- 1Department of General Surgery, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, China
- 2Shantou University Medical College, Shantou University, Shantou, China
- 3School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
- 4The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Large‐volume central lymph node metastasis (large-volume CLNM) is associated with high recurrence rate in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) patients. However, sensitivity in investigating large-volume CLNM on preoperative ultrasonography (US) is not high. The aim of this study is to investigate the clinical factors associated with large-volume CLNM in clinical N0 PTC patients. We reviewed 976 PTC patients undergoing total thyroidectomy with central lymph node dissection during 2017 to 2019. The rate of large-volume LNM was 4.1% (40 of 967 patients). Multivariate analysis showed that male gender and young age (age<45 years old) were independent risk factors for large-volume CLNM with odds ratios [(OR), 95% confidence interval (CI)] of 2.034 (1.015-4.073) and 2.997 (1.306–6.876), respectively. In papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC), capsule invasion was associated with large-volume CLNM with OR (95% CI) of 2.845 (1.110–7.288). In conventional papillary thyroid cancer (CPTC), tumor diameter (>2cm) was associated with large-volume CLNM, with OR (95% CI) 3.757 (1.061–13.310), by multivariate analysis. In ROC curve analysis on the diameter of the CPTC tumor, the Area Under Curve (AUC) =0.682(p=0.013), the best cut-off point was selected as 2.0cm. In conclusion, male gender and young age were predictors for large-volume CLNM of cN0 PTC. cN0 PTMC patient with capsule invasion and cN0 CPTC patient with tumor diameter >2cm were correlated with large-volume CLNM. Total thyroidectomy with central lymph node dissection may be a favorable primary treatment option for those patients.
Introduction
Papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) is the most common type of differentiated thyroid cancer, which account for 85%-90% of all cases (1). The incidence of PTC has been rapidly increasing globally because of early detection (2). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), PTMC is defined as PTC with maximum diameter of 10mm. Those with maximum diameter of more than 10mm is called CPTC (3).
PTC has a high metastasis rate especially central lymph node metastasis (CLNM), approximately 30%-80% of PTC patients have CLNM (4). It has been reported that 30% to 65% of patients with cN0 PTC are detected CLNM (5). The recurrence rate of patients with CLNM mainly depends on the number of involved lymph node and the size of the largest lymph node (6). Patients with large-volume lymph node metastasis (>5 involved lymph nodes) can significantly increase the risk of recurrence during long-time survival, associated with 20% recurrence rates, while small-volume metastasis (≤5 involved lymph nodes) accounts for 5% recurrence rates (7).
In the previous study, young age and male sex have been highlighted with large-volume CLNM in PTMC patient, suggesting surgery may be the primary option for young male patients (8). PTMC with multifocality, tumor diameter>0.5cm and extrathyroidal extension (ETE) also tends to have large-volume CLNM (9, 10). However, the clinicopathologic factors associated with large-volume CLNM in CPTC are not well-established (11). Sensitivity of ultrasound examination for central neck lymph node metastasis was not high (12). Therefore, identifying risk factors for large-volume CLNM in clinical N0 PTC patients might be helpful in deciding on a management strategy in PTC patients.
Materials and Methods
Study Population
A total of 976 PTC patients who received primary total thyroidectomy with central lymph node dissection treatment in the Department of General Surgery at Guangdong General Hospital between October 2017 to September 2019 were reviewed retrospectively in this study. The study was approved by Research Ethics Committee of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences. All patients gave their informed consent to the collection of data according to the local ethic committee indications. Ultrasound examination (US) was routinely performed to assess the thyroid and lymph node status in all these patients. Computed tomography scan (CT) and positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) were used only in some patients as needed. Patients were diagnosed PTC with LNM by pathological examination in the Pathology Department. LNM was defined as preoperatively cN1 with following signs in preoperative ultrasound examination: the ration of transverse/long diameter in cervical lymph node >0.5, blurred corticomedullary boundary, vanished medulla structure, microcalcification or cystic changes (13). Patients were excluded if they exhibited the following criteria (I) pathologic-confirmed not PTC; (II) met preoperatively cN1 diagnostic criteria; (III) received prior surgery or radiotherapy of the neck. (IV) confirmed distant metastasis or gross extrathyroidal extension.
