
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol., 15 December 2020
Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics
Volume 10 - 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.615415
This article is part of the Research TopicTargeted Cancer Therapies, from Small Molecules to Antibodies, Volume IView all 54 articles
This article is a correction to:
Glucose-Regulated Protein 78 Signaling Regulates Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in A549 Cells
A Corrigendum on
Glucose-Regulated Protein 78 Signaling Regulates Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in A549 Cells
by Sun L-L, Chen C-M, Zhang J, Wang J, Yang C-Z and Lin L-Z (2019). Front. Oncol. 9:137. doi: .10.3389/fonc.2019.00137
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 1 and 2 as published. Category I images were duplicated. The corrected Figure 1 and 2 appear below.
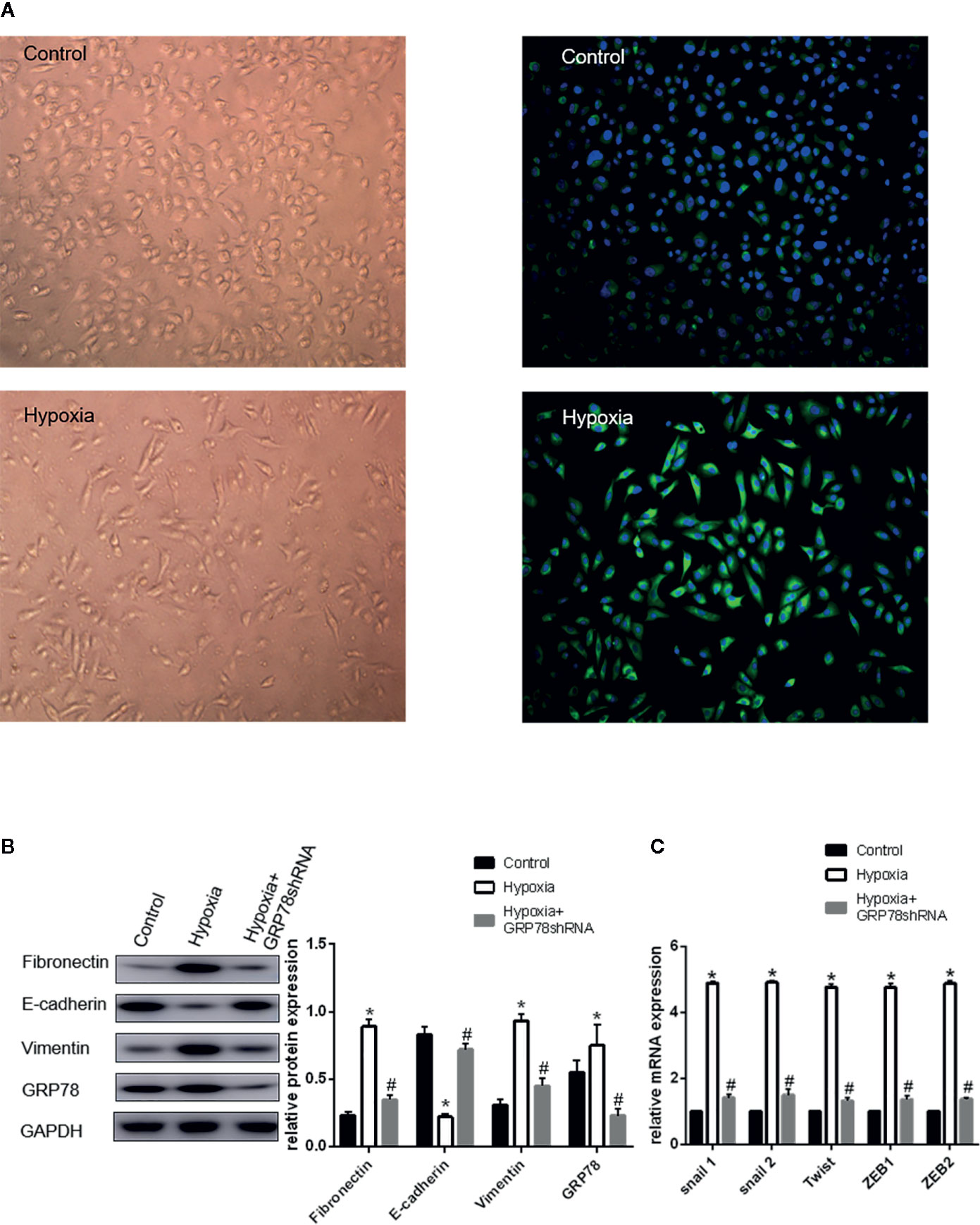
Figure 1 Up-regulation of GRP78 plays an important role in hypoxia-induced EMT in A549 cells. (A) A549 cells acquire spindle-shaped mesenchymal morphology after 72 h of 2% O2 hypoxia (left, 100×). GRP78 (green fluorescence) is highly expressed in A549 cells with spindle-shaped mesenchymal morphology (right, 100×). (B) EMT-related markers (E-cadherin, Vimentin and Fibronectin) and GRP78 were examined by Western blot analysis (left). GAPDH was used as internal control. The protein relative value (GAPDH) is plotted in the right panel (mean ± SD in three separate experiments). *P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells under the