- Department of Hematopathology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, United States
Next generation sequencing (NGS) is routinely used for mutation profiling of acute myeloid leukemia. The extensive application of NGS in hematologic malignancies, and its significant association with the outcomes in multiple large cohorts constituted a proof of concept that AML phenotype is driven by underlying mutational signature and is amenable for targeted therapies. These findings urged incorporation of molecular results into the latest World Health Organization (WHO) sub-classification and integration into risk-stratification and treatment guidelines by the European Leukemia Net. NGS mutation profiling provides a large amount of information that guides diagnosis and management, dependent on the type and number of gene mutations, variant allele frequency and amenability to targeted therapeutics. Hence, molecular mutational profiling is an integral component for work-up of AML and multiple leukemic entities. In addition, there is a vast amount of informative data that can be obtained from routine clinical NGS sequencing beyond diagnosis, prognostication and therapeutic targeting. These include identification of evidence regarding the ontogeny of the disease, underlying germline predisposition and clonal hematopoiesis, serial monitoring to assess the effectiveness of therapy and resistance mutations, which have broader implications for management. In this review, using a few prototypic genes in AML, we will summarize the clinical applications of NGS generated data for optimal AML management, with emphasis on the recently described entities and Food and Drug Administration approved target therapies.
Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (1) is a clonal malignant expansion of immature myeloid precursors due to block in differentiation. Mutation profiling is standard for routine baseline clinical evaluation of AML. Prior to 2008, there were two functional genetic groups for leukemic pathogenesis: class I (activated signaling genes such as FLT3, KIT and RAS mutations) that conferred the proliferative potential, and class II genes involved in transcription and differentiation such as CEBPA and RUNX1 (2). The development of high-throughput NGS sequencing platforms uncovered many somatic mutations in AML. In 2013, the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project expanded the functional genetic classes to nine families involved in the pathogenesis of the myeloid neoplasms. An average of 14 mutations were identified in the AML genome, ranging between five to 23 genetic mutations in each case (3). In 2016, a large cohort that enrolled 1540 AML patients described 11 subgroups of genomic alterations with different clinical outcomes using NGS. The additional separate categories included AML with mutations in genes encoding chromatin and RNA-splicing regulators, AML with TP53 mutations and/or chromosomal aneuploidies, and AML with IDH2 R172 mutations (4). Taken together, these findings supported the fact that AML phenotype is driven by underlying mutational signature (Figure 1).
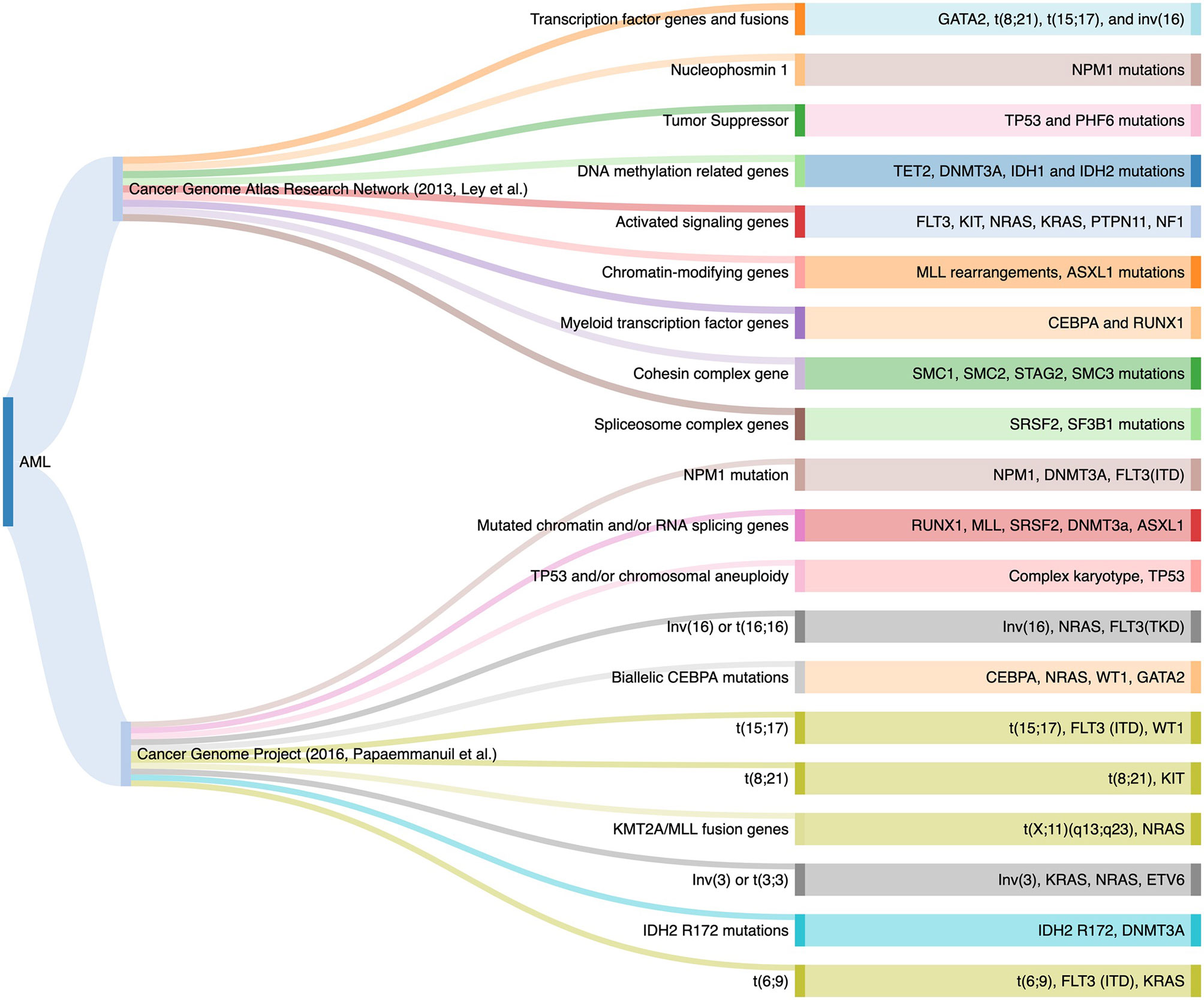
Figure 1 Genomic Classifications of Acute Myeloid Leukemia as Proposed by the TCGA Project and the 2016 Study.
Accordingly, both the 2016 revisions to the WHO and 2017 European LeukemiaNet (5) incorporated gene mutations into the sub-classification and risk-stratification of AML (6, 7). Molecular testing plays a major role in the current World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms. Specific genetic abnormalities are regarded as disease-defining mutations and others have important prognostic and therapeutic implications. The WHO recognizes 3 distinct sub-categories of AML based on somatic mutations: AML with NPM1 mutation, AML with bi-allelic mutations of CEBPA, and AML with mutated RUNX1 (provisional entity). Genes such as TP53, RUNX1, IDH1/2 and FMS-related tyrosine kinase 3 (8), among others, are found to be altered in the different subcategories of AML with prognostic and/or therapeutic implications of utmost importance. The latest 2017 European Leukemia Net (ENL) guidelines for AML recommends molecular profiling for mutations in NPM1, CEBPA, FLT3-ITD, TP53, RUNX1, ASXL1, and BCR-ABL1. Therefore, the complete cytogenetic and molecular work-up is essential at the time of initial AML evaluation. The main goal of genome sequencing is the identification of actionable gene mutations and risk-stratification. Hence, multi-gene panel next-generation sequencing (NGS) based mutation analysis is the primary mode for assessment for multiple AML associated genes (9).
In this review, we will provide an overview of the diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic data that can be obtained from routine clinical NGS data in AML. In addition, we will describe the implications of the vast amount of additional data that can be obtained from routine clinical NGS beyond prognostication and management, such as the ontogeny of AML, clues regarding underlying germline predisposition and clonal hematopoiesis, serial monitoring to assess the effectiveness of therapy and resistance mutations. We will use a few prototypic genes for each section, with emphasis on the recently described entities and actionable mutations, specifically pertaining to the Food and Drug Administration (10) approved target therapies and the ongoing clinical trials. AML-defining translocations are beyond the scope of this review.
Genetic Alterations With FDA-Approved Targeted Therapies
AML With Mutated FLT3
Category: activated signaling genes.
Clinicopathologic and morphologic features: Leukocytosis.
Recommended method of testing: NGS for tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) mutations (25) and small internal tandem duplications (8), Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) followed by capillary electrophoresis (CE) for medium and large internal tandem duplications (8, 31).
FLT3 is a receptor with tyrosine kinase (TK) activity, involved in proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitors. The associated mutations generally affect the juxta-membrane and the TK domain of the receptor. Broadly, mutations in FLT3 are of two types: FLT3-ITD which is the most frequent alteration, and FLT3-TKD which consists of a point mutation in the TK domain (25).