After excluding 612 patients with suspected CLNM preoperatively, 364 patients were involved. Gender, age, ultrasound features and pathologic characteristics are recorded. Patients were divided into two groups by age: (I) age<45 years old; (II)age≥45 years old. In cases of multifocal PTCs, the diameter of the largest tumor was used. ETE only accounted for microscopic extension of tumors. The diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid disease and nodule goiter was determined by general pathological examination.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with IBM SPSS statistics 26.0 software. The relationships between large-volume LNM and clinicopathologic characteristics were investigated by the X2 test or one-way ANOVA to test univariate analyses. The multivariate analysis was performed on the variables that achieved P <0.05 in the univariate analysis and predictive factors for large-volume LNM were tested by the logistic regression analysis and the data was presented as the mean ± SD. P values< 0.05 (two sided) were considered statistically significant.
Results
Clinicopathological Characteristics of the Study Patients
The clinicopathological characteristics of the 364 study patients according to CLNM status are listed in Table 1. Among these, 324 (89.0%) had small‐volume CLNM, and 40 (11.0%) had large-volume CLNM. The mean age was 41.02 ± 11.324. The numbers of patients were 220 (60.4%) and 144 (39.6%) in Groups I‐II, respectively. 235 patients were female (64.6%), and 35.4% (129 patients) were male. 232 (63.7%) patients had PTMC, while 132 (36.3%) patients had tumors larger than 1cm. With the pathology examination, a total of 66 (18.1%) patients were diagnosed with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and 93 (25.5%) patients had nodular goiter. 87 (23.9%) patients had capsule invasion and 56 (15.3%) patients had ETE.
Risk Factors for Large-Volume CLNM in PTC
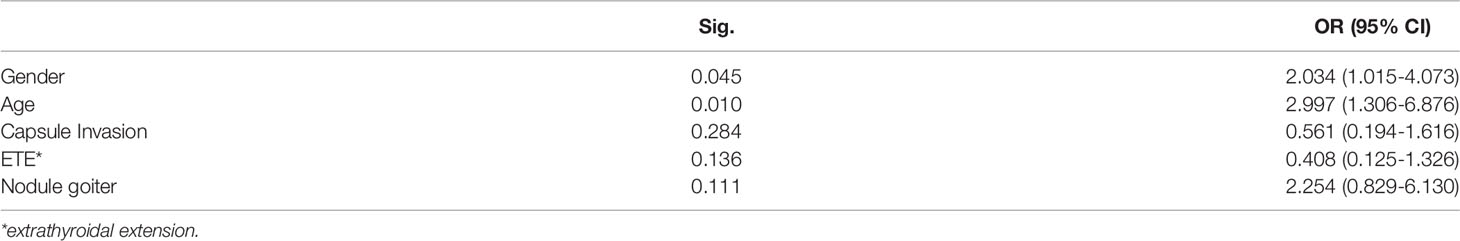
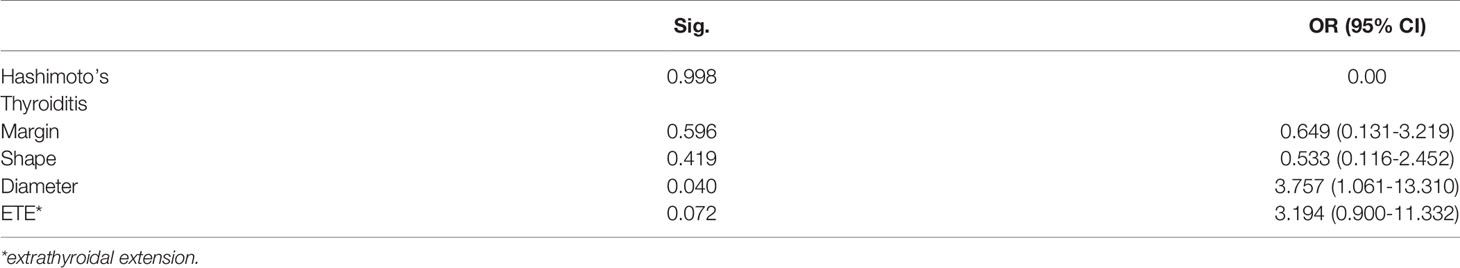
In univariate analysis, young age (<45 years), male, multifocality, nodule goiter and ETE were significantly associated with a high prevalence of large-volume CLNM (Table 1). However, bilateral tumors, marked hypoechoicity, irregular margin and non-well-defined shape were not correlated with the large-volume CLNM. In multivariate analysis, young age [odds ratio (OR): 2.034, 95% confidential interval (CI): 1.015-4.073, P =0.045] and male (OR: 2.997, 95% CI: 1.306–6.876, P= 0.010) were still significant predictive factors for large-volume CLNM (Table 2).
