
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol. , 16 November 2021
Sec. Skin Cancer
Volume 11 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.737399
This article is part of the Research Topic Women in Skin Cancer: 2021 View all 24 articles
 Alessandra Buja1*
Alessandra Buja1* Andrea Bardin1
Andrea Bardin1 Giovanni Damiani2,3,4
Giovanni Damiani2,3,4 Manuel Zorzi5
Manuel Zorzi5 Chiara De Toni1
Chiara De Toni1 Riccardo Fusinato1
Riccardo Fusinato1 Romina Spina6
Romina Spina6 Antonella Vecchiato6
Antonella Vecchiato6 Paolo Del Fiore6
Paolo Del Fiore6 Simone Mocellin6,7
Simone Mocellin6,7 Vincenzo Baldo1
Vincenzo Baldo1 Massimo Rugge5,8
Massimo Rugge5,8 Carlo Riccardo Rossi7
Carlo Riccardo Rossi7Introduction: Among white people, the incidence of cutaneous malignant melanoma (CMM) has been increasing steadily for several decades. Meanwhile, there has also been a significant improvement in 5-year survival among patients with melanoma. This population-based cohort study investigates the five-year melanoma-specific survival (MSS) for all melanoma cases recorded in 2015 in the Veneto Tumor Registry (North-Est Italian Region), taking both demographic and clinical-pathological variables into consideration.
Methods: The cumulative melanoma-specific survival probabilities were calculated with the Kaplan-Meier method, applying different sociodemographic and clinical-pathological variables. Cox’s proportional hazards model was fitted to the data to assess the association between independent variables and MSS, and also overall survival (OS), calculating the hazard ratios (HR) relative to a reference condition, and adjusting for sex, age, site of tumor, histotype, melanoma ulceration, mitotic count, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), and stage at diagnosis.
Results: Compared with stage I melanoma, the risk of death was increased for stage II (HR 3.31, 95% CI: 0.94-11.76, p=0.064), almost ten times higher for stage III (HR 10.51, 95% CI: 3.16-35.02, p<0.001), and more than a hundred times higher for stage IV (HR 117.17, 95% CI: 25.30-542.62, p<0.001). Among the other variables included in the model, the presence of mitoses and histological subtype emerged as independent risk factors for death.
Conclusions: The multivariable analysis disclosed that older age, tumor site, histotype, mitotic count, and tumor stage were independently associated with a higher risk of death. Data on survival by clinical and morphological characteristics could be useful in modelling, planning, and managing the most appropriate treatment and follow-up for patients with CMM.
In recent decades, the incidence of cutaneous malignant melanoma (CMM) in white people has been increasing steadily (1, 2). Meanwhile, a significant improvement in CMM patients’ 5-year overall survival has also been reported, and related mostly to the increasing prevalence of cancers detected in their earliest, “thinner” stage” (3, 4). Both the rising incidence of CMM (all stages), and changes in the treatment panorama (also including the advent of targeted therapies) prompt the collection of updated information which might re-orient both prevention efforts and diagnostic/therapeutic strategies.
Based on the natural history of CMM, a well-established set of clinicopathological variables has been significantly correlated with the clinical outcome of melanoma patients. Unfortunately, these data are often inconsistently recorded and/or scattered over different digital archives. This situation interferes with efforts to validate prognostic variables in the “real world” of large-scale population-based studies.
As for the stage-specific survival of CMM patients, most information comes from national cancer registries, and the USA American Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results program (SEER) in particular (5). To the best of our knowledge, few registry-based studies on the stage-specific survival of CMM patients have been conducted in Italy or elsewhere in Europe in the last two decades (6–10).
The present study investigates the five-year melanoma-specific survival (MSS) for all cases of CMM recorded in 2015 in the resident population of a north-eastern Italian region (Veneto). Both demographic and clinical-pathological variables have been considered to measure their impact on patient survival in this cohort of CMM patients.
The Italian public national health service (NHS) is financed mainly by general taxation, and is largely managed on a regional basis. NHS policies are grounded on fundamental values of universality, free access, freedom of choice, pluralism in provision, and equity.
In the north-eastern Veneto region of Italy, the Regional Authority has endorsed a number of standardized Diagnostic Therapeutic Protocols (DTPs) for the clinical management of cancer patients. All DPTs have been edited by multidisciplinary task forces including dedicated experts belonging to the Regional Oncology Network (ROV).
This retrospective study on the outcome of CMM patients is based on clinico-pathological information recorded by the Veneto Cancer Registry in 2015 (11).
