- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education/Beijing), Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education), Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Radiology, Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education), Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China
By Li S, Zhang Y, Yu Y, Zhu X, Geng J, Teng H, Wang Z, Sun T, Wang L, Wang H, Li Y, Wu A, Cai Y and Wang W (2021). Front. Oncol. 10:627572. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.627572
In the original article, there was a mistake in the legend for Figure 1 and as published.
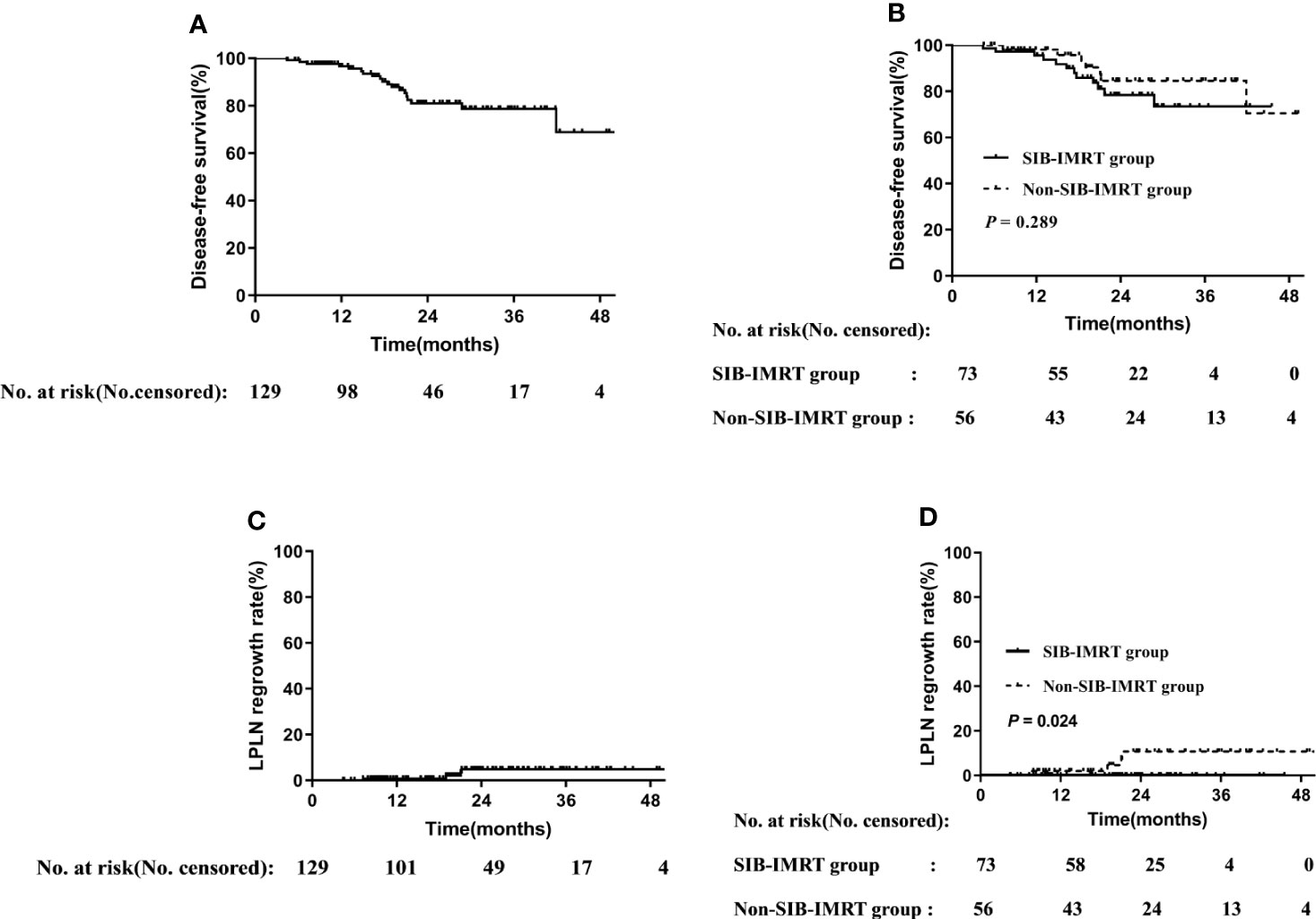
Figure 1 Disease-free survival rate in overall cohort (A) and in subgroups of whether receive SIB-IMRT (B). LPLN regrowth rate in the overall cohort (C) and in subgroups of whether receive SIB-IMRT (D).
The Figure 1D should be an increasing curve, consistent with Figure 1C. The data was correct, and the error occurred when choosing the curve. The correct legend appears below.
In the original article, there was a mistake in the legend for Figure 2 as published. The Figure 2 is same as Figure 1, which is inconsistent with the manuscript at the time of submission. The correct legend appears below.
