approximately 20 mm×15 mm and 10 mm×10 mm, with a broad base and little bleeding upon resection, respectively (Figures 3A, B). Histopathological studies of the resected tumors revealed a large number of proliferating lymphocytes, mainly medium-sized lymphocytes, and some with an empty cytoplasm; lymphoid follicular hyperplasia with irregular enlargement of the marginal area was noted (Figures 4A, B). Immunohistochemical studies of the tumors showed that the lesion was positive for the expression of CD20, CD79a, BCL-2, Ki-67 and CD21 and negative for CD3, CD5, CD10, CD23, CD138, cyclin D1 and lambda (Figures 4C,D). The pathological diagnosis was consistent with MALT lymphoma. CT scans of the chest and abdomen did not reveal any lymphadenopathy or organ enlargement. Metastatic lesions were not detected. Therefore, the final diagnosis was primary bladder MALT lymphoma. According to the patient’s condition, we recommended the patient to undergo radiotherapy and chemotherapy, but considering the age and general condition of the patient, the patient and family refused further treatment. Therefore, regular follow-up of the patient was recommended. Six months and one year after the operation, no discomfort was reported. No obvious abnormality was detected by cystoscopy. Her follow-up chest and abdominal CT scans showed no abnormality, similar to the previous manifestations. However, the patient was advised to attend lifelong follow-up visits for regular reexaminations.
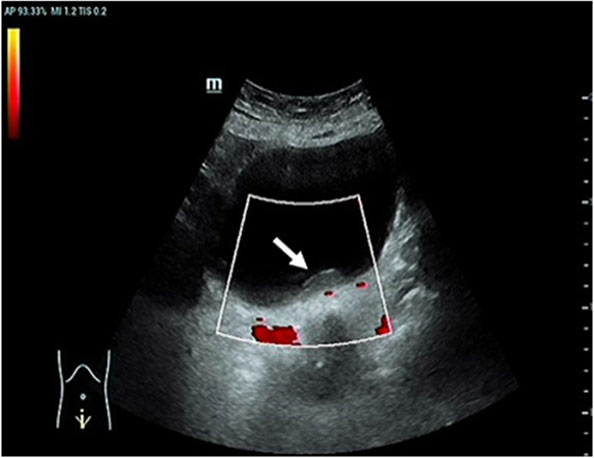
Figure 1 Color ultrasound. This image showed a hypoechoic mass in the posterior wall of the bladder. CDFI: no blood flow signal in the mass [arrow].
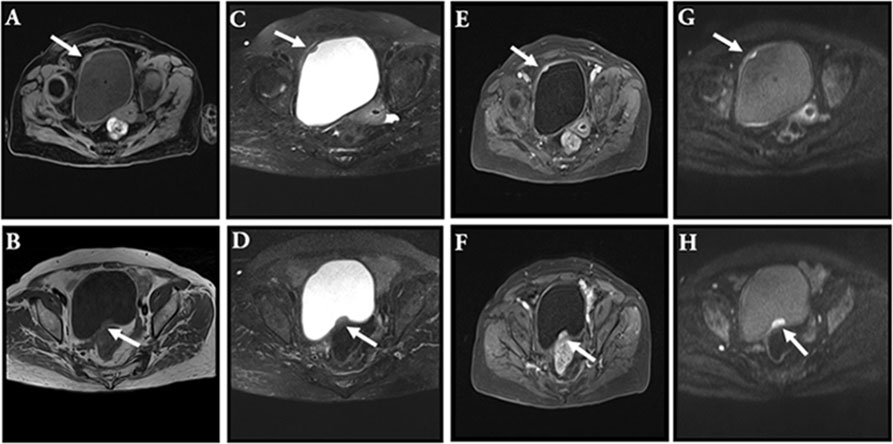
Figure 2 MRI. This image showed a space-occupying lesion with long T1 signal in the right anterior wall of the bladder [(A), arrow]; this image showed a space-occupying lesion with short T2 signal in the right anterior wall of the bladder [(C), arrow]; the enhancement scanning was even [(E), arrow]; diffusion was limited [(G), arrow]. This image showed a space-occupying lesion with long T1 signal in the posterior upper wall of the bladder [(B), arrow]; this image showed a space-occupying lesion with short T2 signal in the posterior upper wall of the bladder [(D), arrow]; the enhancement scanning was even [(F), arrow]; diffusion was limited [(H), arrow].