FLT3-ITD
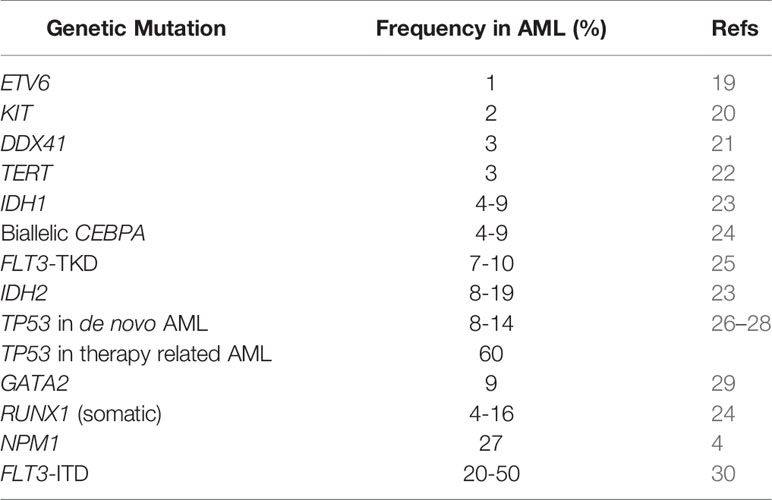
FLT3-ITD are in-frame mutations which consist of duplication of small sequences, ranging from 3 to larger than 400 base pairs resulting in a receptor with an elongated juxta-membrane domain. This leads to constitutive activation of the receptor and activation of intracellular pathways resulting in cellular proliferation (25, 32). The frequency of FLT3-ITD mutations in AML ranges from 20-50% (30). FLT3-ITD is associated with proliferative AML with a high WBC count (25). The prognostic implication of the mutation is dependent on the allelic burden (33). The allele burden of FLT3-ITD can be measured using one of the two parameters (10): allele ratio (AR), defined as the ratio of the area under the curve of mutant to wild-type and (2) allele frequency (AF) which is defined as the ratio of the area under the curve of mutant to total (mutant + wild-type). The 2017 ELN adopts a cut-off of 0.5 to differentiate between low versus high AR (34). AML patients with high AR FLT3-ITD had significantly low complete remission (CR) rates, with poor survival and relapse; only high FLT3-ITD AR patients (≥0.5) benefited from allogeneic stem cell transplantation (32). Per ELN, NPM1 mutated AML with FLT3-ITD AR <0.5 is considered as a favorable prognostic subgroup, similar to AML with absent FLT3-ITD mutation, and stem cell transplant is not recommended (34).
FLT3-TKD
FLT3-TKD mutations are less common than the FLT3-ITD; they consist mainly of missense point mutations, deletions or insertions within the TK domain. The most frequent alteration is a point mutation involving nucleotide substitution on codon 835. NGS can identify numerous mutations outside of D835, including deletions. The definitive implications of these various FLT3-TKD in prognostic stratification are still under review (25).
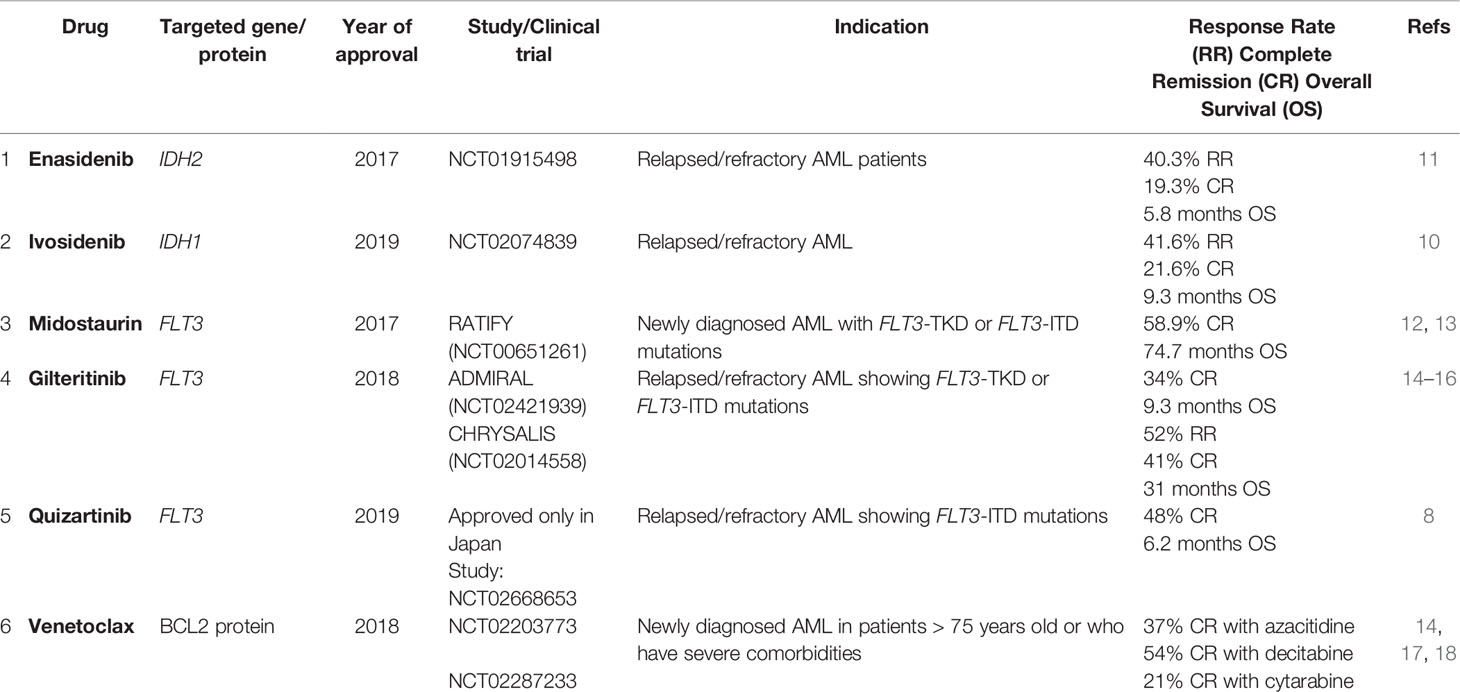
FLT3 mutations can be targeted using tyrosine kinase inhibitor drugs in combination with standard chemotherapy. The addition of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), Midostaurin, to standard chemotherapy protocol for AML led to significantly longer overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) in three FLT3 subgroups: FLT3-TKD, FLT3-ITD low and FLT3-ITD high AR (RATIFY-NCT00651261) (12). Midostaurin, the first FDA approved targeted therapy in AML, is a non-selective first generation TKI that targets multiple other pathways including c-KIT, PKC, PDGFR, VEGFR, resulting in higher toxicity (13). In 2018, a more selective “second-generation” FLT3 inhibitor, Gilteritinib, with fewer side-effects received FDA approval for relapsed or refractory FLT3-ITD or FLT3-TKD mutations-positive AML (14) based on the results of ADMIRAL (NCT02421939) and CHRYSALIS (NCT02014558) clinical trials, both of which demonstrated significantly improved outcomes in the Gilteritinib group (15, 16). Other first and second generation of inhibitors for FLT3 such as Sorafenib (NCT01398501) (31) and Quizartinib (NCT02668653) (in newly diagnosed AML) (8), have currently reached late stages of clinical testing.
While NGS is ideal for identification of mutations across the entire coding region, specifically FLT3 TKD mutations and small FLT3 ITDs, amplicon-based targeted NGS is unable to pick up majority of the medium to larger ITDs. Hence, ITD mutations are always tested concurrently by PCR followed by fragment analysis using capillary electrophoresis (CE). Alternate computational algorithms, such as Pindel to analyze NGS data have shown promising results with 100% sensitivity and specificity in detecting medium and large insertions at 1% VAF (35). Pindel is a pattern growth algorithm to detect breakpoints of medium and large alterations from paired-end short reads (36).
Resistance mutations to FLT3 inhibitors can emerge over the course of therapy via activation of alternative alternate intracellular pathways. Certain type II (second generation) FLT3 inhibitors do not have activity against TKD mutations, therefore the emergence of a FLT3-TKD mutation during treatment, particularly FLT3 D835 mutation would confer resistance to TKI (16). Crenolanib is a second generation inhibitor with activity against ITD and TKD mutations, hence, able to overcome the treatment resistance resulting from FLT3-TKD alteration (25). Other mechanisms of resistance to FLT3 inhibitors include the emergence of leukemia clones harboring mutations that activate RAS/MAPK pathway signaling, or BCR-ABL1 fusions (37). Hence, sequential mutation analysis is important for early detection of these resistant clone to modulate the therapy accordingly, prior to overt morphologic relapse (Tables 1, 2 and Figure 2).
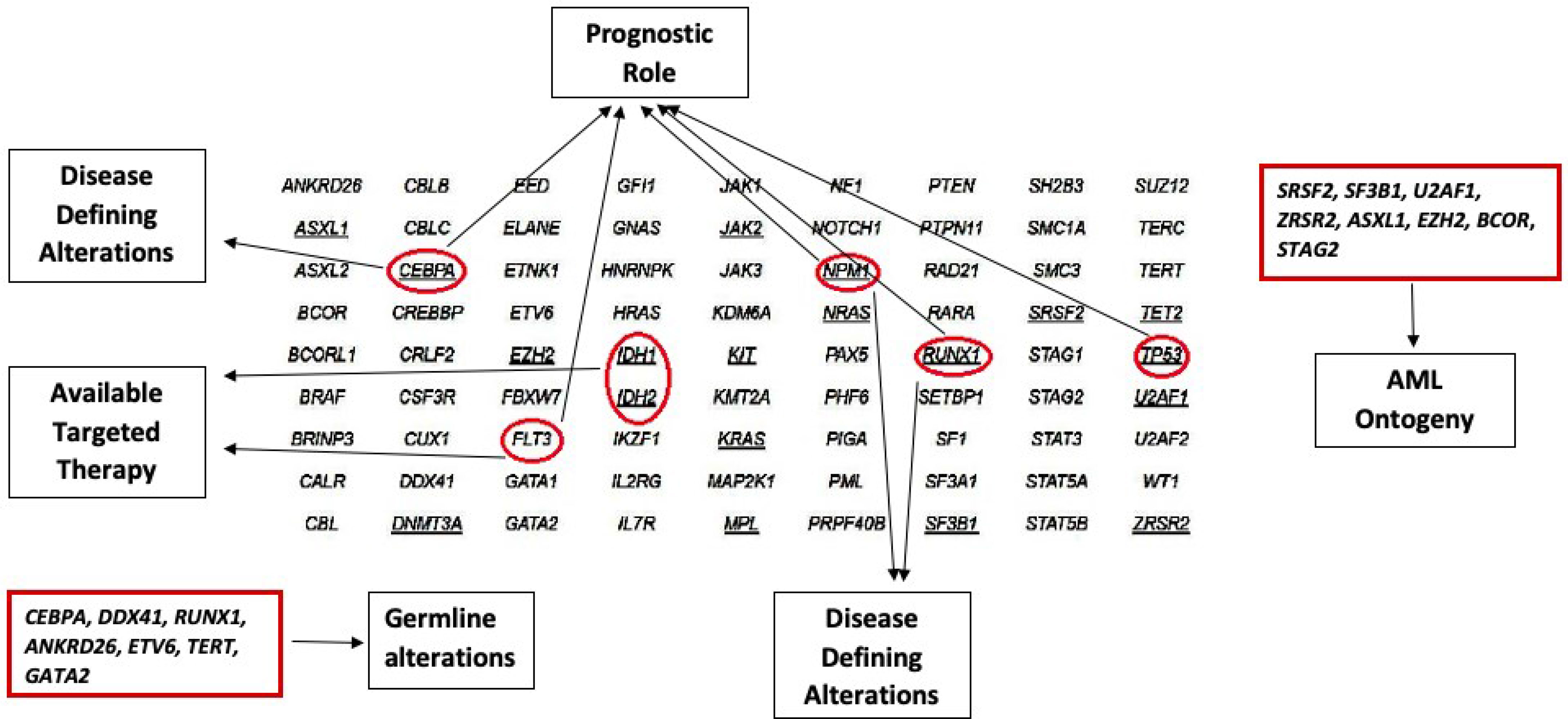
Figure 2 Role of different Genetic Alterations as Diagnostic, and Prognostic markers, as well as the Availability of Targeted Therapy.