Risk Factors for Large-Volume CLNM in PTMC and CPTC
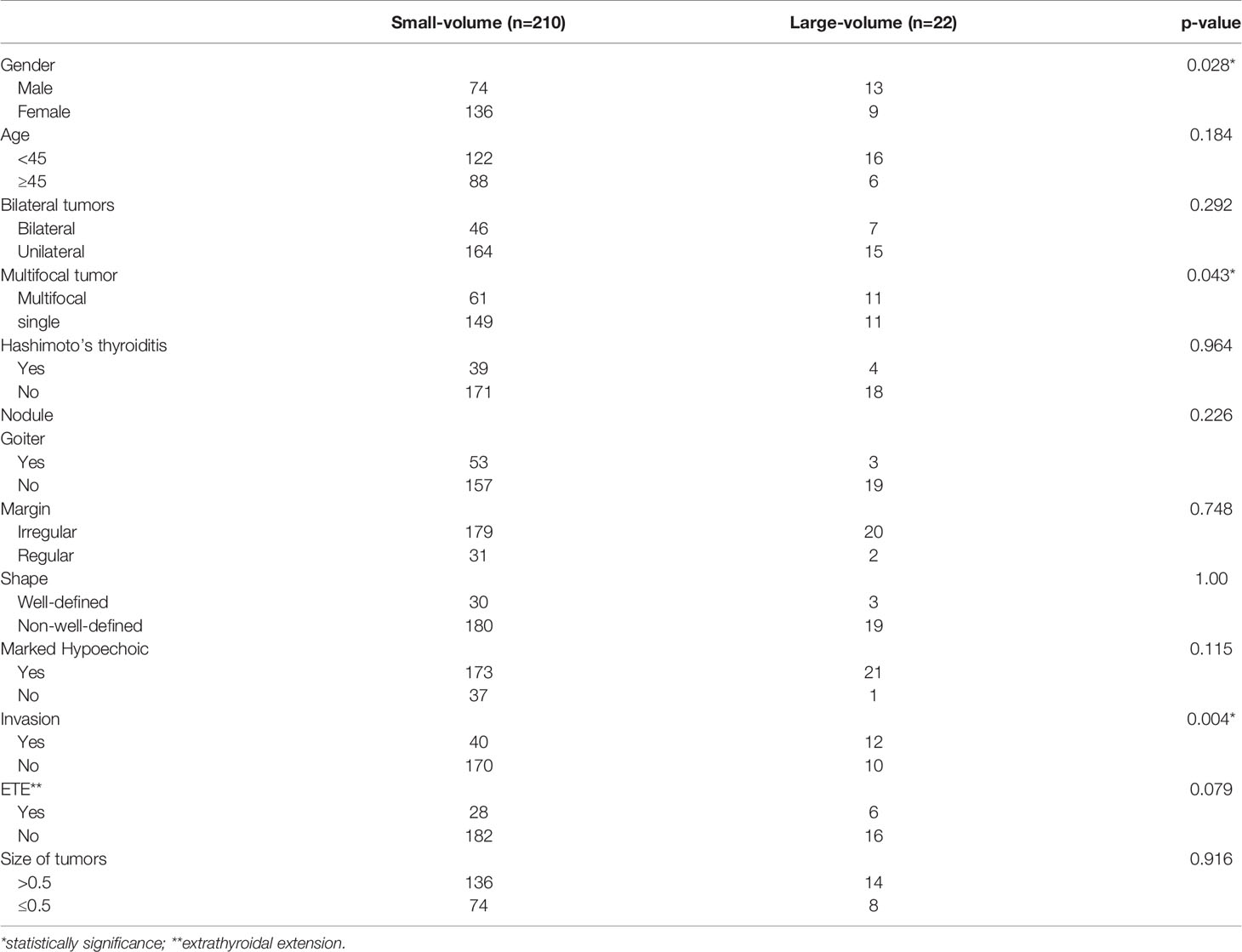
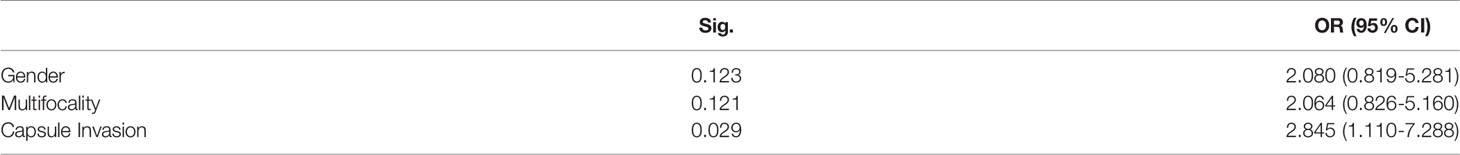
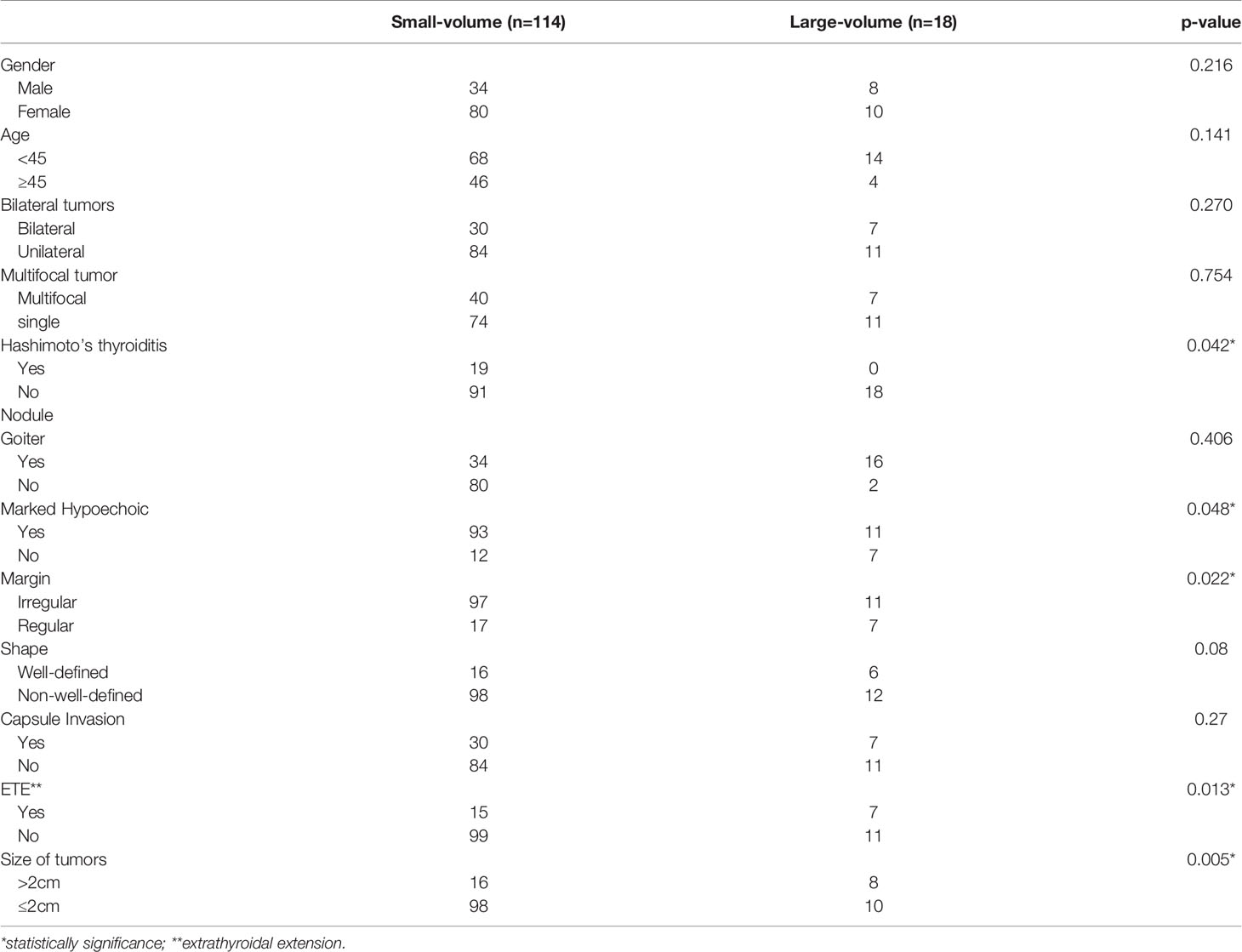
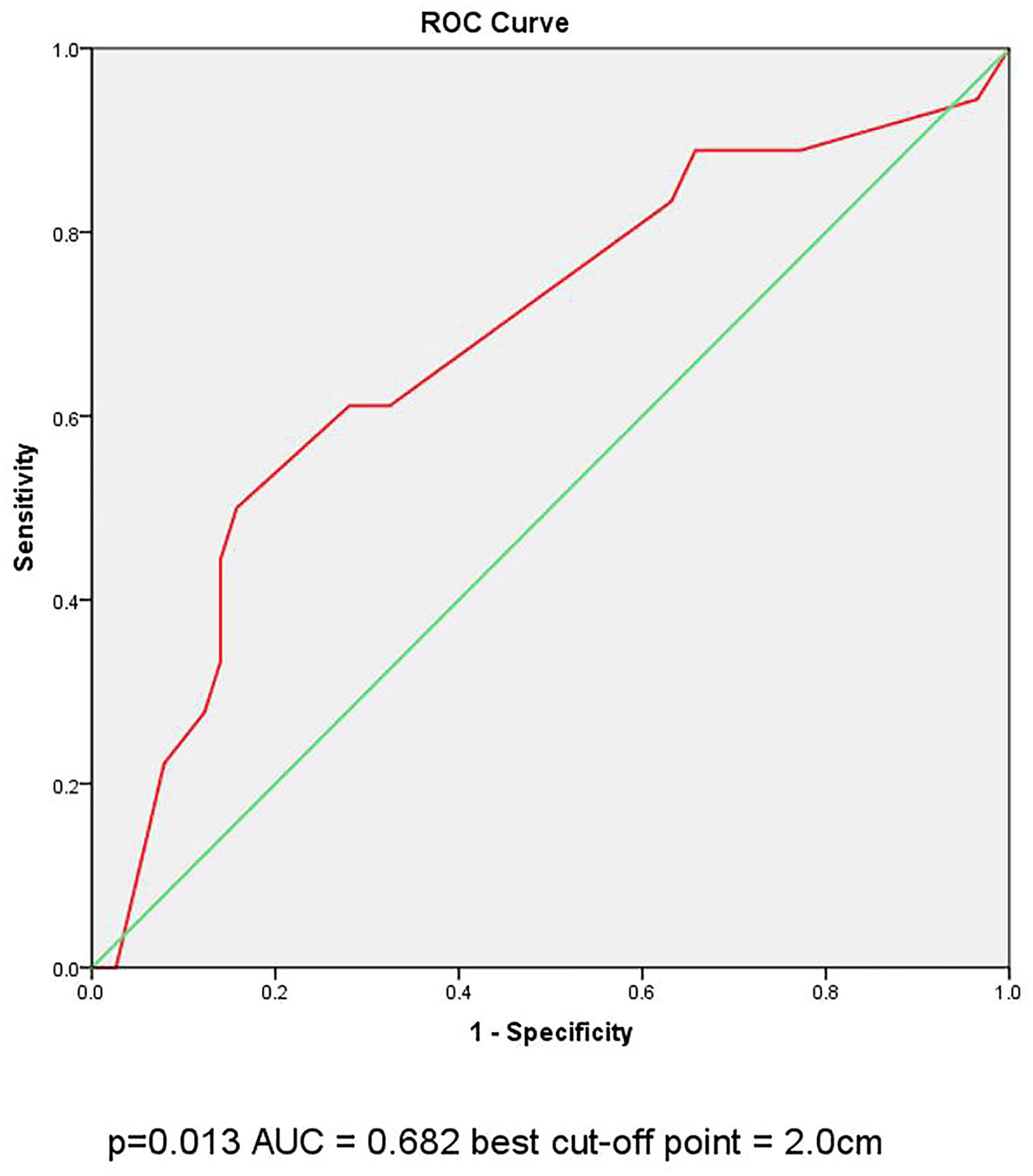
Divided by the maximum diameter of the tumor, clinicopathologic characteristic were tested in PTMC patients and CPTC patients, respectively. In 232 PTMC patients, male, multifocality, nodule goiter and capsule invasion were significantly correlated with large-volume CLNM (Table 3). Age and ETE were not correlated with the large-volume CLNM. In multivariate analysis, shown in Table 4, only capsule invasion (OR: 2.845, 95% CI: 1.110–7.288, P= 0.029) was still significant predictive factors for large-volume CLNM. In 132 CPTC patients, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, marked hypoechoicity, irregular margin and tumor diameter (>2cm) were significantly correlated with large-volume CLNM (Table 5). Age and gender were not correlated with the large-volume CLNM. In multivariate analysis, shown in Table 6, tumor diameter (>2cm) (OR: 3.757, 95% CI: 1.061–13.310, P= 0.04) was significant predictive factors for large-volume CLNM. The high sensitivities and low false-negative rates (1- specificity) associated with the tumor diameter were identified via ROC curve analysis, as depicted in Figure 1. The Area Under Curve (AUC) =0.682(p=0.013), the best cut-off point was selected as 2.0 cm, which meant that CPTC patients with tumor diameter higher than 2.0cm had more likelihood to have large-volume CLNM.