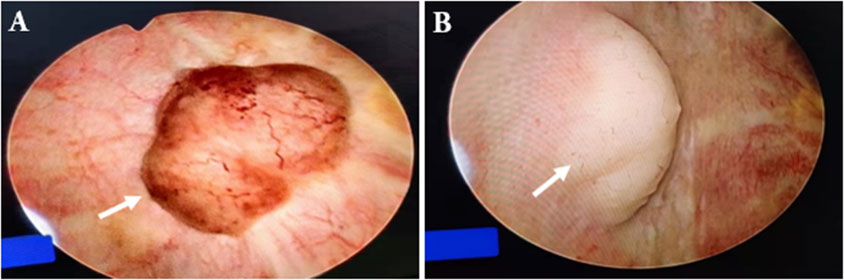
Figure 3 Cystoscope. This image showed a space-occupying lesion in the posterior upper wall of the bladder [(A), arrow]; this image showed a space-occupying lesion in the right anterior wall of the bladder [(B), arrow].
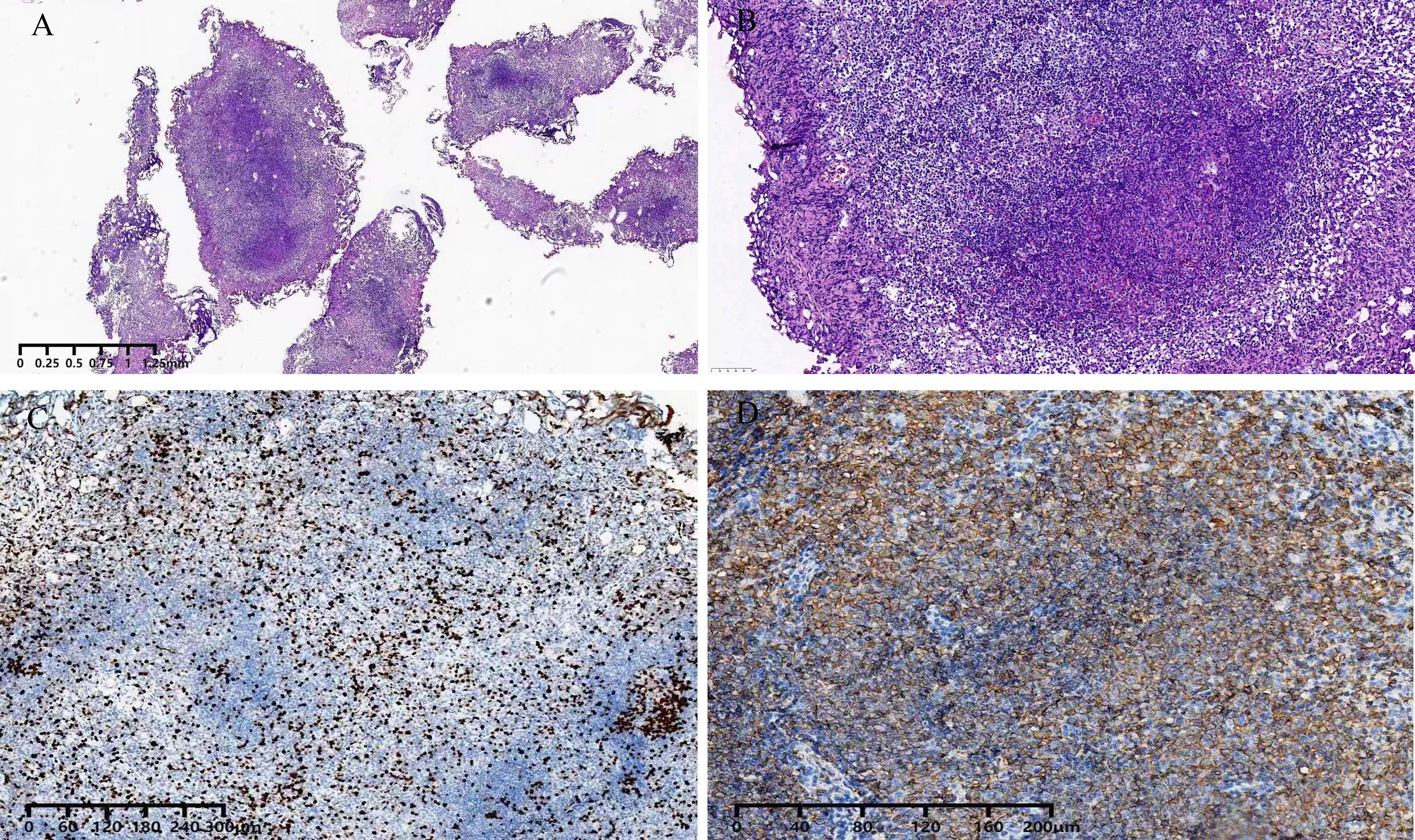
Figure 4 Pathology. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of a surgical specimen. demonstrated MALT lymphoma [(A, B)]; Immunohistochemical staining. demonstrated ki-67 expression (C). Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated. CD20 expression (D).
The PubMed database was systematically searched for bladder MALT lymphoma from 1990 to 2022. The following keywords were used: (bladder mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma) or (bladder MALT lymphoma), and 96 results were retrieved. After excluding secondary bladder mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma and review and unrelated studies, 44 articles describing 64 cases (11 men and 53 women) were finally identified. The ratio of male to female was 1:4.8. The mean age at onset was 65 years (range, 17 to 88 years). Twenty-eight of the 37 patients presented with solitary bladder nodules. Twenty-three patients were reported from Asia, of which 18 were from Japan (2, 4–20).28 cases were from Europe, most of them from the United Kingdom (21–27). Including our patient, only four cases had been reported in China (3, 28, 29). All patients had some urinary symptoms at the time of presentation. Most patients presented with hematuria. Escherichia coli was the most common pathogen.
There were various treatment strategies for primary bladder MALT lymphoma, including antibiotics, surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and combination therapy. Six patients achieved significant results after antibiotic treatment (11, 13, 25, 30–32). Eleven patients underwent some surgery with or without chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (3–5, 