This retrospective population-based study involves a cohort of 1,279 incident cases of CMM diagnosed in the Veneto region in 2015 (resident population: 4,915,123). For each patient, the following set of clinical-pathological features were considered: a) tumor site (lower limbs, upper limbs, head, hands/feet, trunk); b) CMM histological subtype (lentigo maligna, acral lentiginous, blue nevus, desmoplastic, nodular, superficial spreading, spitzoid); b) growth phase (radial versus vertical); c) histologically-proven ulceration (present versus absent); d) number of mitoses (categorized as 0-2 or >2) (12); e) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, ([TILs] absent versus present; f) TNM stage, as established by merging clinical and pathological information available at the time of patient enrolment (13).
Patients were grouped by age in the following brackets: < 40, 40-49, 50-59, 60-69,70-79, 80 years or more.
The number of person-years in the cohort was calculated by taking the date of entry as the time when a tumor was diagnosed, and the date of exit as 31 December 2020 or the time of death or drop-out from follow-up, whichever came first. Patient deaths were considered in the overall survival (OS) analysis regardless of their cause, while only deaths caused by melanoma were considered in the analysis of MSS. The cumulative MSS rates were calculated with the Kaplan-Meier method using different sociodemographic and histopathologic features. Cox’s proportional hazards model was fitted to the data to assess the association between both MSS and OS and the previously-detailed independent variables (except for growth type as this variable perfectly predicted the outcome). In the multivariate analysis, we grouped the less common histological categories (acral-lentiginous, blue nevus, desmoplastic, spitzoid) as “Other”. A sensitivity analysis was performed, excluding stage IV patients from the multivariate analysis. The assumption of proportionality was accepted for all models. Statistical significance was ascertained using an alpha level of 0.05 and two-sided tests. All data analyses were run using the R statistical package (version 3.6.3; R Studio, Boston, MA).
The data analysis was performed on anonymous aggregated data with no chance of individuals being identifiable. Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Veneto Oncological Institute’s Ethics Committee (n. 52/2016).