AML With Mutated IDH1 and IDH2
Category: DNA methylation related.
Clinicopathologic and morphologic features: AML without maturation [French-American-British classification (FAB) M1], AML with maturation (FAB M2), and acute monocytic leukemia (FAB M5).
Recommended method of testing: NGS, droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) for MRD (38).
IDH1 and IDH2 are DNA methylation genes; the mutations in IDH induce dysregulation of epigenetic methylation particularly the function of the TET family of methylators. These aberrations will ultimately result in muting the pathways involved in differentiation of hematopoietic progenitors leading to maturation arrest (5). Moreover, IDH mutations diminish the DNA repair mechanism and result in the accumulation of secondary mutations (39). IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are associated with AML in 4–9% and 8–19% of the cases respectively; they are generally a founding clone sufficient to cause overt leukemia without additional genetic alterations (23). The hotspot mutations involve amino-acid substitutions at codon 132 in exon 4 of the IDH1 gene and codons 140 or 172 in exon 4 of IDH2. IDH2-R172 is mutually exclusive with NPM1 mutation and is regarded as an independent sub-category by genomic analysis, but not currently recognized by the WHO (40).
Similar to FLT3, mutations in IDH1/2 are a prototypic example of targeted therapy in AML. Enasidenib is an oral selective inhibitor of mutant IDH2 enzyme variants R140Q, R172S, and R172K (11); it was FDA approved in 2017 for the treatment of relapsed/refractory AML patients (11). Ivosidenib targets mutant IDH1enzyme leading to normal differentiation and maturation of malignant cells, and was FDA approved in 2019 for treatment of relapsed/refractory AML cases (10).
Despite the presence of hotspot mutations, NGS is ideally suited for baseline identification, serial monitoring of response to therapy and relapse emergence. Droplet digital PCR for specific mutations during serial monitoring can provide a higher sensitivity than standard NGS, however, can miss detection new emerging mutations (Tables 1, 2 and Figure 2).
AML With Mutated KIT
Category: Kinase signaling pathway.
Clinicopathologic and morphologic features:
Seen mostly in core-binding factor (CBF) leukemias that encompass AML with inv(16) and t(8;21). In the absence of either translocations, detection of KIT mutation is a helpful clue to search for underlying mastocytosis.
Recommended method of testing: 1-(10) Allele-specific PCR to detect exon 17 D816V specifically (41); 2- NGS (preferred) or other sequencing techniques covering for exons 17 and 8.
Activating mutations of KIT (encoding a transmembrane glycoprotein) leading to constitutional activation of receptor tyrosine kinase pathway, similar to systemic mastocytosis, GIST and germ cell tumors, are most commonly observed in “core binding factor” (CBF) leukemias which encompass AML with t(8;21) and AML with inv(16). Gain of function mutations in KIT have been found in 2% of AML overall and in a 33% of the CBF leukemias. These mutations tend to occur within exon 17, most importantly the hotspot D816, and exon 8 of the KIT gene (42).
Although CBF-AML has a favorable overall prognosis, most reports indicate that co-occurrence of KIT mutations confer an adverse prognosis in AML with both inv(16) and t(8;21), and a higher incidence of relapse in AML with inv(16) (41–44).
Therefore, CBF-AML with KIT mutations has been reclassified into intermediate-risk group in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommendations (43). Nevertheless, data is still unclear since some authors attributed the negative prognostic effect of KIT alterations to only those present at an allelic burden higher than 25% or 35% (43, 45, 46).
Moreover, the prognostic effect of KIT mutation in pediatric CBF AML patients is still uncertain (47).
Given the prognostic implication of the gain-of-function KIT mutations, and over-expression of KIT observed in most CBF-AML including those with KIT mutations (48), studies have explored the addition of KIT inhibitors such as dasatinib and avapritinib to frontline therapy (49) to improve the outcome. Results are promising in terms of reducing relapse rates of KIT mutated CBF-AML to levels comparable to non-KIT mutated CBF AML (49) (Tables 1, 2 and Figure 2).
WHO Classification Defining Genetic Mutations
AML With Mutated NPM1
Category: DNA replication and cell cycle.
Clinicopathologic and morphologic features: monocytic/myelomonocytic phenotype; blasts with classical fish-mouth morphology.
Recommended method of testing: NGS, PCR followed by CE (50), ddPCR for serial monitoring (51).
NPM1 is a molecular chaperone involved in cell cycle progression with multiple critical functions including ribosome biogenesis and transport, apoptotic response to stress stimuli, maintenance of genomic stability, and DNA repair (52). NPM1 mutations are the most common genetic alteration in AML occurring in 25% to 41% of cases (53). These alterations affect exclusively the C-terminal region, leading to cytoplasmic mis-localization of the NPM1 and leukemogenesis induction by inhibition of p53 activity (54). The most frequent mutation is a 4 base pair insertion of TCTG at position 956–959 (55). Multiple gene variants of NPM1 have been identified, all engendering the same biological effect. They are mostly associated with normal karyotype, and they are mutually exclusive with other known recurrent genetic abnormalities including RUNX1 and CEBPA. Interestingly, NPM1 mutations co-occur with mutations in epigenetic modifiers including DNMT3A, TET2 and IDH1/2 in 73% of the cases (55); these epigenetic alterations, unlike NPM1, are usually identified in pre-leukemic cells, and NPM1 mutations are believed to be a later occurrence (56). NPM1 mutated AML is considered a distinct biological subtype of AML in the latest (2016) WHO classification (57). In the settings of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasms (MDS/MPN), independent studies have suggested that the presence of NPM1 mutation should be an AML-defining mutation, irrespective of the blast percentage, since these patients benefit from AML-type treatment with intensive chemotherapy (58, 59).
NPM1 mutated AML is generally considered a favorable prognostic marker with good response to induction therapy (60). The prognosis is influenced by concurrent mutations in other genes particularly FLT3 allele ratio. AML patients with NPM1 mutation with absent or low FLT3-ITD AR (<0.5) have similar OS, and are classified as favorable risk by 2017 ELN, whereas AML patients with mutated NPM1 and high FLT3 ITD AR are classified as intermediate-risk along with wild-type NPM1 with absent or low FLT3 ITD AR. NPM1 mutations in AML disappear with CR. However, the persistence of the mutation during follow-up is a sign of adverse prognosis (1). Unfortunately, residual leukemia is not always apparent by morphology or flow cytometry. Cocciardi et al. described the loss of NPM1 mutation at relapse in 9% of NPM1 mutated AML, a finding that alters the prognosis through the selection of clones that harbor FLT3 or DNMT3A mutations exclusively (61). Both of the above findings highlight the importance of serial NGS as a follow up tool for AML to identify the clonal evolution of the disease.
A significant improvement of OS was observed in NPM1 mutated AML with Venetoclax, a BCL2 inhibitor, in combination with hypomethylating agents in patients > 65 years old (17). Venetoclax was approved by the FDA in combination with azacitidine or decitabine for the treatment of newly diagnosed AML in patients older than 75 years old or who have severe comorbidities (14, 18). Multiple other targeted therapeutic options for NPM1 mutated AML are ongoing; these include: 1- Deguelin, a selective silencer of the NPM1 mutation that stimulates apoptosis and induces differentiation in AML cells (62); 2- NSC34884 a molecula that disrupts the hydrophobic region that induce NPM1 oligomerization leading to apoptosis; 3- CIGB-300 a molecule that binds NPM1 to prevent the phosphorylation process resulting in induction of apoptosis (63); 4- Selinexor (KPT 330), an inhibitor of exportin 1 responsible of the cytoplasmic mis-localization of mutated NPM1 (64); 6- EAPB0503, a molecule that promotes NPM1 degradation and corrects the NPM1 mis-localization causing an inhibition of the leukemia cell growth (65) (Table 2).
AML With Mutated RUNX1
Category: myeloid transcription factor (22).
Clinicopathologic and morphologic features: minimally differentiated AML (AML-M0).
Recommended method of testing: NGS that includes the whole coding region (66).
RUNX1 is a TF located on chromosome 21q22.12 recurrently involved in leukemia due to multiple types of alterations including chromosomal translocations, mutations, and copy number changes. Somatic mutations occur in up to 15% of the AML, and the frequency is higher in secondary AML arising from MDS (67). De novo AML with mutated RUNX1 have characteristic clinicopathologic features that include male predominance, higher frequency of SRSF2 and ASXL1 mutations, normal karyotype, and absent NPM1 mutations (68).