10, 16, 17, 19, 20, 33–35). The majority of patients (11) received chemotherapy either alone (30) or in combination with radiotherapy (22) (Table 1). Hughes et al. reported a patient who was successfully treated with diathermy (26). There was no information on treatment in the three cases. Overall, the treatment effect was good with the longest follow-up time of 156 months.
Lymphoma is a malignant tumor originating from lymphoid tissue. Due to the absence of lymphoid tissue in various organs of the urinary system, primary lymphoma involving the bladder is extremely rare, which primarily affected older women in our reviews, with a high proportion in Japan and the United Kingdom.
The precise mechanisms of primary bladder MALT lymphoma have not been clarified. Reportedly, 40% of patients with primary bladder lymphoma have a history of chronic cystitis, and Escherichia coli is the most common infectious agent (25, 48), which is consistent with the results of our systematic review. In addition, Morita et al. found that autoimmune interstitial cystitis is associated with the development of bladder MALT lymphoma (14).
The common pathological types of bladder lymphoma include low-grade mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue and high-grade diffuse large B cell type of lymphoma (DLBCL), while anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is rare. Most primary bladder MALT lymphomas have insidious onset, long course and no typical clinical manifestations. Gross hematuria is the most common clinical symptom, followed by frequent urination, urgency, and dysuria. The differential diagnosis is broad, including inflammatory lesions, bladder cancer, and infection. As a result, patients with this disease are often not diagnosed and treated timely. In addition, some cases of low-grade lymphoma are known to transform into high-grade DLBCL (4), which means that early diagnosis of MALT lymphoma is important to improve prognosis.