In 2015, the Veneto Cancer Registry 1,279 incident CMM-patient were registered at. Table 1 shows patients’ demographics (M/F: 1.13; median age: 58 years) and clinical-pathological profiles. Most of the invasive malignancies were diagnosed in the early stage (stage I: 71.8%). The mean follow-up was 1,670 ± 415 days.
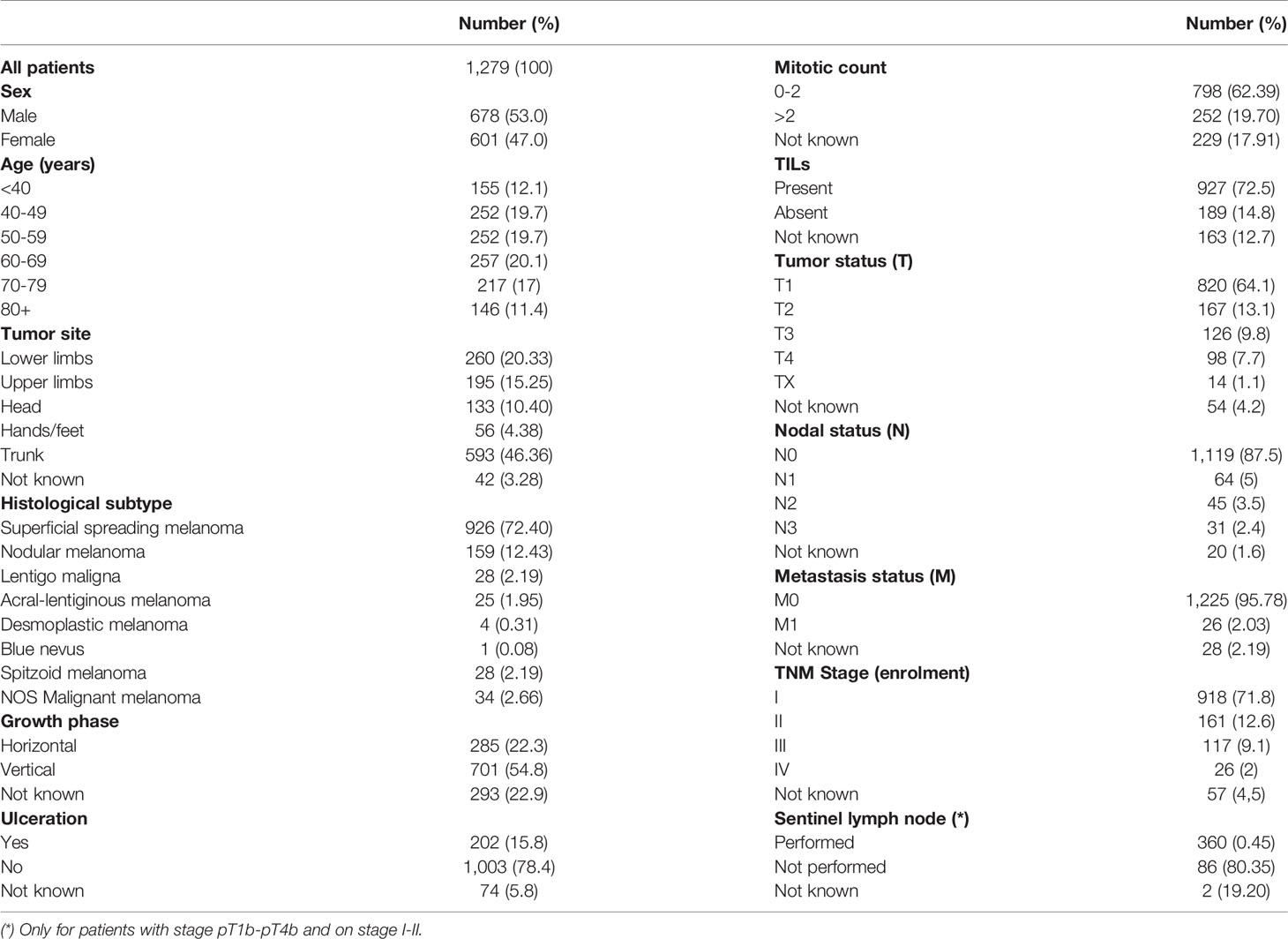
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of the study cohort (NOS, not otherwise specified; TILs, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes).
Overall, the 5-year OS was 83.8% (95% CI: 81.8, 85.8) and it was higher for females (86.6%; 95% CI: 84.0, 89.4) than for males (81.2%; 95% CI: 78.4, 84.2). Five-year MSS was 92.5% (95% CI: 91.0, 94.0), with no significant survival advantage for females (93.6%; CI: 91.7, 95.6) over males (91.5%; CI: 89.4, 93.7).
Figure 1 shows Kaplan-Meier MSS curves by TNM clinical-pathological staging at initial diagnosis, which had a strong impact on survival; T, N and M values are also reported. The 5-year MSS was 99.4% (95% CI: 98.9-100.0) for stage I, 82.6% (95% CI: 76.6-89.0) for stage II, 69.3% (95% CI: 61.0-78.7) for stage III, and only 23.0% (95% CI: 10.3-51.4) for stage IV.
Figures 2, 3 show the Kaplan-Meier MSS curves by each of the pathological variables considered at initial diagnosis (histological subtype, growth phase, mitotic index, ulceration, TILs). The 5-year MSS probability was 99.2% for the category 0-2 mitoses (95% CI: 98.6-99.8), and 76.2% (95% CI: 70.9-82.0) for more than 2 mitoses. Melanoma ulceration significantly affected the probability 5-year MSS (97.6%; 95%CI: 96.7-98.6 without ulceration versus 72.5%; 95% CI: 66.2-79.3). As for the tumor’s growth phase, survival was better for cases described as RGP (radial growth phase) at diagnosis than for those described as VGP (vertical growth phase): the 5-year MSS probability was 100.0% (95%CI: 100.0-100.0) for the former, and 91.6% (95%CI: 89.6- 93.8) for the latter. TIL status (presence versus absence) was associated with a small, but significant impact on 5-year MSS probability(94.4%, 95%CI: 92.9-95.9 versus 90.5%, 95%CI: 86.4-94.9, respectively). Finally, the survival analysis by histological subtype at diagnosis showed that nodular melanoma carried the worst 5-year MSS probability, at 70.3% (95%CI: 63.2-78.1). Superficial spreading melanoma had the highest 5-year MSS probability, at 96.9% (95% CI: 95.8-98.1). Intermediate survival probabilities were revealed for lentigo maligna melanoma (92.9%, 95% CI: 83.8-100.0).