Per 2017 ELN guidelines, mutated RUNX1 is considered as an adverse prognostic factor. You et al. reported the results of a study on 219 patients with AML, those with RUNX1 mutations had shorter relapse-free survival than patients with wild type-RUNX1 (69). In a meta-analysis of four studies, RUNX1 mutation was associated with dismal prognosis in AML (70). Stengel et al. reported a better outcome when RUNX1 mutation was associated with IDH2 mutation, but worse when associated with ASXL1, SF3B1, SRSF2 and PHF6 mutations (71). Based on the poor outcome observed in studies that evaluated AML with RUNX1 mutations, the 2016 revised WHO AML classification system regards de novo AML with mutated RUNX1 as a provisional entity (57, 69, 70). However, when only de novo AML cases are evaluated, the outcome is similar to AML with wild-type RUNX1 cases (68).
Notably, as RUNX1 is a gene implicated in germline predisposition disorders, attention should be given to specific findings in RUNX1 alterations. The presence of double mutations or mutations with near heterozygous or homozygous VAF, presence of mutation in familial clusters and history of thrombocytopenia should prompt investigation for an underlying familial platelet disorder with predisposition to myeloid malignancy (72).
While there are no direct targeted therapies at this time, enhancer suppression using bromodomain and extra-terminal motif (BET) inhibitor prevents aberrant RUNX1 and ERG signal-induced transcription in pre-clinical studies (73). Using CRISPR/Cas9, the BET protein antagonist induced inhibition of RUNX1 resulting in more apoptosis of leukemic cells expressing mutated RUNX1 compared to wild-type cells, inducing an improvement of the survival of mice (74) (Table 2).
AML With Mutated CEBPA
Category: myeloid TF.
Clinicopathologic and morphologic features: AML with or without maturation.
Recommended method of testing: NGS and PCR followed by direct sequencing (sanger-sequencing) (75).
CCAAT enhancer binding protein (CEBPA) is a TF located on chromosome 9q13.11 expressed in myeloid lineage. It plays a major role in proliferation and differentiation of the myeloid precursors to granulocytes or monocytes (76).
CEBPA mutations are found in 10–15% of patients (77). AML with biallelic CEBPA mutations in a heterozygous or homozygous pattern are significantly associated with better overall prognosis and outcomes independently of other molecular markers (77, 78). AML with single CEBPA mutations are uncommon, and more studies are needed to elucidate the clinical significance. Detection of biallelic CEBPA alterations should also prompt investigation for an underlying germline mutation on constitutional DNA with skin fibroblast culture and investigation of underlying familial predisposition (57, 79).
Due to the high GC content, CEBPA is a notoriously difficult gene to sequence. There are reports of successful CEBPA sequencing by NGS. This requires extensive modifications and tweaking of the PCR conditions and probe sequences (75).
Jakobsen et al. identified NT5E that encodes CD73 to be up-regulated in bi-allelic CEBPA mutant leukemia (80). The efficacy of CD73 inhibitors, including synergy with immune checkpoint inhibitors such as PD-1/PD-L1 are being evaluated as targeted therapy in bi-allelic CEBPA mutant AML (NCT03454451) (Table 2).
Genes Involved in Prognostic Risk-Stratification of AML
Tumor Protein p53 (TP53)
Category: tumor suppressor.
Clinicopathologic and morphologic features: associated with complex karyotype and shorter OS.
Recommended method of testing: NGS for detections mutations across the whole coding region and low mutant burden (81).
TP53 is mutated in 8-14% of de novo AML cases, but as high as 73% in AML in older patients and therapy-related AML (26–28). The mutations induce loss-of-function, dominant negative and gain-of-function phenotypes (82). The presence of a TP53 mutation is an independent predictor of poor survival and is associated with a high risk of recurrence and treatment resistance. The 2017 ELN classification regards the presence of TP53 mutation as an adverse risk category (7).
One important additional information obtained from NGS for prognostication, beyond just the presence of a TP53 mutation, is the variant allele frequency (VAF). In MDS, there is significant difference in prognosis between MDS with TP53 VAF >40% vs. <20% (median OS of 124 months vs. OS not reached) (83). Prochazka et al. categorized 98 de novo AML cases using similar cut-offs: VAF >40%, VAF 20% - 40% and VAF <20%; sub-clonal TP53 mutation (VAF <20%) showed a negative prognostic effect in terms of CR rate, OS and EFS (81). These findings highlight the importance of a sensitive molecular assay that detects minute sub-clones of TP53 mutation, and the importance of the genetic data provided by NGS, including accurate VAF.
The development of targeted therapy in TP53 mutated cases should take into consideration multiple factors such as alterations affecting related pathways as well as other therapeutic options such as BCL2 inhibitors’ in the latter, the TP53 activation may overcome resistance to BCL-2 inhibitors (84). Idasanutlin, an MDM2 inhibitor (85) and Cobimetinib a MEK inhibitor (86), both affecting TP53 expression, are being evaluated in combination with Venetoclax (BCL2 inhibitor) in phase I and phase II trials. Also, clinical trials exploring APR-246, a mutant P53 activator, are underway (NCT03931291); recently, in 2020, FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation for APR-246 in Combination with Azacitidine for the treatment of MDS with a TP53 Mutation (87). The different roles of TP53 in chemotherapy response and particularly the work of Zuber et al. on the activation of TP53 gene in mice provide supportive data of the significant role of exogenous activation of TP53 pathway in regard to treatment response (79) (Table 2).
Gene Mutation Signatures for Identification of AML Ontogeny
Lindsley et al. evaluated the differences in gene mutation patterns between secondary AML, therapy-related AML, and de novo AML to decode the ontogeny of different subsets of AML. The authors identified a set of gene mutations that can provide an objective evidence of AML ontogeny irrespective of clinical information. The presence of a mutations in any of these genes: SRSF2, SF3B1, U2AF1, ZRSR2, ASXL1, EZH2, BCOR, or STAG2 was >95% specific for the diagnosis of secondary AML (88). Majority of these genes, SRSF2, SF3B1, U2AF1, ZRSR2, are genes encoding proteins that belong to the spliceosomal complex that encompasses a large number of members including small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and protein factors responsible for removing introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA (89). EZH2 and BCOR mutations are associated with worse OS in AML (55, 90, 91) while STAG2 is a part of the cohesion complex.
The findings have major clinical and diagnostic implications. When detected in “de novo” setting, the presence of secondary AML mutations can identify a subset of patients with worse outcome (88). The “secondary-type” mutations, as expected, are frequently present in MDS (92) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) (93). These findings imply these mutations are unlikely to promote the development of acute leukemia without a co-operating event. It is also to be noted that these mutations occur early in the disease course and persist during follow-up despite morphologic CR, hence should not be used for MRD follow up purposes (Figure 2 and Table 2).
Uncovering Underlying Germline Mutations in AML and Familial Predisposition
Somatic NGS sequencing in AML can potentially uncover incidental germline mutations. The latest WHO recognizes myeloid neoplasms with germline predisposition syndromes as a distinct diagnostic category (57). Recognition of these conditions has major therapeutic implications (94) and different diagnostic and monitoring strategies for the patient himself, as well as the family members. When clinically suspicious, germline mutations testing and proper family screening are important, especially when an allogeneic bone marrow transplant is under consideration.
The new WHO classification introduced four broad categories of AML with germline predisposition: 1-nMyeloid neoplasms with germline predisposition without a pre-existing disorder or organ dysfunction, it includes AML with CEBPA and DDX41 mutations 2- Myeloid neoplasms with germline predisposition and pre-existing platelet disorders, which encompass RUNX1, ANKRD26 and ETV6 mutations 3- Myeloid neoplasms with germline GATA2 mutation and 4- Myeloid neoplasms with germline predisposition associated with inherited bone failure syndromes and telomere biology disorders. Hence, it is recommended to include these genes, CEBPA, DDX41, RUNX1, ANKRD26, ETV6, TERT and GATA2, within the standard NGS panel.
Since most of the mutated genes associated with germline predisposition disorders are also recurrently mutated in sporadic leukemia cases, attention should be given when interpreting the results of sequencing to identify clues suggesting a germline origin, such as double mutations, one with a near heterozygous or homozygous VAF (95). The presence of any of these mutations in a newly diagnosed leukemia is not sufficient to diagnose an AML with germline predisposition. Germline origin by testing constitutional DNA (skin fibroblast culture in most patients with active hematological malignancies) should be performed for confirmation (72, 88). It is important to highlight that targeted sequencing will not detect all the germline alterations such as intronic regions and large deletions spanning multiple exons; additional tests should be done to further investigate when clinically suspicious, such as array comparative hybridization for deletions and whole exome sequencing for novel mutations (96, 97). The confirmation of germline origin requires a prior genetic counseling since the results may cause significant disturbance of the affected individuals and families if not properly interpreted and handled (Figure 2 and Table 2).
Variant Allele Frequency of Gene Mutations Estimated by NGS Is Important for Treatment Decisions
NGS is a quantitative assay that provides information on mutant allele burden, which is critical for management decisions and predict outcome. VAF is defined as the ratio of reads with mutation against total (mutant + wild-type) reads. Hence, current NGS reports are generally not limited to presence or absence of mutations but include the VAF of each alteration. VAF is important for management decisions and outcome prediction in AML and MDS. This was previously elaborated in the context of TP53 mutations in AML and MDS (81, 83). A high mutant allele burden at diagnosis can be a negative prognostic factor. Patel et al. demonstrated a negative prognostic effect of high NPM1 mutant allele burden at diagnosis in de novo AML cases (98). Sasaki et al. investigated the effect of the VAF of clonal hematopoiesis associated genes ASXL1, DNMT3A, JAK2, TET2, and TP53 mutations on survival in 421 newly diagnosed AML using NGS. Higher VAF (cut-off of 30%) was associated with worse survival in AML patients within intermediate-risk cytogenetic group (99).