Discussion
Previous studies have demonstrated that male sex, age, multifocality, tumor diameter>0.5cm and ETE were independent risk factors for LNM in PTMC patients (8–10). In this study, univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that age <45 years and male gender are independent predictive factors for large-volume CLNM in cN0 PTC patients. In addition, capsule invasion is independent predictive factors for large-volume CLNM in cN0 PTMC, while tumor diameter >2cm predicts large-volume CLNM in in cN0 CPTC.
Age is regarded as the most important prognostic factors for thyroid cancer. 45 years is widely adopted as clinically important prognostic marker in PTC patients. Our study demonstrates that the rate of large-volume CLNM was higher in patients < 45 years than that ≥45 years (13.6% vs. 6.9%, P = 0.046). Multivariate analysis shows age < 45 years was independent predictor of large-volume CLNM inpatients with cN0 PTC. Similarly, previous studies have reported that CLNM was more likely to appear in PTC patients with age < 45 years, which may be due to rapid tumor diameter growth in young patient during surveillance period (6, 14, 15). These results indicate that much careful preoperative assessment of the lymph node status must be followed in young patients.
Male gender has been identified as a risk factor for thyroid carcinoma (16). Similarly, recent studies have revealed that men exhibited aggressive behavior and poorer prognosis than women among PTC patients (17). Among PTC patients who did not undergo prophylactic central neck dissection, male gender is a risk factor for further recurrence (18). This study also showed male gender as the predictive factor for large-volume CLNM in cN0 PTC. Therefore, male patient with cN0 PTC should be evaluated carefully and complete central neck dissection may be favorable.
With the increased diagnosis of PTC, a growing number of patients with PTMC have been detected. PTMC appears to account for the majority of the increased incidence of thyroid cancer (19). Capsule invasion is considered as aggressive behavior of PTMC, which is correlated with CLNM, even with lymph nodes posterior to right recurrent laryngeal nerve metastasis (LN-prRLN) (14, 20). In PTMC, previous studies did not demonstrate the clear relationship between capsule invasion and large- volume metastasis. A novel finding in our study is that capsule invasion is more likely to present with large-volume metastasis. (P=0.029, OR =2.845, with 95% CI: ranged from 1.110-7.288). The incidence of large-volume CLNM in capsule invasion and non-capsule invasion were 23% vs. 5.6%, with a P value <0.05 in multivariate analysis. It might be expected that the PTMC with capsule invasion more likely showed extrathyroidal metastasis potential to lymph node and distant organs, which significantly accounted for the high incidence of large-volume CLNM and high recurrence rate.
Tumor size is considered as an important factor in TNM staging for PTC, and larger tumors tend to be more aggressive (21, 22). Recent studies reported that tumor diameter >0.5 cm was independent risk factors for large-volume CLNM in cN0 PTMC (8, 9). However, Shen et al. (10) demonstrated that the tumor diameter >0.5 cm was not significantly different between the large-volume CLNM group and non- large-volume CLNM volume group. We were also unable to investigate the relationship between tumor diameter and large volume metastasis in cN0 PTMC. However, in CPTC, we found that tumor diameter higher than 2cm is associated with large-volume CLNM. Ito et al. (23) and Ma et al. (14) reported that tumor diameter of >2cm is the strongest predictor of CLNM and lymph node recurrence in PTC. Compared with tumor diameter <2cm, tumor diameter >2cm was correlated with the five times higher risk of recurrence in PTC patients aged ≥55 years old (24). ROC curve analysis was used to determine the cutoff point of tumor size for predicting large-volume metastasis and found that tumor diameter higher than 2cm was the strongest predictor of large-volume CLNM in cN0 CPTC. Therefore, tumor diameter higher than 2cm should be evaluated carefully for possible large-volume CLNM of PTC. In addition, careful prophylactic central node dissection should be recommended for N0 CPTC with a large tumor diameter (tumor diameter >2cm).
In our study, ultrasound features are analyzed to study the correlation with large-volume CLNM in PTMC and CPTC. However, no predictive factor is established. The possible reason is that ultrasonography in investigating CLNM is not sensitive and ultrasonography diagnosis is subjective, mainly relying on doctor’s clinical experience (25, 26). In presence studies, radiomics and deep machinery learning are gradually conducted to investigate the CLNM. The highest sensitivity has reach 0.858 in the existing predictive models of CLNM, which is significantly higher than the current situation (lower than 0.5 for predicting CLNM) (27). It may provide more dependable evidence for performing central lymph node dissection.