Bladder lymphoma usually grows at the base and the trigone of the bladder (35). Commonly, such lesions are initially misdiagnosed as bladder cancer. Imaging examinations usually can not provide much diagnostic information because of their low sensitivity. However, on cystoscopy, these tumors appear as well-defined intracapsular masses typically (33). Diagnosis depends on histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses. Typical MALT lymphoma cells often appear as small to medium-sized lymphocytes with moderate cell size and irregular nuclei, similar to follicular center cells, so they are called “centrocyte-like cells”. Immunohistochemical staining for MALT lymphoma is positive for CD20 and CD79a (3). In this case, the patient’s clinical symptoms, histopathology, and immunophenotype were consistent with MALT lymphoma.
To date, there is no consensus on the optimal treatment strategy for primary bladder MALT lymphoma. There are different therapeutic strategies available for primary bladder MALT lymphoma, depending on the clinical behavior of the tumor, the patient’s general condition, and life expectancy. In all of the cases in our review study, the majority of the patients had presented with localized lesions. A variety of treatment options have achieved a good prognosis. Combined with literature review, it is recommended that TURBT should be attempted first, followed by chemotherapy, or radiotherapy alone, or in combination. In our study, the patient underwent transurethral resection of the bladder tumor to remove the tumor and absence of recurrence at follow-up. All treatment regimens (R-CHOP, CHOP, ChlVP, ChlD) for bladder lymphoma have achieved significant efficacy; R-CHOP was the most frequently used. The R-CHOP chemotherapy regimen has achieved remarkable results in the treatment of both low-grade and high-grade primary bladder lymphomas as monotherapy or in combination therapy (35). Rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) has been shown to be effective in MALT lymphomas with response rates of 55% to 73% (49). Radiotherapy can be used for initial treatment, especially for low-grade or adjuvant treatment after resection (35). Although the prognosis of primary bladder MALT lymphoma is good. It is necessary to regularly follow-up patients who have MALT lymphoma. It must include at least urinary ultrasound and cystoscopy examination. Our reviews indicated that 52 patients were free of recurrence during follow-up of 3 months to 13 years. However, we need to accumulate more cases and long-term follow-up to help better understand the optimal treatment and prognosis of the disease.
My frequent and painful urination affected my quality of life and causes me great distress. The doctors helped me make the right diagnosis and chose minimally invasive surgery to completely remove the tumor and eliminated the symptoms of frequent and painful urination. My fear and worry about the tumor disappeared. I achieved physical and psychological healing. I think I’ve been treated very successfully.
We have described the clinical features, pathology, treatment and prognosis of primary bladder MALT lymphoma to further improve people’s understanding of this rare disease, and primary bladder MALT lymphoma should be included in the differential diagnosis of bladder neoplasm.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Chengdu Second People’s Hospital. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
XT was the patient’s urologists, reviewed the literature and contributed to manuscript drafting. XZ reviewed the literature and prepared figures. YQ, FL and CH were responsible for the revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
CT, Computed tomography; CDFI, Color doppler flow image; MRI, Magnetic resonance imaging; MALT, Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue; DLBCL, Diffuse large B cell type of lymphoma; ALCL, Anaplastic large cell lymphoma.
1. Sonmezer M, Ustun Y, Gungor M, Ensari A. Primary lymphoma of the urinary bladder presenting as a large pelvic mass. J Pak Med Assoc (2002) 52(5):228–30.
2. Matsuda I, Zozumi M, Tsuchida YA, Kimura N, Liu NN, Fujimori Y, et al. Primary extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type with malakoplakia in the urinary bladder: A case report. Int J Clin Exp Pathol (2014) 7(8):5280–4.