condition of normal oxygen, the expression of E-cadherin decreases, while those of Vimentin and Fibronectin increase in A549 cells under hypoxia (2% O2 72 h). The expression of GRP78 also increases in A549 cells under hypoxia. #P < 0.05, compared with the A549 cells under the condition of hypoxia; the expression of E-cadherin increases, and those of Vimentin and Fibronectin decrease in GRP78 knockdown A549 cells under hypoxia. (C) EMT-related genes including Snail1, Snail2, Twist, ZEB1, and ZEB2 were examined by real-time quantitative PCR; mRNA expression relative value (control group) is plotted (mean ± SD in three separate experiments). *P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells in the control group, the mRNA expression levels of EMT-related genes including Snail1, Snail2, Twist, ZEB1, and ZEB2 increase under hypoxic condition (2% O2 72 h); #P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells under the condition of hypoxia, the mRNA expression levels of EMT-related genes decrease in GRP78 knockdown A549 cells under hypoxia.
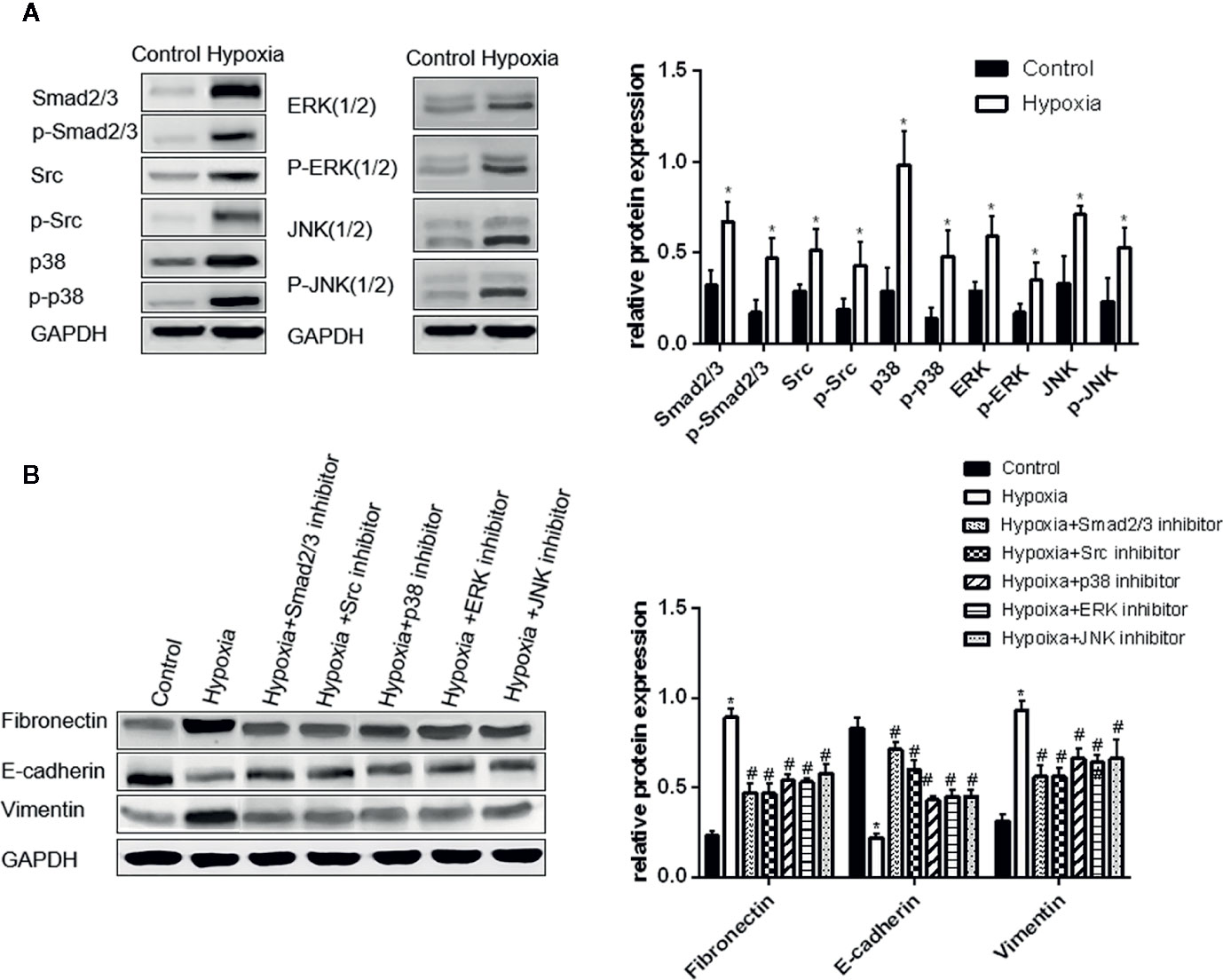
Figure 2 Activation of Smad2/3, Src, p38, ERK, and JNK is important in hypoxia-induced EMT in A549 cells. (A) Smad2/3, Src, p38, ERK, JNK, and their phosphorylated forms were examined by Western blot analysis (left). GAPDH was used as internal control. The protein relative value (GAPDH) is plotted in the right panel (mean ± SD in three separate experiments). *P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells in the normal oxygen environments, the Smad2/3, Src, and