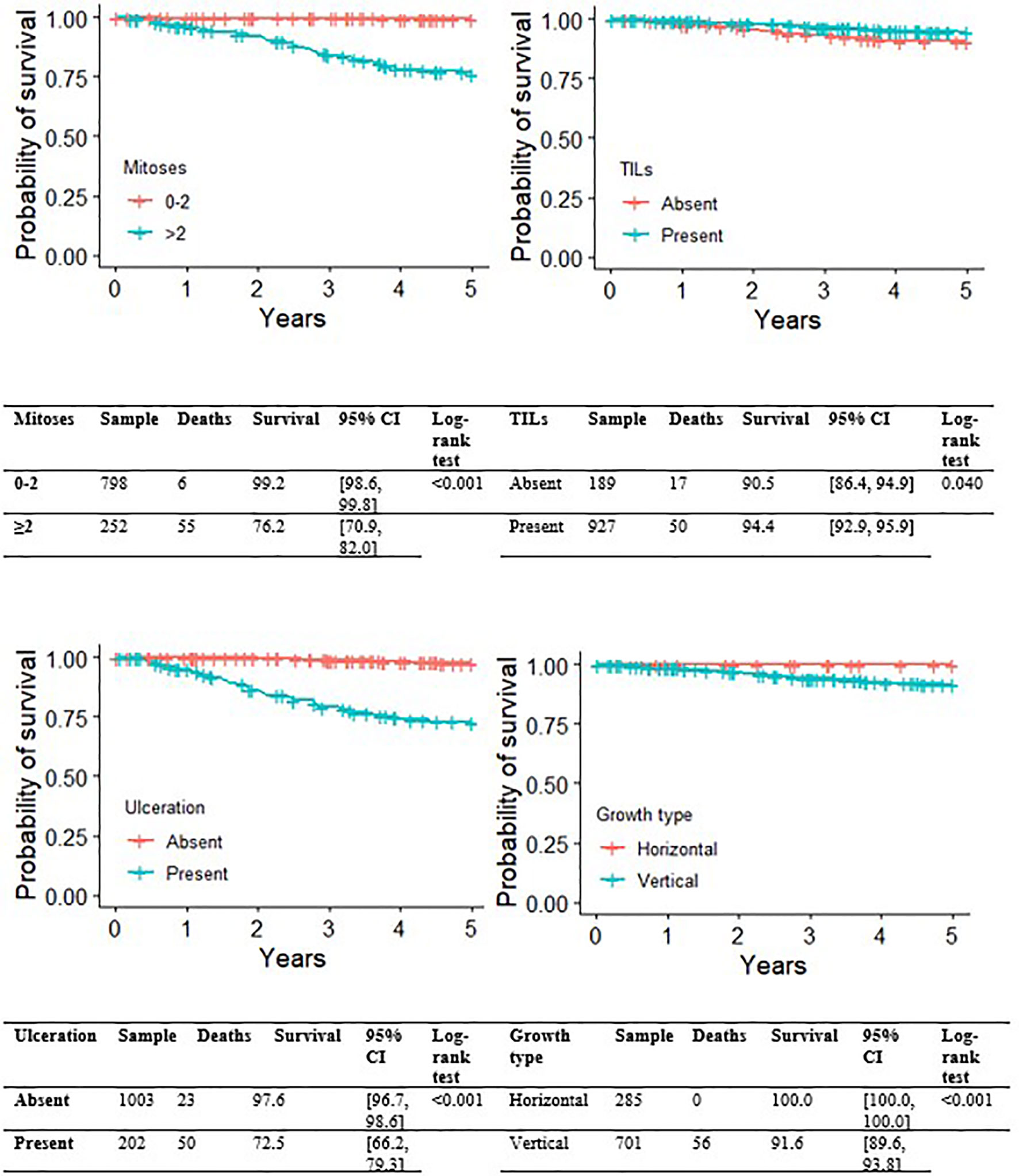
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier curves for melanoma-specific survival by presence of ulceration, growth phase, presence of TIL.
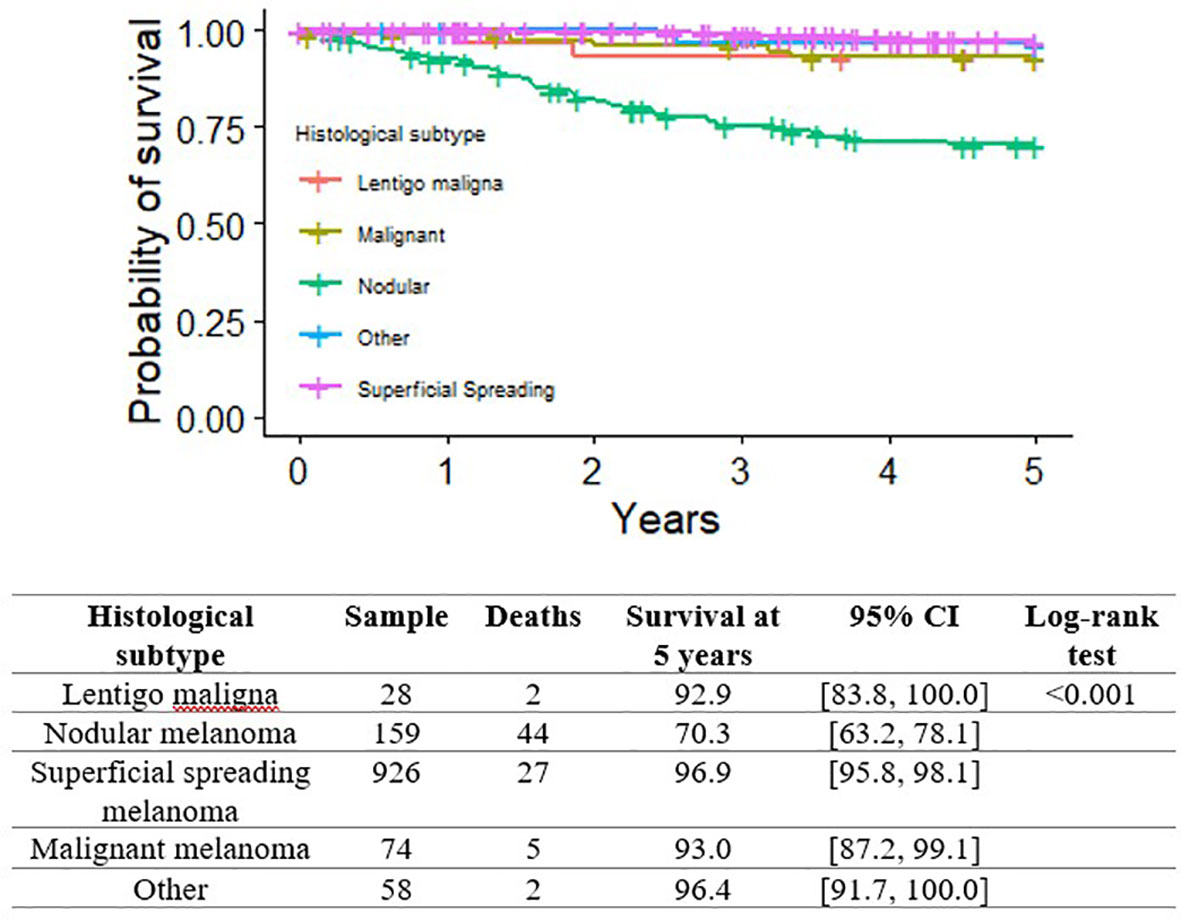
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier curves for melanoma-specific survival by histological subtype and presence of mitoses.
Table 2 shows the results of Cox’s regression model for MSS, adjusting for sex, age, histological subtype, ulceration, mitoses, site of tumor, stage at diagnosis and TILs. Compared with patients with a melanoma in stage I, the risk of death was increased for stage II (HR=3.31, 95% CI: 0.94-11.76, p=0.064), it was almost ten times higher for stage III (HR=10.51, 95% CI: 3.16-35.02, p<0.001), and it was more than a hundred times higher for stage IV (HR=117.17, 95% CI: 25.30-542.62, p<0.001). Superficial spreading melanoma carried a more than eleven times greater risk of death than lentigo maligna (HR=12.61, 95% CI: 1.42-112.02, p=0.023), and nodular melanoma a fourteen times higher risk (HR=15.04, 95% CI: 1.69-133.30, p=0.015). Sites of tumor involving the lower limbs, upper limbs and trunk had a better prognosis than those involving the hands and feet, with the difference reaching borderline statistical significance (p=0.058, p=0.083, p=0.066). Among the other variables included the model, the presence of mitoses emerged as an independent risk factor for death (HR=6.85, 95%CI: 2.21-21.28, p<0.001). The sensitivity analysis, excluding stage IV, generated much the same results as the previous model (data not shown). The analysis of overall survival produced similar results too, except that male sex coincided with a significantly worse prognosis (HR=1.75, % CI: 1.18-2.60, p=0.005).