Sequential NGS Assessment for MRD Chemoresistance and Early Relapse Detection
Serial NGS is ideal for monitoring AML patients for mutational clearance and/or clonal evolution and relapse. Clearance of somatic mutations in non-preleukemia genes at the time of CR was associated with better OS and decreased risk for relapse (100). Sequential analysis for persistent mutations is particularly helpful to evaluate residual disease in patients treated using novel targeted therapeutic agents, such as IDH inhibitors, as these can pose diagnostic challenges on morphology and/flow cytometry. Therefore, NGS is particularly useful to objectively evaluate evidence of residual disease in these circumstances.
The implications of NGS include assessment of effectiveness of therapy and detection of resistance mutations which can have implications on management and therapeutic regimen choices. Most importantly, sequencing of blast cells can detect TP53 mutations which are independent predictors of poor survival and treatment resistance (7). Moreover, mutations that trigger resistance to FLT3 inhibitors can be identified in AML cases including emergence of leukemic clones harboring mutations that activate RAS/MAPK pathway signaling (37). On the other hand, emergence of FLT3-TKD mutation during treatment can engender resistance to TKI; therefore, sequential mutational analysis is mandatory for early detection of potential treatment resistance and the choice of alternative drugs. Finally, the acquisition of IDH1, WT1, ASXL1 variants in certain AML clones, either present at diagnosis or gained at relapse confer chemotherapy resistance (101).
While NGS facilitates identification of disease evolution and treatment resistance mutations, there are several caveats. First, the sensitivity of standard NGS panels used in clinical laboratories, currently limited to 2-5% VAF (102) is less or comparable to standard flow cytometry techniques for detection of residual disease at the time of morphologic remission. Yet, NGS results are more helpful than latter in settings where blasts show monocytic differentiation or in settings with limited sample quality. The identification of the mutations is partly limited by the intrinsic error rates (0.1% to 1%), that can be potentially overcome using the error correction methodologies such as molecular barcoding (103). Alternately, ultra-deep sequencing NGS with an ultra-high depth of coverage or individual gene assays such as ddPCR assays can be helpful (104). In one study, a high-throughput deep sequencing NGS method showed a detection sensitivity of 10-4 for SNVs and 10-5 for insertions/deletions (105).
Second, persistence of “pre-leukemia” mutation signature cannot be used for MRD detection. NGS enables the identification of background clonal hematopoiesis. Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP), defined as the presence of a somatic alterations (either a somatic mutation associated with myeloid malignancy present at least 2% VAF or cytogenetic abnormality) in apparently healthy individuals. These patients have an increased risk of developing a hematologic malignancy, higher risk of developing therapy related myeloid neoplasms following chemotherapy for a solid tumor and increased frequency of adverse cardiovascular events (106).
Most of the CHIP alterations belong to genes DNMT3A, TET2 and ASXL1 (DTA) (106, 107). All three genes are involved in epigenetic regulation of myeloid differentiation and are considered to be within preleukemic hematopoetic stem cells (108). DTA gene mutations cannot induce leukemia without a co-operating second hits (109). The mutations in either one of the DTA genes impart negative prognostic outcomes in AML (110–112). The 2017 ELN classifies ASXL1 mutations as adverse risk category (7), and its presence was >95% specific for AML of secondary origin (88).
Mutations in all three genes can be seen within the entire coding region, and include missense, frameshift, nonsense and splice-site mutations leading to a non-functional protein. The only exception being DNMT3A, which has a hotspot point mutation in codon R882 (113, 114). Loss of TET2 function can also occur via mutations in IDH1, IDH2 and WT1 (115, 116), that explain the mutual exclusivity between IDH1/2-TET2-WT1 mutations in AML (116). Hence, NGS is an ideal technique for detection of all these mutations.
Importantly, DTA gene mutations likely persist at the time of remission of AML in pre-leukemic clones, hence they cannot be used to detect MRD (109). DNMT3A R882 mutation persists in 75% of AML patients during remission without any negative impact on outcomes (117). Interestingly, ascorbate supplementation can restore methylation patterns and minimize proliferation of blasts (118). A clinical trial evaluating the efficacy of azacitidine and high dose ascorbic acid in AML with mutated TET2 is ongoing (NCT03397173).
9- Subclonal evolution in AML using single-cell technology:
All malignancies are genetically heterogeneous, composed of mutationally-defined subclonal cell populations characterized by distinct phenotypes. Precise identification of clonal and sub-clonal architecture is mandatory to understand the temporal evolution of tumor and the emergence of treatment resistance. Bulk sequencing cannot definitively resolve the actual complex clonal composition of neoplasms generally and AML specifically. Therefore, there is great interest in understanding the genetic alterations at a single-cell level using the newly designed sequencing platforms. Multiple reports published recently highlighted the subclonal selection during the treatment journey. Morita et al. reported the sub-clonal complexity in 37, clonal architecture and mutational histories of 123 AML patients. The authors explored single cell-level mutation co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity revealing novel clonal relationships; and emergence and selection of resistant subclones under therapies by longitudinal analysis (119). Interestingly, current emerging single-cell multi-omics technology, aid in profiling simultaneously single-cell mutations and cell surface proteins in AML cases, allowing correlation of genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity (120). Using the novel features of this technology, Petti et al., using a high-throughput platform to distinguish tumor and non-tumor cells in AML, identified tumor cells showing phenotypic aberrancies and lineage infidelity, evaluated the sub-clonal progression of tumor samples with time with a molecular signature for each sample, and cell-surface markers that could be used to isolate specific cells for downstream studies (121). Another study showed that FLT3-ITD mutation was present in the primitive cells, whereas FLT3-TKD mutation was present in the more differentiated cells within the same tumor. The study demonstrated that FLT3 variants differentially affected AML differentiation that explained the worse prognosis associated with certain alleles (122).
Discussion
We believe that NGS is an exciting tool that has helped pathologists and oncologists tremendously to improve their understanding of AML pathogenesis and clonal evolution of the disease. It has played a major role in designing therapies targeting the disease and control relapse. Genomic analysis of cases at diagnosis and relapse have uncovered the alterations and clonal evolution of the genetic profile of the tumor cells during disease progression. The cited studies and clinical trial results highlight the unique genetic signature of every patient’s disease, not only with respect to different combinations of mutations, but also in terms of clonal burden of different mutations, sequence of mutations, and concurrent chromosomal gain and losses. As a consequence of this, 1- the prognostic outcome of each patient can be unique and cannot be simply generalized based on the presence or absence of mutations; 2- the therapeutic molecules should be targeted to attack both the primary clone and emerging sub-clones with potential resistance mechanisms. Hence, a better understanding of each patient’s AML genome by NGS is mandatory to make decisions related to appropriate personalized therapy.
Nevertheless, a lot more standardization is needed for implementing NGS in daily clinical practice; for instance, so far there is no universal consensus, yet on which target genes should be included in the sequencing panels. Moreover, the sequencing depth of coverage is still a subjective number chosen by each laboratory for the validation of their sequencer. Furthermore, there is no consistent practice for quality assessment of sequencing data; the accuracy of results is compromised at genome locations with highly repetitive sequences, or in GC-rich locations, common problems encountered during sequencing and data analysis. Finally, results interpretation can be time-consuming and requires specific expertise from bioinformatics and pathology (or equivalent degree). Further standardizations are needed when NGS is used for serial follow-up to assess measurable residual disease. It is important to keep in mind that bulk NGS represents the “average” findings per cell, and hence the data on genomic complexity is only inferred. On the other hand, single-cell NGS can accurately provide concrete information on sub-clonal architecture, but it has not reached the mainstream clinical work-flow yet (123).
At the same time, while NGS is an important component of AML workup, other testing needs to be performed to accurately sub-classify the disease, specify the prognosis, and determine the best targeted therapy. A comprehensive workup for AML should include a karyotype to identify the disease defining chromosomal translocations including t(8;21), t(15;17), t(16;16) and the new WHO entity AML with BCR/ABL (57); however, some fusions can be cryptic (57), and other testing is required to highlight these aberrations including Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), RT-PCR, RNAseq, and other targeted fusions assays. Moreover copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity (cnLOH) has prognostic significance in patients with acute leukemia (124); Walker et al. showed that LOH mediated by uniparental disomy (UPD) is a common finding in cytogenetically normal AML. Also, UPD involving 13q and 11p are important for genetic risk stratification in these cases (125). FISH and karyotyping can be used to depict copy number aberrations; however, they are limited by low resolution or restriction to targeted assessment. The alternative method of testing is Chromosomal microarray which can characterize chromosomal copy number changes and cnLOH in myeloid malignancies (126).
Overall, NGS has enabled phenomenal advances in understanding of molecular genetics of AML and opened up new horizons for development of highly effective therapeutic molecules and protocols for individualized treatment and monitoring that are completely reshaping the management of the different subtypes of AML.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to writing the manuscript, reviewing the final version and preparing the figures and tables. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Ivey A, Hills RK, Simpson MA, Jovanovic JV, Gilkes A, Grech A, et al. Assessment of Minimal Residual Disease in Standard-Risk AML. N Engl J Med (2016) 374(5):422–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1507471
2. Gilliland DG ed. Molecular Genetics of Human Leukemias: New Insights Into Therapy. Semin Hematol. (2002) 39(4 Suppl 3):6–11. doi: 10.1053/shem.2002.36921
3. Cancer Genome Atlas Research N, Ley TJ, Miller C, Ding L, Raphael BJ, Mungall AJ, et al. Genomic and Epigenomic Landscapes of Adult De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med (2013) 368(22):2059–74. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1301689
4. Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L, Gaidzik VI, Paschka P, Roberts ND, et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med (2016) 374(23):2209–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1516192
5. Figueroa ME, Abdel-Wahab O, Lu C, Ward PS, Patel J, Shih A, et al. Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations Result in a Hypermethylation Phenotype, Disrupt TET2 Function, and Impair Hematopoietic Differentiation. Cancer Cell (2010) 18(6):553–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.11.015
6. Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. The 2016 Revision to the World Health Organization Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemia. Blood (2016) 127(20):2391–405. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-06-721662
7. Dohner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Buchner T, et al. Diagnosis and Management of AML in Adults: 2017 ELN Recommendations From an International Expert Panel. Blood (2017) 129(4):424–47. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-733196
8. Quizartinib With Standard of Care Chemotherapy and as Continuation Therapy in Patients With Newly Diagnosed FLT3-ITD (+) Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) (QuANTUM-First) . Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02668653 (Accessed September 2020).