3. Xu HW, Chen ZS, Shen BX, Wei ZQ. Primary bladder mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: a case report and literature review. Medicine (2020) 99(28):e20825. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020825
4. Kuhara H, Tamura Z, Suchi T, Hattori R, Kinukawa T. Primary malignant lymphoma of the urinary bladder. a case report. Acta Pathol Jpn (1990) 40(10):764–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1990.tb01541.x
5. Ando K, Matsuno Y, Kanai Y, Sakamoto M, Fujimoto H, Narabayashi M, et al. Primary low-grade lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue ofthe urinary bladder: A case report with special reference to the use of ancillary diagnostic studies. Jpn J Clin Oncol (1999) 29(12):636–9. doi: 10.1093/jjco/29.12.636
6. Kawakami K, Oka K, Kato M, Shiku H. Whole-bladder irradiation and doxorubicin-containing chemotherapy as successful treatment for a primary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the bladder. Int J Hematol (2000) 72(3):346–8.
7. Takahara Y, Kawashima H, YS H, Sugimura N, Nakatani T, Tanaka K, et al. Primary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma of the urinary bladder. Hinyokika Kiyo (2005) 51(1):45–8.
8. Kakuta Y, Katoh T, Saitoh J, Yazawa K, Hosomi M, Itoh K. A case of primary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the bladder regressed after rituximab in combination with CHOP chemotherapy. Hinyokika Kiyo (2006) 52(12):951–4.
9. Hatano K, Sato M, Tsujimoto Y, Takada T, Honda M, Matsumiya K, et al. Primary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma of the urinary bladder associated with left renal pelvic carcinoma: a case report. Hinyokika Kiyo (2007) 53(1):57–60.
10. Ueno Y, Sakai H, Tsuruta T, Wajiki M. Mucosa-associated lymphoma of the bladder with relapse in the stomach after successful local treatment. Hinyokika Kiyo (2007) 53(8):575–9.
11. Fujimura M, Chin K, Sekita N, Kajimoto S, Kamijima S, Suzuki H, et al. Regression of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the bladder after antibiotic therapy: a case report. Hinyokika Kiyo (2008) 54(12):783–6.
12. Terasaki Y, Okumura H, Ishiura Y, Yokawa S, Kuribayashi M, Kodama K, et al. Primary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the urinary bladder successfully treated by radiotherapy and rituximab. Rinsho Ketsueki (2008) 49(1):30–4.
13. Terada T. Primary CD5-positive mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the urinary bladder. Ann Diagn Pathol (2011) 15(5):382–4. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2011.02.006
14. Morita K, Nakamura F, Nannya Y, Nomiya A, Arai S, Ichikawa M, et al. Primary MALT lymphoma of the urinary bladder in the background of interstitial cystitis. Ann Hematol (2012) 91(9):1505–6. doi: 10.1007/s00277-012-1419-0
15. Mizuno K, Nakanishi S, Sakatani T, Kimura R, Asai S, Okazoe H, et al. A case of primary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue-type lymphoma of the urinary bladder that progressed after antibiotic therapy. Hinyokika Kiyo (2013) 59(4):239–42.