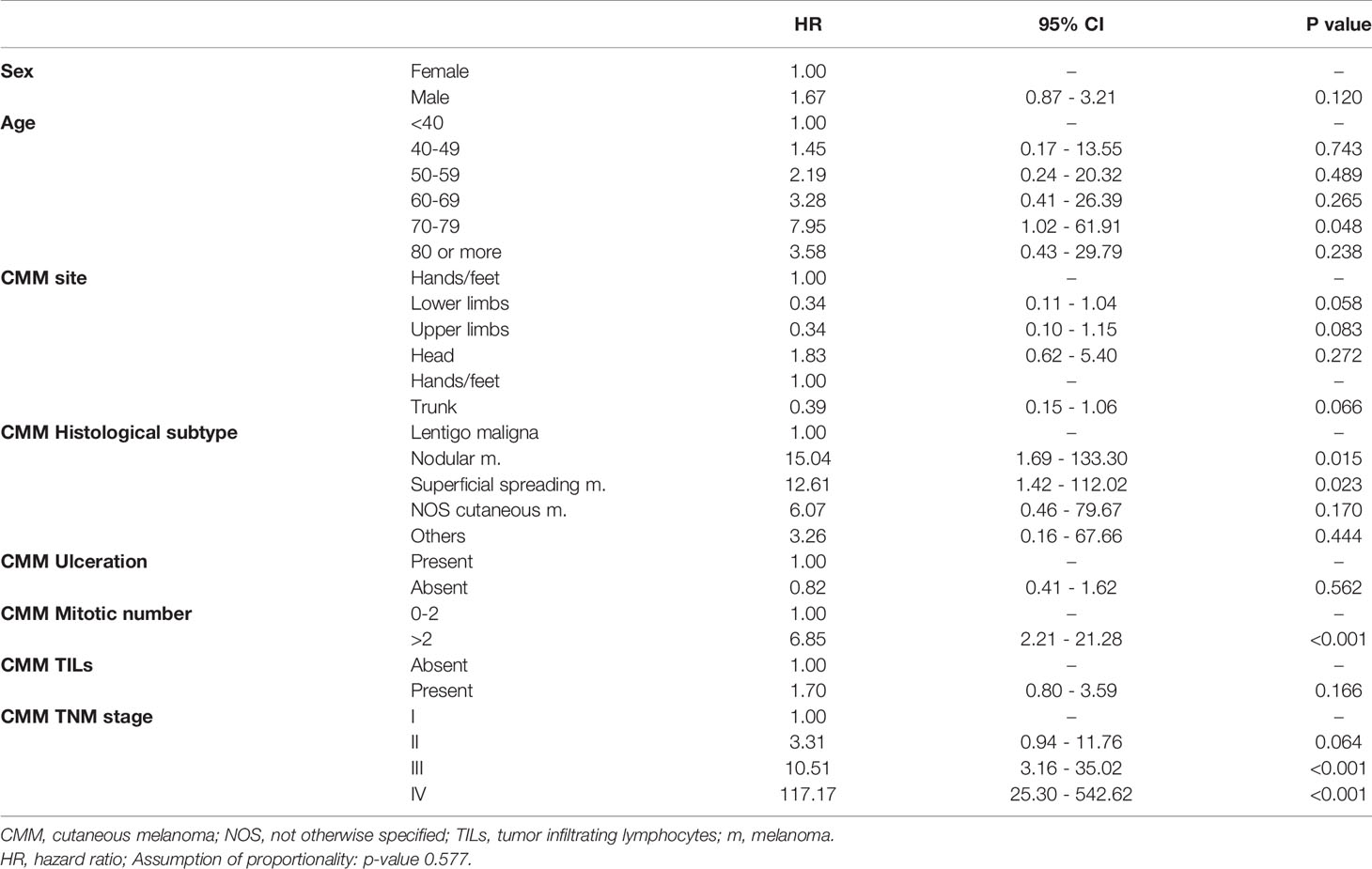
Table 2 Cox’s regression analysis on cutaneous melanoma-specific survival patients, adjusting for sex, age, histological subtype, ulceration, mitotic count, CMM site, stage and TILs, as assessed at the patient’s enrolment.
In a population-based cohort of 1,279 incident CMM patients, this study focuses on the prognostic impact of both demographics and clinical-pathological variables, as recorded in a high-resolution Italian cancer registry.
The results obtained prompt two main types of consideration: one refers to the validation of the CMM-associated prognostic variables in a large cohort of consecutive patients; the other relates to the value of population-based trials for the purpose of updating/improving patient management based on a critical analysis of real-world clinical practice.
As regards the first point, the present results support the prognostic impact of (mostly) well-established clinical-pathological variables (6, 14, 15). In particular, the Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that none of the RGP CMMs resulted in a melanoma-specific death within 5 years after the initial diagnosis (16). The present results also provide evidence to show that extra-nodal metastases from RGP CMMs are extremely rare (less than 3%), while almost all extra-nodal metastatic implants result from “vertically-growing” CMMs (17). Consistently with these findings, both the worst MSS rate and the highest risk of CMM-related death were associated with nodular CMMs. Based on the assumption that any greater risk associated with a nodular histology overlaps with the prognostic impact of a melanoma’s thickness and ulceration, the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC)’s staging system does not include the CMM subtype among the “discriminating” prognostic variables (14, 15). A recent analysis of the SEER cohort (18) nonetheless identifies the histological subtype as an independent predictor of survival, even after adjusting for CMM stage, thickness, ulceration, and mitotic index.
Previous studies found that the mitotic rate (more than neoplastic ulceration) is an independent prognostic factors in primary CMMs (irrespective of their thickness) (19–26). The present results associate a number of mitoses with a worse survival, further supporting the inclusion of the mitotic rate in the staging of thin, non-ulcerated CMMs.