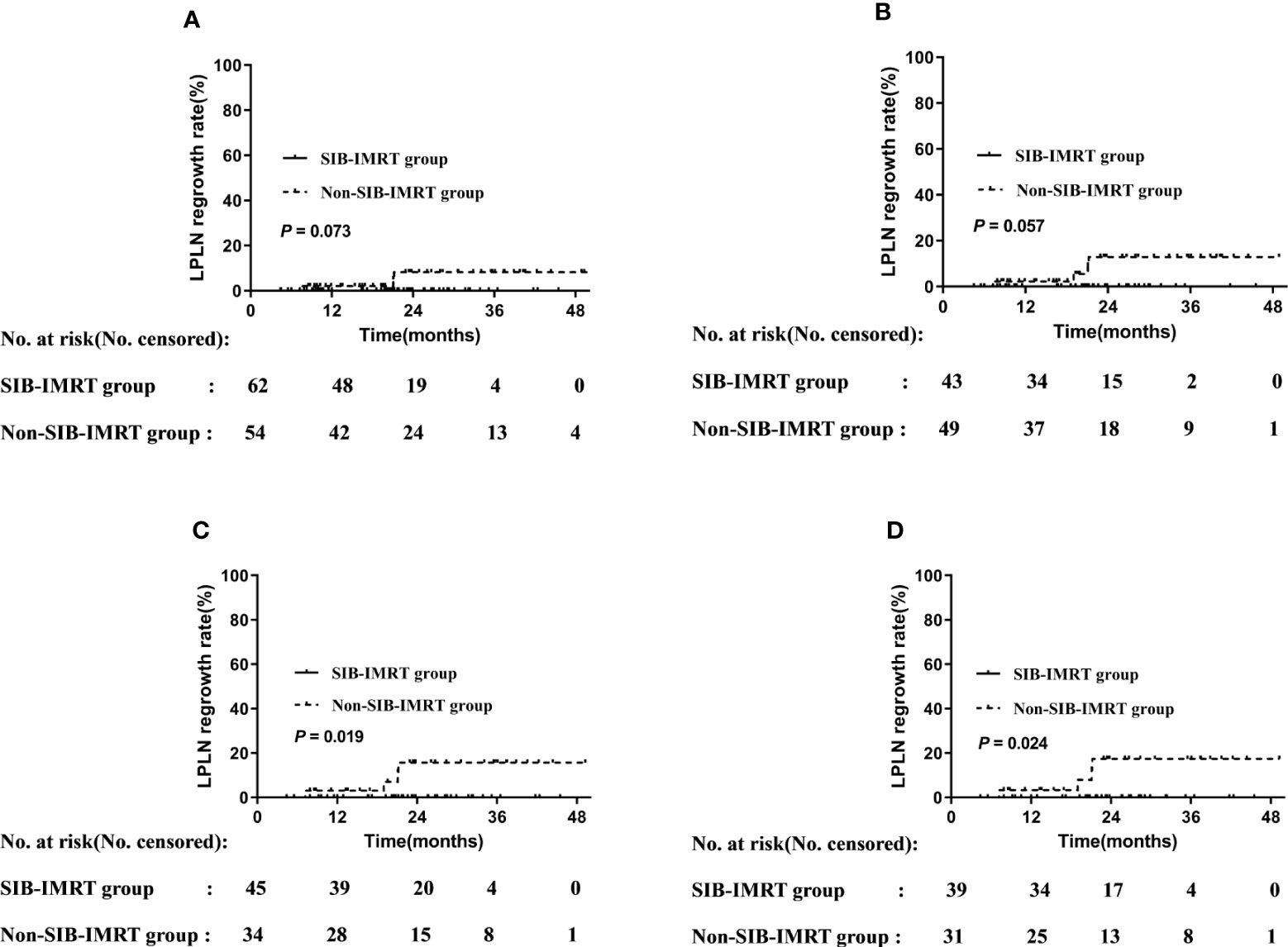
Figure 2 LPLN regrowth rate by subgroup. (A) Patients who did not undergo LPLD. (B) Patients administered synchronous single-agent chemotherapy. (C) Patients whose LPLN short axis was ≥8 mm. (D) Patients whose LPLN long axis was ≥10 mm.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: simultaneous integrated boost intensity-modulated radiation therapy, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, lateral pelvic lymph node, local advanced rectal cancer, regrowth rate, disease-free survival
Citation: Li S, Zhang Y, Yu Y, Zhu X, Geng J, Teng H, Wang Z, Sun T, Wang L, Wang H, Li Y, Wu A, Cai Y and Wang W (2021) Corrigendum: Simultaneous Integrated Boost Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy Can Benefit the Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Patients with Clinically Positive Lateral Pelvic Lymph Node. Front. Oncol. 11:790945. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.790945
Received: 07 October 2021; Accepted: 26 November 2021;
Published: 14 December 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Alessio G. Morganti, University of Bologna, ItalyCopyright © 2021 Li, Zhang, Yu, Zhu, Geng, Teng, Wang, Sun, Wang, Wang, Li, Wu, Cai and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weihu Wang, d2FuZ3dlaWh1ODhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Yong Cai, Y2FpeW9uZzEwOUBzb2h1LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shuai Li
Shuai Li Yangzi Zhang1†
Yangzi Zhang1† Yang Yu
Yang Yu Huajing Teng
Huajing Teng Lin Wang
Lin Wang Yongheng Li
Yongheng Li Aiwen Wu
Aiwen Wu Weihu Wang
Weihu Wang