16. Takahashi H, Shimazaki H, Oda T, Endo H, Sekitsuka H, Maekawa K, et al. Malignant lymphoma case with urinary cytology mimicking that of urothelial carcinoma. Cytopathology (2013) 24(6):412–4. doi: 10.1111/cyt.12026
17. Ozawa M, Suenaga S, Ishii T, Suzuki H, Tsuchiya N, Ohtake H. Primary malignant lymphoma of the bladder diagnosed by transurethral bladder tumor resection: A case report. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi (2018) 109(1):45–9. doi: 10.5980/jpnjurol.109.45
18. Isono M, Sato A, Kimura F, Asano T. A case of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the bladder successfully treated with radiotherapy. . Urol Case Rep (2017) 16:1–3. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2017.09.011
19. Yamamoto A, Nishikawa R, Hosoda R, Omura H, Tanaka T, Muraoka K, et al. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the bladder: Case report. Urol Case Rep (2021) 37:101623. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2021.101623
20. Ishibashi N, Nakanishi Y, Nishimaki H, Maebayashi T, Masuda S, Okada M. Bladder mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma progressed from chronic cystitis along with a comparative genetic analysis during long-term follow-up: a case report. Transl Androl Urol (2021) 10(10):3899–906. doi: 10.21037/tau-21-602
21. Pawade J, Banerjee SS, Harris M, Isaacson P, Wright D. Lymphomas of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue arising in the urinary bladder. Histopathology (1993) 23(2):147–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00472.x
22. Yuille FA, Angus B, Roberts JT, Vadanan BS. Low grade MALT lymphoma of the urinary bladder. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) (1998) 10(4):265–6. doi: 10.1016/S0936-6555(98)80016-2
23. Bates AW, AJ N, Baithun SI. Malignant lymphoma of the urinary bladder:a clinicopathological study of 11 cases. J Clin Pathol (2000) 53(6):458–61. doi: 10.1136/jcp.53.6.458
24. Wazait HD, Chahal R, Sundurum SK, Rajkumar GN, Wright D, Aslam MM. MALT-type primary lymphoma of the urinary bladder: clinicopathological study of 2 cases and review of the literature. Urol Int (2001) 66(4):220–4. doi: 10.1159/000056619
25. Oscier D, Bramble J, Hodges E, Wright D. Regression of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the bladder after antibiotic therapy. J Clin Oncol (2002) 20(3):882. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.20.3.882
26. Hughes M, Morrison A, Jackson R. Primary bladder lymphoma: management and outcome of 12 patients with a review of the literature. Leuk Lymphoma (2005) 46(6):873–7. doi: 10.1080/10428190500079829
27. Sen S, Macaulay JH, Allford SL. A case of cerebral arteriovenous malformation in pregnancy associated with MALT lymphoma. . J Obstet Gynaecol (2010) 30(3):308–10. doi: 10.3109/01443610903585234
28. Chen YR, Hung LY, Chang KC. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue-type lymphoma presenting as a urethral caruncle with urinary bladder involvement. Int J Urol (2014) 21(10):1073–4. doi: 10.1111/iju.12507
29. Hsu JS, Lin CC, Chen YT, Lee YC. Primary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the urinary bladder. Kaohsiung J Med Sci (2015) 31(7):388–9. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2015.04.001
30. van den Bosch J, Kropman RF, Blok P, Wijermans PW. Disappearance of a mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma of the urinary bladder after treatment for helicobacter pylori. Eur J Haematol (2002) 68(3):187–8. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0609.2002.01649.x
31. Kröber SM, Aepinus C, Ruck P, Müller-Hermelink HK, Horny HP, Kaiserling E. Extranodal marginal zone b cell lymphoma of MALT type involving the mucosa of both the urinary bladder and stomach. J Clin Pathol (2002) 55(7):554–7. doi: 10.1136/jcp.55.7.554
32. Lucioni M, Nicola M, Riboni R, Croci GA, Rattotti S, Gotti M, et al. Antibiotic therapy-induced remission of bladder mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma carrying t (11,18)(q21;q21) apoptosis inhibitor 2-MALT1. J Clin Oncol (2013) 31(19):e304–6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.4800
33. Maninderpal KG, Amir FH, Azad HA, Mun KS. Imaging findings of a primary bladder maltoma. Br J Radiol (2011) 84(1005):e186–90. doi: 10.1259/bjr/66130737
34. Vempati P, Knoll MA, Alqatari M, Strauchen J, Malone AK, Bakst RL. MALT lymphoma of the bladder: A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Hematol (2015) 2015:934374. doi: 10.1155/2015/934374
35. Bhutani DN, Goel DV, Kajal DP, Pawar DD, Sharma DP, Sen DR. Primary extra nodal non-hodgkin's lymphoma of urinary bladder presenting as a bladder tumor: A case report. Ann Med Surg (2020) 56:68–71. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2020.05.045
36. Fernández Aceñero MJ, Martín Rodilla C, López García-Asenjo J, Coca Menchero S, Sanz Esponera J. Primary malignant lymphoma of the bladder Report of three cases. Pathol Res Pract (1996) 192(2):164–5. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(96)80211-1
37. Kempton CL, Kurtin PJ, Inwards DJ, Wollan P, Bostwick DG. Malignant lymphoma of the bladder: evidence from 36 cases that low-grade lymphoma of the MALT-type is the most common primary bladder lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol (1997) 21(11):1324–33. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199711000-00007
38. Gallardo J, Gamargo C, Fodor M, Comparini B, Salman P, Yanez M. MALT lymphoma of the bladder: report of a case. Rev Med Chil (1998) 126(2):199–201.