A high-resolution cancer registry primarily needs to contain comprehensive, reliable, and accessible clinical information. All these conditions are hard to achieve, and the present study is no exception. In fact, our study suffered from the difficulty of assembling the necessary clinicopathological data, largely because of inconsistencies in the data format and/or their location in different digital repositories. The present study also suffers from a lack of important information on patients’ socio-economic profiles and - even more important - data on the molecular biology profile of the malignancies considered (27). In this respect, the present study further supports the crucial importance of promoting standardized/synoptic formats in the recording of clinicopathological variables, as obtained by the main clinical actors involved in patient management (especially oncologists, radiologists, and clinical and surgical pathologists).
Inconsistencies in the recording of diagnostic procedures and the “scattering” of results in different datasets represent major limits to operative efforts to pursue the high-resolution cancer registration potentially capable of providing both clinicians and healthcare policy-makers with reliable information on the clinical management of CMM patients.
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: The dataset generated as part of the present study is not publicly available, but available from the corresponding author (YWxlc3NhbmRyYS5idWphQHVuaXBkLml0) on reasonable request. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to YWxlc3NhbmRyYS5idWphQHVuaXBkLml0.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Veneto Oncological Institute Ethics Committee (n 695/20.10.2016). Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
ABu and GD conceived the presented idea. MZ, RS, AV, PF, and SM collected the data, verified its accuracy, and developed the methods. CT verified the analyses. ABa, ABu, and RF wrote the draft. MR, VB, GD, and ABu. supervised the project and revised the draft. CR found the financial support for the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
CARIPARO - Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Padova e Rovigo.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Arnold M, Holterhues C, Hollestein LM, Coebergh JW, Nijsten T, Pukkala E, et al. Trends in Incidence and Predictions of Cutaneous Melanoma Across Europe Up to 2015. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol (2014) 28(9):1170–8. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12236
2. Jemal A, Saraiya M, Patel P, Cherala SS, Barnholtz-Sloan J, Kim J, et al. Recent Trends in Cutaneous Melanoma Incidence and Death Rates in the United States, 1992-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol (2011) 65(5 Suppl 1):S17–25.e1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2011.04.032
3. Thomas L, Tranchand P, Berard F, Secchi T, Colin C, Moulin G. Semiological Value of ABCDE Criteria in the Diagnosis of Cutaneous Pigmented Tumors. Dermatology (1998) 197(1):11–7. doi: 10.1159/000017969
4. Leiter U, Keim U, Garbe C. Epidemiology of Skin Cancer: Update 2019. Adv Exp Med Biol (2020) 1268:123–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-46227-7_6
5. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, et al. eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2018. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute (2021). Available at: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2018/. based on November 2020 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2021.
6. Svedman FC, Pillas D, Taylor A, Kaur M, Linder R, Hansson J. Stage-Specific Survival and Recurrence in Patients With Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma in Europe - A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin Epidemiol (2016) 8:109–22. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S99021
7. Mandalà M, Imberti GL, Piazzalunga D, Belfiglio M, Labianca R, Barberis M, et al. Clinical and Histopathological Risk Factors to Predict Sentinel Lymph Node Positivity, Disease-Free and Overall Survival in Clinical Stages I-II AJCC Skin Melanoma: Outcome Analysis From a Single-Institution Prospectively Collected Database. Eur J Cancer (2009) 45(14):2537–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2009.05.034
8. Balzi D, Carli P, Giannotti B, Buiatti E. Skin Melanoma in Italy: A Population-Based Study on Survival and Prognostic Factors. Eur J Cancer (1998) 34(5):699–704. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(97)10119-8
9. Cascinelli N, Bombardieri E, Bufalino R, Camerini T, Carbone A, Clemente C, et al. Sentinel and Nonsentinel Node Status in Stage IB and II Melanoma Patients: Two-Step Prognostic Indicators of Survival. J Clin Oncol (2006) 24(27):4464–71. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.3198
10. Testori A, De Salvo GL, Montesco MC, Trifirò G, Mocellin S, Landi G, et al. Clinical Considerations on Sentinel Node Biopsy in Melanoma From an Italian Multicentric Study on 1,313 Patients (SOLISM-IMI). Ann Surg Oncol (2009) 16(7):2018–27. doi: 10.1245/s10434-008-0273-8
11. Guzzinati S, Zorzi M, Rossi CR, Buja A, Italiano I, Fiore AR, et al. High Resolution Registry of Melanoma and Care Pathways Monitoring in the Veneto Region, Italy. In: ENCR Scientific Meeting. Copenaghen. Available at: https://www.registrotumoriveneto.it/it/pubblicazioni/convegni/poster/101-2018/234-high-resolution-registry-of-melanoma-and-care-pathways-monitoring-in-the-veneto-region-italy (Accessed Last accessed July 2021).