9. Luthra R, Patel KP, Reddy NG, Haghshenas V, Routbort MJ, Harmon MA, et al. Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Multigene Mutational Screening for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Using MiSeq: Applicability for Diagnostics and Disease Monitoring. Haematologica (2014) 99(3):465–73. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.093765
10. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-ivosidenib-first-line-treatment-aml-idh1-mutation (Accessed September 2020).
11. Stein EM, DiNardo CD, Fathi AT, Pollyea DA, Stone RM, Altman JK, et al. Molecular Remission and Response Patterns in Patients With Mutant-IDH2 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treated With Enasidenib. Blood (2019) 133(7):676–87. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-08-869008
12. Sakaguchi M, Yamaguchi H, Najima Y, Usuki K, Ueki T, Oh I, et al. Prognostic Impact of Low Allelic Ratio FLT3-ITD and NPM1 Mutation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood Adv (2018) 2(20):2744–54. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018020305
13. Stone RM, Mandrekar SJ, Sanford BL, Laumann K, Geyer S, Bloomfield CD, et al. Midostaurin Plus Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia With a FLT3 Mutation. N Engl J Med (2017) 377(5):454–64. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1614359
14. Administration USFaD. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-approves-gilteritinib-relapsed-or-refractory-acute-myeloid-leukemia-aml-flt3-mutatation (Accessed September 2020).
15. Perl AE, Altman JK, Cortes J, Smith C, Litzow M, Baer MR, et al. Selective Inhibition of FLT3 by Gilteritinib in Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukaemia: A Multicentre, First-in-Human, Open-Label, Phase 1-2 Study. Lancet Oncol (2017) 18(8):1061–75. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30416-3
16. Perl AE, Martinelli G, Cortes JE, Neubauer A, Berman E, Paolini S, et al. Gilteritinib or Chemotherapy for Relapsed or Refractory FLT3-Mutated AML. N Engl J Med (2019) 381(18):1728–40. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1902688
17. Lachowiez CA, Loghavi S, Kadia TM, Daver N, Borthakur G, Pemmaraju N, et al. Outcomes of Older Patients With NPM1-Mutated AML: Current Treatments and the Promise of Venetoclax-Based Regimens. Blood Adv (2020) 4(7):1311–20. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019001267
18. FDA Approves Venetoclax in Combination for AML in Adults. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-approves-venetoclax-combination-aml-adults.
19. Zhou F, Chen B. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Carrying ETV6 Mutations: Biologic and Clinical Features. Hematology (2018) 23(9):608–12. doi: 10.1080/10245332.2018.1482051
20. Zaker F, Mohammadzadeh M, Mohammadi M. Detection of KIT and FLT3 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Different Subtypes. Arch Iran Med (2010) 13(1):21–5.
21. Sébert M, Passet M, Raimbault A, Rahmé R, Raffoux E, Sicre de Fontbrune F, et al. Germline DDX41 Mutations Define a Significant Entity Within Adult MDS/AML Patients. Blood (2019) 134(17):1441–4. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000909
22. Mosrati MA, Willander K, Falk IJ, Hermanson M, Höglund M, Stockelberg D, et al. Association Between TERT Promoter Polymorphisms and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Risk and Prognosis. Oncotarget (2015) 6(28):25109–20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4668
23. Dohner H, Weisdorf DJ, Bloomfield CD. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med (2015) 373(12):1136–52. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1406184
24. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J eds. WHO Classif Ication of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Revised 4th edition. Lyon: IARC (2017).
25. Daver N, Schlenk RF, Russell NH, Levis MJ. Targeting FLT3 Mutations in AML: Review of Current Knowledge and Evidence. Leukemia (2019) 33(2):299–312. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0357-9
26. Barbosa K, Li S, Adams PD, Deshpande AJ. The Role of TP53 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Challenges and Opportunities. Genes Chromosomes Cancer (2019) 58(12):875–88. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22796
27. Kadia TM, Jain P, Ravandi F, Garcia-Manero G, Andreef M, Takahashi K, et al. TP53 Mutations in Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Clinicomolecular Characteristics, Response to Therapy, and Outcomes. Cancer (2016) 122(22):3484–91. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30203
28. Boddu P, Kantarjian H, Ravandi F, Garcia-Manero G, Borthakur G, Andreeff M, et al. Outcomes With Lower Intensity Therapy in TP53-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma (2018) 59(9):2238–41. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1422864
29. Fasan A, Eder C, Haferlach C, Grossmann V, Kohlmann A, Dicker F, et al. GATA2 Mutations are Frequent in Intermediate-Risk Karyotype AML With Biallelic CEBPA Mutations and are Associated With Favorable Prognosis. Leukemia (2013) 27(2):482–5. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.174
30. Schneider F, Hoster E, Schneider S, Dufour A, Benthaus T, Kakadia PM, et al. Age-Dependent Frequencies of NPM1 Mutations and FLT3-ITD in Patients With Normal Karyotype AML (NK-AML). Ann Hematol (2012) 91(1):9–18. doi: 10.1007/s00277-011-1280-6
31. Levis M. FLT3 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: What is the Best Approach in 2013? Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program (2013) 2013:220–6. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2013.1.220
32. Gale RE, Green C, Allen C, Mead AJ, Burnett AK, Hills RK, et al. The Impact of FLT3 Internal Tandem Duplication Mutant Level, Number, Size, and Interaction With NPM1 Mutations in a Large Cohort of Young Adult Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood (2008) 111(5):2776–84. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-08-109090
33. Schlenk RF, Kayser S, Bullinger L, Kobbe G, Casper J, Ringhoffer M, et al. Differential Impact of Allelic Ratio and Insertion Site in FLT3-ITD-Positive AML With Respect to Allogeneic Transplantation. Blood (2014) 124(23):3441–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-578070
34. Boddu PC, Kadia TM, Garcia-Manero G, Cortes J, Alfayez M, Borthakur G, et al. Validation of the 2017 European LeukemiaNet Classification for Acute Myeloid Leukemia With NPM1 and FLT3-Internal Tandem Duplication Genotypes. Cancer (2019) 125(7):1091–100. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31885
35. Spencer DH, Abel HJ, Lockwood CM, Payton JE, Szankasi P, Kelley TW, et al. Detection of FLT3 Internal Tandem Duplication in Targeted, Short-Read-Length, Next-Generation Sequencing Data. J Mol Diagn (2013) 15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2012.08.001
36. Ye K, Schulz MH, Long Q, Apweiler R, Ning Z. Pindel: A Pattern Growth Approach to Detect Break Points of Large Deletions and Medium Sized Insertions From Paired-End Short Reads. Bioinformatics (2009) 25(21):2865–71. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp394
37. McMahon CM, Ferng T, Canaani J, Wang ES, Morrissette JJD, Eastburn DJ, et al. Clonal Selection With RAS Pathway Activation Mediates Secondary Clinical Resistance to Selective FLT3 Inhibition in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Discovery (2019) 9(8):1050–63. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1453
38. Petrova L, Vrbacky F, Lanska M, Zavrelova A, Zak P, Hrochova K. IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations in Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Suitable Targets for Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring? Clin Biochem (2018) 61:34–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.08.012
39. Aref S, Kamel Areida el S, Abdel Aaal MF, Adam OM, El-Ghonemy MS, El-Baiomy MA, et al. Prevalence and Clinical Effect of IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations Among Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk (2015) 15(9):550–5. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2015.05.009
40. Marcucci G, Maharry K, Wu YZ, Radmacher MD, Mrozek K, Margeson D, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 Gene Mutations Identify Novel Molecular Subsets Within De Novo Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol (2010) 28(14):2348–55. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.3730
41. Gulley ML, Shea TC, Fedoriw Y. Genetic Tests to Evaluate Prognosis and Predict Therapeutic Response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Mol Diagn: JMD (2010) 12(1):3–16. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2010.090054
42. Paschka P, Marcucci G, Ruppert AS, Mrózek K, Chen H, Kittles RA, et al. Adverse Prognostic Significance of KIT Mutations in Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia With inv(16) and t(8;21): A Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol (2006) 24(24):3904–11. doi: 10.1200/jco.2006.06.9500
43. Kuykendall A, Duployez N, Boissel N, Lancet JE, Welch JS. Acute Myeloid Leukemia: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book (2018) 38):555–73. doi: 10.1200/edbk_199519
44. Jin H, Zhu Y, Hong M, Wu Y, Qiu H, Wang R, et al. Co-Occurrence of KIT and NRAS Mutations Defines an Adverse Prognostic Core-Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma (2021) 1–10. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2021.1919660
45. Allen C, Hills RK, Lamb K, Evans C, Tinsley S, Sellar R, et al. The Importance of Relative Mutant Level for Evaluating Impact on Outcome of KIT, FLT3 and CBL Mutations in Core-Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia (2013) 27(9):1891–901. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.186
46. Duployez N, Marceau-Renaut A, Boissel N, Petit A, Bucci M, Geffroy S, et al. Comprehensive Mutational Profiling of Core Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood (2016) 127(20):2451–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-12-688705
47. Pollard JA, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Ho PA, Zeng R, Ravindranath Y, et al. Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of KIT Mutations in Pediatric Patients With Core Binding Factor AML Enrolled on Serial Pediatric Cooperative Trials for De Novo AML. Blood (2010) 115(12):2372–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-241075
48. Lück SC, Russ AC, Du J, Gaidzik V, Schlenk RF, Pollack JR, et al. KIT Mutations Confer a Distinct Gene Expression Signature in Core Binding Factor Leukaemia. Br J Haematol (2010) 148(6):925–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.08035.x
49. Borthakur G, Kantarjian H. Core Binding Factor Acute Myelogenous Leukemia-2021 Treatment Algorithm. Blood Cancer J (2021) 11(6):114. doi: 10.1038/s41408-021-00503-6
50. Szankasi P, Jama M, Bahler DW. A New DNA-Based Test for Detection of Nucleophosmin Exon 12 Mutations by Capillary Electrophoresis. J Mol Diagn (2008) 10(3):236–41. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2008.070167
51. Wertheim GBW, Bagg A. NPM1 for MRD? Droplet Like It’s Hot! J Mol Diagn (2017) 19(4):498–501. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2017.04.008
52. Zarka J, Short NJ, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Issa GC. Nucleophosmin 1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Genes (Basel) (2020) 11(6):649. doi: 10.3390/genes11060649
53. Rau R, Brown P. Nucleophosmin (NPM1) Mutations in Adult and Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukaemia: Towards Definition of a New Leukaemia Entity. Hematol Oncol (2009) 27(4):171–81. doi: 10.1002/hon.904
54. Colombo E, Marine JC, Danovi D, Falini B, Pelicci PG. Nucleophosmin Regulates the Stability and Transcriptional Activity of P53. Nat Cell Biol (2002) 4(7):529–33. doi: 10.1038/ncb814
55. Damiani D, Tiribelli M. Molecular Landscape in Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Where We are Where We Going? J Lab Prec Med (2019) 4(0):17. doi: 10.21037/jlpm.2018.09.08
56. Villanueva MT. Genetics: Acute Myeloid Leukaemia: Driving the Driver. Nat Rev Cancer (2016) 16(8):479. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.75