However, the present study has several limitations. The risk factors we identified were based on our retrospective design and the relatively small number of patients with large-volume CLNM, and thus may need further exploration. In addition, our study has no information about follow-up evaluation of the patients for potential development of recurrence and future distant metastases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, age<45 years and male gender are independent predictors of large-volume CLNM metastasis in patients with cN0 PTC. Total thyroidectomy with central neck dissection may be a favorable option for surgeons when treating young male patients with cN0 PTC. Besides, cN0 PTMC patient with capsule invasion and cN0 CPTC patient with tumor diameter >2cm have higher prevalence of large-volume CLNM. Therefore, these factors should be considered by the surgeons when evaluating the risk of large-volume CLNM of PTC. Follow-up visits for post-operative patients with these pathologic characteristics should be regarded.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
The study was approved by Research Ethics Committee of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences. All patients gave their informed consent to the collection of data according to the local ethics committee’s indications.
Author Contributions
JH, MS, and HS designed this study. JH, MS, HS, ZH, and SJW collected the data. JH, MS, and HS analyzed the data. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2020A1515010126), Scientific Research Staring Foundation for the Returned Overseas from Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (No. 2017x02) and Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital Scientific Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Guangdong Province (No. KJ012019441).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin (2019) 69(1):7–34. doi: 10.3322/caac.21551
2. Vigneri R, Malandrino P, Vigneri P. The Changing Epidemiology of Thyroid Cancer: Why is Incidence Increasing? Curr Opin Oncol (2015) 27(1):1–7. doi: 10.1097/cco.0000000000000148
3. Thompson L. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours. Ear Nose Throat J (2006) 85:74. doi: 10.1177/014556130608500201
4. Lee YM, Sung TY, Kim WB, Chung KW, Yoon JH, Hong SJ. Risk Factors for Recurrence in Patients With Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Undergoing Modified Radical Neck Dissection. Br J Surg (2016) 103(8):1020–5. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10144
5. Wada N, Duh QY, Sugino K, Iwasaki H, Kameyama K, Mimura T, et al. Lymph Node Metastasis From 259 Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinomas: Frequency, Pattern of Occurrence and Recurrence, and Optimal Strategy for Neck Dissection. Ann Surg (2003) 237(3):399–407. doi: 10.1097/01.Sla.0000055273.58908.19
6. Adam MA, Pura J, Goffredo P, Dinan MA, Reed SD, Scheri RP, et al. Presence and Number of Lymph Node Metastases are Associated With Compromised Survival for Patients Younger Than Age 45 Years With Papillary Thyroid Cancer. J Clin Oncol (2015) 33(21):2370–5. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.59.8391
7. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients With Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid (2016) 26(1):1–133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020
8. Oh HS, Park S, Kim M, Kwon H, Song E, Sung TY, et al. Young Age and Male Sex Are Predictors of Large-Volume Central Neck Lymph Node Metastasis in Clinical N0 Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinomas. Thyroid (2017) 27(10):1285–90. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0250
9. Liu C, Liu Y, Zhang L, Dong Y, Hu S, Xia Y, et al. Risk Factors for High-Volume Lymph Node Metastases in cN0 Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma. Gland Surg (2019) 8(5):550–6. doi: 10.21037/gs.2019.10.04
10. Shen G, Ma H, Huang R, Kuang A. Predicting Large-Volume Lymph Node Metastasis in the Clinically Node-Negative Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Study. Nucl Med Commun (2020) 41(1):5–10. doi: 10.1097/mnm.0000000000001119
11. Wang JB, Sun YY, Shi LH, Xie L. Predictive Factors for non-Small-Volume Central Lymph Node Metastases (More Than 5 or ≥ 2 Mm) in Clinically Node-Negative Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Med (Baltimore) (2019) 98(1):e14028. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000014028
12. Hwang HS, Orloff LA. Efficacy of Preoperative Neck Ultrasound in the Detection of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis From Thyroid Cancer. Laryngoscope (2011) 121(3):487–91. doi: 10.1002/lary.21227
13. Podnos YD, Smith D, Wagman LD, Ellenhorn JD. The Implication of Lymph Node Metastasis on Survival in Patients With Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Am Surg (2005) 71(9):731–4. doi: 10.1177/000313480507100907
