RAB42 Promotes Glioma Pathogenesis via the VEGF Signaling Pathway
- 1Central Laboratory, Key Laboratory of Tumor Biology, Key Laboratory of Neurophysiology, Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi, China
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi, China
- 3Neuropathological laboratory, Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi, China
- 4Department of Hematology, Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi, China
- 5Department of Neurology, Linyi People’s Hospital, Linyi, China
A corrigendum on:
RA B42 promotes glioma pathogenesis via the VEGF signaling pathway.
by Liu B, Su Q, Xiao B, Zheng G, Zhang L, Yin j, Wang L, Che F, Heng X (2021) Front. Oncol. 11:657029. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.657029
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 6. In Figure 6H, the author mistakenly uploaded the “Control” image as the “NC” image. The corrected Figure 6H appears below.
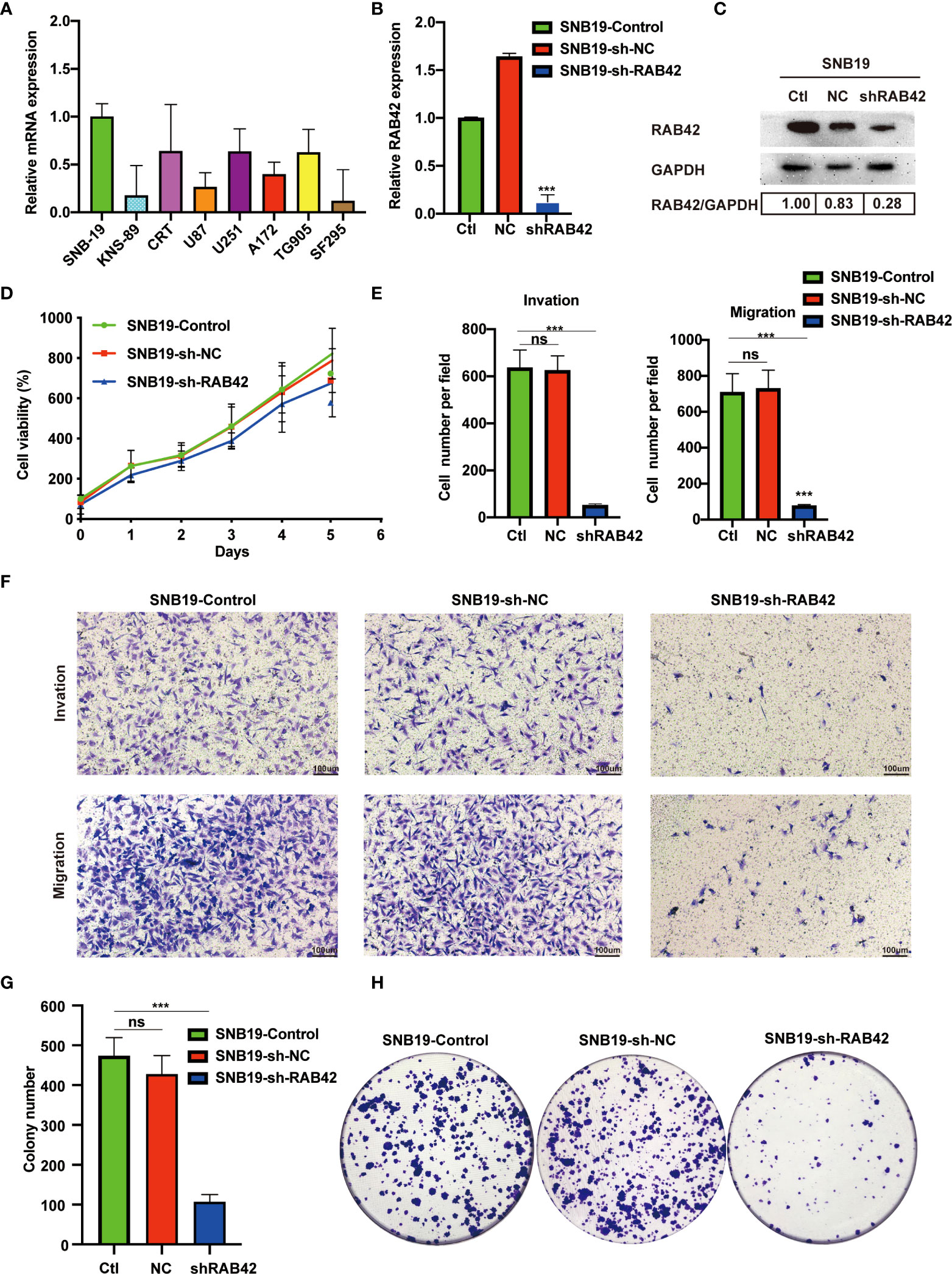
Figure 6 Validation of RAB42 gene functions in vitro. (A) Relative mRNA expression of SNB-19, KNS-89, CRT, U87, U251, A172, TG905 and SF295. (B) Relative expression of RAB42 in SNB19 cell lines after RAB42 knockdown (SNB19-sh-RAB42), parental cell line SNB19 (SNB19-Control) and control corresponding to the parental cell line transfected with the empty expression vector (SNB19-sh-NC). (C) Relative protein expression of SNB19-sh-RAB42, SNB19-Control and SNB19-sh-NC. (D) Cellular viability by CCK8 assay. (E) Quantification of invasion and migration assays. (F) Transwell invasion and migration assays. (G) Quantification of colony number in clonogenic assay. (H) Clonogenic assays. “ns” means “not significant”, *** means P < 0.001.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: glioma, RAB42, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), tumorigenesis, CGGA
Citation: Liu B, Su Q, Xiao B, Zheng G, Zhang L, Yin J, Wang L, Che F and Heng X (2022) Corrigendum: RAB42 promotes glioma pathogenesis via the VEGF signaling pathway. Front. Oncol. 12:1034167. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1034167
Received: 01 September 2022; Accepted: 21 September 2022;
Published: 07 October 2022.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Kamalakannan Palanichamy, The Ohio State University, United StatesCopyright © 2022 Liu, Su, Xiao, Zheng, Zhang, Yin, Wang, Che and Heng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lijuan Wang, d2FuZ2xqNzMwQDE2My5jb20=; Fengyuan Che, Y2hlMTk3MUAxMjYuY29t; Xueyuan Heng, eHVleXVhbmhlbmdAeWFob28uY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Baoling Liu
Baoling Liu Quanping Su1
Quanping Su1 Jiawei Yin
Jiawei Yin Lijuan Wang
Lijuan Wang Fengyuan Che
Fengyuan Che