39. Tasu JP, Geffroy D, Rocher L, Eschwege P, Strohl D, Benoit G, et al. Primary malignant lymphoma of the urinary bladder: report of three cases and review of the literature. Eur Radiol (2000) 10(8):1261–4. doi: 10.1007/s003300000343
40. Al-Maghrabi J, Kamel-Reid S, Jewett M, Gospodarowicz M, Wells W, Banerjee D. Primary low-grade b-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type arising in the urinary bladder: report of 4 cases with molecular genetic analysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med (2001) 125(3):332–6. doi: 10.5858/2001-125-0332-PLGBCL
41. Painemal Duarte C, Gallardo J, Valdebenito JP, Gamargo C, Rubio B, Harbst H. MALT lymphoma of the bladder Report of a case. . Arch Esp Urol (2001) 54(10):1138–40.
42. Bacalja J, Ulamec M, Rako D, Bošković L, Trnski D, Vrdoljak E, et al. Persistence of primary MALT lymphoma of the urinary bladder after rituximab with CHOP chemotherapy and radiotherapy. In Vivo (Brooklyn) (2013) 27(4):545–9.
43. Haddad-Lacle JE, Haddad CJ, Villas B. A rare urinary bladder tumour. BMJ Case Rep (2014) 16 2014:bcr2013202994. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-202994
44. Jitani AK, Mishra J, Sailo SL, Raphael V. Primary urinary bladder mucosa associated lymphoid tissue type lymphoma presenting as a close mimic for genitourinary tuberculosis: case report and review of literature. Urol Ann (2016) 8(1):108–10. doi: 10.4103/0974-7796.171491
45. Kadam PD, Han HC, Kwok JL. An uncommon case of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) tumor of the bladder. Int Urogynecol J (2018) 30(6):1017–8. doi: 10.1007/s00192-018-3813-1
46. Lyapichev KA, Ivashkevich Y, Chernov Y, Chinenov D, Shpot E, Bessonov AA, et al. MALT lymphoma of the urinary bladder shows a dramatic female predominance, uneven geographic distribution, and possible infectious etiology. Res Rep Urol (2021) 13:49–62. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S283366
47. Mandal S, Dadeboyina C, Baniya Sharma S, Dadeboyina S, Poulose J. A case of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the bladder: An extremely rare presentation. Cureus (2021) 13(7):e16767. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16767
48. Guthman DA, Malek RS, Chapman WR, Farrow GM. Primary malignant lymphoma of the bladder. J Urol (1990) 144(6):1367–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39743-4
Keywords: bladder, MALT lymphoma, NHL, diagnosis, treatment
Citation: Tu X, Zhuang X, Li F, Huang C and Qian Y (2023) Rare primary bladder mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: A case report and review of literature. Front. Oncol. 12:1042459. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1042459
Received: 12 September 2022; Accepted: 13 December 2022;
Published: 05 January 2023.
Edited by:
Haoran Liu, Stanford University, United StatesReviewed by:
Atsuto Katano, The University of Tokyo Hospital, JapanCopyright © 2023 Tu, Zhuang, Li, Huang and Qian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Youliang Qian, MjczMDI1NjI5MkBxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.