12. Piñero-Madrona A, Ruiz-Merino G, Cerezuela Fuentes P, Martínez-Barba E, Rodríguez-López JN, Cabezas-Herrera J. Mitotic Rate as an Important Prognostic Factor in Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma. Clin Transl Oncol (2019) 21(10):1348–56. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02064-4
13. Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual and the Future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol (2010) 17(6):1471–4. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4
14. Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, et al. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to Build a Bridge From a Population-Based to a More “Personalized” Approach to Cancer Staging. CA Cancer J Clin (2017) 67(2):93–9. doi: 10.3322/caac.21388
15. Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong SJ, Atkins MB, Cascinelli N, Coit DG, et al. New TNM Melanoma Staging System: Linking Biology and Natural History to Clinical Outcomes. Semin Surg Oncol (2003) 21(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/ssu.10020
16. Betti R, Agape E, Vergani R, Moneghini L, Cerri A. An Observational Study Regarding the Rate of Growth in Vertical and Radial Growth Phase Superficial Spreading Melanomas. Oncol Lett (2016) 12(3):2099–102. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4813
17. Elder D. Pathology of Melanoma. Clin Cancer Res (2006) 12)(7):2308s–11s. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2504
18. Lattanzi M, Lee Y, Simpson D, Moran U, Darvishian F, Kim RH, et al. Primary Melanoma Histologic Subtype: Impact on Survival and Response to Therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst (2019) 111(2):180–8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djy086
19. Barnhill RL, Katzen J, Spatz A, Fine J, Berwick M. The Importance of Mitotic Rate as a Prognostic Factor for Localized Cutaneous Melanoma. J Cutan Pathol (2005) 32(4):268–73. doi: 10.1111/j.0303-6987.2005.00310.x
20. Vollmer RT. Malignant Melanoma: A Multivariate Analysis of Prognostic Factors. Pathol Annu (1989) 24:383.
21. Donizy P, Kaczorowski M, Leskiewicz M, Zietek M, Pieniazek M, Kozyra C, et al. Mitotic Rate Is a More Reliable Unfavorable Prognosticator Than Ulceration for Early Cutaneous Melanoma: A 5-Year Survival Analysis. Oncol Rep (2014) 32(6):2735–43. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3531
22. Evans JL, Vidri RJ, MacGillivray DC, Fitzgerald TL. Tumor Mitotic Rate Is an Independent Predictor of Survival for Nonmetastatic Melanoma. Surgery (2018) 164(3):589–93. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2018.04.016
23. Thompson JF, Soong SJ, Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Ding S, Coit DG, et al. Prognostic Significance of Mitotic Rate in Localized Primary Cutaneous Melanoma: An Analysis of Patients in the Multi-Institutional American Joint Committee on Cancer Melanoma Staging Database. J Clin Oncol (2011) 29(16):2199–205. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.5812
24. Kashani-Sabet M, Miller JR 3rd, Lo S, Nosrati M, Stretch JR, Shannon KF, et al. Reappraisal of the Prognostic Significance of Mitotic Rate Supports its Reincorporation Into the Melanoma Staging System. Cancer (2020) 126(21):4717–25. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33088
25. Tejera-Vaquerizo A, Pérez-Cabello G, Marínez-Leborans L, Gallego E, Oliver-Martínez V, Martín-Cuevas P, et al. Is Mitotic Rate Still Useful in the Management of Patients With Thin Melanoma? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol (2017) 31(12):2025–9. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14485
26. Damiani G, Buja A, Grossi E, Rivera M, De Polo A, De Luca G, et al. Use of an Artificial Neural Network to Identify Patient Clusters in a Large Cohort of Patients With Melanoma by Simultaneous Analysis of Costs and Clinical Characteristics. Acta Derm Venereol (2020) 100(18):adv00323. doi: 10.2340/00015555-3680
Keywords: melanoma, clinical characteristics, survival, epidemiology, cancer survival
Citation: Buja A, Bardin A, Damiani G, Zorzi M, De Toni C, Fusinato R, Spina R, Vecchiato A, Del Fiore P, Mocellin S, Baldo V, Rugge M and Rossi CR (2021) Prognosis for Cutaneous Melanoma by Clinical and Pathological Profile: A Population-Based Study. Front. Oncol. 11:737399. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.737399
Received: 06 July 2021; Accepted: 25 October 2021;
Published: 16 November 2021.
Edited by:
Elisabeth Livingstone, University Hospital of Essen, GermanyReviewed by:
Piotr Rutkowski, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, PolandCopyright © 2021 Buja, Bardin, Damiani, Zorzi, De Toni, Fusinato, Spina, Vecchiato, Del Fiore, Mocellin, Baldo, Rugge and Rossi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Alessandra Buja, YWxlc3NhbmRyYS5idWphQHVuaXBkLml0
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.