- 1Department of Medical Oncology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Anticancer Drugs and Biotherapy of Liaoning Province, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 3Liaoning Province Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Shenyang, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Tumors, Ministry of Education, Shenyang, China
- 5Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
A Corrigendum on
CircHIPK3 Promotes Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via miR-653-5p/miR-338-3p-NRP1 Axis Under a Long-Term Hypoxic Microenvironment
By Jin Y, Che X, Qu X, Li X, Lu W, Wu J, Wang Y, Hou K, Li C, Zhang X, Zhou J and Liu Y (2020). 10:1612. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01612
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 2D as published. The picture of migration of sicircHIPK3 in BGC823/Hypo cells in Figure 2D was misused. The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
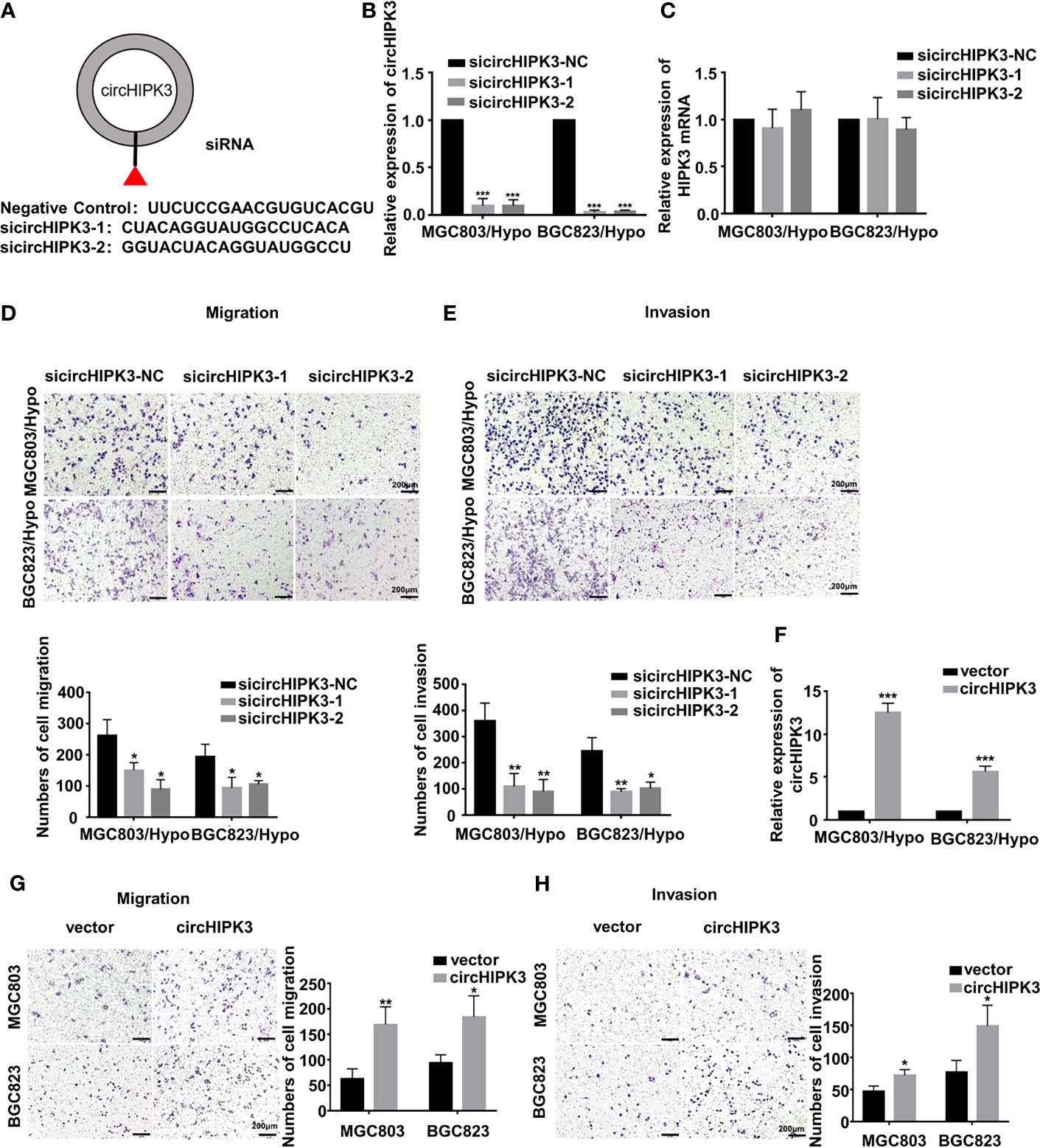
Figure 2 CircHIPK3 promoted migration and invasion of HRGC cells. (A) The sequence of two siRNAs targeted to back-splicing site of circHIPK3 and the negative control siRNA. (B, C) The relative expression of circHIPK3 and linear HIPK3 mRNA in HRGC cells after transfected with negative control siRNA (siNC) or circHIPK3 siRNAs was detected by qRT-PCR. 18S was used as an internal control. (D, E) The migration and invasion ability of HRGC cells after transfected with siNC or circHIPK3 siRNAs was examined by transwell assay (original magnification, 100×). The columns on the down panels are quantified by counting 3 fields, and presented as the mean ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (F) The overexpression efficiency of circHIPK3 in MGC803 and BGC823 cells was detected by qRT-PCR. 18S was used as an internal control. (G, H) The migration and invasion ability of MGC803 and BGC823 cells after transfected with circHIPK3 overexpression plasmids and empty vectors was examined by transwell assay (original magnification, 100×). The columns on the right are quantified by counting three fields, and presented as the mean ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: CircHIPK3, long-term hypoxic microenvironment, HIF-2α, gastric cancer, metastasis
Citation: Jin Y, Che X, Qu X, Li X, Lu W, Wu J, Wang Y, Hou K, Li C, Zhang X, Zhou J and Liu Y (2021) Corrigendum: CircHIPK3 Promotes Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via miR-653-5p/miR-338-3p-NRP1 Axis Under a Long-Term Hypoxic Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 11:783320. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.783320
Received: 29 September 2021; Accepted: 29 October 2021;
Published: 12 November 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Bin Li, Jinan University, ChinaCopyright © 2021 Jin, Che, Qu, Li, Lu, Wu, Wang, Hou, Li, Zhang, Zhou and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianping Zhou, empwaGFtYUAxNjMuY29t; Yunpeng Liu, eXBsaXVAY211LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yue Jin1,2,3,4†
Yue Jin1,2,3,4† Xiaofang Che
Xiaofang Che Wenqing Lu
Wenqing Lu Jie Wu
Jie Wu Yizhe Wang
Yizhe Wang Ce Li
Ce Li Jianping Zhou
Jianping Zhou Yunpeng Liu
Yunpeng Liu