57. Swerdlow SHCE, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised 4th edition. (2017).
58. Montalban-Bravo G, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Sasaki K, Patel K, Ganan-Gomez I, Jabbour E, et al. NPM1 Mutations Define a Specific Subgroup of MDS and MDS/MPN Patients With Favorable Outcomes With Intensive Chemotherapy. Blood Adv (2019) 3(6):922–33. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018026989
59. Patel SS, Ho C, Ptashkin RN, Sadigh S, Bagg A, Geyer JT, et al. Clinicopathologic and Genetic Characterization of Nonacute NPM1-Mutated Myeloid Neoplasms. Blood Adv (2019) 3(9):1540–5. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000090
60. DiNardo CD, Cortes JE. Mutations in AML: Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program (2016) 2016(1):348–55. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2016.1.348
61. Cocciardi S, Dolnik A, Kapp-Schwoerer S, Rucker FG, Lux S, Blatte TJ, et al. Clonal Evolution Patterns in Acute Myeloid Leukemia With NPM1 Mutation. Nat Commun (2019) 10(1):2031. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09745-2
62. Yi S, Wen L, He J, Wang Y, Zhao F, Zhao J, et al. Deguelin, a Selective Silencer of the NPM1 Mutant, Potentiates Apoptosis and Induces Differentiation in AML Cells Carrying the NPM1 Mutation. Ann Hematol (2015) 94(2):201–10. doi: 10.1007/s00277-014-2206-x
63. Di Matteo A, Franceschini M, Chiarella S, Rocchio S, Travaglini-Allocatelli C, Federici L. Molecules That Target Nucleophosmin for Cancer Treatment: An Update. Oncotarget (2016) 7(28):44821–40. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8599
64. Talati C, Sweet KL. Nuclear Transport Inhibition in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Int J Hematol Oncol (2018) 7(3):IJH04. doi: 10.2217/ijh-2018-0001
65. Nabbouh AI, Hleihel RS, Saliba JL, Karam MM, Hamie MH, Wu HJM, et al. Imidazoquinoxaline Derivative EAPB0503: A Promising Drug Targeting Mutant Nucleophosmin 1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer (2017) 123(9):1662–73. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30515
66. Kohlmann A, Nadarajah N, Alpermann T, Grossmann V, Schindela S, Dicker F, et al. Monitoring of Residual Disease by Next-Generation Deep-Sequencing of RUNX1 Mutations Can Identify Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients With Resistant Disease. Leukemia (2014) 28(1):129–37. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.239
67. Dicker F, Haferlach C, Sundermann J, Wendland N, Weiss T, Kern W, et al. Mutation Analysis for RUNX1, MLL-PTD, FLT3-ITD, NPM1 and NRAS in 269 Patients With MDS or Secondary AML. Leukemia (2010) 24(8):1528–32. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.124
68. Quesada AE, Montalban-Bravo G, Luthra R, Patel KP, Sasaki K, Bueso-Ramos CE, et al. Clinico-Pathologic Characteristics and Outcomes of the World Health Organization (WHO) Provisional Entity De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Mutated RUNX1. Modern Pathol (2020) 33(9):1678–89. doi: 10.1038/s41379-020-0531-2
69. You E, Cho YU, Jang S, Seo EJ, Lee JH, Lee JH, et al. Frequency and Clinicopathologic Features of RUNX1 Mutations in Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia Not Otherwise Specified. Am J Clin Pathol (2017) 148(1):64–72. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqx046
70. Jalili M, Yaghmaie M, Ahmadvand M, Alimoghaddam K, Mousavi SA, Vaezi M, et al. Prognostic Value of RUNX1 Mutations in AML: A Meta-Analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev (2018) 19(2):325–9. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.2.325
71. Stengel A, Kern W, Meggendorfer M, Nadarajah N, Perglerova K, Haferlach T, et al. Number of RUNX1 Mutations, Wild-Type Allele Loss and Additional Mutations Impact on Prognosis in Adult RUNX1-Mutated AML. Leukemia (2018) 32(2):295–302. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.239
72. Kanagal-Shamanna R, Loghavi S, DiNardo CD, Medeiros LJ, Garcia-Manero G, Jabbour E, et al. Bone Marrow Pathologic Abnormalities in Familial Platelet Disorder With Propensity for Myeloid Malignancy and Germline RUNX1 Mutation. Haematologica (2017) 102(10):1661–70. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.167726
73. Antony J, Gimenez G, Taylor T, Khatoon U, Day R, Morison IM, et al. BET Inhibition Prevents Aberrant RUNX1 and ERG Transcription in STAG2 Mutant Leukaemia Cells. J Mol Cell Biol (2020) 12(5):397–9. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz114
74. Mill CP, Fiskus W, DiNardo CD, Qian Y, Raina K, Rajapakshe K, et al. RUNX1-Targeted Therapy for AML Expressing Somatic or Germline Mutation in RUNX1. Blood (2019) 134(1):59–73. doi: 10.1182/blood.2018893982
75. Grossmann V, Schnittger S, Schindela S, Klein HU, Eder C, Dugas M, et al. Strategy for Robust Detection of Insertions, Deletions, and Point Mutations in CEBPA, a GC-Rich Content Gene, Using 454 Next-Generation Deep-Sequencing Technology. J Mol Diagn (2011) 13(2):129–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2010.09.001
76. Song G, Wang L, Bi K, Jiang G. Regulation of the C/EBPalpha Signaling Pathway in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Review). Oncol Rep (2015) 33(5):2099–106. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3848
77. Walker A, Marcucci G. Molecular Prognostic Factors in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Expert Rev Hematol (2012) 5(5):547–58. doi: 10.1586/ehm.12.45
78. Li HY, Deng DH, Huang Y, Ye FH, Huang LL, Xiao Q, et al. Favorable Prognosis of Biallelic CEBPA Gene Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Eur J Haematol (2015) 94(5):439–48. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12450
79. Zuber J, Radtke I, Pardee TS, Zhao Z, Rappaport AR, Luo W, et al. Mouse Models of Human AML Accurately Predict Chemotherapy Response. Genes Dev (2009) 23(7):877–89. doi: 10.1101/gad.1771409
80. Jakobsen JS, Laursen LG, Schuster MB, Pundhir S, Schoof E, Ge Y, et al. Mutant CEBPA Directly Drives the Expression of the Targetable Tumor-Promoting Factor CD73 in AML. Sci Adv (2019) 5(7):eaaw4304. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw4304
81. Prochazka KT, Pregartner G, Rucker FG, Heitzer E, Pabst G, Wolfler A, et al. Clinical Implications of Subclonal TP53 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica (2019) 104(3):516–23. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.205013
82. Oren M, Rotter V. Mutant P53 Gain-of-Function in Cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol (2010) 2(2):a001107. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a001107
83. Sallman DA, Komrokji R, Vaupel C, Cluzeau T, Geyer SM, McGraw KL, et al. Impact of TP53 Mutation Variant Allele Frequency on Phenotype and Outcomes in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Leukemia (2016) 30(3):666–73. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.304
84. Pan R, Ruvolo V, Mu H, Leverson JD, Nichols G, Reed JC, et al. Synthetic Lethality of Combined Bcl-2 Inhibition and P53 Activation in AML: Mechanisms and Superior Antileukemic Efficacy. Cancer Cell (2017) 32(6):748–60 e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.11.003
85. Khurana A, Shafer DA. MDM2 Antagonists as a Novel Treatment Option for Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Perspectives on the Therapeutic Potential of Idasanutlin (RG7388). Onco Targets Ther (2019) 12:2903–10. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S172315
86. Han L, Zhang Q, Dail M, Shi C, Cavazos A, Ruvolo VR, et al. Concomitant Targeting of BCL2 With Venetoclax and MAPK Signaling With Cobimetinib in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Models. Haematologica (2020) 105(3):697–707. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.205534
87. PatentScope . Available at: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2019134070&docAn=CN2018070051 (Accessed September 2020).