14. Ma B, Wang Y, Yang S, Ji Q. Predictive Factors for Central Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With cN0 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Surg (2016) 28:153–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.02.093
15. Jiang LH, Yin KX, Wen QL, Chen C, Ge MH, Tan Z. Predictive Risk-scoring Model For Central Lymph Node Metastasis and Predictors of Recurrence in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Sci Rep (2020) 10(1):710. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55991-1
16. Lee YH, Lee YM, Sung TY, Yoon JH, Song DE, Kim TY, et al. Is Male Gender a Prognostic Factor for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma? Ann Surg Oncol (2017) 24(7):1958–64. doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-5788-4
17. Ding J, Wu W, Fang J, Zhao J, Jiang L. Male Sex is Associated With Aggressive Behaviour and Poor Prognosis in Chinese Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Sci Rep (2020) 10(1):4141. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60199-9
18. Nixon IJ, Wang LY, Ganly I, Patel SG, Morris LG, Migliacci JC, et al. Outcomes for Patients With Papillary Thyroid Cancer Who do Not Undergo Prophylactic Central Neck Dissection. Br J Surg (2016) 103(3):218–25. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10036
19. Leboulleux S, Tuttle RM, Pacini F, Schlumberger M. Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Time to Shift From Surgery to Active Surveillance? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol (2016) 4(11):933–42. doi: 10.1016/s2213-8587(16)30180-2
20. Li C, Xiang J, Wang Y. Risk Factors for Predicting Lymph Nodes Posterior to Right Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (LN-Prrln) Metastasis in Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Int J Endocrinol (2019) 2019:7064328. doi: 10.1155/2019/7064328
21. Kim M, Kim HI, Jeon MJ, Kim HK, Kim EH, Yi HS, et al. Eighth Edition of Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging System Improve Survival Predictability for Papillary, But Not Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Oral Oncol (2018) 87:97–103. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.10.029
22. Tuttle RM, Haugen B, Perrier ND. Updated American Joint Committee on Cancer/Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging System for Differentiated and Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer (Eighth Edition): What Changed and Why? Thyroid (2017) 27(6):751–6. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0102
23. Ito Y, Fukushima M, Higashiyama T, Kihara M, Takamura Y, Kobayashi K, et al. Tumor Size is the Strongest Predictor of Microscopic Lymph Node Metastasis and Lymph Node Recurrence of N0 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocr J (2013) 60(1):113–7. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej12-0311
24. Tam S, Amit M, Boonsripitayanon M, Busaidy NL, Cabanillas ME, Waguespack SG, et al. Effect of Tumor Size and Minimal Extrathyroidal Extension in Patients With Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid (2018) 28(8):982–90. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0513
25. Chen J, Li XL, Zhao CK, Wang D, Wang Q, Li MX, et al. Conventional Ultrasound, Immunohistochemical Factors and BRAF(V600E) Mutation in Predicting Central Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Ultrasound Med Biol (2018) 44(11):2296–306. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.06.020
26. Huang XP, Ye TT, Zhang L, Liu RF, Lai XJ, Wang L, et al. Sonographic Features of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma Predicting High-Volume Central Neck Lymph Node Metastasis. Surg Oncol (2018) 27(2):172–6. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2018.03.004
Keywords: central lymph node metastasis, total thyroidectomy, tumor diameter, conventional papillary thyroid cancer, capsule invasion
Citation: Huang J, Song M, Shi H, Huang Z, Wang S, Yin Y, Huang Y, Du J, Wang S, Liu Y and Wu Z (2021) Predictive Factor of Large‐Volume Central Lymph Node Metastasis in Clinical N0 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients Underwent Total Thyroidectomy. Front. Oncol. 11:574774. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.574774
Received: 21 June 2020; Accepted: 30 April 2021;
Published: 19 May 2021.
Edited by:
Mitali Dandekar, Paras Cancer Centre, IndiaReviewed by:
Ioannis Vasileiadis, Brighton and Sussex Medical School, United KingdomZhihui Li, Sichuan University, China
Copyright © 2021 Huang, Song, Shi, Huang, Wang, Yin, Huang, Du, Wang, Liu and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zeyu Wu, d3UuemV5dUBob3RtYWlsLmNvbQ==; Yongchen Liu, YXZhdGFybGFyYUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jianhao Huang
Jianhao Huang Muye Song
Muye Song Hongyan Shi
Hongyan Shi Ziyang Huang1,2
Ziyang Huang1,2 Shujie Wang
Shujie Wang Ying Yin
Ying Yin Yijie Huang
Yijie Huang Yongchen Liu
Yongchen Liu Zeyu Wu
Zeyu Wu