MAPK proteins of A549 cells are highly regulated and activated in hypoxia environments. (B) EMT markers were examined by Western blot analysis (left). GAPDH was used as internal control. The protein relative value (GAPDH) is plotted in the right panel (mean ± SD in three separate experiments). *P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells in the normal oxygen environments, the EMT process of A549 cells under hypoxia is activated; #P < 0.05, compared with A549 cells in the hypoxia environments, the EMT process of A549 cells under hypoxia is inhibited separately by Smad2/3, Src, p38, ERK, and JNK inhibitors. The expression levels of Fibronectin and Vimentin decrease, and that of E-cadherin increases.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: lung cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, epithelial mesenchymal transition, hypoxia, glucose-regulated protein 78, GRP78
Citation: Sun L-L, Chen C-M, Zhang J, Wang J, Yang C-Z and Lin L-Z (2020) Corrigendum: Glucose-Regulated Protein 78 Signaling Regulates Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in A549 Cells. Front. Oncol. 10:615415. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.615415
Received: 09 October 2020; Accepted: 05 November 2020;
Published: 15 December 2020.
Edited and reviewed by: Yunkai Zhang, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, United States
Copyright © 2020 Sun, Chen, Zhang, Wang, Yang and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li-Zhu Lin, bGl6aHVsaW4yNkB5YWhvby5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.