88. Lindsley RC, Mar BG, Mazzola E, Grauman PV, Shareef S, Allen SL, et al. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Ontogeny is Defined by Distinct Somatic Mutations. Blood (2015) 125(9):1367–76. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-11-610543
89. Taylor J, Lee SC. Mutations in Spliceosome Genes and Therapeutic Opportunities in Myeloid Malignancies. Genes Chromosomes Cancer (2019) 58(12):889–902. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22784
90. Mechaal A, Menif S, Abbes S, Safra I. EZH2, New Diagnosis and Prognosis Marker in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Adv Med Sci (2019) 64(2):395–401. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2019.07.002
91. Zhang Q, Han Q, Zi J, Ma J, Song H, Tian Y, et al. Mutations in EZH2 are Associated With Poor Prognosis for Patients With Myeloid Neoplasms. Genes Dis (2019) 6(3):276–81. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.05.001
92. Walter MJ, Shen D, Shao J, Ding L, White BS, Kandoth C, et al. Clonal Diversity of Recurrently Mutated Genes in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Leukemia (2013) 27(6):1275–82. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.58
93. Itzykson R, Kosmider O, Renneville A, Morabito M, Preudhomme C, Berthon C, et al. Clonal Architecture of Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemias. Blood (2013) 121(12):2186–98. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-440347
94. University of Chicago Hematopoietic Malignancies Cancer Risk T. How I Diagnose and Manage Individuals at Risk for Inherited Myeloid Malignancies. Blood (2016) 128(14):1800–13. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-05-670240
95. Kanagal-Shamanna R. The Emerging Role of Hematopathologists and Molecular Pathologists in Detection, Monitoring, and Management of Myeloid Neoplasms With Germline Predisposition. Curr Hematol Malig Rep (2021) 24:1–9. doi: 10.1007/s11899-021-00636-2
96. Wlodarski MW, Hirabayashi S, Pastor V, Stary J, Hasle H, Masetti R, et al. Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Prognosis of GATA2-Related Myelodysplastic Syndromes in Children and Adolescents. Blood (2016) 127(11):1387–97. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-669937
97. Jongmans MC, Kuiper RP, Carmichael CL, Wilkins EJ, Dors N, Carmagnac A, et al. Novel RUNX1 Mutations in Familial Platelet Disorder With Enhanced Risk for Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Clues for Improved Identification of the FPD/AML Syndrome. Leukemia (2010) 24(1):242–6. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.210
98. Patel SS, Pinkus GS, Ritterhouse LL, Segal JP, Dal Cin P, Restrepo T, et al. High NPM1 Mutant Allele Burden at Diagnosis Correlates With Minimal Residual Disease at First Remission in De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Am J Hematol (2019) 94(8):921–8. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25544
99. Sasaki K, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Montalban-Bravo G, Assi R, Jabbour E, Ravandi F, et al. Impact of the Variant Allele Frequency of ASXL1, DNMT3A, JAK2, TET2, TP53, and NPM1 on the Outcomes of Patients With Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer (2020) 126(4):765–74. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32566
100. Jongen-Lavrencic M, Grob T, Hanekamp D, Kavelaars FG, Al Hinai A, Zeilemaker A, et al. Molecular Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med (2018) 378(13):1189–99. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1716863
101. Ding L, Ley TJ, Larson DE, Miller CA, Koboldt DC, Welch JS, et al. Clonal Evolution in Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Revealed by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Nature (2012) 481(7382):506–10. doi: 10.1038/nature10738
102. Petrackova A, Vasinek M, Sedlarikova L, Dyskova T, Schneiderova P, Novosad T, et al. Standardization of Sequencing Coverage Depth in NGS: Recommendation for Detection of Clonal and Subclonal Mutations in Cancer Diagnostics. Front Oncol (2019) 9:851. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00851
103. Levine RL, Valk PJM. Next-Generation Sequencing in the Diagnosis and Minimal Residual Disease Assessment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica (2019) 104(5):868–71. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.205955
104. Kanagal-Shamanna R. Digital PCR: Principles and Applications. Methods Mol Biol (2016) 1392:43–50. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3360-0_5
105. Onecha E, Linares M, Rapado I, Ruiz-Heredia Y, Martinez-Sanchez P, Cedena T, et al. A Novel Deep Targeted Sequencing Method for Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica (2019) 104(2):288–96. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.194712
106. Jaiswal S, Fontanillas P, Flannick J, Manning A, Grauman PV, Mar BG, et al. Age-Related Clonal Hematopoiesis Associated With Adverse Outcomes. N Engl J Med (2014) 371(26):2488–98. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1408617
107. Young AL, Challen GA, Birmann BM, Druley TE. Clonal Haematopoiesis Harbouring AML-Associated Mutations is Ubiquitous in Healthy Adults. Nat Commun (2016) 7:12484. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12484
108. Jan M, Snyder TM, Corces-Zimmerman MR, Vyas P, Weissman IL, Quake SR, et al. Clonal Evolution of Preleukemic Hematopoietic Stem Cells Precedes Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Sci Transl Med (2012) 4(149):149ra18. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004315
109. Voso MT, Ottone T, Lavorgna S, Venditti A, Maurillo L, Lo-Coco F, et al. MRD in AML: The Role of New Techniques. Front Oncol (2019) 9:655. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00655
110. Kumar D, Mehta A, Panigrahi MK, Nath S, Saikia KK. DNMT3A (R882) Mutation Features and Prognostic Effect in Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Coexistent With NPM1 and FLT3 Mutations. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther (2018) 11(2):82–9. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2017.09.004
111. Wang R, Gao X, Yu L. The Prognostic Impact of Tet Oncogene Family Member 2 Mutations in Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic-Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer (2019) 19(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5602-8
112. Khan M, Cortes J, Kadia T, Naqvi K, Brandt M, Pierce S, et al. Clinical Outcomes and Co-Occurring Mutations in Patients With RUNX1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int J Mol Sci (2017) 18(8):1618. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081618
113. Gale RE, Lamb K, Allen C, El-Sharkawi D, Stowe C, Jenkinson S, et al. Simpson’s Paradox and the Impact of Different DNMT3A Mutations on Outcome in Younger Adults With Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol (2015) 33(18):2072–83. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.2022
114. Gowher H, Loutchanwoot P, Vorobjeva O, Handa V, Jurkowska RZ, Jurkowski TP, et al. Mutational Analysis of the Catalytic Domain of the Murine Dnmt3a DNA-(Cytosine C5)-Methyltransferase. J Mol Biol (2006) 357(3):928–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.01.035
115. Solary E, Bernard OA, Tefferi A, Fuks F, Vainchenker W. The Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (TET2) Gene in Hematopoiesis and Hematopoietic Diseases. Leukemia (2014) 28(3):485–96. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.337
116. Pan F, Weeks O, Yang FC, Xu M. The TET2 Interactors and Their Links to Hematological Malignancies. IUBMB Life (2015) 67(6):438–45. doi: 10.1002/iub.1389
117. Bhatnagar B, Eisfeld AK, Nicolet D, Mrozek K, Blachly JS, Orwick S, et al. Persistence of DNMT3A R882 Mutations During Remission Does Not Adversely Affect Outcomes of Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Br J Haematol (2016) 175(2):226–36. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14254
118. Cimmino L, Dolgalev I, Wang Y, Yoshimi A, Martin GH, Wang J, et al. Restoration of TET2 Function Blocks Aberrant Self-Renewal and Leukemia Progression. Cell (2017) 170(6):1079–95 e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.032
119. Kiyomi Morita FW, Jahn K, Hu T, Tanaka T, Sasaki Y. Author Correction: Clonal Evolution of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Revealed by High-Throughput Single-Cell Genomics. Nat Commun (2021) 12(1):2823. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23280-z
120. Hu Y, An Q, Sheu K, Trejo B, Fan S, Guo Y. Single Cell Multi-Omics Technology: Methodology and Application. Front Cell Dev Biol (2018) 6:28(28). doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00028
121. Petti AA, Williams SR, Miller CA, Fiddes IT, Srivatsan SN, Chen DY, et al. A General Approach for Detecting Expressed Mutations in AML Cells Using Single Cell RNA-Sequencing. Nat Commun (2019) 10(1):3660. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11591-1
122. van Galen P, Hovestadt V, Wadsworth Ii MH, Hughes TK, Griffin GK, Battaglia S, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals AML Hierarchies Relevant to Disease Progression and Immunity. Cell (2019) 176(6):1265–81.e24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.031
123. Miles LA, Bowman RL, Merlinsky TR, Csete IS, Ooi AT, Durruthy-Durruthy R, et al. Single-Cell Mutation Analysis of Clonal Evolution in Myeloid Malignancies. Nature (2020) 587(7834):477–82. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2864-x
124. Gronseth CM, McElhone SE, Storer BE, Kroeger KA, Sandhu V, Fero ML, et al. Prognostic Significance of Acquired Copy-Neutral Loss of Heterozygosity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer (2015) 121(17):2900–8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29475
125. Walker CJ, Kohlschmidt J, Eisfeld AK, Mrozek K, Liyanarachchi S, Song C, et al. Genetic Characterization and Prognostic Relevance of Acquired Uniparental Disomies in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin Cancer Res (2019) 25(21):6524–31. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0725
Keywords: AML, acute myeloid leukemia, next generation sequencing, actionable mutations, targeted therapy, FDA
Citation: El Achi H and Kanagal-Shamanna R (2021) Biomarkers in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Leveraging Next Generation Sequencing Data for Optimal Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Oncol. 11:748250. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.748250
Received: 27 July 2021; Accepted: 14 September 2021;
Published: 30 September 2021.
Edited by:
Julia T. Geyer, Weill Cornell Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Gang Zheng, Mayo Clinic, United StatesDeepshi Thakral, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Copyright © 2021 El Achi and Kanagal-Shamanna. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rashmi Kanagal-Shamanna, UkthbmFnYWxAbWRhbmRlcnNvbi5vcmc=
 Hanadi El Achi
Hanadi El Achi Rashmi Kanagal-Shamanna
Rashmi Kanagal-Shamanna